Control Effect of a Novel Polyurethane (W-OH) on Colluvial Deposit Slope Erosion in the Benggang Area of Southern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
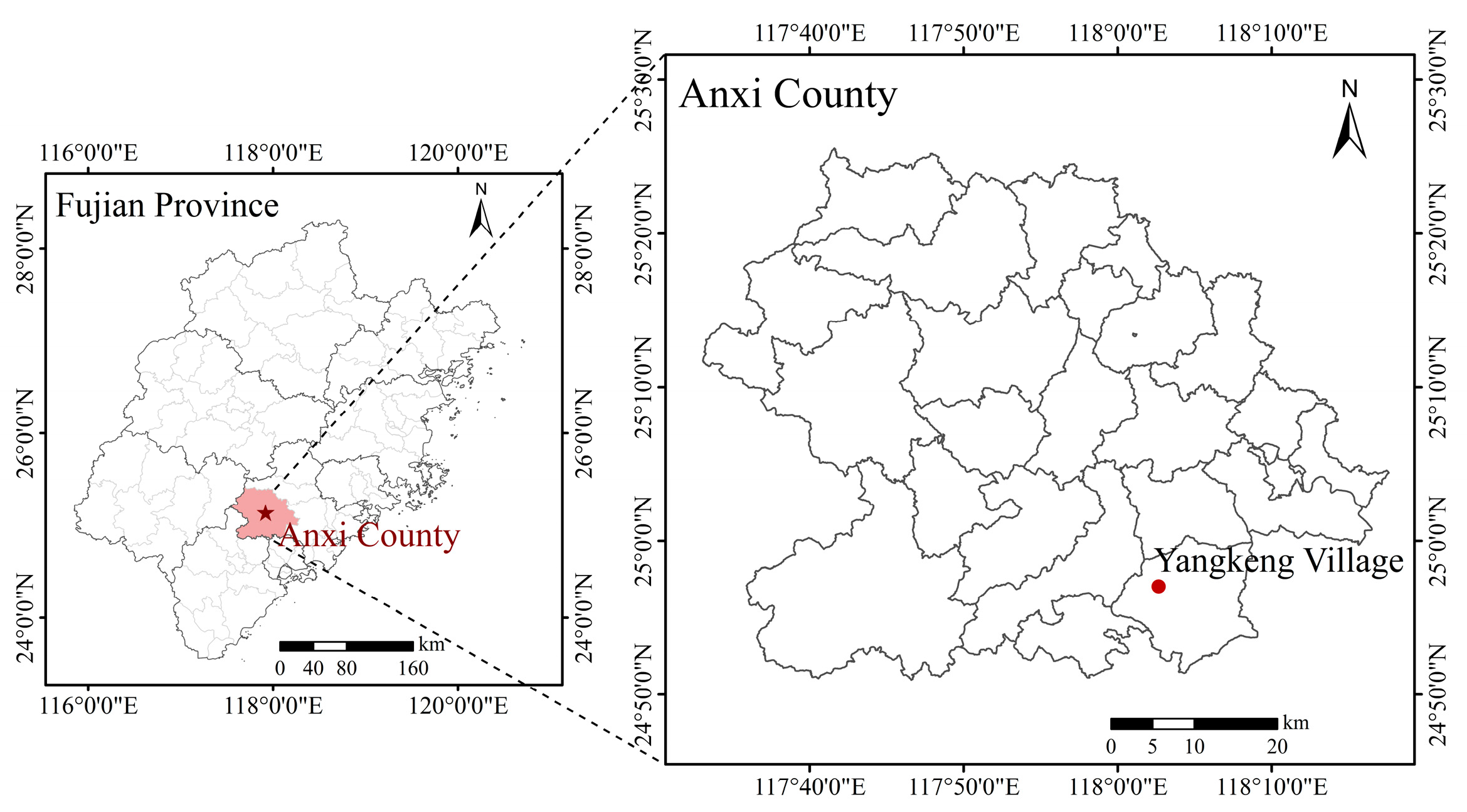
2.1. Study Area
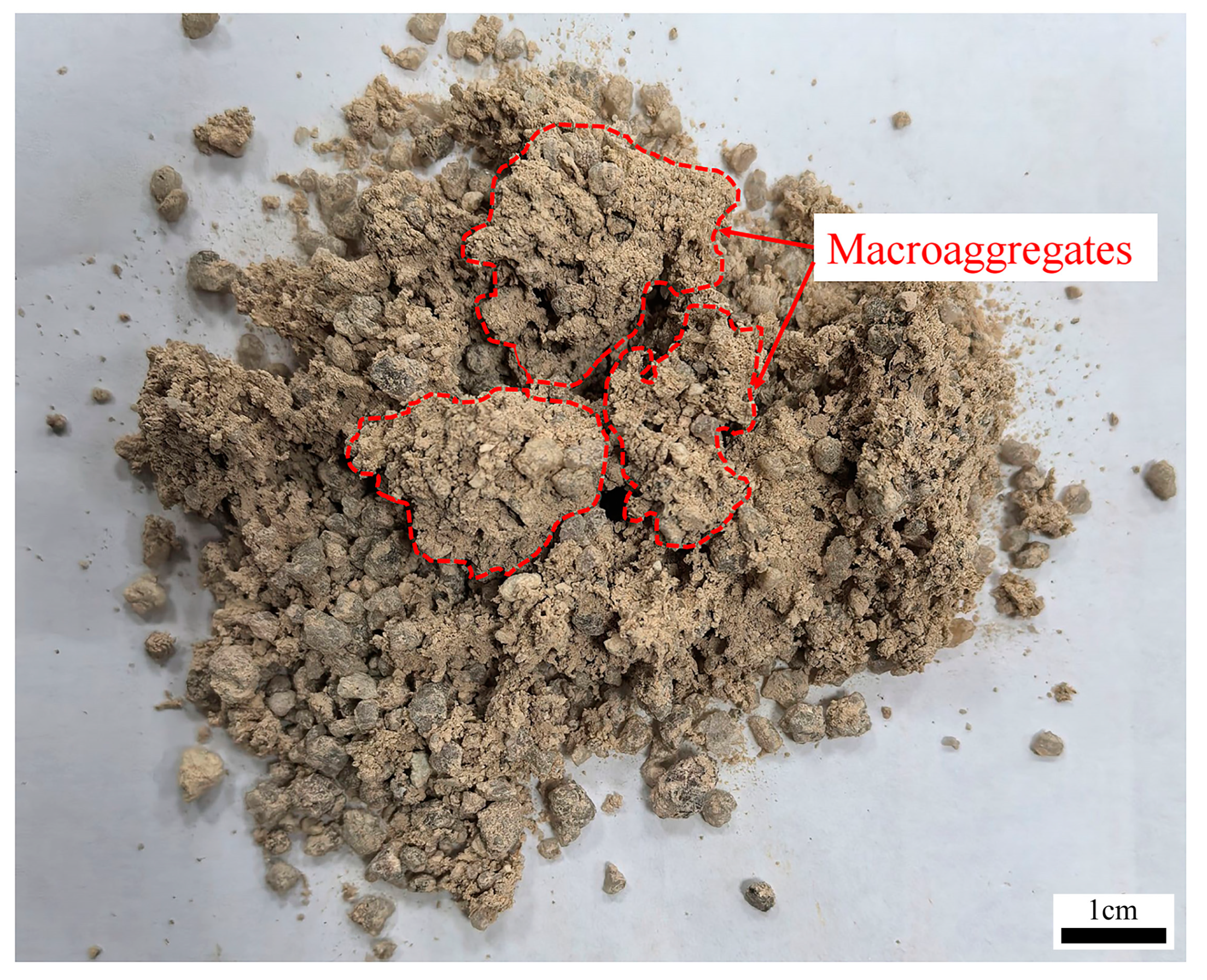
2.2. Collection and Treatment of Soil Samples
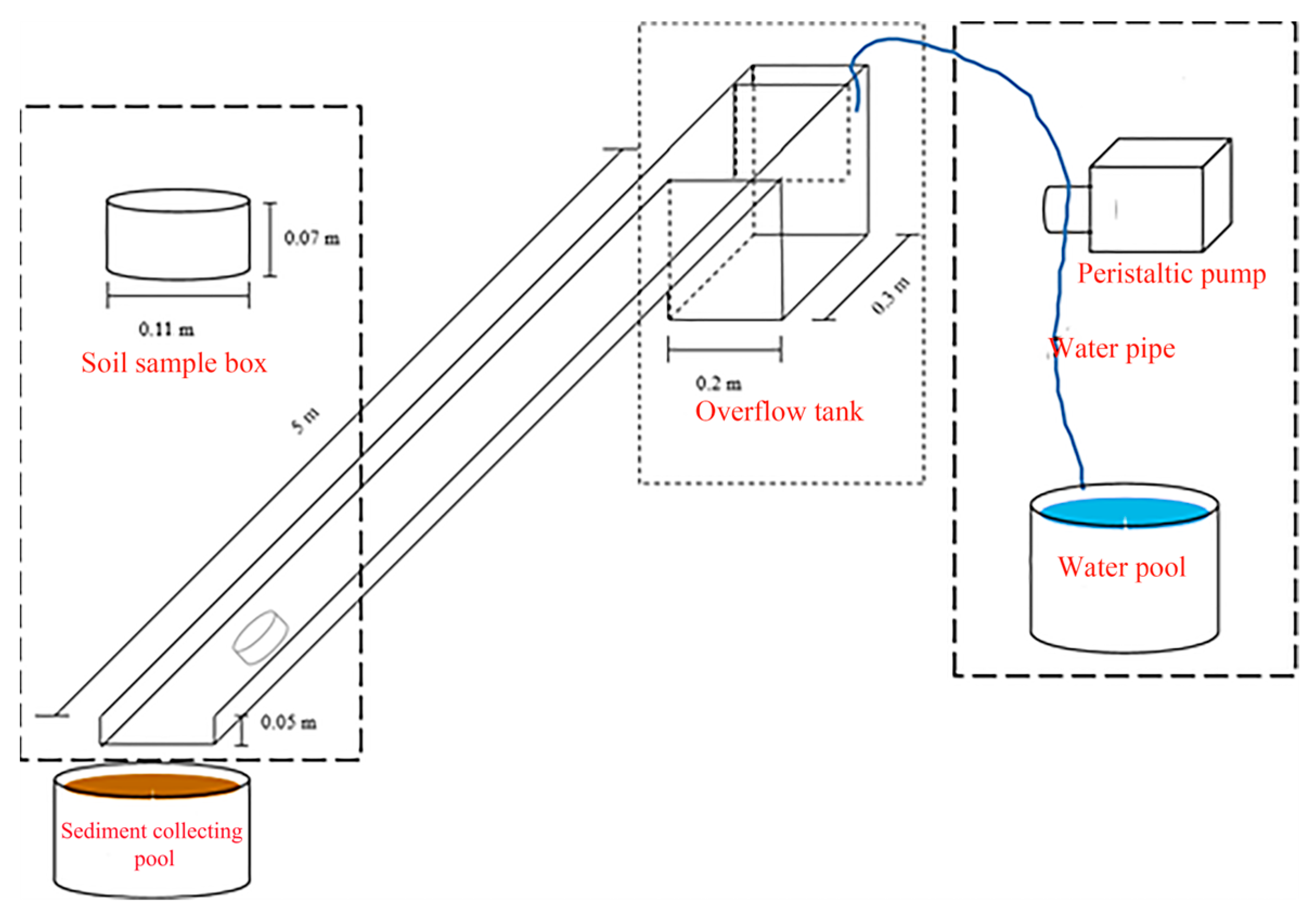
2.3. Experimental Design and Setup
2.4. Indicator Calculation
- (1)
- Mean weight diameter
- (2)
- Shear strength
- (3)
- Soil detachment capacity
- (4)
- Hydrodynamic parameters
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
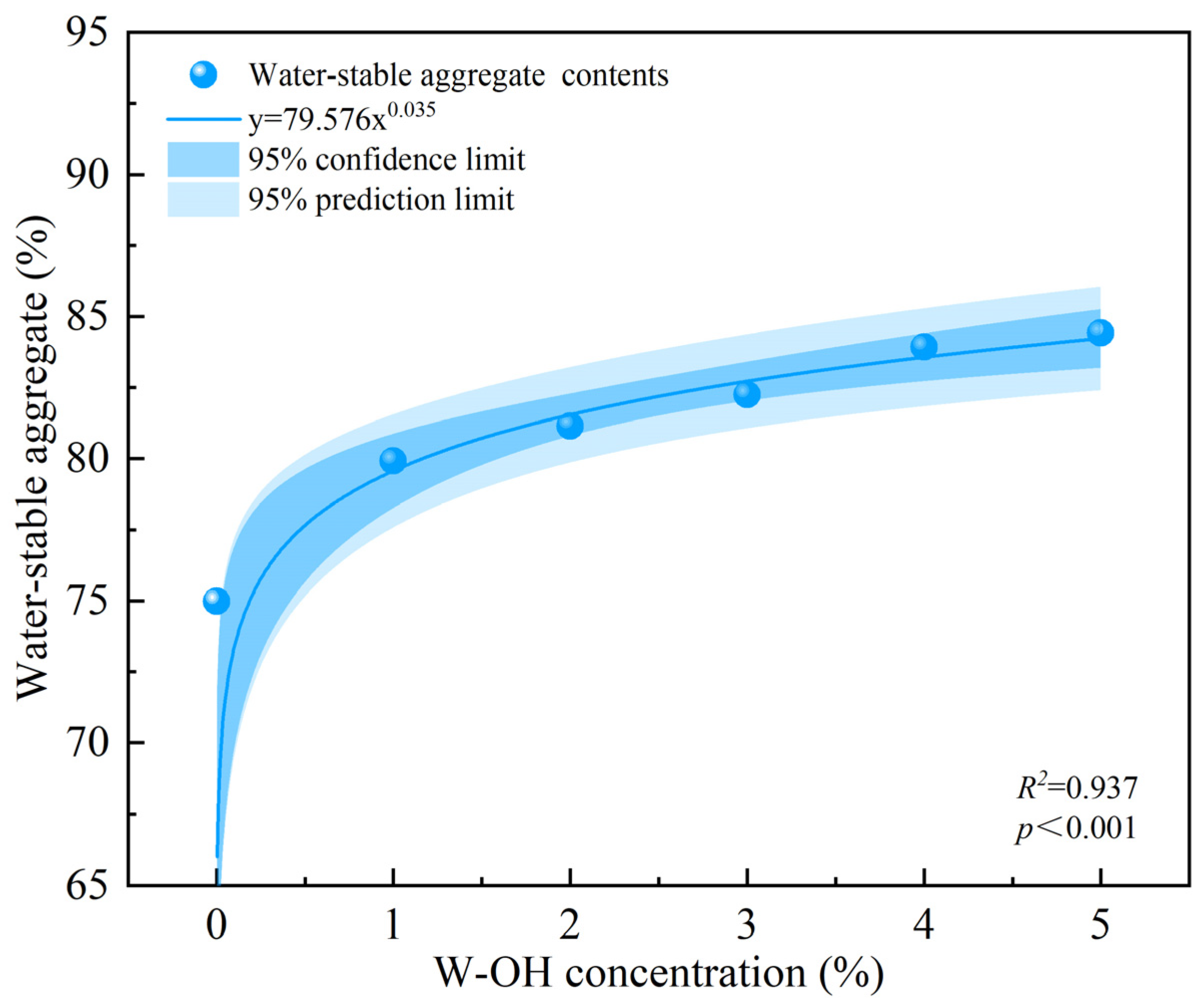
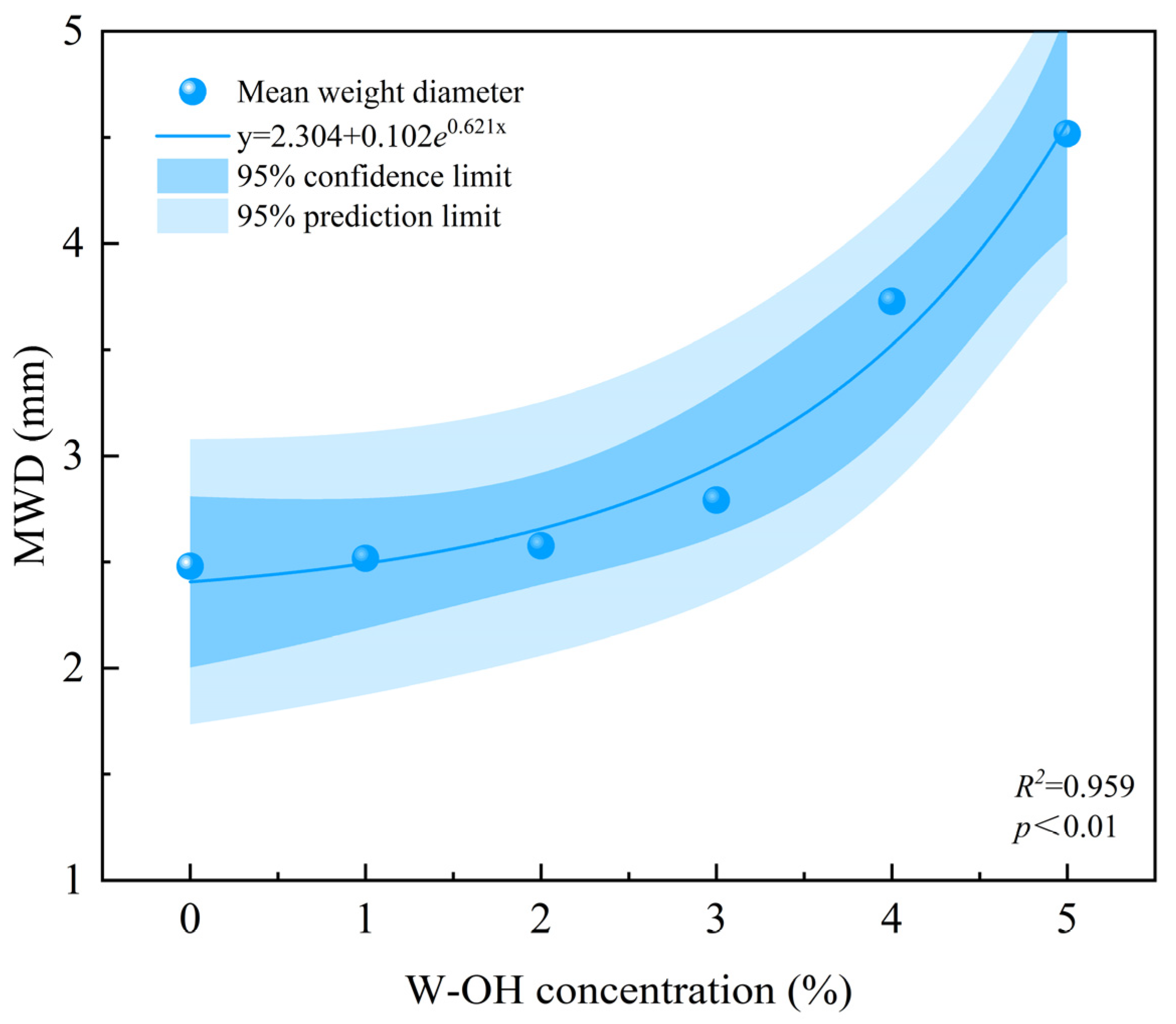
3.1. The Effects of W-OH on the Physical and Mechanical Properties of Colluvial Deposits
3.2. The Effects of W-OH on Soil Detachment Capacity
3.3. Relationship Among the Soil Detachment Capacity, Physical and Mechanical Properties, and Hydrodynamic Parameters
3.4. Magnitude of the Influences of the Flow Discharge and W-OH Concentration on the Soil Detachment Capacity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nearing, M.A.; Polyakov, V.O.; Nichols, M.H.; Hernandez, M.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Armendariz, G. Slope–velocity equilibrium and evolution of surface roughness on a stony hillslope. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 3221–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Wang, F.; Gao, J. The effect of storm movement on infiltration, runoff and soil erosion in a semi-arid catchment. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 4526–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Xu, X.; Iversen, B.V.; Weber, P.L.; de Jonge, L.W.; Wang, X.; Bai, Y. Effect of different underlying surfaces on hydraulic parameters of overland flow. Soil. Tillage Res. 2023, 232, 105776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, C.; Ferro, V. Establishing soil loss tolerance: An overview. J. Agric. Eng. 2016, 47, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Pan, C.; Xu, X.; Wu, T.; Yang, T.; Zhang, L. A field investigation on rill development and flow hydrodynamics under different upslope inflow and slope gradient conditions. Hydrol. Res. 2020, 51, 1201–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, J. Soil erosion in the Anthropocene: Research needs. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 2018, 43, 64–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, G.; Wang, H.; Shrestha, S.; Xue, B.; Sun, W.; Yu, J. Macrozoobenthos variations in shallow connected lakes under the influence of intense hydrologic pulse changes. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584, 124755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyssen, J.; Poesen, J.; Deckers, J. Land degradation and soil and water conservation in tropical highlands. Soil. Tillage Res. 2009, 103, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefera, B.; Sterk, G. Land management, erosion problems and soil and water conservation in Fincha’a watershed, western Ethiopia. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, Z.; Govers, G. Soil and water conservation measures reduce soil and water losses in China but not down to background levels: Evidence from erosion plot data. Geoderma 2019, 337, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.-C.; Ni, A.-C.; Zhang, N.; Chen, Z.-H. Erosion control and growth promotion of W-OH material on red clay highway slopes: A case study in South China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.F.; Wu, P.T.; Feng, H.; Bu, C.F. Influence of amendments on soil structure and soil loss under simulated rainfall China’s loess plateau. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 6116–6121. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Saha, A. Effect of polyacrylamide and gypsum on surface runoff, sediment yield and nutrient losses from steep slopes. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentz, R.D. Polyacrylamide and biopolymer effects on flocculation, aggregate stability, and water seepage in a silt loam. Geoderma 2015, 241–242, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, B.; Tsunekawa, A.; Haregeweyn, N.; Tsubo, M.; Mulualem, T.; Mamedov, A.I.; Meshesha, D.T.; Adgo, E.; Fenta, A.A.; Ebabu, K.; et al. Effect of Polyacrylamide integrated with other soil amendments on runoff and soil loss: Case study from northwest Ethiopia. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2022, 10, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Iwashita, K.; Wu, Z.; Inagaki, H. Experimental study on evaluation and control of ultraviolet resistance of sand stabilized with organic slurry containing hydrophilic polyurethane. J. Soc. Mater. Sci. Jpn. 2008, 57, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gao, W.; Wu, Z.; Wu, Z. Study of Mechanism of the W-OH Sand Fixation. J. Environ. Prot. 2012, 3, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Linag, Z.; Wu, Z.; Noori, M.; Yang, C.; Yao, W. A new ecological control method for Pisha sandstone based on hydrophilic polyurethane. J. Arid. Land 2017, 9, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Wang, X.; Qiu, X. Effect of W-OH, a hydrophilic polyurethane polymer, in controlling erosion of two typical erodible soils in southern China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tang, C.-S.; Xu, J.-J.; Wei, Y.; Dong, Z.-H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Shi, B. Exploring an eco-friendly approach to improve soil tensile behavior and cracking resistance. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2024, 16, 4272–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Li, D.; Zheng, M.; Huang, B.; Xie, Z.; Wu, X.; Luo, X. What kind of gully can develop into benggang? CATENA 2023, 225, 107024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Zhuo, M.; Huang, B.; Nie, X.; Xie, Z.; Tang, C.; Li, D. Coupling effects of erosion and surface roughness on colluvial deposits under continuous rainfall. Soil. Tillage Res. 2019, 191, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.-S.; Huang, Y.-H.; Wang, M.-K.; Lin, J.-S.; Zhao, G.; Ge, H.-L. Effects of rainfall intensity and slope gradient on steep colluvial deposit erosion in Southeast China. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 1741–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Gao, L.; Wei, X.; Li, T.; Shao, M. Progress and prospect of studies of Benggang erosion in southern China. Geoderma 2023, 438, 116656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Li, P.; Hu, J.; Yan, L.; Latifi, H.; Yao, W.; Hao, M.; Gao, J.; Dang, T.; Zhang, S. Development of gully erosion processes: A 3D investigation based on field scouring experiments and laser scanning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 265, 112683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Cai, C. Linking rill development characteristics to sediment production on different coarse-textured granite topsoils. CATENA 2022, 214, 106295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Chen, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Shuai, F.; Li, H.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y. Modeling the sediment transport capacity of rill flow using a soil-rock mixture on steep slopes. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 49, 101512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, F.; Huang, M.; Zhan, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, F. Effects of herbaceous plant roots on the soil shear strength of the collapsing walls of benggang in Southeast China. Forests 2022, 13, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tao, C.; Ha, F.; Wang, H.; Shen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, F. An Experimental Study on the Effects of Sediment Particle Characteristics on the Flow Velocity Correction Factor for Runoff in Steep Nonerodible Rills. Hydrol. Process. 2024, 38, e70010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-T.; Shuai, F.; Chen, L.-B.; Huang, Y.-H.; Lin, J.-S.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, H.-L.; Jiang, F.-S. Effect of gravel content on the detachment of colluvial deposits in Benggang. J. Mt. Sci. 2022, 19, 3088–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, H.; Wu, B. Modelling soil detachment capacity by rill flow with hydraulic variables on a simulated steep loessial hillslope. Hydrol. Res. 2019, 50, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Guo, C. Regional dynamic early warning model for rainfall-induced landslide in Fujian, China. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2024, 15, 2435510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, B.; Nearing, M.A.; Huang, C.; Zhang, K. Soil detachment by shallow flow. Trans. ASAE 2002, 45, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Abrahams, A.D.; Atkinson, J.F. Correction factors in the determination of mean velocity of overland flow. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1996, 21, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wang, Z.; Shen, N.; Wang, S. Modelling sediment transport capacity of rill flow for loess sediments on steep slopes. CATENA 2016, 147, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, G.; Banerjee, S.; Edlinger, A.; Oliveira, E.M.; Herzog, C.; Wittwer, R.; Philippot, L.; Maestre, F.T.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. A closer look at the functions behind ecosystem multifunctionality: A review. J. Ecol. 2021, 109, 600–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmo, J.R.; Perkins, K.S. 2.6 Aggregate stability and size distribution. Methods Soil Anal. Part 4 Phys. Methods 2002, 5, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, K.; Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Wu, F. Response of seasonal variation in soil detachment capacity to straw incorporation in sloping farmland on the Loess Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 1740–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govers, G.; Everaert, W.; Poesen, J.; Rauws, G.; De Ploey, J.; Lautridou, J.P. A long flume study of the dynamic factors affecting the resistance of a loamy soil to concentrated flow erosion. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1990, 15, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-X.; Wang, B.; Duan, X.-W.; Yang, Y.-F.; Liu, G.-B. Seasonal variation in soil erosion resistance to overland flow in gully-filled farmland on the Loess Plateau, China. Soil. Tillage Res. 2022, 218, 105297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Wang, K.; Geng, J.; Wang, L.; Fang, N. Systematic evaluation of the effects of the length, depth, and amount of incorporated maize straw on rill flow velocity. J. Hydrol. 2023, 621, 129550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Fu, S.; Liu, B.; Yu, B.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, H. Effects of Pinus tabulaeformis litter cover on the sediment transport capacity of overland flow. Soil. Tillage Res. 2020, 204, 104685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edlinger, A.; Garland, G.; Banerjee, S.; Degrune, F.; García-Palacios, P.; Herzog, C.; Pescador, D.S.; Romdhane, S.; Ryo, M.; Saghaï, A.; et al. The impact of agricultural management on soil aggregation and carbon storage is regulated by climatic thresholds across a 3000 km European gradient. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 3177–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, H.; Moussavi, A.; Ghadiri, H.; Rose, C. Flow-driven soil erosion processes and the size selectivity of sediment. J. Hydrol. 2011, 406, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yang, C. Performance evaluation of the polyurethane-based composites prepared with recycled polymer concrete aggregate. Materials 2020, 13, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.Y.; Cao, L.X.; Wu, Z.R.; Chen, C.; Liang, Y. Impact of W-OH on soil detachment rate of colluvial deposits in collapsing hill. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2017, 54, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

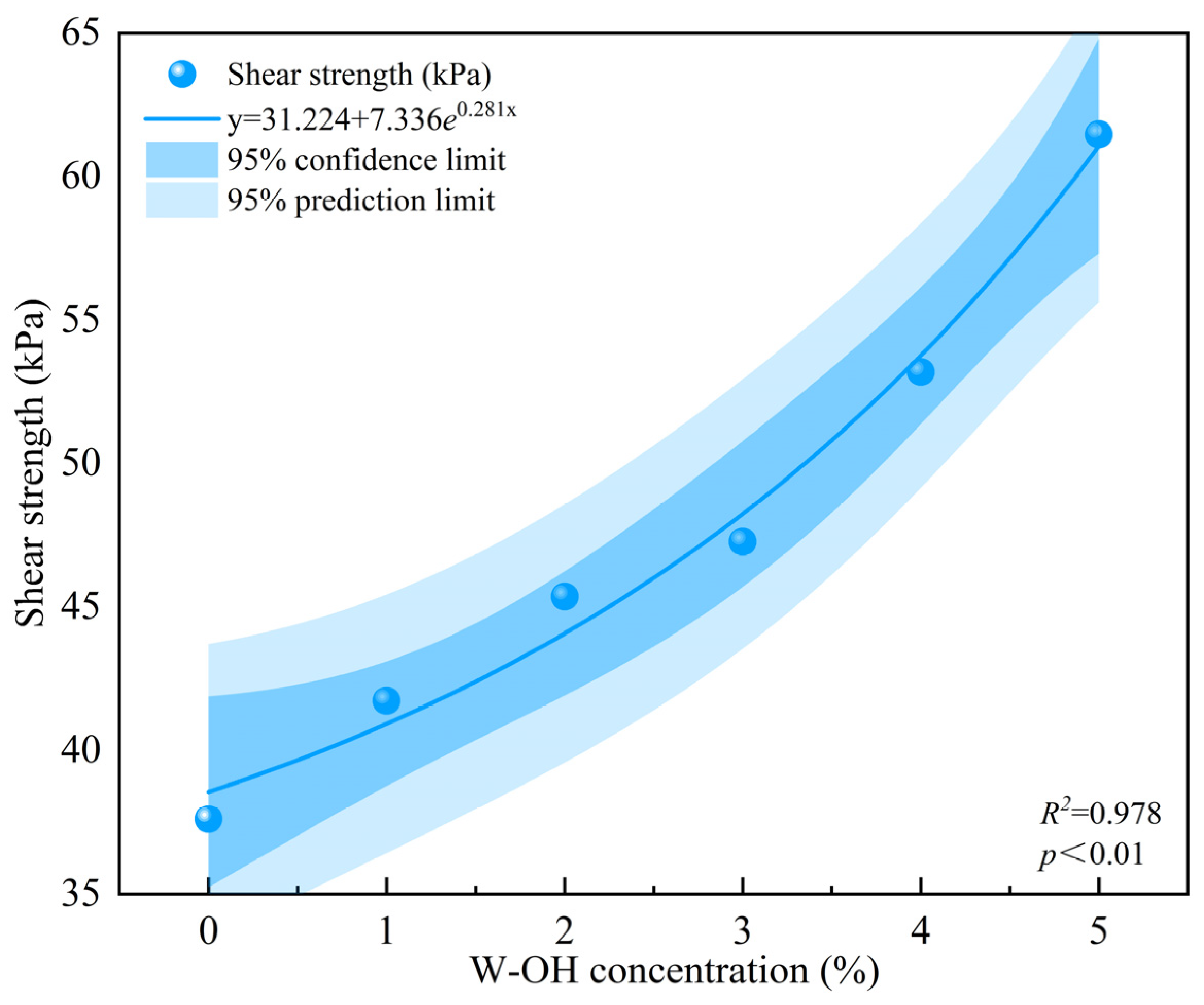
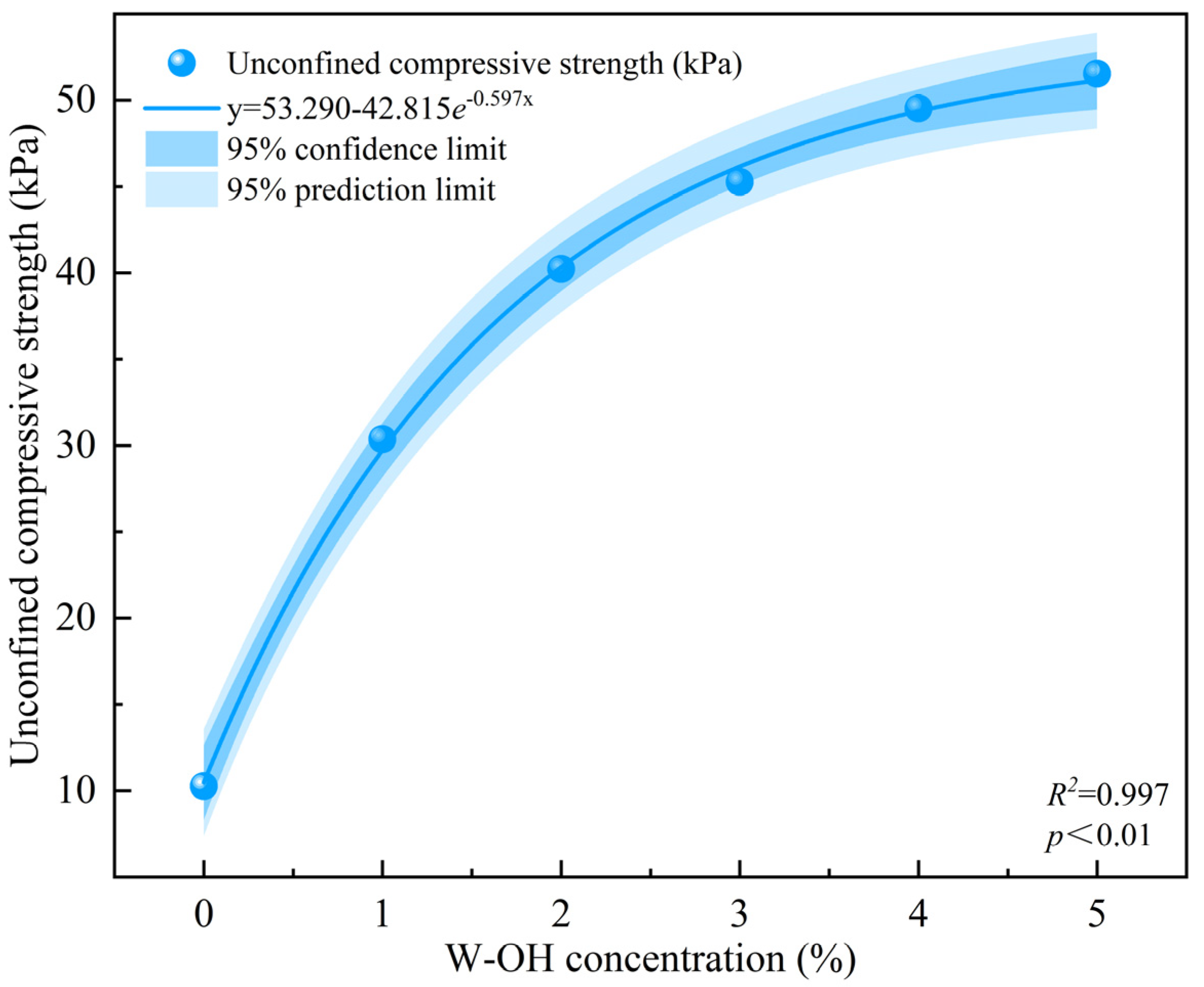

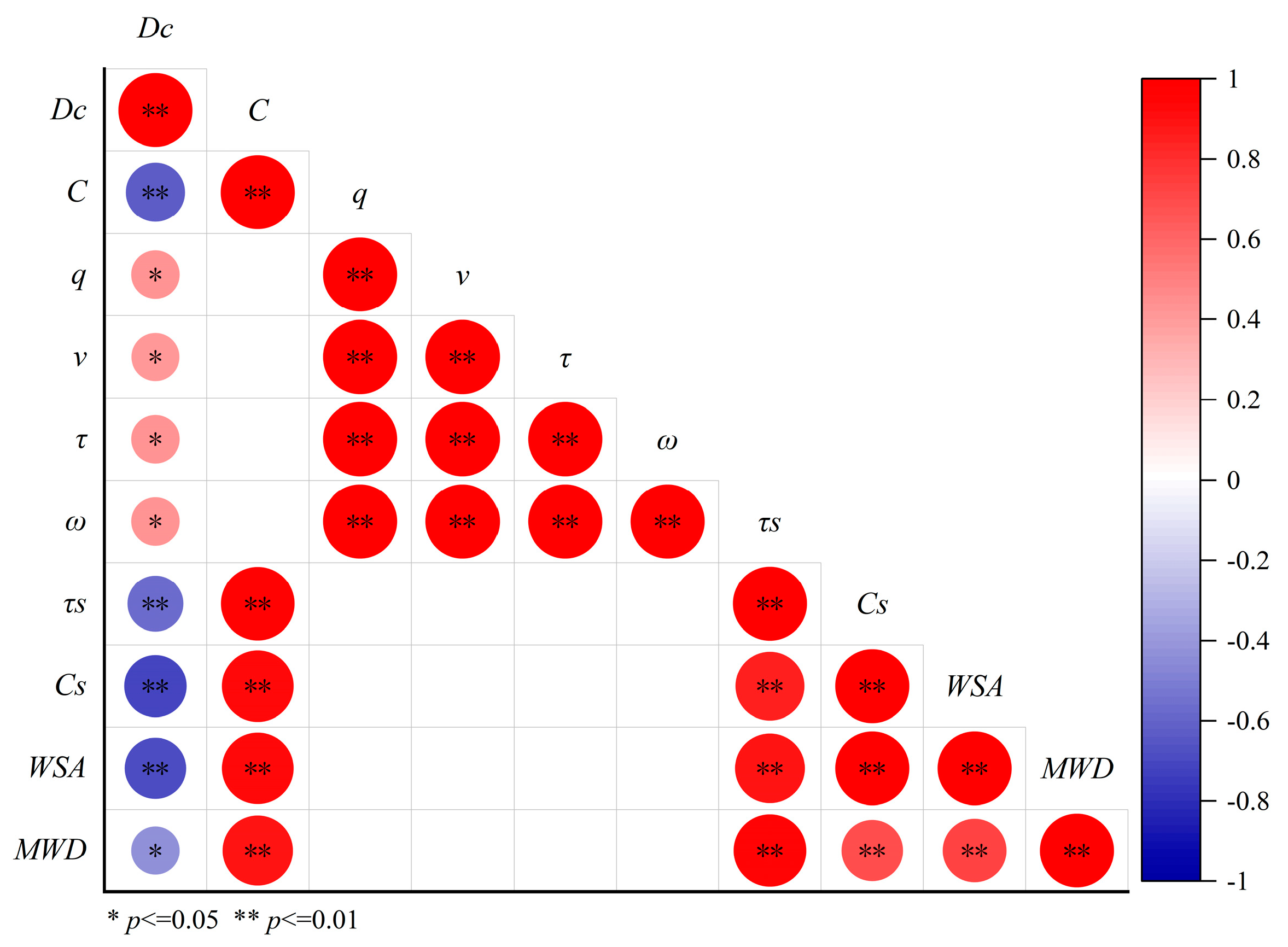

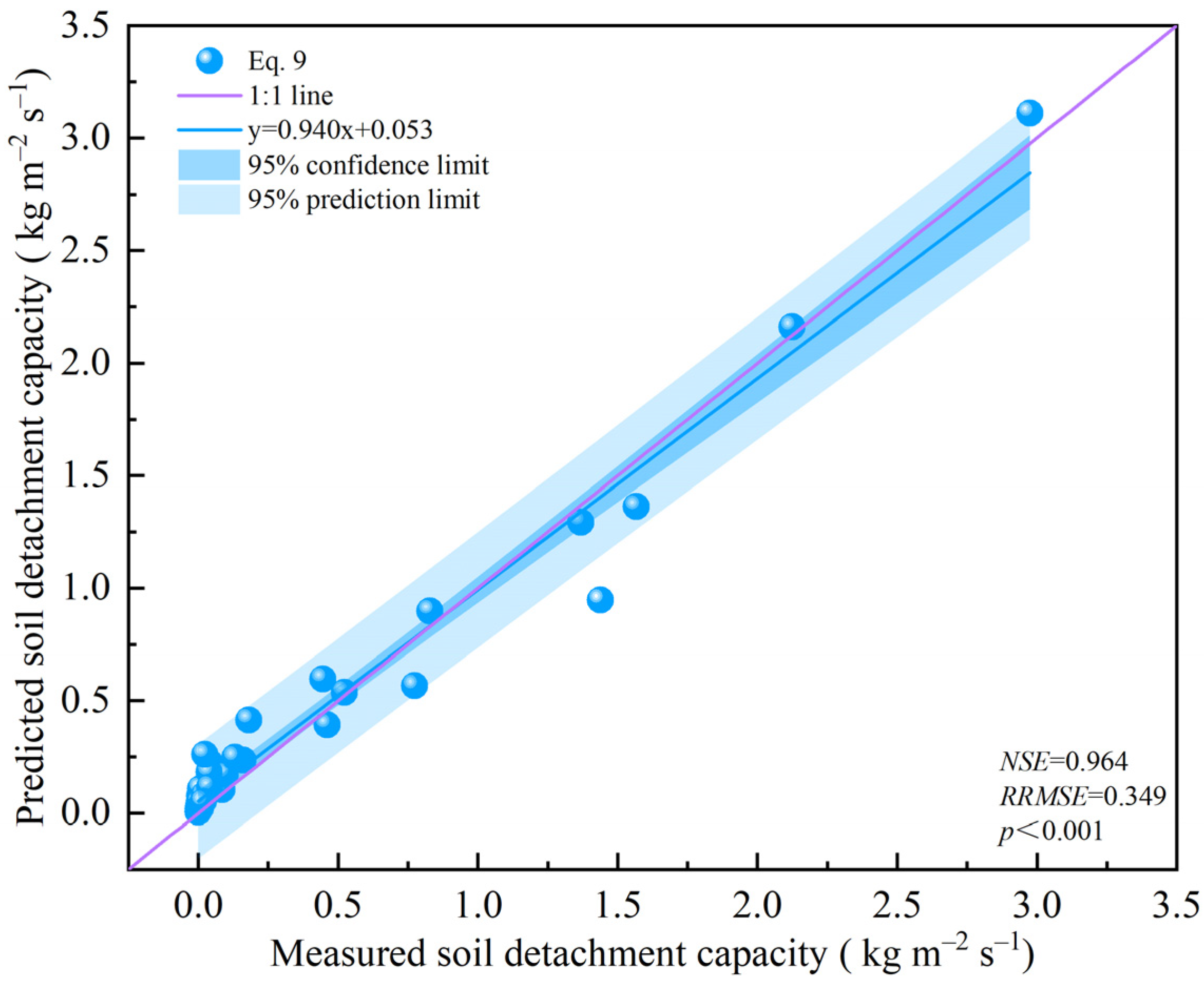


| Unit Flow Discharge (×10−3 m2 s−1) | Equation | R2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.33 | Dc = −0.007 + 0.053e−0.497C | 0.886 | 0.001 |
| 0.67 | Dc = −0.003 + 0.524e−1.084C | 0.994 | 0.001 |
| 1.00 | Dc = −0.061 + 0.909e−0.710C | 0.978 | 0.001 |
| 1.33 | Dc = −0.097 + 1.501e−0.723C | 0.971 | 0.001 |
| 2.00 | Dc = −0.219 + 2.434e−0.622C | 0.940 | 0.001 |
| 2.67 | Dc = −0.176 + 3.200e−0.724C | 0.987 | 0.001 |
| W-OH Concentration (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Average soil detachment capacity (kg s−1 m−2) | 1.31 a | 0.7394 ab | 0.158 b | 0.013 b | 0.012 b | 0.007 b |
| Reduction rate (%) | - | 42.068 b | 88.134 a | 99.022 a | 99.291 a | 99.555 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Meng, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, F. Control Effect of a Novel Polyurethane (W-OH) on Colluvial Deposit Slope Erosion in the Benggang Area of Southern China. Water 2025, 17, 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040548
Zhang Z, Chen Y, Zhu Z, Meng Y, Wu W, Zhou Y, Zhang Y, Lin J, Huang Y, Jiang F. Control Effect of a Novel Polyurethane (W-OH) on Colluvial Deposit Slope Erosion in the Benggang Area of Southern China. Water. 2025; 17(4):548. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040548
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhenggang, Yuyang Chen, Zhehao Zhu, Ying Meng, Wei Wu, Yiyang Zhou, Yue Zhang, Jinshi Lin, Yanhe Huang, and Fangshi Jiang. 2025. "Control Effect of a Novel Polyurethane (W-OH) on Colluvial Deposit Slope Erosion in the Benggang Area of Southern China" Water 17, no. 4: 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040548
APA StyleZhang, Z., Chen, Y., Zhu, Z., Meng, Y., Wu, W., Zhou, Y., Zhang, Y., Lin, J., Huang, Y., & Jiang, F. (2025). Control Effect of a Novel Polyurethane (W-OH) on Colluvial Deposit Slope Erosion in the Benggang Area of Southern China. Water, 17(4), 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040548






