Developing Insights into Pretreatment Optimization: Effects of Eliminating Lime and Soda Ash in Groundwater RO Desalination
Abstract
Research Highlights
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
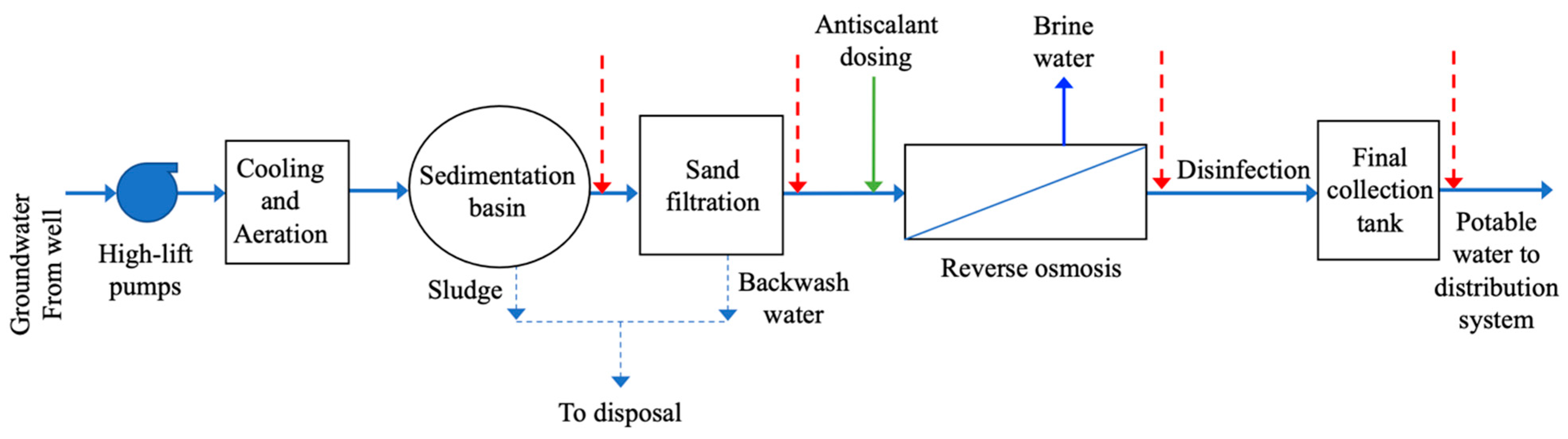
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
- Water quality following the sedimentation stage;
- The quality of water fed to the RO unit (particularly in terms of its compatibility with membrane design and operational specifications);
- Water quality after the RO unit;
- The final product water quality and its compliance with the Saudi Standards for Unbottled Drinking Water.
2.3. Water Quality Parameters and Analytical Tools
2.4. RO Membrane Performance
2.5. Economic Assessment Calculations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Water Quality Analysis After the Sedimentation Stage
3.2. Water Quality Analysis After the Filtration Stage
3.3. Performance of the RO Stage
3.3.1. Water Quality
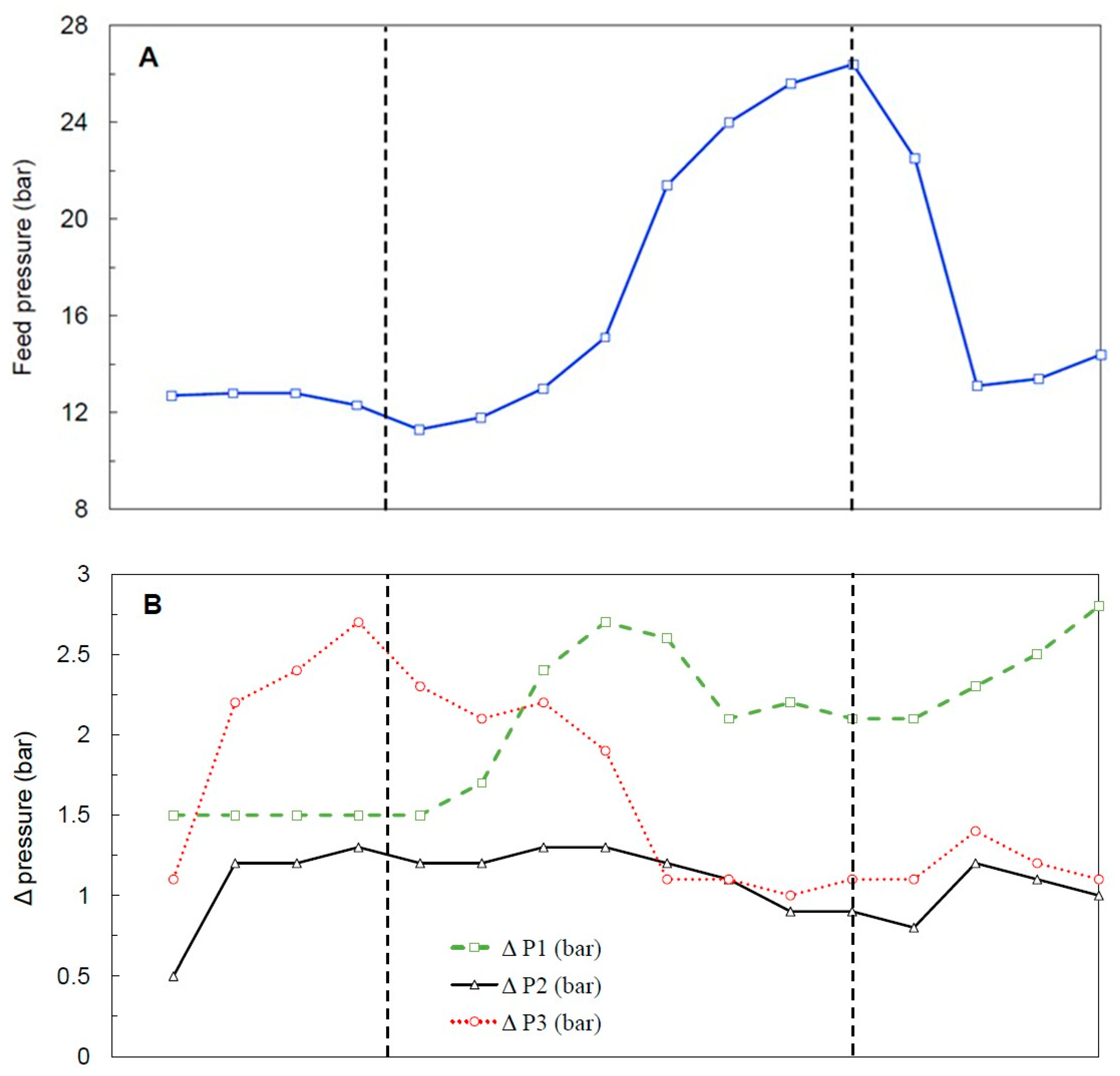
3.3.2. Feed Pressure and Hydraulic Behavior
3.4. Final Produced Water Quality and Regulatory Compliance
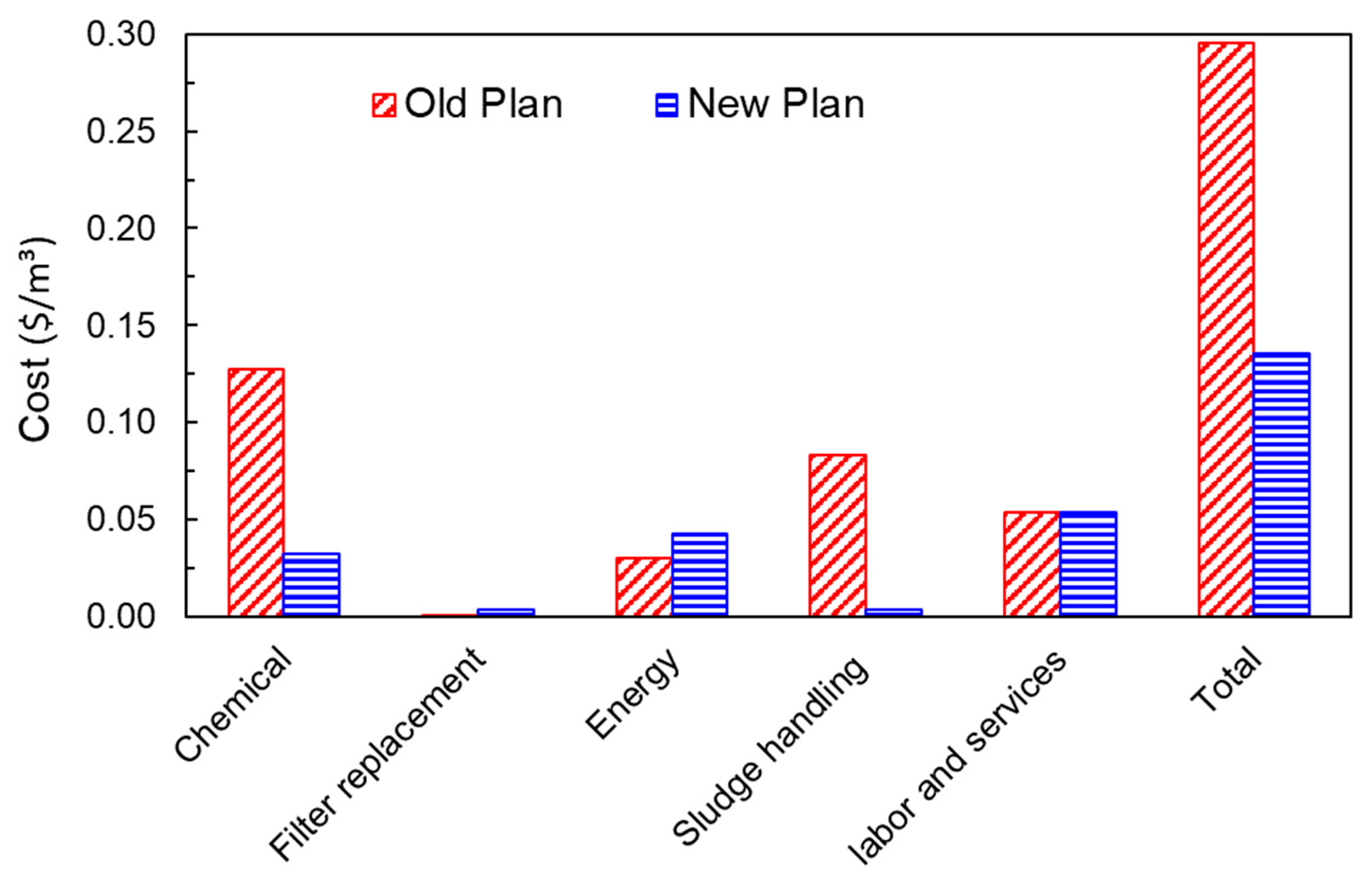
3.5. Economic Assessment
4. Environmental Perspective
5. Recommendations and Future Work
- Investigate Seasonal and Hydrogeochemical Variability
- 2.
- Expand Temporal and Spatial Scope of Data Collection
- 3.
- Incorporate Comprehensive Economic Assessment
- 4.
- Optimize Pretreatment Configurations
- 5.
- Standardize Post-Treatment Blending and Remineralization
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chowdhury, T.N.; Battamo, A.; Nag, R.; Zekker, I.; Salauddin, M. Impacts of Climate Change on Groundwater Quality: A Systematic Literature Review of Analytical Models and Machine Learning Techniques. Environ. Res. Lett. 2025, 20, 033003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaidy, A.; Yimer, E.A.; Mogheir, Y.; Huysmans, M.; Villani, L.; van Griensven, A. Groundwater Drought and Anthropogenic Amplifiers: A Review of Assessment and Response Strategies in Arid and Semi-Arid Areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 978, 179406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davamani, V.; John, J.E.; Poornachandhra, C.; Gopalakrishnan, B.; Arulmani, S.; Parameswari, E.; Santhosh, A.; Srinivasulu, A.; Lal, A.; Naidu, R. A Critical Review of Climate Change Impacts on Groundwater Resources: A Focus on the Current Status, Future Possibilities, and Role of Simulation Models. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaie, Y.; Ismail, S.; Soussa, H.; Gado, M.; Balah, A. Water Desalination in Egypt; Literature Review and Assessment. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023, 14, 101998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Taani, A.A.; Nazzal, Y.; Howari, F.M. Groundwater Scarcity in the Middle East. In Global Groundwater; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 163–175. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Farraj, A.S.; Al-Wabel, M.I.; El-Saeid, M.H.; El-Naggar, A.H.; Ahmed, Z. Evaluation of Groundwater for Arsenic Contamination Using Hydrogeochemical Properties and Multivariate Statistical Methods in Saudi Arabia. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 812365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahal, A.Y. Groundwater Quality Analysis in Hail Region of Northwest Saudi Arabia Based on Physicochemical Investigation. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2024, 36, 103384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerroumi, S.; Amarine, M.; Gourich, B. Technological Trends in Manganese Removal from Groundwater: A Review. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 56, 104365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebil, S.; Ruiz-García, A.; Farhat, S.; Bali, M. Long-Term Performance Evaluation and Fouling Characterization of a Full-Scale Brackish Water Reverse Osmosis Desalination Plant. Water 2024, 16, 1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amoudi, A.; Lovitt, R.W. Fouling Strategies and the Cleaning System of NF Membranes and Factors Affecting Cleaning Efficiency. J. Memb. Sci. 2007, 303, 4–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushawish, A.; Bouaziz, I.; Almanassra, I.W.; AL-Rajabi, M.M.; Jaber, L.; Khalil, A.K.A.; Takriff, M.S.; Laoui, T.; Shanableh, A.; Atieh, M.A.; et al. Desalination Pretreatment Technologies: Current Status and Future Developments. Water 2023, 15, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algurainy, Y.; Call, D.F. Cathodic Precipitation of Calcium Carbonate and Its Impact on the Electrosorption of Sodium in Flow-through Capacitive Deionization. Desalination 2024, 586, 117853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayeh, Y.A.; Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Alzghoul, T.M.; Bashir, M.J. A Comprehensive Review of RO Membrane Fouling: Mechanisms, Categories, Cleaning Methods and Pretreatment Technologies. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 18, 100684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Amin, S.; Mohamed, A.A. Fouling in Reverse Osmosis Membranes: Monitoring, Characterization, Mitigation Strategies and Future Directions. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugo, A.; Mejía-Saucedo, C.; Senanayake, P.S.; Stoll, Z.; Sitterley, K.; Wang, H.; Kota, K.; Kuravi, S.; Fthenakis, V.; Kurup, P.; et al. Technical, Economic, Energetic, and Environmental Evaluation of Pretreatment Strategies for Scaling Control in Brackish Water Desalination Brine Treatment. Water 2025, 17, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchobanoglus, G.; Burton, F.; Stensel, H.D. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment and Reuse, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2003; ISBN 007-041878-0. [Google Scholar]
- Gude, V.G. Desalination and Sustainability—An Appraisal and Current Perspective. Water Res. 2016, 89, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, X.; Tang, B.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Gao, X. Scaling in Reverse Osmosis Seawater Desalination: Mechanism and Prevention—A Literature Review. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2025, 103, 503–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Yadav, S.; Ibrar, I.; Al Juboori, R.A.; Razzak, S.A.; Deka, P.; Subbiah, S.; Shah, S. Fouling and Performance Investigation of Membrane Distillation at Elevated Recoveries for Seawater Desalination and Wastewater Reclamation. Membranes 2022, 12, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.K.; Biesheuvel, P.M.; Elimelech, M. Energy Consumption of Brackish Water Desalination: Identifying the Sweet Spots for Electrodialysis and Reverse Osmosis. ACS ES T Eng. 2021, 1, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, R.; Avci, A.H.; Curcio, E.; Domene, D.S.; Villa González, C.; Gallart, J.J.E.; Argurio, P. Selective Calcium Removal at Near-Ambient Temperature in a Multimineral Recovery Process from Seawater Reverse Osmosis Synthetic Brine and Ex Ante Life Cycle Assessment. Water 2024, 16, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarak, M.F.; Khedr, G.E.; El Sharkawy, H.M. Environmentally-Friendly Calcite Scale Mitigation: Encapsulation of CDs@ MS Composite within Membranes Framework for Nanofiltration. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 999, 175061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, K.; Oshchepkov, M.; Pervov, A.; Golovesov, V.; Ryabova, A.; Trukhina, M.; Tkachenko, S. A Case Study of Calcium Carbonate Crystallization during Reverse Osmosis Water Desalination in Presence of Novel Fluorescent-Tagged Antiscalants. Membranes 2022, 12, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, W.; Ji, X.; Yang, H. Evaluation of a Novel Non-Ionic Graft Starch-Based Antiscalant in Reduction of CaSO4 Scaling by Static and Reverse Osmosis Test. J. Memb. Sci. 2025, 713, 123394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odabaşı, Ç.; Dologlu, P.; Gülmez, F.; Kuşoğlu, G.; Çağlar, Ö. Investigation of the Factors Affecting Reverse Osmosis Membrane Performance Using Machine-Learning Techniques. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2022, 159, 107669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Alshraideh, H.; Alsuwaidi, F. A Holistic Framework for Improving the Prediction of Reverse Osmosis Membrane Performance Using Machine Learning. Desalination 2024, 574, 117253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, J.L.; Michael, P.R.; Ghaffour, N.; Missimer, T.M. Membranes Economics and Energy Consumption of Brackish Water Reverse Osmosis Desalination: Innovations and Impacts of Feedwater Quality. Membranes 2021, 11, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, C.; Jiang, L.; Li, X. Pilot-Scale Evaluation of the Sustainability of Membrane Desalination Systems for the Concentrate Volume Minimization of Coal Chemical Wastewater. Environ. Sci. 2024, 10, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, M.M. Water Chemistry; Waveland Press, Inc.: Long Grove, IL, USA, 2015; ISBN 147862308X. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, M.N.V.; de Campos Favas, P.J.; Vithanage, M.; Mohan, S.V. Industrial and Municipal Sludge: Emerging Concerns and Scope for Resource Recovery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780128159071. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Byun, J.; Park, K.; Park, Y.-G. Comprehensive Analysis of Energy Saving and High-Quality Permeate Production Strategies for a Large-Scale Seawater Reverse Osmosis Desalination Plant with Diverse Process Configurations and External Resource Utilization. Desalination 2025, 596, 118292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagnambhatt, S.; Khanmohammadi, S.; Maisonneuve, J. Reducing the Specific Energy Use of Seawater Desalination with Thermally Enhanced Reverse Osmosis. Desalination 2024, 573, 117163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Dong, L.; Shon, H.K.; Kim, J. Specific Energy Consumption of Seawater Reverse Osmosis Desalination Plants Using Machine Learning. Desalination 2025, 602, 118654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffour, N.; Missimer, T.M.; Amy, G.L. Technical Review and Evaluation of the Economics of Water Desalination: Current and Future Challenges for Better Water Supply Sustainability. Desalination 2013, 309, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgante, C.; Vassallo, F.; Battaglia, G.; Cipollina, A.; Vicari, F.; Tamburini, A.; Micale, G. Influence of Operational Strategies for the Recovery of Magnesium Hydroxide from Brines at a Pilot Scale. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 15355–15368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham Le, T.P.; Abuhatab, F.; Lai, Q.D.; Sgouridis, S.; AlSuwaidi, M.; Alhseinat, E. Fouling in Reverse Osmosis Desalination: Emphasis on Composite Fouling and Coprecipitation. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2025, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.M.; Yeon, K.M.; Park, C.H. Silica Treatment Technologies in Reverse Osmosis for Industrial Desalination: A Review. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 25, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furcas, F.E.; Mundra, S.; Lothenbach, B.; Angst, U.M. Speciation Controls the Kinetics of Iron Hydroxide Precipitation and Transformation at Alkaline PH. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 19851–19860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algurainy, Y.; Call, D.F. Asymmetrical Removal of Sodium and Chloride in Flow-through Capacitive Deionization. Water Res. 2020, 183, 116044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, N.A.; O’Reilly, T.; Sanciolo, P.; Ostarcevic, E.; Beighton, M.; Taylor, K.; Mullett, M.; Tarquin, A.J.; Gray, S.R. Chemistry of Silica Scale Mitigation for RO Desalination with Particular Reference to Remote Operations. Water Res. 2014, 65, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.; Zhao, S.; Boo, C.; Hashmi, S.M.; Elimelech, M. Relating Silica Scaling in Reverse Osmosis to Membrane Surface Properties. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4396–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algurainy, Y.; Call, D.F. Improving Long-Term Anode Stability in Capacitive Deionization Using Asymmetric Electrode Mass Ratios. ACS ES T Eng. 2022, 2, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, S.; Dong, Y.; Wang, J.; Nie, Y. Removal of Hardness and Silicon by Precipitation from Reverse Osmosis Influent: Process Optimization and Economic Analysis. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 55, 104147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshami, A.; Taylor, T.; Ismail, N.; Buelke, C.; Schultz, L. RO System Scaling with Focus on the Concentrate Line: Current Challenges and Potential Solutions. Desalination 2021, 520, 115370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; You, S.; Wang, X. Forward Osmosis Coupled with Lime-Soda Ash Softening for Volume Minimization of Reverse Osmosis Concentrate and CaCO3 Recovery: A Case Study on the Coal Chemical Industry. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2021, 15, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangal, M.N.; Salinas-Rodriguez, S.G.; Dusseldorp, J.; Blankert, B.; Yangali-Quintanilla, V.A.; Kemperman, A.J.B.; Schippers, J.C.; van der Meer, W.G.J.; Kennedy, M.D. Foulant Identification and Performance Evaluation of Antiscalants in Increasing the Recovery of a Reverse Osmosis System Treating Anaerobic Groundwater. Membranes 2022, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Zhao, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J. Reverse Osmosis Membranes with Sulfonate and Phosphate Groups Having Excellent Anti- Scaling and Anti-Fouling Properties. Desalination 2021, 509, 115076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangal, M.N.; Salinas-Rodriguez, S.G.; Dusseldorp, J.; Kemperman, A.J.B.; Schippers, J.C.; Kennedy, M.D.; van der Meer, W.G.J. Effectiveness of Antiscalants in Preventing Calcium Phosphate Scaling in Reverse Osmosis Applications. J. Memb. Sci. 2021, 623, 119090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitaraman, H.; Battiato, I. Impact of Large-Scale Effects on Mass Transfer and Concentration Polarization in Reverse Osmosis Membrane Systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 303, 122121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Clavijo, N.; Cespedes, S.; Farinha, A.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Picioreanu, C.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Blankert, B. Optical Coherence Tomography for Early Detection, Visualization and Characterization of Growth and Deposition-Driven Scaling in Reverse Osmosis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 378, 134664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, L.; Takizawa, S.; Yang, Y. Insights into Dynamic Evolution of Combined Scaling-Biofouling in Reverse Osmosis. J. Memb. Sci. 2024, 692, 122295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Han, J.; Ao, N.; Ya, R.; Ding, W. Scaling and Cleaning of Silica Scales on Reverse Osmosis Membrane: Effective Removal and Degradation Mechanisms Utilizing Gallic Acid. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangal, M.N.; Yangali-Quintanilla, V.A.; Salinas-Rodriguez, S.G.; Dusseldorp, J.; Blankert, B.; Kemperman, A.J.B.; Schippers, J.C.; Kennedy, M.D.; van der Meer, W.G.J. Application of a Smart Dosing Pump Algorithm in Identifying Real-Time Optimum Dose of Antiscalant in Reverse Osmosis Systems. J. Memb. Sci. 2022, 658, 120717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.Z.J.; Shafeeq, A.; Sajjad, M.; Hassan, S.; Aslam, M.S.; Saeed, T.; Walsh, F.C. Benchmarking of Scaling and Fouling of Reverse Osmosis Membranes in a Power Generation Plant of Paper and Board Mill: An Industrial Case of a Paper and Board Mill Study. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 2511–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, E.M.V.; Weigand, T.M.; Edalat, A. Reverse Osmosis Membrane Biofouling: Causes, Consequences and Countermeasures. npj Clean Water 2022, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Davies, P.A. Comparison of Configurations for High-Recovery Inland Desalination Systems. Water 2012, 4, 690–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environment, Water and Agriculture of Saudi Arabia. Saudi Standards for Unbottled Drinking Water; Ministry of Environment, Water and Agriculture of Saudi Arabia: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2024.
- Dawoud, M.A.; Sallam, G.R.; Abdelrahman, M.A.; Emam, M. The Performance and Feasibility of Solar-Powered Desalination for Brackish Groundwater in Egypt. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). National Primary Drinking Water Regulations. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ground-water-and-drinking-water/national-primary-drinking-water-regulations (accessed on 17 July 2025).
- Zeggar, H.; Addar, F.Z.; El-Ghzizel, S.; Kitanou, S.; Tahaikt, M.; Taky, M.; Elmidaoui, A. Nitrate Removal by Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis: Comparison and Modeling. Desalination Water Treat. 2023, 316, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoinkis, J.; Valero-Freitag, S.; Caporgno, M.P.; Pätzold, C. Removal of Nitrate and Fluoride by Nanofiltration—A Comparative Study. Desalination Water Treat. 2011, 30, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naggar, A.H.; Bakr, A.S.A. Pretreatment for Brackish Water Reverse Osmosis of Desalination Plants by Dual-Media Filter. Egypt J. Chem. 2024, 67, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.; Al-Obaidi, M.A.; Hadadian, Z.; Moradi, M.; Haghighi, A.; Mujtaba, I.M. Performance Evaluation of a Brackish Water Reverse Osmosis Pilot-Plant Desalination Process under Different Operating Conditions: Experimental Study. Clean Eng. Technol. 2021, 4, 100134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, J.; Shirazi, S. Cost of Brackish Groundwater Desalination in Texas; Texas Water Development Board: Austin, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Amusat, O.O.; Atia, A.A.; Dudchenko, A.V.; Bartholomew, T.V. Modeling Framework for Cost Optimization of Process-Scale Desalination Systems with Mineral Scaling and Precipitation. ACS ES T Eng. 2024, 4, 1028–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouhi, A.; Almohammadi, K.M. Towards Green Desalination: A Multi-Site Analysis of Hybrid Renewable Energy Integration in Saudi Arabian RO Plants. Desalination 2024, 592, 118087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-García, A.; Feo-García, J. Antiscalant Cost and Maximum Water Recovery in Reverse Osmosis for Different Inorganic Composition of Groundwater. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 73, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feo-García, J.; Pulido-Alonso, A.; Florido-Betancor, A.; Florido-Suárez, N.R. Cost Studies of Reverse Osmosis Desalination Plants in the Range of 23,000–33,000 m3/Day. Water 2024, 16, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesarakloo, V.; Hassani, A.H.; Alipour, V.; Javid, A.H. Technical and Economic of Various Pretreatment Methods for Desalination of Seawater Using Reverse Osmosis. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 8519–8534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P. A Comprehensive Review of Saline Effluent Disposal and Treatment: Conventional Practices, Emerging Technologies, and Future Potential. J. Water Reuse Desalination 2021, 11, 33–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olufisayo, O.E.; Olanrewaju, O. A Review of Renewable Energy Powered Seawater Desalination Treatment Process for Zero Waste. Water 2024, 16, 2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.K. Sustainable Water Management through Integrated Technologies and Circular Resource Recovery. Environ. Sci. 2025, 11, 1822–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.; Zaneldin, E.K.; Al-Marzouqi, A.H.; Ahmed, W.K. A Review of Reject Brine Disposal, Management, and Construction Applications. Buildings 2025, 15, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saidi, M.; Saadaoui, I.; Ben-Hamadou, R. Governing Desalination, Managing the Brine: A Review and Systematization of Regulatory and Socio-Technical Issues. Water Resour. Ind. 2023, 30, 100225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, M.N.; Guen, F.Z.; Ahmed, S.A.; Saleem, H.; Zaidi, S.J. Environmental Impact Assessment of Desalination Plants in the Gulf Region. In Water-Energy-Nexus in the Ecological Transition: Natural-Based Solutions, Advanced Technologies and Best Practices for Environmental Sustainability; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 173–177. [Google Scholar]
- Al Kubaish, A.; Salama, J. Impacts of Climate Change on Seawater Temperature and Total Dissolved Solids: Challenges and Sustainable Solutions for Reverse Osmosis Desalination in the Arabian Gulf Region. Comput. Water Energy Environ. Eng. 2024, 13, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos-Escalera, A.; Pous, N.; Balaguer, M.D.; Puig, S. Electrochemical Water Softening as Pretreatment for Nitrate Electro Bioremediation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | Old | New |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 9.94 ± 0.25 | 8.08 ± 0.59 |
| TOT hardness (mg/L as CaCO3) | 371.86 ± 9.75 | 821.56 ± 23.49 |
| Ca hardness (mg/L as CaCO3) | 202.46 ± 9.07 | 563.18 ± 19.09 |
| Mg hardness (mg/L as CaCO3) | 168.73 ± 7.25 | 213.56 ± 9.51 |
| Silica (mg/L) | 17.06 ± 2.30 | 37.23 ± 4.85 |
| Iron (mg/L) | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.18 ± 0.00 |
| Alkalinity (mg/L as CaCO3) | 43.86 ± 4.47 | 70.06 ± 14.31 |
| Parameter | Old | New |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.34 ± 0.26 | 6.99 ± 0.25 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 1919.16 ± 21.99 | 1810.31 ± 31.07 |
| TOT hardness (mg/L as CaCO3) | 363.97 ± 29.19 | 818.93 ± 11.55 |
| Ca hardness (mg/L as CaCO3) | 186.69 ± 14.66 | 562.17 ± 8.60 |
| Mg hardness (mg/L as CaCO3) | 162.16 ± 5.79 | 256.83 ± 12.99 |
| Silica (mg/L) | 15.94 ± 2.56 | 36.46 ± 5.31 |
| Iron (mg/L) | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.04 ± 0.00 |
| Alkalinity (mg/L as CaCO3) | 37.72 ± 4.19 | 68.09 ± 4.87 |
| Parameter | Old | New |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.07 ± 0.35 | 7.21 ± 0.11 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 79.83 ± 4.48 | 162.25 ± 17.36 |
| TOT hardness (mg/L as CaCO3) | 37.56 ± 2.07 | 80.43 ± 5.79 |
| Ca hardness (mg/L as CaCO3) | 21.93 ± 1.64 | 45.93 ± 1.68 |
| Mg hardness (mg/L as CaCO3) | 17.67± 2.07 | 29.07 ± 4.99 |
| Alkalinity (mg/L as CaCO3) | 26.38 ± 4.07 | 32.42 ± 2.59 |
| Chlorine (mg/L) | 0.29 ± 0.02 | 0.31 ± 0.03 |
| Parameter | Concentration | SSUDW [57] |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.18 ± 0.09 | 6.5–8.5 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 978.27 ± 9.26 | 1000 |
| Conductivity (μS/cm) | 1387.33 ± 8.57 | 1500 |
| Free chlorine residual (mg/L) | 0.15 ± 0.00 | 0.5 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 1.05 ± 0.08 | 5 |
| Total hardness (mg/L as CaCO3) | 447.66 ± 6.07 | 320 |
| Ca hardness (mg/L as CaCO3) | 280.33 ± 3.56 | >30 |
| Mg hardness (mg/L as CaCO3) | 168.16 ± 10.38 | Not regulated |
| Alkalinity (mg/L as CaCO3) | 86.86 ± 2.60 | Not regulated |
| Chloride (mg/L) | 220.6 ± 12.50 | 250 |
| Sulfate (mg/L) | 210.67 ± 8.11 | 250 |
| Ammonia (mg/L) | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 0.5 |
| Nitrite (mg/L as N) | 0.007 ± 0.00 | 3 |
| Nitrate (mg/L as N) | 5.72 ± 0.08 | 50 |
| Iron (mg/L) | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Algurainy, Y.; Refaat, A.; Alrehaili, O. Developing Insights into Pretreatment Optimization: Effects of Eliminating Lime and Soda Ash in Groundwater RO Desalination. Water 2025, 17, 3186. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223186
Algurainy Y, Refaat A, Alrehaili O. Developing Insights into Pretreatment Optimization: Effects of Eliminating Lime and Soda Ash in Groundwater RO Desalination. Water. 2025; 17(22):3186. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223186
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlgurainy, Yazeed, Ashraf Refaat, and Omar Alrehaili. 2025. "Developing Insights into Pretreatment Optimization: Effects of Eliminating Lime and Soda Ash in Groundwater RO Desalination" Water 17, no. 22: 3186. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223186
APA StyleAlgurainy, Y., Refaat, A., & Alrehaili, O. (2025). Developing Insights into Pretreatment Optimization: Effects of Eliminating Lime and Soda Ash in Groundwater RO Desalination. Water, 17(22), 3186. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223186






