Regional Circulation and Fate of Typical Antibiotic Discharges in the Yangtze River Estuarine Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
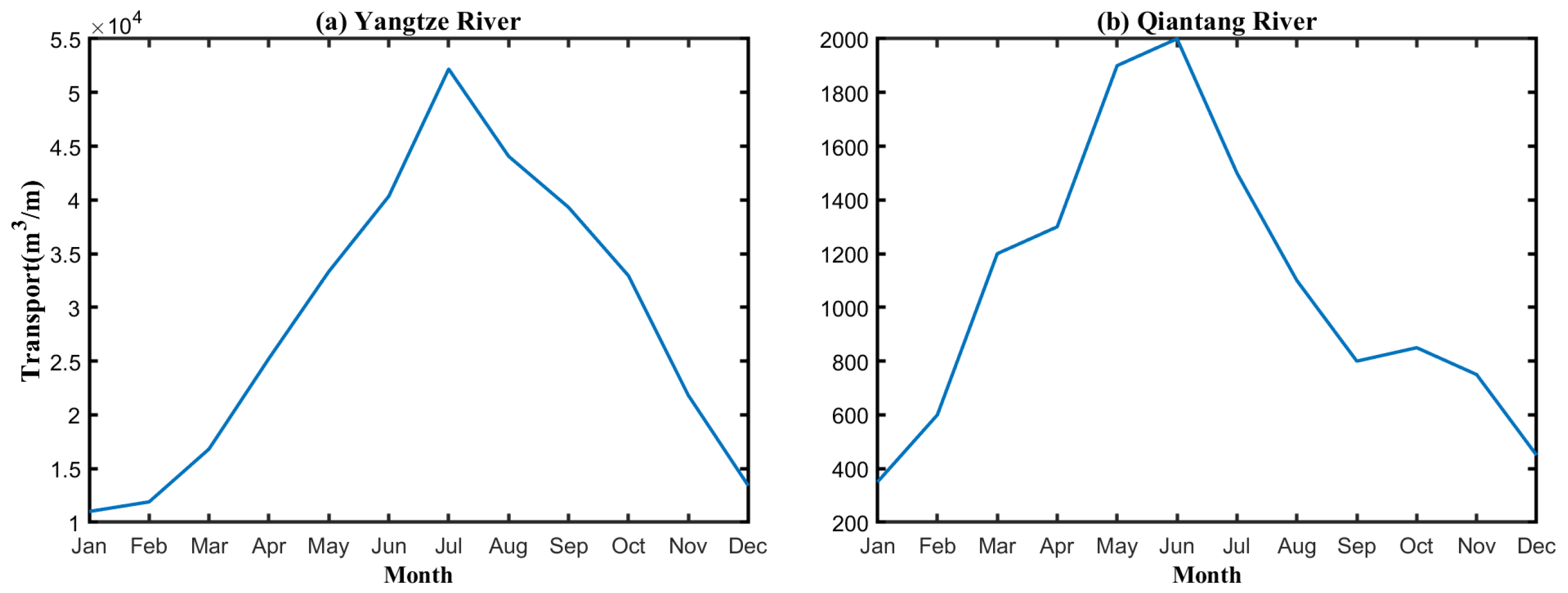
2.1. Study Domain
2.2. Model
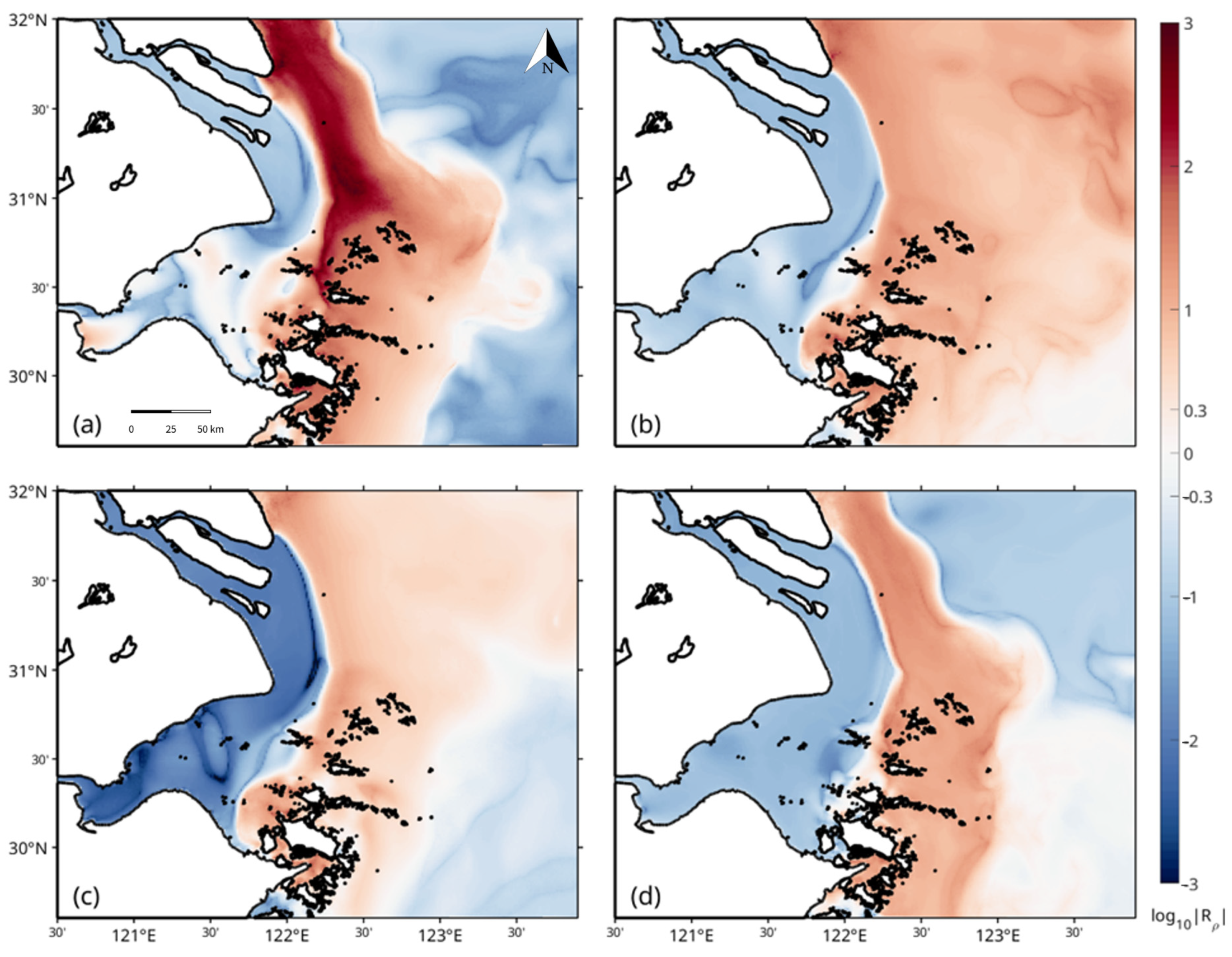
2.3. Density Ratio Calculation
3. Results and Analysis
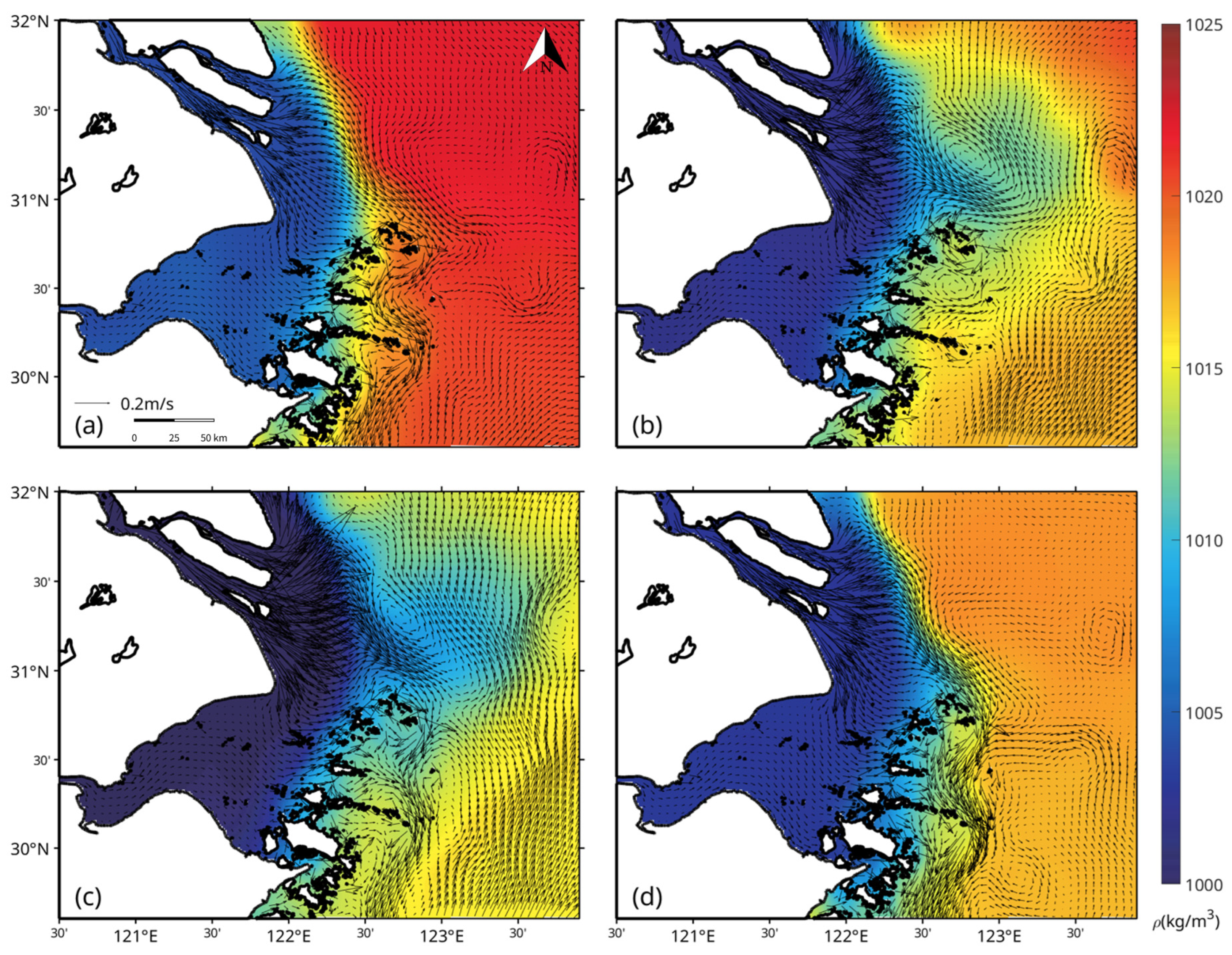
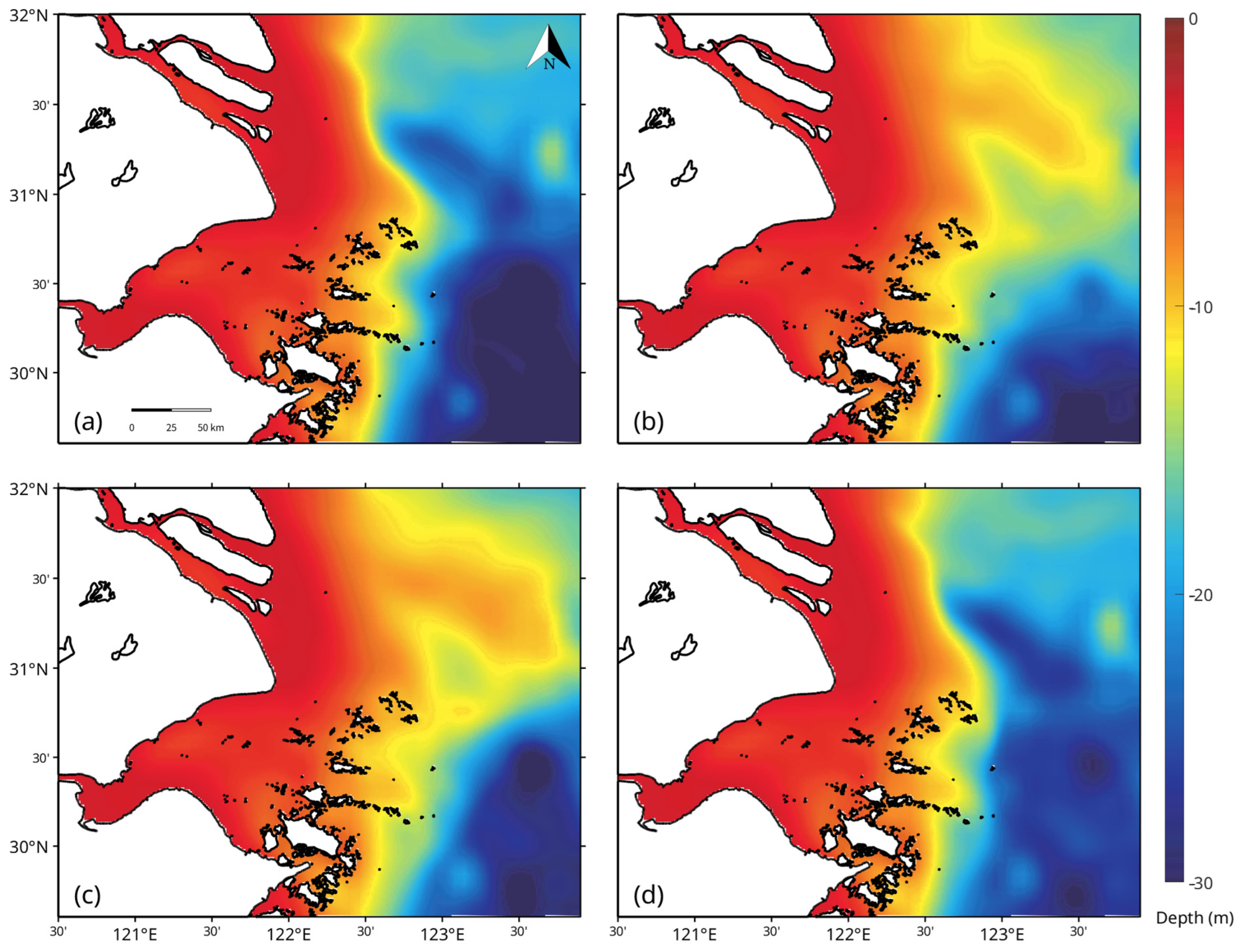
3.1. Seasonal Circulation and Density Structure of the East China Sea
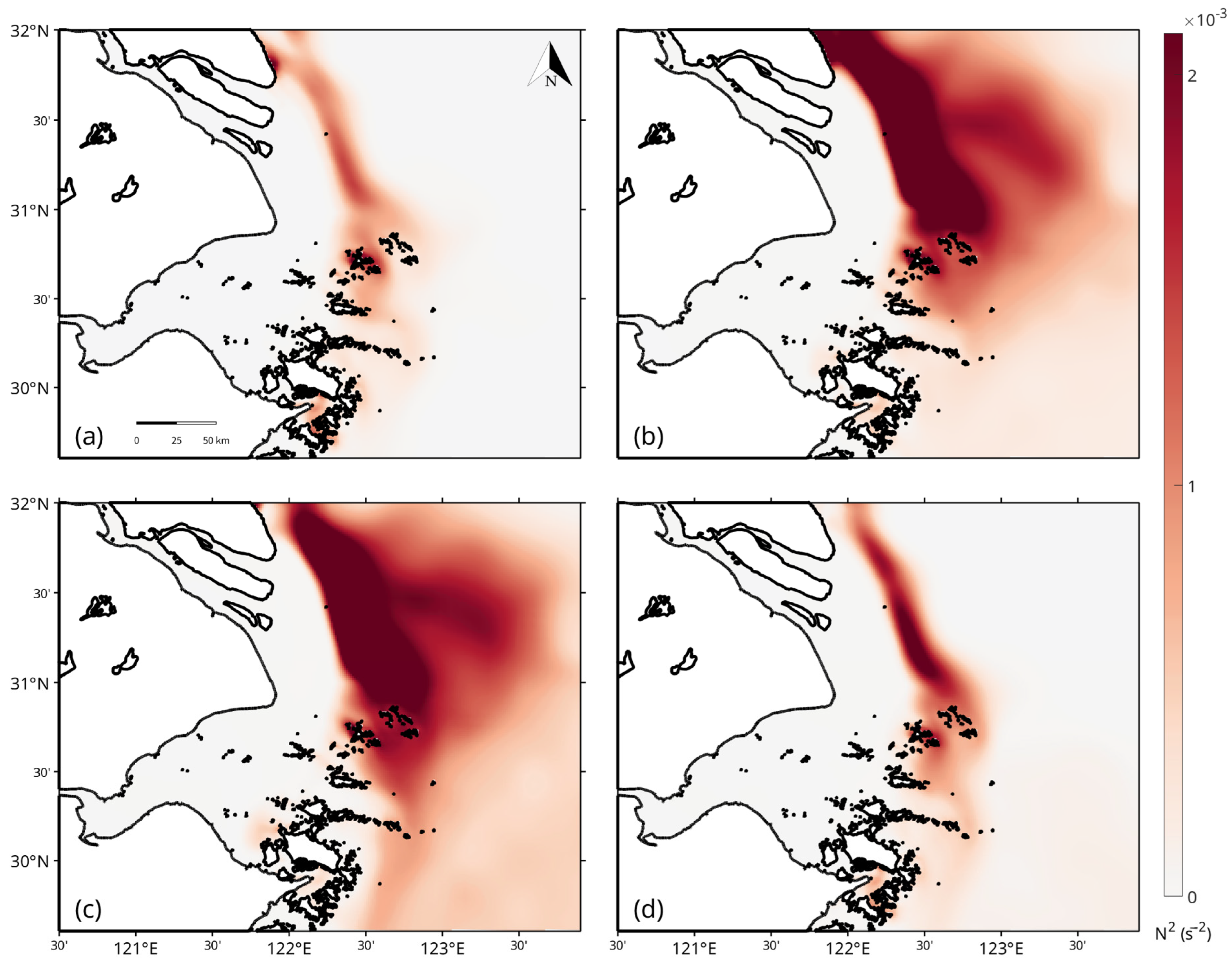
3.2. Stratification Regimes
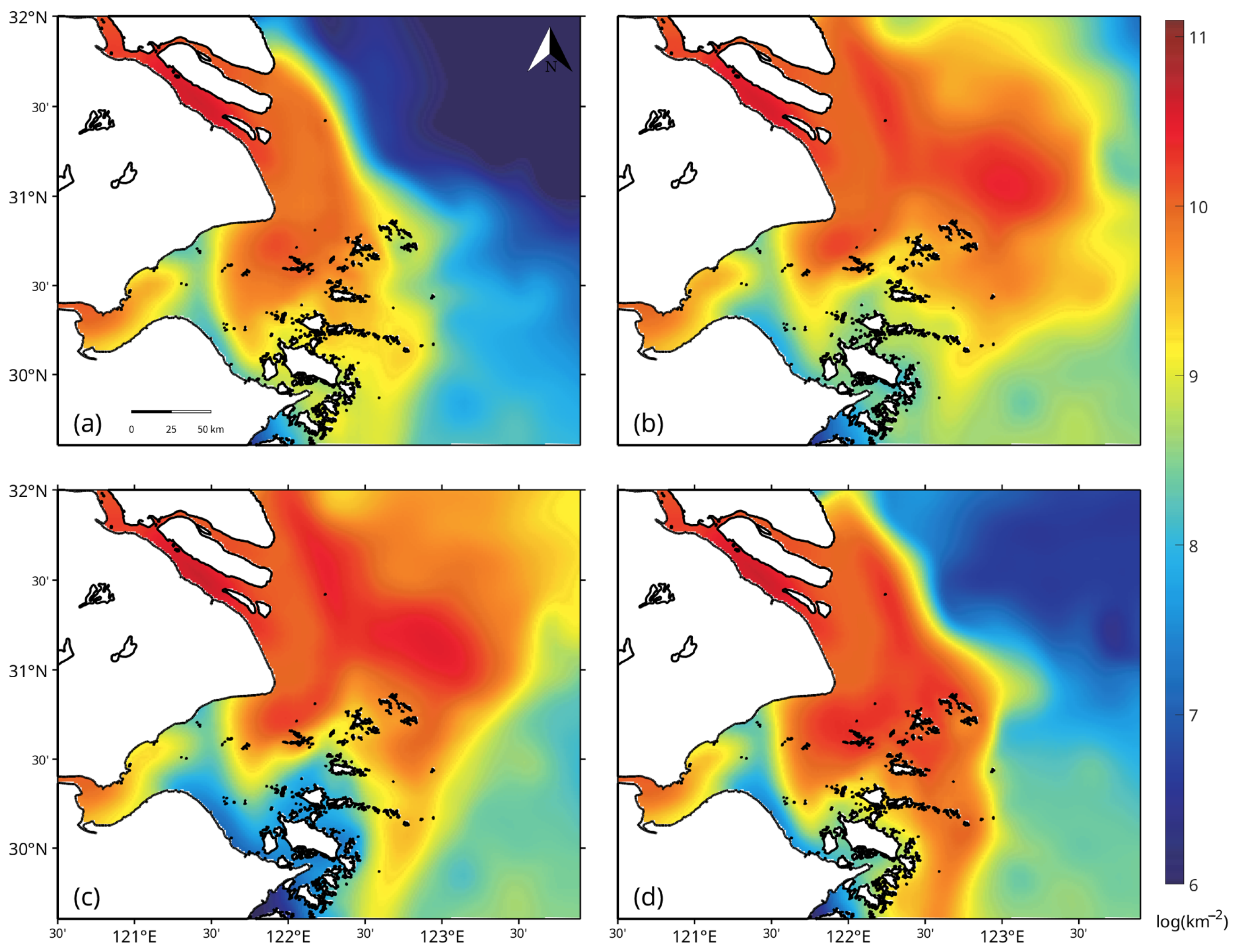
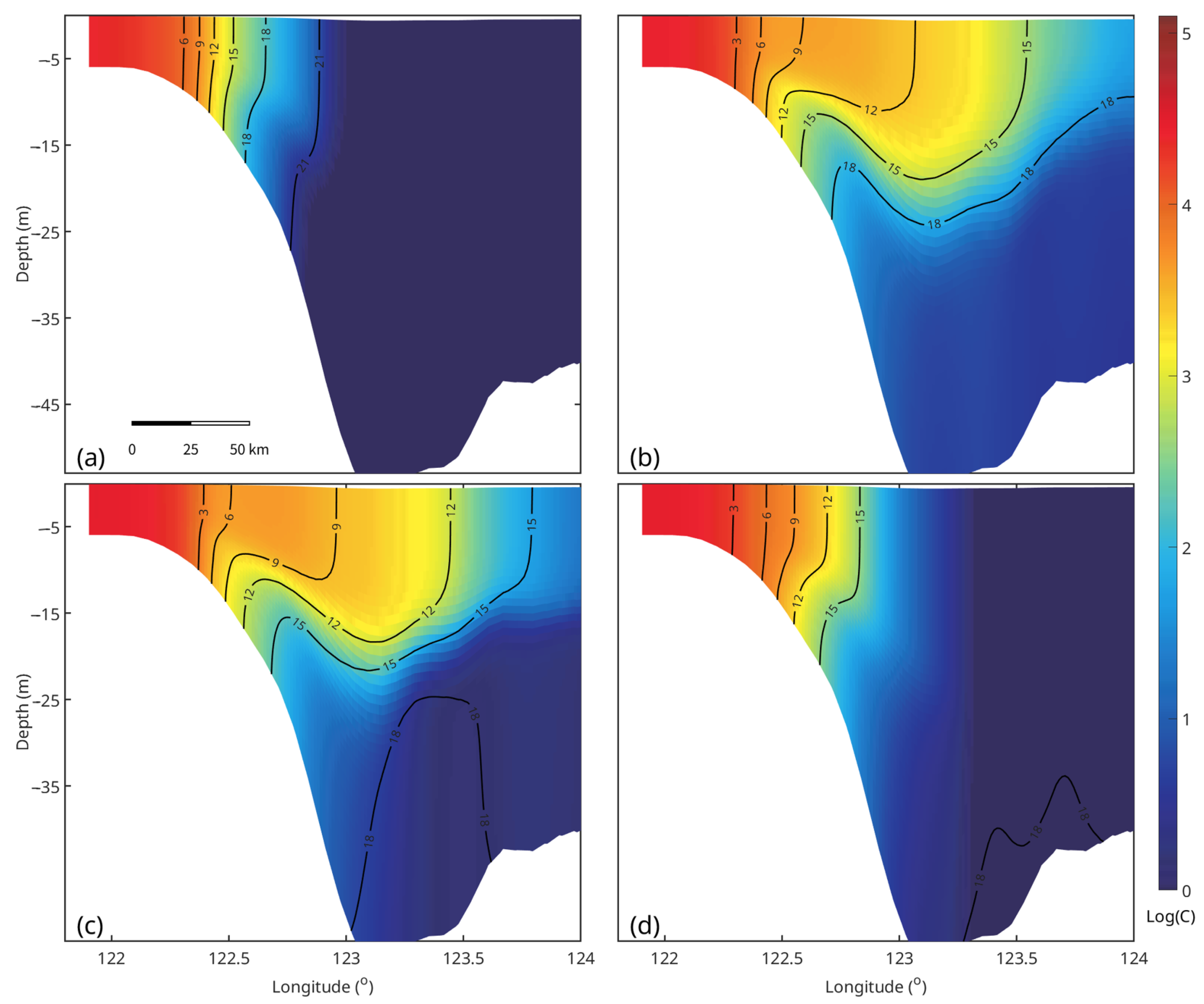
3.3. Tracer Transport and Vertical Distribution
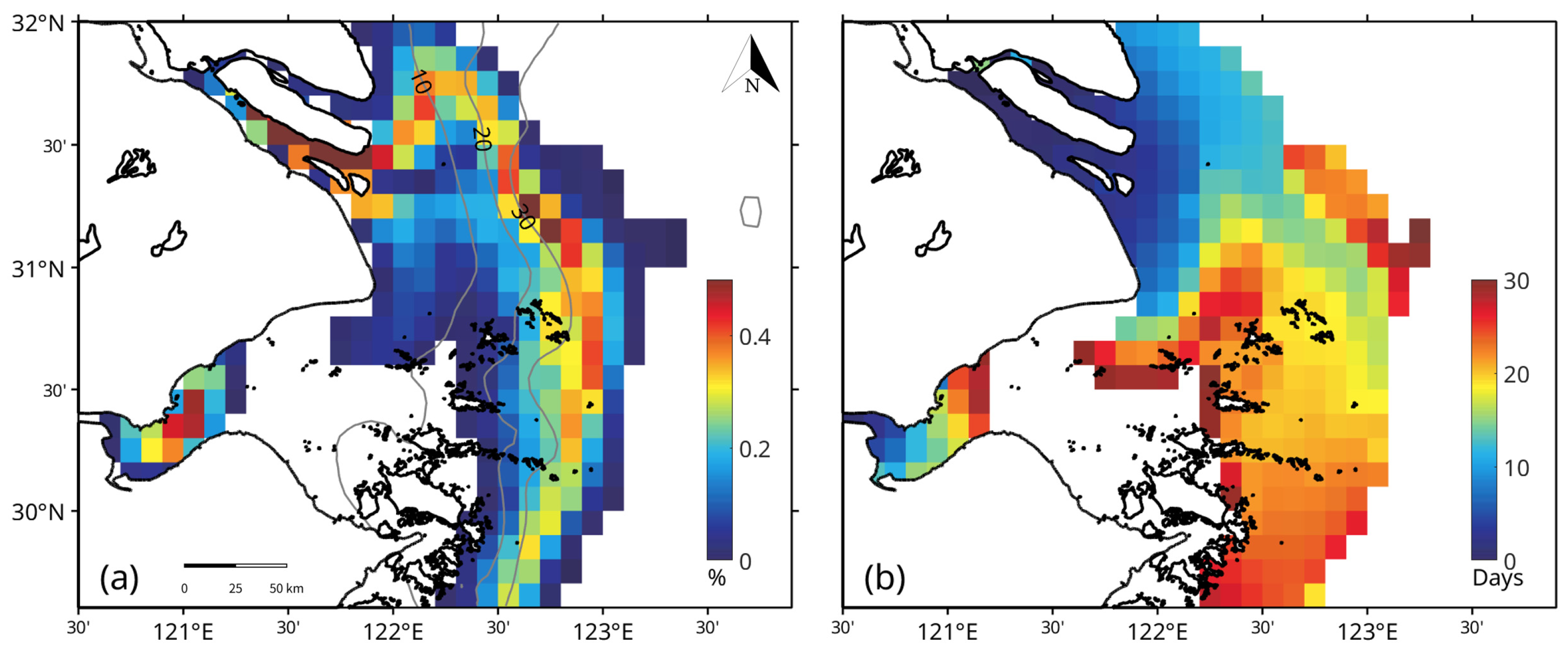
3.4. Particle-Tracking Pathways and Transport Timescales
4. Summary and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARGs | antibiotic resistance genes |
| CMS | Connectivity Modeling System |
| CDW | Changjiang Diluted Water |
| ECS | East China Sea |
| ECMWF | European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts |
| ROMS | Regional Ocean Modeling System |
| YRE | Yangtze River Estuary |
References
- Kuang, C.; Chen, K.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Xia, Z. Responses of Hydrodynamics and Saline Water Intrusion to Typhoon Fongwong in the North Branch of the Yangtze River Estuary. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gan, J.; Wu, H.; Hu, J.; Cai, Z.; Deng, Y. Advances on Coastal and Estuarine Circulations Around the Changjiang Estuary in the Recent Decades (2000–2020). Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 615929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Ke, J.; Show, P.L.; Ge, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, R.; Chen, J. Antibiotics: An Overview on the Environmental Occurrence, Toxicity, Degradation, and Removal Methods. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 7376–7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, M.; Nie, M.; Shi, H.; Gu, L. Antibiotics in the Surface Water of the Yangtze Estuary: Occurrence, Distribution and Risk Assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 175, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Feng, C.; Gu, E.; Tian, C.; Shen, Z. Spatial Distribution, Source Apportionment and Risk Assessment of Antibiotics in the Surface Water and Sediments of the Yangtze Estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, E.; Variatza, E.; Balcazar, J.L. The Role of Aquatic Ecosystems as Reservoirs of Antibiotic Resistance. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhao, S.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Hou, L.; Liu, M.; Yang, Y. Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Sediments of the Yangtze Estuary: From 2007 to 2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z. Distribution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Typical Antibiotics in the Surface Waters of Seven Major Rivers, China. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2021, 23, 1088–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Li, P.; Zang, Y.; Liu, X. Antibiotics in Aquatic Environments of China: A Review and Meta-Analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 199, 110668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Huang, M.; Zhao, L.; He, P.; Liu, Y.; Pan, H.; Cao, S.; Liu, X. Adsorption Performance and Mechanisms of Tetracycline on Clay Minerals in Estuaries and Nearby Coastal Areas. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Deng, W.-J.; Ying, G.-G.; Tsang, E.P.K.; Hong, H.-C. Occurrence and Distribution of Antibiotics in Surface Water. Ecotoxicology 2022, 31, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maghsodian, Z.; Sanati, A.M.; Mashifana, T.; Sillanpää, M.; Feng, S.; Nhat, T.; Ramavandi, B. Occurrence and Distribution of Antibiotics in the Water, Sediment, and Biota of Freshwater and Marine Environments: A Review. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Helbling, D.E.; Xu, N.; Sun, W.; Ni, J. Animal Production Predominantly Contributes to Antibiotic Profiles in the Yangtze River. Water Res. 2023, 242, 120214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, S.; Hu, J.; Sun, W.; Ni, J. Profiles, Drivers, and Prioritization of Antibiotics in China’s Major Rivers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 477, 135399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Han, Y.; Li, Y.; Duan, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, Y. Simulation and Risk Assessment of Typical Antibiotics in the Multi-Media Environment of the Yangtze River Estuary under Tidal Effect. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 81875–81891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-B.; Duan, Y.-P.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Tu, Y.-J.; Luo, P.-C.; Gao, J.; Dai, C.-M.; Zhou, L. Multimedia Fate Model and Risk Assessment of Typical Antibiotics in the Integrated Demonstration Zone of the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wei, Z.; Xu, T.; Sun, M.; Liu, K.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, H.; Yin, X.; Feng, W.; et al. Development of a Fine-Resolution Atmosphere-Wave-Ocean Coupled Forecasting Model for the South China Sea and Its Adjacent Seas. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2019, 38, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-R.; Duan, Y.-P.; Zhang, Z.-B.; Gao, Y.-F.; Dai, C.-M.; Tu, Y.-J.; Gao, J. Comprehensive Evaluation of Antibiotics Pollution the Yangtze River Basin, China: Emission, Multimedia Fate and Risk Assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhong, G.; Huang, Y.; Jones, K.C. Comprehensive Assessment of Environmental Emissions, Fate, and Risks of Veterinary Antibiotics in China: An Environmental Fate Modeling Approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 5534–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addis, T.Z.; Adu, J.T.; Kumarasamy, M.; Demlie, M. Assessment of Existing Fate and Transport Models for Predicting Antibiotic Degradation and Transport in the Aquatic Environment: A Review. Water 2023, 15, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagi, A.; Pampanin, D.M.; Brakstad, O.G.; Kommedal, R. Estimation of Hydrocarbon Biodegradation Rates in Marine Environments: A Critical Review of the Q10 Approach. Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 89, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batchu, S.R.; Panditi, V.R.; O’Shea, K.E.; Gardinali, P.R. Photodegradation of Antibiotics under Simulated Solar Radiation: Implications for Their Environmental Fate. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, L.; Chen, J.; Qiao, X.; Lin, J.; Cai, X. Light-Source-Dependent Effects of Main Water Constituents on Photodegradation of Phenicol Antibiotics: Mechanism and Kinetics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3101–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tan, L.; Zhang, L.; Tian, W.; Ma, L. A Review of the Distribution of Antibiotics in Water in Different Regions of China and Current Antibiotic Degradation Pathways. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 692298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, C.B.; Helgers, J.; Van Sebille, E.; Srinivasan, A. Connectivity Modeling System: A Probabilistic Modeling Tool for the Multi-Scale Tracking of Biotic and Abiotic Variability in the Ocean. Environ. Model. Softw. 2013, 42, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, P.; Yao, F.; Kartadikaria, A.R.; Viswanadhapalli, Y.; Gopalakrishnan, G.; Hoteit, I. Far-Field Ocean Conditions and Concentrate Discharges Modeling Along the Saudi Coast of the Red Sea. In Intakes and Outfalls for Seawater Reverse-Osmosis Desalination Facilities; Missimer, T.M., Jones, B., Maliva, R.G., Eds.; Environmental Science and Engineering; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 501–520. ISBN 978-3-319-13202-0. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, P.; Krokos, G.; Langodan, S.; Guo, D.; Dasari, H.; Papadopoulos, V.P.; Lermusiaux, P.F.J.; Knio, O.M.; Hoteit, I. Coastal Circulation and Water Transport Properties of the Red Sea Project Lagoon. Ocean. Model. 2021, 161, 101791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhan, P.; Li, J.; Sasaki, J.; Qiu, Z.; Chen, C.; Zou, S.; Yang, X.; Gu, H. Physical Drivers of Noctiluca Scintillans (Dinophyceae) Blooms Outbreak in the Northern Taiwan Strait: A Numerical Study. Harmful Algae 2024, 133, 102586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carstens, K.L.; Gross, A.D.; Moorman, T.B.; Coats, J.R. Sorption and Photodegradation Processes Govern Distribution and Fate of Sulfamethazine in Freshwater–Sediment Microcosms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10877–10883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimmett, M.E. Adsorption of Sulfamethazine from Environmentally Relevant Aqueous Matrices onto Hypercrosslinked Adsorbent MN250. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrower, J.; McNaughtan, M.; Hunter, C.; Hough, R.; Zhang, Z.; Helwig, K. Chemical Fate and Partitioning Behavior of Antibiotics in the Aquatic Environment—A Review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 3275–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, H.A. World Ocean Density Ratios. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1996, 26, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, D.L.; Martin, J.P. On the Horizontal Density Ratio in the Upper Ocean. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 2002, 36, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y. Modulation of Shelf Circulations Under Multiple River Discharges in the East China Sea. JGR Ocean. 2021, 126, e2020JC016990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S. Longitudinal Residual Circulation in the South Passage of Yangtze Estuary: Combined Influences from Runoff, Tide and Bathymetry. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 2129–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagi, T.; Takahashi, S. Seasonal Variation of Circulations in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea. J. Oceanogr. 1993, 49, 503–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beardsley, R.C.; Limeburner, R.; Yu, H.; Cannon, G.A. Discharge of the Changjiang (Yangtze River) into the East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 1985, 4, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Chu, P.C. Thermal and Haline Fronts in the Yellow/East China Seas: Surface and Subsurface Seasonality Comparison. J. Oceanogr. 2006, 62, 617–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.; Johnson, E.R. The Dispersive Potential-Vorticity Dynamics of Coastal Outflows. J. Fluid Mech. 2025, 1010, A39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozovatsky, I.; Lee, J.; Fernando, H.J.S.; Kang, S.K.; Jinadasa, S.U.P. Turbulence in the E Ast C Hina S Ea: T He Summertime Stratification. JGR Ocean. 2015, 120, 1856–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Feng, T.; Qin, G.; Meng, Y.; Zhao, S.; Yang, G.; Wang, L.; Sun, W. Simulations of Water Pollutants in the Hangzhou Bay, China: Hydrodynamics, Characteristics, and Sources. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 200, 116140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, X.; Sun, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhan, P. Regional Circulation and Fate of Typical Antibiotic Discharges in the Yangtze River Estuarine Region. Water 2025, 17, 3384. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17233384
Feng X, Sun J, Zhou H, Zhan P. Regional Circulation and Fate of Typical Antibiotic Discharges in the Yangtze River Estuarine Region. Water. 2025; 17(23):3384. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17233384
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Xiang, Junchuan Sun, Han Zhou, and Peng Zhan. 2025. "Regional Circulation and Fate of Typical Antibiotic Discharges in the Yangtze River Estuarine Region" Water 17, no. 23: 3384. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17233384
APA StyleFeng, X., Sun, J., Zhou, H., & Zhan, P. (2025). Regional Circulation and Fate of Typical Antibiotic Discharges in the Yangtze River Estuarine Region. Water, 17(23), 3384. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17233384





