Mechanistic Study of Methyl Orange Removal by Fe3O4@MIL-53(Fe Cu) Composite Material
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Component
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Material Preparation
2.2.1. Preparation of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
2.2.2. Preparation of Fe3O4@MIL-53(Fe)
2.2.3. Preparation of Fe3O4@MIL-53(Fe Cu)
2.3. Test and Characterization
2.4. Adsorption Tests
2.5. Recyclability Analysis Test of Adsorbent
2.6. Adsorption Kinetics
2.7. Adsorption Isotherms
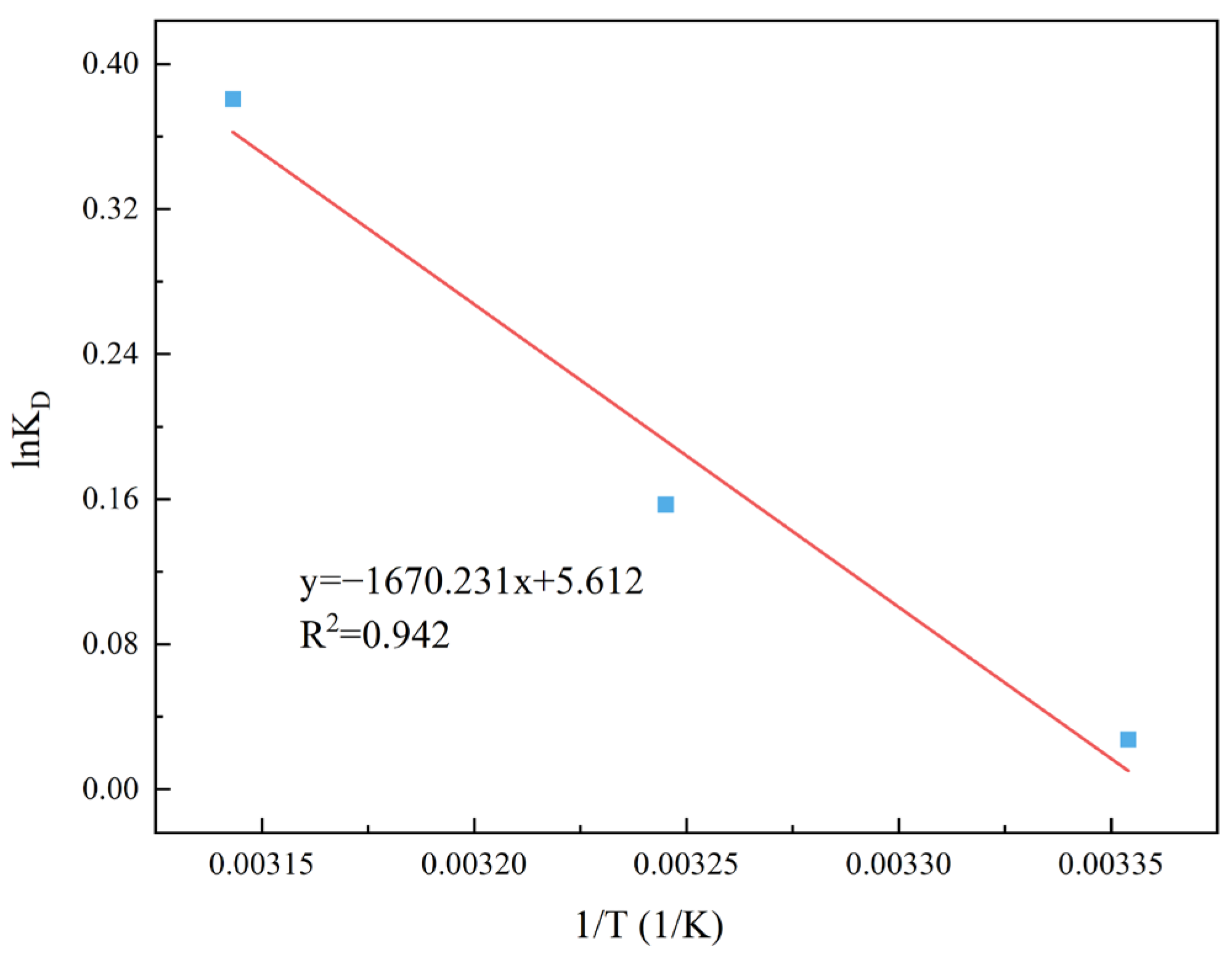
2.8. Thermodynamic Study
3. Results
3.1. Material Characterization
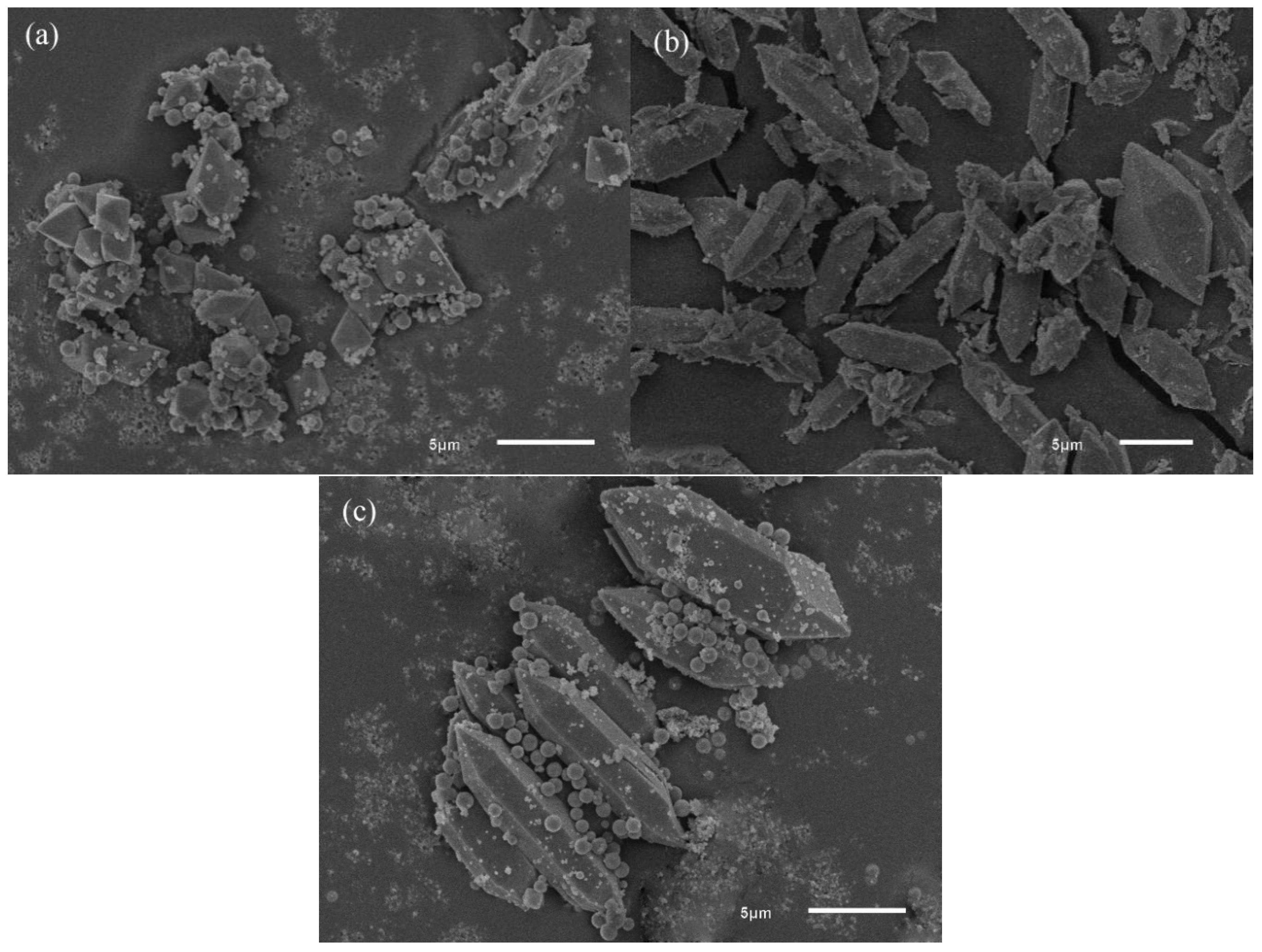
3.1.1. SEM
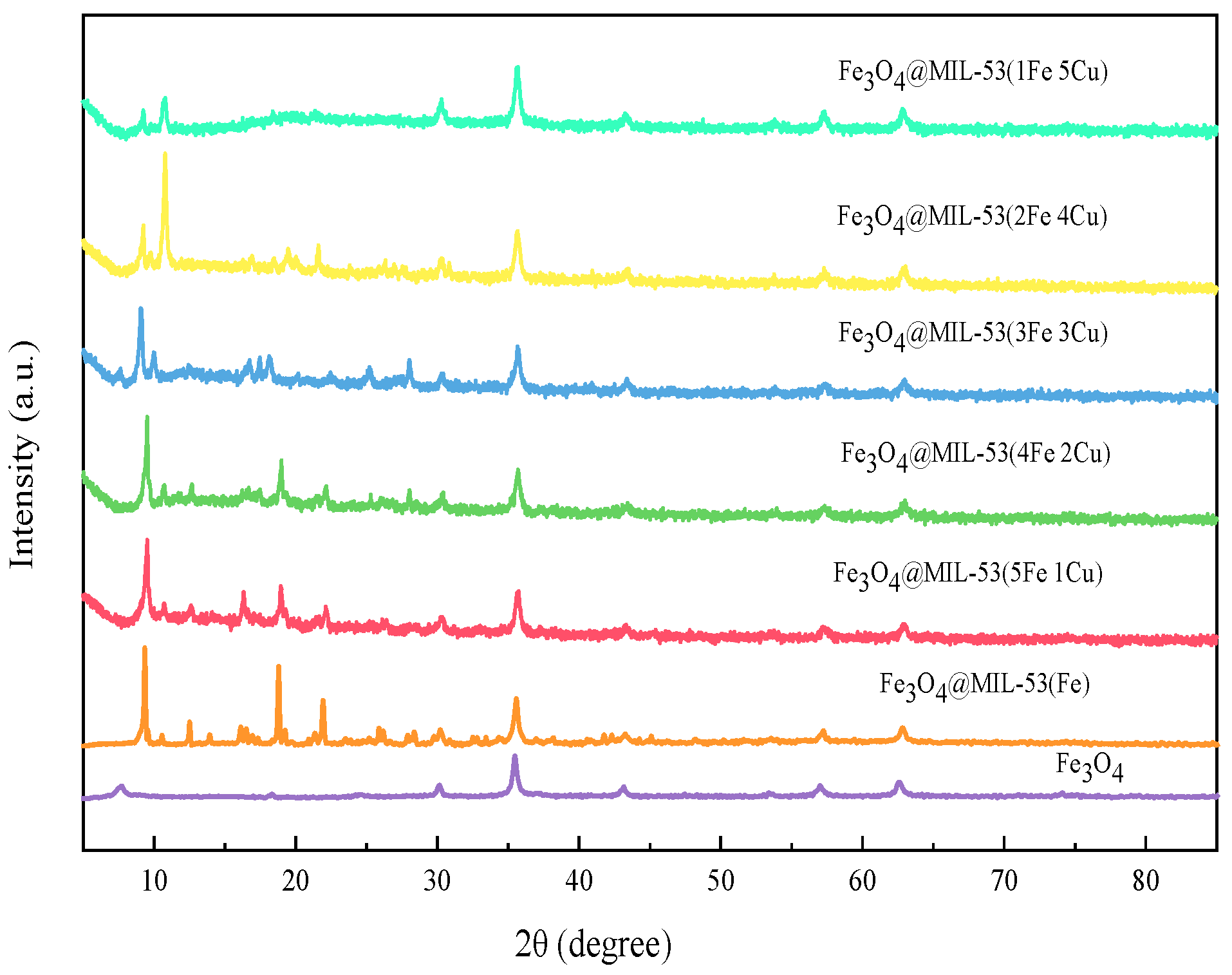
3.1.2. XRD
3.1.3. BET
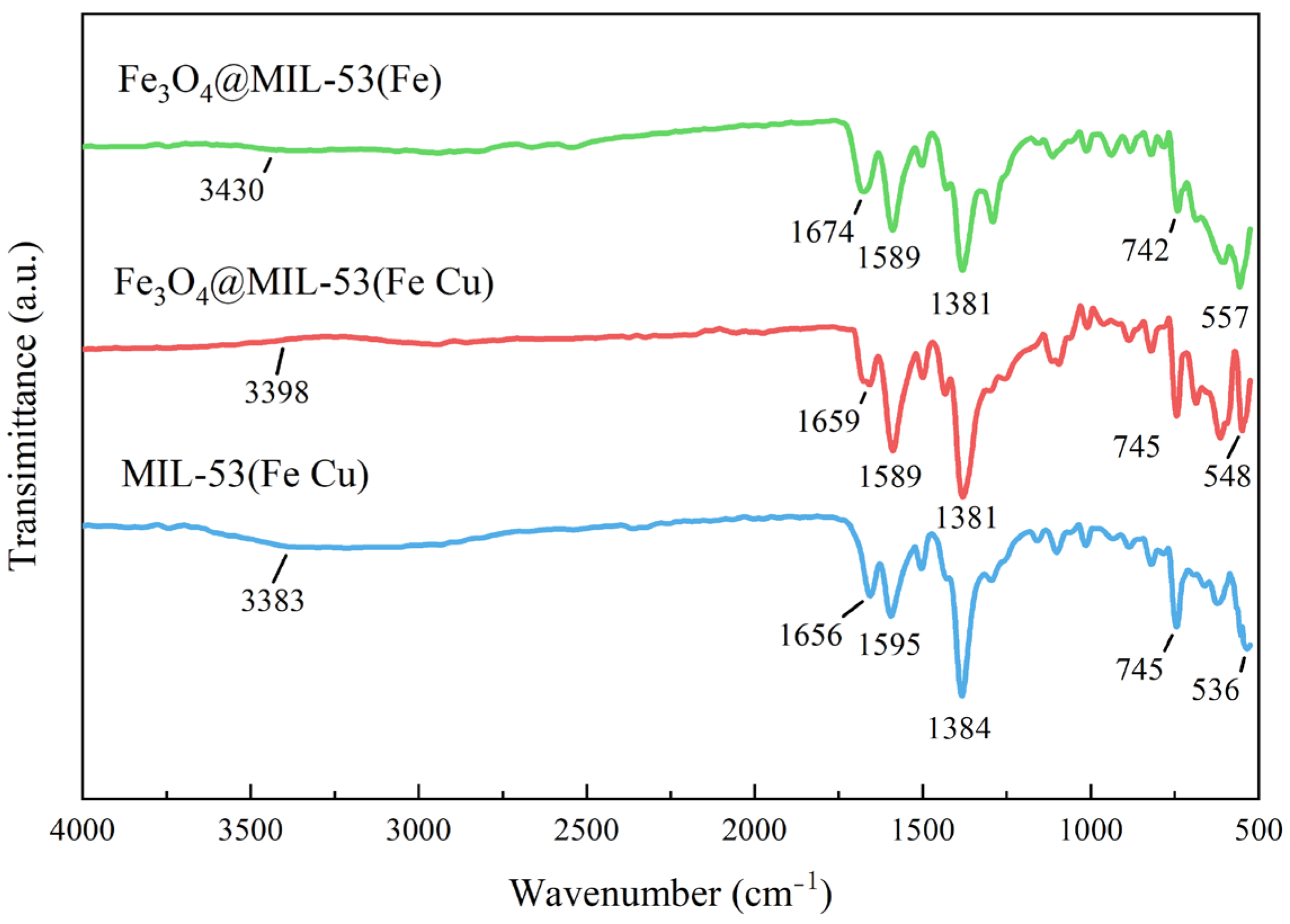
3.1.4. FTIR
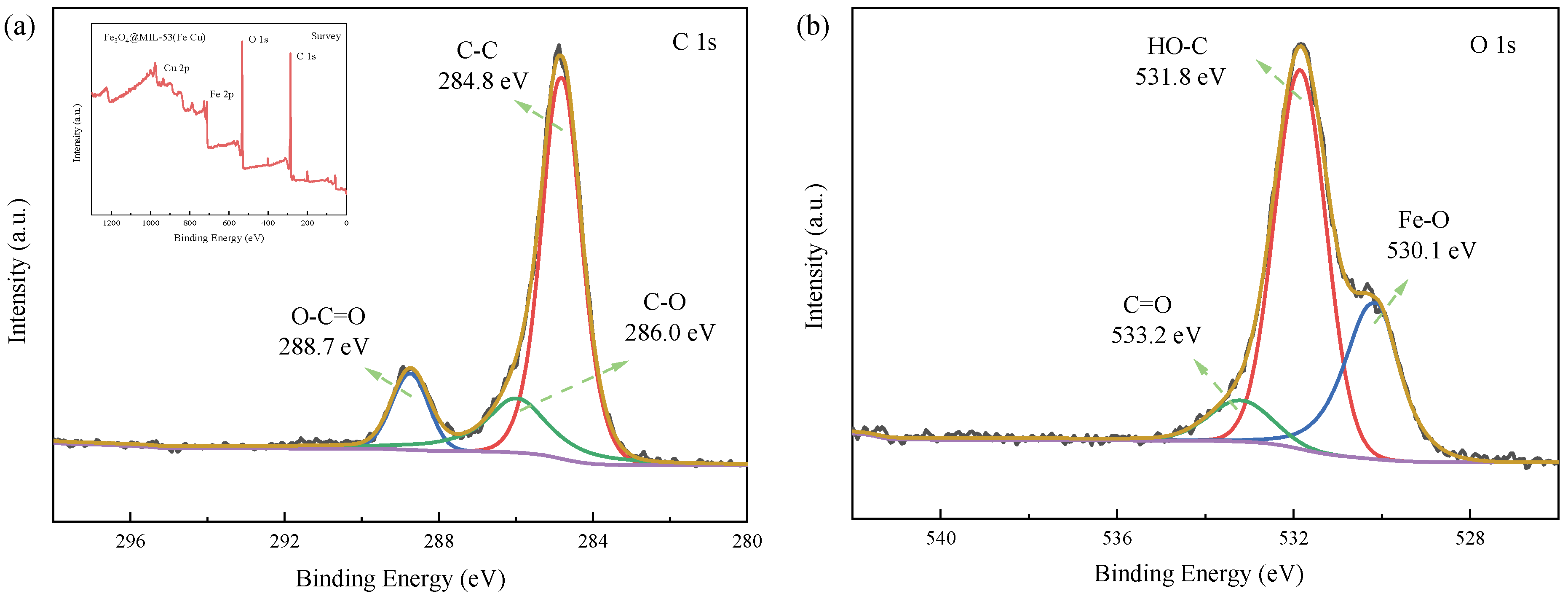
3.1.5. XPS
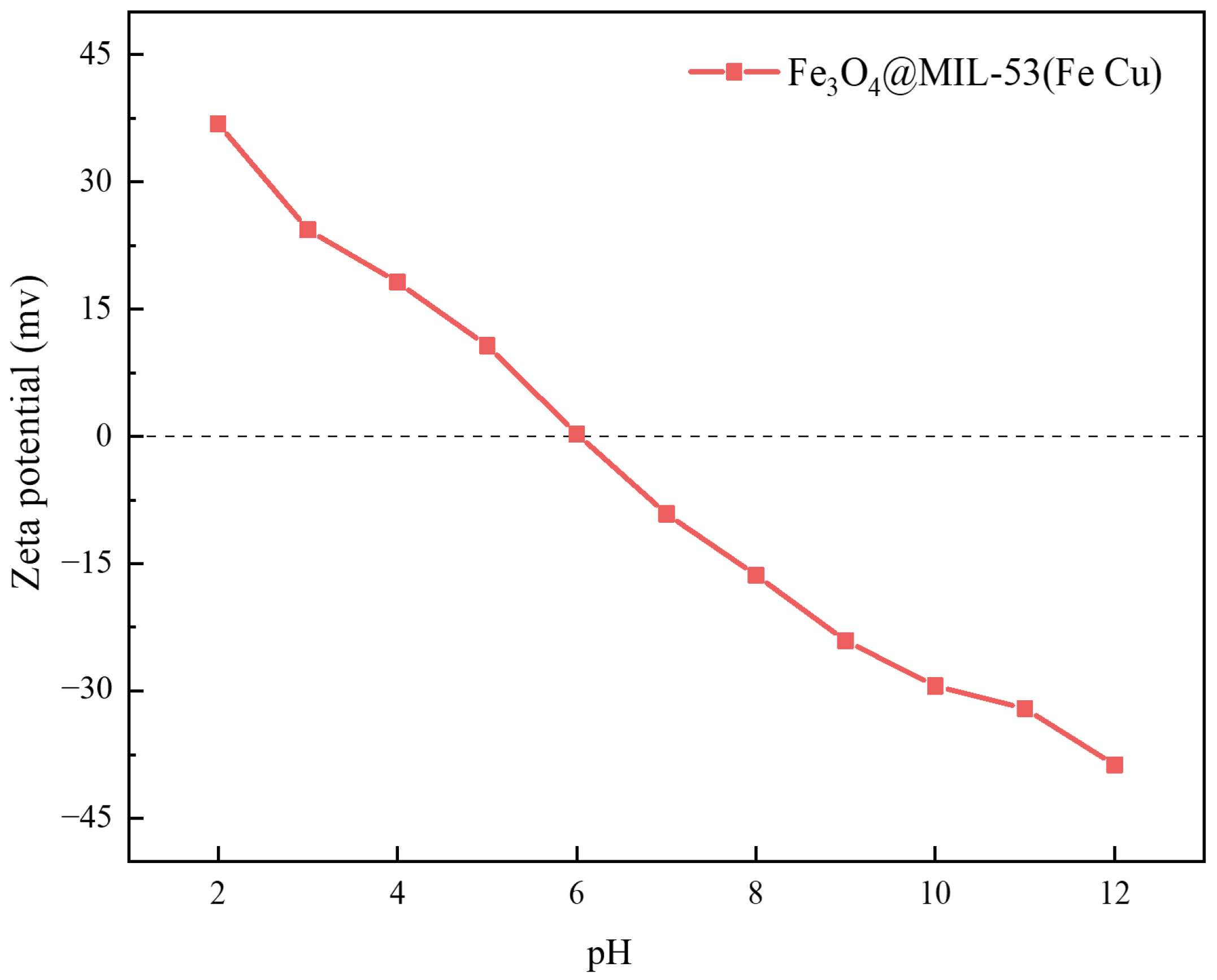
3.1.6. Zeta Potential Analysis
3.2. Adsorption Properties
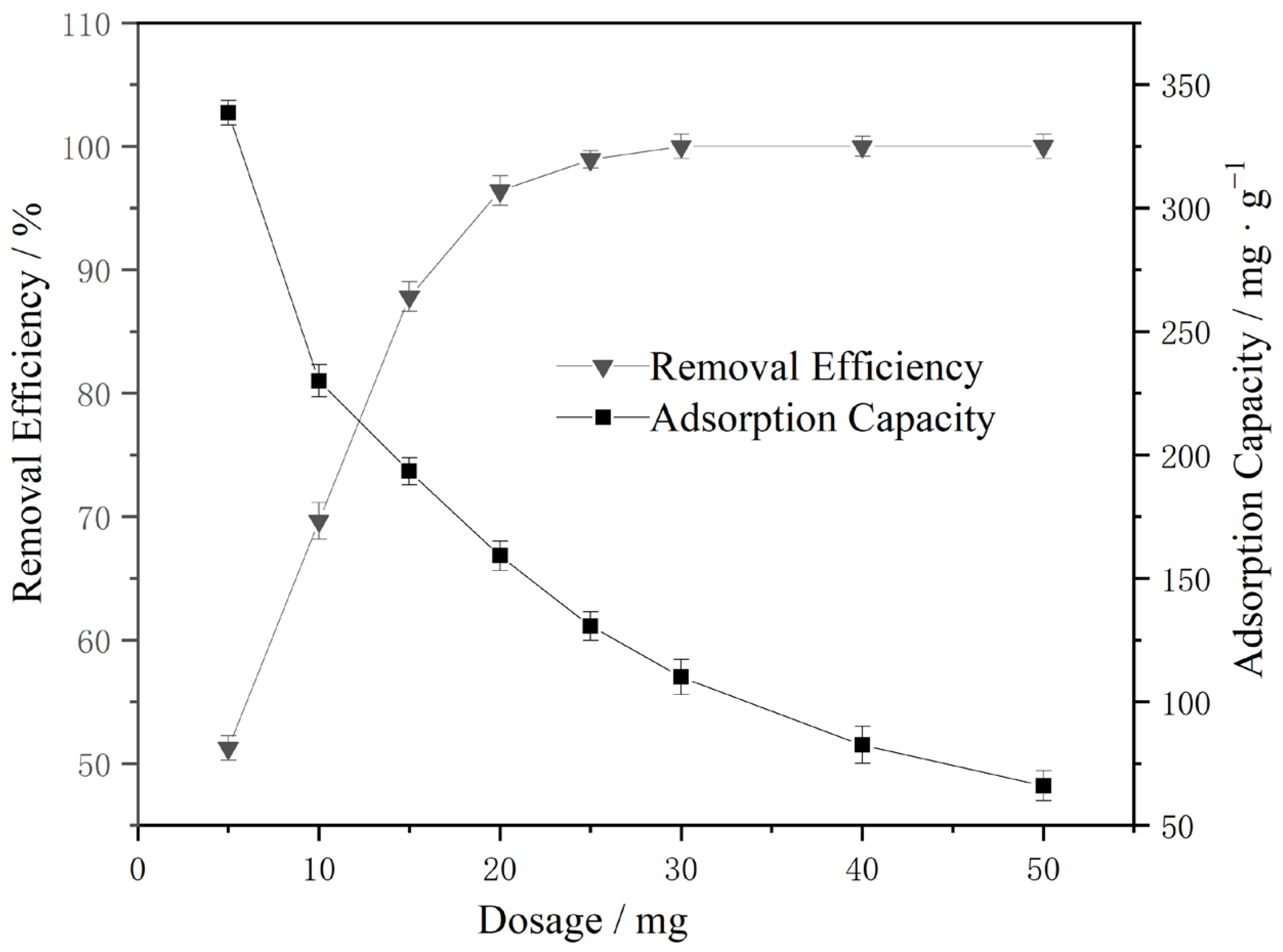
3.2.1. Fe3O4@MIL-53(Fe Cu) Dosage
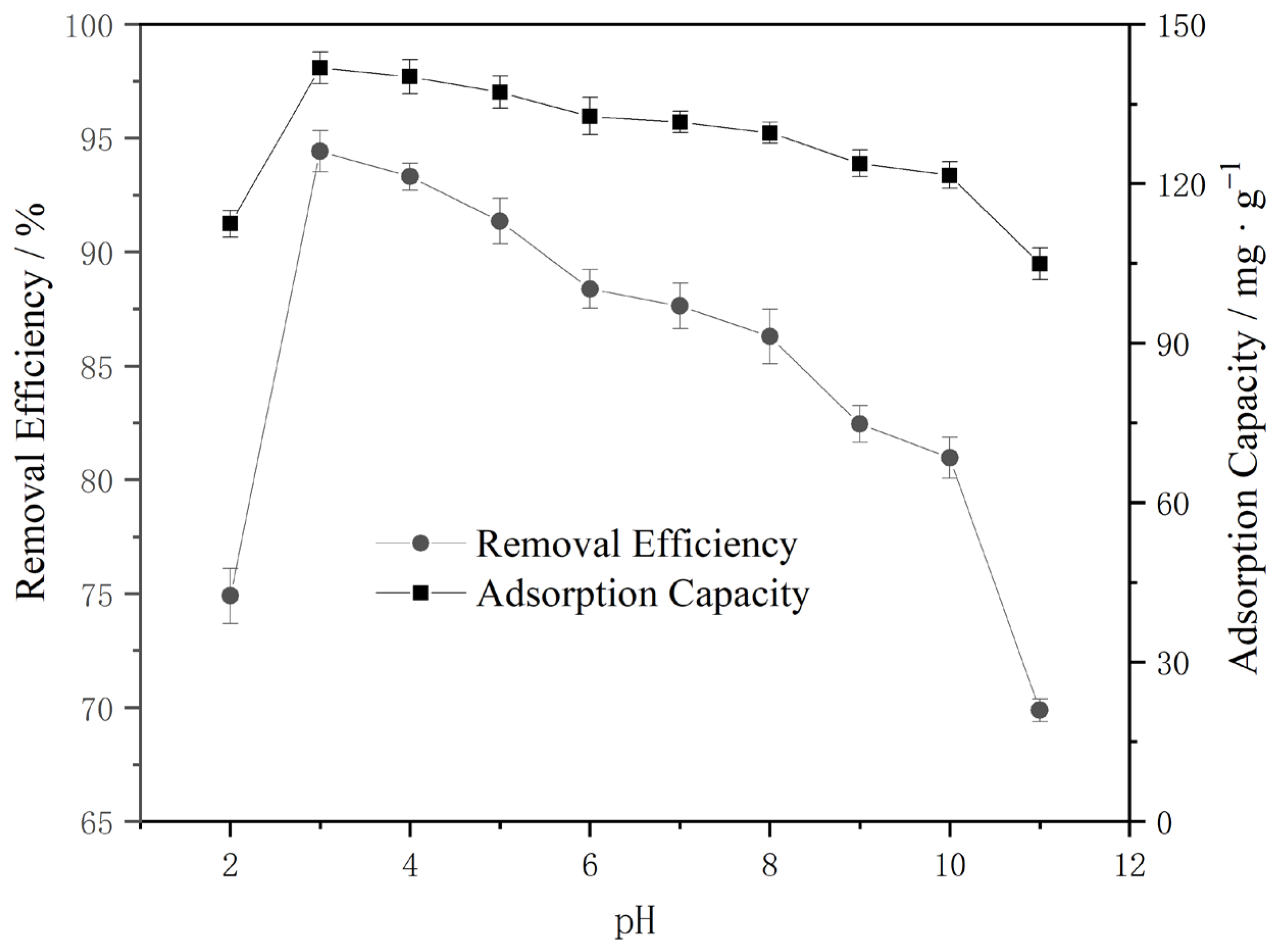
3.2.2. pH
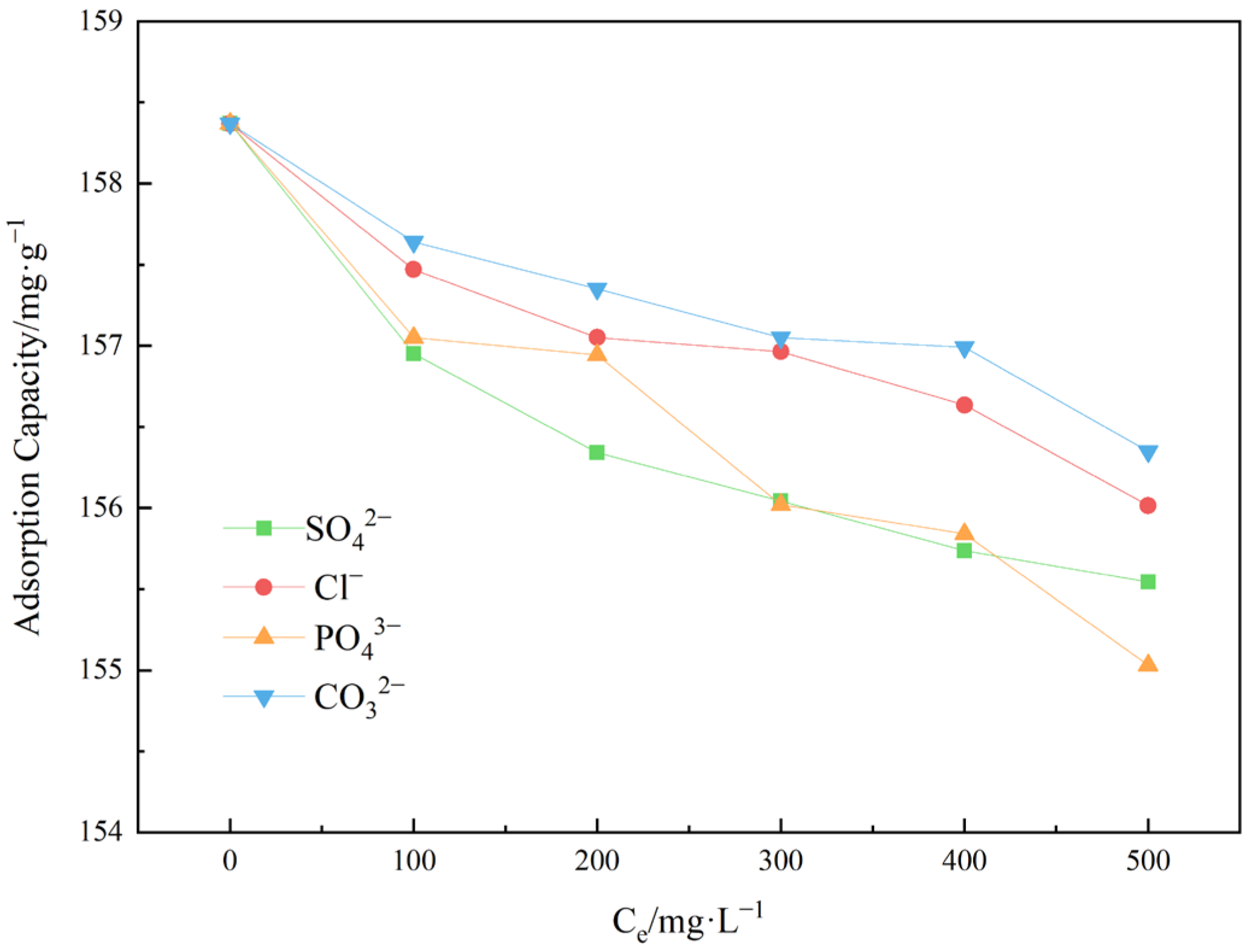
3.2.3. Co-Existing Anions
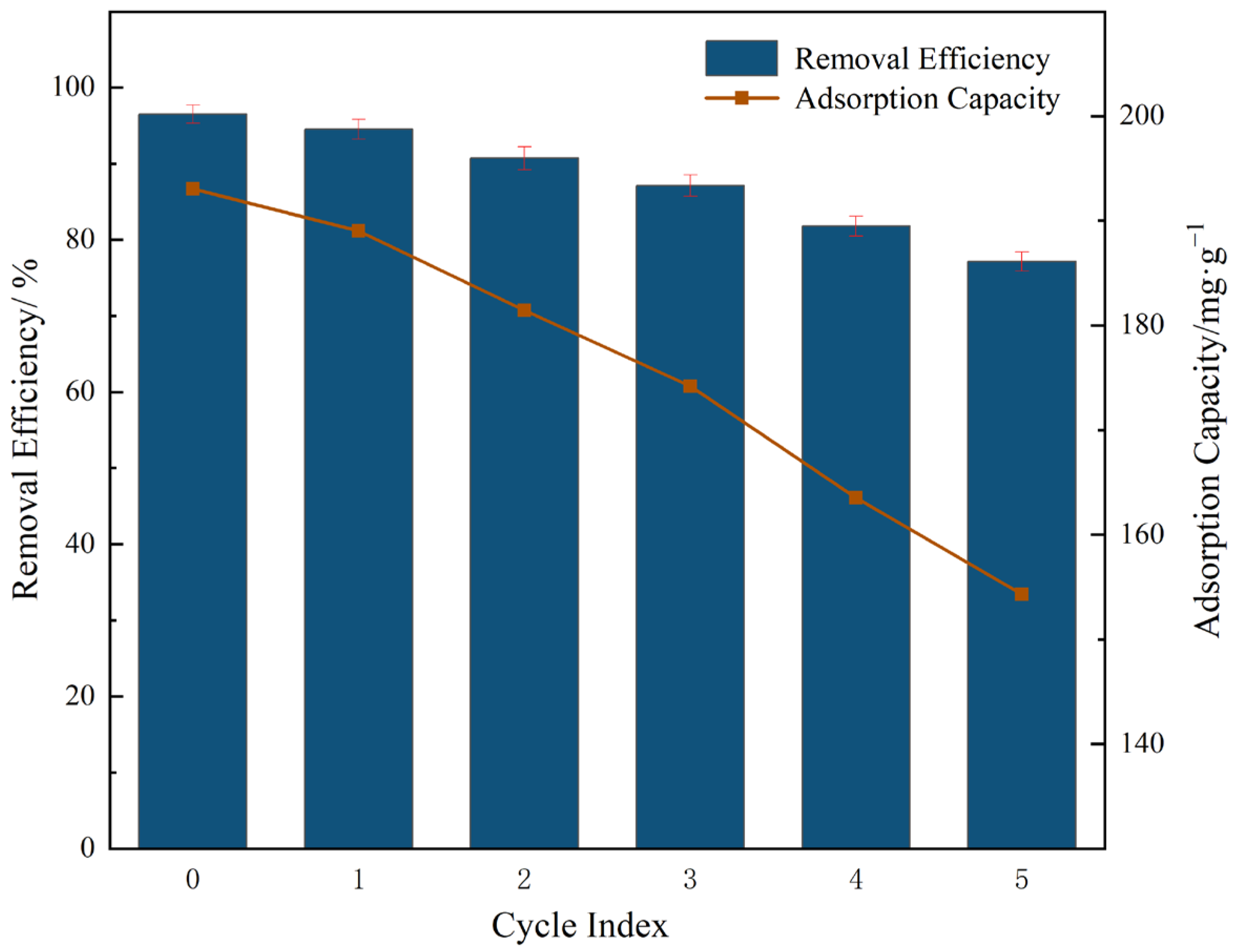
3.2.4. Recyclability Analysis
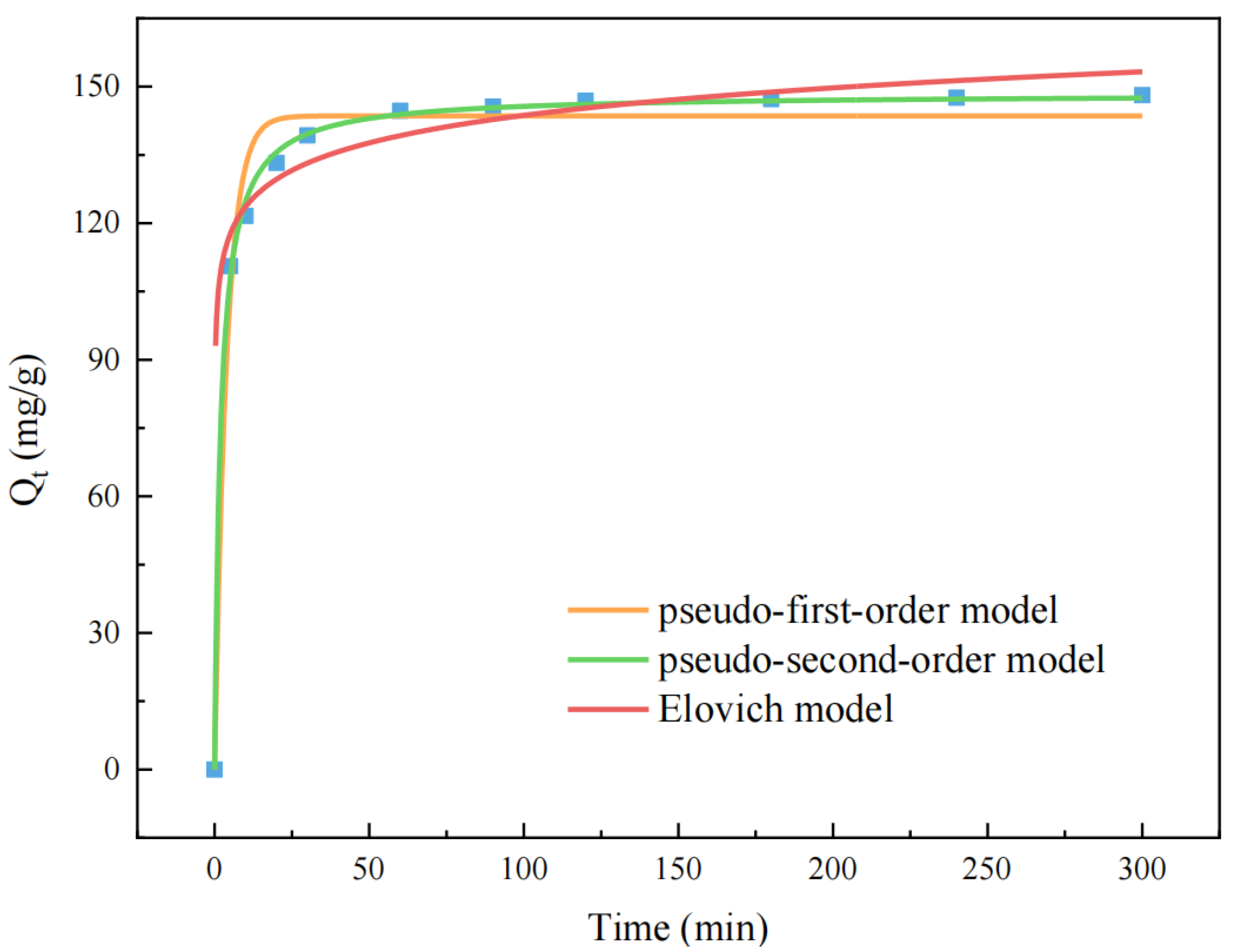
3.2.5. Adsorption Kinetics Analysis
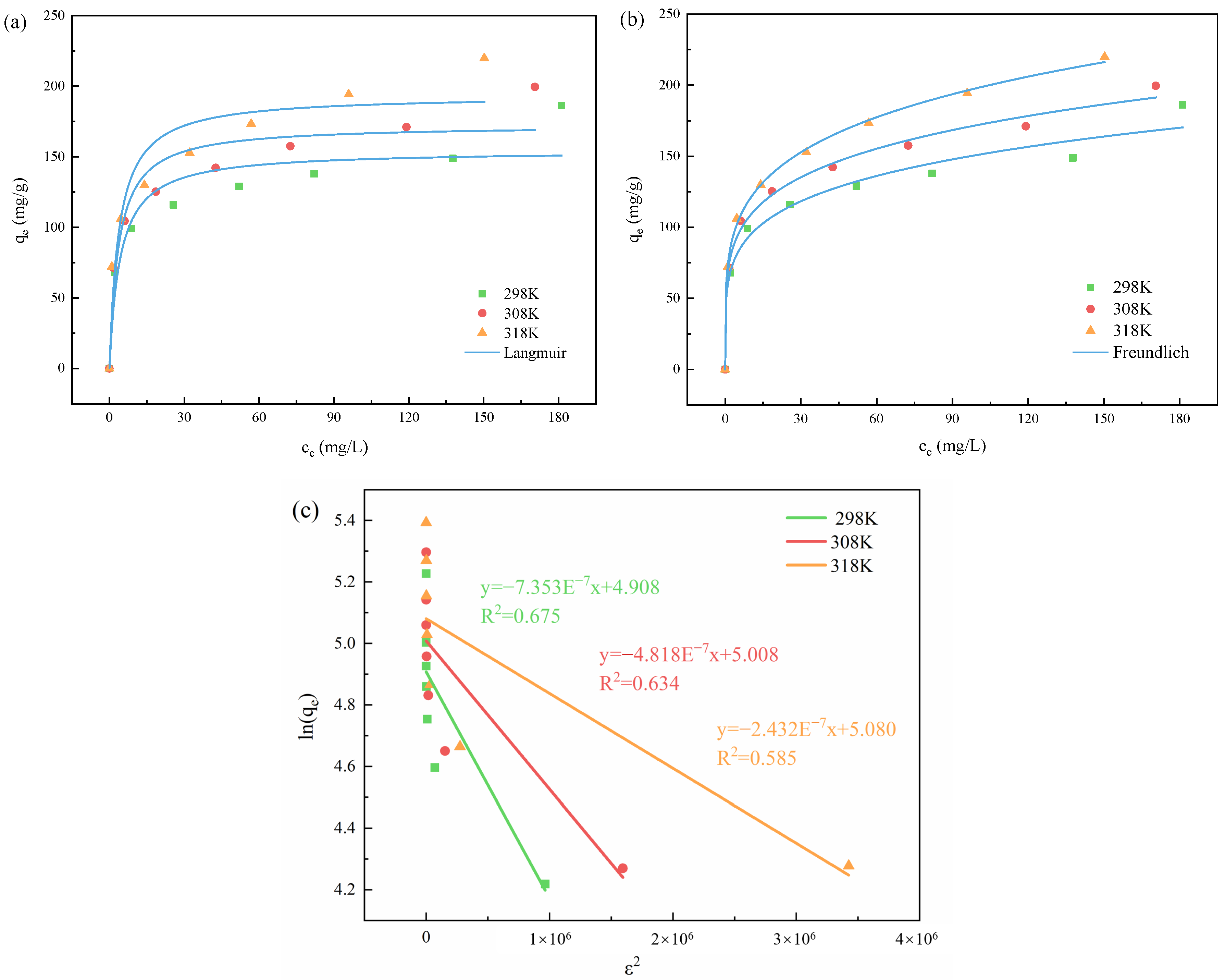
3.2.6. Adsorption Isotherms Analysis
| Makings | Adsorption Objects | pH | Adsorption Capacity/mg g−1 | Bibliography |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni-Fe-SO4 LDH | MO | 4 | 82.45 | [53] |
| ZIF-67 | / | 75.59 | [54] | |
| Ni@ZIF-67 | 6 | 151.74 | [55] | |
| UiO-66 | 5.90 | 84.8 | [56] | |
| UiO-66/cellulose aerogels | / | 71.70 | [57] | |
| MIL-53(Al)@CWS | / | 99.39 | [58] | |
| magnetic lignin-based carbon nanoparticles | 5 | 113 | [59] | |
| Fe3O4@MIL-53(Fe Cu) | 3 | 193.68 | this study |
3.2.7. Adsorption Thermodynamics Analysis
3.3. Adsorption Mechanism Study
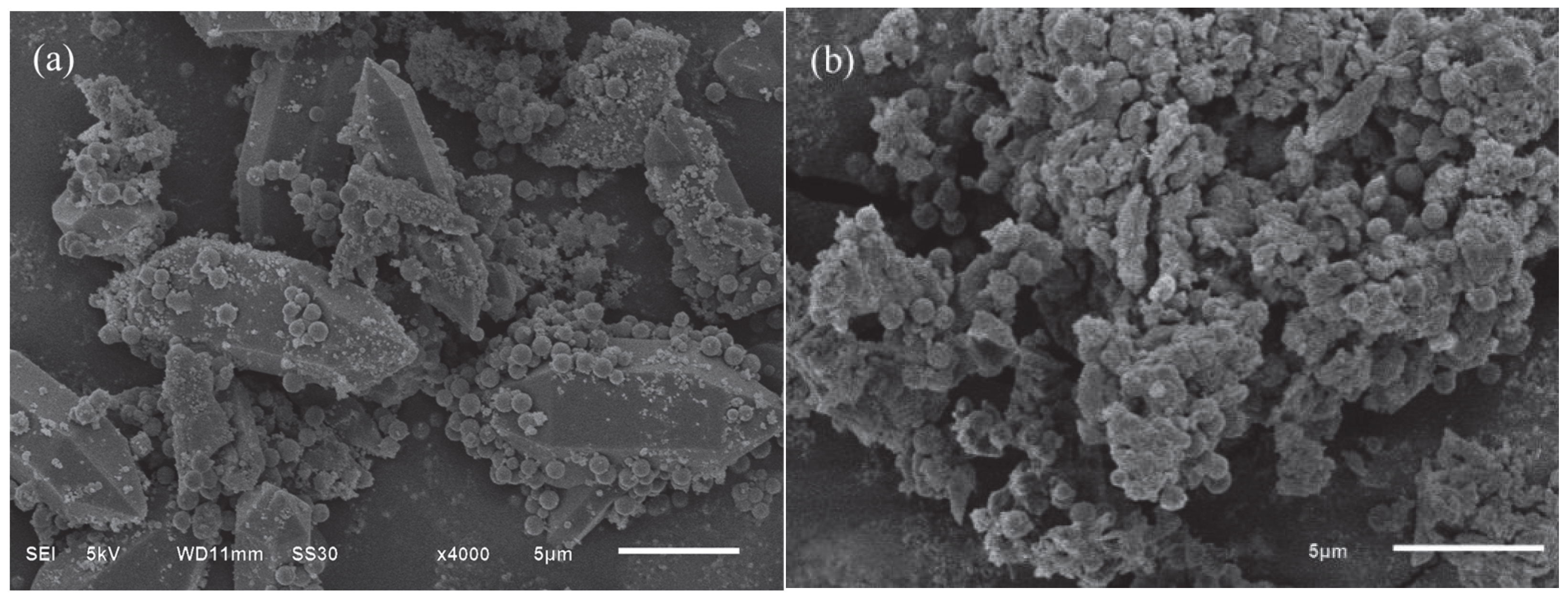
3.3.1. SEM Analysis
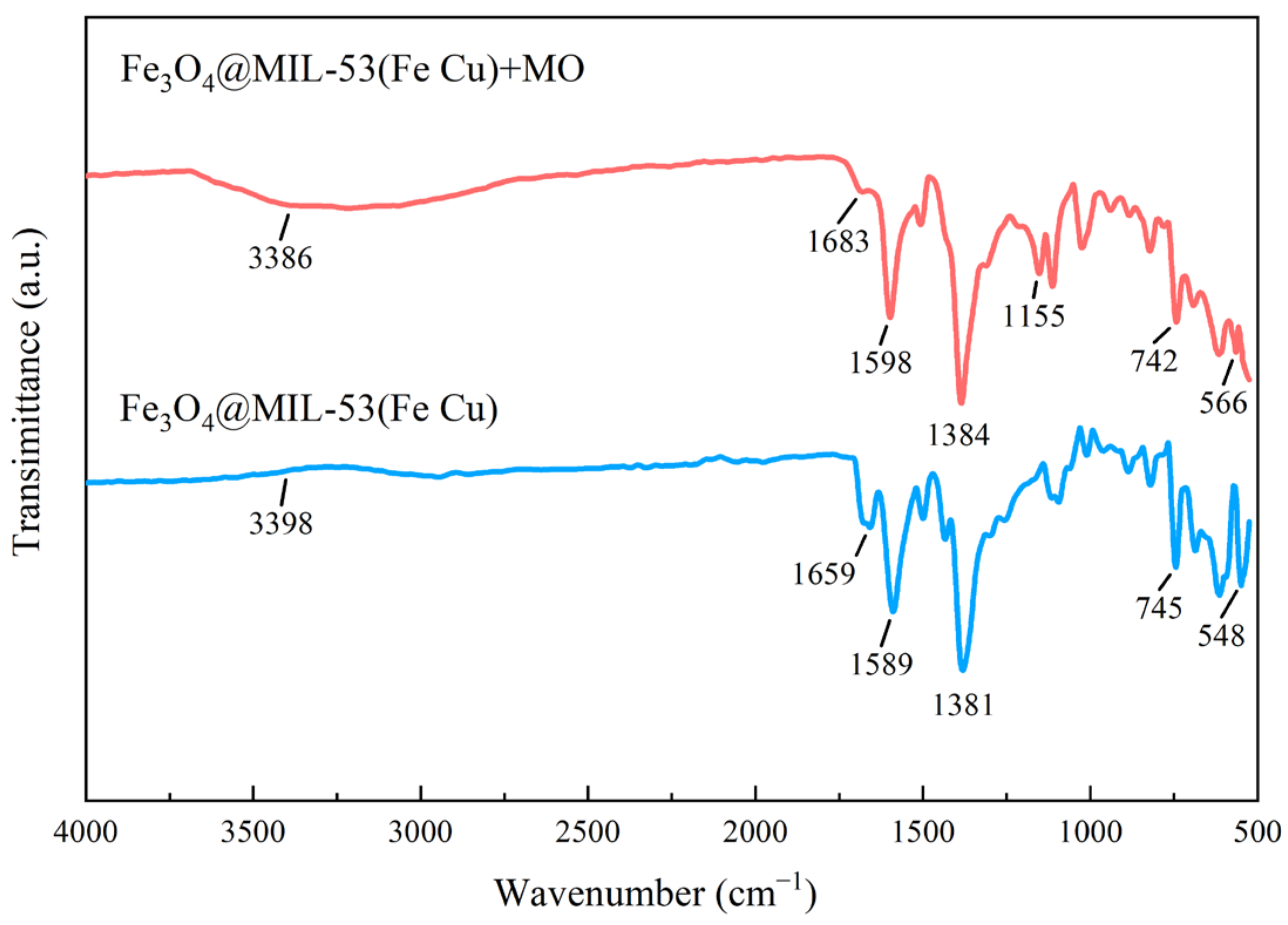
3.3.2. FTIR Analysis
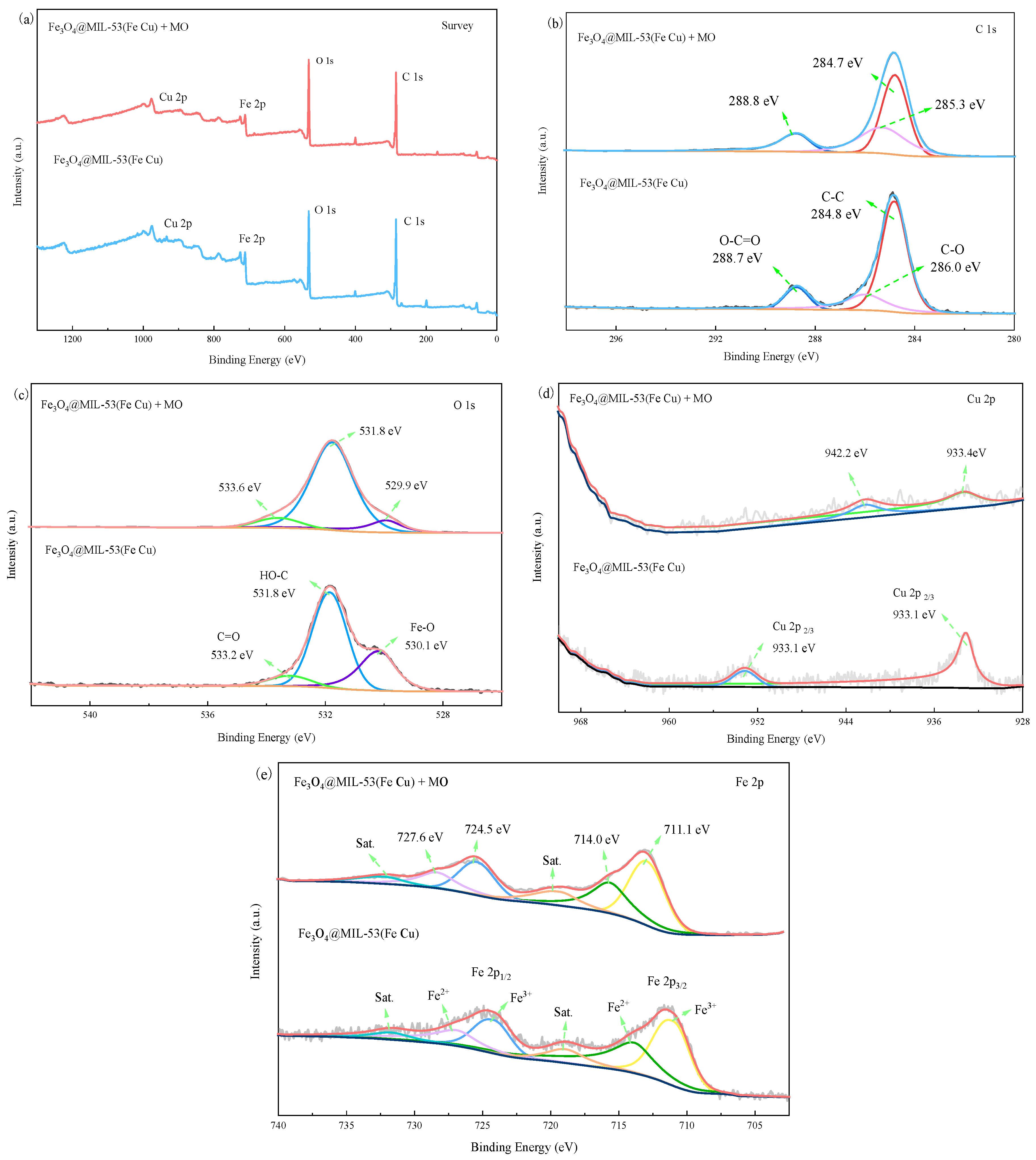
3.3.3. XPS Analysis
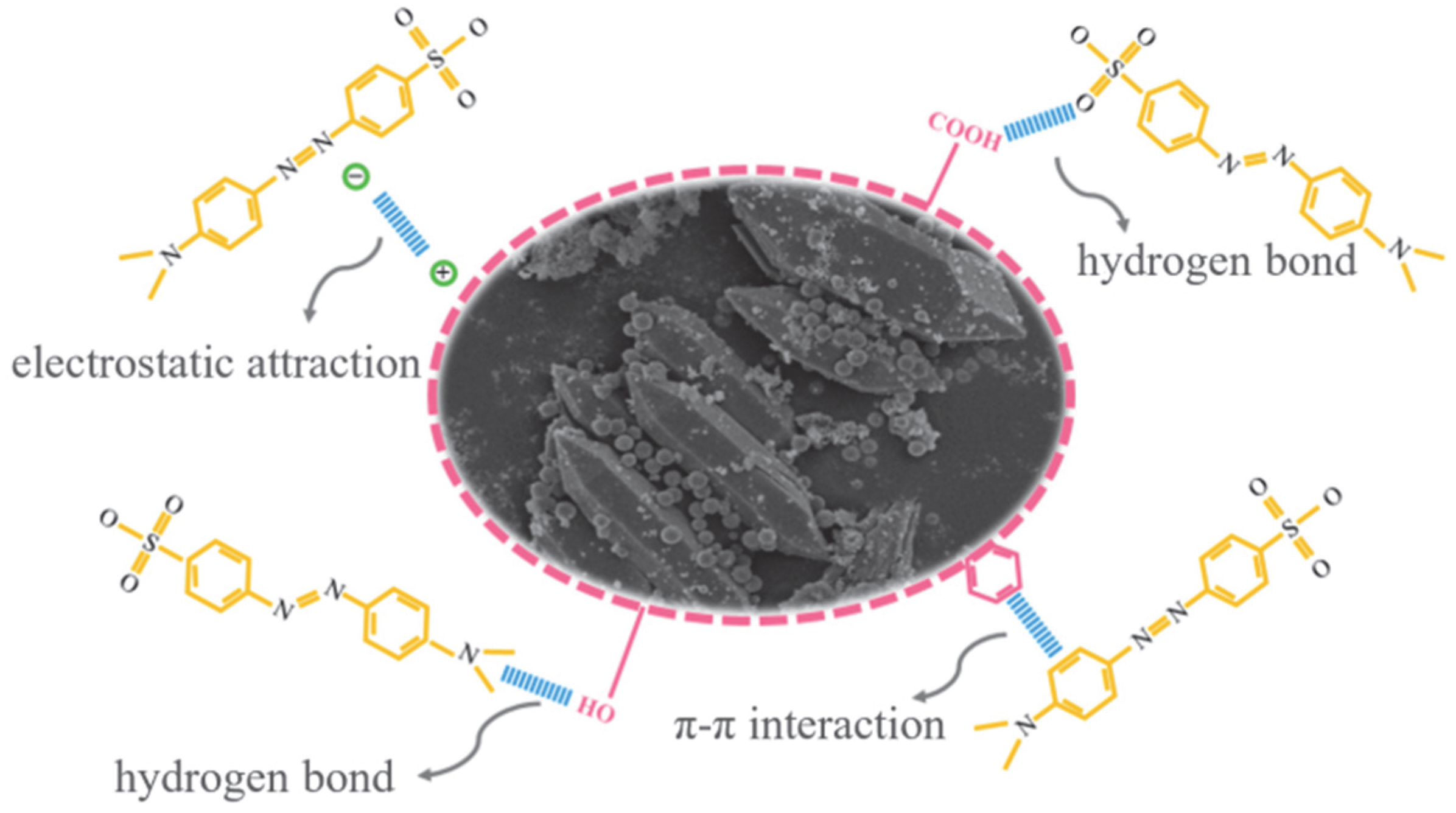
3.3.4. Adsorption Mechanism
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lellis, B.; Fávaro-Polonio, C.Z.; Pamphile, J.A.; Polonio, J.C. Effects of Textile Dyes on Health and the Environment and Bioremediation Potential of Living Organisms. Biotechnol. Res. Innov. 2019, 3, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, T.; Kahandawala, N.; Kaur, J.; Thounaojam, L.; Choudhary, I.; Bera, S. Bioremediation of Synthetic Dyes from Wastewater by Using Microbial Nanocomposites: An Emerging Field for Water Pollution Management. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2023, 51, 102767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zango, Z.U.; Binzowaimil, A.M.; Aldaghri, O.A.; Eisa, M.H.; Garba, A.; Ahmed, N.M.; Lim, J.W.; Ng, H.-S.; Daud, H.; Jumbri, K.; et al. Applications of Covalent Organic Frameworks for the Elimination of Dyes from Wastewater: A State-of-the-Arts Review. Chemosphere 2023, 343, 140223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tohamy, R.; Ali, S.S.; Li, F.; Okasha, K.M.; Mahmoud, Y.A.-G.; Elsamahy, T.; Jiao, H.; Fu, Y.; Sun, J. A Critical Review on the Treatment of Dye-Containing Wastewater: Ecotoxicological and Health Concerns of Textile Dyes and Possible Remediation Approaches for Environmental Safety. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandanshive, V.; Kadam, S.; Rane, N.; Jeon, B.-H.; Jadhav, J.; Govindwar, S. In Situ Textile Wastewater Treatment in High Rate Transpiration System Furrows Planted with Aquatic Macrophytes and Floating Phytobeds. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.; Kamran, M.; Khan, S.A.; Shaheen, K.; Shah, Z.; Suo, H.; Khan, Q.; Shah, A.B.; Rehman, W.U.; Al-Ghamdi, Y.O.; et al. Adsorption, Kinetics and Thermodynamics Studies of Methyl Orange Dye Sequestration through Chitosan Composites Films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.S.; Joshiba, G.J.; Femina, C.C.; Varshini, P.; Priyadharshini, S.; Karthick, M.S.A.; Jothirani, R. A Critical Review on Recent Developments in the Low-Cost Adsorption of Dyes from Wastewater. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 172, 395–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwuozor, K.O.; Ighalo, J.O.; Emenike, E.C.; Ogunfowora, L.A.; Igwegbe, C.A. Adsorption of Methyl Orange: A Review on Adsorbent Performance. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 4, 100179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Mei, Y.; Pan, B. Treatment of Reverse-Osmosis Concentrate of Printing and Dyeing Wastewater by Electro-Oxidation Process with Controlled Oxidation-Reduction Potential (ORP). Chemosphere 2018, 201, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, Z.; Chen, J.; Ma, J.; Ying, J.; Cui, S.; Yu, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jia, Y. Lead-Free Sodium Niobate Nanowires with Strong Piezo-Catalysis for Dye Wastewater Degradation. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 11703–11708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugai, D.Y.; Benincá, C.; Zanoelo, E.F. Electrogenerated Iron-Based Adsorbents: A Case Study of an Azo Dye Removal Viewed from a Fundamental Physico-Chemical Perspective. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavi, N.; Kazemi, A.S.; Bonakdarpour, B. The Development of Aerobic Granules from Conventional Activated Sludge under Anaerobic-Aerobic Cycles and Their Adaptation for Treatment of Dyeing Wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 312, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acedo-Mendoza, A.G.; Infantes-Molina, A.; Vargas-Hernández, D.; Chávez-Sánchez, C.A.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Tánori-Córdova, J.C. Photodegradation of Methylene Blue and Methyl Orange with CuO Supported on ZnO Photocatalysts: The Effect of Copper Loading and Reaction Temperature. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2020, 119, 105257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Adsorption Performance and Mechanism of Iron-Loaded Biochar to Methyl Orange in the Presence of Cr6+ from Dye Wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Shen, L.; Lin, H.; Yu, W.; Xu, Y.; Li, R.; Huang, L. Facile Preparation of Recyclable Magnetic Ni@filter Paper Composite Materials for Efficient Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl Orange. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 582, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, K.U.; Singh, R.; Baruah, I.; Choudhury, H.; Sharma, M.R. Equilibrium and Kinetics Modeling of Fluoride Adsorption onto Activated Alumina, Alum and Brick Powder. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 7, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Li, J.; Cao, X.; Xie, F.; Yang, H.; Wang, C.; Bittencourt, C.; Li, W. Regenerated Cellulose/Chitosan Composite Aerogel with Highly Efficient Adsorption for Anionic Dyes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 244, 125067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, S.; Das, R. Strong Adsorption of CV Dye by Ni Ferrite Nanoparticles for Waste Water Purification: Fits Well the Pseudo Second Order Kinetic and Freundlich Isotherm Model. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 16199–16215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lan, J.; Bo, C.; Gong, B.; Ou, J. Adsorption of Heavy Metal onto Biomass-Derived Activated Carbon. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 4275–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrich, J.R. Activated Carbon Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, M.; Yu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Dong, L.; Zan, Q.; Li, R. Heavy Metal Adsorption with Zeolites: The Role of Hierarchical Pore Architecture. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.A.; Najam, T.; Shahzad, K.; Wattoo, M.A.; Hussain, T.; Tufail, M.K.; Shah, S.S.A.; ur Rehman, A. Heterointerface Engineering of Water Stable ZIF-8@ ZIF-67: Adsorption of Rhodamine B from Water. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 34, 102324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Jin, W.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, Y. Adsorption Behavior of Arsenicals on MIL-101 (Fe): The Role of Arsenic Chemical Structures. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 554, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Cheng, R.; Wang, J. Adsorption of Diclofenac from Aqueous Solution Using UiO-66-Type Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Chu, M.; Dong, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, P.; Qu, D.; Duan, J.; Li, X. MOF(Ni)/CNT Composites with Layer Structure for High Capacitive Performance. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 643, 128802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, S.; Yang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis of TiO2/MOF-801(Zr) by a Wet Impregnation at Room Temperature for Highly Efficient Photocatalytic Reduction of Cr(VI). Solid State Sci. 2022, 129, 106912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, G.; Wu, H.; Chen, H.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Y.; Tan, S.; Yang, L.; et al. A Review of Metal Organic Framework (MOFs)-Based Materials for Antibiotics Removal via Adsorption and Photocatalysis. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Xie, Y.; Guo, X.; Sun, D. Self-Supporting Electrochemical Sensors for Monitoring of Cell-Released H2O2 Based on Metal Nanoparticle/MOF Nanozymes. Microchem. J. 2022, 181, 107715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Chen, Y.; Dong, X.; Huang, H. Simultaneous Voltammetric Determination of Dopamine and Uric Acid Based on MOF-235 Nanocomposite. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 142, 109584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Wu, H.; Wen, X.; Zhang, J.; Tang, H.; Deng, Y.; Liao, S.; Tian, X. Recent Advances in MOFs/MOF Derived Nanomaterials toward High-Efficiency Aqueous Zinc Ion Batteries. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 468, 214642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jin, L.; Zhou, L.; Du, X. A Molecular Study of Humid CO2 Adsorption Capacity by Mg-MOF-74 Surfaces with Ligand Functionalization. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2022, 209, 111407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyamparambil, V.J.; Kandasubramanian, B. A Mini-Review on the Recent Advancement of Electrospun MOF-Derived Nanofibers for Energy Storage. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 11, 100355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, E.; Sert, E.; Atalay, F.S. Synthesis, Characterization of a Metal Organic Framework: MIL-53 (Fe) and Adsorption Mechanisms of Methyl Red onto MIL-53 (Fe). J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 65, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, T.; Jia, M.; Yang, J.; Zhao, P.; Cai, K.; Ma, W.; Huang, Y. Resin Modified MIL-53 (Fe) MOF for Improvement of Photocatalytic Performance. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 203, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.A.; Najam, T.; Jabeen, S.; Wattoo, M.A.; Bashir, M.S.; Shah, S.S.A.; ur Rehman, A. Facile Synthesis of Tri-Metallic Layered Double Hydroxides (NiZnAl-LDHs): Adsorption of Rhodamine-B and Methyl Orange from Water. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 145, 110008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Li, Y.; Du, Q.; Chen, B.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, S.; Jing, Z.; et al. Efficient Adsorption of Congo Red by MIL-53(Fe)/Chitosan Composite Hydrogel Spheres. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2023, 348, 112404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Li, M.; Fu, J.; Wang, Y.; Muhammad, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Z. Construction of Cu-Bridged Cu2O/MIL(Fe/Cu) Catalyst with Enhanced Interfacial Contact for the Synergistic Photo-Fenton Degradation of Thiacloprid. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 395, 125184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, B.; Salari, D.; Zarei, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetic Fe3O4@SiO2-MIL-53(Fe) Metal-Organic Framework and Its Application for Efficient Removal of Arsenate from Surface and Groundwater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.M.; Emran, K.M.; Alrashedee, F.M.M. Removal of Organic Pollutants by Lanthanide-Doped MIL-53 (Fe) Metal–Organic Frameworks: Effect of Dopant Type in Magnetite Precursor. J. Rare Earths 2023, 41, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Zhu, L.; Tao, X.; Wang, X. One-Step Fabrication of Novel MIL-53(Fe, Al) for Synergistic Adsorption-Photocatalytic Degradation of Tetracycline. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 133032. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised Effective Ionic Radii and Systematic Studies of Interatomic Distances in Halides and Chalcogenides. Found. Crystallogr. 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Bakhtari, M.F.; Luo, J. Preparation of GO/MIL-101(Fe,Cu) Composite and Its Adsorption Mechanisms for Phosphate in Aqueous Solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 51391–51403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.K.; Zayed, M.A.; El-dek, S.I.; Hady, M.A.; El Sherbiny, D.H.; Uskoković, V. Nanofibrous ε-Polycaprolactone Scaffolds Containing Ag-Doped Magnetite Nanoparticles: Physicochemical Characterization and Biological Testing for Wound Dressing Applications in Vitro and in Vivo. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2070–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hou, F.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; Yang, Y. A Strawsheave-like Metal Organic Framework Ce-BTC Derivative Containing High Specific Surface Area for Improving the Catalytic Activity of CO Oxidation Reaction. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 259, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.V.; Cao, V.D.; Nguyen, V.H.; Hoang, B.N.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Nguyen, T.D.; Bach, L.G. MIL-53 (Fe) Derived Magnetic Porous Carbon as a Robust Adsorbent for the Removal of Phenolic Compounds under the Optimized Conditions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 102902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yuan, X.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H.; Zeng, G. Highly Efficient As(III) Removal through Simultaneous Oxidation and Adsorption by N-CQDs Modified MIL-53(Fe). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 286, 120409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xiong, W.; Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Cao, J.; Jia, M.; Xu, R.; Zhang, Y. Functionalized MIL-53(Fe) as Efficient Adsorbents for Removal of Tetracycline Antibiotics from Aqueous Solution. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 290, 109642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, X.; Liang, X.; Lei, C.; Wei, Y.; He, P.; Lv, B.; Ma, H.; Lei, Z. MIL-53(Fe)-Graphene Nanocomposites: Efficient Visible-Light Photocatalysts for the Selective Oxidation of Alcohols. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 198, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.; Yue, Y.; Yang, P. Interface Effect in MIL-53(Fe)/Metal-Phenolic Network (Ni, Co, and Mn) Nanoarchitectures for Efficient Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 608, 155184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, B.S.; Dasgupta, S. Effect of Time, pH, and Temperature on Kinetics for Adsorption of Methyl Orange Dye into the Modified Nitrate Intercalated MgAl LDH Adsorbent. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 137, 109203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Aldrich, C.; Eksteen, J.J.; Arrigan, D.W.M. Removal of Arsenic from Alkaline Process Waters of Gold Cyanidation by Use of γ-Fe2O3@ ZrO2 Nanosorbents. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 174, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, D.-D.; Chen, M.; Cao, Y.-W.; Zhuang, L.-Y.; Lu, Z.-H.; Yang, Z.-H. Adsorption Behavior of Azole Fungicides on Polystyrene and Polyethylene Microplastics. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmoubarki, R.; Boumya, W.; Mahjoubi, F.Z.; Elhalil, A.; Sadiq, M.; Barka, N. Ni-Fe-SDS and Ni-Fe-SO4 Layered Double Hydroxides: Preparation, Characterization and Application in Dyes Removal. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 37, 3871–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.A.; Khan, N.A.; Cheng, C.; Shah, S.S.A.; Najam, T.; Arshad, M.; Sharif, A.; Akhtar, S.; ur Rehman, A. Surface Induced Growth of ZIF-67 at Co-Layered Double Hydroxide: Removal of Methylene Blue and Methyl Orange from Water. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 190, 105564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.A.; Najam, T.; Zarin, K.; Shahzad, K.; Javed, M.S.; Jamshaid, M.; Bashir, M.A.; Shah, S.S.A.; Rehman, A.U. Enhanced Adsorption Removal of Methyl Orange from Water by Porous Bimetallic Ni/Co MOF Composite: A Systematic Study of Adsorption Kinetics. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 103, 4841–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jia, M.; Yao, J. Acid-Promoted Synthesis of UiO-66 for Highly Selective Adsorption of Anionic Dyes: Adsorption Performance and Mechanisms. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 499, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Song, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.-F.; Hao, D.; Feng, Y.; Yao, J. Lightweight UiO-66/Cellulose Aerogels Constructed through Self-Crosslinking Strategy for Adsorption Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, P.; Dai, X.; Guan, H.; Wang, X. Carboxylated Lamellar Wood Sponge Enables High Loading and Uniform Dispersion of MIL-53(Al) for Efficient Organic Dye Adsorption. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 356, 123400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Zheng, D.; Mo, Z.; Dong, R.; Qiu, X. Magnetic Lignin-Based Carbon Nanoparticles and the Adsorption for Removal of Methyl Orange. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 559, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.-W.; Liu, J.-M.; Ma, H.; Wang, Z.-H.; Li, C.-Y.; Zhao, N.; Wang, S. Simultaneous Adsorption of Methyl Orange and Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution Using Amino Functionalized Zr-Based MOFs. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 282, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tian, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, N.; Mi, S.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Z. Enhanced Dyes Adsorption from Wastewater via Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Functionalized Activated Carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Xu, X.; Yu, X.; Yu, S.; Wang, S.; Qu, X. Bimetallic Organic Gel for Effective Methyl Orange Dye Adsorption. Gels 2024, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Gao, Y.; El-Naggar, A.; Niazi, N.K.; Sun, C.; Shaheen, S.M.; Hou, D.; Yang, X.; Tang, Z.; Liu, Z. Enhanced Sorption of Trivalent Antimony by Chitosan-Loaded Biochar in Aqueous Solutions: Characterization, Performance and Mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Xu, C.; Li, N.; Rao, T.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, C.; Xu, S.; Tang, J. Synthesis of Bimetallic FeCu-MOF and Its Performance as Catalyst of Peroxymonosulfate for Degradation of Methylene Blue. Materials 2022, 15, 7252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
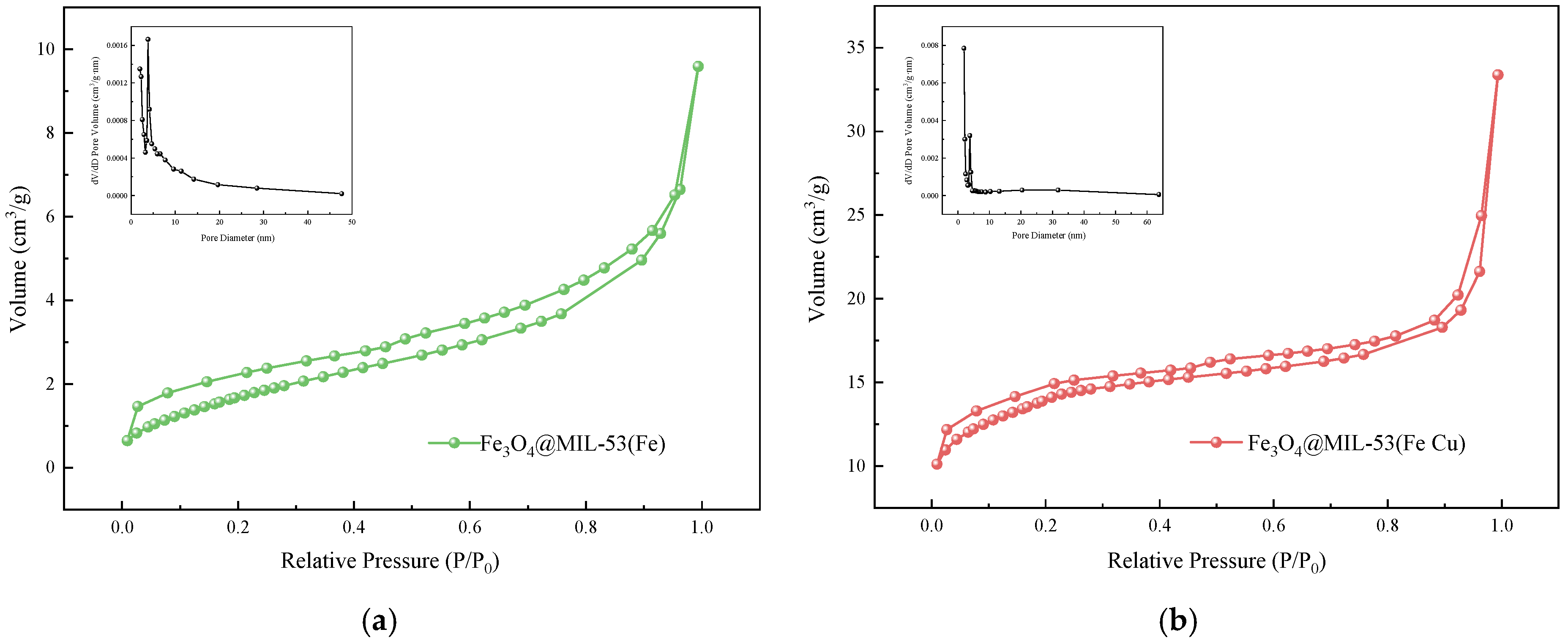
| Physical Property | Fe3O4@MIL-53(Fe) | Fe3O4@MIL-53(Fe Cu) |
|---|---|---|
| Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | 6.770 | 46.109 |
| Average Pore Fiameter (nm) | 9.174 | 10.352 |
| Micropore Volume (cm3/g) | 0.0008 | 0.020 |
| Pore Volume (cm3/g) | 0.015 | 0.052 |
| Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | Elovich |
|---|---|---|
| = 143.566 mg/g | = 148.425 mg/g | = 1,264,413.579 mg/mg.min |
| = 0.256 min−1 | = 0.004 g·mg−1·min−1 | = 0.115 g/mg |
| = 0.980 | = 0.998 | = 0.989 |
| T(K) | Langmuir | Freundlich | Dubinin–Radushkevich |
|---|---|---|---|
| 298.15 | = 154.417 mg/g = 0.237 L/mg = 0.889 | = 59.452 mg/g = 0.202 = 0.973 | = 7.353 × 10−7 mol2/J2 |
| = 4.908 mg/g | |||
| = 0.825 kJ/mol | |||
| = 0.675 | |||
| 308.15 | = 172.500 mg/g = 0.105 L/mg = 0.915 | = 68.553 mg/g = 0.199 = 0.991 | = 4.818 × 10−8 mol2/J2 |
| = 5.008 mg/g | |||
| = 1.019 kJ/mol | |||
| = 0.634 | |||
| 318.15 | = 193.647 mg/g = 0.113 L/mg = 0.899 | = 73.429 mg/g = 0.215 = 0.998 | = 2.432 × 10−8 mol2/J2 |
| = 5.080 mg/g | |||
| = 1.434 kJ/mol | |||
| = 0.585 |
| T(K) | ΔS (kJ/mol) | ΔH (kJ/mol) | ΔG (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 298.15 | 0.047 | 13.886 | −0.025 |
| 308.15 | −0.491 | ||
| 318.15 | −0.958 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Yue, X.; He, T.; Wang, C. Mechanistic Study of Methyl Orange Removal by Fe3O4@MIL-53(Fe Cu) Composite Material. Water 2025, 17, 2980. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202980
Yang X, Yue X, He T, Wang C. Mechanistic Study of Methyl Orange Removal by Fe3O4@MIL-53(Fe Cu) Composite Material. Water. 2025; 17(20):2980. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202980
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xiuzhen, Xiaochen Yue, Tianjiao He, and Changye Wang. 2025. "Mechanistic Study of Methyl Orange Removal by Fe3O4@MIL-53(Fe Cu) Composite Material" Water 17, no. 20: 2980. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202980
APA StyleYang, X., Yue, X., He, T., & Wang, C. (2025). Mechanistic Study of Methyl Orange Removal by Fe3O4@MIL-53(Fe Cu) Composite Material. Water, 17(20), 2980. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202980





