Bacterioplankton Community Structure and Its Relationship with Environmental Factors in the Coastal Waters Around the Changli Gold Coast National Nature Reserve in Northern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
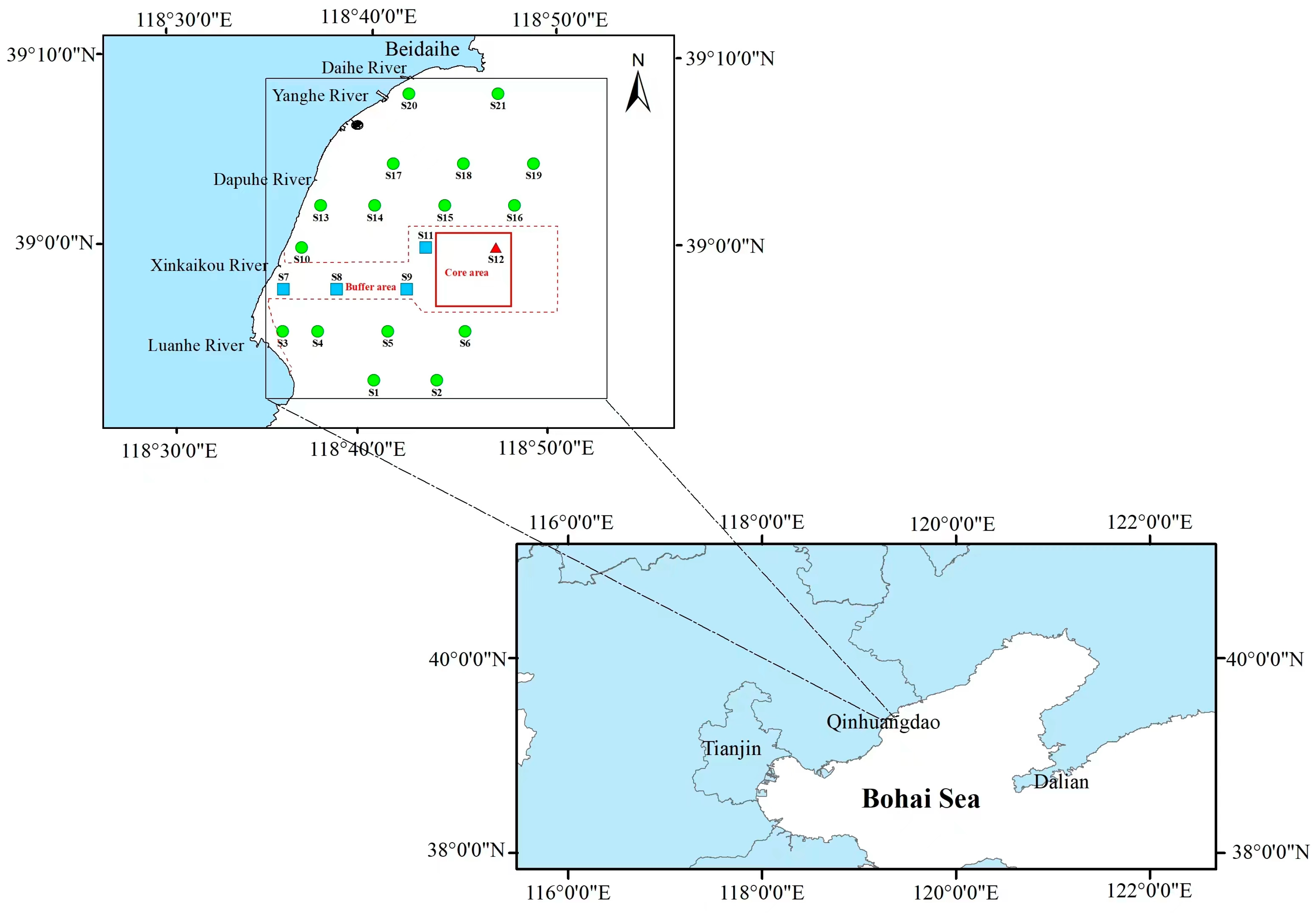
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Determination of Environmental Parameters
2.3. High-Throughput Sequencing and Data Analysis and Statistics
2.4. Data Analysis and Statistics
3. Result
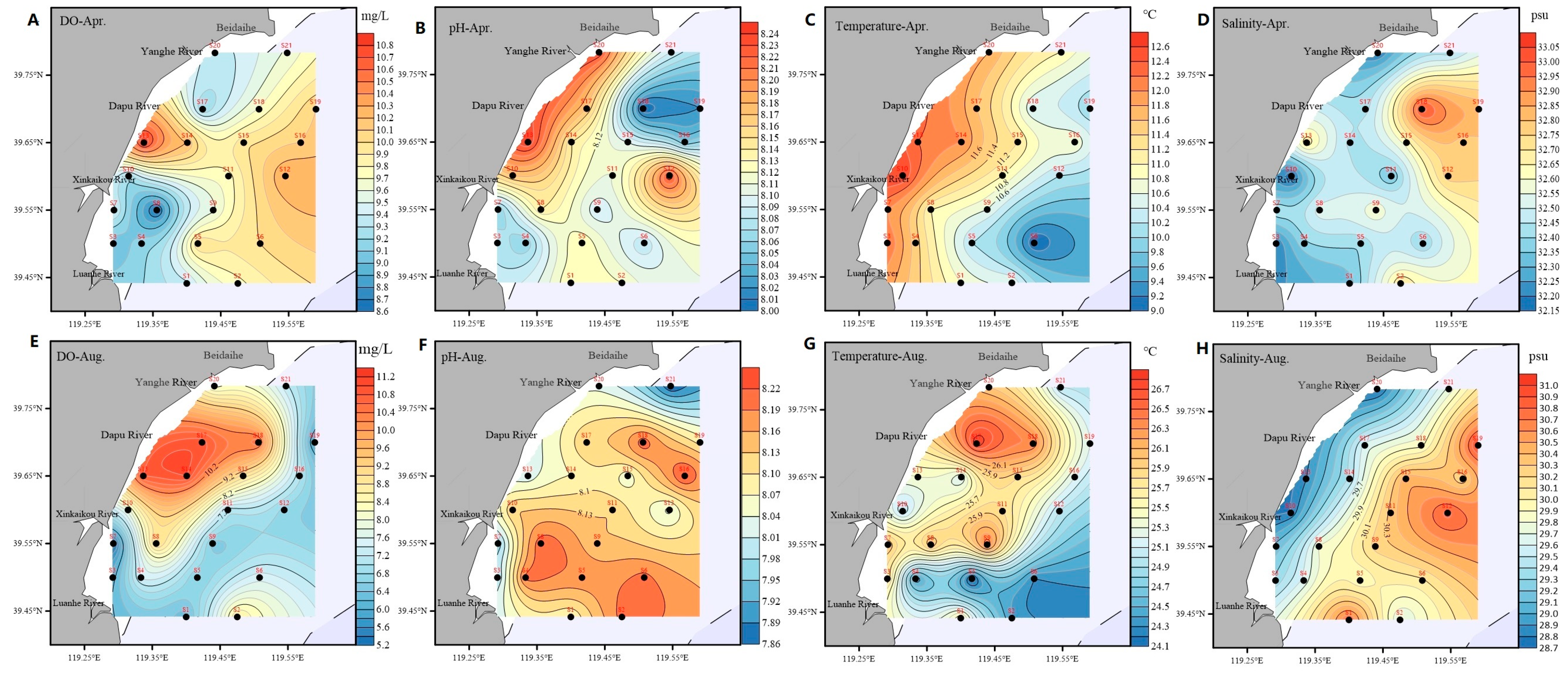
3.1. Spatiotemporal Distributions of Basic Physical Environment Factors
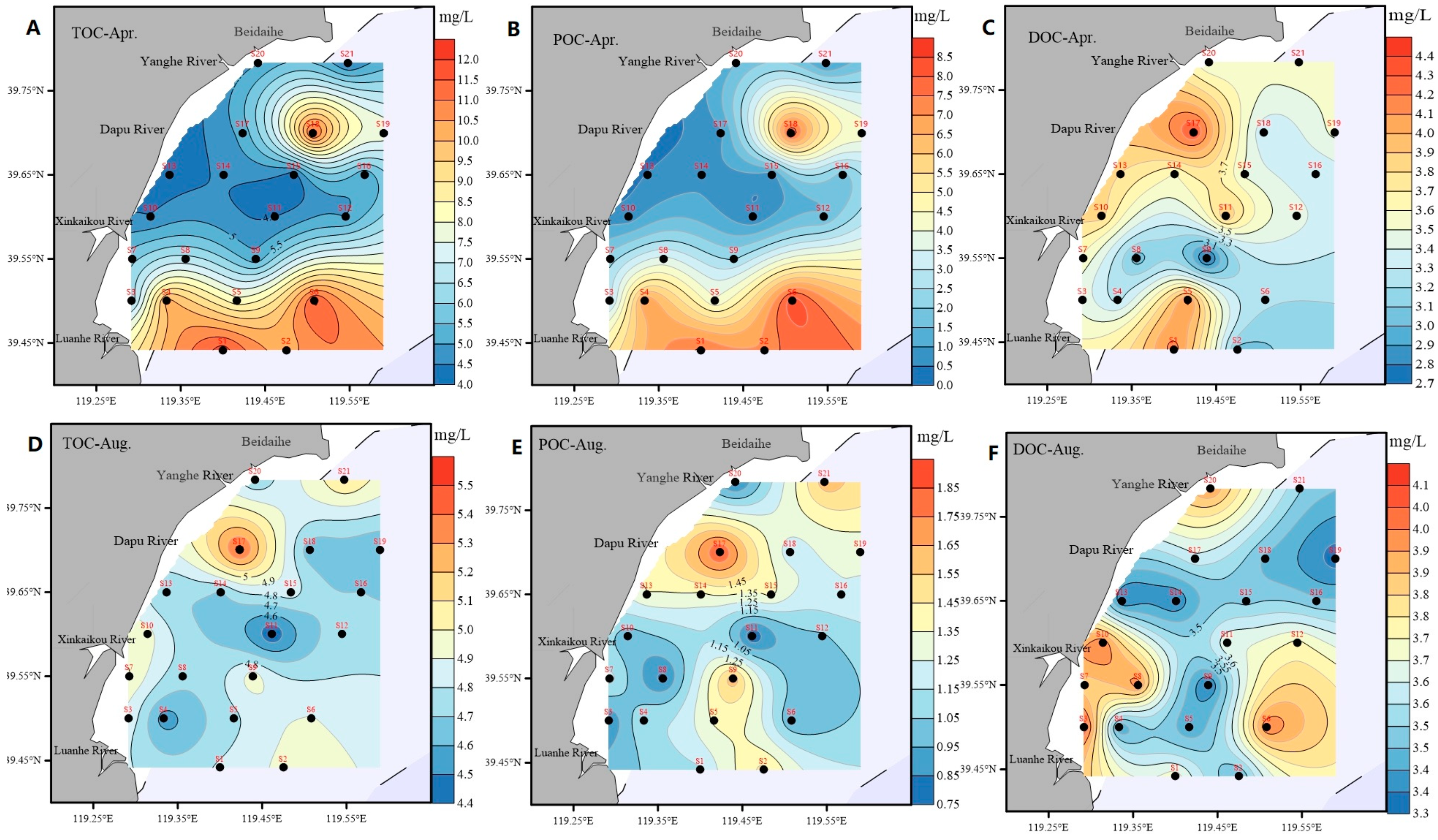
3.2. Spatiotemporal Distributions of Different Forms of Carbon
3.3. Spatiotemporal Distributions of Different Forms of Nitrogen
3.4. Spatiotemporal Distributions of Different Forms of Phosphorus
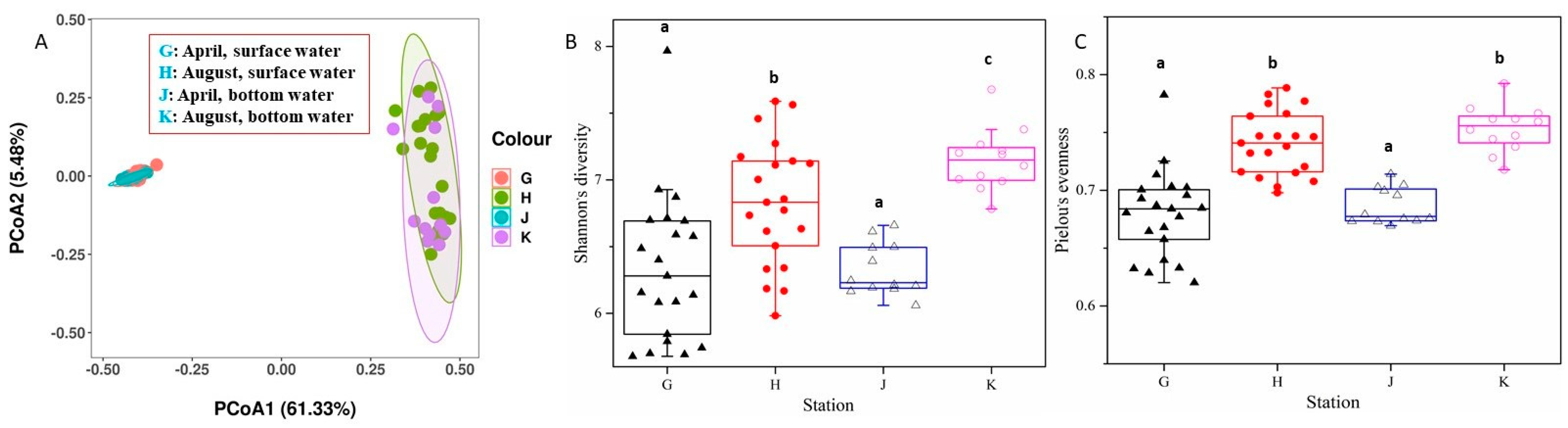
3.5. Bacterioplankton Diversity
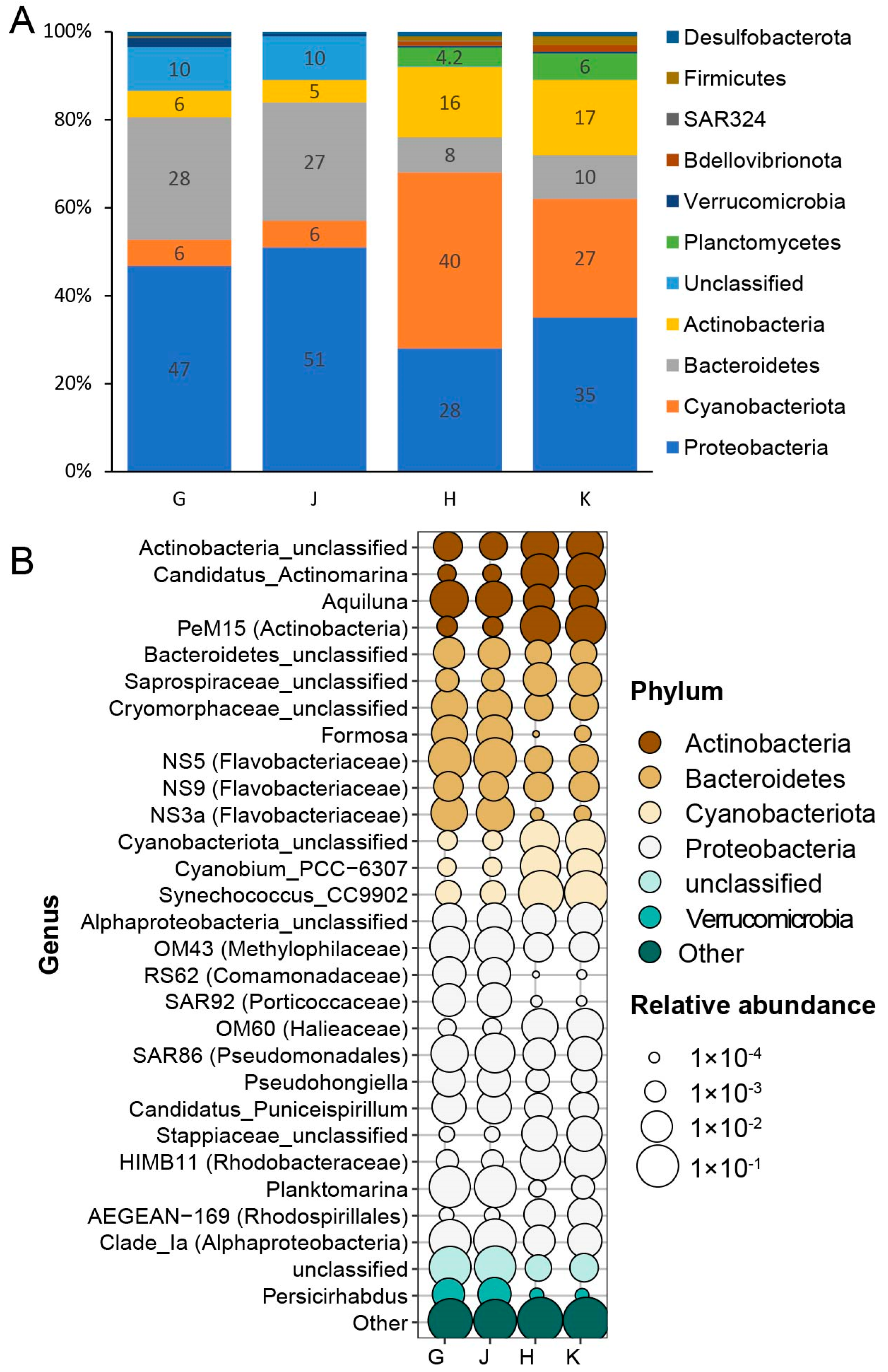
3.6. Bacterioplankton Communities
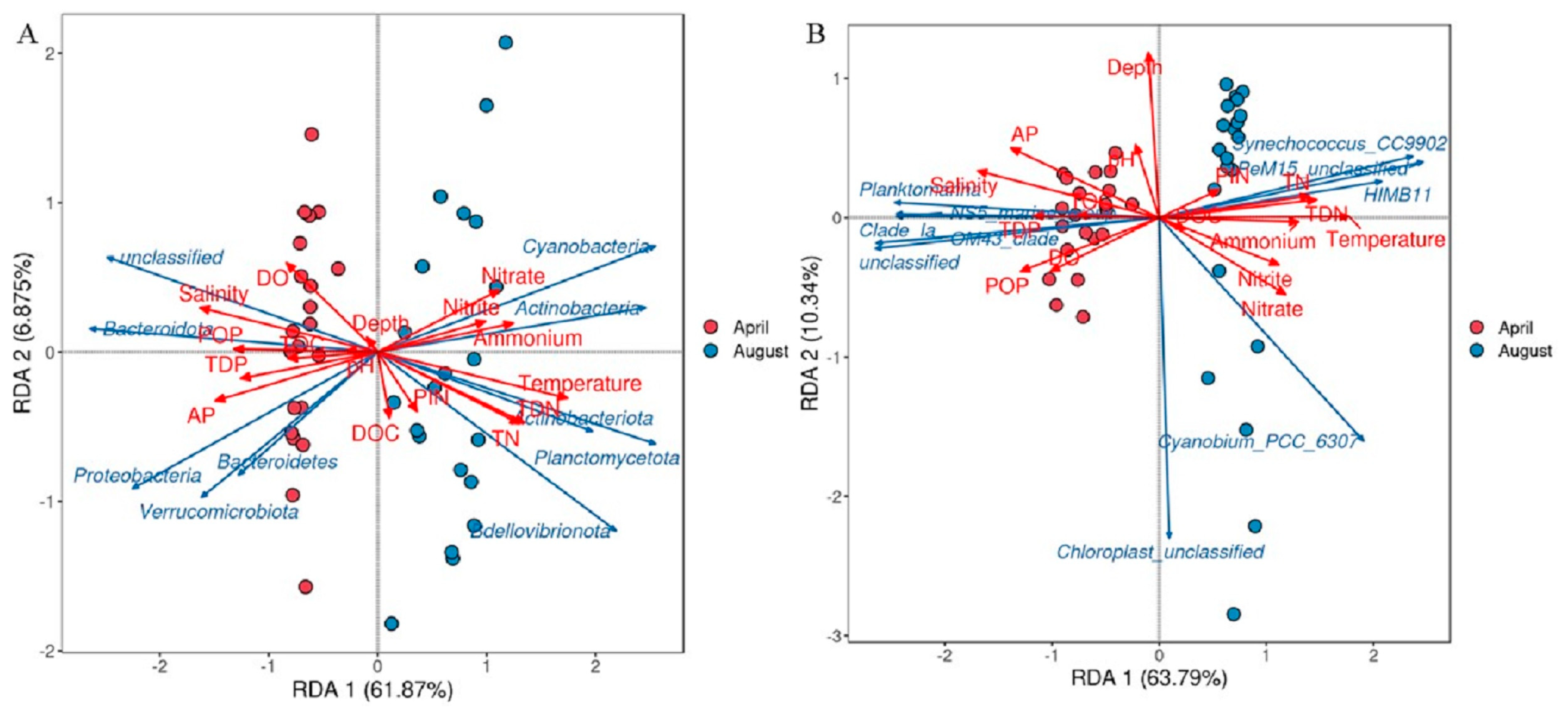
3.7. Relationship Between Distribution of Bacterioplankton Communities and Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Potential Causes Related to the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus
4.2. Phosphorus, Nitrogen, and Carbon Element Cycling and Transformation Processes
4.3. Adaptability of Coastal Bacterioplankton Communities
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wåhlström, I.; Höglund, A.; Almroth-Rosell, E.; MacKenzie, B.R.; Gröger, M.; Eilola, K.; Plikshs, M.; Andersson, H.C. Combined climate change and nutrient load impacts on future habitats and eutrophication indicators in a eutrophic coastal sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020, 65, 2170–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Kim, K.-T.; Kim, H.-C.; Lee, W.-C.; Choi, D.; Choi, S.-H.; Choi, J.-H.; Lee, H.-J.; Shin, J.-H. Aquaculture farming effect on benthic respiration and nutrient flux in semi-enclosed coastal waters of Korea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, F.O.; Sampaio, E.; Santos, C.P.; Rosa, R. Impacts of low oxygen on marine life: Neglected, but a crucial priority for research. Biol. Bull. 2022, 243, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Yu, M.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Guan, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Lv, Z.; Qu, F.; Yang, J. Impacts of inland pollution input on coastal water quality of the Bohai Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 142691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, N.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, W.a.; Ma, Y.; Niu, Z. Colonization characteristics of bacterial communities on plastic debris influenced by environmental factors and polymer types in the Haihe Estuary of Bohai Bay, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10763–10773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, L.A.; Corbett, D.R.; Fitzgerald, A.M.; Lemley, D.A.; Quigg, A.; Steppe, C.N. Impacts of urbanization and development on estuarine ecosystems and water quality. Estuaries Coasts 2019, 42, 1821–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeamsripong, S.; Khant, W.; Chuanchuen, R. Distribution of phenotypic and genotypic antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes in Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from cultivated oysters and estuarine water. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grogan, A.E.; Mallin, M.A. Successful mitigation of stormwater-driven nutrient, fecal bacteria and suspended solids loading in a recreational beach community. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 281, 111853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Song, Z.; Hu, X. Divergent patterns of bacterial community structure and function in response to estuarine output in the middle of the Bohai Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 630741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S. The nutrient, total petroleum hydrocarbon and heavy metal contents in the seawater of Bohai Bay, China: Temporal–spatial variations, sources, pollution statuses, and ecological risks. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-R.; Guo, X.-P.; Feng, J.-N.; Lu, D.-P.; Niu, Z.-S.; Tou, F.-Y.; Hou, L.-J.; Liu, M.; Yang, Y. Impact of ZnO nanoparticles on the antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in estuarine water: ARG variations and their association with the microbial community. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 2405–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dai, J.; Chen, G.; Jiang, F. Role of sulfur biogeochemical cycle in mercury methylation in estuarine sediments: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 126964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.-M.; Xu, M.N.; Lin, Y.; Chen, H.; Jin, H.; Han, L.-L.; Zou, W.; Kao, S.-J. The biological transformation of ammonium and urea in a eutrophic estuarine system in Southern China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1040554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Wu, W.; Liang, W.; Wang, Y.; Hou, J.; Chen, Y.; Elvert, M.; Hinrichs, K.-U.; Wang, F. Anaerobic degradation of organic carbon supports uncultured microbial populations in estuarine sediments. Microbiome 2023, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M.; Heil, C.A.; Madden, C.J.; Kelly, S.P. Dissolved organic nutrients at the interface of fresh and marine waters: Flow regime changes, biogeochemical cascades and picocyanobacterial blooms—The example of Florida Bay, USA. Biogeochemistry 2023, 164, 229–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zheng, Y.; Hou, L.; Niu, Y.; Gao, D.; An, Z.; Zhou, J.; Yin, G.; Dong, H.; Han, P. Microbial abundance and activity of nitrite/nitrate-dependent anaerobic methane oxidizers in estuarine and intertidal wetlands: Heterogeneity and driving factors. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Dong, X.; Liu, S.; Lin, X. Advances in estuarine and coastal nitrogen cycle. Front. Media SA 2023, 10, 1130839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Lin, Z.; Zhou, C.; Zhu, P.; Yan, X. Succession of bacterioplankton communities over complete Gymnodinium-diatom bloom cycles. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 135951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.; Qi, Z.; Han, T.; Dai, M.; Zhang, S.; Huang, H. Responses of bacterioplankton, particle-and colony-attached bacterial communities to Phaeocystis globosa blooms in Mirs Bay, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1075059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, Z.; Wei, Q.; Yao, Q. Long-term nutrient variations in the Bohai Sea over the past 40 years. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 124, 703–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Mu, J.; Yu, X.; Hui, R. Seasonal and anthropogenic influences on bacterioplankton communities: Ecological impacts in the coastal waters of Qinhuangdao, Northern China. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1431548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, X.-z. Eutrophication control strategies for highly anthropogenic influenced coastal waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Walters, W.A.; González, A.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R. Using QIIME to analyze 16S rRNA gene sequences from microbial communities. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2011, 10, 10.7.1–10.7.20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Liang, B.; Li, S.; Hu, J. A study on the response of carbon cycle system in the Pearl River Estuary to riverine input variations. J. Mar. Syst. 2021, 215, 103498. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, A.; Hajima, T.; Yamazaki, D.; Noguchi Aita, M.; Ito, A.; Kawamiya, M. Competing and accelerating effects of anthropogenic nutrient inputs on climate-driven changes in ocean carbon and oxygen cycles. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabl9207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.; Zhao, Y.; Chai, F.; Chen, M.; Chen, N.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, D.; Gan, J.; Guan, D.; Hong, Y. Persistent eutrophication and hypoxia in the coastal ocean. Camb. Prism. Coast. Futures 2023, 1, e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, A.M.; King, C.K.; Stark, J.S.; McMinn, A.; Davidson, A.T. Effects of ocean acidification on Antarctic marine organisms: A meta-analysis. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 4495–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abirami, B.; Radhakrishnan, M.; Kumaran, S.; Wilson, A. Impacts of global warming on marine microbial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 147905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Huang, X.; Yang, B.; Dan, S.F.; Kang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Lao, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Wu, H. Composition and distributions of nitrogen and phosphorus and assessment of eutrophication status in the Maowei Sea. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2021, 20, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Ma, J.; Xu, H.; Xu, Z.; Liu, W.; Pan, K. Multiple isotopic compositions reveal complex nitrogen cycling in a subtropical estuary. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 116410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrerizo, M.J.; Medina-Sánchez, J.M.; González-Olalla, J.M.; Sánchez-Gómez, D.; Carrillo, P. Microbial plankton responses to multiple environmental drivers in marine ecosystems with different phosphorus limitation degrees. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 151491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, B.J.; Lazar, C.S.; Teske, A.P.; Dick, G.J. Genomic resolution of linkages in carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur cycling among widespread estuary sediment bacteria. Microbiome 2015, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.; Song, L.; Wang, J.; Luo, Y.; Yu, G. Dynamic carbon-nitrogen coupling under global change. Sci. China Life Sci. 2023, 66, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, D.A.; Capone, D.G. The marine nitrogen cycle: New developments and global change. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Pan, F.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Guo, Z.; Wang, X.; Zheng, C. Coastal aquaculture regulates phosphorus cycling in estuarine wetlands: Mobilization, kinetic resupply, and source-sink process. Water Res. 2023, 234, 119832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuirk Flynn, A. Organic matter and nutrient cycling in a coastal plain estuary: Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus distributions, budgets, and fluxes. J. Coastal Res. 2008, 10055, 76–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Sen, B.; Zhou, S.; Xie, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G. Distinct seasonal patterns of bacterioplankton abundance and dominance of phyla α-Proteobacteria and cyanobacteria in Qinhuangdao coastal waters off the Bohai sea. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louca, S.; Parfrey, L.W.; Doebeli, M. Decoupling function and taxonomy in the global ocean microbiome. Science 2016, 353, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crump, B.C.; Bowen, J.L. The microbial ecology of estuarine ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2024, 16, 335–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louca, S.; Jacques, S.M.; Pires, A.P.; Leal, J.S.; González, A.L.; Doebeli, M.; Farjalla, V.F. Functional structure of the bromeliad tank microbiome is strongly shaped by local geochemical conditions. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 3132–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Zou, Y.; Grebmeier, J.M.; He, J.; Zheng, T. Culture-independent and-dependent methods to investigate the diversity of planktonic bacteria in the northern Bering Sea. Polar Biol. 2012, 35, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltar, F.; Martínez-Pérez, C.; Amano, C.; Vial, M.; Robaina-Estévez, S.; Reinthaler, T.; Herndl, G.J.; Zhao, Z.; Logares, R.; Morales, S.E.; et al. A ubiquitous gammaproteobacterial clade dominates expression of sulfur oxidation genes across the mesopelagic ocean. Nat. Microbiol. 2023, 8, 1137–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Tran, P.Q.; Cowley, E.S.; Trembath-Reichert, E.; Anantharaman, K. Diversity and ecology of microbial sulfur metabolism. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2025, 23, 122–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Hwang, J.; Kang, I.; Cho, J.-C. A sulfate-reducing bacterial genus, Desulfosediminicola gen. nov., comprising two novel species cultivated from tidal-flat sediments. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, H.P.; Puthusseri, R.M.; Vincent, H.; Bhat, S.G. 16S rDNA-based bacterial diversity analysis of Arabian Sea sediments: A metagenomic approach. Ecol. Genet. Genom. 2017, 3, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannoni, S.J. SAR11 Bacteria: The most abundant plankton in the oceans. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2017, 9, 231–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.; Kube, M.; Teeling, H.; Richter, M.; Lombardot, T.; Allers, E.; Würdemann, C.A.; Quast, C.; Kuhl, H.; Knaust, F. Whole genome analysis of the marine Bacteroidetes ‘Gramella forsetii’reveals adaptations to degradation of polymeric organic matter. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 2201–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, H.; Stübner, M.; Simon, M.; Brinkhoff, T. Phylogeny of Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes from oxic habitats of a tidal flat ecosystem. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2005, 54, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Xiao, N.; Wang, Q.; Wu, H. Seasonal variation of bacterial community diversity in Yangshan Port. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 7758–7767. [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst, J.A.; Sagulenko, E. Beyond the bacterium: Planctomycetes challenge our concepts of microbial structure and function. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speirs, L.B.; Rice, D.T.; Petrovski, S.; Seviour, R.J. The phylogeny, biodiversity, and ecology of the Chloroflexi in activated sludge. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeuf, D.; Eppley, J.M.; Mende, D.R.; Malmstrom, R.R.; Woyke, T.; DeLong, E.F. Metapangenomics reveals depth-dependent shifts in metabolic potential for the ubiquitous marine bacterial SAR324 lineage. Microbiome 2021, 9, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flieder, M.; Buongiorno, J.; Herbold, C.W.; Hausmann, B.; Rattei, T.; Lloyd, K.G.; Loy, A.; Wasmund, K. Novel taxa of Acidobacteriota implicated in seafloor sulfur cycling. ISME J. 2021, 15, 3159–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpakumara, B.U.; Tandon, K.; Willis, A.; Verbruggen, H. Unravelling microalgal-bacterial interactions in aquatic ecosystems through 16S rRNA gene-based co-occurrence networks. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xie, P.; Dai, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X. Variation in Structure and Functional Diversity of Surface Bacterioplankton Communities in the Eastern East China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, C.; Kirstein, I.V.; Meunier, C.L.; Rick, J.; Fofonova, V.; Wiltshire, K.H.; Steinke, N.; Vidal-Melgosa, S.; Hehemann, J.-H.; Huettel, B. Dissolved storage glycans shaped the community composition of abundant bacterioplankton clades during a North Sea spring phytoplankton bloom. Microbiome 2023, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, A.; Mao, Y.; Li, Q.; Zong, H.; Wang, L.; Li, X. Spatial distribution and sources of heavy metals and petroleum hydrocarbon in the sand flats of Shuangtaizi Estuary, Bohai Sea of China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Xing, R.; Sun, M.; Gao, Y.; An, L. Microplastics in sediments from an interconnected river-estuary region. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 139025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Yin, G.; Liu, M.; Chen, C.; Jiang, Y.; Hou, L.; Zheng, Y. A systematic review of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in estuarine and coastal environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Wu, W.; Shan, J.; Xiang, S.; Wei, G. Bacterioplankton Community Structure and Its Relationship with Environmental Factors in the Coastal Waters Around the Changli Gold Coast National Nature Reserve in Northern China. Water 2025, 17, 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030311
Li J, Wu W, Shan J, Xiang S, Wei G. Bacterioplankton Community Structure and Its Relationship with Environmental Factors in the Coastal Waters Around the Changli Gold Coast National Nature Reserve in Northern China. Water. 2025; 17(3):311. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030311
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jianyang, Wenxuan Wu, Jinjie Shan, Shizheng Xiang, and Guangshan Wei. 2025. "Bacterioplankton Community Structure and Its Relationship with Environmental Factors in the Coastal Waters Around the Changli Gold Coast National Nature Reserve in Northern China" Water 17, no. 3: 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030311
APA StyleLi, J., Wu, W., Shan, J., Xiang, S., & Wei, G. (2025). Bacterioplankton Community Structure and Its Relationship with Environmental Factors in the Coastal Waters Around the Changli Gold Coast National Nature Reserve in Northern China. Water, 17(3), 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030311




