Evaluating Disinfection Performance and Energy Efficiency of a Dual-Wavelength UV-LED Flow-Through Device for Point-of-Use Water Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganisms Preparation and Enumeration
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. UV Irradiation
2.4. UV-LED Flow-Through System Inactivation Tests
2.5. Specific Energy Consumption
3. Results and Discussion
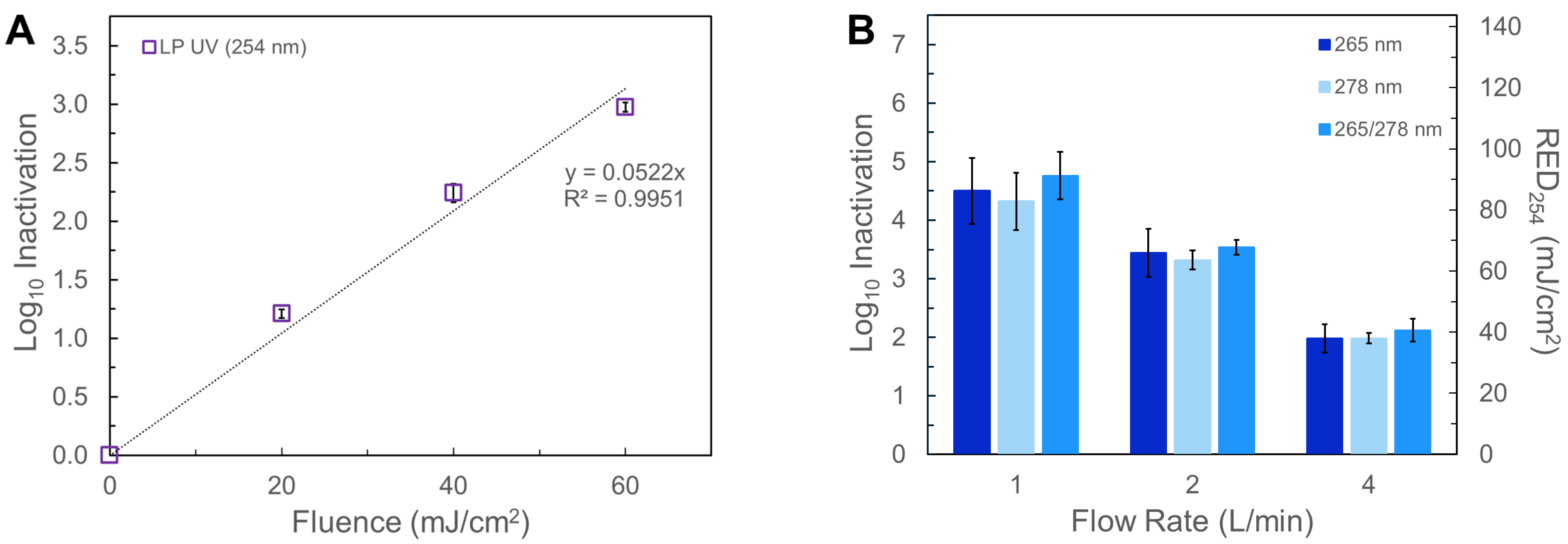
3.1. Biodosimetry and Fluence Estimation
3.2. Inactivation of HPC Bacteria and E. coli
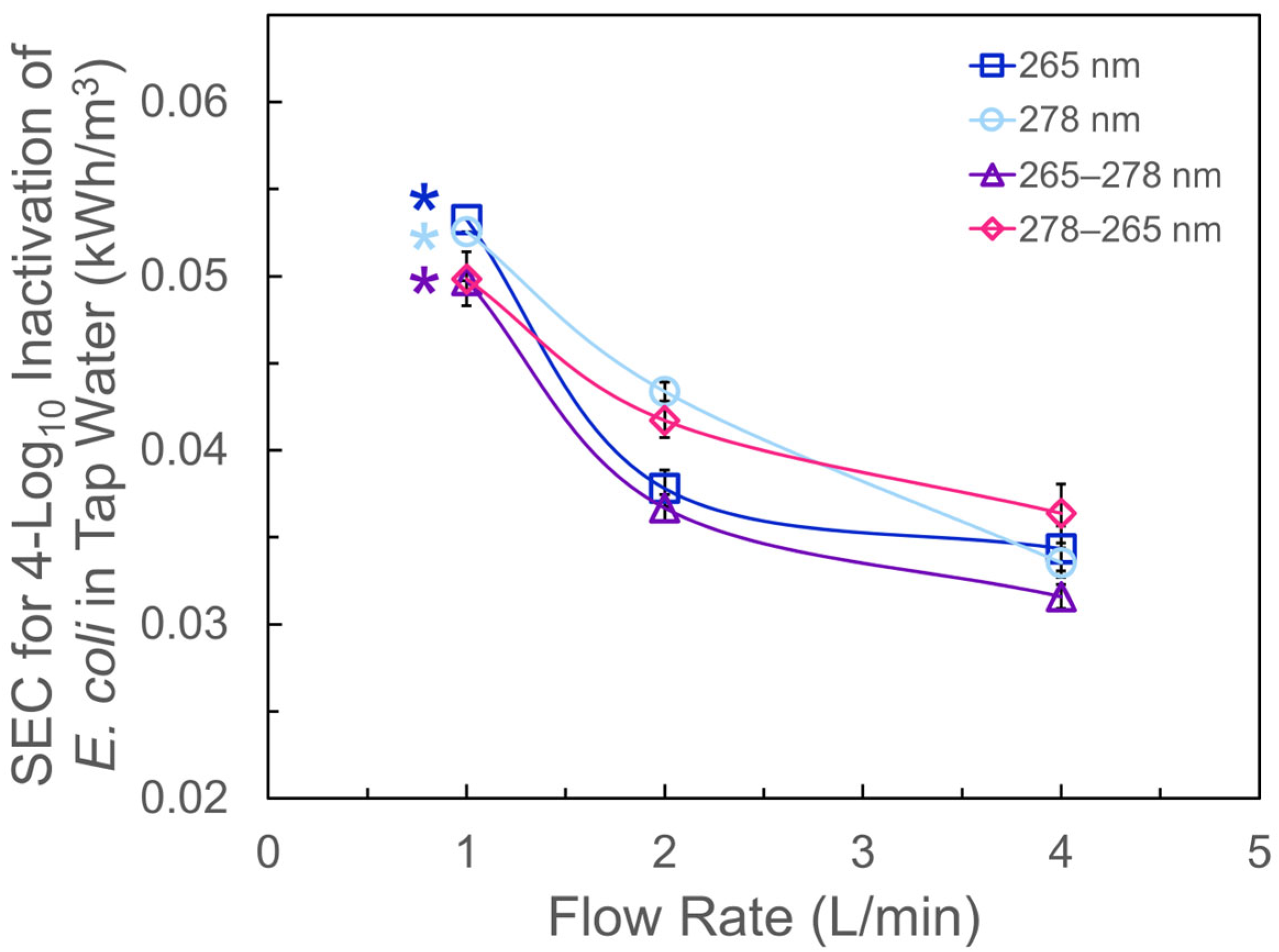
3.3. Specific Energy Consumption and Implication
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gomez-Alvarez, V.; Ryu, H.; McNeely, M.; Muhlen, C.; Williams, D.; Lytle, D.; Boczek, L. Vertical stratification of the water microbiome in an electric water heater tank: Implications for premise plumbing opportunistic pathogens. J. Water Health 2024, 22, 2346–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Alvarez, V.; Ryu, H.; Tang, M.; Mcneely, M.; Muhlen, C.; Urbanic, M.; Williams, D.; Lytle, D.; Boczek, L. Assessing residential activity in a home plumbing system simulator: Monitoring the occurrence and relationship of major opportunistic pathogens and phagocytic amoebas. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1260460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, E.; Hinds, J.; Hai, F.I. Causes, Factors, and Control Measures of Opportunistic Premise Plumbing Pathogens-A Critical Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, C.; Ross, K.E.; Brown, M.H.; Bentham, R.; Whiley, H. The Presence of Opportunistic Premise Plumbing Pathogens in Residential Buildings: A Literature Review. Water 2022, 14, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Point-of-Use or Point-of-Entry Treatment Options for Small Drinking Water Systems; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2006.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Ultraviolet Disinfection Guidance Manual for the Final Long Term 2 Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2006.
- Hijnen, W.A.; Beerendonk, E.F.; Medema, G.J. Inactivation credit of UV radiation for viruses, bacteria and protozoan (oo)cysts in water: A review. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barstow, C.K.; Dotson, A.D.; Linden, K.G. Assessing point-of-use ultraviolet disinfection for safe water in urban developing communities. J. Water Health 2014, 12, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Mohseni, M.; Taghipour, F. Application of ultraviolet light-emitting diodes (UV-LEDs) for water disinfection: A review. Water Res. 2016, 94, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Loeb, S.; Kim, J.H. LED revolution: Fundamentals and prospects for UV disinfection applications. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2017, 3, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, K.Y.; McMartin, D.W.; Yost, C.K.; Runtz, K.J.; Ono, T. Point-of-use water disinfection using UV light-emitting diodes to reduce bacterial contamination. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5441–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montazeri, M.M.; Hejazi, S.A.; Taghipour, F. Ultraviolet light-emitting diode (UV-LED) water disinfection photoreactors: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 386, 125678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Sómer, M.; Pablos, C.; Adán, C.; van Grieken, R.; Marugán, J. A review on LED technology in water photodisinfection. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 885, 163963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Sangsanont, J.; Woo, H.; Boczek, L.A.; Linden, K.G.; Ryu, H. Inactivation efficacy and mechanisms of wavelength-specific UV sources for various strains of Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguma, K.; Rattanakul, S.; Masaike, M. Inactivation of health-related microorganisms in water using UV light-emitting diodes. Water Supply 2019, 19, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilhunen, S.; Sarkka, H.; Sillanpaa, M. Ultraviolet light-emitting diodes in water disinfection. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2009, 16, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattanakul, S.; Oguma, K. Inactivation kinetics and efficiencies of UV-LEDs against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Legionella pneumophila, and surrogate microorganisms. Water Res. 2018, 130, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, H.; Beck, S.E.; Boczek, L.A.; Carlson, K.M.; Brinkman, N.E.; Linden, K.G.; Lawal, O.R.; Hayes, S.L.; Ryu, H. Efficacy of Inactivation of Human Enteroviruses by Dual-Wavelength Germicidal Ultraviolet (UV-C) Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). Water 2019, 11, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Q.; Wang, W.L.; Huo, Z.Y.; Lu, Y.; Hu, H.Y. Comparison of UV-LED and low pressure UV for water disinfection: Photoreactivation and dark repair of Escherichia coli. Water Res. 2017, 126, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholtes, K.; Linden, K.G. Pulsed and continuous light UV LED: Microbial inactivation, electrical, and time efficiency. Water Res. 2019, 165, 114965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Mohseni, M.; Taghipour, F. Mechanisms investigation on bacterial inactivation through combinations of UV wavelengths. Water Res. 2019, 163, 114875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Taghipour, F.; Mohseni, M. Microorganisms inactivation by wavelength combinations of ultraviolet light-emitting diodes (UV-LEDs). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betzalel, Y.; Gerchman, Y.; Cohen-Yaniv, V.; Mamane, H. Multiwell plates for obtaining a rapid microbial dose-response curve in UV-LED systems. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2020, 207, 111865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, S.E.; Ryu, H.; Boczek, L.A.; Cashdollar, J.L.; Jeanis, K.M.; Rosenblum, J.S.; Lawal, O.R.; Linden, K.G. Evaluating UV-C LED disinfection performance and investigating potential dual-wavelength synergy. Water Res. 2017, 109, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterley, C.; Linden, K. Demonstration and evaluation of germicidal UV-LEDs for point-of-use water disinfection. J. Water Health 2010, 8, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtele, M.A.; Kolbe, T.; Lipsz, M.; Kulberg, A.; Weyers, M.; Kneissl, M.; Jekel, M. Application of GaN-based ultraviolet-C light emitting diodes—UV LEDs—For water disinfection. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguma, K.; Kita, R.; Sakai, H.; Murakami, M.; Takizawa, S. Application of UV light emitting diodes to batch and flow-through water disinfection systems. Desalination 2013, 328, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenny, R.M.; Simmons, O.D.; Shatalov, M.; Ducoste, J.J. Modeling a continuous flow ultraviolet Light Emitting Diode reactor using computational fluid dynamics. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 116, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguma, K.; Kita, R.; Takizawa, S. Effects of Arrangement of UV Light-Emitting Diodes on the Inactivation Efficiency of Microorganisms in Water. Photochem. Photobiol. 2016, 92, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oguma, K.; Kanazawa, K.; Kasuga, I.; Takizawa, S. Effects of UV Irradiation by Light Emitting Diodes on Heterotrophic Bacteria in Tap Water. Photochem. Photobiol. 2018, 94, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.H.; Suwan, P.; Koottatep, T.; Beck, S.E. Application of a novel, continuous-feeding ultraviolet light emitting diode (UV-LED) system to disinfect domestic wastewater for discharge or agricultural reuse. Water Res. 2019, 153, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.P.; Chang, C.S.; Lin, W.C. Efficiency improvement of a flow-through water disinfection reactor using UV-C light emitting diodes. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.P.; Li, M.H.; Lo, C.L. Investigation of baffle configurations on the water disinfection efficiency using ultraviolet C light-emitting diodes. Environ. Technol. 2024, 45, 5359–5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.P.; Liao, J.Y. Effect of UV-C LED arrangement on the sterilization of in planar water disinfection reactors. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 56, 104399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarzfathy, M.; Hosoi, Y.; Oguma, K.; Taghipour, F. Experimental and computational evaluation of a flow-through UV-LED reactor for MS2 and adenovirus inactivation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 407, 127058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarzfathy, M.; Taghipour, F. Computational modeling of ultraviolet light-emitting diode (UV-LED) reactor for water treatment. Water Res. 2019, 166, 115022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Bae, J.; Park, S.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.; Yoon, C.; Ryu, C. Design optimization of a cylindrical UV-C LED reactor for effective water disinfection with numerical simulations and test reactor fabrication. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, H.Y.; Hall, J.S.; Hunter, G.L.; Goodrich, J.A. Differences in UV-C LED Inactivation of Legionella pneumophila Serogroups in Drinking Water. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.C.; Shang, X.; Cai, Q.Q.; Hu, J.Y. Lab- and pilot-scale evaluation of bacterial inactivation and reactivation influenced by UV-LEDs arrangements in continuous flow water disinfection reactors. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 55, 104093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.J.X.; Oguma, K. UV-LED-incorporated showerhead for point-of-use disinfection of drinking water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Method 1601: Male-Specific (F+) and Somatic Coliphage in Water by Two-Step Enrichment Procedure; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2001.
- Bolton, J.R.; Linden, K.G. Standardization of methods for fluence (UV dose) determination in bench-scale UV experiments. J. Environ. Eng. 2003, 129, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeOreo, W.B.; Mayer, P.; Dziegielewski, B.; Kiefer, J. Residential End Uses of Water, Version 2: Executive Report; Water Research Foundation: Denver, CO, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- United States Energy Information Administration. Average Price of Electricity to Ultimate Customers. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/electricity/annual/table.php?t=epa_02_04.html (accessed on 25 August 2025).
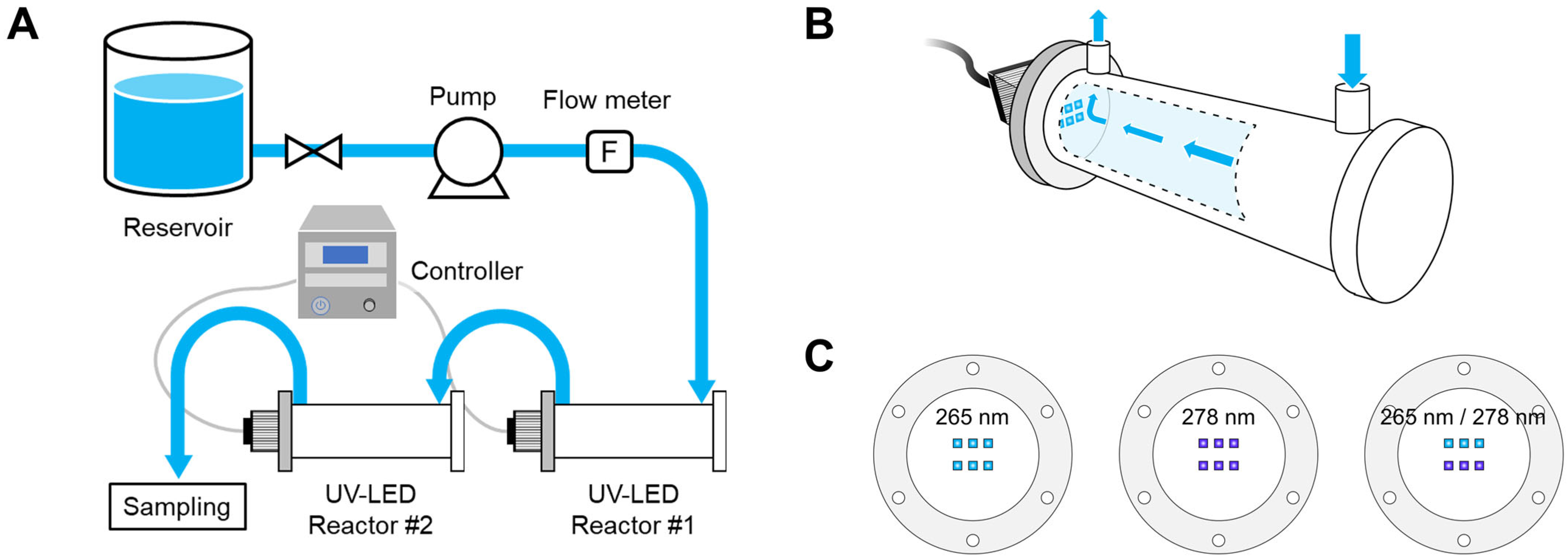
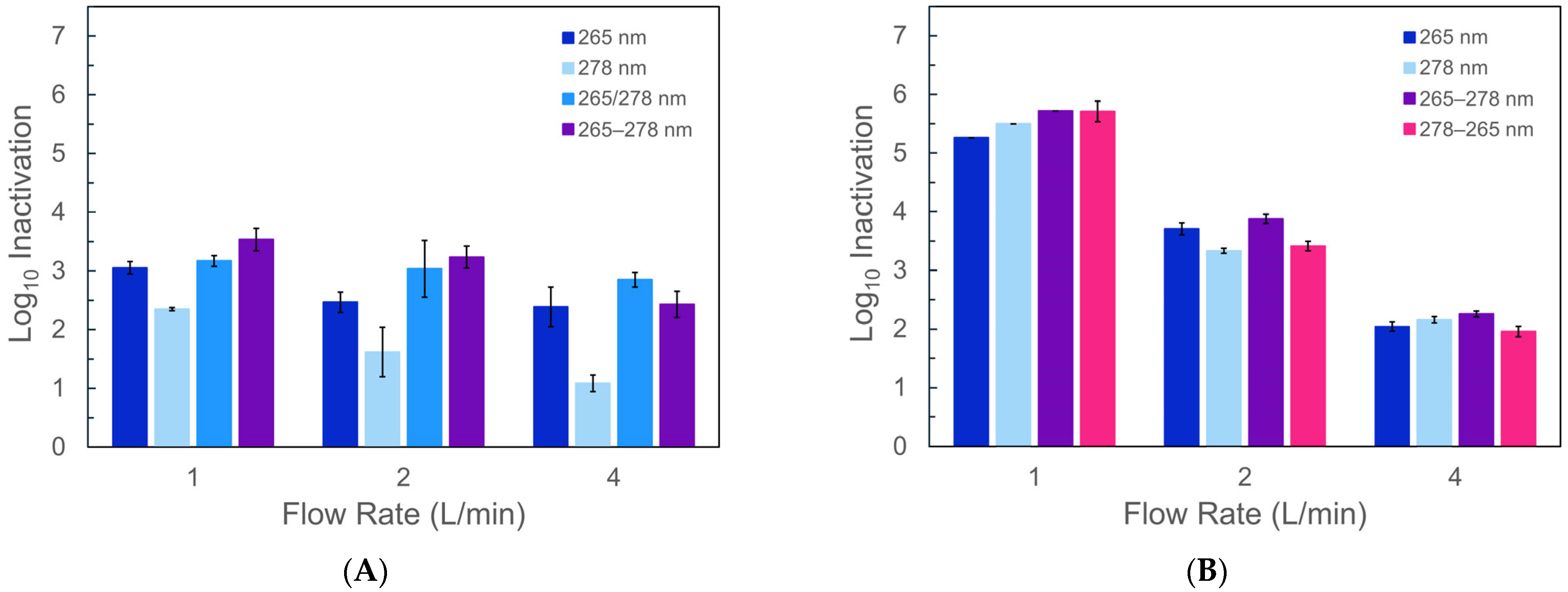
| Combination | Reactor #1 | Reactor #2 | Configuration Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 265 nm | 265 nm | Sequential single-wavelength |
| 2 | 278 nm | 278 nm | Sequential single-wavelength |
| 3 | 265 nm/278 nm | 265 nm/278 nm | Simultaneous dual-wavelength |
| 4-1 | 265 nm | 278 nm | Sequential dual-wavelength |
| 4-2 | 278 nm | 265 nm | Sequential dual-wavelength (reversed) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, Y.; Kim, H.-C.; Boczek, L.; Ryu, H. Evaluating Disinfection Performance and Energy Efficiency of a Dual-Wavelength UV-LED Flow-Through Device for Point-of-Use Water Treatment. Water 2025, 17, 2965. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202965
Oh Y, Kim H-C, Boczek L, Ryu H. Evaluating Disinfection Performance and Energy Efficiency of a Dual-Wavelength UV-LED Flow-Through Device for Point-of-Use Water Treatment. Water. 2025; 17(20):2965. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202965
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Yoontaek, Hyun-Chul Kim, Laura Boczek, and Hodon Ryu. 2025. "Evaluating Disinfection Performance and Energy Efficiency of a Dual-Wavelength UV-LED Flow-Through Device for Point-of-Use Water Treatment" Water 17, no. 20: 2965. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202965
APA StyleOh, Y., Kim, H.-C., Boczek, L., & Ryu, H. (2025). Evaluating Disinfection Performance and Energy Efficiency of a Dual-Wavelength UV-LED Flow-Through Device for Point-of-Use Water Treatment. Water, 17(20), 2965. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202965







