The Decreased Incidence of Raphidiopsis raciborskii Bloom in a Temperate Floodplain Lake in the Middle Danube Affected by Extreme Hydrological Events
Abstract
1. Introduction
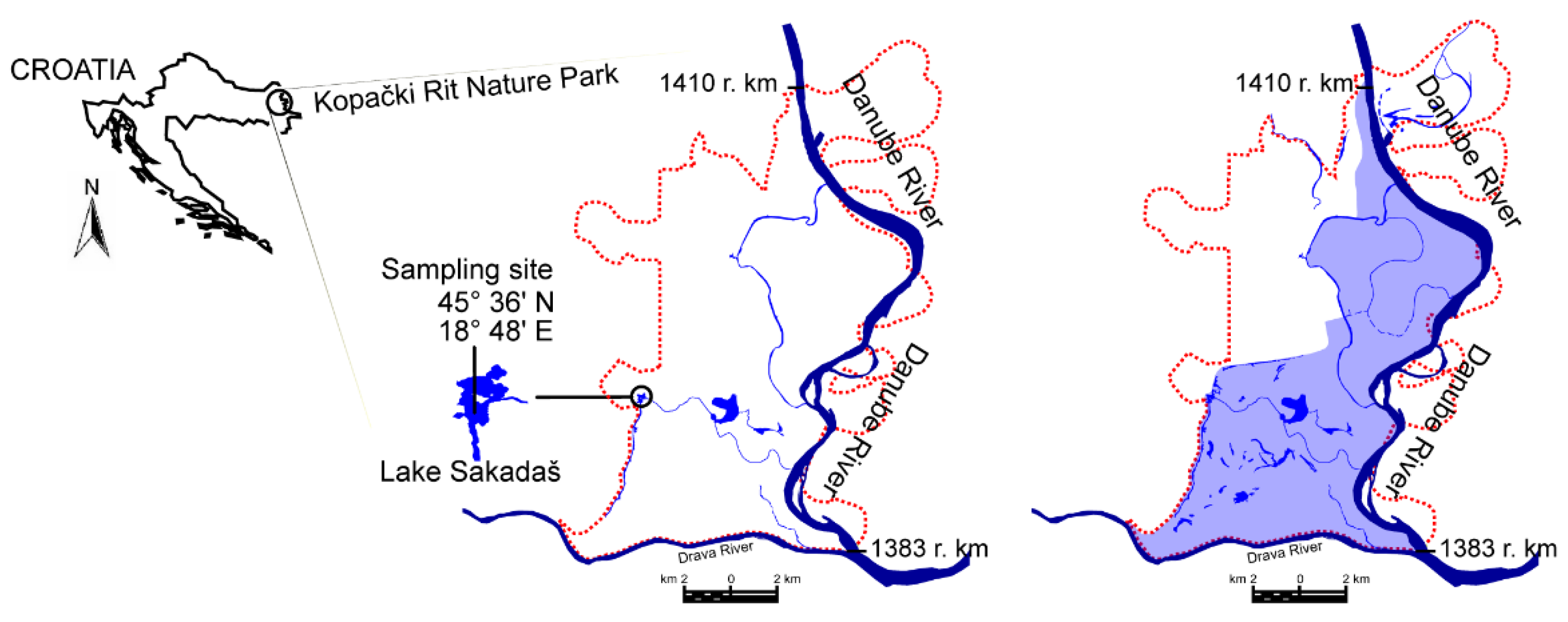
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
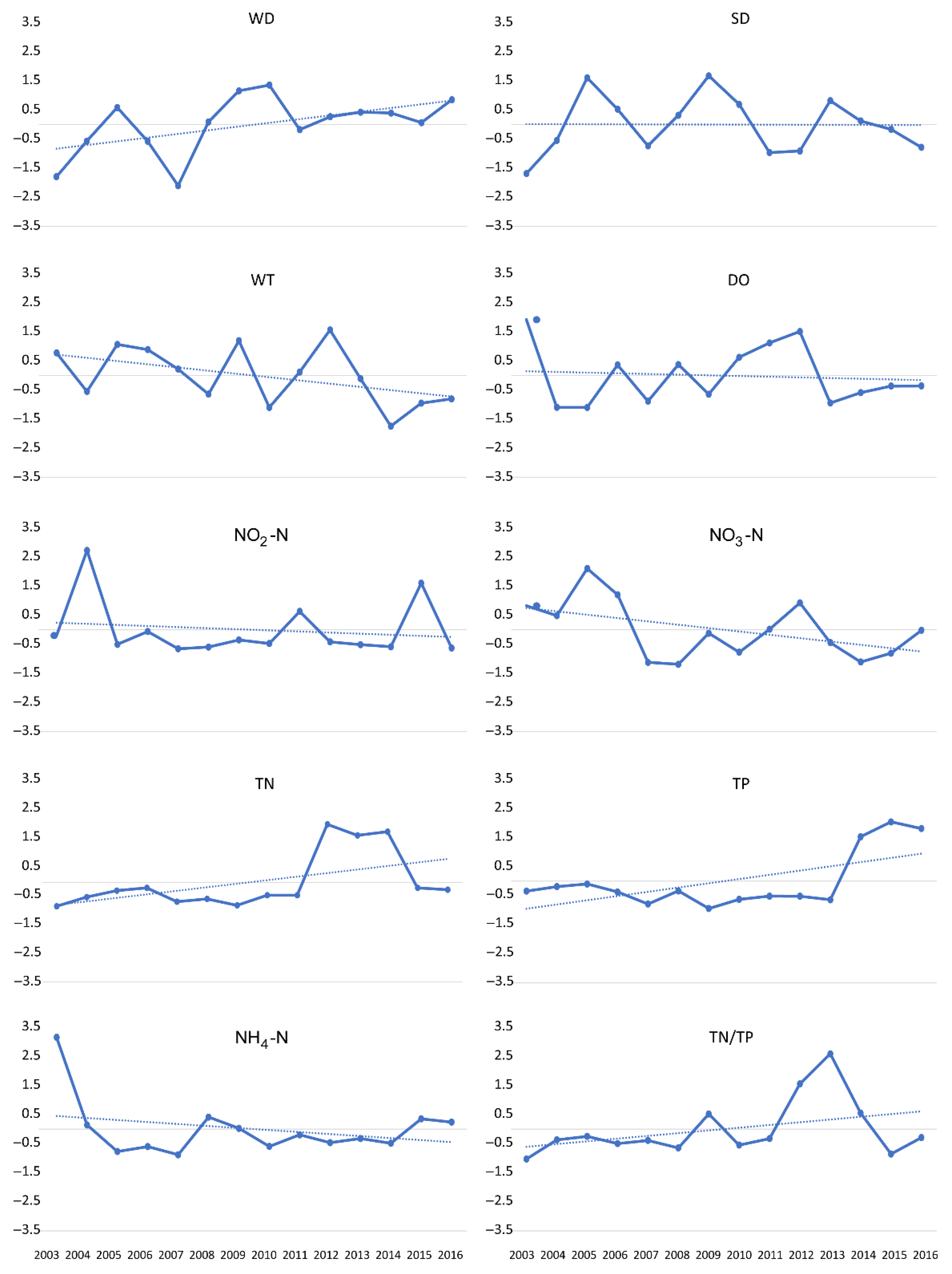
3.1. Flooding Patterns and Environmental Parameters
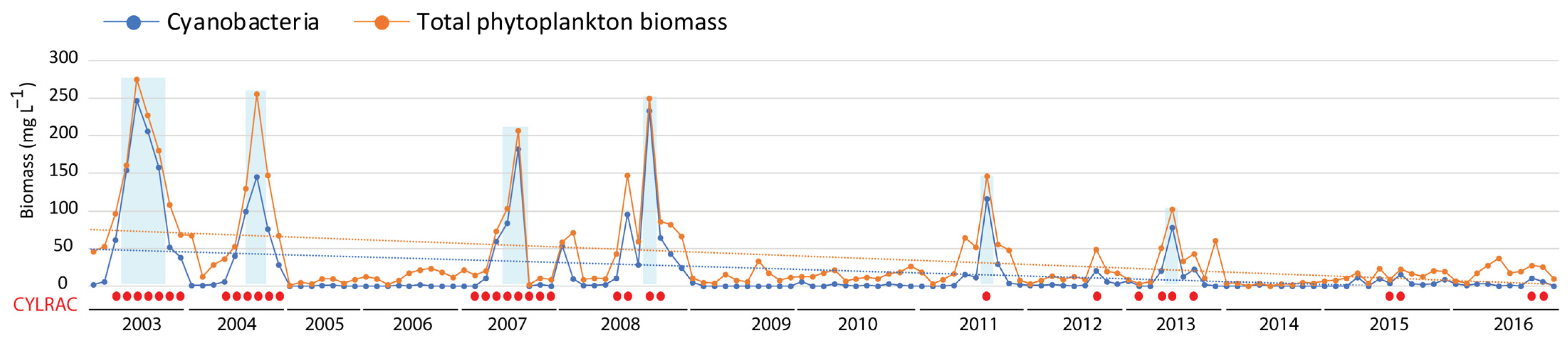
3.2. Phytoplankton Biomass Dynamic
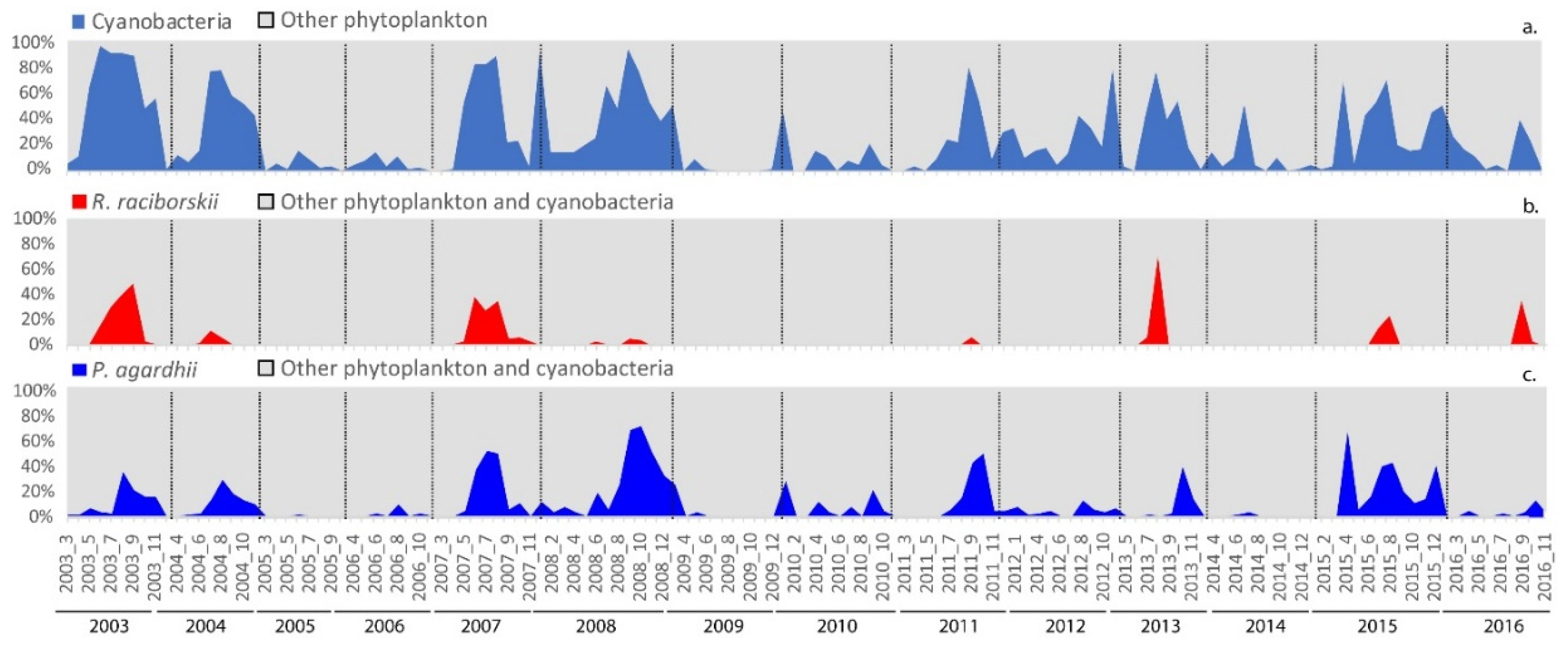
3.3. Raphidiopsis raciborskii Blooming
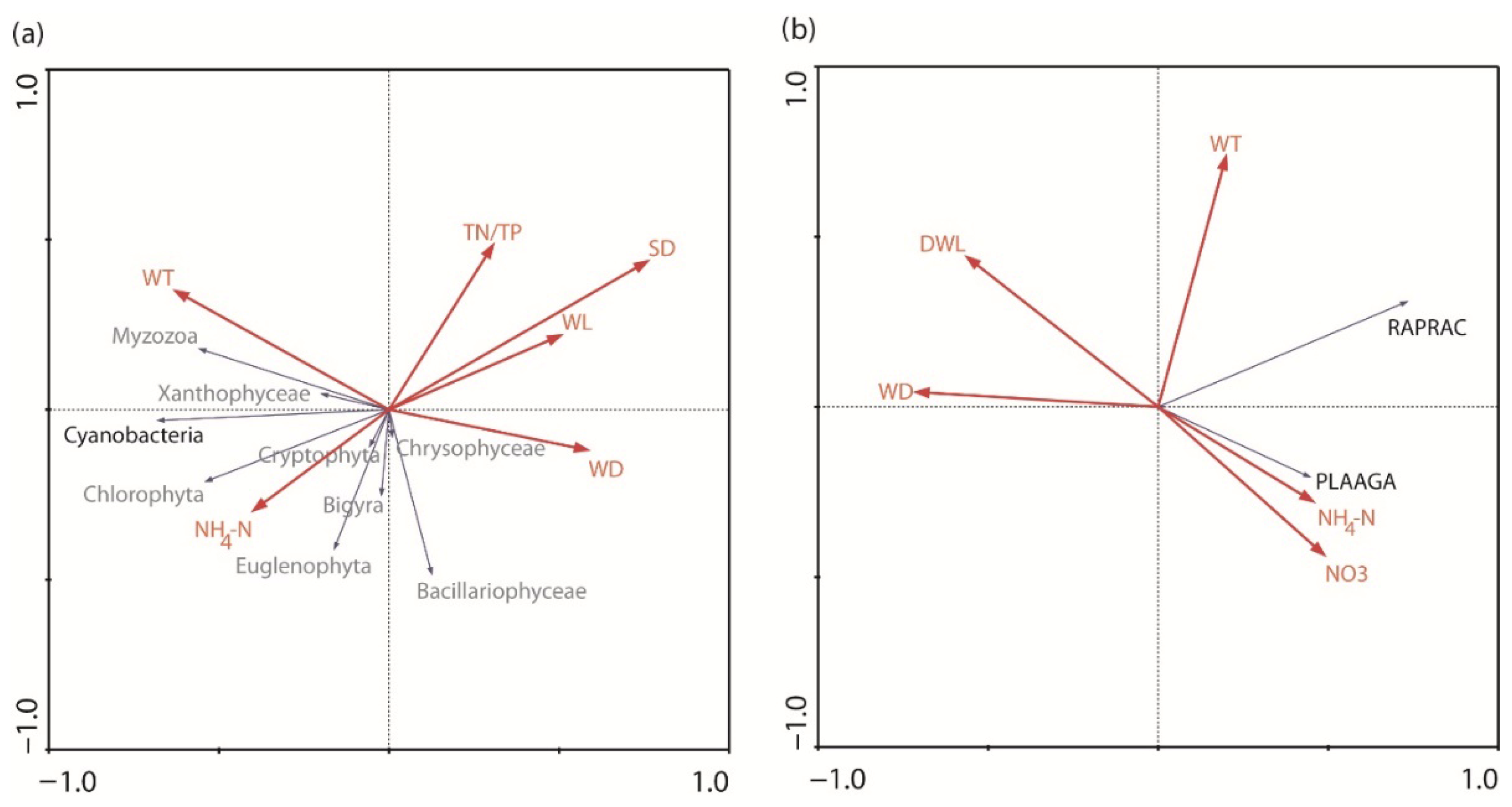
3.4. Ordinations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ledger, M.; Milner, A. Extreme Events in Running Waters. Freshw. Biol. 2015, 60, 2455–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattermann, F.; Wortmann, M.; Liersch, S.; Toumi, R.; Sparks, N.; Genillard, C.; Schröter, K.; Steinhausen, M.; Gyalai-Korpos, M.; Máté, K.; et al. Simulation of Flood Hazard and Risk in the Danube Basin with the Future Danube Model. Clim. Serv. 2018, 12, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, A.; Haensel, S.; Skalák, P.; Ustrnul, Z.; Bochnicek, O. The Extreme European Summer of 2015 in a Long-Term Perspective. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 943–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The 2015 Droughts in the Danube River Basin|ICPDR—International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River. Available online: https://www.icpdr.org/resources/2015-droughts-danube-river-basin (accessed on 3 December 2024).
- Mikhailov, V.; Morozov, V.; Cheroy, N.; Mikhailova, M.; Zav’yalova, Y. Extreme Flood on the Danube River in 2006. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2008, 33, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Home|ICPDR—International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River. Available online: https://www.icpdr.org/ (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- Leščešen, I.; Basarin, B.; Pavic, D.; Mudelsee, M.; Pekarova, P.; Mészáros, M. Are Extreme Floods in the Danube River Getting More Frequent?: A Case Study of the Bratislava Station. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2024, 15, 1300–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, G.; Bonada, N.; Brown, L.E.; Death, R.G.; Durance, I.; Gray, C.; Hladyz, S.; Ledger, M.E.; Milner, A.M.; Ormerod, S.J.; et al. The Effects of Climatic Fluctuations and Extreme Events on Running Water Ecosystems. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, J.; Feuchtmayr, H.; Miller, C.; Hunter, P.D.; Maberly, S.C.; Carvalho, L. Response of Cyanobacteria and Phytoplankton Abundance to Warming, Extreme Rainfall Events and Nutrient Enrichment. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 3365–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Climate Change: A Catalyst for Global Expansion of Harmful Cyanobacterial Blooms. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2009, 1, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, A.; Berrendero, E.; Kaštovský, J.; Echenique, R.; Salerno, G. The Polyphasic Analysis of Two Native Raphidiopsis Isolates Supports the Unification of the Genera Raphidiopsis and Cylindrospermopsis (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria). Phycologia 2018, 57, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberato Pagni, R.; de Falco, P.; Dos Santos, A. Autecology of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszynska) Seenayya et Subba Raju. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2020, 32, e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, J.; Leao, P.; Vasconcelos, V. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii: Review of the Distribution, Phylogeography, and Ecophysiology of a Global Invasive Species. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padisak, J. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszynska) Seenayya et Subba Raju, an Expanding, Highly Adaptive Cyanobacterium: Worldwide Distribution and Review of Its Ecology. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1997, 107, 563–593. [Google Scholar]
- Maileht, K.; Nõges, T.; Nõges, P.; Ott, I.; Mischke, U.; Carvalho, L.; Dudley, B. Water Colour, Phosphorus and Alkalinity Are the Major Determinants of the Dominant Phytoplankton Species in European Lakes. Hydrobiologia 2013, 704, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roll, Y.V. Fitoplankton Sovetskogo Ychastka Dynaya, Ego Rukavov Zalivov (Phytoplankton of the Soviet section of the Danube, its branches of the bays). Tr. Instituta Gidrobiol. AN USSR 1961, 36, 70–93. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bartalis, É.T. A Duna Szigetközi Szakaszának és Hullámaetéri Vizeinek Biológiai Vízminosége (Biological Water Quality of the Szigetköz Section of River Danube). Kisalföldi Dunaszakasz Ökológiája 1987, 42–77. (In Hungarian) [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, A. Contribution to the Knowledge about the Algae of Water of Southern Hungary I. Bot. Közlemények 1987, 183–195. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, A. Main Characteristics of the Phytoplankton of the Southern Hungarian Section of the River Danube. Hydrobiologia 1994, 289, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyneva, M.P. Steady-State Phytoplankton Assemblages in Shallow Bulgarian Wetlands. Hydrobiologia 2003, 502, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokulil, M.T.; Mayer, J. Population Dynamics and Photosynthetic Rates of a Cylindrospermopsis—Limnothrix Association in a Highly Eutrophic Urban Lake, Alte Donau, Vienna, Austria. Arch. Für Hydrobiol. Suppl. Algol. Stud. 1996, 83, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokulil, M.T.; Donabaum, K.; Pall, K. Alternative Stable States in Floodplain Ecosystems. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2006, 6, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.; Pearson, L.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.A.; Orr, P.T.; Neilan, B.A. Increased Incidence of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in Temperate Zones - Is Climate Change Responsible? Wat. Res. 2012, 46, 1408–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briand, J.; Leboulanger, C.; Humbert, J.; Bernard, C.; Dufour, P. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) Invasion at Mid-Latitudes: Selection, Wide Physiological Tolerance, or Global Warming? J. Phycol. 2004, 40, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaljević, M.; Stević, F.; Horvatić, J.; Hackenberger Kutuzović, B. Dual Impact of the Flood Pulses on the Phytoplankton Assemblages in a Danubian Floodplain Lake (Kopački Rit Nature Park, Croatia). Hydrobiologia 2009, 618, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stević, F. Složenost Utjecaja Poplava na Strukturu i Dinamiku Fitoplanktona Poplavnog Područja; Poslijediplomski sveučilišni interdisciplinarni znanstveni studij Zaštita prirode i okoliša: Osijek, Zagreb, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mihaljević, M.; Getz, D.; Tadić, Z.; Živanović, B.; Gucunski, D.; Topić, J.; Kalinović, I.; Mikuska, J. Kopački Rit-Research Survey and Bibliography; Croatian Academy of Arts and Sciences: Zagreb, Croatia, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Buijse, A.D.; Coops, H.; Staras, M.; Jans, L.; Van Geest, G.J.; Grift, R.; Ibelings, B.; Oosterberg, W.; Roozen, F. Restoration Strategies for River Floodplain Along Large Lowland Rivers in Europe. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 889–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, U. Landschaftsökologische Charakterisierung Des Kopački Rit Unter Besonderer Berücksichtigung von Flusslandschaftsformen Sowie Deren Genese Und Typologie; University of Wien: Vienna, Austria, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- HRN ISO 7150-1:1998 ISO; Water Quality—Determination of Ammonium—Part 1: Manual Spectrometric Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998.
- HRN ISO 7890-3:1998 ISO; Water Quality—Determination of Nitrate—Part 3: Spectrometric Method Using Sulfosalicylic Acid. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998.
- HRN EN 26777:1998 ISO; Water Quality—Determination of Nitrite—Molecular Absorption Spectrometric Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998.
- HRN ISO 5663:2001 ISO; Water Quality—Determination of Total Nitrogen—Method after Mineralization with Selenium. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001.
- HRN ISO 6878:2008 ISO; Water Quality—Determination of Phosphorus—Ammonium Molybdate Spectrometric Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- Hustedt, F. Bacillariophyta (Diatomeae), 2nd ed.; Koeltz: Königstein, Germany, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Hindák, F.; Cyrus, Z.; Marvan, P.; Javornicky, P.; Komarek, J.; Etll, H.; Rosa, K.; Sladečkova, A.; Popovsky, J.; Punčocharova, M.; et al. Slatkovodne Riasy; Hindák, F., Ed.; Slovenske Pedagogicke Nakladelstvo: Bratislava, Slovakia, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Meffert, M.-E.; Oberhäuser, R.; Overbeck, J. Morphology and Taxonomy of Oscillatoria Redekei (Cyanophyta). Br. Phycol. J. 1981, 16, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, J.; Anagnostidis, K. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, Bd. 19/2: Cyanoprokaryota, Bd. 2/Part 2: Oscillatoriales; Spektrum Akademischer Verlag Heidelberg: Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, Bd. 19/3: Cyanoprokaryota, 3. Teil/3rd Part: Heterocytous Genera; Springer Spektrum: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Utermöhl, H. Zur Vervollkommnung der quantitativen Phytoplankton-Methodik. Int.Ver. Theor. Angew. Limnol. 1958, 9, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rott, E. Some Results from Phytoplankton Counting Intercalibrations. Schweiz. Z. Hydrol. 1981, 43, 34–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javornický, P.; Komárková, J. The Changes in Several Parameters of Plankton Primary Productivity in Slapy Reservoir 1960–1967, Their Mutual Correlations and Correlations with the Main Ecological Factors. In Hydrobiological studies; Academia: Prague, Czech Republic, 1973; pp. 155–211. [Google Scholar]
- Sakshaug, E. Phytoplankton Manual—Monographs on Oceanographic Methodology, 6A. Sournia (Editor) UNESCO, Paris, 1978, 337 Pp. Ocean Manag. 1981, 6, 247–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leps, J.; Smilauer, P. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data Using CANOCO; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003; Volume 3, ISBN 978-0-521-89108-0. [Google Scholar]
- Mihaljević, M.; Stević, F. Cyanobacterial Blooms in a Temperate River-Floodplain Ecosystem: The Importance of Hydrological Extremes. Aquat. Ecol. 2011, 45, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M. Multiplicity of Stable States in Freshwater Systems. Hydrobiologia 1990, 200, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Jeppesen, E. Regime Shifts in Shallow Lakes. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loverde-Oliveira, S.; Huszar, V.; Mazzeo, N.; Scheffer, M. Hydrology-Driven Regime Shifts in a Shallow Tropical Lake. Ecosystems 2009, 12, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M. Ecology of Shallow Lakes; Chapman & Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-0-412-74920-9. [Google Scholar]
- van Nes, E.H.; Rip, W.J.; Scheffer, M. A Theory for Cyclic Shifts between Alternative States in Shallow Lakes. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blindow, I.; Andersson, G.; Hargeby, A.; Johansson, S. Long-Term Pattern of Alternative Stable States in Two Shallow Eutrophic Lakes. Freshw. Biol. 1993, 30, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Carpenter, S.; Foley, J.A.; Folke, C.; Walker, B. Catastrophic Shifts in Ecosystems. Nature 2001, 413, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargeby, A.; Blindow, I.; Hansson, L.-A. Shifts between Clear and Turbid States in a Shallow Lake: Multi-Causal Stress from Climate, Nutrients and Biotic Interactions. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2005, 161, 433–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembowska, E.A. Impacts of Different Hydrological Conditions on Phytoplankton Communities in Floodplain Lakes of a Regulated River (Lower Vistula, Poland). Hydrobiologia 2022, 849, 2549–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Farrell, I.; Izaguirre, I.; Chaparro, G.; Unrein, F.; Sinistro, R.; Pizarro, H.; Rodriguez, P.; de Tezanos Pinto, P.; Lombardo, R.; Tell, G. Water Level as the Main Driver of the Alternation between a Free-Floating Plant and a Phytoplankton Dominated State: A Long-Term Study in a Floodplain Lake. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 73, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Geest, G.J.; Coops, H.; Scheffer, M.; Nes, E. Long Transients Near the Ghost of a Stable State in Eutrophic Shallow Lakes with Fluctuating Water Levels. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustaka-Gouni, M.; Vardaka, E.; Tryfon, E. Phytoplankton Species Succession in a Shallow Mediterranean Lake (L. Kastoria, Greece): Steady-State Dominance of Limnothrix redekei, Microcystis aeruginosa and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Hydrobiologia 2007, 575, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokocinski, M.; Stefaniak, K.; Mankiewicz-Boczek, J.; Izydorczyk, K.; Soininen, J. The Ecology of the Invasive Cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Nostocales, Cyanophyta) in Two Hypereutrophic Lakes Dominated by Planktothrix agardhii (Oscillatoriales, Cyanophyta). Eur. J. Phycol. 2010, 45, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, U.; Padisak, J.; Reynolds, C.; Juhász-Nagy, P. Hutchison Heritage—The Diversity Disturbance Relationship in Phytoplankton. Hydrobiologia 1993, 249, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, S.; Aubriot, L.; Soares, M.C.S.; González-Piana, M.; Fabre, A.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Lürling, M.; Antoniades, D.; Padisák, J.; Kruk, C. What Drives the Distribution of the Bloom-Forming Cyanobacteria Planktothrix agardhii and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii? FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 79, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, W.W.; Sauter, S. Distribution and Abundance of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in Indiana Lakes and Reservoirs. 2005. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Distribution-and-Abundance-of-Cylindrospermopsis-in-Jones-Sauter/b9dcf7c2a440c34cc0461e0de576c86d4403c83e (accessed on 19 December 2024).
- Présing, M.; Herodek, S.; Vörös, L.; Kóbor, I. Nitrogen Fixation, Ammonium and Nitrate Uptake during a Bloom of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in Lake Balaton. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1996, 136, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isvánovics, V.; Shafik, H.; Présing, M.; Juhos, S. Growth and Phosphate Uptake Kinetics of the Cyanobacterium, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanophyceae) in Throughflow Cultures. Freshw. Biol. 2008, 43, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, E.F.; Hamilton, D.P.; Barnes, G.E. Recent Occurrence of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in Waikato Lakes of New Zealand. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2003, 37, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R.S.; Neudeck, M.J.; Heath, A.E.; Barker, K.B.; Brown, K.M.; Buchholz, S.; Ward, C.S.; Bullerjahn, G.S. The Recent Disappearance of a Persistent Planktothrix Bloom: Characterization of a Regime Shift in the Phytoplankton of Sandusky Bay (USA). Harmful Algae 2024, 136, 102656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenken, T.; Brandenburg, K.; Van de Waal, D. Long-Term Nutrient Load Reductions and Increasing Lake TN: TP Stoichiometry Decrease Phytoplankton Biomass and Diversity in a Large Shallow Lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2023, 68, 2389–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chislock, M.F.; Sharp, K.L.; Wilson, A.E. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii Dominates under Very Low and High Nitrogen-to-Phosphorus Ratios. Water Res. 2014, 49, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burford, M.A.; Willis, A.; Chuang, A.; Man, X.; Orr, P.T. Recent Insights into Physiological Responses to Nutrients by the Cylindrospermopsin Producing Cyanobacterium, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. J. Ocean. Limnol. 2018, 36, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferencz, B.; Toporowska, M.; Dawidek, J. Role of Hydrology in Cyanobacterial Blooms in the Floodplain Lakes. Water 2023, 15, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.; Huszar, V.; Kruk, C.; Naselli-Flores, L.; Melo, S. Towards a Functional Classification of the Freshwater Phytoplankton. J. Plankton Res. 2002, 24, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueredo, C.; Giani, A. Phytoplankton Community in the Tropical Lake of Lagoa Santa (Brazil): Conditions Favoring a Persistent Bloom of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Limnologica 2009, 39, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Environmental Parameter | SI | Mean ± SD | Minimal | Maximal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WD | m | 6.54 ± 1.53 | 3.10 | 10.90 |
| SD | m | 1.16 ± 0.55 | 0.35 | 3.49 |
| WT | °C | 17.3 ± 7.3 | 3.3 | 30.6 |
| DO | mg L−1 | 9.69 ± 3.39 | 0.94 | 19.66 |
| pH | 7.94 ± 0.41 | 6.68 | 8.98 | |
| Cond | µS cm−1 | 547 ± 169 | 285 | 960 |
| NH4-N | mg L−1 | 0.1571 ± 0.2734 | 0.0004 | 1.3988 |
| NO2-N | mg L−1 | 0.0300 ± 0.0897 | 0.0013 | 0.8516 |
| NO3-N | mg L−1 | 0.5069 ± 0.6201 | 0.0010 | 3.9500 |
| TN | mg L−1 | 1.7202 ± 1.7655 | 0.1400 | 11.6642 |
| TP | mg L−1 | 0.3512 ± 0.5354 | 0.0080 | 2.8810 |
| TN/TP | 11.33 ± 15.09 | 0.06 | 83.73 |
| Years | 2003–2004, 2007–2008, 2011, and 2013 | |||
| RDA analysis based on | environmental parameters and phytoplankton groups | environmental parameters and cyanobacteria species | ||
| RDA axes | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Eigenvalues | 0.243 | 0.059 | 0.292 | 0.057 |
| Species–environment correlations | 0.713 | 0.589 | 0.874 | 0.717 |
| Cumulative percentage variance | ||||
| - of species data | 24.3 | 30.1 | 29.2 | 34.9 |
| - of species–environment relation | 71.1 | 88.2 | 73.0 | 87.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stević, F.; Mihaljević, M.; Špoljarić Maronić, D.; Žuna Pfeiffer, T.; Zahirović, V. The Decreased Incidence of Raphidiopsis raciborskii Bloom in a Temperate Floodplain Lake in the Middle Danube Affected by Extreme Hydrological Events. Water 2025, 17, 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030309
Stević F, Mihaljević M, Špoljarić Maronić D, Žuna Pfeiffer T, Zahirović V. The Decreased Incidence of Raphidiopsis raciborskii Bloom in a Temperate Floodplain Lake in the Middle Danube Affected by Extreme Hydrological Events. Water. 2025; 17(3):309. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030309
Chicago/Turabian StyleStević, Filip, Melita Mihaljević, Dubravka Špoljarić Maronić, Tanja Žuna Pfeiffer, and Vanda Zahirović. 2025. "The Decreased Incidence of Raphidiopsis raciborskii Bloom in a Temperate Floodplain Lake in the Middle Danube Affected by Extreme Hydrological Events" Water 17, no. 3: 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030309
APA StyleStević, F., Mihaljević, M., Špoljarić Maronić, D., Žuna Pfeiffer, T., & Zahirović, V. (2025). The Decreased Incidence of Raphidiopsis raciborskii Bloom in a Temperate Floodplain Lake in the Middle Danube Affected by Extreme Hydrological Events. Water, 17(3), 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030309








