Investigation on Lanthanum Modified Kaolinite for Control of Cyanobacterial Growth and Microcystin Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Treatment of M. aeruginosa by HKL-LH
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.3.1. Kinetic Model
2.3.2. Growth Assessment of M. aeruginosa
2.3.3. Fv/Fm and Cell Integrity Analysis
2.3.4. Determination of Cyanobacterial Cell Morphology
2.3.5. MC-LR Analysis
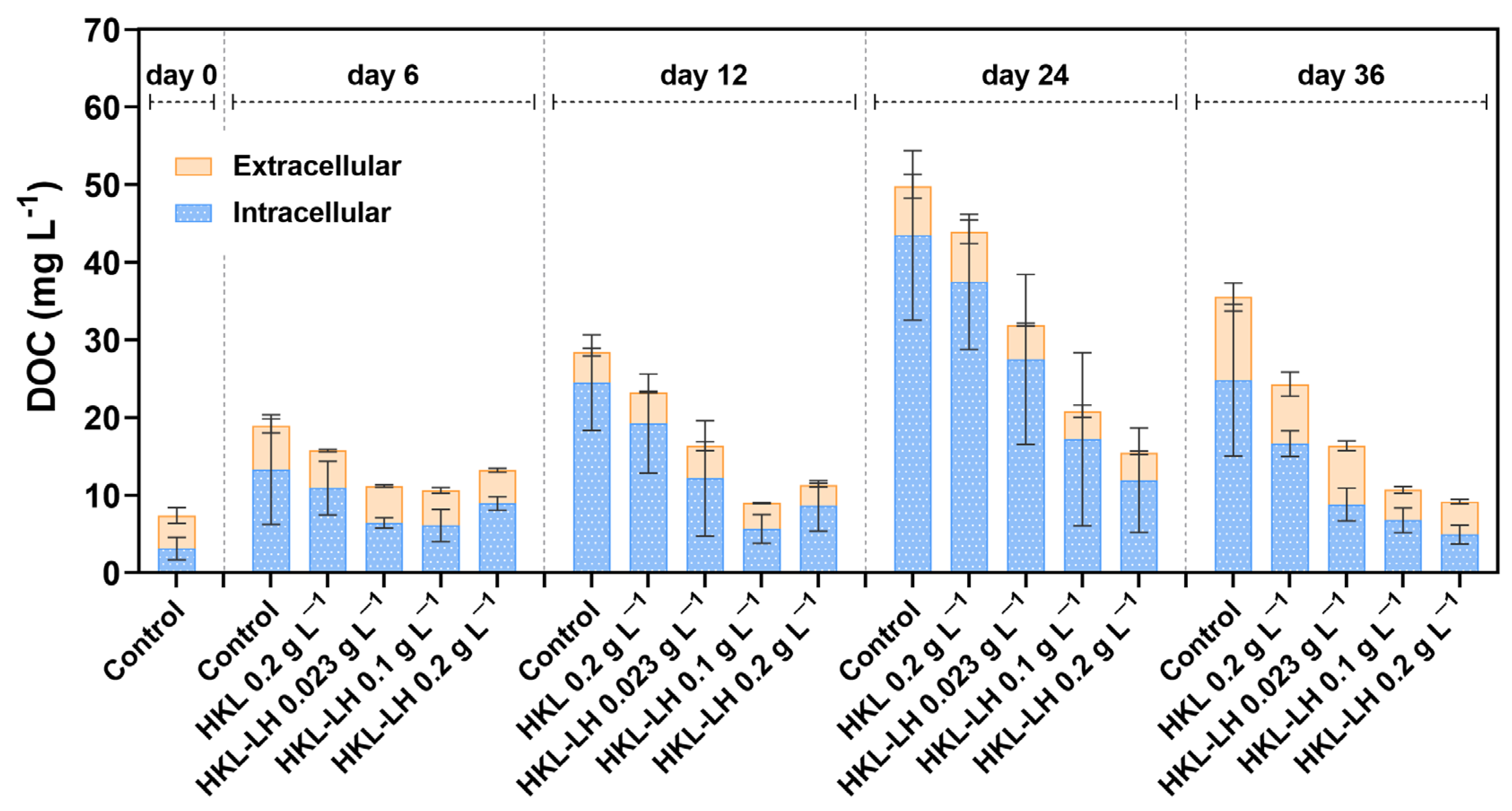
2.3.6. Measurement of Phosphate and AOMs
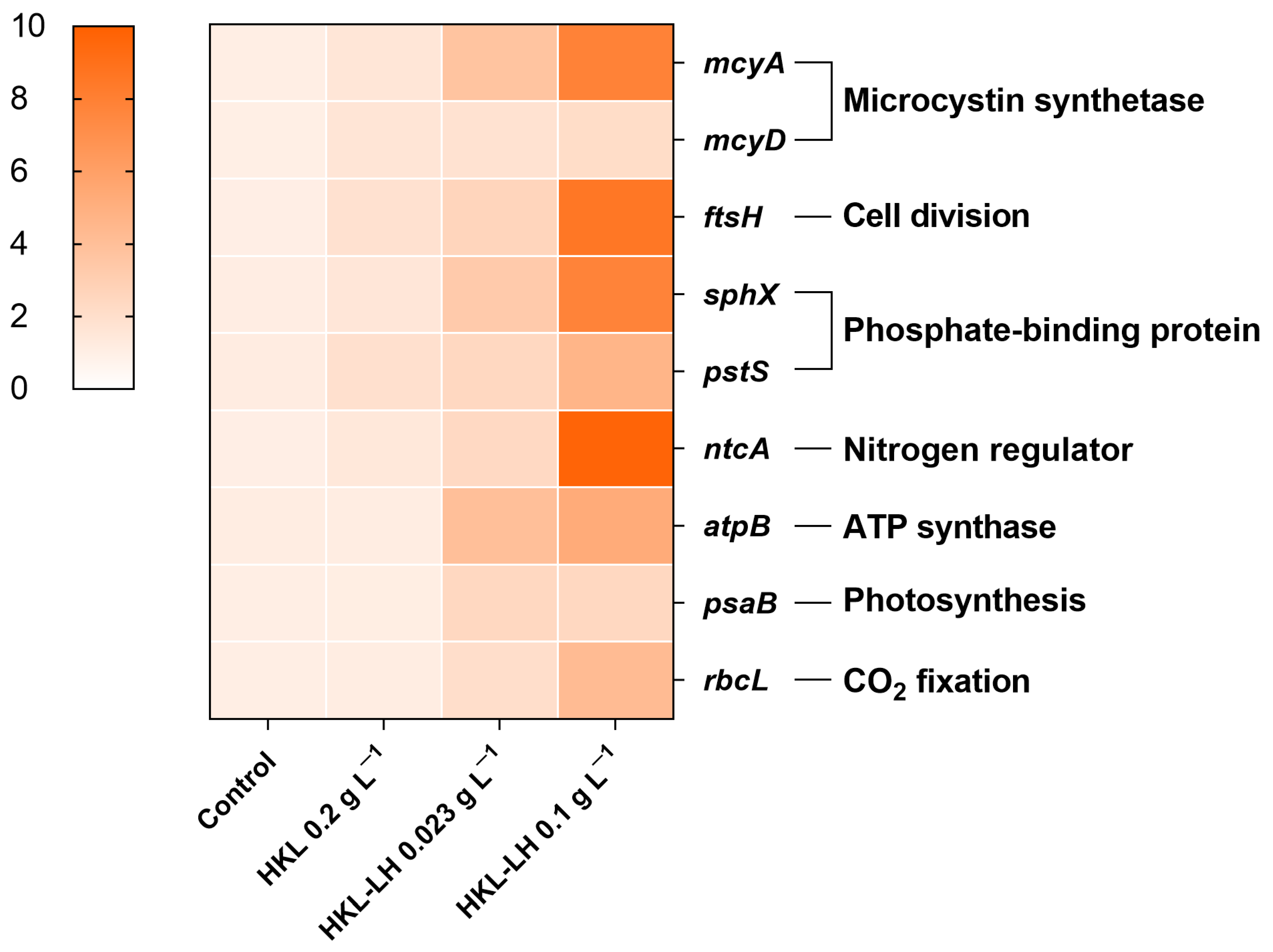
2.3.7. Gene Expression Test
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phosphate Removal by HKL-LH in M. aeruginosa Samples
3.2. The Impact of HKL-LH on the Growth of M. aeruginosa
3.3. Impacts of HKL-LH on the Viability of M. aeruginosa
3.4. Changes in MCs and AOMs by HKL-LH Treatment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Climate. Blooms like it hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facey, J.A.; Michie, L.E.; King, J.J.; Hitchcock, J.N.; Apte, S.C.; Mitrovic, S.M. Severe cyanobacterial blooms in an Australian lake; causes and factors controlling succession patterns. Harmful. Algae 2022, 117, 102284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, K.V.; Li, C.; Cai, H.; Krumholz, L.R.; Hambright, K.D.; Paerl, H.W.; Steffen, M.M.; Wilson, A.E.; Burford, M.A.; Grossart, H.-P.; et al. The global Microcystis interactome. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020, 65, S194–S207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codd, G.A.; Morrison, L.F.; Metcalf, J.S. Cyanobacterial toxins: Risk management for health protection. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 203, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Torres, A.; Pivokonsky, M.; Henderson, R.K. The impact of cell morphology and algal organic matter on algal floc properties. Water Res. 2019, 163, 114887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Rietveld, L.C.; Gao, N.; Hu, J.; Yin, D.; Yu, S. Comparison of the effects of extracellular and intracellular organic matter extracted from Microcystis aeruginosa on ultrafiltration membrane fouling: Dynamics and mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 14549–14557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, A.; Drikas, M.; Brookes, J.D. The role of phytoplankton as pre-cursors for disinfection by-product formation upon chlorination. Water Res. 2016, 102, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsanullah, I.; Khan, M.T.; Hossain, M.F.; Bilal, M.; Ali Shah, I. Eco-Friendly Solutions to Emerging Contaminants: Unveiling the Potential of Bioremediation in Tackling Microplastic Pollution in Water. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2024, 8, 2400172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, A.; Almanza, V.; Haakonsson, S.; Palacio, H.; Benitez Rodas, G.A.; Barros, M.U.G.; Capelo-Neto, J.; Urrutia, R.; Aubriot, L.; Bonilla, S. Cyanobacterial bloom monitoring and assessment in Latin America. Harmful. Algae 2023, 125, 102429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.C.; Michalak, A.M.; Pahlevan, N. Widespread global increase in intense lake phytoplankton blooms since the 1980s. Nature 2019, 574, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, D.; Gan, N.; Geng, R.; Cao, Q.; Song, L.; Yu, G.; Li, R. Cyanobacterial blooms in China: Diversity, distribution, and cyanotoxins. Harmful. Algae 2021, 109, 102106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.J.; Paerl, H.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Boesch, D.F.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Havens, K.E.; Lancelot, C.; Likens, G.E. Ecology. Controlling eutrophication: Nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 2009, 323, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.Q.; Xie, P.; Tang, H.J. Enhancement of dissolved phosphorus release from sediment to lake water by Microcystis blooms--an enclosure experiment in a hyper-eutrophic, subtropical Chinese lake. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 122, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correll, D.L. The Role of Phosphorus in the Eutrophication of Receiving Waters: A Review. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nollet, L.M.L.; Gelder, L.S.P.D. (Eds.) Handbook of Water Analysis, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, P.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J.; Bolan, N.S. Removal and Recovery of Phosphate from Water Using Sorption. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 847–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xia, D.; Cui, S.; Yu, W.; Wang, B.; Liu, H. A high-capacity nanocellulose aerogel uniformly immobilized with a high loading of nano-La(OH)3 for phosphate removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 134439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Haese, P.C.; Douglas, G.; Verhulst, A.; Neven, E.; Behets, G.J.; Vervaet, B.A.; Finsterle, K.; Lürling, M.; Spears, B. Human health risk associated with the management of phosphorus in freshwaters using lanthanum and aluminium. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Hu, W.; Pei, H.; Xu, H.; Pei, R. Enhancing integrated removal of Microcystis aeruginosa and adsorption of microcystins using chitosan-aluminum chloride combined coagulants: Effect of chemical dosing orders and coagulation mechanisms. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 490, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitzel, K.; Andersen, F.Ø.; Egemose, S.; Jensen, H.S. Phosphate adsorption by lanthanum modified bentonite clay in fresh and brackish water. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2787–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Ren, C.; Li, W. Introducing hydrate aluminum into porous thermally-treated calcium-rich attapulgite to enhance its phosphorus sorption capacity for sediment internal loading management. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 348, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltaweil, A.S.; Omer, A.M.; El-Aqapa, H.G.; Gaber, N.M.; Attia, N.F.; El-Subruiti, G.M.; Mohy-Eldin, M.S.; Abd El-Monaem, E.M. Chitosan based adsorbents for the removal of phosphate and nitrate: A critical review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 274, 118671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lürling, M.; Noyma, N.P.; de Magalhães, L.; Miranda, M.; Mucci, M.; van Oosterhout, F.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Marinho, M.M. Critical assessment of chitosan as coagulant to remove cyanobacteria. Harmful. Algae 2017, 66, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.E.; López-Galindo, A.; Setti, M.; El-Rahmany, M.M.; Iborra, C.V. Kaolinite in pharmaceutics and biomedicine. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 533, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detellier, C. Functional Kaolinite. Chem. Rec. 2018, 18, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.B.G.; Arshad, S.E. Hydrothermally synthesized zeolites based on kaolinite: A review. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 97–98, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, H.G. Kaolin: Soil, rock and ore: From the mineral to the magmatic, sedimentary and metamorphic environments. Earth Sci. Rev. 2016, 161, 16–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, K.I.; Quezada, G.R.; Arumí, J.L.; Toledo, P.G. Phosphate aggregation, diffusion, and adsorption on kaolinite in saline solutions by molecular dynamics simulation. Appl. Clay Sci. 2023, 233, 106844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Wang, Z.; Lu, S.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, H. Removal and recovery of phosphate from water by lanthanum hydroxide materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Hou, J.; Pan, Z.; Wu, M.; Zhang, M.; Yin, X.; Wu, J.; Miao, L.; Liu, Q. A novel La(OH)3 decorated co-graft tannin and polyethyleneimine co-coating magnetic adsorbent for effective and selective phosphate removal from natural water and real wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 369, 133345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Fan, J.; Lu, X. Heated kaolinite-La(III) hydroxide complex for effective removal of phosphate from eutrophic water. Appl. Clay Sci. 2023, 231, 106729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M.; Faassen, E.J. Controlling toxic cyanobacteria: Effects of dredging and phosphorus-binding clay on cyanobacteria and microcystins. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1447–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschek, G.A.; Obinger, C.; Renger, G. (Eds.) Bioenergetic Processes of Cyanobacteria; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briddon, C.L.; Szekeres, E.; Hegedüs, A.; Nicoară, M.; Chiriac, C.; Stockenreiter, M.; Drugă, B. The combined impact of low temperatures and shifting phosphorus availability on the competitive ability of cyanobacteria. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: Causes, consequences, and controls. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacelo, H.; Pintor, A.M.A.; Santos, S.C.R.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Botelho, C.M.S. Performance and prospects of different adsorbents for phosphorus uptake and recovery from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Pei, H.-Y.; Hu, W.-R.; Ma, C.-X. The lysis of Microcystis aeruginosa in AlCl3 coagulation and sedimentation processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 193–194, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Chen, Z.; Mao, G.; Chen, L.; Crittenden, J.; Li, R.Y.M.; Chai, L. Evaluation of eutrophication in freshwater lakes: A new non-equilibrium statistical approach. Ecol. Indic 2019, 102, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Farias Silva, C.E.; de Oliveira Cerqueira, R.B.; de Lima Neto, C.F.; de Andrade, F.P.; de Oliveira Carvalho, F.; Tonholo, J. Developing a kinetic model to describe wastewater treatment by microalgae based on simultaneous carbon, nitrogen and phosphorous removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Ho, L.; Hobson, P.; Brookes, J. Evaluating the effectiveness of copper sulphate, chlorine, potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide and ozone on cyanobacterial cell integrity. Water Res. 2013, 47, 5153–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, R.S.; Lombardi, A.T.; Omachi, C.Y.; Rörig, L.R. Effects of the herbicide bentazon on growth and photosystem II maximum quantum yield of the marine diatom Skeletonema costatum. Toxicol. Vitr. 2008, 22, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wei, G.; Tan, X.; Li, L.; Li, M. Species-dependent variation in sensitivity of Microcystis species to copper sulfate: Implication in algal toxicity of copper and controls of blooms. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, D.; Hurry, V.; Clarke, A.K.; Gustafsson, P.; Öquist, G. Chlorophyll Fluorescence Analysis of Cyanobacterial Photosynthesis and Acclimation. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 667–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Yu, X.; Fang, J.; Fan, J. Influences of the micropollutant erythromycin on cyanobacteria treatment with potassium permanganate. Water Res. 2020, 177, 115786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, B.C.; Rositano, J.; Burch, M.D. Destruction of cyanobacterial peptide hepatotoxins by chlorine and chloramine. Water Res. 1994, 28, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knochen, M.; Rodríguez-Silva, J.C.; Silva-Silva, J. Exploitation of reaction mechanisms for sensitivity enhancement in the determination of phosphorus by sequential injection analysis. Talanta 2020, 209, 120589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Gao, N.; Deng, Y.; Yao, J.; Zhang, K. Characterization of intracellular & extracellular algae organic matters (AOM) of Microcystic aeruginosa and formation of AOM-associated disinfection byproducts and odor & taste compounds. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Zhao, H.; Teng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Hoffmann, M.R. Phosphate removal and recovery by lanthanum-based adsorbents: A review for current advances. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, B.; Yu, W.; Huang, H.; Han, J.-C.; Huang, Y.; Wu, X.; Young, B.; Wang, G. Lanthanum-based adsorbents for phosphate reutilization: Interference factors, adsorbent regeneration, and research gaps. Sustain. Horiz. 2022, 1, 100011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lucena-Silva, D.; Molozzi, J.; Severiano, J.D.S.; Becker, V.; de Lucena Barbosa, J.E. Removal efficiency of phosphorus, cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins by the “flock & sink” mitigation technique in semi-arid eutrophic waters. Water Res. 2019, 159, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Wang, D.; Xu, Q.; Yao, F.; Chen, F.; Tao, Z.; Huang, X. Hydrated lanthanum oxide-modified diatomite as highly efficient adsorbent for low-concentration phosphate removal from secondary effluents. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correll, D.L. Phosphorus: A rate limiting nutrient in surface waters. Poult. Sci. 1999, 78, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Ding, K.; Sha, M.; Cao, Y.; Kong, F.; Wang, S. Recovery of phosphorus from eutrophic water using nano zero-valent iron-modified biochar and its utilization. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, S.; Chen, Z.; Yuen Koh, K.; Cui, F.; Paul Chen, J. Development and application of lanthanum peroxide loaded sepiolite nanocomposites for simultaneous removal of phosphate and inhibition of cyanobacteria growth. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 624, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Mucci, M.; Lürling, M. Compounds to mitigate cyanobacterial blooms affect growth and toxicity of Microcystis aeruginosa. Harmful. Algae 2022, 118, 102311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.L.; Loftin, K.A.; Ziegler, A.C.; Meyer, M.T. Guidelines for Design and Sampling for Cyanobacterial Toxin and Taste-and-Odor Studies in Lakes and Reservoirs; Scientific Investigations Report No. 2008–5038; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipka, G.B.; Magyar, M.; Mezzetti, A.; Akhtar, P.; Zhu, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Han, G.; Santabarbara, S.; Shen, J.-R.; Lambrev, P.H.; et al. Light-adapted charge-separated state of photosystem II: Structural and functional dynamics of the closed reaction center. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 1286–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Lin, Q.; Liu, B.; Huang, S.; Yan, W.; Zhang, L.; Ge, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z. Effect of submerged plant coverage on phytoplankton community dynamics and photosynthetic activity in situ. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Zeng, B.; Li, R.; Song, L. Physiological regulation of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria) in response to inorganic phosphorus limitation. Harmful. Algae 2012, 15, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butusov, M.; Jernelöv, A. Phosphorus in the Organic Life: Cells, Tissues, Organisms. In Phosphorus: An Element That Could Have Been Called Lucifer; Butusov, M., Jernelöv, A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, G.; Wang, Y.; Guo, C.; Zhou, J. Physiological and molecular responses of Prorocentrum donghaiense to dissolved inorganic phosphorus limitation. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 129, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Huang, S.; Xu, L.; Li, Q.; Luo, X.; Zheng, Z. Response of Magnetite/Lanthanum hydroxide composite on cyanobacterial bloom. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Shi, W.; Mynett, A.E.; Yan, H.; Hu, L. Physiological effects of nitrate, ammonium, and urea on the growth and microcystins contamination of Microcystis aeruginosa: Implication for nitrogen mitigation. Water Res. 2019, 163, 114890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, G.; Fastner, J.; Erhard, M.; Börner, T.; Dittmann, E. Microcystin biosynthesis in planktothrix: Genes, evolution, and manipulation. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKeigan, P.W.; Zastepa, A.; Taranu, Z.E.; Westrick, J.A.; Liang, A.; Pick, F.R.; Beisner, B.E.; Gregory-Eaves, I. Microcystin concentrations and congener composition in relation to environmental variables across 440 north-temperate and boreal lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 884, 163811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, R.; Yu, X.; Fan, J. Physiological, biochemical and transcriptional responses of cyanobacteria to environmentally relevant concentrations of a typical antibiotic-roxithromycin. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, R.; Li, Z.; Yan, F.; An, L.; Du, W.; Li, X. Evaluation of changes in M. aeruginosa growth and microcystin production under phosphorus starvation via transcriptomic surveys. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 893, 164848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantala, A.; Fewer, D.P.; Hisbergues, M.; Rouhiainen, L.; Vaitomaa, J.; Börner, T.; Sivonen, K. Phylogenetic evidence for the early evolution of microcystin synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qian, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, F.; An, D.; Yang, G.; Dai, R. Application of fluorescence spectra and molecular weight analysis in the identification of algal organic matter-based disinfection by-product precursors. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Shao, Y.; Gao, N.; Deng, Y.; Li, L.; Deng, J.; Tan, C. Characterization of algal organic matters of Microcystis aeruginosa: Biodegradability, DBP formation and membrane fouling potential. Water Res. 2014, 52, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harke, M.J.; Berry, D.L.; Ammerman, J.W.; Gobler, C.J. Molecular response of the bloom-forming cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa, to phosphorus limitation. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 63, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaebernick, M.; Neilan, B.A.; Börner, T.; Dittmann, E. Light and the transcriptional response of the microcystin biosynthesis gene cluster. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3387–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Kang, X.; Chu, L.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Zhao, X.; Cao, X. Algicidal mechanism of Raoultella ornithinolytica against Microcystis aeruginosa: Antioxidant response, photosynthetic system damage and microcystin degradation. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Shi, L.; Kong, F. Changes in the physiology and gene expression of Microcystis aeruginosa under EGCG stress. Chemosphere 2014, 117, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muro-Pastor, M.I.; Florencio, F.J. Regulation of ammonium assimilation in cyanobacteria. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2003, 41, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, J.S.M.; Giani, A. Microcystin production and regulation under nutrient stress conditions in toxic microcystis strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5836–5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Yu, S.; Sun, Z.; Xie, X.; Liu, W.; Fu, Z. Effects of copper sulfate, hydrogen peroxide and N-phenyl-2-naphthylamine on oxidative stress and the expression of genes involved photosynthesis and microcystin disposition in Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 99, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinta-Kanto, J.M.; Ouellette, A.J.A.; Boyer, G.L.; Twiss, M.R.; Bridgeman, T.B.; Wilhelm, S.W. Quantification of toxic Microcystis spp. during the 2003 and 2004 blooms in western Lake Erie using quantitative real-time PCR. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4198–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
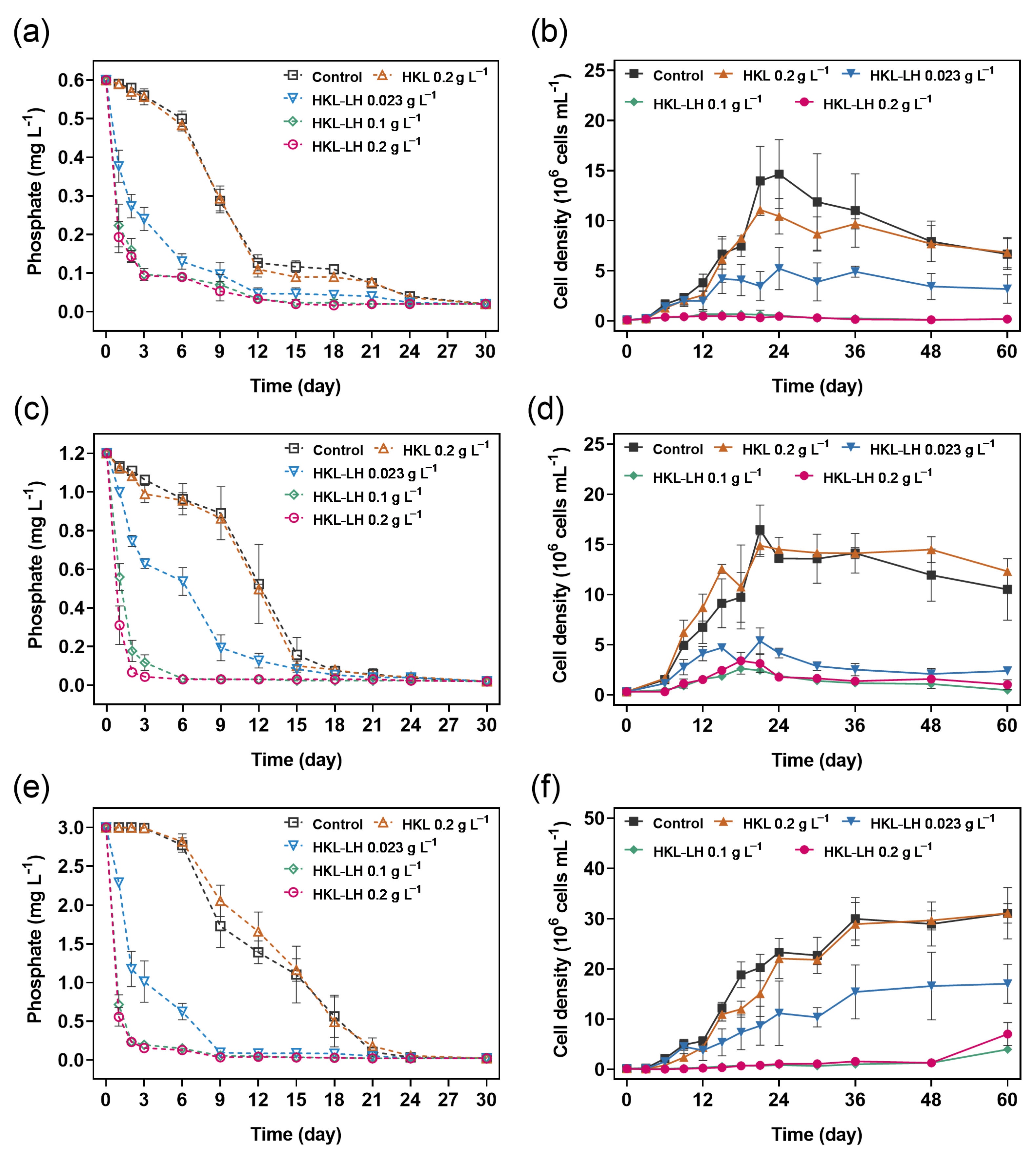
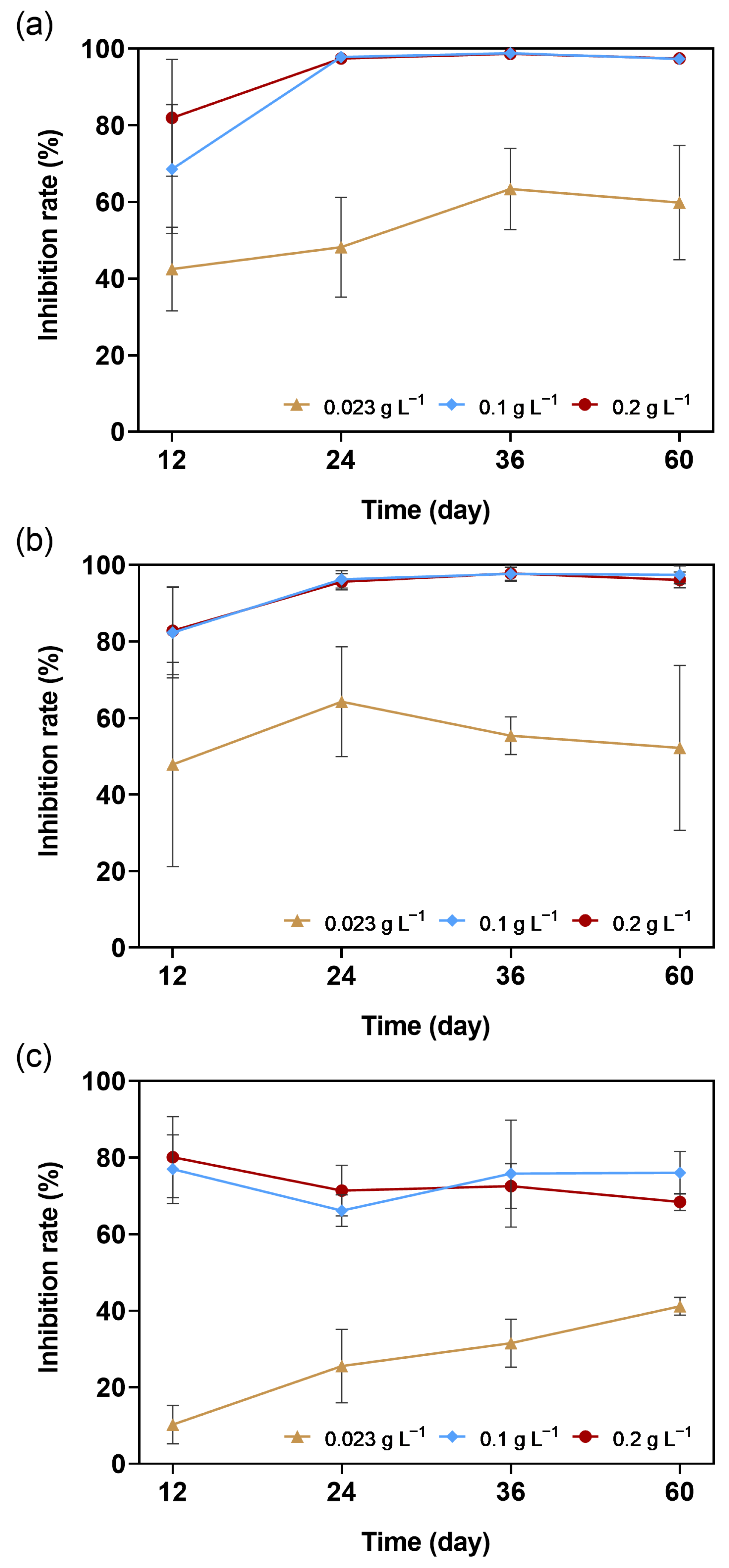
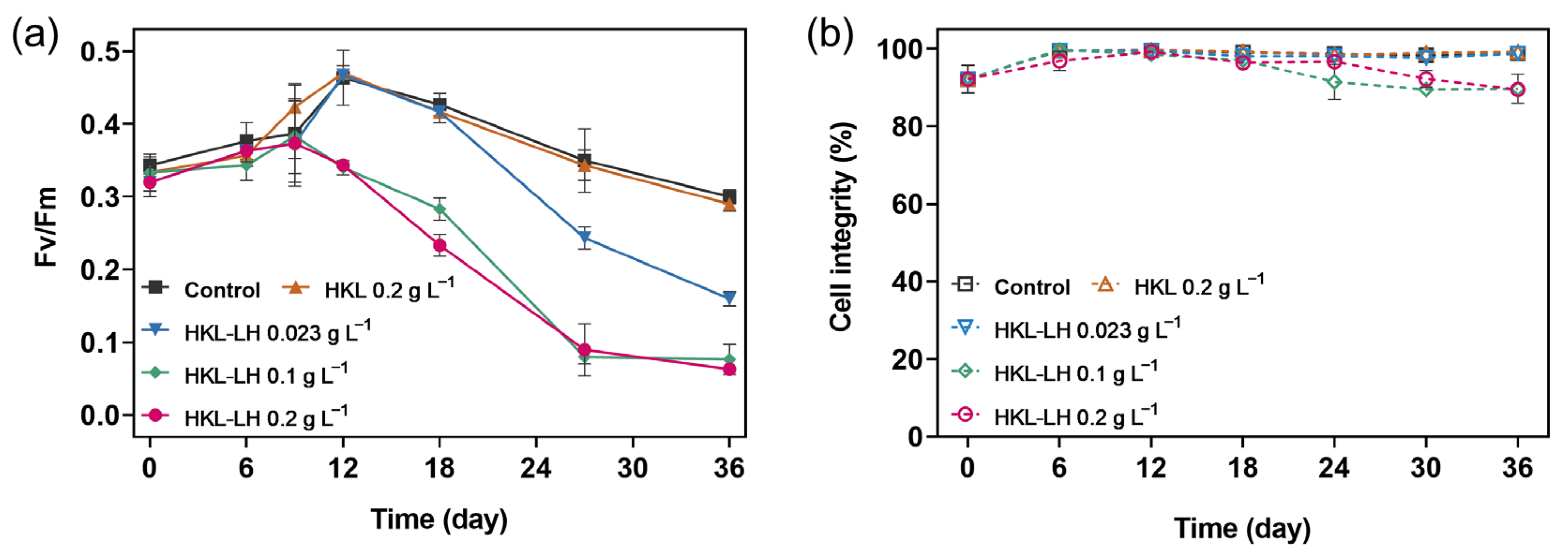
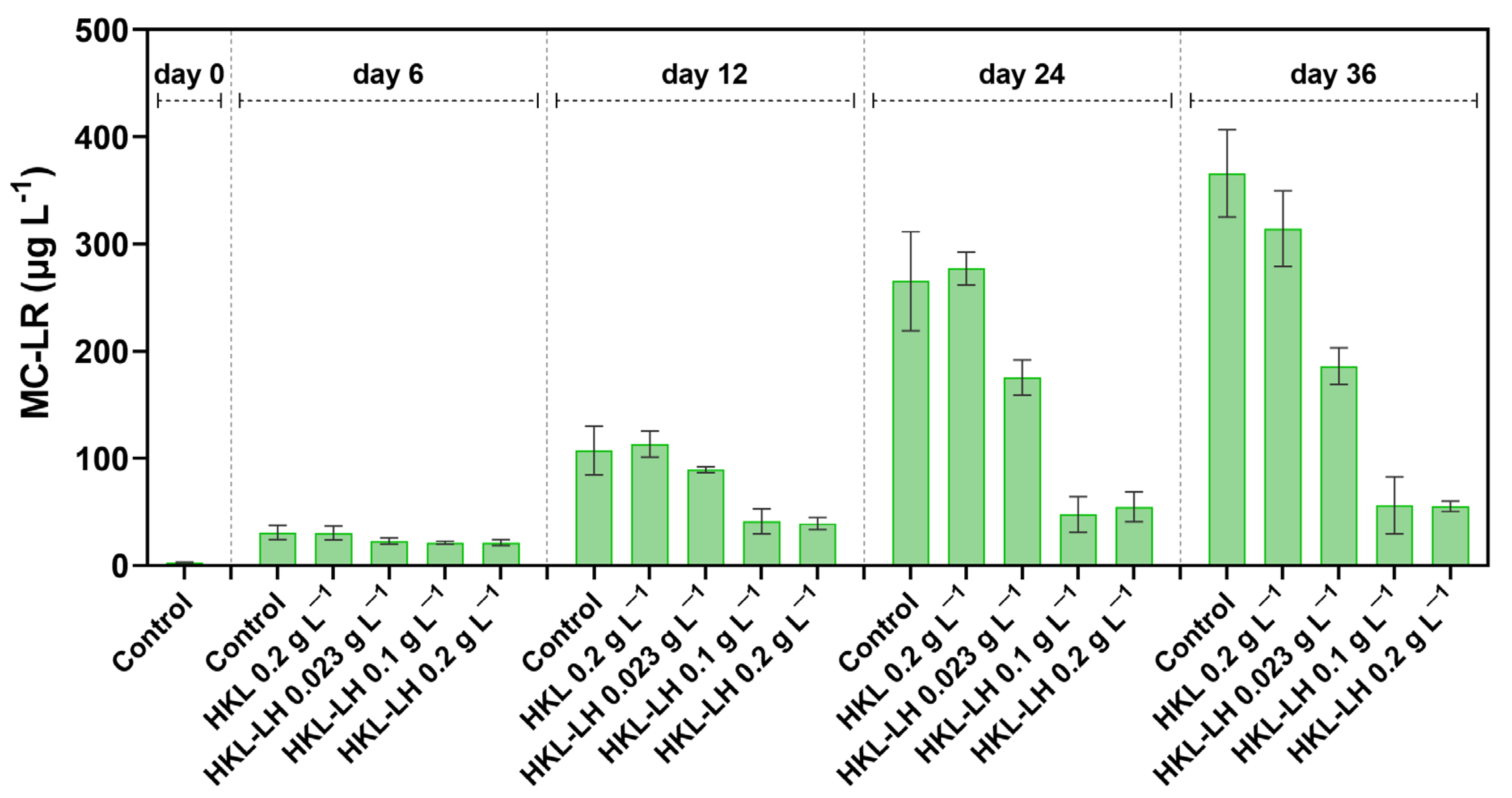
| [HKL-LH] (g L−1) | Initial Phosphate Concentrations (mg L−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.6 | 1.2 | 3.0 | ||||
| k (L mg−1 d−1) | R2 | k (L mg−1 d−1) | R2 | k (L mg−1 d−1) | R2 | |
| 0.023 | 0.86 | 0.9908 | 0.21 | 0.9853 | 0.22 | 0.9721 |
| 0.1 | 2.68 | 0.9904 | 2.38 | 0.9704 | 1.67 | 0.9823 |
| 0.2 | 2.91 | 0.9943 | 6.93 | 0.9670 | 2.00 | 0.9943 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miao, Y.; Zheng, S.; Lu, X.; Zhang, K.; Fan, J. Investigation on Lanthanum Modified Kaolinite for Control of Cyanobacterial Growth and Microcystin Production. Water 2025, 17, 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030428
Miao Y, Zheng S, Lu X, Zhang K, Fan J. Investigation on Lanthanum Modified Kaolinite for Control of Cyanobacterial Growth and Microcystin Production. Water. 2025; 17(3):428. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030428
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiao, Yige, Songhai Zheng, Xiancai Lu, Kejia Zhang, and Jiajia Fan. 2025. "Investigation on Lanthanum Modified Kaolinite for Control of Cyanobacterial Growth and Microcystin Production" Water 17, no. 3: 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030428
APA StyleMiao, Y., Zheng, S., Lu, X., Zhang, K., & Fan, J. (2025). Investigation on Lanthanum Modified Kaolinite for Control of Cyanobacterial Growth and Microcystin Production. Water, 17(3), 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030428







