Impact of Artificial Water Replenishment on Spatiotemporal Distribution of Local Water Renewal Time in West Lake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
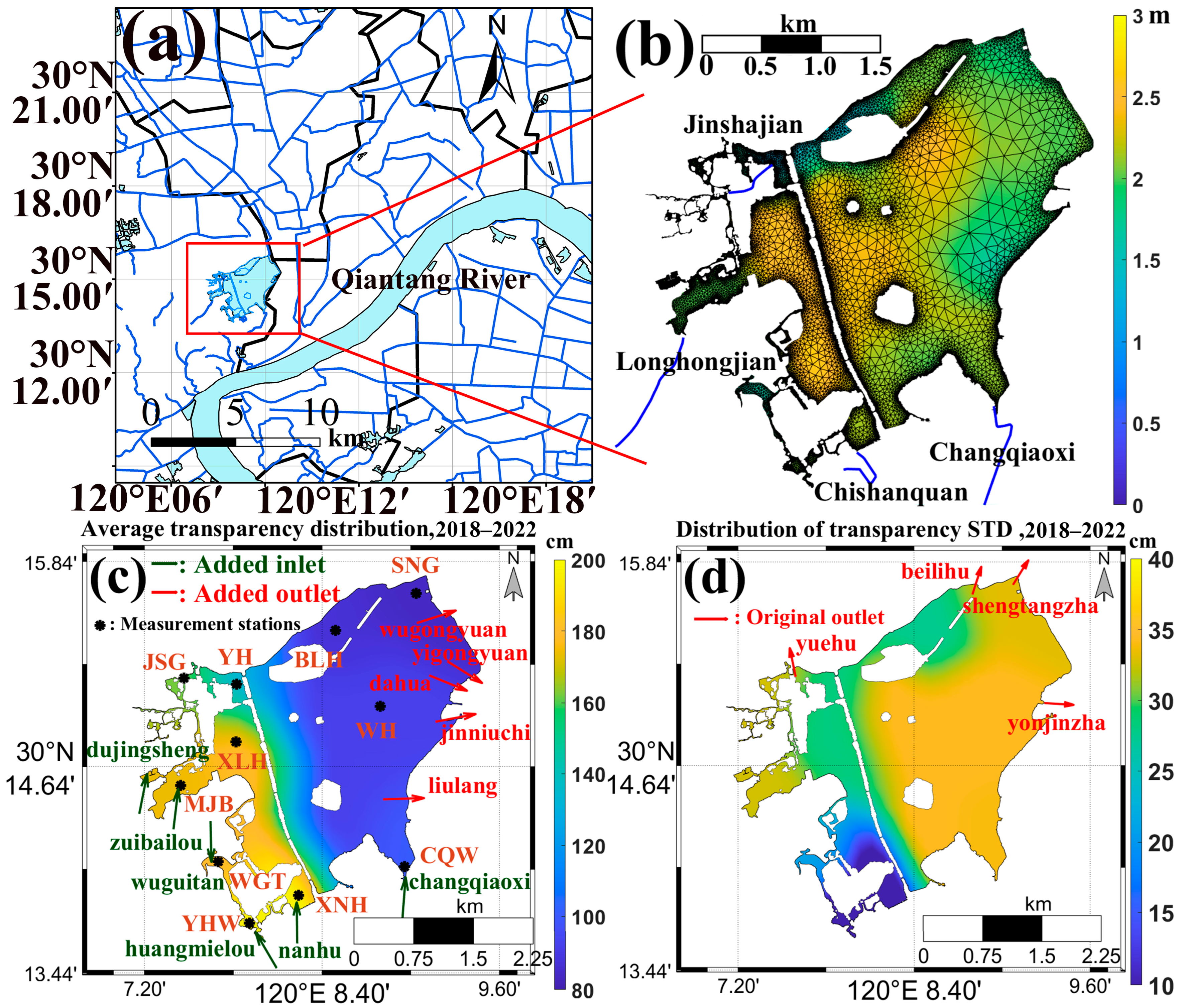
2.1. Description of the Study Area
2.2. Data Description
2.3. Experimental Configuration: Natural Runoff and Actual Implementation of WRP
2.4. Numerical Model Configuration
2.5. Local Water Renewal Time and Statistical Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
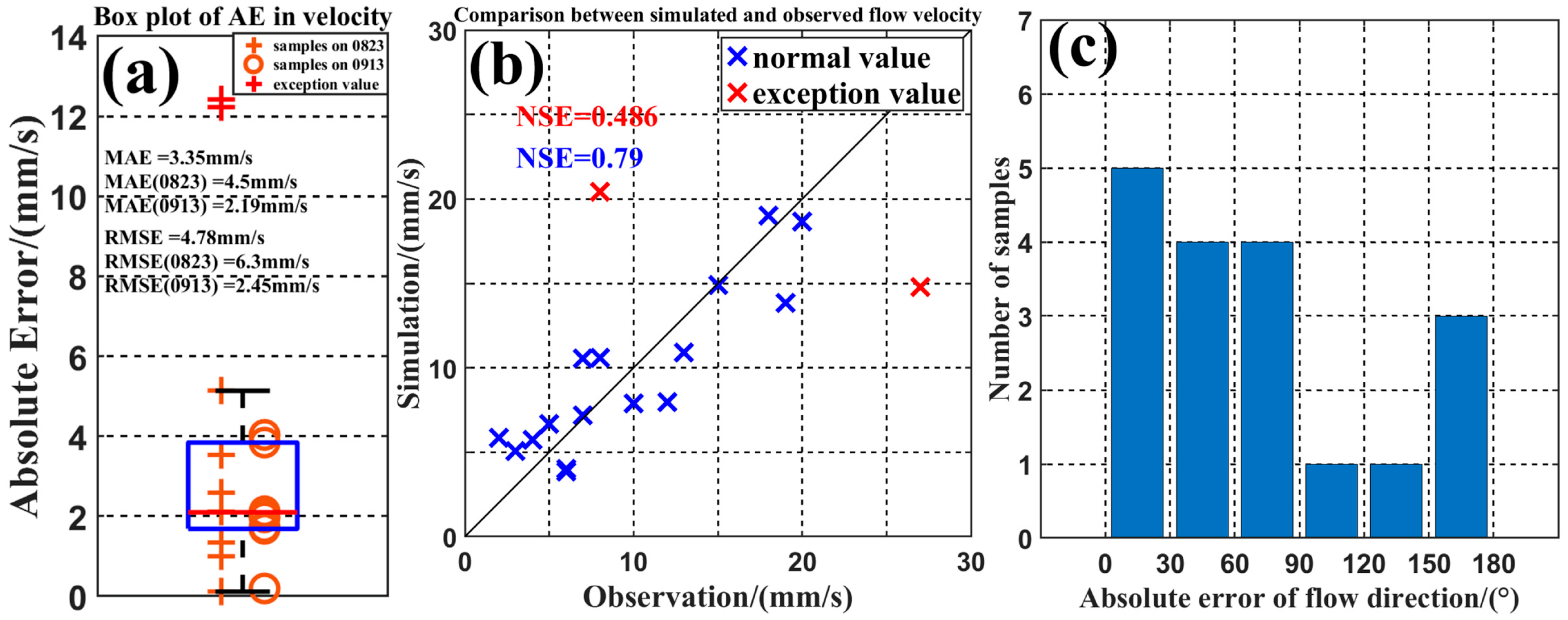
3.1. Model Validation
3.2. Correlation Between LWRT and Key Water Quality Parameters
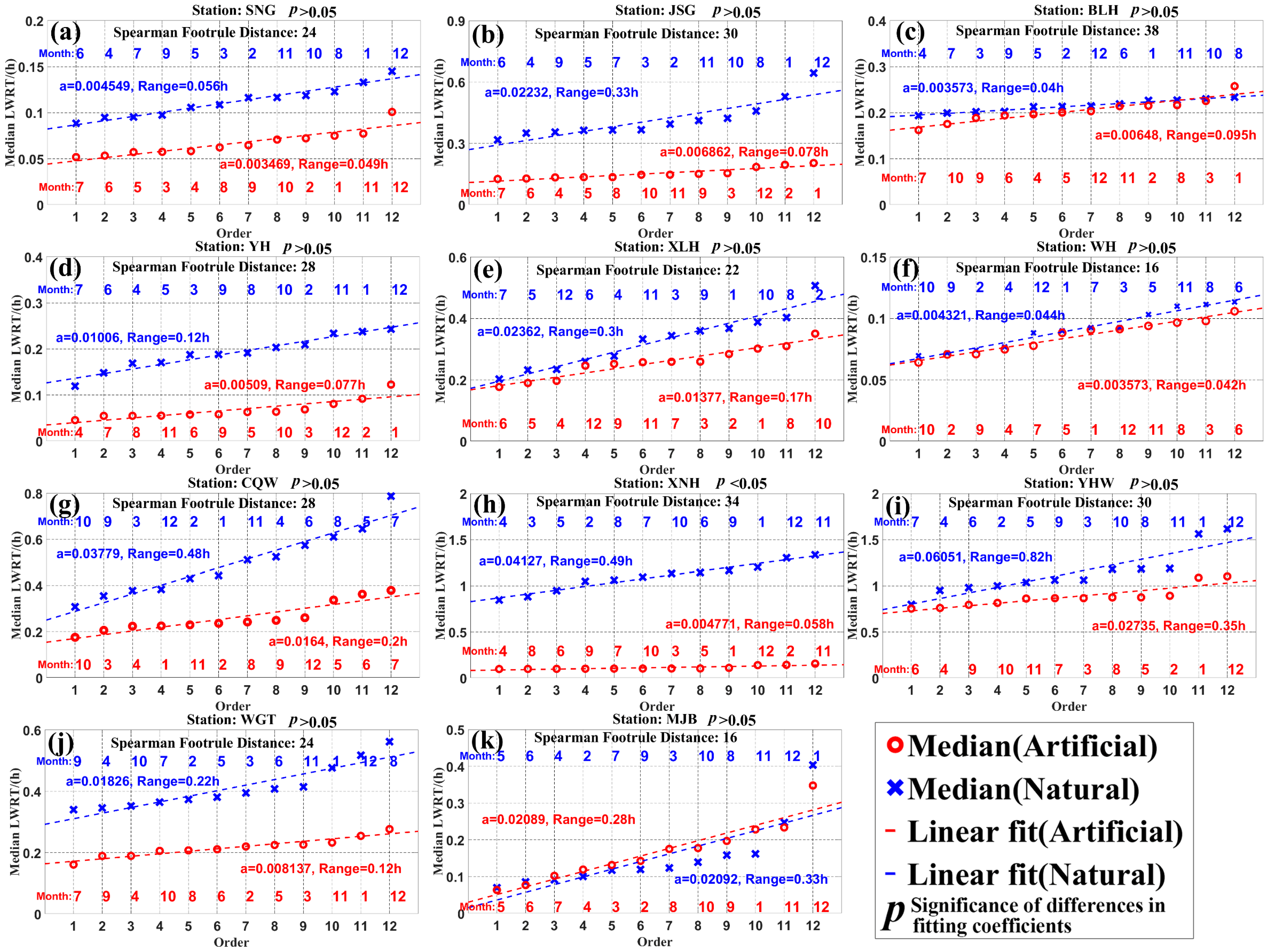
3.3. Impact of the WRP on Monthly LWRT at Key Stations
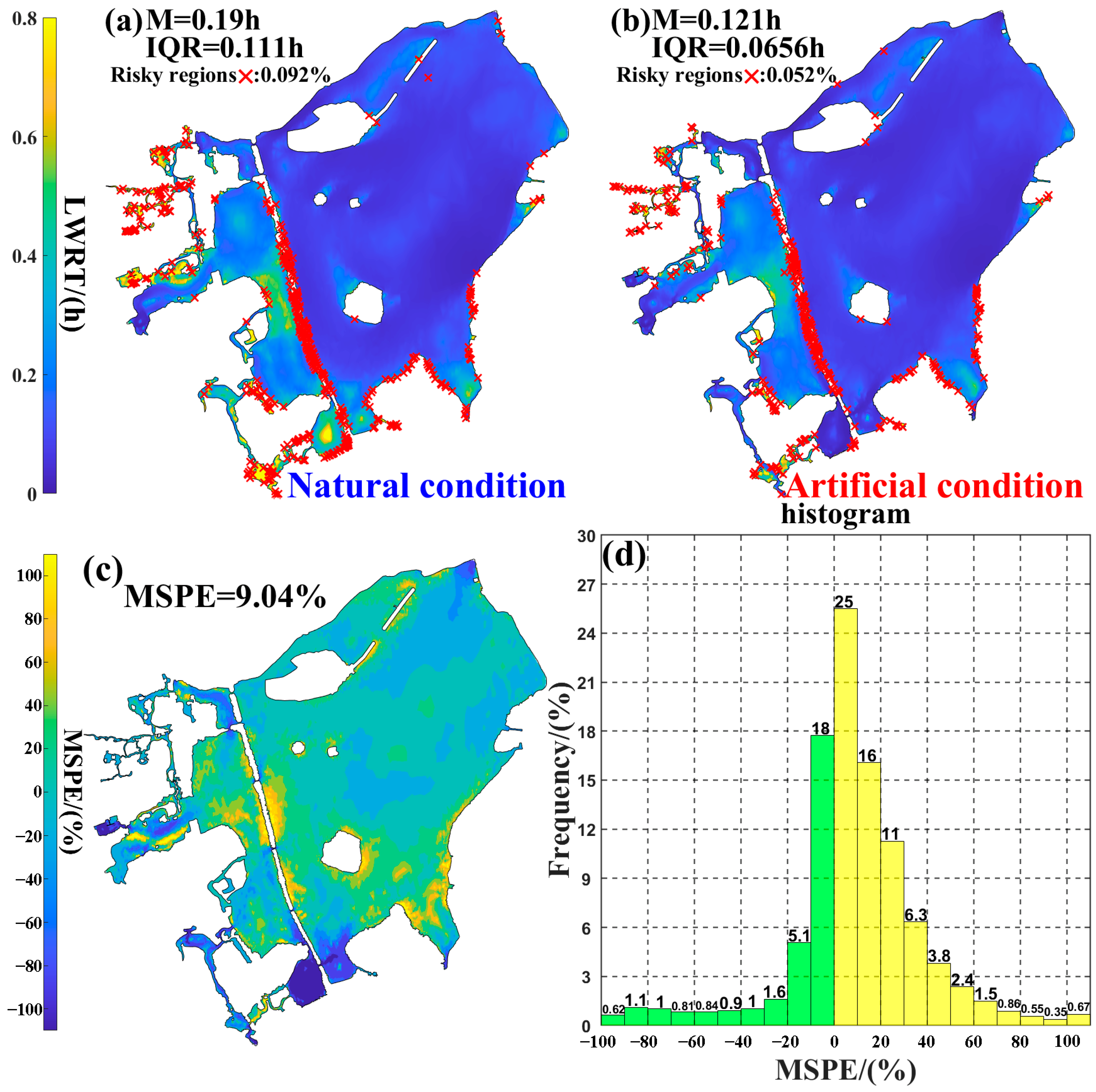
3.4. Seasonal Differences in the Influence of WRP on the Spatial Distribution of LWRT
3.5. Impacts of the WRP on Flow Directions at Key Stations
4. Discussion
4.1. WRP Increased the Stagnant Water Risk at Several Stations by Amplifying the SK of LWRT
4.2. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity in the Impact of the WRP on LWRT
4.3. WRP Increased the Differences in the Seasonal Rhythm of LWRT Between Various Stations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weyhenmeyer, G.A.; Chukwuka, A.V.; Anneville, O.; Brookes, J.; Carvalho, C.R.; Cotner, J.B.; Grossart, H.P.; Hamilton, D.P.; Hanson, P.C.; Hejzlar, J.; et al. Global Lake Health in the Anthropocene: Societal Implications and Treatment Strategies. Earths Future 2024, 12, e2023EF004387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, X.H.; Luo, Q.Q.; Feng, L.; Xu, Y.; Tang, J.; Liang, X.Y.; Ma, E.Z.; Cheng, R.; Fensholt, R.; Brandt, M.; et al. Mapping global lake dynamics reveals the emerging roles of small lakes. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, L.; Devey, M.; Leavitt, P.R.; Power, M.J.; Brothers, S.; Brahney, J. Anthropogenic forcing leads to an abrupt shift to phytoplankton dominance in a shallow eutrophic lake. Freshw. Biol. 2024, 69, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Shi, K.; Wang, X.W.; Zhang, Y.L.; Qin, B.Q.; Zhang, Y.B.; Woolway, R.I. The impact of extreme heat on lake warming in China. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslennikova, A.; Udachin, V.; Deryagin, V.; Artemyev, D.; Filippova, K.; Gulakov, V.; Udachin, N.; Aminov, P. Sediment records of lake eutrophication and oligotrophication under the influence of human activity and climate warming in the Urals metallurgical region (Russia). Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 1669–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.G.; Melack, J.M.; Liu, M.; Kutser, T.; Duan, H.T.; Ma, R.H. Shifts, Trends, and Drivers of Lake Color Across China Since the 1980s. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2023GL103225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grineski, S.E.; Mallia, D.; Collins, T.W.; Araos, M.; Lin, J.C.; Anderegg, W.R.L.; Perry, K. Harmful dust from drying lakes: Preserving Great Salt Lake (USA) water levels decreases ambient dust and racial disparities in population exposure. One Earth 2024, 7, 1056–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Her, Y.; Muñoz-Carpena, R.; Yu, X. Quantifying the contribution of external loadings and internal hydrodynamic processes to the water quality of Lake Okeechobee. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 883, 163713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, P., II; Welch, Z. Understanding the ups and downs: Application of hydrologic restoration measures for a large subtropical lake. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2022, 38, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.E.; Swenson, E.M.; Lee, J.M.; Milan, C.S. Mass removal efficiencies in water and consequences after a river diversion into coastal wetlands: Second thoughts. Hydrobiologia 2024, 851, 1607–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaie, A.; Jamaat, A. Numerical study of hydrodynamics and salinity transport processes in a hypersaline lake: A case study of Lake Urmia. Adv. Water Resour. 2024, 185, 104632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, F.; Rocheta, E.; Steinfeld, C.; Colloff, M.J.; Moggridge, B.; Carmody, E.; Hillman, T.; Kingsford, R.T.; Pittock, J. Are environmental water requirements being met in the Murray-Darling Basin, Australia? Mar. Freshw. Res. 2024, 75, MF23172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, J.; Bino, G.; Hawke, T. Impacts of river regulation and fragmentation on platypuses in the northern Murray-Darling Basin. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2024, 75, MF24037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, A.M.; Yu, T.; Xu, W.Q.; Lei, J.Q.; Jiapaer, G.; Chen, X.; Komiljon, T.; Khabibullo, S.; Sagidullaevich, X.B.; Kamalatdin, I. Ecological problems and ecological restoration zoning of the Aral Sea. J. Arid Land 2024, 16, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.X.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, T.T.; Xu, C.; Gu, R.; Liu, J.M. Effects of a proposed hydraulic project on the surface water connectivity in Poyang Lake floodplain system, China: Numerical simulation and geostatistical analysis. J. Hydrol.-Reg. Stud. 2023, 50, 101593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Liu, X.; Peng, W.; Dong, F.; Ma, B.; Li, J.; Wang, W. Spatiotemporal characteristics, influencing factors and evolution laws of water exchange capacity of Poyang Lake. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609, 127717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, K.; Yang, W.; Zhao, Y.-W. Ecological water replenishment through optimal allocation of lake water in water-scarce areas based on channel selection and replenishment period: A case study of China’s Baiyangdian Lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 956, 177340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.W.; Chen, W.; Li, N.; Wang, W.J.; Fu, C.F.; Liu, Y.Z.; Gao, X.P. Quantifying the effects of submerged aquatic vegetation on internal loading in lake: A modeling study of the largest shallow lake in North China br. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 853, 158593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.-z.; Wang, Y.-s.; Yin, D.-c.; Wang, X.-q. Seasonal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of Surface Water Quality and Influencing Factors in Baiyangdian Lake. Huanjing Kexue 2025, 46, 1382–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, B.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Gao, X.; Han, Z.; Liu, X. Water quality evolution of water-receiving lakes under the impact of multi-source water replenishments. J. Hydrol.-Reg. Stud. 2024, 53, 101832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Shi, X.; Sun, B.; Zhao, S.; Wang, S.; Yang, Z.; Han, Y.; Kang, R.; Chen, L. Effects of water replenishment on lake water quality and trophic status: An 11-year study in cold and arid regions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 281, 116621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Yang, L.; Cui, C.; Wan, W.; Liang, S. Is water replenishment an effective way to improve lake water quality? Case study in Lake Ulansuhai, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1392768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, S.; Sun, B.; Yu, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Q. Evaluating the effects of ecological water replenishment on lake water exchange in semi-arid regions insights from an 11-year modeling study. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 391, 126491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Wang, G.; Chen, W.; Li, W.; Kong, F.; Li, N.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X. Integrated modeling framework to evaluate the impacts of multi-source water replenishment on lacustrine phytoplankton communities. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Guo, Z.; Luo, M. A Simulation Experiment on Quality Dynamics of Reclaimed Water under Different Flow Exchanges. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Li, N.; Wang, G.; Gao, X.; Zhou, X.; Kong, F. Contribution for lake phytoplankton community succession under multi-source artificial hydrological regulation. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 372, 123351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; He, C.; Li, Y.; Acharya, K. Diverse responses of hydrodynamics, nutrients and algal biomass to water diversion in a eutrophic shallow lake. J. Hydrol. 2021, 593, 125933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.; Ye, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhu, C. River-Lake System Connectivity Effectively Reduced the Salinity of Lake Water in Bosten Lake, Northwest China. Water 2022, 14, 4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Hu, W.; Chen, Q.; Peng, Z.; Qin, H.; Luo, J. Hydrodynamic effects and water environment improvement of topographic reconstruction in shallow lakes. J. Hydrol. 2024, 634, 131125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Luo, M.; Ba, D.; Wu, G.; Xu, L.; Jeong, T. Numerical Simulation Study on the Layered Phenomenon of Lakes and Reservoirs Destroyed by a Forced Circulation Device. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, A.; Wu, Z.; Han, Z.; Yang, J.; Hua, L. Spatial and temporal distributions and variations of nutrients in the West Lake, Hangzhou, after the implementation of integrated water management program (1985–2013). Hupo Kexue 2015, 27, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, H.; Cheng, B.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, B. A Study of the Effect of Lake Shape on Hydrodynamics and Eutrophication. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qi, P. Numerical optimization study of the nanfei river ecological water replenishment plan. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2024, 23, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, D.; Wei, L.; Pei, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, L. Simulation Study on the Optimisation of Replenishment of Landscape Water with Reclaimed Water Based on Transparency. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroes, D.E.; Day, R.H.; Kaller, M.D.; Demas, C.R.; Kelso, W.E.; Pasco, T.; Harlan, R.; Roberts, S. Hydrologic Connectivity and Residence Time Affect the Sediment Trapping Efficiency and Dissolved Oxygen Concentrations of the Atchafalaya River Basin. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR030731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Duan, B.; He, S.; Lu, Y. Simulation study on the impact of ecological water replenishment on reservoir water environment based on Mike21—Taking Baiguishan reservoir as an example. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lv, Y.; Dong, J.; Yuan, J.; Hui, X. Factors Influencing Transparency in Urban Landscape Water Bodies in Taiyuan City Based on Machine Learning Approaches. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lv, Y.; Dong, J.; Yuan, J.; Hui, X. Sensitivity Analysis of Urban Landscape Lake Transparency Based on Machine Learning in Taiyuan City. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Li, Y.; Shu, J.; Wan, Z.; Jia, B.; Fan, Z. Water Transparency Prediction of Plain Urban River Network: A Case Study of Yangtze River Delta in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, A.; Hua, L.; Han, Z.; Zhang, J. Field observation and simulation study of three-dimensional flows in West Lake, Hangzhou. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2017, 36, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Ma, F.; Kuang, W.; Sun, Y. Study on the effect of ecological water replenishment on the spatial and temporal distribution of water quality in Chaohu Lake based on MIKE21. Environ. Pollut. Control 2024, 46, 463–470,477. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, D.H.; Kim, K.M.; Choi, Y.H.; Nguyen, H.H.T.; Jeong, Y.H. Evaluating vulnerable zones and spatiotemporal dynamics in Saemangeum lake under sluice gate operation. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2025, 90, 104442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.N.; Wu, D.X.; Huang, C.Q.; Wu, Q.Y.; Guan, Y.T. Impacts of hydraulic retention time and inflow water quality on algal growth in a shallow lake supplied with reclaimed water. Water Cycle 2022, 3, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. Sluice Gate Operation and Managed Water Levels Improve Predicted Estuarine Lake Water Quality. Civ. Eng. J.-Tehran 2025, 11, 244–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.P.; Yang, B.; Li, Y. Study of artificial water replenishment for wetland restoration. Water Environ. J. 2022, 36, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hipsey, M.R.; Zhang, G.X.; Busch, B.; Li, H.Y. Simulation of multiple water source ecological replenishment for Chagan Lake based on coupled hydrodynamic and water quality models. Water Sci. Technol.-Water Supply 2017, 17, 1774–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, M.; Xu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, L.; Sun, Q. Tracer movement and residence time distribution simulation: An initiative to improve the wetland water environment in the Helan Mountain impact plain. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 82, 102682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhong, R.; Bao, A.; Liu, T. Diagnostic Simulation of Water Age in Small Lake of Bosten Lake. Water 2021, 13, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Li, K.; Liang, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Yuan, Q.; Ji, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y. Shallow lake water exchange process before and after water diversion projects as affected by wind field. J. Hydrol. 2021, 592, 125785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Liu, X.; Dong, F.; Peng, W.; Ma, B.; Han, Z.; Yang, X. Long-term variations in hydraulic residence time of floodplain lakes and their response to water conservancy projects. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 169, 112778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M. Modeling Water Residence Time and Connectivity in the Northern Indian River Lagoon. Estuaries Coasts 2023, 46, 1170–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Xu, G.; Niu, X.; Fu, Z.; Liao, X. Study on Water Replacement Characteristics of Xinghai Lake Wetland Based on Landscape Water Quality Objectives. Water 2023, 15, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawidek, J.; Ferencz, B. Water Renewal Time in Lakes with Transformed Water Distribution in the Catchment Areas. Water 2024, 16, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Ye, X.; Jiao, L.; Wu, Z.; Yang, J.; Xu, J. Effects of comprehensive protection project to the ecological environment of West Lake in Hangzhou. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2007, 18, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Xu, J.; Yang, J.; Mao, Y.; Jiang, H. Benifits of the restoration projects on West Lake: Evidence of chlorophyll-a change (1998–2007). Hupo Kexue 2009, 21, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Luo, N.; Pei, H. Assessment of Spatio-Temporal Changes of Water Quality in West Lake, Hangzhou Using SOFM Neural Network. J. Biomath. 2007, 22, 317–322. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Jin, J.; Shao, D.; Shao, Y. Application of Mathematical Modeling Method in Test Area of Hangzhou. China Water Wastewater 2013, 29, 148–150. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Jiang, Y.-f.; Wang, C.-c.; Huang, X.-n.; Wu, Z.-y.; Chen, L. Characteristics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Losses in Longhong Ravine Basin of Westlake in Rainstorm Runoff. Huanjing Kexue 2016, 37, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Mao, Z.; Rao, L.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Y. Simulation of Water Renewal Time in West Lake Based on Delft3D and Its Environmental Impact Analysis. Water 2025, 17, 2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Luo, L.; Wang, X.C.; Xiong, J.; Han, J. Current status and characteristics of urban landscape lakes in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 135669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.; Luo, L.; Wang, X.C.; Song, J.; Han, J.; Ao, D. A novel index for assessing the water quality of urban landscape lakes based on water transparency. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Xu, W.; Yan, W.; Wu, T.; He, X.; Cheng, N. Comparison between Machine-Learning-Based Turbidity Models Developed for Different Lake Zones in a Large Shallow Lake. Water 2023, 15, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.J.; Pan, J.Y.; Devlin, A.T. Variations in chlorophyll-a concentration in response to hydrodynamics in a flow-through lake: Remote sensing and modeling studies. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Cao, F.; Lou, Z. A Study on the Numerical Simulation of Flow Field in West Lake in Response to Diversion Works. Shanghai Environ. Sci. 2008, 27, 99–103,128. [Google Scholar]
- Gilboa, Y.; Friedler, E.; Talhami, F.; Gal, G. A novel approach for accurate quantification of lake residence time—Lake Kinneret as a case study. Water Res. X 2022, 16, 100149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, Y.; Lee, H. Changes in hydrology, water quality, and algal blooms in a freshwater system impounded with engineered structures in a temperate monsoon river estuary. J. Hydrol.-Reg. Stud. 2020, 32, 100744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Qin, F.; Cai, Y.; Wang, X. Impact of multi-temporal and spatial landscape patterns on the water quality of the Nanfei River. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2024, 43, 1580–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Buta, B.; Wiatkowski, M.; Gruss, L.; Tomczyk, P.; Kasperek, R. Spatio-temporal evolution of eutrophication and water quality in the Turawa dam reservoir, Poland. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, R.; Matsuzaki, S.I.S.; Watanabe, M.; Nakagawa, M.; Yoshida, H.; Kohzu, A. Heat Waves Can Cause Hypoxia in Shallow Lakes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2023GL102967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Su, B.L.; Wu, H.X.; Wang, S.R.; Wang, G.Q.; Ratnaweera, H.; Weerakoon, S.B.; Zhang, Z.B.; Yao, B. Scenario optimization of water supplement and outflow management in the Yilong Lake based on the EFDC model. Hydrol. Res. 2022, 53, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, T.; Font, E.; Soler, M.; Barcelona, A.; Colomer, J. Mean residence time of lagoons in shallow vegetated floodplains. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zhan, X.; Xu, H.; Zhu, G.; Zou, W.; Zhu, M.; Kang, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. New insights into eutrophication management: Importance of temperature and water residence time. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 111, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Cao, J.; Xiong, W.; He, H.; Ren, P. Spatiotemporal pattern of water age in Dongting Lake before and after the operation of the Three Gorges Project. J. Hydrol.-Reg. Stud. 2024, 55, 101902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, H.F.; Yang, W.; Xing, L.M.; Tu, G.Q.; Ru, Z.M.; Xu, Z.H. The assessment of ecological water replenishment scheme based on the two-dimensional lattice-Boltzmann water age theory. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2019, 25, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.N.; Shintani, T.; Nakayama, K. A Detailed Analysis on Hydrodynamic Response of a Highly Stratified Lake to Spatio-Temporally Varying Wind Field. Water 2023, 15, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ye, Q.H.; Wu, S.Q.; Stive, M.J.F. Wind Effects on the Water Age in a Large Shallow Lake. Water 2020, 12, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Lu, X.; Wang, K.; Liu, W.; Yao, Y.; Chen, L. Temporal variation of hydrological regime and water quality status between 2014–2020 in Gucheng Lake. Hydro-Sci. Eng. 2023, 6, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




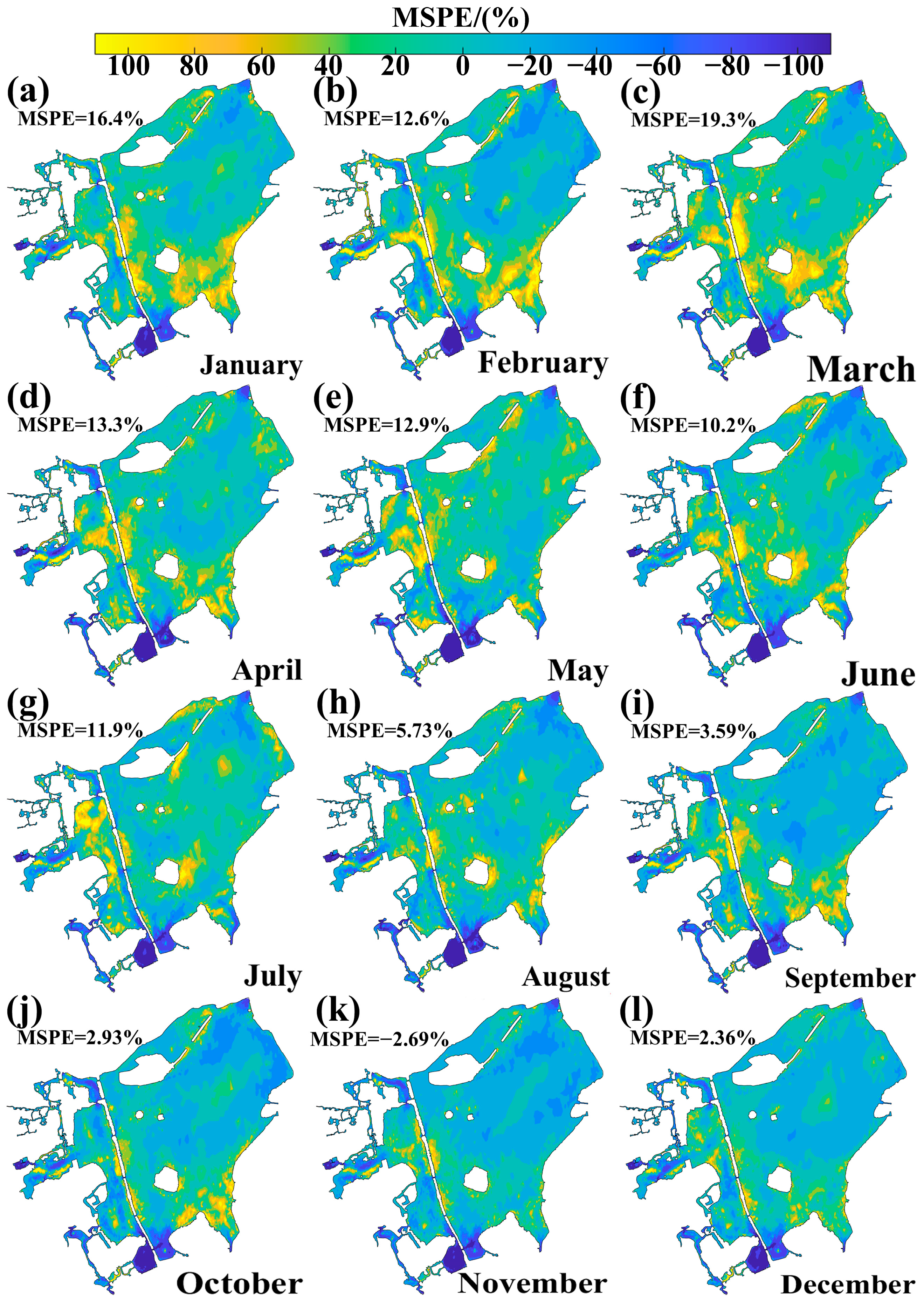

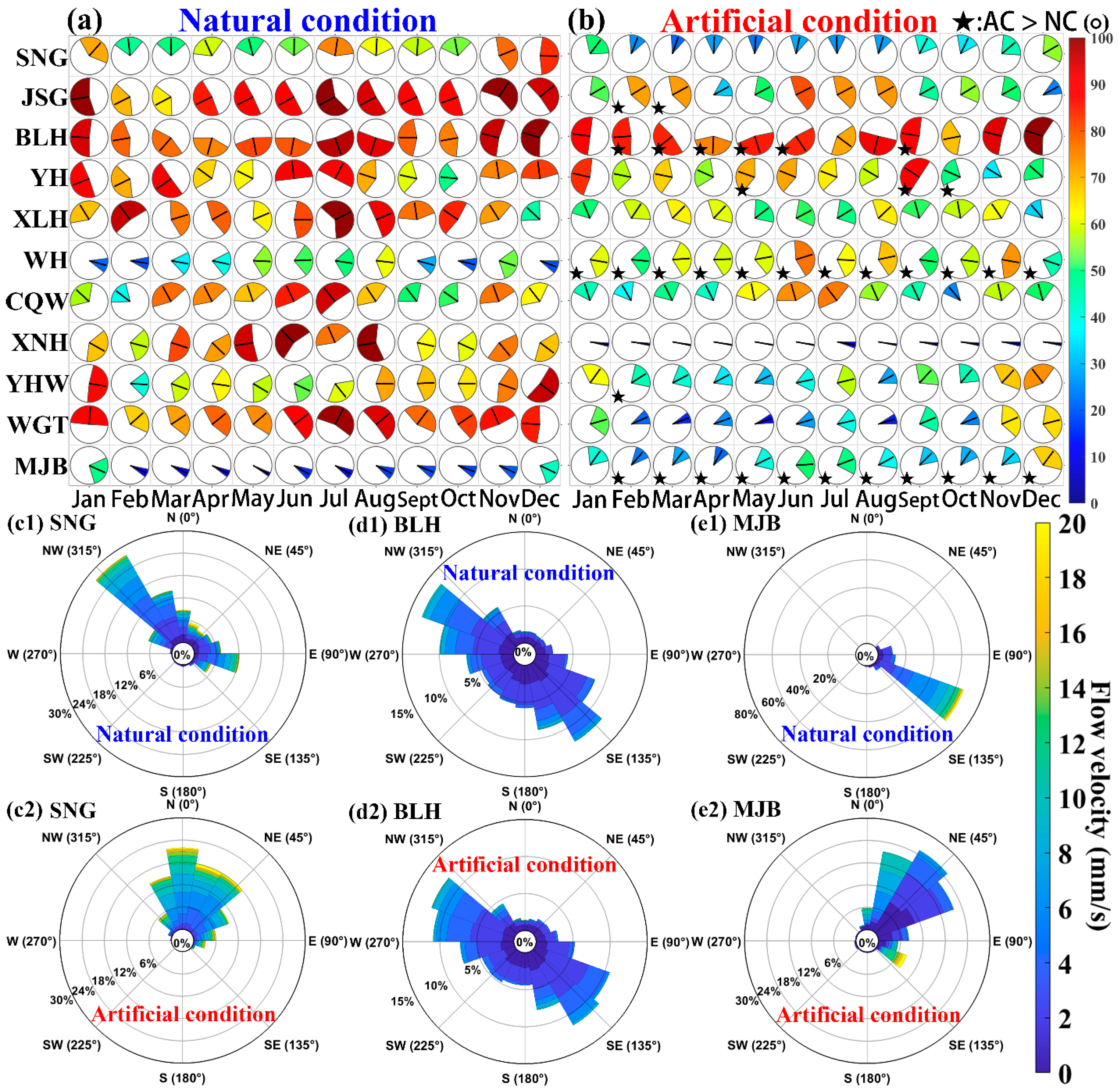

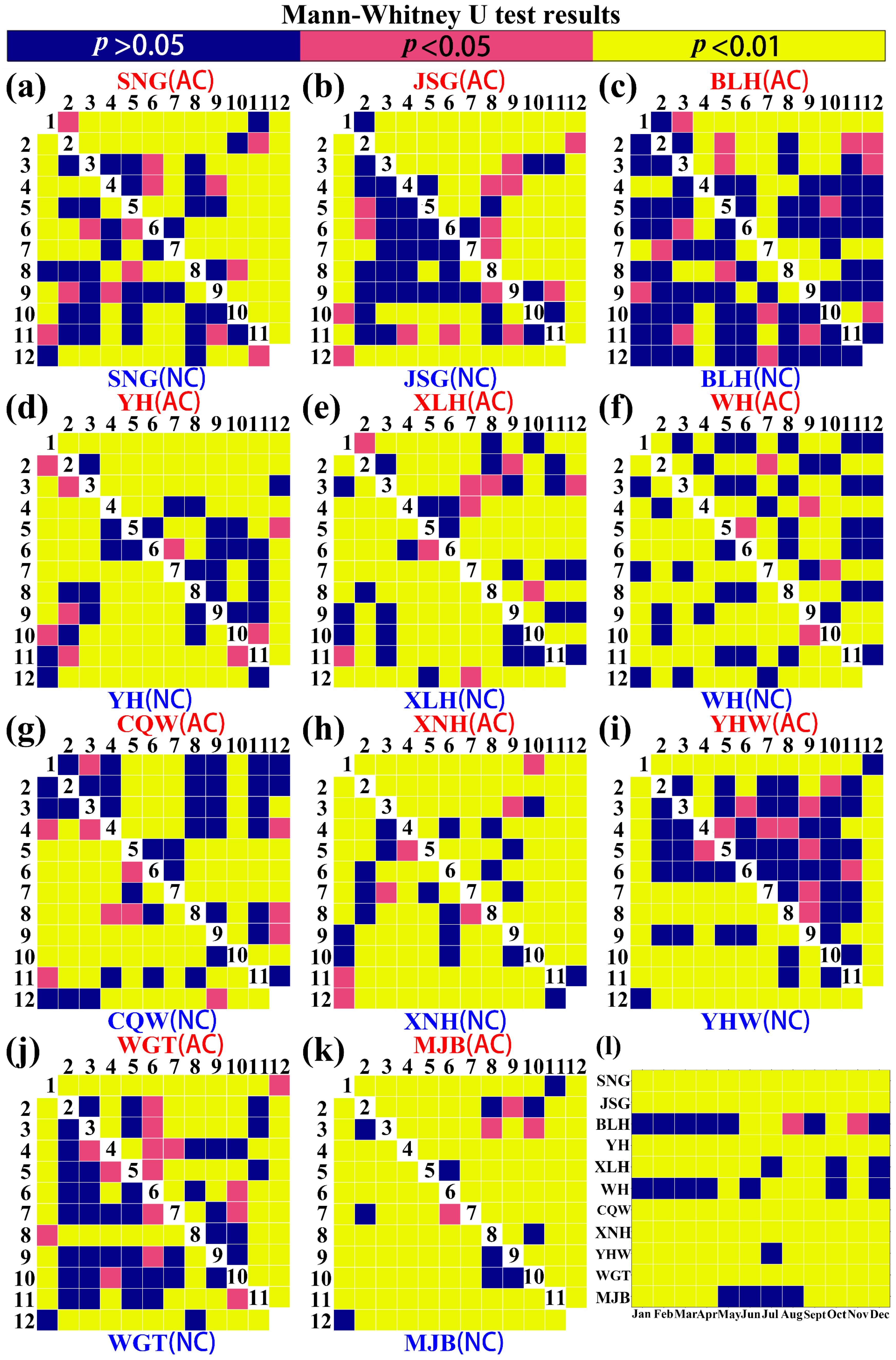


| Data Category | Time Period | Data Source | Temporal Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transparency (SDD) | January 2018 to December 2022 | Measured data | Monthly |
| TP | January 2021 to December 2022 | Measured data | Monthly |
| TN | January 2021 to December 2022 | Measured data | Monthly |
| Water level | 1 January 2021 to 31 October 2024 | Measured data | Daily |
| Precipitation | 1 January 2021 to 31 October 2024 | Measured data | Daily |
| Drainage volume | 1 January 2021 to 31 October 2024 | Measured data | Daily |
| Diversion volume | 1 January 2021 to 31 October 2024 | Measured data | Daily |
| Runoff | 1 January 2021 to 31 October 2024 | Empirical model results | Daily |
| Wind speed | 1 January 2021 to 1 January 2024 | Measured data | Daily |
| Flow velocity | 23 August 2017 and 13 September 2017 | Literature data | / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Mao, Z.; Rao, L.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Y. Impact of Artificial Water Replenishment on Spatiotemporal Distribution of Local Water Renewal Time in West Lake. Water 2025, 17, 3563. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243563
Xu P, Zhang X, Zhang L, Wang Q, Mao Z, Rao L, Yang J, Zhou Y. Impact of Artificial Water Replenishment on Spatiotemporal Distribution of Local Water Renewal Time in West Lake. Water. 2025; 17(24):3563. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243563
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Pinyan, Xianliang Zhang, Longwei Zhang, Qifei Wang, Zhihua Mao, Lihua Rao, Jun Yang, and Yinying Zhou. 2025. "Impact of Artificial Water Replenishment on Spatiotemporal Distribution of Local Water Renewal Time in West Lake" Water 17, no. 24: 3563. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243563
APA StyleXu, P., Zhang, X., Zhang, L., Wang, Q., Mao, Z., Rao, L., Yang, J., & Zhou, Y. (2025). Impact of Artificial Water Replenishment on Spatiotemporal Distribution of Local Water Renewal Time in West Lake. Water, 17(24), 3563. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243563







