Abstract
The degradation of Brilliant Coomassie Blue G-250 (BCB) was investigated using the thermally activated persulfate (TAP) process in deionized water. A kinetic model incorporating both hydroxyl (●OH) and sulfate (SO4●–) radicals was developed to predict pseudo-first-order rate constants (kₒ) for the interaction of BCB with these radicals. Experimental results demonstrated efficient BCB degradation under TAP treatment. A parametric study examining the effects of initial conditions such as solution pH, persulfate concentration, initial BCB concentration, and temperature revealed that higher persulfate dosages, lower BCB concentrations, and alkaline pH enhanced degradation performance. Complete removal of BCB was achieved within 20 min under optimal conditions ([BCB]0 = 10 mg/L, [PS]0 = 2 mg/L, neutral pH). The kinetic model showed strong agreement with experimental data across a broad range of pH and persulfate concentrations. The rate constants for BCB reactions with ●OH and SO4●– were determined through simulation to be 4.731 × 109 M−1s−1 and 1.07 × 109 M−1s−1, respectively. The selectivity analysis results revealed that SO4●– radicals played a dominant role in the degradation process across the various initial persulfate concentration scenarios. The remaining degradation was attributed to the contribution of ●OH radicals. These findings are linked to the higher reactivity of BCB with SO4●– compared to ●OH. Overall, the results demonstrate that TAP process is an effective method for the removal of emerging contaminants such as BCB from water.
1. Introduction
Synthetic dyes are extensively used across a variety of industrial sectors including textiles, food processing, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals owing to their strong coloration and binding properties. Among these, Brilliant Coomassie Blue G-250 (BCB) is a particularly common reagent in protein assays for detection and quantification. However, residual BCB in aqueous effluents is of great concern because of its toxicity, chemical stability, and poor biodegradability, making it resistant to conventional wastewater treatments [1,2].
To address this, advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) have gained considerable attention as viable technologies for degrading such recalcitrant organic pollutants. Typical AOPs include the Fenton and photo-Fenton processes, ozone oxidation, hydrogen peroxide oxidation, and radical-based oxidation schemes. In radical-based AOPs, reactive species (●OH, SO4●−, etc.) generated in situ attack and mineralize target pollutants [3]. A particularly promising variant is thermally activated persulfate (TAP), in which peroxydisulfate (S2O82−) is thermally decomposed to produce sulfate radicals (SO4●−); these species exhibit high redox potentials (E° ≈ 2.5–3.1 V) and can further transform into hydroxyl radicals (●OH) under aqueous conditions, enabling the degradation of a wide range of recalcitrant contaminants [4,5,6]. These radicals are potent oxidants capable of degrading and eventually mineralizing organic molecules [7]. Compared to hydrogen peroxide or ozone, persulfate systems often offer advantages in terms of longer shelf stability, lower risk of spontaneous decomposition, and cost-effective handling [8,9]. The efficiency of TAP is governed by operational parameters such as temperature, persulfate dosage, and matrix composition, while elevated temperatures accelerate radical generation, excessive heating may promote scavenging or undesired decomposition pathways, thereby reducing oxidant efficiency [4,5]. The presence of natural organic matter, inorganic ions, or soil solids can further attenuate radical availability, highlighting the need for site-specific treatability assessments [6]. Applications of TAP treatment range from in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) of soils and aquifers to the treatment of industrial effluents containing dyes, pharmaceuticals, or petroleum hydrocarbons [5,10]. Recent developments focus on photo-thermal hybrid activation, sustained-release persulfate formulations, and catalytic supports designed to lower the required temperature and enhance radical yield [10,11]. These advances illustrate the growing potential of TAP as a versatile and scalable technology for environmental remediation.
In a TAP system, the key radical generation pathways are typically represented by
These reactions (or analogous ones) are often used as a mechanistic basis in kinetic models (e.g., Table 1) [12,13,14].
In this study, we apply TAP to degrade aqueous BCB solutions by combining experimental trials and kinetic modeling. We systematically assess the influence of operational parameters (temperature, persulfate concentration, initial dye concentration, pH) on removal efficiency and kinetics. Concurrently, we propose a mechanistic model, grounded in experimental data, to elucidate the radical pathways involved and to assist in identifying optimal operating regimes.
Many recent studies confirm that TAP is effective in degrading various organic contaminants, including dyes, pharmaceuticals, and micropollutants [15,16]. For example, a comprehensive review by Arvaniti et al. [17] details how heat-activated persulfate performs under different conditions, and emphasizes the importance of matrix effects and hybrid activation strategies. More recent work has extended this to photo-thermal activation, coupling mild heating and light irradiation to further enhance radical yield and degradation rates. In particular, Habache et al. [18] demonstrated efficient TAP-based oxidation of the dye Basic Fuchsin under moderate temperatures. There is also growing interest in hybrid activation methods (e.g., thermal + ultrasound or thermal + catalysts) to improve efficiency and reduce energy costs [19].
In this study, a simulation approach has been adopted for the first time to simulate the reaction trend in TAP process. A reaction scheme consisting of 34 chemical reactions including a number of reactive radicals (SO4•–, ●OH, SO5●–, O●–, HO2●, O2●–, O3●–) and non-radical intermediates/products (HSO5−, OH−, HSO4−, H+, HO2−, O2, SO42−) has been developed for simulating the reaction system evolution in TAP treatment. The model has been validated over different conditions via degradation experiments conducted on BCB, which is selected as the target contaminant.
Accordingly, the objectives of the present work are (1) to investigate the kinetics of BCB degradation by TAP under controlled conditions; (2) to identify and quantify the radical species (SO4•−, •OH) contributing to dye removal; (3) to examine how temperature, persulfate dose, initial BCB concentration, and initial pH affect performance and reaction kinetics; and (4) to develop a mechanistic kinetic model that links experimental data to reaction pathways and that may guide scale-up or optimization.
Ultimately, our results aim to deepen the understanding of BCB removal via TAP and to support the design of efficient treatment processes for dye-contaminated waters.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Products
The reagents used in this study Brilliant Coomassie Blue G-250 (C47H48N3NaO7S2, MW: 854.02 g/mol), potassium persulfate (K2O8S2, MW: 270.32 g/mol), and sodium hydroxide (NaOH, MW: 40 g/mol) were provided by SIGMA-ALDRICH (St. Louis, MI, USA), and hydrochloride HCl (P: 36.5–38%), MW: 36.46 g/mol) was provided by Honeywell (International Inc., Charlotte, NC, USA).
In this study, all the solutions were prepared in distilled water.
2.2. Experimental Procedure
The degradation of Brilliant Coomassie Blue G-250 was carried out in a reactor equipped with a double stainless steel jacket, fitted with a glass cover. It includes a stirring system with speed display, consisting of a PTEF-coated stainless steel stirring shaft and a three-blade PTEF propeller. A glass measuring funnel with a liquid lifting device is also present. The reflux head and condenser are made of glass with a coil, and a glass condenser is used for distillation. The thermoregulating unit operates using a thermal fluid. The instrumentation includes a digital display thermometer, a needle vacuum gauge and a float flow meter as mentioned in Figure 1.
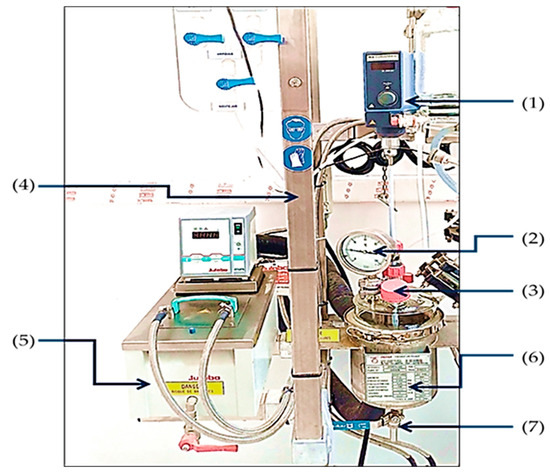
Figure 1.
Experimental equipment: (1) Agitator. (2) Thermometer. (3) Inlet of reactor. (4) Apparatus support. (5) Heating thermostat. (6) Reactor. (7) Outlet of reactor.
BCB and PS solutions were prepared by dissolving them in distilled water at the desired concentration. The degradation of BCB was carried out in a reactor by maintaining a constant volume of solution of 1000 mL. The temperature was monitored using a thermocouple. During degradation, the solution was stirred at a constant speed equals 250 rpm to ensure the homogeneity of the reaction system. Samples (3 mL) were collected using a syringe at well-defined time intervals to determine the dye concentration during the treatment process. The pH of the BCB solutions was adjusted by adding either sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or hydrochloric acid (HCl).
A Shimadzu UV-1800 UV–visible spectrophotometer (Shimadzu UV-1800, Kyoto, Japan) was used to record the spectral scans of BCB solutions, enabling identification of the maximum absorption wavelength of 584 nm in the UV–visible range.
3. Kinetic Model and Calculation Algorithm
COPASI is a powerful software package used to simulate and analyze biological, biochemical, and chemical systems. It allows the modeling of chemical reaction networks, complex biological processes, and more. COPASI offers functionalities such as modeling, simulation, optimization, and system analysis. It provides analysis tools to study system behavior, adjust model parameters to experimental data, and explore the system’s dynamic properties [20]. The kinetic modeling of the reaction network presented in Table 1 was conducted using the COPASI kinetic simulation software (version 4.27, Build 217, free license) [21]. Beyond its open-source accessibility, COPASI enables the resolution of complex reaction schemes—such as that of Table 1 or even more intricate systems—with the capability to optimize unknown rate constants through various advanced optimization algorithms, including genetic algorithms, evolutionary programming, and stochastic ranking evolutionary strategies (SRES), among others. COPASI has been previously employed to address similar reaction kinetic problems, such as the acetic acid degradation in the aqueous UV/persulfate process [22], persulfate conversion into sulfate and hydroxyl radicals via radiolysis [23], and the formation of iodate and iodo-trihalomethanes during chlorination of iodide-containing waters [24].

Table 1.
Reaction system for the degradation of the pollutant BCB by the TAP process.
Table 1.
Reaction system for the degradation of the pollutant BCB by the TAP process.
| Equation | Reaction | Kinetic Constant | Unit | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | (0.42−3.21) × 10−5 | (s−1) | Model | |
| 02 | ●OH + SO4●−⟶ HSO5− | 1 × 1010 | (M−1 s−1) | [25] |
| 03 | O●−+ H2O ⟷ ●OH + OH− | pKa = 11.9 k3 = 108 k −3 = 1.2 × 1010 | (M−1 s−1) | [26] |
| 04 | HSO5− + ●OH ⟶ SO5●− + H2O | 1.7 × 107 | (M−1 s−1) | [27] |
| 05 | HSO5− + SO4●−⟶ SO5●− + HSO4− | 1 × 106 | (M−1 s−1) | [25] |
| 06 | 2 * SO4●− ⟶ PS | 7 × 108 | (M−1 s−1) | [25] |
| 07 | H2O2 ⟶ 2 * ●OH | 1.16 × 10−5 | (M−1 s−1) | [28] |
| 08 | H2O ⟶ H+ + OH− | 1 × 10−3 | (s−1) | [29] |
| 09 | H+ + OH−⟶ H2O | 1 × 1011 | (M−1 s−1) | [29] |
| 10 | H2O2 ⟶ HO2− + H+ | 1.3 × 10−1 | (s−1) | [29] |
| 11 | HO2− + H+⟶ H2O2 | 5 × 1010 | (M−1 s−1) | [26] |
| 12 | HO2● ⟶ O2●− + H+ | 7 × 105 | (s−1) | [30] |
| 13 | O2●−+ H+⟶ HO2● | 5 × 1010 | (M−1 s−1) | [31] |
| 14 | HO2● + O2●−⟶ HO2− + O2 | 9.7 × 107 | (M−1 s−1) | [32] |
| 15 | 2 * HO2●⟶ H2O2 + O2 | 8.3 × 105 | (M−1 s−1) | [30] |
| 16 | ●OH + HO2● ⟶ H2O + O2 | 7.1 × 109 | (M−1 s−1) | [26] |
| 17 | ●OH + O2●− ⟶ OH− + O2 | 1 × 1010 | (M−1 s−1) | [26] |
| 18 | ●OH + H2O2 ⟶ HO2● + H2O | 2.7 × 107 | (M−1 s−1) | [26] |
| 19 | ●OH + HO2− ⟶H2O + O2●− | 7.5 × 109 | (M−1 s−1) | [31] |
| 20 | 2 * H2O2 ⟶ 2 * H2O + O2 | 2.3 × 10−2 | (M−1 s−1) | [33] |
| 21 | 2 * ●OH ⟶ H2O2 | 5 × 109 | (M−1 s−1) | [26] |
| 22 | ●OH + O●− ⟶ HO2− | 2 × 1010 | (M−1 s−1) | [33] |
| 23 | H2O2 + O●− ⟶ O2●−+ H2O | 5 × 108 | (M−1 s−1) | [26] |
| 24 | HO2− + O●− ⟶ O2●−+ OH− | 4 × 108 | (M−1 s−1) | [26] |
| 25 | O●− + O2 ⟶ O3●− | 3.6 × 109 | (M−1 s−1) | [26] |
| 26 | O●− + O2●− + H+⟶ OH− + O2 | 6 × 108 | (M−1 s−1) | [33] |
| 27 | 2 * SO5●− ⟶ 2 * SO4●− + O2 | 2.1 × 108 | (M−1 s−1) | [25] |
| 28 | PS + ●OH ⟶ S2O8●− + OH− | 1.2 × 107 | (M−1 s−1) | [25] |
| 29 | SO4●− + H2O ⟶ H+ + SO42− + ●OH | 660 | (s−1) | [34,35] |
| 30 | SO4●− + OH− ⟶ SO42− + ●OH | 7 × 107 | (M−1 s−1) | [34,35] |
| 31 | SO4●− + PS ⟶ SO42− + S2O8●− | 6.5 × 105 | (M−1 s−1) | [36] |
| 32 | ●OH + P ⟶Prod-●OH | 4.731 × 109 | (M−1 s−1) | Model |
| 33 | SO4●− + P ⟶ Prod-SO4●− | 1.07 × 108 | (M−1 s−1) | Model |
| 34 | •OH + S2O82− ⟶ OH− + S2O8−• | 1.2 × 107 | (M−1 s−1) | [25] |
The simulation of this work using the software proceeds according to the following steps:
First, the complete reaction system of process is introduced into the software using the process-specific data.
A reaction mechanism comprising 34 chemical reactions is used to simulate the generation of oxidative radicals (●OH, SO4●−, SO5●−, O2●−, O3−, O●−, HO2−, S2O8−) and non-radical intermediates/products (HSO5−, OH−, HSO4−, H+, HO2−, O2, SO42−) used to simulate the generation of oxidative radicals and the degradation of BCB by thermal activation of persulfate.
All reactions are introduced into the software, which automatically detects all the chemical species involved in the reactions as well as the initial concentrations of the different reactants. The estimation of kinetic constants is performed based on experimental data.
Once the optimization is launched, the software calculates the kinetic constants that provide the best simulation of the experimental results. The values of the kinetic constants, as well as the different degradation curves of the BCB as a function of time under different operating parameters, are presented in Table 1.
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Brilliant Coomassie Blue G 250 Degradation by TAP Process in Water
Figure 2 illustrates the degradation behavior of Brilliant Coomassie Blue G 250 in water under three distinct treatment scenarios: heating alone, persulfate alone (PS 2 mg/L), and thermally activated persulfate (TAP), all conducted at pH 7 and 60 (+/−2) °C. The degradation efficiency is evaluated by monitoring the normalized concentration C/C0 as a function of time over a 1200 s range.
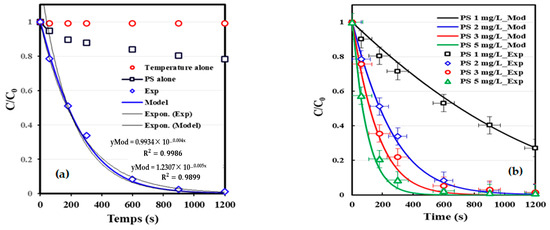
Figure 2.
(a) Kinetic model of BCB degradation by thermally activated persulphate (TAP) process (conditions: C0 = 10 mg/L, pHi = 7, [PS] = 2 mg/L, T = 60 °C). (b) Experimental and modeling effect of initial persulfate concentration on the removal kinetics of BCB (conditions: C0 = 10 mg/L, [S2O82–]0 = 1–5 mg/L, pHi = 7, T = 60 °C).
The results clearly demonstrate that temperature alone has a negligible effect on BCB removal, as indicated by the nearly constant C/C0 ratio (blue diamonds). In contrast, the use of persulfate alone without thermal activation led to a modest decrease in BCB concentration (~20% after 1200 s), suggesting limited radical generation at ambient activation levels (black squares). However, the combination of heat and persulfate (red circles) resulted in a substantial and rapid decrease in BCB concentration, with over 90% removal achieved within the timeframe studied. The kinetic model (red line) accurately reproduces the experimental degradation trend, reinforcing the hypothesis that sulfate radical (SO4●−) formation is significantly enhanced by thermal activation of the persulfate at high temperatures [26].
These findings corroborate previous studies showing that thermal activation is a critical step in initiating and sustaining the radical chain reactions necessary for efficient degradation of recalcitrant organic pollutants [27]. The marginal effect observed with persulfate or temperature alone underlines the necessity of a synergistic activation process to ensure optimal performance of advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) based on persulfate.
4.2. Determination of Rate Constants
Many reaction rate constants have been optimized from the above best finding of the experimental data, using the genetic algorithm. The rate constants of the thermal activation of persulfate are k#1 = 1.17 × 10−5 s−1, meaning that the free radical pathway (Eq1#: S2O82− → 2 SO4⦁−) at the conditions of [RG12]0 = 10 mg/L, pH = 7, [PS] = 2 mg/L and T = 60 °C.
Ma et al. [37] have determined the rate constants of the thermal activation of persulfate for oxidation of phenol at conditions of T = 30–70 °C and diverse pH (1.3–13.9). The obtained values vary between 0.003 h−1 and 0.962 h−1 at 70 °C and between ~1.184 and ~9.91 h−1 depending on pH. The work of Ahmadi et al. [38] found values of k ≈ 0.0009–0.0018 min−1 at the temperatures of 303–333 K during the application of thermally activated persulfate for degradation of Acid Blue 92 in aqueous solution. More recent results like those of Zhao et al. [39] (k ~0.0014 min−1 at 30 °C and ~0.0303 min−1 at 60 °C) were found using the TAP method under conditions of temperatures 30–60 °C and pH ≈ 4.
Finally, the rate constants of RG12 with •OH and SO4●− were found to be k32# = 4.73 × 109 M−1 s−1 and k33# = 1.07 × 108 M−1s−1, respectively. For most aromatic organic compounds, (•OH) is generally around (109–1010 M−1·s−1), and k(SO4●−) is more variable (105–109 M−1·s−1) depending on mechanism (H abstraction, double bond addition, electron transfer) and molecular structure [40].
It is important to note that the contribution of each reactive species (RS) is governed not only by its intrinsic rate constant but also by its concentration in the reaction medium, as expressed by rate = k[RS][RG12]. In the analyses addressing the effects of pH and initial persulfate dosage, only the parameter k1 was refined to fit the experimental profiles, whereas all other kinetic constants were fixed at the values reported in Table 1.
4.3. Initial Persulfate Concentration Effect on BCB Degradation TAP System
The efficiency of the TAP system for degrading Brilliant Coomassie Blue G 250 dye is evaluated as a function of the initial persulfate concentration S2O82−. Figure 3, shows the time-dependent evolution of the normalized concentration C/C0 of BCB at different persulfate concentrations ranging from 1 to 5 mg/L, under neutral pH, at a temperature of 60 °C, and an initial pollutant concentration of 10 mg/L. The experimental results clearly show a significant enhancement in the degradation kinetics of BCB as a function of an increasing oxidant concentration. At 1 mg/L, degradation is moderate, with about 60% of BCB removed after 1200 s, while at 5 mg/L, over 90% of the dye is degraded within less than 300 s.
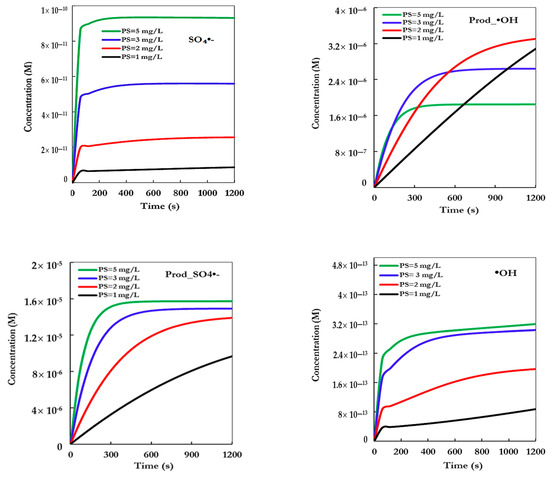
Figure 3.
Concentration profiles of ●OH and SO4●─ and their organic products, obtained from their direct reactions with BCB, for various concentrations of persulfate (conditions: C0 = 10 mg/L, [S2O82]0 = 1–5 mg/L, pHi = 7, T = 60 °C).
This improvement is attributed to the increased generation of sulfate radicals (SO4●−) from the thermal decomposition of persulfate, which is promoted at elevated temperatures. These radicals, with a high redox potential (E0 = 2.6 V), show strong reactivity toward aromatic organic compounds such as BCB [28,29]. The kinetic modeling integrated into the COPASI software showed good agreement with the experimental data for persulfate concentrations up to 3 mg/L, suggesting that the proposed reaction mechanism is correct within this concentration range. However, at higher concentrations (5 mg/L), slight deviations were observed, possibly due to secondary effects such as radical recombination or saturation of reactive sites [26].
Previous studies have also reported a positive correlation between initial persulfate concentration and the degradation rate of dyes in TAP systems [27]. Nevertheless, beyond a certain threshold, further increases in [PS] may no longer enhance efficiency and may even hinder reactivity due to radical quenching or the formation of inhibitory by-products [30].
Figure 3 presents the simulated temporal profiles of the reactive species concentration (presumably sulfate radicals, SO4●− generated from thermally activated persulfate (TAP) at different initial [PS] values (1 to 5 mg/L), under typical TAP conditions (60 °C, pH 7)). As shown, the concentration of radicals rapidly increases during the first few seconds and then reaches a quasi-steady state for all tested PS doses.
A clear dependence on the initial persulfate concentration is observed: higher [PS] leads to proportionally greater radical production, with concentrations rising from ~1.2 × 10−11 M for 1 mg/L PS to ~9.2 × 10−11 M for 5 mg/L PS. The steep rise at early timepoints reflects the fast thermal decomposition of persulfate at elevated temperatures, followed by stabilization due to concurrent radical consumption via reactions with the pollutant or self-quenching mechanisms [24,28]. This behavior confirms that the amount of generated sulfate radicals is a key factor controlling the degradation kinetics observed experimentally, as previously shown in similar advanced oxidation systems [29,30].
These simulation results support the experimental findings (see Figure 2) and model predictions, suggesting that the degradation efficiency of BCB is directly linked to the steady-state concentration of sulfate radicals, which in turn depends on the initial oxidant dose.
In a thermally activated process (TAP), the true degradation rate of a pollutant, e.g., is r = kRS[RS][pollutant]. Even if k(•OH) > k(SO4●−) for a given compound, if [SO4●−] ≫ [•OH] (or vice versa), the dominant pathway may change. TAP studies often show coexistence and interconversion SO4●− ⟷ •OH (especially in basic media) [41].
4.4. Effect of pH Solution on BCB Degradation by TAP System
To examine the influence of pH, one of the most critical parameters controlling the distribution of dominating species in aqueous solutions, a series of experiments were conducted with pH values ranging from 3 to 11. In Figure 4, the experimental results are presented alongside the model that was developed. After only 180 s, the estimated yields show a dye removal efficiency of 36.45% at pH 3. At moderately neutral pH values (5 and 7), the yields increase to 42.93% and 48.84%, respectively. Yields at basic pH levels (9 and 11) are significantly higher, reaching 63.25% and 91.96%.
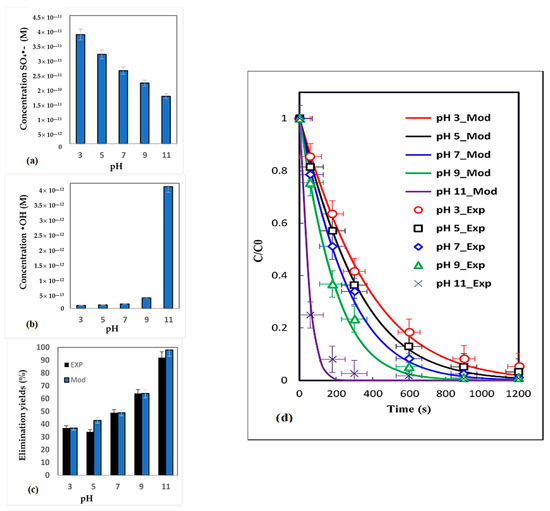
Figure 4.
SO4−• concentrations (a), HO• concentrations (b), elimination yields (c), kinetic model and experimental elimination of BCB at different pH values (d) (conditions: C0 = 10 mg/L, [S2O82–]0 = 2 mg/L, pHi = 7, T = 60 °C).
The results obtained are attributable to the pKa values of both the dye and the oxidizing radical species generated, specifically SO4●− and ●OH, with E0 = 2.5−3.1 V and E0 = 2.8 V oxidizing potential, respectively [42].
After 180 s of oxidation, at the acidic pH ranges, SO42− is the predominant form, resulting in higher amounts of the SO4−• radical compared to other pH values and hydroxyl radicals at similar acidity levels [43].
At pH 3, SO4●− and ●OH have values of 3.83 × 10−11 M and 1.04 × 10−13 M, respectively. At alkaline pHs (9 and 11), the predominant species are inverted, with the majority being ●OH [44].
The recorded hydroxyl radical concentration is equal to 6.19 × 10−12 M, while that of SO4-• is on the order of 1.67 × 10−11 M. The sum concentrations of the oxidizing species give rise to high elimination efficiencies, as demonstrated by Equation 30 (k30 = 7 × 107 M−1 s−1) [45].
Alkaline pH: SO4●− + OH− → SO42− + ●OH
Moreover, as demonstrated in Equation 34 (k34 = 1.2 × 107 M−1 s−1), HO• in the persulphate system is able to react with persulphate anions [46]. Greater persulphate degradation may be induced by the presence of HO• radicals. Consequently, at alkaline pH, persulphate-induced degradation occurs at a faster rate [25].
●OH + S2O82− → OH− + S2O8−•
In addition, at pH 9, where Blue Brillant G 250 groups are fully deprotonated, the increased negative charge which favors the electrophilic attack of oxidizing species [47].
5. Conclusions
This study successfully employed COPASI software to develop and validate a kinetic model describing the thermal activation of persulfate for the degradation of BCB. The kinetic constants k32 and k33, associated with secondary radical reactions, were found to be stable across varying conditions, with values of 4.7317 × 109 M−1·s−1 and 1.0735 × 108 M−1·s−1, respectively. In contrast, the kinetic constant k1, corresponding to the primary thermal decomposition of persulfate, showed a marked sensitivity to pH and persulfate concentration, ranging from 1.137 × 105 s−1 to 7.25 × 105 s−1, and from 3.909 × 105 s−1 to 3.2175 × 106 s−1, respectively. These variations underscore the crucial influence of reaction conditions on radical generation dynamics. Under alkaline conditions, the system favored the production of ●OH radicals, whereas at higher persulfate concentrations, the contribution of SO4●− radicals was predominant. This mechanistic insight highlights the dual-radical pathway of the thermally activated persulfate (TAP) process and its capacity to adapt to different treatment environments. Overall, the excellent agreement between simulated and experimental results confirms that the TAP process, supported by kinetic modeling, provides a robust and tunable approach for the effective degradation of emerging contaminants such as BCB. The selectivity analysis confirmed that sulfate radicals (SO4●−) were the primary reactive species responsible for BCB degradation, while hydroxyl radicals (●OH) played a secondary role. Overall, the results confirm that the TAP process is a promising advanced oxidation technology for the removal of persistent organic pollutants from water, offering both high efficiency and target selectivity in radical-driven degradation pathways.
Finally, this study will help to better understand the removal of BCB by the TAP process for the successful implementation of this technology in the treatment of water contaminated with dyes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.K., Z.B., A.B. and D.K.; methodology, N.K., M.L.D., A.L. and D.K.; formal analysis, N.K., A.B. and D.K.; investigation, N.K., M.L.D., A.L. and A.P. (Antonio Pizzi); data curation, N.K., Z.B., D.K. and A.B.; writing—original draft preparation, N.K., A.B., D.K. and A.P. (Antonio Pizzi); writing—review and editing, N.K., A.B., D.K., A.P. (Antonio Panico) and A.P. (Antonio Pizzi); supervision, A.B., D.K., A.P. (Antonio Panico) and A.P. (Antonio Pizzi); project administration, A.B. and D.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Polytechnic School of Constantine (Algeria).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Forgacs, E.; Cserháti, T.; Oros, G. Removal of Synthetic Dyes from Wastewaters: A Review. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 953–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, T.; McMullan, G.; Marchant, R.; Nigam, P. Remediation of Dyes in Textile Effluent: A Critical Review on Current Treatment Technologies with a Proposed Alternative. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 77, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyadarshini, M.; Das, I.; Ghangrekar, M.M.; Blaney, L. Advanced Oxidation Processes: Performance, Advantages, and Scale-up of Emerging Technologies. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wu, S.; Dai, H.; Cheng, Z.; Peng, W.; Yan, B.; Chen, G.; Wang, S.; Duan, X. Thermal Activation of Persulfates for Organic Wastewater Purification: Heating Modes, Mechanism and Influencing Factors. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 137976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Y. A Comprehensive Review on Persulfate Activation Treatment of Wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Zhu, F.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Wei, L.; Li, Q.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Q. A Review Study on Sulfate-Radical-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes for Domestic/Industrial Wastewater Treatment: Degradation, Efficiency, and Mechanism. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 592056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, W.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Wei, L.; Sun, A. Tuning Hard Phase towards Synergistic Improvement of Toughness and Self-Healing Ability of Poly (Urethane Urea) by Dual Chain Extenders and Coordinative Bonds. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 393, 124583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anipsitakis, G.P.; Dionysiou, D.D. Radical Generation by the Interaction of Transition Metals with Common Oxidants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 3705–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhao, R. Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) in Wastewater Treatment. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim-Ortega, J.K.T.; Liang, C.; Rollon, A.P.; De Luna, M.D.G. Evaluation of Sustained Persulfate Oxidant Release for Remediating Trichloroethylene Contaminated Low Permeability Soil in the Phreatic Zone. ACS Environ. Au 2025, 5, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-monem, H.A.; Mahanna, H.; El-Halwany, M.; Samy, M. Photo-Thermal Activation of Persulfate for the Efficient Degradation of Synthetic and Real Industrial Wastewaters: System Optimization and Cost Estimation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 24153–24162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, V.C.; Rosso, J.A.; Mártire, D.O.; Gonzalez, M.C. Phenol Depletion by Thermally Activated Peroxydisulfate at 70 °C. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Gao, J.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Liu, C.; Zhou, D. Activation of Persulfate by Quinones: Free Radical Reactions and Implication for the Degradation of PCBs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4605–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; de la Cruz, A.A.; Dionysiou, D.D. Destruction of Cyanobacterial Toxin Cylindrospermopsin by Hydroxyl Radicals and Sulfate Radicals Using UV-254 nm Activation of Hydrogen Peroxide, Persulfate and Peroxymonosulfate. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2013, 251, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Shao, Y.; Gao, N.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, S.; Hu, X. Thermally Activated Persulfate (TAP) Oxidation of Antiepileptic Drug Carbamazepine in Water. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 228, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Gao, N.; Deng, Y.; Li, L.; Deng, J.; Zhou, S. Kinetic Oxidation of Antipyrine in Heat-Activated Persulfate. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 53, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvaniti, O.S.; Ioannidi, A.A.; Mantzavinos, D.; Frontistis, Z. Heat-Activated Persulfate for the Degradation of Micropollutants in Water: A Comprehensive Review and Future Perspectives. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 318, 115568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habache, N.; Bechiri, O. Thermally Activated Persulfate Oxidation of Basic Fuchsin Dye: Effect of Different Operating Parameters, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Study. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2024, 56, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathuria, T.; Mehta, A.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, S. Review on Ultrasound-Enhanced Activation of Persulfate/Peroxymonosulfate in Hybrid Advanced Oxidation Technologies. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2024, 211, 1645–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoops, S.; Sahle, S.; Gauges, R.; Lee, C.; Pahle, J.; Simus, N.; Singhal, M.; Xu, L.; Mendes, P.; Kummer, U. COPASI—A Complex Pathway Simulator. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 3067–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COPASI. Available online: https://copasi.org/ (accessed on 5 October 2025).
- Criquet, J.; Leitner, N.K.V. Degradation of Acetic Acid with Sulfate Radical Generated by Persulfate Ions Photolysis. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criquet, J.; Leitner, N.K.V. Electron Beam Irradiation of Aqueous Solution of Persulfate Ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 169, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criquet, J.; Allard, S.; Salhi, E.; Joll, C.A.; Heitz, A.; Von Gunten, U. Iodate and Iodo-Trihalomethane Formation during Chlorination of Iodide-Containing Waters: Role of Bromide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7350–7357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.N. Reactivity and Role of SO5•− Radical in Aqueous Medium Chain Oxidation of Sulfite to Sulfate and Atmospheric Sulfuric Acid Generation. J. Phys. Chem. A 2001, 105, 9142–9155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, G.V.; Greenstock, C.L.; Helman, W.P.; Ross, A.B. Critical Review of Rate Constants for Reactions of Hydrated Electrons, Hydrogen Atoms and Hydroxyl Radicals (•OH/•O−) in Aqueous Solution. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1988, 17, 515–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruthamuthu, P.; Neta, P. Reactions of Phosphate Radicals with Organic Compounds. J. Phys. Chem. 1977, 81, 1622–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Ramjaun, S.N.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. Concentration Profiles of Chlorine Radicals and Their Significances in OH-Induced Dye Degradation: Kinetic Modeling and Reaction Pathways. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 209, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djaballah, M.L.; Merouani, S.; Bendjama, H.; Hamdaoui, O. Development of a Free Radical-Based Kinetics Model for the Oxidative Degradation of Chlorazol Black in Aqueous Solution Using Periodate Photoactivated Process. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2021, 408, 113102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Wu, Z.; Shang, C.; Yao, B.; Hou, S.; Yang, X.; Song, W.; Fang, J. Radical Chemistry and Structural Relationships of PPCP Degradation by UV/Chlorine Treatment in Simulated Drinking Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10431–10439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, W.; Sun, J.; Zhu, S.; Li, K.; Meng, X.; Luo, J.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, D.; Crittenden, J.C. Oxidation Mechanisms of the UV/Free Chlorine Process: Kinetic Modeling and Quantitative Structure Activity Relationships. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4335–4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielski, B.H.; Cabelli, D.E.; Arudi, R.L.; Ross, A.B. Reactivity of HO2/O-2 Radicals in Aqueous Solution. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1985, 14, 1041–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulman, D.M.; Mezyk, S.P.; Remucal, C.K. The Impact of pH and Irradiation Wavelength on the Production of Reactive Oxidants during Chlorine Photolysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4450–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutze, H.V.; Bircher, S.; Rapp, I.; Kerlin, N.; Bakkour, R.; Geisler, M.; Von Sonntag, C.; Schmidt, T.C. Degradation of Chlorotriazine Pesticides by Sulfate Radicals and the Influence of Organic Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Dong, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Qiang, Z. Accelerated Oxidation of Iopamidol by Ozone/Peroxymonosulfate (O3/PMS) Process: Kinetics, Mechanism, and Simultaneous Reduction of Iodinated Disinfection by-Product Formation Potential. Water Res. 2020, 173, 115615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Brigante, M.; Zhang, H.; Mailhot, G. Phenanthrene Degradation Using Fe(III)-EDDS Photoactivation under Simulated Solar Light: A Model for Soil Washing Effluent Treatment. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, H.; Chi, L.; Chen, H.; Chen, C. Changes in Activation Energy and Kinetics of Heat-Activated Persulfate Oxidation of Phenol in Response to Changes in pH and Temperature. Chemosphere 2017, 189, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Igwegbe, C.A.; Rahdar, S. The Application of Thermally Activated Persulfate for Degradation of Acid Blue 92 in Aqueous Solution. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2019, 10, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, S.; Geng, J.; Wei, R.; Wen, Y.; Sun, S. Degradation of Norfloxacin by Thermally Activated Persulfate: Kinetics, Optimization and Pathways. Discov. Chem. 2025, 2, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojnárovits, L.; Takács, E. Rate Constants of Sulfate Radical Anion Reactions with Organic Molecules: A Review. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 1014–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonawane, S.; Rayaroth, M.P.; Landge, V.K.; Fedorov, K.; Boczkaj, G. Thermally Activated Persulfate-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes—Recent Progress and Challenges in Mineralization of Persistent Organic Chemicals: A Review. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2022, 37, 100839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huie, R.E.; Clifton, C.L.; Neta, P. Electron Transfer Reaction Rates and Equilibria of the Carbonate and Sulfate Radical Anions. Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrum. Part C Radiat. Phys. Chem. 1991, 38, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Su, H.-W. Identification of Sulfate and Hydroxyl Radicals in Thermally Activated Persulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 5558–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogliotti, L.; Hayon, E. Flash Photolysis of per[Oxydi]Sulfate Ions in Aqueous Solutions. The Sulfate and Ozonide Radical Anions. J. Phys. Chem. 1967, 71, 2511–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huie, R.E.; Clifton, C.L. Rate Constants for Hydrogen Abstraction Reactions of the Sulfate Radical, SO4−. Alkanes and Ethers. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 1989, 21, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, G.V.; Barlow, S.; McGowan, S.; Salmon, G.A.; Williams, J.E. The Reaction of the SO3− Radical with Fe II in Acidic Aqueous Solution—A Pulse Radiolysis Study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1999, 1, 3111–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chial, H.J.; Thompson, H.B.; Splittgerber, A.G. A Spectral Study of the Charge Forms of Coomassie Blue G. Anal. Biochem. 1993, 209, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).