Three Gorges Dam Reshaping of the Runoff–Sediment Relationship in the Reservoir, 1970 to 2023
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
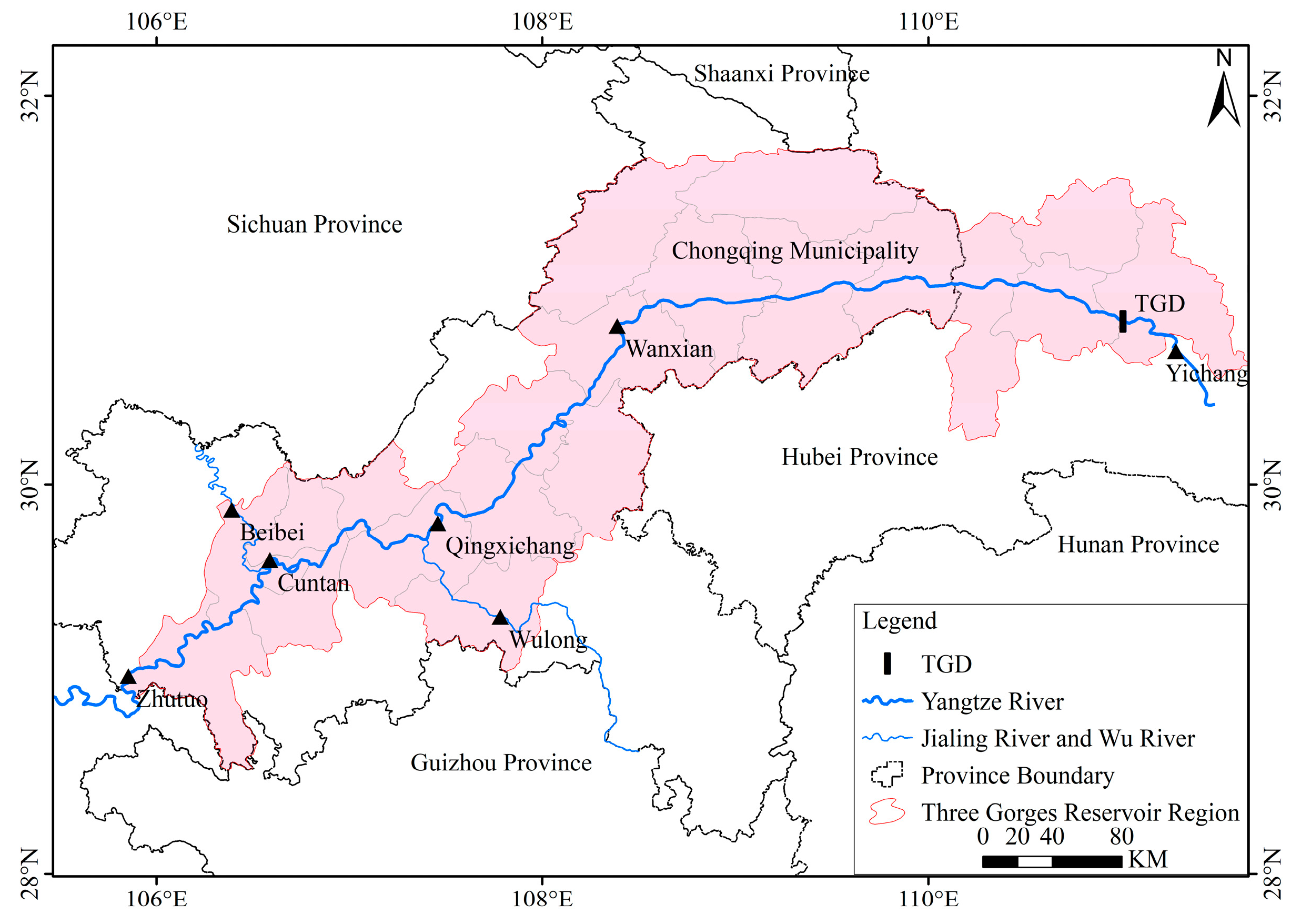
2.1. Study Area and Data
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Trend Analysis and Abrupt Detection
2.2.2. Mean Difference t-Test
2.2.3. Wavelet Analysis Methods
2.2.4. Cross-Wavelet Transform
2.2.5. Double Accumulation Curve
3. Results
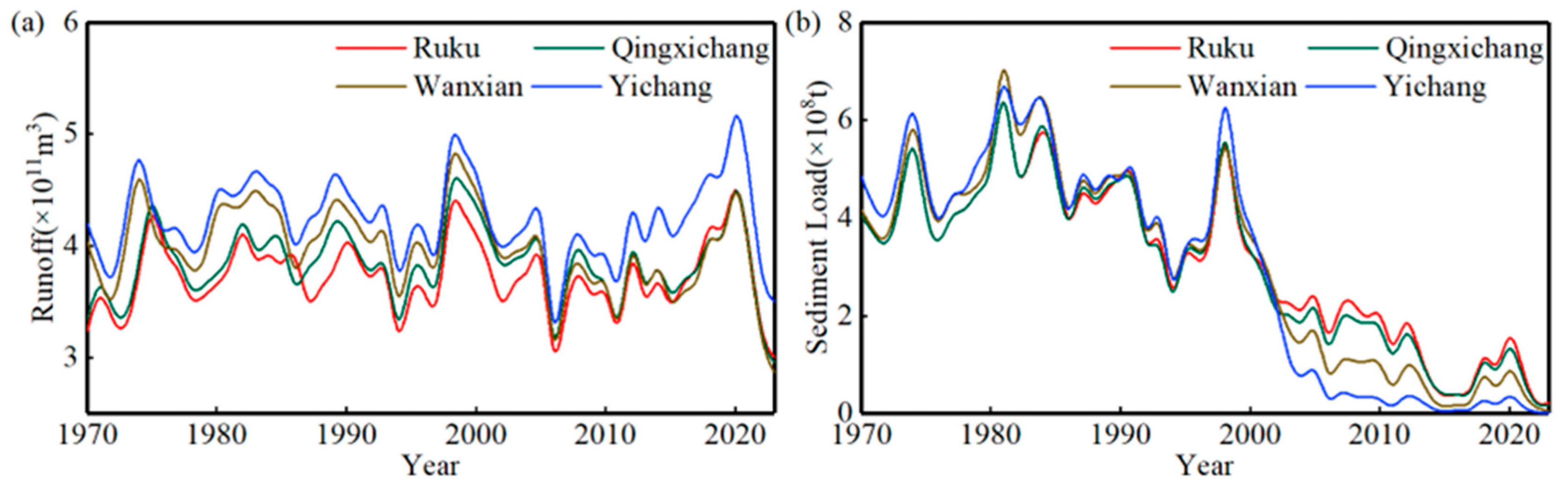
3.1. Runoff and Sediment Time-Varying Characteristics
3.2. Runoff and Sediment Situation Variation Identification
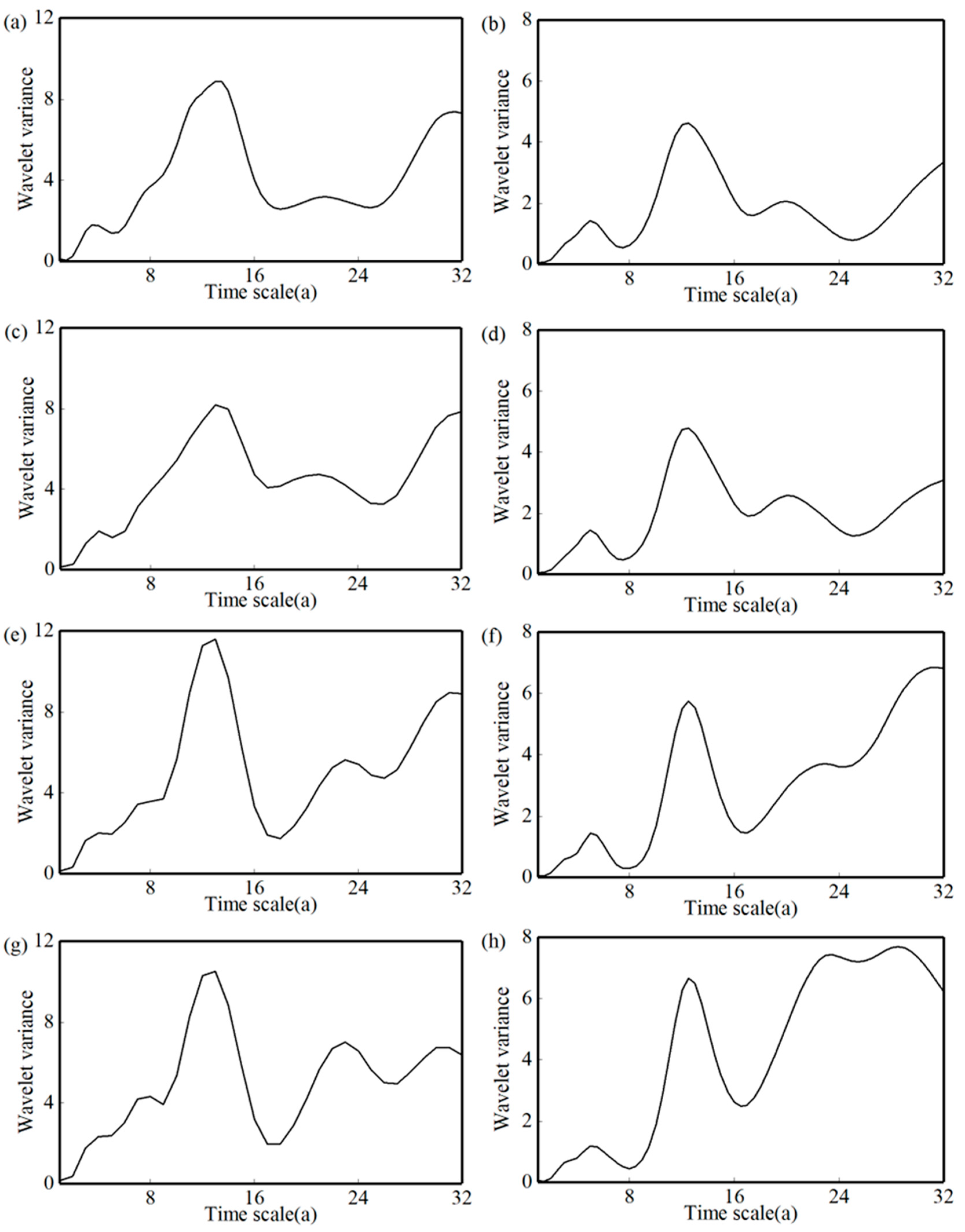
3.3. Periodic Fluctuations in Runoff and Sediment
3.4. Synergistic Evolution of Runoff and Sediment
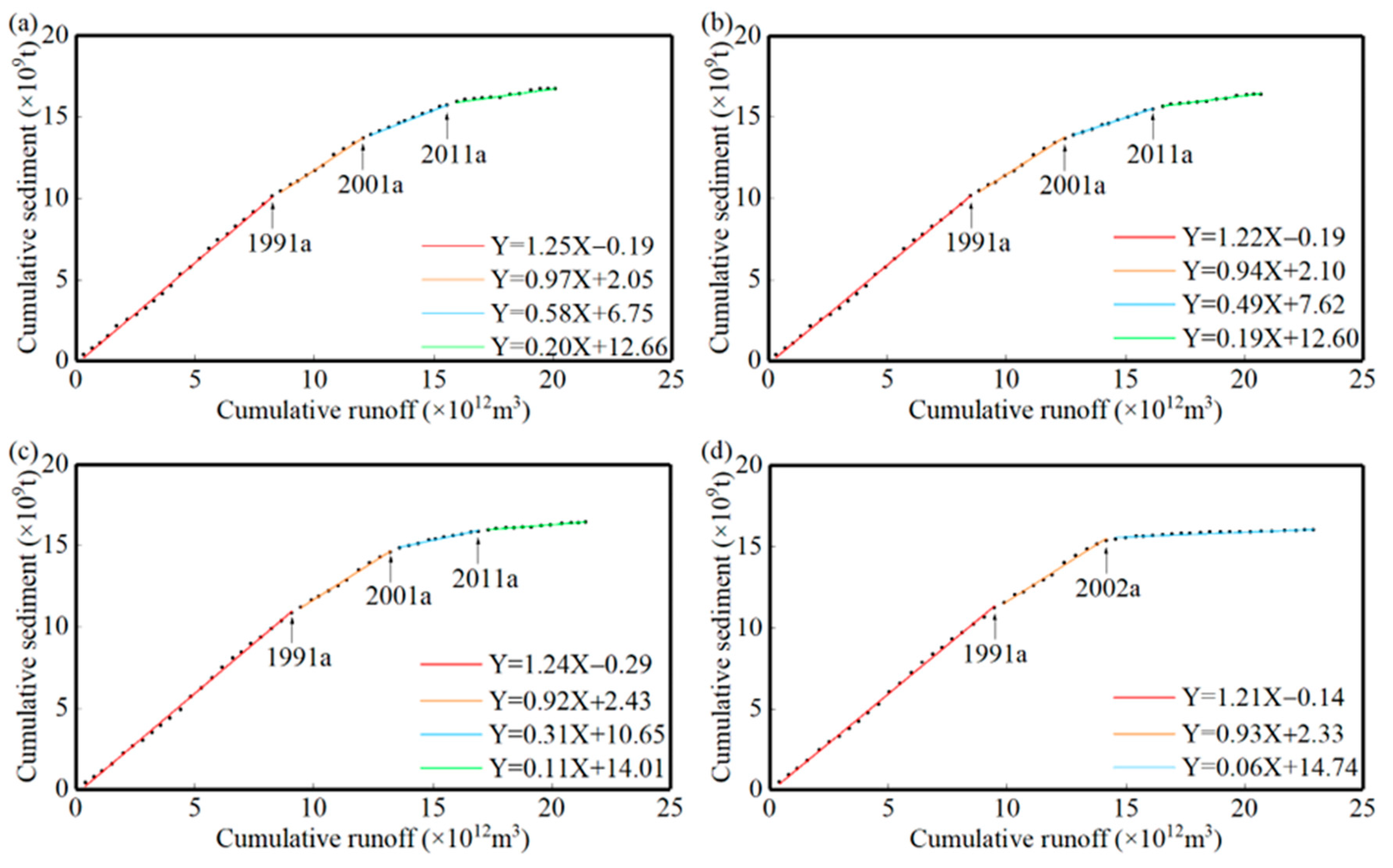
3.5. Runoff and Sediment Relationship in Different Periods
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of the TGD on Runoff and Sediment Transport Processes
4.2. Impacts of the TGD Operation on Abrupt Changes and Periodicity of Runoff and Sediment Load
4.3. Spatial Characteristics and Underlying Mechanisms of Runoff–Sediment Relationship Evolution in the TGR Region
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The influence of the TGD on runoff and sediment load exhibits marked spatial and temporal variability. Regulation effects increase progressively along the flow path, with stronger impacts observed closer to the dam.
- (2)
- Sediment transport processes have shifted from limited influence upstream to strong regulation downstream, establishing the TGD as the dominant control on reservoir sediment fluxes.
- (3)
- The TGD has progressively reshaped the runoff–sediment relationship, underscoring its central role in driving hydrological and sedimentary changes in the Yangtze River.
- (4)
- Understanding the impacts of the TGP on the water–sediment relationship in the reservoir area provides a practical basis for coordinated operation of the TGD and upstream cascade reservoirs, as well as for refined sediment management in the reservoir.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Fortesa, J.; Ricci, G.F.; García-Comendador, J.; Gentile, F.; Estrany, J.; Sauquet, E.; Datry, T.; De Girolamo, A.M. Analysing hydrological and sediment transport regime in two Mediterranean intermittent rivers. CATENA 2021, 196, 104865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petts, G.E.; Amoros, C. The Fluvial Hydrosystems; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Z.; Cai, Y.; Lin, J.; Xie, Y.; Yao, L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H. Coupled high-resolution GCM downscaling framework for projecting dynamics and drivers of ecosystem services in Pearl River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercruysse, K.; Grabowski, R.C.; Rickson, R.J. Suspended Sediment Transport Dynamics in Rivers: Multi-Scale Drivers of Temporal Variation. Earth Sci. Rev. 2017, 166, 3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohl, E.; Bledsoe, B.P.; Jacobson, R.B.; Poff, N.L.; Rathburn, S.L.; Walters, D.M.; Wilcox, A.C. The natural sediment regime in rivers: Broadening the foundation for ecosystem management. BioScience 2015, 65, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, D.F.; Deng, J.Y.; Yue, Y.; Zhou, J.X.; Chai, Y.F.; Li, Y.T. Mechanisms controlling water-level variations in the Middle Yangtze River following the operation of the Three Gorges Dam. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2022WR032338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvitski, J.P.; Milliman, J.D. Geology, geography, and humans battle for dominance over the delivery of fluvial sediment to the coastal ocean. J. Geol. 2007, 115, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, G.; Xie, Y.; Duan, X.W.; Wang, D.A.; Zhang, S. Annual variation of ephemeral gully erosion in a cultivated catchment. Geoderma 2021, 401, 115166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E. Measuring Sediment Yield from River Basin. In Soil Erosion Research Methods; Soil and Water Conservation Society (U. S.), Lal, R., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994; pp. 39–81. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.C.; Zhang, X.F.; Xu, Q. Variation of runoff and sediment inflows to the Three Gorges Reservoir: Impact of upstream cascade reservoirs. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuazo, V.D.; Pleguezuelo, C.R.; Peinado, F.M.; De Graaff, J.; Martínez, J.F.; Flanagan, D.C. Environmental impact of introducing plant covers in the taluses of terraces: Implications for mitigating agricultural soil erosion and runoff. CATENA 2011, 84, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Song, J.X.; Wang, Y.R.; Sun, H.T.; Li, Q. Threshold effects of vegetation coverage on runoff and soil loss in the Loess Plateau of China: A meta-analysis. Geoderma 2022, 412, 115720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Yu, K.X.; Li, Z.B.; Li, P.; Zhang, J.Z.; Wang, A.N.; Ma, L.; Xu, G.C.; Zhang, X. Temporal and spatial variation of rainfall erosivity in the Loess Plateau of China and its impact on sediment load. CATENA 2022, 210, 105931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Meng, C.C.; Wang, Y.J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Li, M. Comprehensive evaluation of the effects of climate change and land use and land cover change variables on runoff and sediment discharge. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buendia, C.; Bussi, G.; Tuset, J.; Vericat, D.; Sabater, S.; Palau, A.; Batalla, R.J. Effects of afforestation on runoff and sediment load in an upland Mediterranean catchment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 540, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Mu, X.; He, Y.; Chen, K. Variations in runoff, sediment load, and their relationship for a major sediment source area of the Jialing River basin, southern China. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shi, B.; Zhao, E.; Yuan, Q.; Chen, X. The Long-Term Spatial and Temporal Variations of Sediment Loads and Their Causes of the Yellow River Basin. CATENA 2022, 209, 105850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Gao, G.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.J.; Turner, R.E.; Ran, L.; Wang, X.; Fu, B. Long-Term Trends of Streamflow, Sediment Load and Nutrient Fluxes From the Mississippi River Basin: Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities. J. Hydrol. 2023, 616, 128822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Y.; Xie, Y.H.; Tang, Y.; Li, F.; Zou, Y.A. Changes of vegetation distribution in the east Dongting Lake after the operation of the Three Gorges Dam, China. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.W.; Feng, L.; Liu, Y.J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, D.; Liu, Z.X. Impact of dam construction on sediment transport capacity: A case study of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Hydrol. Process. 2024, 38, e15147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yang, G.; Wan, R.; Lai, X.; Wagner, P.D. Impacts of hydrological alteration on ecosystem services changes of a large river-connected lake (Poyang Lake), China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 310, 114750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Xia, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, M.; Mao, Y.; Xu, Q. Contributions of different sources to sediment transport in the Middle Yangtze River under intensive channel degradation. CATENA 2022, 217, 106511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Su, N.; Zhu, C.; He, Q. How have the river discharges and sediment loads changed in the Changjiang River basin downstream of the Three Gorges Dam? J. Hydrol. 2018, 560, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.H.; Jia, J.P.; Hou, Y.B.; Jiang, J.; Li, M.T.; Chen, J.; Wei, W. Changes in riverbed morphology in the middle Yangtze River (Yichang–Chenglingji) after the construction of the Three Gorges Dam. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2023, 68, 2373–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.S.; Wang, H.J.; Saito, Y.; Milliman, J.D.; Xu, K.; Qiao, S.; Shi, G. Dam impacts on the Changjiang (Yangtze) River sediment discharge to the sea: The past 55 years and after the Three Gorges Dam. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W04407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Xu, K.H.; Milliman, J.D.; Yang, H.F.; Wu, C.S. Decline of Yangtze River water and sediment discharge: Impact from natural and anthropogenic changes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.Y.; Chen, X.H.; Zhong, R.D.; Pan, Y.J.; Zhao, T.; Liu, Z.Y.; Tu, X.J. Joint probability analysis of water and sediment and predicting sediment load based on copula function. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2022, 37, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.W.; Li, D.X.; Liu, D.H.; Zhang, X.F.; Wang, Z.L. Characteristics of sedimentation and sediment trapping efficiency in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. CATENA 2022, 208, 105715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ren, J.Q.; Chen, Y.Q.; Yuan, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.Y. The important role of tributaries and flood events in sediment transport: A study on the spatiotemporal variability of water and sediment discharge upstream and downstream of the Three Gorges Reservoir. CATENA 2024, 234, 107594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Wang, Z.Y.; Siegel, D. Spatial and temporal sedimentation changes in the Three Gorges Reservoir of China. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2015, 20, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ge, H.; Ping, Y.R.; Dong, X.Y.; Zhu, L.L.; Ma, Y.C. Sedimentation Characteristics of the Fluctuating Backwater Area at the Tail of Cascade Reservoirs: A Case Study of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Water 2023, 15, 4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.Q.; Gao, J.N.; Luo, H. Changes and implications of the relationship between rainfall, runoff and sediment load in the Wuding River basin on the Chinese Loess Plateau. CATENA 2019, 175, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Tian, H.; Singh, V.P.; Chen, M.; Liu, J.; Ma, H.; Wang, J. Quantitative assessment of drivers of sediment load reduction in the Yangtze River basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 580, 124242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.C.; Xu, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.X. Comprehensive analysis on the evolution characteristics and causes of river runoff and sediment load in a mountainous basin of China’s subtropical plateau. J. Hydrol. 2020, 591, 125597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Salvador, A.; Conesa-García, C. Estimation of suspended sediment and dissolved solid load in a Mediterranean semiarid karst stream using log-linear models. Hydrol. Res. 2019, 50, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.D.; Liu, C.L. Spatial and temporal variability of precipitation over China, 1951–2005. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2009, 95, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderpour, E.; Ince, E.S.; Pagiatakis, S.D. Least-squares cross-wavelet analysis and its applications in geophysical time series. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 1223–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Xu, X.X.; Yu, B.F.; Xu, C.H.; Liu, M.X.; Wang, K.L. Quantifying the impacts of climate and human activities on water and sediment discharge in a karst region of southwest China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 836–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.W.; Shi, K.B. Comprehensive analysis of water-sediment variation characteristics at the confluence of the upper reaches of the Weigan River and Heizi River with multiple methods and multiple influencing factors. Water Supply 2022, 22, 1275–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.M.; Xiong, D.H.; Zhang, B.J.; He, K.L.; Wu, H.; Zhang, W.D.; Lu, X.N. Long-term response of runoff and sediment load to spatiotemporally varied rainfall in the Lhasa River basin, Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2023, 618, 129154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Ruan, L.; Li, H.; Zhou, W.J.; Yang, D.; Yu, J.H. Changes of meteorological parameters and lightning current during water impounded in Three Gorges area. Atmos. Res. 2013, 134, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.J.; Yang, H.B.; Li, Z.; Lu, H.F.; Yang, D.W. Modeling of flood routing for Three Gorges reservoir area based on MIKE11. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2014, 33, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Jiu, J.Z.; Wu, H.J.; Li, S. The Implication of land-use/land-cover change for the declining soil erosion risk in the Three Gorges Reservoir region, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, C.H.; Peng, H.; Xiao, S.B.; Yan, D.H. Contribution of moisture sources to precipitation changes in the Three Gorges Reservoir region. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 4759–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akihiko, I. Constraining size-dependence of vegetation respiration rates. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, M.G. Further contributions to the theory of paired comparisons. Biometrics 1955, 11, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Lacruz, J.; Morán-Tejeda, E.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Hannaford, J.; García, C.; Peña-Angulo, D.; Murphy, C. Streamflow frequency changes across western Europe and interactions with North Atlantic atmospheric circulation patterns. Glob. Planet. Change 2022, 212, 103797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinsted, A.; Moore, J.C.; Jevrejeva, S. Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2004, 11, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.L.; Shi, H.W.; Chen, C.C.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, J. The study on the time lag of water level in the three gorges reservoir under the regulation processes. Hydrol. Res. 2021, 52, 734–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searcy, J.K.; Hardison, C.H. Double-Mass Curves (No. 1541); US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1960.
- Ashagrie, A.G.; De Laat, P.J.; De Wit, M.J.; Tu, M.; Uhlenbrook, S. Detecting the influence of land use changes on discharges and floods in the Meuse River Basin—The predictive power of a ninety-year rainfall-runoff relation? Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 10, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirnia, A.; Golshan, M.; Darabi, H.; Adamowski, J.; Rozbeh, S. Using the Mann–Kendall test and double mass curve method to explore stream flow changes in response to climate and human activities. J. Water Clim. Change 2019, 10, 725–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.S.; Deng, A.J.; Chen, J.G.; Wang, D.W.; Lu, Q.; Xie, Y.Q. Improving the double mass curve method to analyse the variation trend of runoff and sediment load in watersheds. LHB 2023, 109, 2236971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E.; Fang, D. Recent trends in the suspended sediment loads of the world’s rivers. Glob. Planet. Change 2003, 39, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; He, X.B.; Bao, Y.H. Anthropogenic impacts on suspended sediment load in the Upper Yangtze river. Reg. Environ. Change 2011, 11, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.P.; Zhu, Y.L.; Dong, S.F.; Becker, S.; Chen, Y.F. Attribution of decreasing annual and autumn inflows to the Three Gorges Reservoir, Yangtze River: Climate variability, water consumption or upstream reservoir operation? J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Tong, S.; Xu, G.; Huang, G.; Wang, T. Delayed response of sedimentation in the flood seasons to the pool level of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Adv. Water Sci. 2019, 30, 528–536. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.Y.; Tong, S.H.; Huang, G.X.; Xu, G.G.; Li, X.H.; Lei, K.; Yao, S.M. Characteristics of sedimentation and channel adjustment linked to the Three Gorges Reservoir. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2021, 36, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Yan, H.C.; Yue, Y.; Xu, Q.X. Quantifying natural and anthropogenic impacts on runoff and sediment load: An investigation on the middle and lower reaches of the Jinsha River Basin. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2019, 25, 100617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.Y.; Xu, F.; Ma, C.Y.; Yang, C.R.; Zhao, Z.C.; Yue, H.Y. Analysis of the sediment deposition characteristics in the Three Gorges Reservoir and its influence factors. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 476. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.Q.; Li, R.; Wu, M.; Zhao, W.H.; Zhao, L.Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; Bowes, M.J. Influence of turbid flood water release on sediment deposition and phosphorus distribution in the bed sediment of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liro, M.; Ruiz-Villanueva, V.; Mikuś, P.; Wyżga, B.; Castellet, E.B. Changes in the hydrodynamics of a mountain river induced by dam reservoir backwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Pang, Y.; He, C.; Li, P.H.; Xiao, S.B.; Shi, Q.; He, D. Three Gorges Reservoir construction induced dissolved organic matter chemistry variation between the reservoir and non-reservoir areas along the Xiangxi tributary. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.T.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.M.; Yang, Y.G.; Liang, R.F.; Peng, F.J.; Xue, S.D.; Zhu, Z.X.; Li, K.F. Hydrodynamic and environmental characteristics of a tributary bay influenced by backwater jacking and intrusions from a main reservoir. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 5057–5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, R.; Wang, L.J.; Li, H.; Tian, Z.B.; Zheng, B.H. Water quality variation in tributaries of the Three Gorges Reservoir from 2000 to 2015. Water Res. 2021, 195, 116993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Operation Stage | Control Stations | |
|---|---|---|
| Ruku | Outflow | |
| From Jan 1970 to May 2003 | Qingxichang | Yichang |
| From Jun 2003 to Aug 2006 | Qingxichang | |
| From Sep 2006 to Sep 2008 | Cuntan + Wulong | |
| From Oct 2008 to Dec 2023 | Zhutuo + Beibei + Wulong | |
| Station | Runoff (×1011 m3) | Sediment Load (×108 t) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1970–2023 | 1970–2002 | 2003–2023 | Rate of Change | 1970–2023 | 1970–2002 | 2003–2012 | 2013–2023 | Cumulative Rate | |
| Ruku | 3.723 | 3.750 | 3.680 | 1.8% | 3.098 | 4.208 | 2.027 | 0.741 | 82.4% |
| Qingxichang | 3.835 | 3.888 | 3.753 | 3.5% | 3.039 | 4.205 | 1.788 | 0.6767 | 83.9% |
| Wanxian | 3.966 | 4.124 | 3.718 | 9.8% | 3.042 | 4.498 | 1.138 | 0.409 | 90.9% |
| Yichang | 4.240 | 4.295 | 4.154 | 3.3% | 2.965 | 4.656 | 0.482 | 0.148 | 96.8% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Y.; Duan, H.; Tang, X.; Chen, J.; Wu, S.; Ju, J. Three Gorges Dam Reshaping of the Runoff–Sediment Relationship in the Reservoir, 1970 to 2023. Water 2025, 17, 3548. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243548
Luo Y, Duan H, Tang X, Chen J, Wu S, Ju J. Three Gorges Dam Reshaping of the Runoff–Sediment Relationship in the Reservoir, 1970 to 2023. Water. 2025; 17(24):3548. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243548
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Yixia, Hengyi Duan, Xiaoya Tang, Jilong Chen, Shengjun Wu, and Jialing Ju. 2025. "Three Gorges Dam Reshaping of the Runoff–Sediment Relationship in the Reservoir, 1970 to 2023" Water 17, no. 24: 3548. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243548
APA StyleLuo, Y., Duan, H., Tang, X., Chen, J., Wu, S., & Ju, J. (2025). Three Gorges Dam Reshaping of the Runoff–Sediment Relationship in the Reservoir, 1970 to 2023. Water, 17(24), 3548. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243548







