Effects of Hydraulic Retention Time on the Performance and Microbial Communities of a High-Load Partial Nitrification Reactor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reactor
2.2. Inoculated Sludge and Wastewater Compositions
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Determination of Microbial Communities
2.5. High-Throughput Sequencing
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Start-Up Period
3.2. Effects of HRTs
3.3. PCR-DGGE
3.4. High-Throughput Sequencing Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Puigagut, J.; Salvadó, H.; García, J. Short-term harmful effects of ammonia nitrogen on activated sludge microfauna. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4397–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.J.R.D.; Lima, F.R.S.; Vale, D.A.D.; Sá, M.V.D.C.E. High levels of total ammonia nitrogen as NH4+ are stressful and harmful to the growth of Nile tilapia juveniles. Acta Sci. Biol. Sci. 2013, 35, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.S.; Qin, L.; Yan, D.H. Nutrient removal by hybrid subsurface flow constructed wetlands for high concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, L. Advanced nitrogen removal from municipal wastewater via two-stage partial nitrification-simultaneous anammox and denitrification (PN-SAD) process. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 304, 1230669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.-J.; Li, X.-Y.; Quan, X.-C.; Yang, Z.-F. Aerobic Sludge Granulation for Partial Nitrification of Ammonia-Rich Inorganic Wastewater. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2013, 12, 1375–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenen, J.G. Anammox bacteria: From discovery to application. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetten, M.S.M.; Wagner, M.; Fuerst, J.; van Loosdrecht, M.; Kuenen, G.; Strous, M. Microbiology and application of the anaerobic ammonium oxidation (‘ANAMMOX’) process. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2001, 12, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Yusof, N.; Yusoff, M.Z.M.; Hassan, M.A. Enrichment of anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) bacteria for short start-up of the anammox process: A review. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 13958–13978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, R.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, W. Application of the Anammox in China—A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Peng, Y.; Li, B.; Liang, H. Shortcut nitrification-denitrification by real-time control strategies. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2298–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Ju, K.; Chen, X.; Miao, R.; Wang, X.-D. Micro profiles of activated sludge aggregates using microelectrodes in completely autotrophic nitrogen removal over nitrite (CANON) reactor. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2016, 10, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joss, A.; Salzgeber, D.; Eugster, J.; König, R.; Rottermann, K.; Burger, S.; Fabijan, P.; Leumann, S.; Mohn, J.; Siegrist, H. Full-scale nitrogen removal from digester liquid with partial nitritation and anammox in one SBR. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5301–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu-Xia, S.; Ali, M.; Fan, F.; Chai, X.-L.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Tang, C.-J. Performance of a high-rate anammox reactor under high hydraulic loadings: Physicochemical properties, microbial structure and process kinetics. J. Cent. South Univ. 2020, 27, 1197–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Lackner, S.; Gilbert, E.M.; Vlaeminck, S.E.; Joss, A.; Horn, H.; van Loosdrecht, M.C. Full-scale partial nitritation/anammox experiences--an application survey. Water Res. 2014, 55, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, M.; Eldyasti, A. Development of partial nitrification as a first step of nitrite shunt process in a Sequential Batch Reactor (SBR) using Ammonium Oxidizing Bacteria (AOB) controlled by mixing regime. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Z.L.; Zhao, L.T.; Zhang, X.L.; Jin, C.; Guo, L.; Yang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, M. Partial nitrification and denitrification in a sequencing batch reactor treating high-salinity wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 288, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, W. Carbon sequestration pathway of inorganic carbon in partial nitrification sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 293, 122101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, W. Use of bamboo charcoal reduced the cultivated anammox seed sludge dosage during the start-up period. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 57, 20248–20253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenjie, Z.; Huaqin, W.; Joseph, D.R.; Yue, J. Granular activated carbon as nucleus for formation of anammox granules in an expanded granular-sludge-bed reactor. Glob. Nest J. 2015, 17, 508–514. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W. Treatment of high-strength rare-earth ammonia wastewater with a two-stage anaerobic ammonium oxidation (Anammox) process. Glob. Nest J. 2016, 18, 186–194. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, R.J.; Lemaire, R.; Yuan, Z.; Keller, J. Simultaneous nitrification, denitrification, and phosphorus removal in a lab-scale sequencing batch reactor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2010, 84, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthonisen, A.-C.; Loehr, R.C.; Prakasam, T.B.S. Inhibition of nitrification by free ammonia and nitrous acid. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1976, 48, 835–852. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Bae, W. Modeling kinetics of ammonium oxidation and nitrite oxidation under simultaneous inhibition by free ammonia and free nitrous acid. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huihao, W.; Guan, W.; Xiaoying, G.; Yifei, G.; Yue, J.; Chunfang, Z.; Wenjie, Z. Bibliometric analysis of wastewater treatment processes based on anaerobic ammonia oxidation process. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 319, 100418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, T.; Tokura, M.; Jojima, Y.; Hiraishi, A.; Yamanaka, S.; Fudou, R. Enrichment and Phylogenetic Analysis of Moderately Thermophilic Myxobacteria from Hot Springs in Japan. Microbes Environ. 2006, 21, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.L.; Kim, Y.J.; Hoang, V.A.; Subramaniyam, S.; Kang, J.-P.; Kang, C.H.; Yang, D.-C. Bacterial Diversity and Community Structure in Korean Ginseng Field Soil Are Shifted by Cultivation Time. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatayama, R.; Takahashi, R.; Ohshima, M.; Shibasaki, R.; Tokuyama, T. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from an ammonia-oxidizing bacterium, Nitrosomonas sp. K1: Purification and properties. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2000, 90, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, J.R.; Mareš, J.; Pietrasiak, N.; Bohunická, M.; Zima, J.; Štenclová, L.; Hauer, T. Highly divergent 16S rRNA sequences in ribosomal operons of Scytonema hyalinum (Cyanobacteria). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Niu, C.Y.; Lei, C.L.; Cui, J.-J.; Desneux, N. Use of an innovative T-tube maze assay and the proboscis extension response assay to assess sublethal effects of GM products and pesticides on learning capacity of the honey bee Apis mellifera L. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 1612–1619. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, J.M.; Badri, D.V.; Vivanco, J.M. Rhizosphere microbiome assemblage is affected by plant development. Int. Soc. Microb. Ecol. J. 2014, 8, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walke, J.B.; Becker, M.H.; Hughey, M.C.; Swartwout, M.C.; Jensen, R.V.; Belden, L.K. Most of the dominant members of amphibian skin bacterial communities can be readily cultured. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 6589–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Teramoto, M.; Harayama, S. An outbreak of nonflocculating catabolic populations caused the breakdown of a phenol-digesting activated-sludge process. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 2813–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, N.; Rohde, C.; Munk, C. Complete genome sequence of Truepera radiovictrix type strain (RQ-24T). Stand. Genom. Sci. 2011, 4, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.J.; Krieg, N.R.; Staley, J.T. Bergey’s Manual® of Systematic Bacteriology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, E.R. Thermomonas haemolytica gen. nov., sp. nov., a gamma-proteobacterium from kaolin slurry. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52 Pt 2, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; He, S.; Wu, C.; Du, D. Characteristics of heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification bacterium Acinetobacter sp. T1 and its application for pig farm wastewater treatment. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2018, 127, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, M.D.; Lund, B.M.; Farrow, J.A.E. Chemotaxonomic Study of an Alkalophilic Bacterium, Exiguobacterium aurantiacum gen. nov. sp. nov. Microbiology 1983, 129, 2037–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madigan, M.T.; Martinko, J.M. Brock Biology of Microorganisms; Pearson Education North Asia Ltd.: Hong Kong, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]

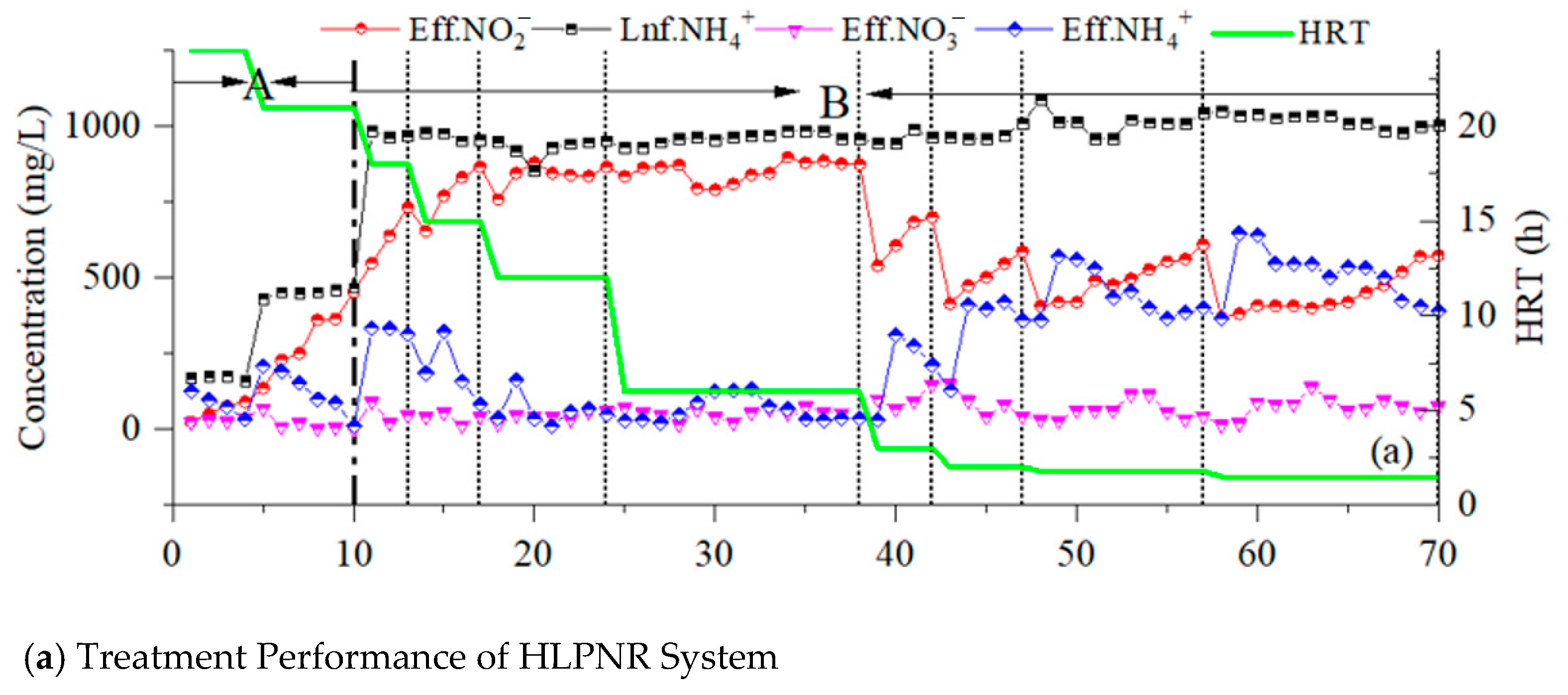
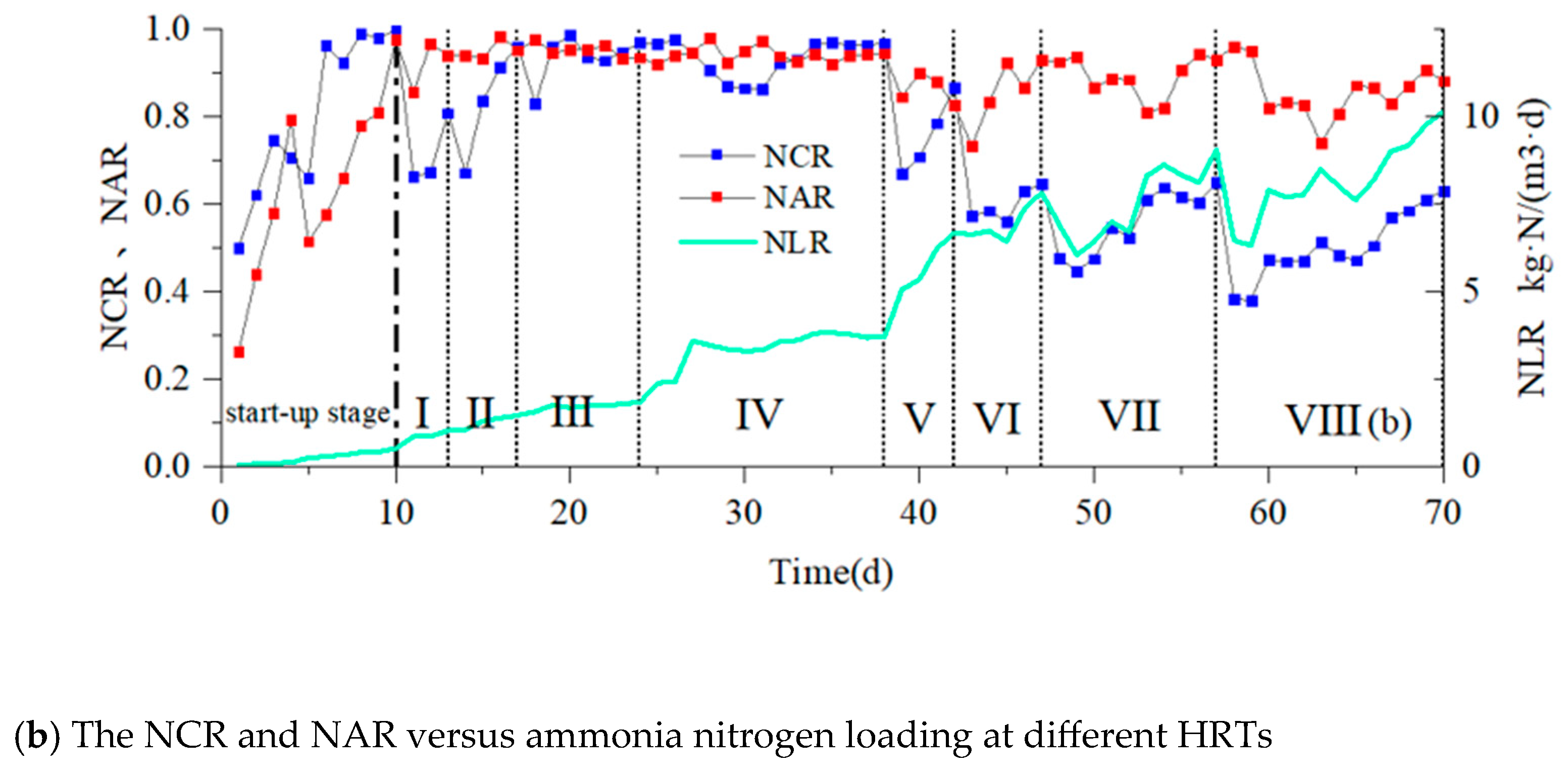



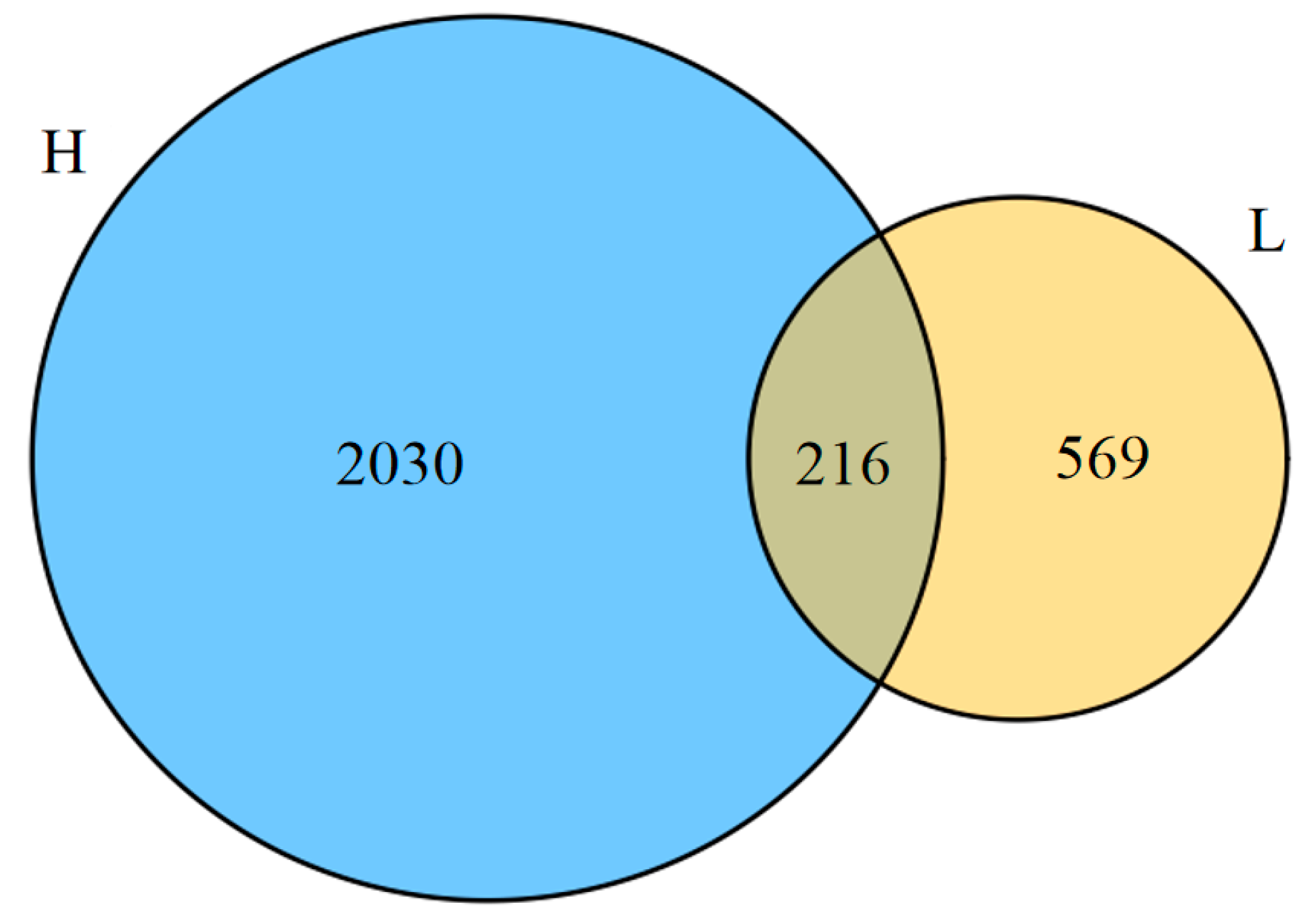
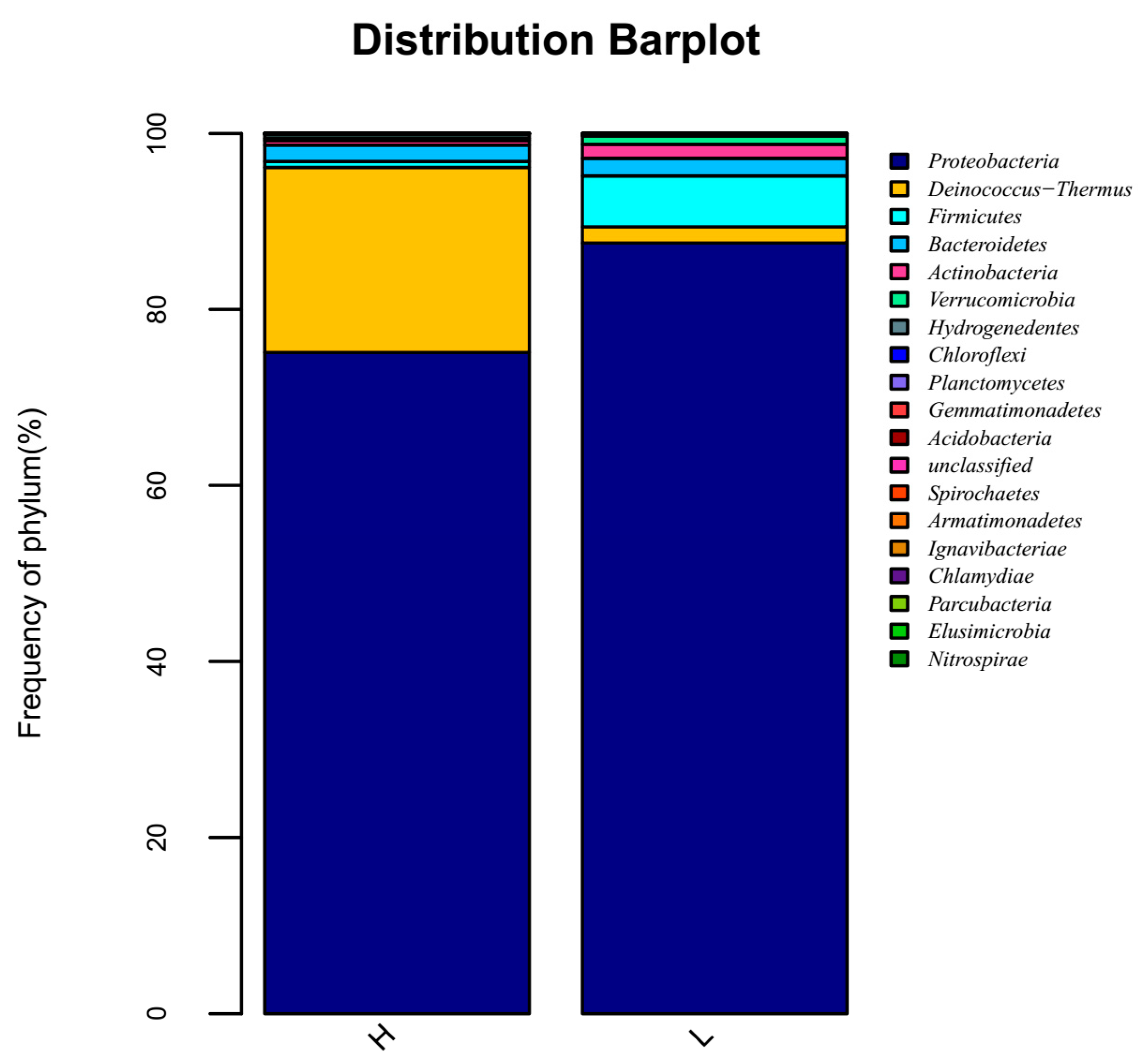

| Components (mg/L) | Start-Up Period | The Period of Continuous HRT Shortening | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stages I | Stages II | Stages I | Stages II | Stages III | Stages IV | Stages V | Stages VI | Stages VII | Stages VIII | |
| NH4HCO3 | 159~178 | 431~469 | 1000 | |||||||
| HRT (h) | 24 | 21 | 18 | 15 | 12 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 1.8 | 1.5 |
| Time (d) | 4 | 6 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 14 | 4 | 5 | 10 | 13 |
| KH2PO4 (mg/L) | 50 | |||||||||
| NaHCO3 (mg/L) | 1000 | |||||||||
| CaCl2·2H2O (mg/L) | 100 | |||||||||
| MgSO4·7H2O (mg/L) | 100 | |||||||||
| Primer | Sequences |
|---|---|
| 968F | AACGCGAAGAACCTTAC |
| GC-968F | CGCCCGGGGCGCGCCCCGGGCGGGGCGGGGGCACGGGGGGAACGCGAAGAACCTTAC |
| 1401R | CGGTGTGTACAAGACCC |
| Number | Similarity | Gene Bank Number | Bacterial Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100% | KF771448.1 | uncultured bacterium |
| 2 | 99% | JN366634.1 | bacterium enrichment culture clone 3_83 |
| 3 | 98% | AB246772.1 | myxobacterium AT3-01 |
| 4 | 89% | AB245340.1 | Myxococcales bacterium Gsoil 473 |
| 5 | 100% | KY365505.1 | Brasilonema sp. CR6-5A G1 |
| 6 | 98% | AF353155.1 | Nitrosomonas sp. |
| 7 | 96% | AB021341.1 | bacterium rM6 |
| 8 | 99% | KC238409.1 | uncultured bacterium |
| 9 | 89% | AB245340.1 | Myxococcales bacterium Gsoil 473 |
| 10 | 99% | MF689018.1 | Curvibacter sp. |
| 11 | 99% | KM187617.1 | Limnohabitans sp. PRE28D2 |
| 12 | 94% | LT221244.1 | Paracoccus alkenifer |
| 13 | 99% | KX815269.1 | Curvibacter lanceolatus |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; He, S.; Li, H.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W. Effects of Hydraulic Retention Time on the Performance and Microbial Communities of a High-Load Partial Nitrification Reactor. Water 2025, 17, 3130. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213130
Liu Y, He S, Li H, Jin Y, Zhang C, Zhang W. Effects of Hydraulic Retention Time on the Performance and Microbial Communities of a High-Load Partial Nitrification Reactor. Water. 2025; 17(21):3130. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213130
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yuhan, Shuyan He, Hangyi Li, Yue Jin, Chunfang Zhang, and Wenjie Zhang. 2025. "Effects of Hydraulic Retention Time on the Performance and Microbial Communities of a High-Load Partial Nitrification Reactor" Water 17, no. 21: 3130. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213130
APA StyleLiu, Y., He, S., Li, H., Jin, Y., Zhang, C., & Zhang, W. (2025). Effects of Hydraulic Retention Time on the Performance and Microbial Communities of a High-Load Partial Nitrification Reactor. Water, 17(21), 3130. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17213130








