Identifying Variations in Ecosystem Health of Wetlands in the Western Songnen Plain (2000–2020)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
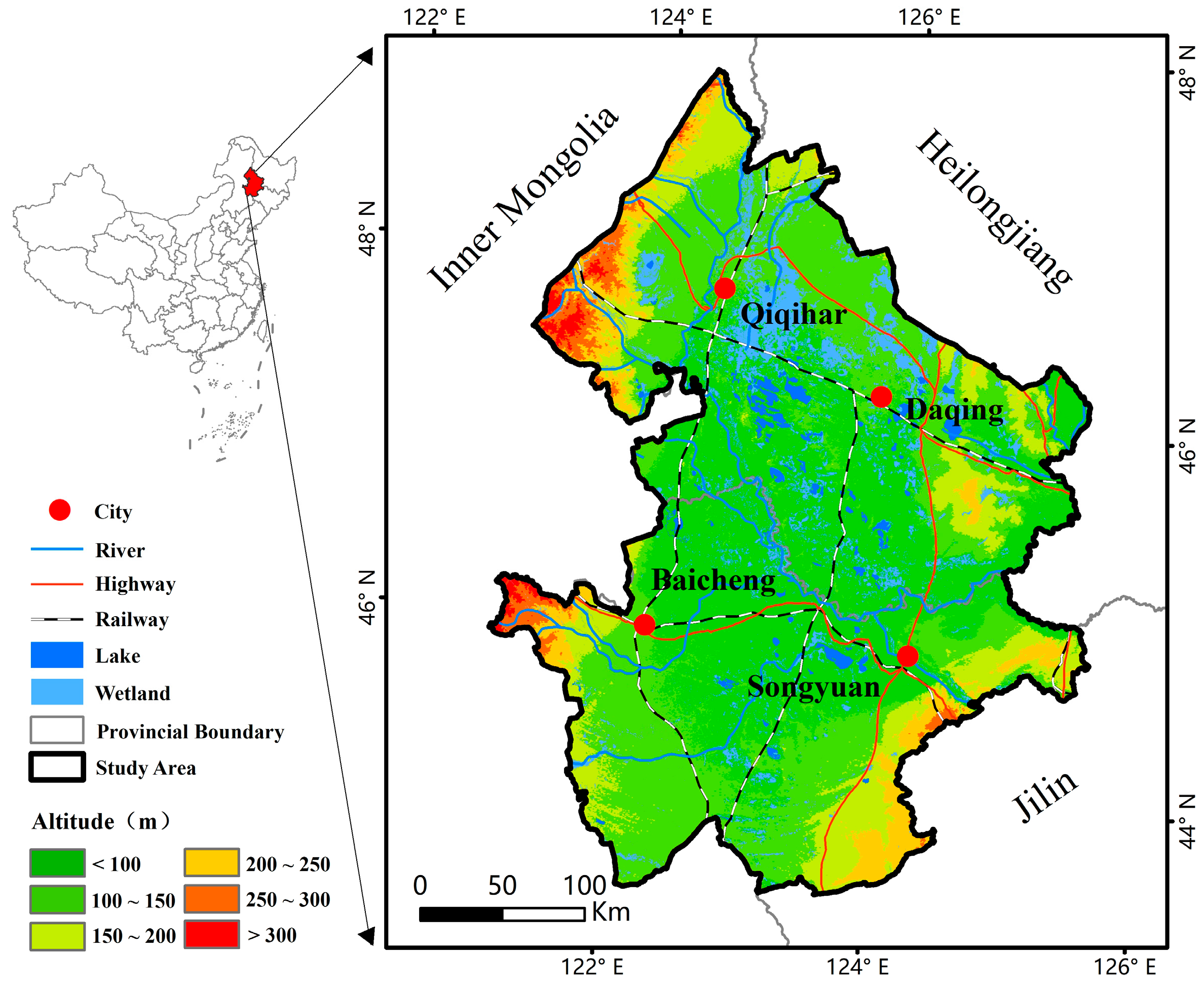
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Remote Sensing Data
2.2.1. Wetland Distribution Dataset
2.2.2. MODIS Products
2.2.3. Other Data
2.3. Assessment Method
2.3.1. Selection of Assessment Indictors
2.3.2. Weight Calculation of Assessment Indicators
2.3.3. Grading Ecosystem Health of Wetlands
3. Results
3.1. Ecological Variations in Wetlands from 2000 to 2020
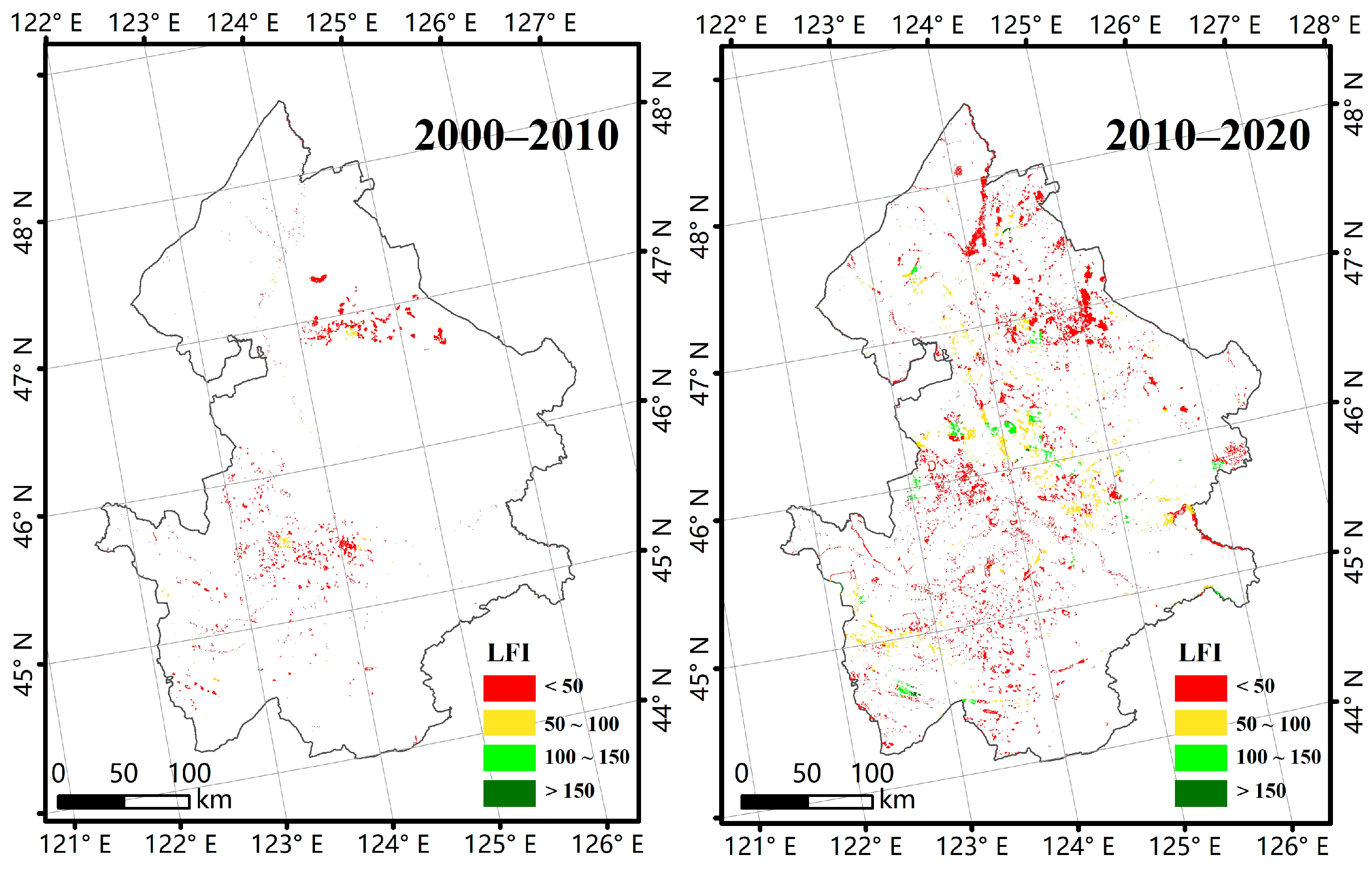
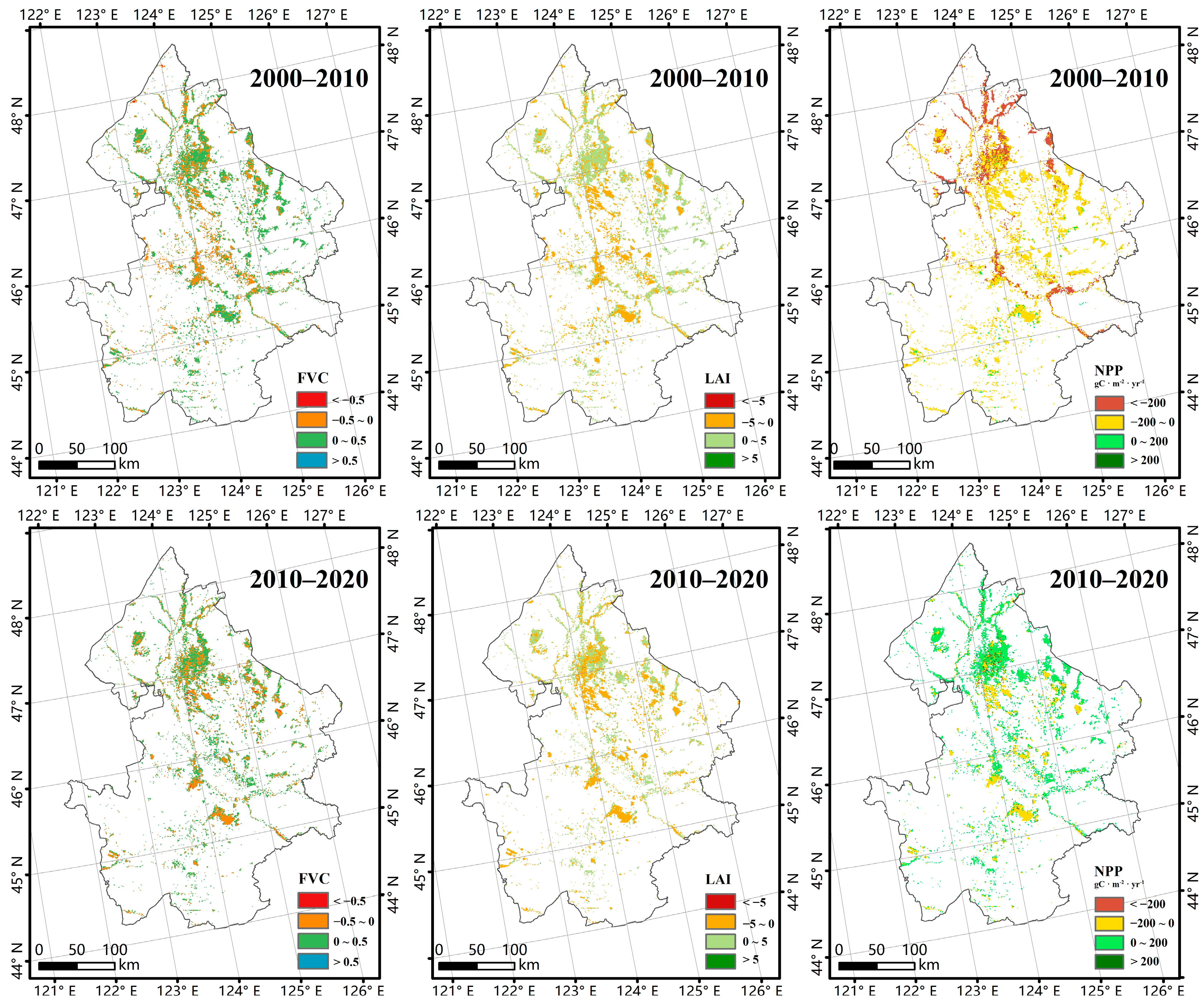
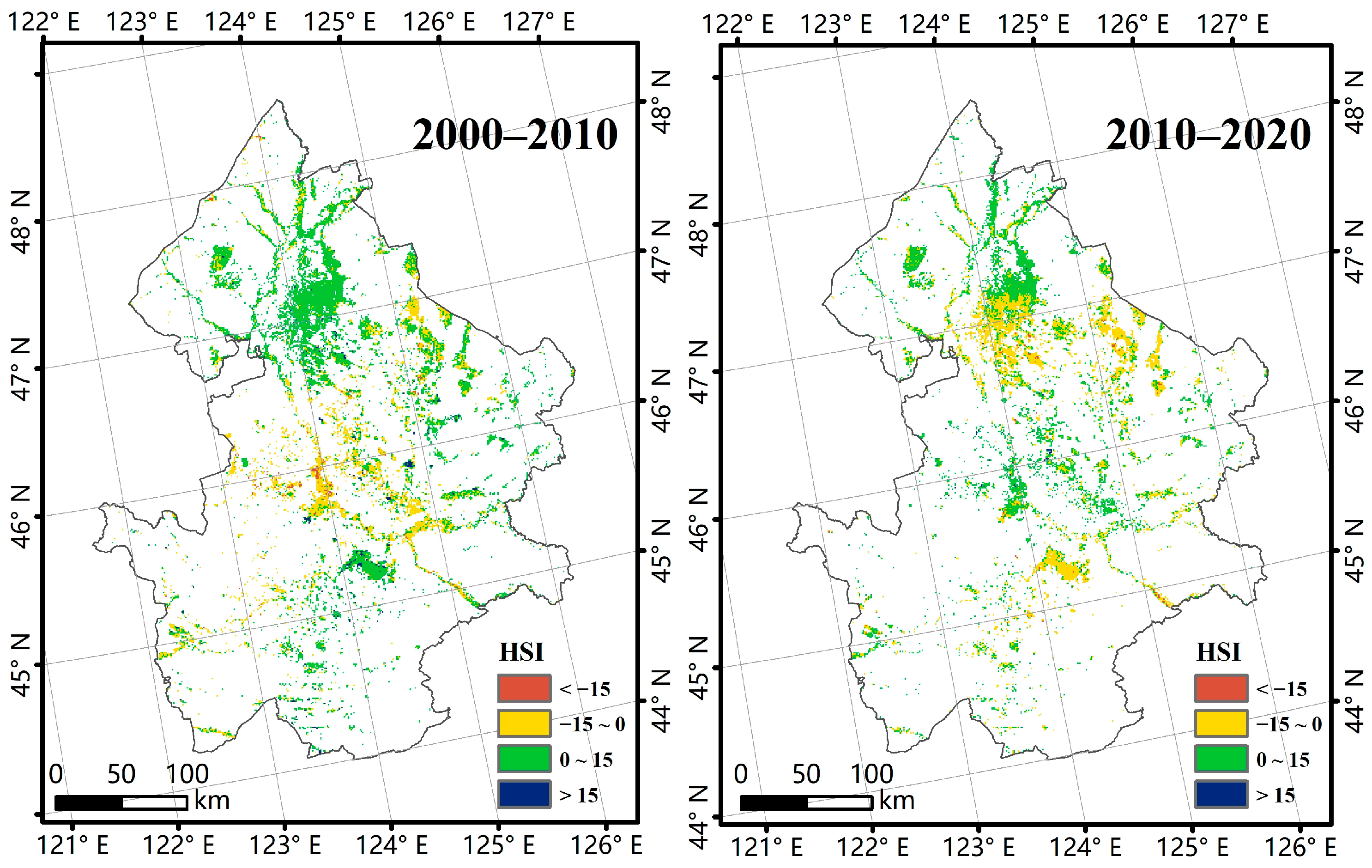
3.2. Spatiotemporal Changes in Wetland Ecosystem Health
3.3. Variations in Wetland Ecosystem Health Among the Ramsar Sites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, W.; Fan, X.; Ma, J.; Pimm, S.L.; Kong, L.; Zeng, Y.; Li, X.; Xiao, Y.; Zheng, H.; Liu, J.; et al. Hidden loss of wetlands in China. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 3065–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, P.E.R.; Connelly, R. Wetlands and human health: An overview. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 20, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsar Convention on Wetlands (RCW). Global Wetland Outlook: State of the World’s Wetlands and Their Services to People; Ramsar Convention Secretariat: Gland, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdianpari, M.; Granger, J.E.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Salehi, B.; Brisco, B.; Homayouni, S.; Gill, E.; Huberty, B.; Lang, M. Meta-analysis of wetland classification using remote sensing: A systematic review of a 40-year trend in North America. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Guo, Z.; Jiang, B.; Lu, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Cui, L. Improving wetland ecosystem health in China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Luo, J.; Xu, Y.; Xin, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Bai, S.; Duan, H. Estimation models for pixel-scale coverage of aquatic vegetation in lakes based on Landsat and Sentinel data. J. Remote Sens. 2025, 5, 0616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.K.; Jha, P.; Joy, M.S.; Bansal, T. Ecosystem health assessment of East Kolkata Wetlands, India: Implications for environmental sustainability. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 366, 121809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, J.C.; Baldwin, J.D.; Bass, O.L.; Browder, J.A.; Cook, M.I.; Frederick, P.C.; Frezza, P.E.; Galvez, R.A.; Hodgson, A.B.; Meyer, K.D.; et al. Waterbirds as indicators of ecosystem health in the coastal marine habitats of Southern Florida: 1. Selection and justification for a suite of indicator species. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 44, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, J.C.; Baldwin, J.D.; Bass, O.L.; Browder, J.A.; Cook, M.I.; Frederick, P.C.; Frezza, P.E.; Galvez, R.A.; Hodgson, A.B.; Meyer, K.D.; et al. Waterbirds as indicators of ecosystem health in the coastal marine habitats of Southern Florida: 2. Conceptual ecological models. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 44, 128–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Wu, H.; Guan, Q.; Lu, X. Aquatic invertebrate assemblages as potential indicators of restoration conditions in wetlands of Northeastern China. Restor. Ecol. 2021, 29, e13283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fentaw, G.; Mezgebu, A.; Wondie, A.; Getnet, B. Ecological health assessment of Ethiopian wetlands: Review and synthesis. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2022, 15, 100194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Pradhan, B.; Shit, P.K.; Alamri, A.M. Assessment of wetland ecosystem health using the Pressure-State-Response (PSR) model: A case study of Mursidabad district of West Bengal (India). Sustainability 2020, 12, 5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekumah, B.; Armah, F.A.; Afrifa, E.K.A.; Aheto, D.W.; Odoi, J.O.; Afitiri, A. Geospatial assessment of ecosystem health of coastal urban wetlands in Ghana. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2020, 193, 105226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Lin, W.; Chen, G.; Guo, P.; Zeng, Y. Wetland ecosystem health assessment through integrating remote sensing and inventory data with an assessment model for the Hangzhou Bay, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agboola, J.; Ndimele, P.E.; Odunuga, S.; Akanni, A.; Kosemani, B.; Ahove, M.A. Ecological health status of the Lagos wetland ecosystems: Implications for coastal risk reduction. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 183, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, M.; Pandey, A.; Gupta, P.K.; Yadav, B.; Patel, J.G. A novel framework for wetland health assessment using hydro-ecological indicators and landscape metrics. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2025, 11, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Yao, P.; Wang, W.; Yue, B.; Liu, G. Assessment of wetland ecosystem health in the Yangtze and Amazon River Basins. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-inf. 2017, 6, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, D.; Guo, X. Remote sensing of ecosystem health: Opportunities, challenges, and future perspectives. Sensors 2014, 14, 21117–21139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbach, S.; Hentschel, E.; Hentze, K.; Rienow, A.; Umulisa, V.; Zwart, S.J.; Nelson, A. Automatization and evaluation of a remote sensing-based indicator for wetland health assessment in East Africa on national and local scales. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 75, 102032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Sun, Y.; Chen, P.; Jia, M. Assessing the Ecosystem Health of Coastal Wetland Vegetation (Suaeda salsa) Using the pressure state response model, a case of the Liao River Estuary in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W. Dynamic identification and health assessment of wetlands in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River basin under changing environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 345, 131105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, W. Indicator system construction and health assessment of wetland ecosystem—Taking Hongze Lake Wetland, China as an example. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Du, B.; Yan, H.; Zhang, B. Remote sensing and GIS support to identify potential areas for wetland restoration from cropland: A case study in the west Songnen Plain, Northeast China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, Z.; Mao, D.; Li, L.; Liu, M.; Jia, M.; Man, W.; Lu, C. Remote observation in habitat suitability changes for waterbirds in the west Songnen Plain, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, M.; Yuan, W.; Luo, L.; Feng, K.; Wang, D.; Xiang, H.; Ren, Y.; et al. The trajectory of wetland change in China between 1980 and 2020: Hidden losses and restoration effects. Sci. Bull. 2025, 70, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.J.; Senarath, U.; Lee, A.; Zeppel, M.; Nightingale, J.M.; Williams, R.J.; McVicar, T.R. Assessment of the MODIS LAI product for Australian ecosystems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 101, 495–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.S.; Running, S.W. Drought-induced reduction in global terrestrial net primary production from 2000 through 2009. Science 2020, 329, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijiati, N.; Rusuli, Y.; Maimaitiaili, K.; Kuluwan, Y. Spatiotemporal variations and driving forces analysis of ecosystem health in the Bosten Lake wetland in China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2025, 36, 5035–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Lu, K.; Wang, X.; Sun, G.; Liang, Q.; Song, H.; Liu, S. Assessing the Landscape Ecological Health (LEH) of Wetlands: Research Content and Evaluation Methods (2000–2022). Water 2023, 15, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Dou, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, L.; Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Jia, Y.; Bakker, M.; et al. Examining health of wetlands with multiple ecosystem services as targets in China’s coastal region. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 600–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, X.; Tong, S.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, M.; Lu, X. Aboveground biomass of wetland vegetation under climate change in the western Songnen Plain. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 941689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Mao, D.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Xi, Y.; Feng, K. Aboveground biomass of marshes in Northeast China: Spatial pattern and annual changes responding to climate change. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 1043811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Tong, S.; Zhang, M.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, D.; Xing, X.; An, Y.; Cui, G.; Liu, G. Revealing the spatiotemporal dynamics and nonlinear interaction-driven mechanisms of wetland ecosystem health in Northeast China using interpretable machine learning. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 178, 113878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Choi, C.Y.; Jia, M.; Jackson, M.V.; Fuller, R.A. Remote observations in China’s Ramsar sites: Wetland dynamics, anthropogenic threats, and implications for sustainable development goals. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 2021, 9849343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Wang, Z.; Mao, D.; Zhang, J.; Xi, Y.; Du, B.; Zhang, B. What did China’s national wetland conservation program achieve? Observations of changes in land cover and ecosystem services in the Sanjiang Plain. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 267, 110623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
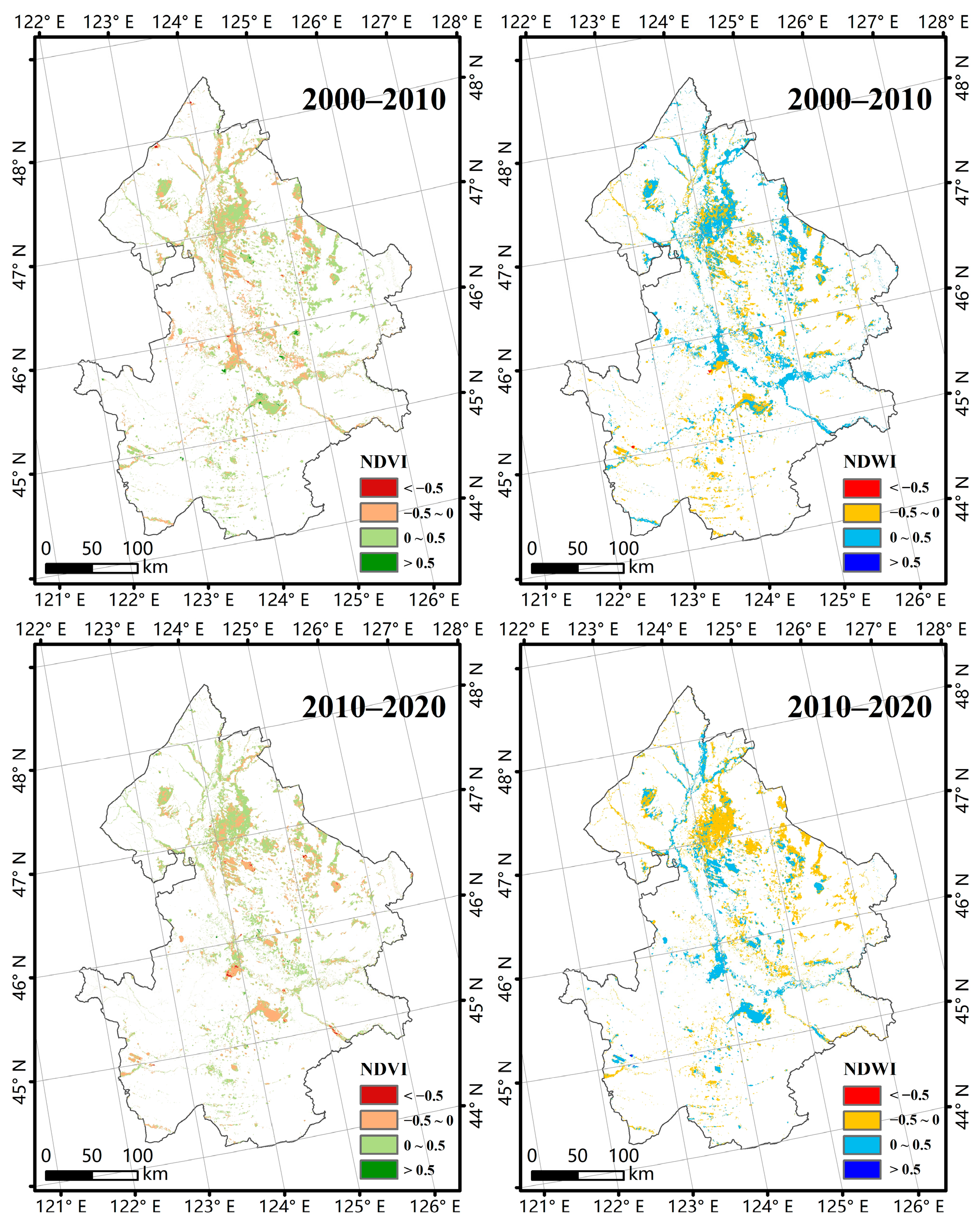
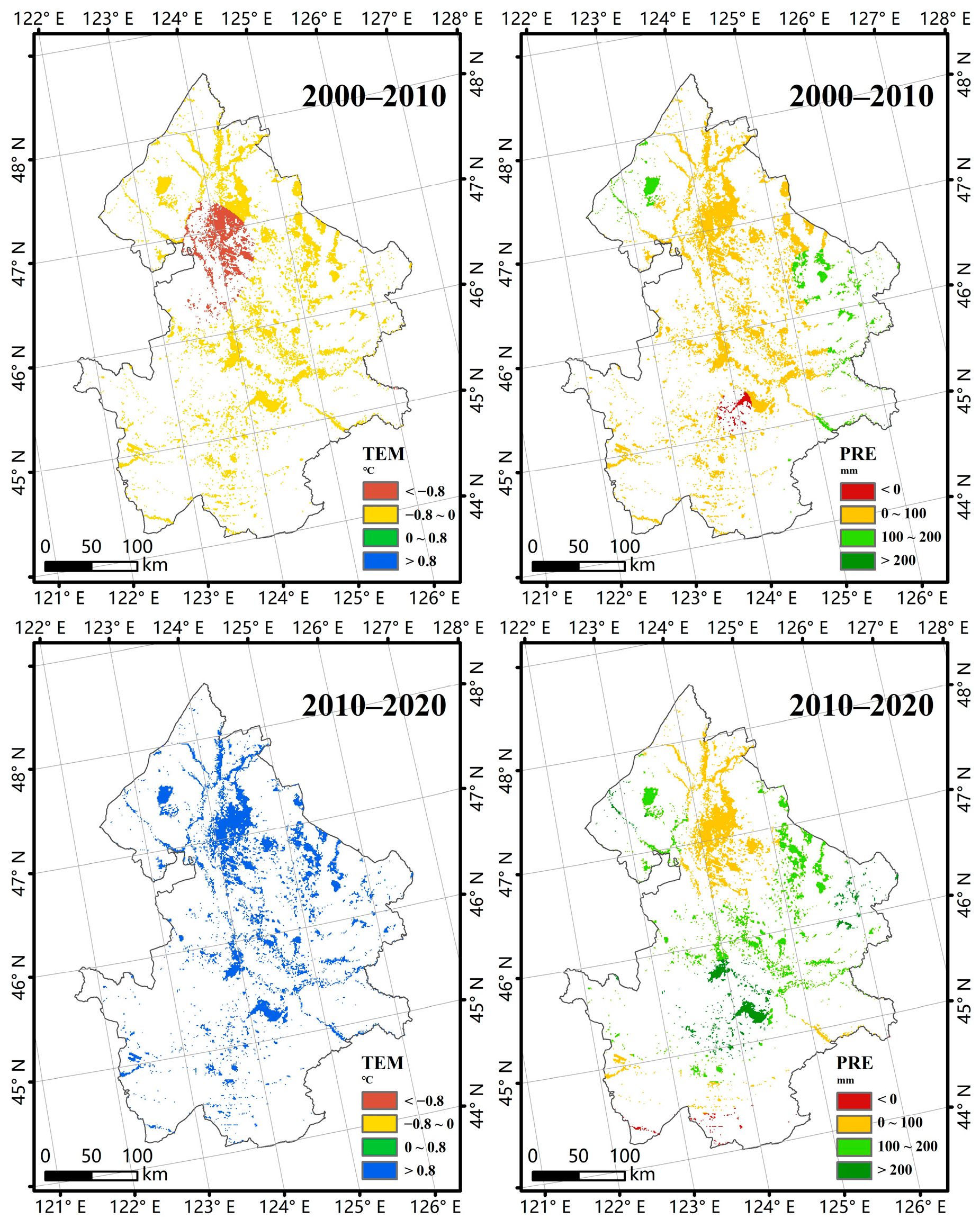

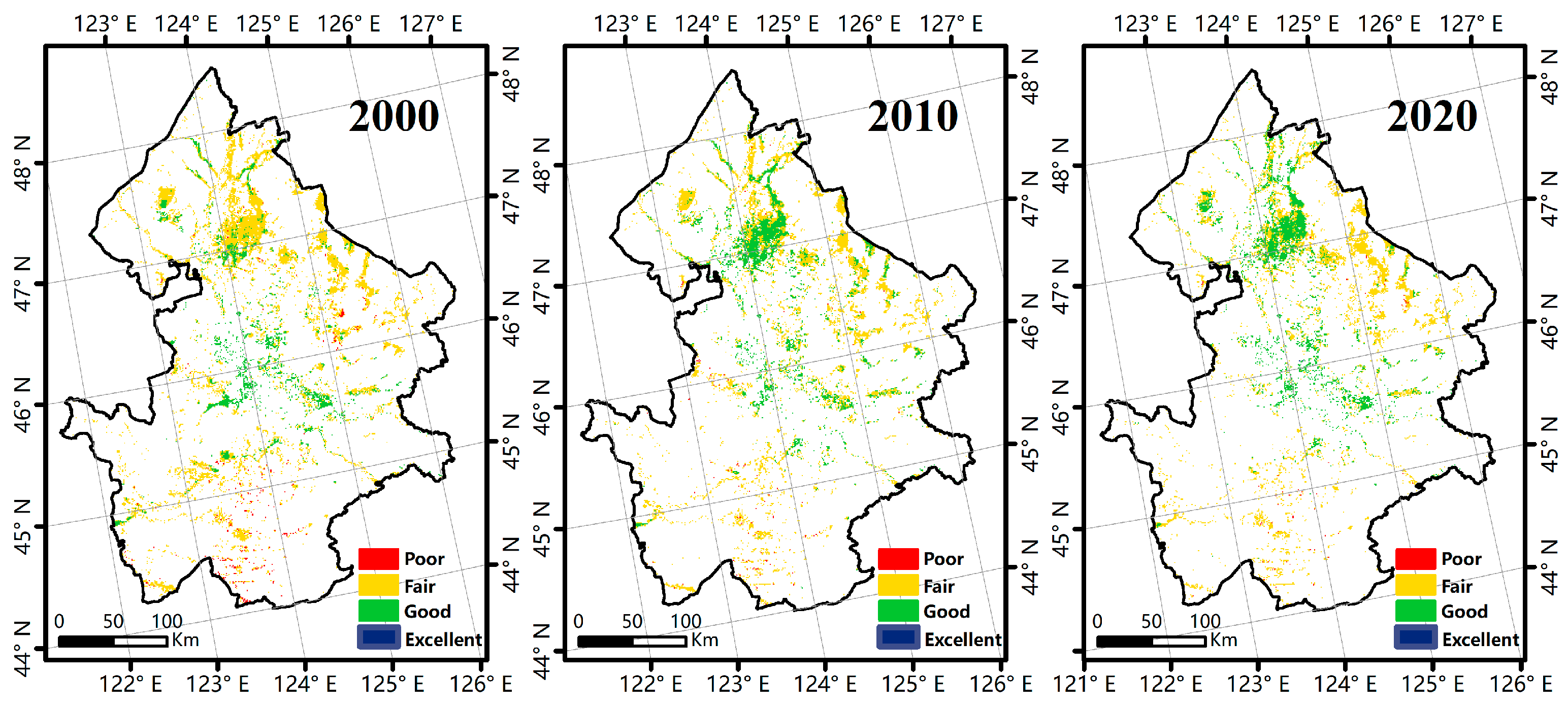
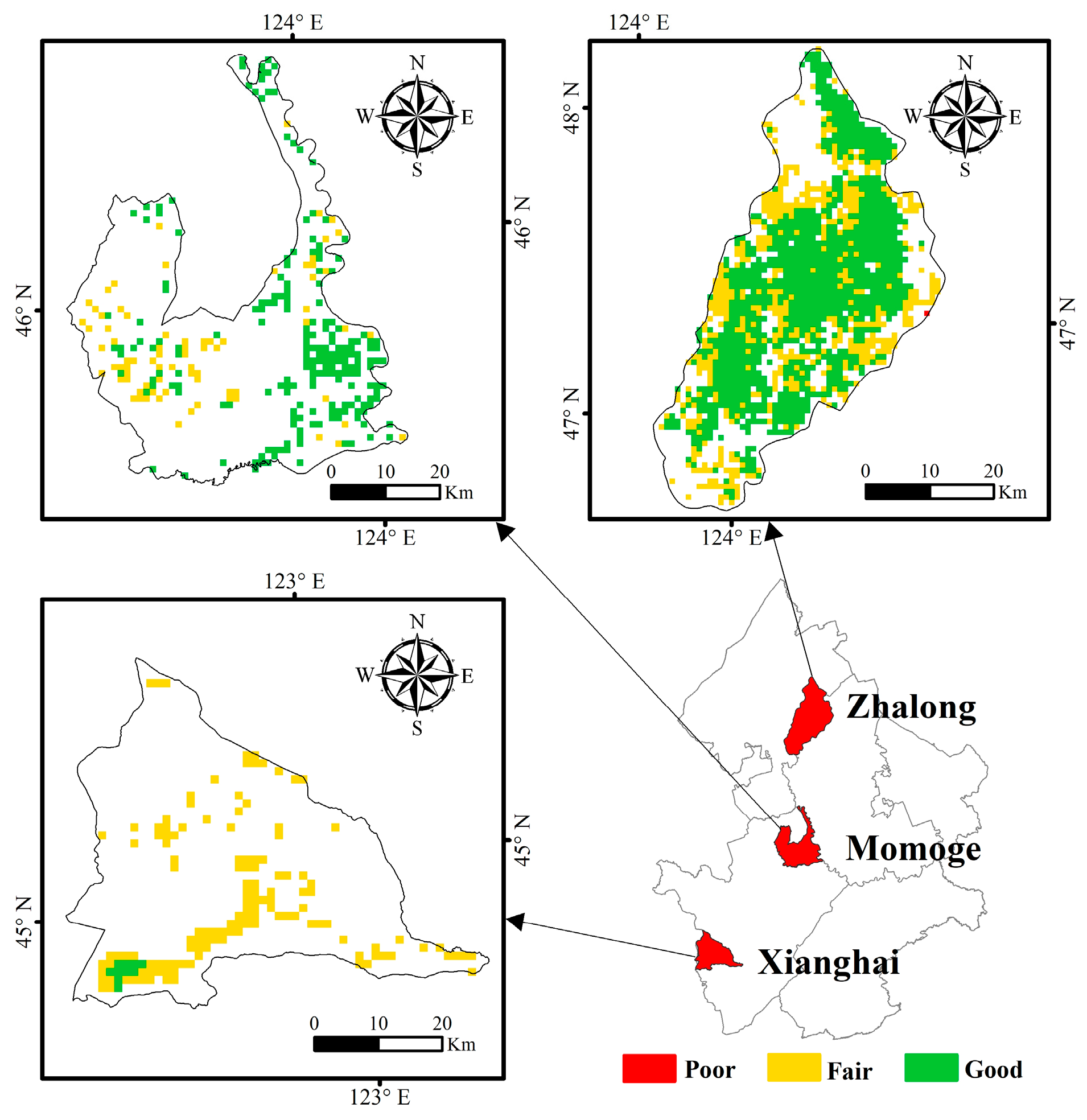
| Criterion Layer | Index Layer | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Ecosystem pattern | Landscape fragmentation index (LFI) | 0.2183 |
| Ecosystem quality | leaf area index (LAI) | 0.0574 |
| Fractional Vegetation Cover (FVC) | 0.0735 | |
| Net Primary Productivity (NPP) | 0.0501 | |
| Ecosystem service | Habitat Suitability Index (HSI) | 0.4946 |
| Normalized Differential Vegetation Index (NDVI) | 0.0225 | |
| Normalized Differential Water Index (NDWI) | 0.0961 | |
| Ecosystem threats | Population (POP) | 0.0477 |
| Gross Domestic Product (GDP) | 0.0272 | |
| Temperature (TEM) | 0.0125 | |
| Precipitation (PRE) | 0.0151 |
| Health Grade | WEHI Threshold | Health Status | Wetland Ecosystem Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | 0–0.25 | Poor | Irrational wetland ecosystem structure, lacking vitality, unable to provide basic ecosystem services. |
| II | 0.25–0.50 | Fair | Relatively disordered ecosystem structure, low system vitality, unstable ecosystem services, showing initial signs of wetland degradation. |
| III | 0.50–0.75 | Good | Complete ecosystem structure, strong ecosystem services, relatively good self-regulation capacity. |
| IV | 0.75–1 | Excellent | Rational ecosystem structure, high system vitality, strong ecosystem services, stable system with ecological sustainability. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z. Identifying Variations in Ecosystem Health of Wetlands in the Western Songnen Plain (2000–2020). Water 2025, 17, 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213175
Luo L, Wang X, Wang Z. Identifying Variations in Ecosystem Health of Wetlands in the Western Songnen Plain (2000–2020). Water. 2025; 17(21):3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213175
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Ling, Xi Wang, and Zongming Wang. 2025. "Identifying Variations in Ecosystem Health of Wetlands in the Western Songnen Plain (2000–2020)" Water 17, no. 21: 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213175
APA StyleLuo, L., Wang, X., & Wang, Z. (2025). Identifying Variations in Ecosystem Health of Wetlands in the Western Songnen Plain (2000–2020). Water, 17(21), 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213175







