Digital-Twin-Based Management of Sewer Systems: Research Strategy for the KaSyTwin Project
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Enhanced data availability and integration: KaSyTwin seeks to integrate heterogeneous and decentralized data into a cohesive digital twin that is easy to access by authorized users. The integration process involves combining laser scanning data, existing documentation (such as sewer system assessment data and structural condition reports), and sensor data recorded from sewer systems in operation.
- Proactive maintenance and resilience: By using digital twins, KaSyTwin aims to shift from reactive to proactive maintenance strategies. Digital models may enable real-time monitoring and early damage detection, facilitating timely interventions. Additionally, KaSyTwin emphasizes resilience forecasting, allowing for better preparation and response to extreme weather events and other disruptions.
- The development of a multi-sensor robotic platform: To achieve accurate and comprehensive data collection under a variety of operational conditions, a prototype of a multi-sensor robotic platform will be developed in the KaSyTwin project.
- AI-driven data processing: AI algorithms will be employed in the KaSyTwin project for advanced data analysis to enable real-time damage detection as part of structural health monitoring strategies for sewer systems.
2. Background and Research Questions
- Q1: How can proactive maintenance management for sewer systems be designed using digital twins?
- Q2: How can AI methods be employed for the automated generation and verification of digital 3D sewer models in real time?
- Q3: What predictions can be made to enhance the resilience of existing sewer systems using AI?
- Q4: How can diverse data from various sources be integrated with a digital twin?
- Q5: How can different sensor technologies for the 3D visualization of sewer structures be optimally fused on an autonomous robotic system?
- Q6: How can AI be used to detect damage in sewer systems in real time?
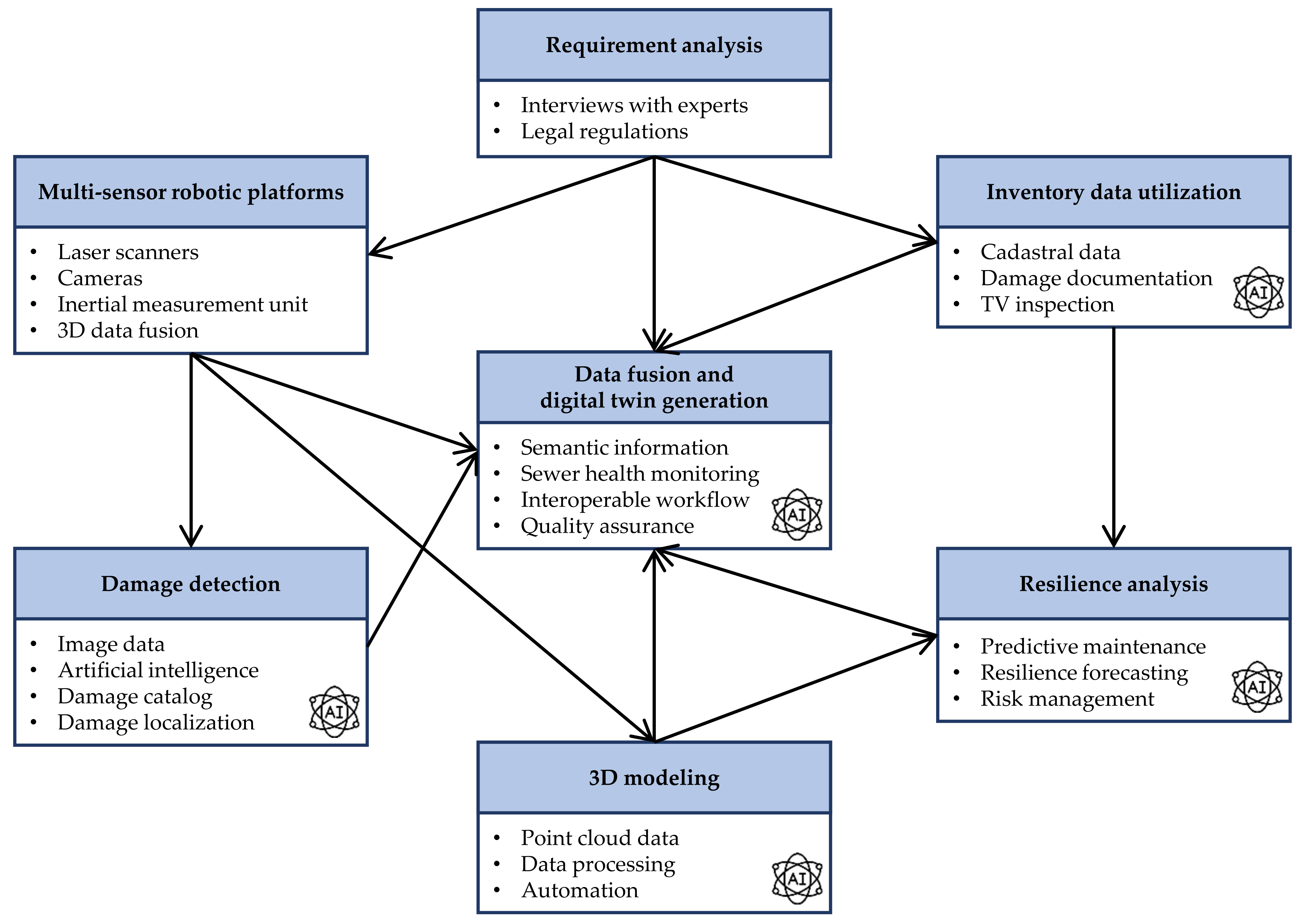
3. The KaSyTwin Project: Approaches and Methodological Concepts
3.1. Requirements Analysis
3.2. Multi-Sensor Robotic Platforms and 3D Modeling
3.3. Damage Detection
3.4. Inventory Data Utilization
3.5. Data Fusion and Digital Twin Generation
3.6. Resilience Analysis
4. Initial Results
4.1. Requirements Analysis
4.2. Multi-Sensor Robotic Platforms
4.3. Damage Detection
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Feo, G.; Antoniou, G.; Fardin, H.; El-Gohary, F.; Zheng, X.; Reklaityte, I.; Butler, D.; Yannopoulos, S.; Angelakis, A. The Historical Development of Sewers Worldwide. Sustainability 2014, 6, 3936–3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.L.; Cornwell, D.A. Introduction to Environmental Engineering, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-0-07-340114-0. [Google Scholar]
- General-Anzeiger. Wie es um die Sanierung der Bonner Kanalisation steht. Drohender Straßeneinbruch auf Adenauerallee. Available online: https://ga.de/bonn/stadt-bonn/bonn-wie-es-um-die-sanierung-der-kanalisation-steht_aid-116708905 (accessed on 27 July 2024).
- WTVR. Broken Pipe Leaking Sewage into James River Is Being Repaired; Why Permanent Solutions Could Be a ‘Challenge’. Available online: https://www.wtvr.com/news/local-news/broken-pipe-leaking-sewage-into-james-river-is-being-repaired-july-18-2024 (accessed on 18 July 2024).
- Berger, C.; Falk, C.; Hetzel, F.; Pinnekamp, J.; Ruppelt, J.; Schleiffer, P.; Schmitt, J. Zustand der Kanalisation in Deutschland: Ergebnisse der DWA-Umfrage 2020. KA Korresp. Abwasser Abfall 2020, 67, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Aydan, Ö. Abandoned lignite mines in Mitake, Japan, and some issues. Environ. Geotech. 2020, 9, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.C.; Shen, S.-L.; Zhu, H.-H.; Zhang, X.-L. Land subsidence due to groundwater drawdown in Shanghai. Geotechnique 2004, 54, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundesregierung Deutschland. Von der Kohle zur Zukunft. Available online: https://www.bundesregierung.de/breg-de/schwerpunkte/klimaschutz/kohleausstieg-1664496 (accessed on 16 October 2024).
- Abw, S.A.S. Verordnung zur Selbstüberwachung von Abwasseranlagen-Selbstüberwachungsverordnung Abwasser-SüwVO Abw. Gesetz-und Verordnungsblatt (GV. NRW.) 2013, Nr. 33, 601–612. [Google Scholar]
- Landesanstalt für Umweltschutz Baden-Württemberg (Siedlungswasserwirtschaft). Die neue Eigenkontroll—Verordnung (EKVO)—Hinweise für Betreiber kommunaler Abwasseranlagen. 2001. Available online: https://www.dwa-bw.de/files/_media/content/PDFs/LV_Baden-Wuerttemberg/Homepage/BW-Dokumente/Homepage%202013/Nachbarschaften/73263-Hinweise_f%C3%BCr_Betreiber_kommunaler_Abwasseranlagen.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Hamburgisches Abwassergesetz—Technische Betriebsbestimmungen—Entwässerungsanlagen (HmbAbwG). Grundstücksentwässerungsanlagen. 2014. Available online: https://www.hamburg.de/resource/blob/160214/cfd5fb34c42601bb28769049a2cab6bb/techn-betriebsbest-grunstuecksentw-data.pdf (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- Zhang, Y.; Yuen, K.-V. Review of artificial intelligence-based bridge damage detection. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2022, 14, 16878132221122770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrmann, A.; König, M.; Koch, C.; Beetz, J. (Eds.) Building Information Modeling; Springer: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2021; ISBN 978-3-658-33360-7. [Google Scholar]
- Errandonea, I.; Beltrán, S.; Arrizabalaga, S. Digital Twin for Maintenance: A Literature Review. Comput. Ind. 2020, 123, 103316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmous-Edwards, G.; Tomić, S.; Cooper, J.P. Developing a unified definition of digital twins. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2020, 114, 76–78. Available online: https://awwa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/awwa.1946 (accessed on 16 October 2024). [CrossRef]
- Smarsly, K.; Peralta Abadía, P.; Dragos, K.; Ahmad, M.; Al-Zuriqat, T.; Chillón Geck, C.; Al-Nasser, H. A Multivocal Literature Review of Digital Twins, Architectures, and Elements in Civil Engineering. In Proceedings of the 11th European Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring (EWSHM 2024), Potsdam, Germany, 10 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Alsaleh, A.; Sattler, M. Comprehensive life cycle assessment of large wind turbines in the US. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2019, 21, 887–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, J.; Poças Martins, J.; Marques de Almeida, N.; Patrício, H.; Gomes Morgado, J. Towards Resilient and Sustainable Rail and Road Networks: A Systematic Literature Review on Digital Twins. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewunruen, S.; AbdelHadi, M.; Kongpuang, M.; Pansuk, W.; Remennikov, A.M. Digital Twins for Managing Railway Bridge Maintenance, Resilience, and Climate Change Adaptation. Sensors 2022, 23, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Xu, J.; Miller-Hooks, E.; Zhou, W.; Chen, C.-H.; Lee, L.H.; Chew, E.P.; Li, H. Analytics with Digital-Twinning: A Decision Support System for Maintaining a Resilient Port. Decis. Support Syst. 2021, 143, 113496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agapaki, E. Airport Digital Twins for Resilient Disaster Management Response. In Learning and Intelligent Optimization; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Simos, D.E., Rasskazova, V.A., Archetti, F., Kotsireas, I.S., Pardalos, P.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 13621, pp. 467–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abioye, S.O.; Oyedele, L.O.; Akanbi, L.; Ajayi, A.; Davila Delgado, J.M.; Bilal, M.; Akinade, O.O.; Ahmed, A. Artificial Intelligence in the Construction Industry: A Review of Present Status, Opportunities and Future Challenges. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 103299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadoulis, G.; Manolis, G.D.; Katakalos, K.; Al-Zuriqat, T.; Dragos, K.; Smarsly, K. Towards Detecting Damage in Lightweight Bridges with Traveling Masses Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2024 European Conference on Computing in Construction (EC3), Chania, Crete, Greece, 14 July 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, G.; Cheuk, H.; Cheung Chun, L.; Singh, S.; Sharma, B. Deep Learning-Based Collision Detection System for Construction Sites: System Architecture and Working of viAct’s Smart Module. Int. J. Eng. Invent. 2021, 10, 24–29, e-ISSN: 2278-7461, p-ISSN: 2319-6491. [Google Scholar]
- Çelik, F.; Faltin, B.; König, M. Improving 2D Construction Plans with Cycle-Consistent Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the Computing in Civil Engineering 2021, Orlando, FL, USA, 12 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Poku-Agyemang, K.N.; Reiterer, A. 3D Reconstruction from 2D Plans Exemplified by Bridge Structures. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, L.A.; Schenk, D. Automatische Zusammenführung zertrennter Konstruktionspläne von Wasserbauwerken. Bautechnik 2022, 99, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, A.H.; Capener, A.M.; Sowby, R.B. Adoption of artificial intelligence in drinking water operations: A survey of progress in the United States. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2023, 149, 06023002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Cong, A.; Guo, S. Sewer Damage Detection from Imbalanced CCTV Inspection Data Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks with Hierarchical Classification. Autom. Constr. 2019, 101, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smarsly, K.; Ahmad, M.E.; Peralta, P.; Al-Zuriqat, T.; Al-Nasser, H.; Dragos, K.; Chillón Geck, C. Digital Twins, Architectures, and Elements in Civil Engineering—A Multivocal Literature Review. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Computing in Civil and Building Engineering (ICCCBE), Montréal, Canada, 25 August 2024. [Google Scholar]
- mFUND mdfBIM+. Teilautomatisierte Erstellung Objektbasierter Bestandsmodelle Mittels Multi-Daten-Fusion—mdfBIM+. Available online: https://bmdv.bund.de/SharedDocs/DE/Artikel/DG/mfund-projekte/mdfbim-plus.html (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Herbers, M.; Bartels, J.-H.; Richter, B.; Collin, F.; Ulbrich, L.; Al-Zuriqat, T.; Chillón Geck, C.; Naraniecki, H.; Hahn, O.; Jesse, F.; et al. openLAB—Eine Forschungsbrücke zur Entwicklung eines digitalen Brückenzwillings. Beton und Stahlbetonbau 2024, 119, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zuriqat, T.; Chillón Geck, C.; Dragos, K.; Smarsly, K. Adaptive Fault Diagnosis for Simultaneous Sensor Faults in Structural Health Monitoring Systems. Infrastructures 2023, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- mFUND DIANE. Drohneneinsatz zur Inspektion von Abwassernetzen—DIANE. Available online: https://bmdv.bund.de/SharedDocs/DE/Artikel/DG/mfund-projekte/diane.html (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- mFUND KomIT. Harmonisierung von Asset-Daten in einem Kommunalen Infrastruktur-Zwilling zur Effizienten Gestaltung von Planungs- und Baumaßnahmen—KomIT. Available online: https://bmdv.bund.de/SharedDocs/DE/Artikel/DG/mfund-projekte/komit.html (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Smarsly, K.; Al-Hakim, Y.; Peralta, P.; Beier, S.; Klümper, C. A Systematic Review and Recommendation of Software Architectures for SARS-CoV-2 Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Health Informatics, Lisbon, Portugal, 18 February 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Davis, P.; Taylor, K.; Gould, S. Linked Data Approach for Automated Failure Detection in Pressure Sewers Using Real-Time Sensor Data. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Hydroinformatics, New York, NY, USA, 8 January 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Preventing and Managing Pollution from Urban Water Runoff (D4RUNOFF). Available online: https://d4runoff.eu/ (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Höttges, J. QKan—Management of drainage system data with QGIS. In Proceedings of the Free and Open Source Software for Geospatial (FOSS4G), Boston, MA, USA, 14 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- DIN EN 13508-2:2011-08; Untersuchung und Beurteilung von Entwässerungssystemen außerhalb von Gebäuden—Teil 2: Kodiersystem für die Optische Inspektion; Deutsche Fassung EN 13508-2:2003+A1:2011. DIN Media GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, S.; Al-Zuriqat, T.; Peralta, P.; Valles Gomez, R.; Gölzhäuser, P.; Al-Hakim, Y.; Mackenbach, S.; Klemt-Albert, K.; Smarsly, K. Digital twins for sewer systems maintenance: A systematic literature review. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Construction Applications of Virtual Reality (CONVR), Sydney, Australia, 4 November 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ramin, P.; Flores-Alsina, X.; Gernaey, K.V. Transforming data into actionable knowledge for fault detection, diagnosis and prognosis in urban wastewater systems with AI techniques: A mini-review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 172, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Jin, Y.; Sun, S.; Yuan, Z.; Butler, D. The role of deep learning in urban water management: A critical re-view. Water Res. 2022, 223, 118973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villinger, G.; Reiterer, A. Robotic Systems for Sewer Inspection and Monitoring Tasks: Applications and Advanced Technologies. IEEE Sens. J. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.T.; Reiterer, A. Improving Sewer Damage Inspection: Development of a Deep Learning Integration Concept for a Multi-Sensor System. Sensors 2024, 24, 7786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haurum, J.B.; Moeslund, T.B. Sewer-ML: A multi-label sewer defect classification dataset and benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2021, Virtual Event, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 13456–13467. [Google Scholar]
- Gangelhoff, J.; Werner, C.S.; Reiterer, A. Lightweight dual-wavelength bathymetric LiDAR for accurate seabed mapping. In Proceedings of the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Optical Metrology 2023, Munich, Germany, 26 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hartmann, S.; Valles, R.; Schmitt, A.; Al-Zuriqat, T.; Dragos, K.; Gölzhäuser, P.; Jung, J.T.; Villinger, G.; Varela Rojas, D.; Bergmann, M.; et al. Digital-Twin-Based Management of Sewer Systems: Research Strategy for the KaSyTwin Project. Water 2025, 17, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030299
Hartmann S, Valles R, Schmitt A, Al-Zuriqat T, Dragos K, Gölzhäuser P, Jung JT, Villinger G, Varela Rojas D, Bergmann M, et al. Digital-Twin-Based Management of Sewer Systems: Research Strategy for the KaSyTwin Project. Water. 2025; 17(3):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030299
Chicago/Turabian StyleHartmann, Sabine, Raquel Valles, Annette Schmitt, Thamer Al-Zuriqat, Kosmas Dragos, Peter Gölzhäuser, Jan Thomas Jung, Georg Villinger, Diana Varela Rojas, Matthias Bergmann, and et al. 2025. "Digital-Twin-Based Management of Sewer Systems: Research Strategy for the KaSyTwin Project" Water 17, no. 3: 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030299
APA StyleHartmann, S., Valles, R., Schmitt, A., Al-Zuriqat, T., Dragos, K., Gölzhäuser, P., Jung, J. T., Villinger, G., Varela Rojas, D., Bergmann, M., Pullmann, T., Heimer, D., Stahl, C., Stollewerk, A., Hilgers, M., Jansen, E., Schoenebeck, B., Buchholz, O., Papadakis, I., ... Smarsly, K. (2025). Digital-Twin-Based Management of Sewer Systems: Research Strategy for the KaSyTwin Project. Water, 17(3), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17030299







