Long-Term Runoff Prediction Using Large-Scale Climatic Indices and Machine Learning Model in Wudongde and Three Gorges Reservoirs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
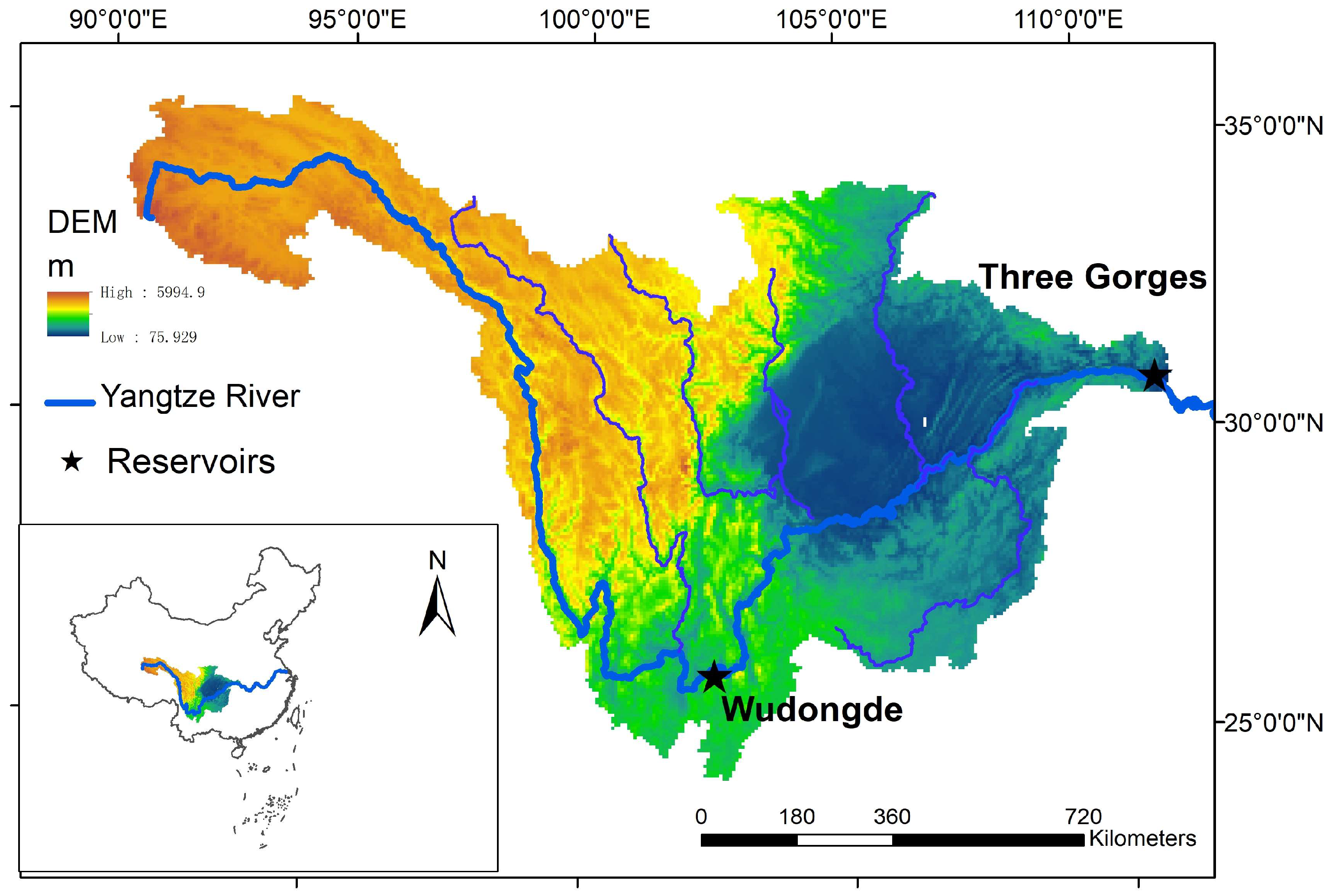
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
3. Methodology
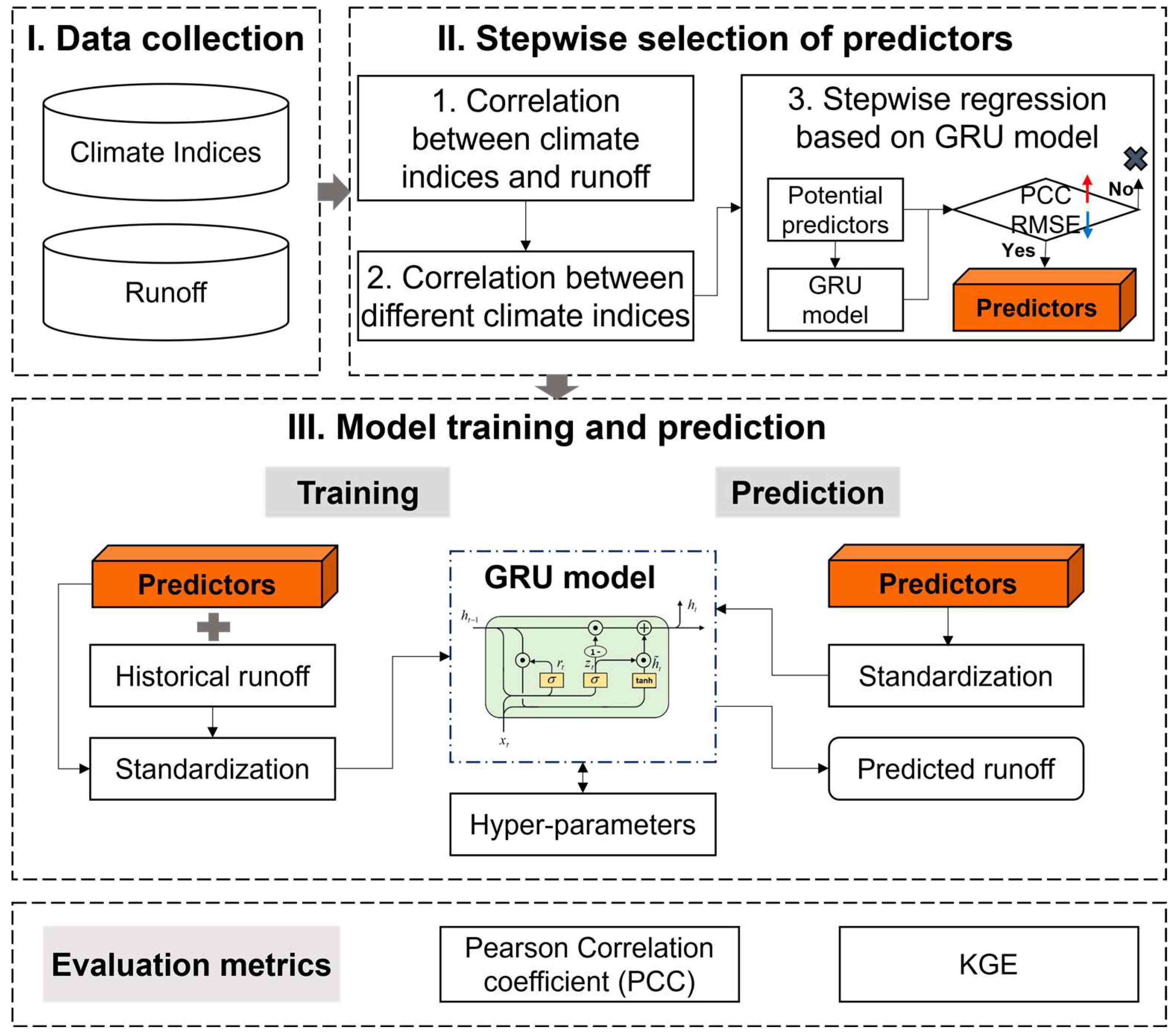
3.1. The Framework of Runoff Prediction
3.2. Stepwise Selection of Predictors
3.3. Model Training and Prediction
3.4. Model Evaluation Metrics
4. Results and Discussion
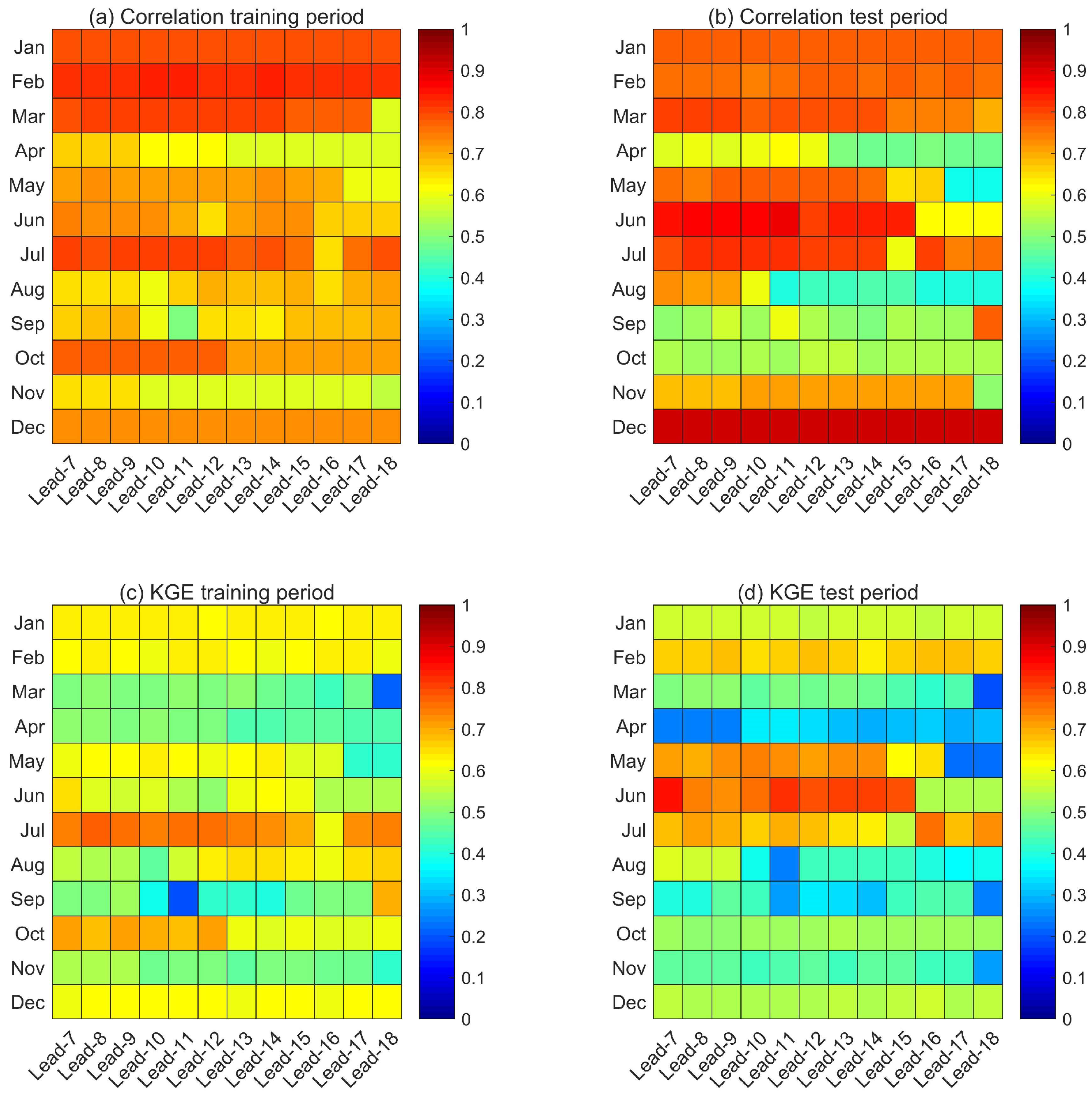
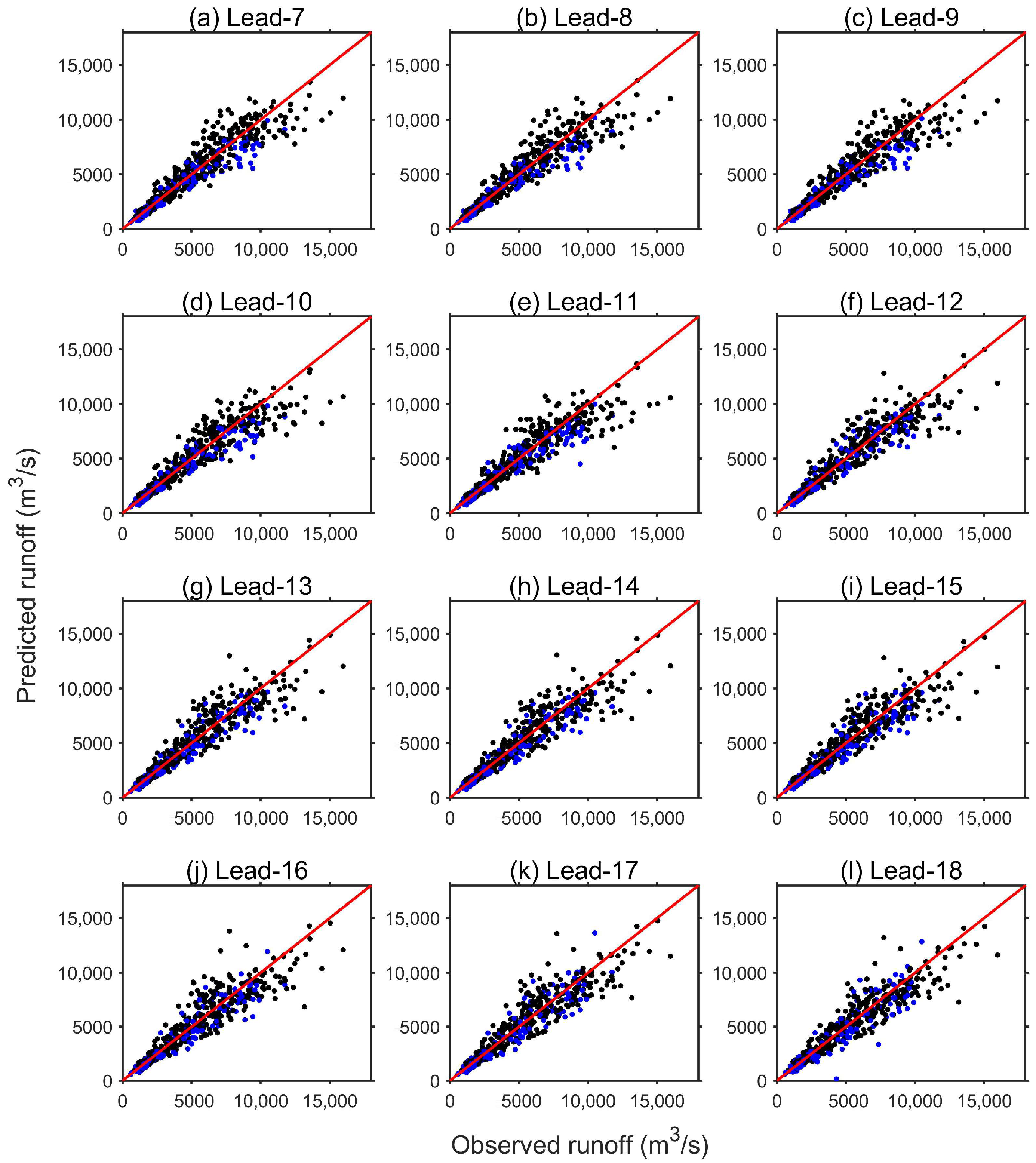
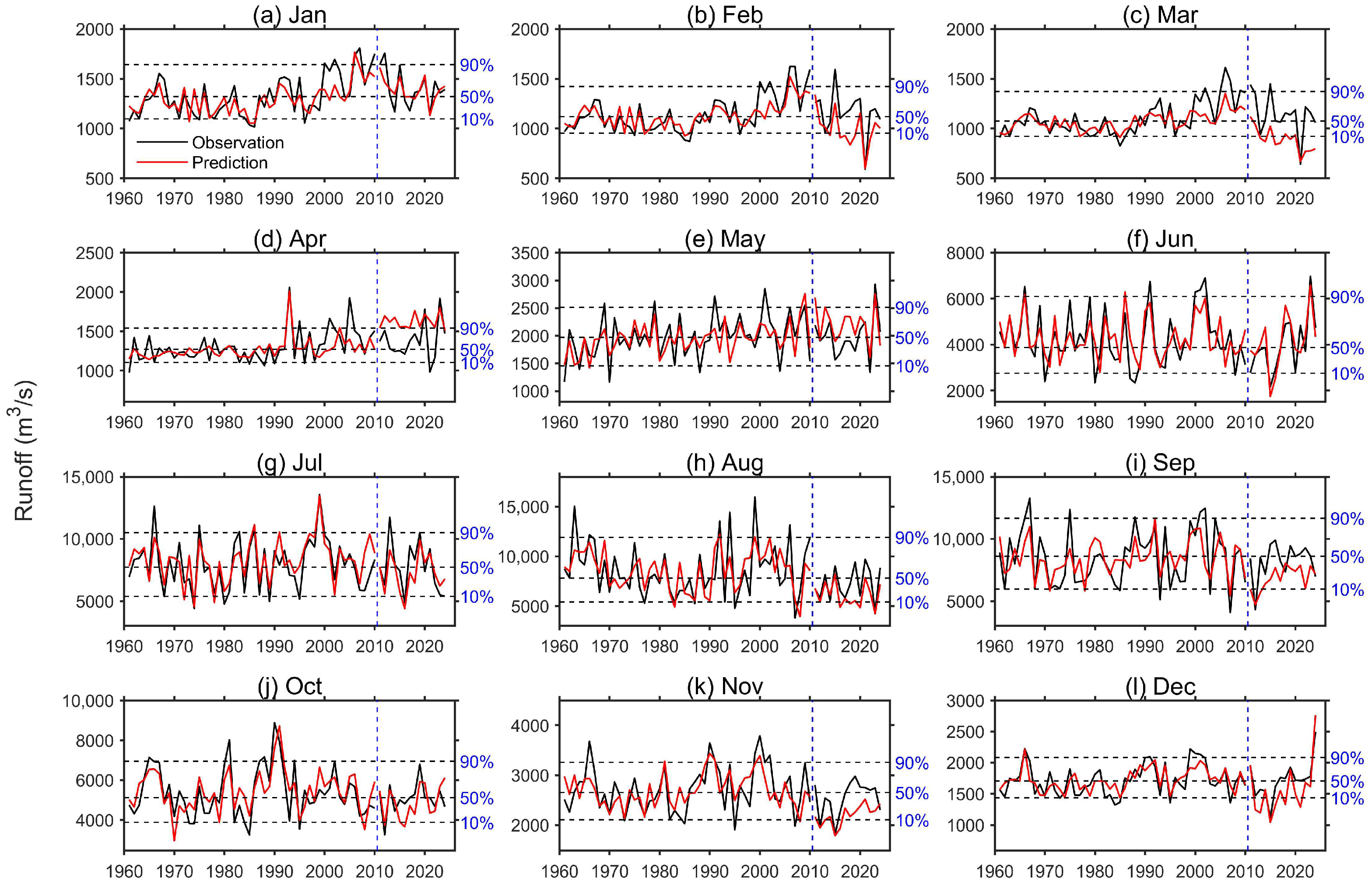
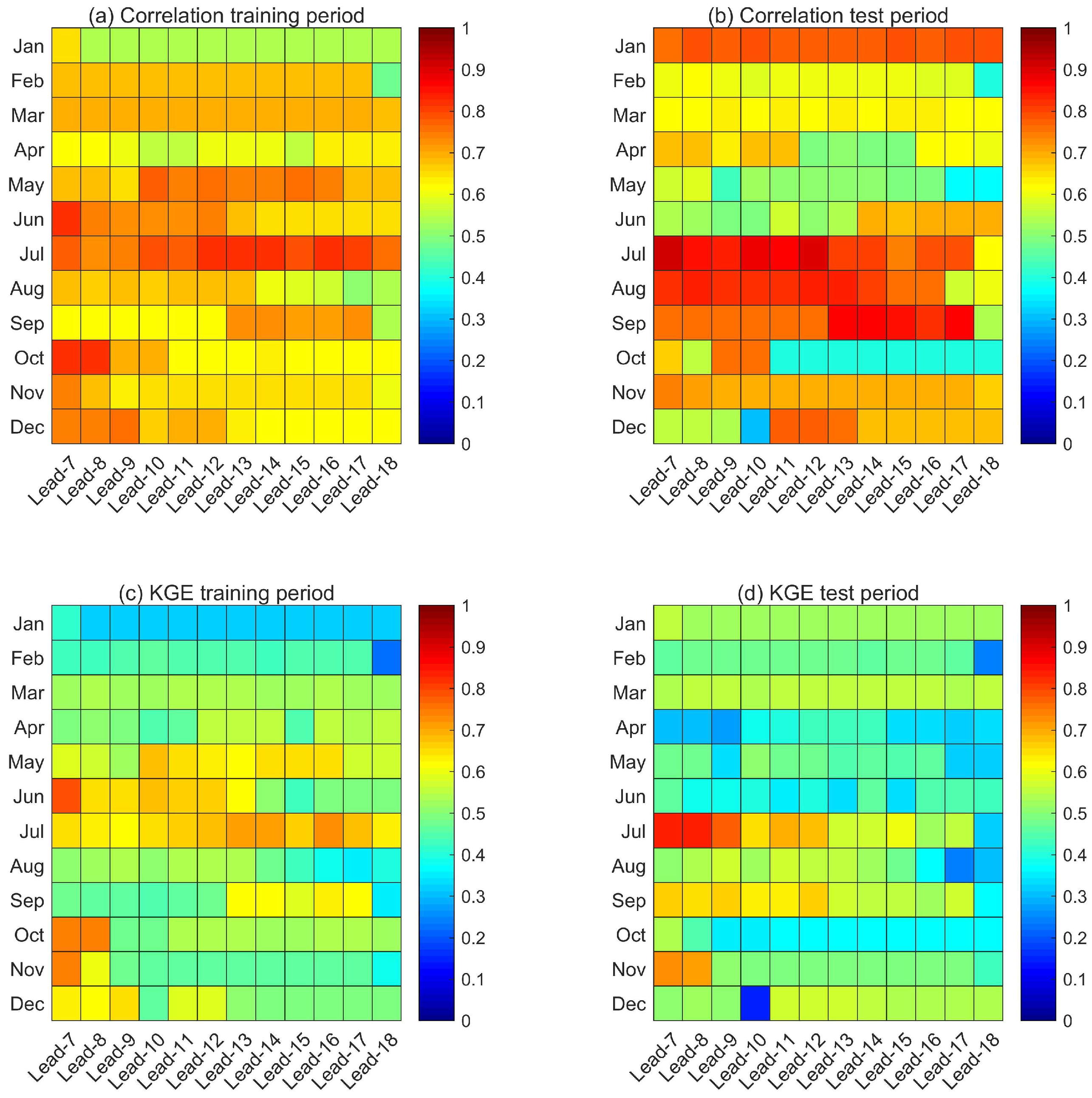
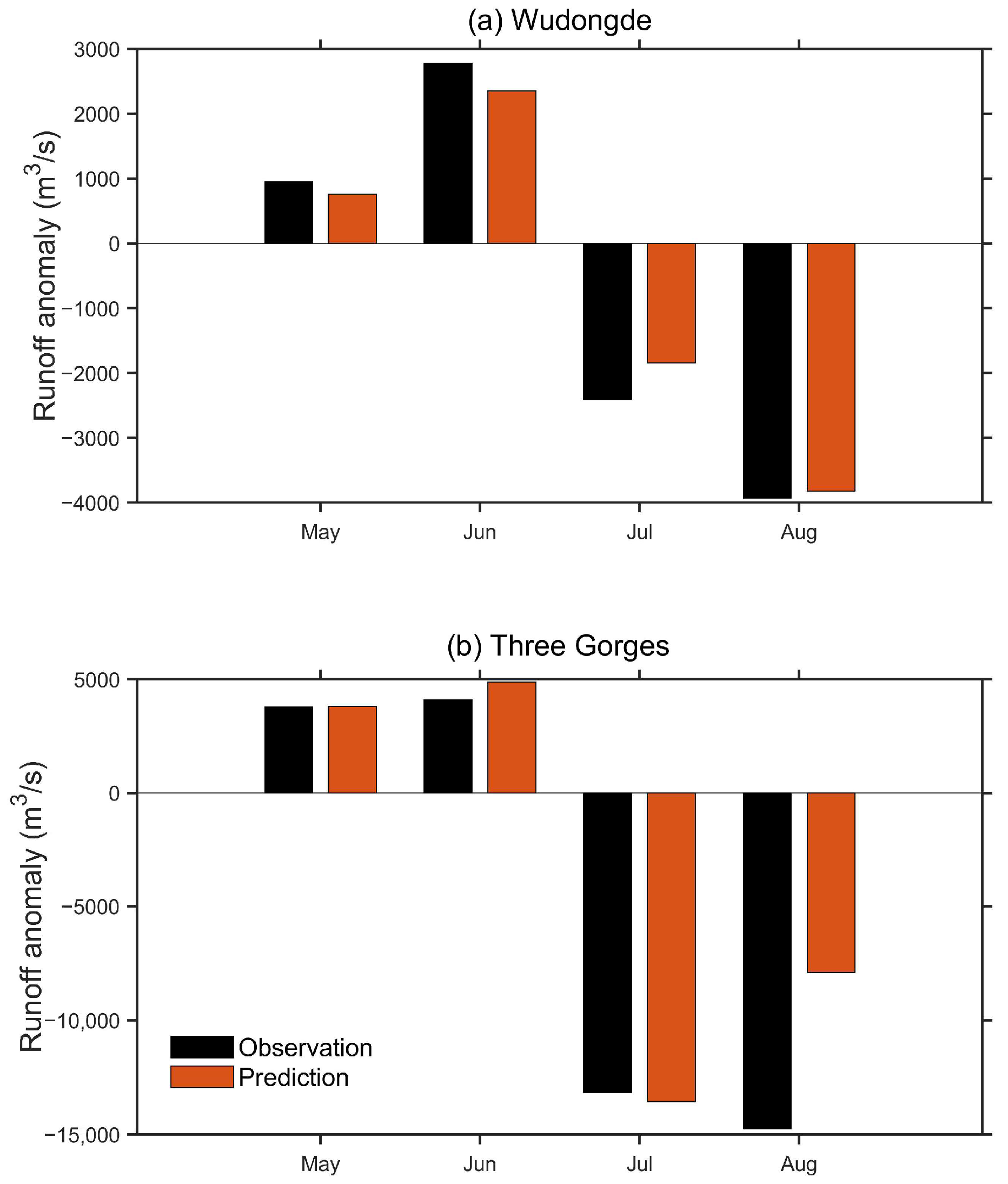
4.1. The Key Predictors and Performance of Runoff Prediction Model at the Wudongde Reservoir
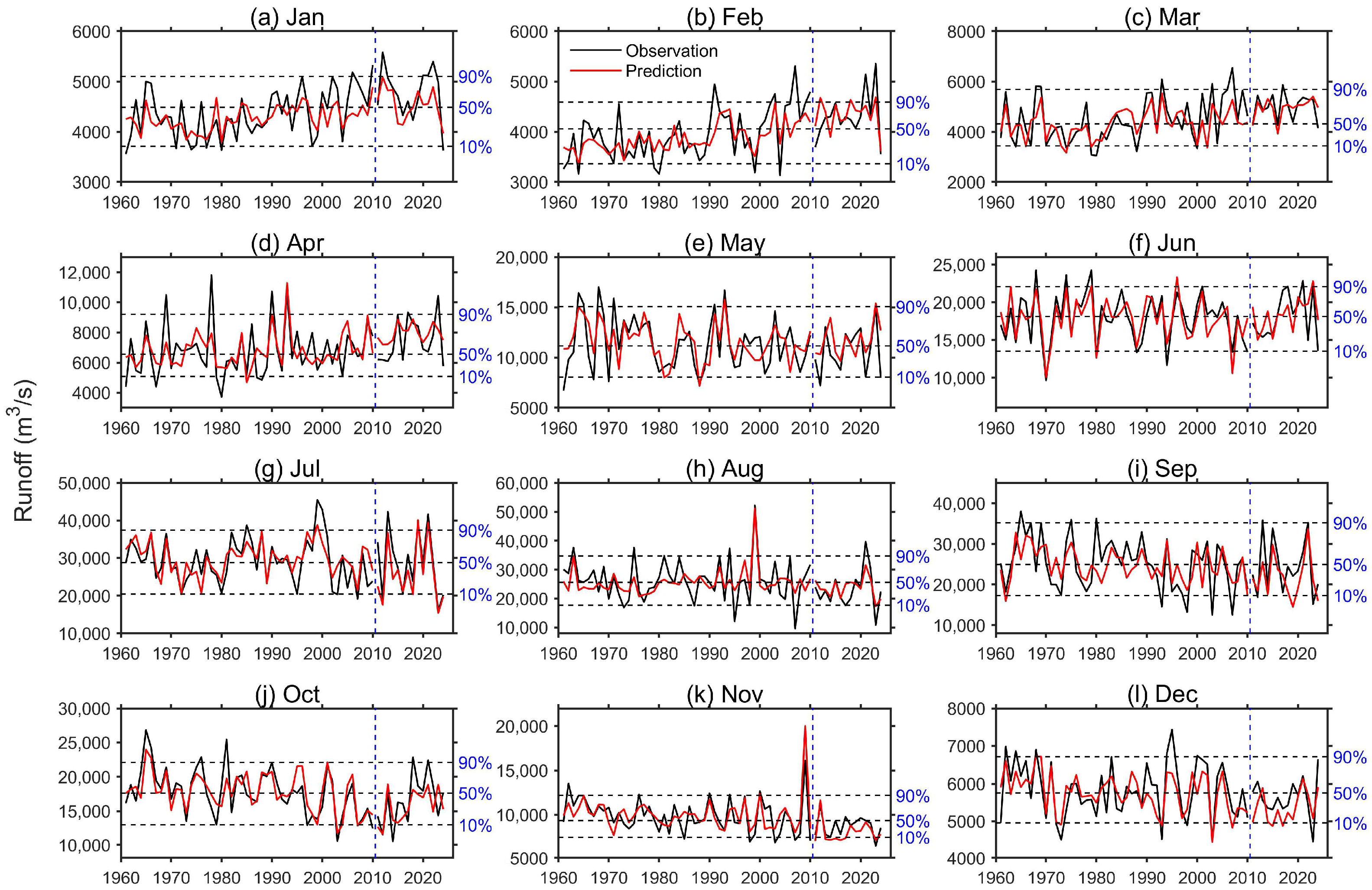
4.2. The Key Predictors and Performance of Runoff Prediction Model at the Three Gorges Reservoir
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, K.; Liu, X.; Cui, P.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, J.; Liu, C.; Gosling, S.N. China’s nationwide streamflow decline driven by landscape changes and human interventions. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eadu8032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Costello, C.; Baffaut, C.; Thompson, A.; Svoma, B.; Phung, Q.; Sadler, E. Assessing Long-Term hydrological impact of climate change using an ensemble approach and comparison with global gridded Model-A case study on goodWater creek experimental Watershed. Water 2018, 10, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Wood, E.F.; Burges, S.J. A simple hydrologically based model of land surface water and energy fluxes for general circulation models. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 14415–14428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Corbari, C.; Mancini, M.; Niu, G.; Zeng, W. Improving the Xin’anjiang hydrological model based on mass–energy balance. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 3359–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X. An experimental seasonal hydrological forecasting system over the Yellow River basin-Part 2: The added value from climate forecast models. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 2453–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xiao, C.; Du, L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, G. Extended-Range Runoff Forecasting Using a One-Way Coupled Climate-Hydrological Model: Case Studies of the Yiluo and Beijiang Rivers in China. Water 2019, 11, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatichi, S.; Vivoni, E.R.; Ogden, F.L.; Ivanov, V.Y.; Mirus, B.; Gochis, D.; Downer, C.W.; Camporese, M.; Davison, J.H.; Ebel, B.; et al. An overview of current applications, challenges, and future trends in distributed process-based models in hydrology. J. Hydrol. 2016, 537, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, H.; Schmidt, A.R.; Wang, K.; Ye, L. Examining the effects of urban agglomeration polders on flood events in Qinhuai River basin, China with HEC-HMS model. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 2130–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, J.; Bin, Z.; Qian, J.; Pei, R.; Zhu, H. Application study of IFAS and LSTM models on runoff simulation and flood prediction in the Tokachi River basin. J. Hydroinform. 2021, 23, 1098–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rujner, H.; Leonhardt, G.; Marsalek, J.; Viklander, M. High-resolution modelling of the grass swale response to runoff inflows with Mike SHE. J. Hydrol. 2018, 562, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, R.; Xu, B.; Zhong, P.; Zhu, F.; Huang, X.; Liu, W.; Xu, S.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J. Dynamic long-term streamflow probabilistic forecasting model for a multisite system considering real-time forecast updating through spatio-temporal dependent error correction. J. Hydrol. 2021, 601, 126666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, R.; Xu, B.; Zhong, P.; Dong, Y.; Wang, H.; Yue, H.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J. Long-term probabilistic streamflow forecast model with “inputs–structure–parameters” hierarchical optimization framework. J. Hydrol. 2023, 622, 129736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.C.; Chau, K.W.; Xu, D.M.; Chen, X.Y. Improving forecasting accuracy of annual runoff time series using ARIMA based on EEMD decomposition. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 2655–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, R.; Tarasova, L.; Basso, S. The flood cooking book: Ingredients and regional flavors of floods across Germany. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 114024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, L.K.; Qin, X.; Zhang, C.L.; Guo, P.; Wu, H. Application, interpretability and prediction of machine learning method combined with LSTM and LightGBM-a case study for runoff simulation in an arid area. J. Hydrol. 2023, 625, 130091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.H.; Wang, Z.C.; Wu, J.H.; Cui, X.F.; Pei, R.L. A Novel Runoff Prediction Model Based on Support Vector Machine and Gate Recurrent unit with Secondary Mode Decomposition. Water Resour. Manag. 2024, 38, 1655–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosavi, A.; Ozturk, P.; Chau, K.W. Flood prediction using machine learning models: Literature review. Water 2018, 10, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, Z.M.; El-Shafie, A.; Jaafar, O.; Afan, H.A.; Sayl, K.N. Artificial intelligence based models for stream-flow forecasting: 2000–2015. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 829–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Yang, Q.; Yang, J.; Luo, Z.; Shao, J.; Wang, G. Incorporating multiple grid-based data in CNN-LSTM hybrid model for daily runoff prediction in the source region of the Yellow River Basin. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 51, 101652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.I.; Elias, E.; Carroll, K.C.; Brown, C. Exploring random forest machine learning and remote sensing data for streamflow prediction: An alternative approach to a process-based hydrologic modeling in a snowmelt-driven watershed. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhai, P. Synoptic-scale precursors of the East Asia/Pacific teleconnection pattern responsible for persistent extreme precipitation in the Yangtze River Valley. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 2015, 141, 1389–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Niu, Y.; Li, G.; Sun, S.; Lu, B.; Li, C.; Xu, B.; Huang, J.; Sun, X. The Enhancing effect of the East Asian Subtropical Westerly Jet on Summer Extreme High-Temperature events over Central-Eastern China since the late 1990s. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2025, 42, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yu, Y.Y.; Guan, Z.Y.; Wang, X. Dominant Coupling Mode of SST in Maritime Continental Region and East Asian Summer Monsoon Circulation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2022JD036739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, R.G.; Fu, X.H. Pacific–East Asian teleconnection: How does ENSO affect East Asian climate? J. Clim. 2000, 13, 1517–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Zhang, X. Medium and Long-term Runoff Prediction of Three Gorges Reservoir Based on Teleconnection. J. North China Univ. Water Resour. Electr. Power (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2016, 37, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.; Yan, B.; Sun, M.; Gu, D.; Zhou, X. Integrated forecasting of monthly runoff considering the combined effects of teleconnection factors. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stu. 2025, 58, 102206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; Ai, P.; Xiong, C.; Hong, M.; Song, Y. Mid-to long-term runoff prediction by combining the deep belief network and partial least-squares regression. J. Hydroinform. 2020, 22, 1283–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Dong, H.; Xing, Z.; Sun, M.; Fu, Q.; Liu, D. Application of the decomposition-prediction-reconstruction framework to medium- and long-term runoff forecasting. Water Supply 2021, 21, 696–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Lei, Q.; Jiang, C.; Yan, P.; Ren, Z.; Liu, B.; Liu, Z. Climate-informed monthly runoff prediction model using machine learning and feature importance analysis. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1049840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Liu, P.; Xie, K.; Li, H.; Xia, Q.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, J. An attention-based LSTM model for long-term runoff forecasting and factor recognition. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 024004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Hou, T.; Zhu, O.; Sun, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhao, L.; Guo, X.; Li, M.; Zhong, P. Multi-step ahead probabilistic runoff forecasting with SHAP interpretability: A GPR-enhanced deep learning ensemble approach integrating teleconnection factors. Environ. Model. Softw. 2025, 193, 106647. [Google Scholar]
- Waqas, M.; Humphries, U.W. A critical review of RNN and LSTM variants in hydrological time series predictions. MethodsX 2024, 12, 102946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, L.; Lei, H.; Deng, S. Hyperparameter Optimization for Machine Learning Models Based on Bayesian Optimization. J. Electron. Sci. Technol. 2019, 17, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Yang, S.; Yu, R. Long-Term Changes in Rainfall over Eastern China and Large-Scale Atmospheric Circulation Associated with Recent Global Warming. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1544–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Li, Z.; Feng, Q.; Song, L.; Xu, B.; Liu, X.; Gui, J. Where does the runoff come from in dry season in the source region of the Yangtze River? Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 330, 109314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Cui, F.; Wu, K.; Xie, F. Spring floods and their major influential factors in the upper reaches of Jinsha River basin during 2001–2020. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stu. 2023, 45, 101318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Peng, X.; Tian, Q.; Ding, A.; Xie, J.; Su, J. Interaction between the East Asian summer monsoon and westerlies as shown by tree-ring records. Clim. Past 2024, 20, 1687–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Peng, J.; Xu, C.; Singh, V.P. Spatiotemporal variations of precipitation regimes across Yangtze River Basin, China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 115, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Jain, V.; Goyal, M.K. Evaluating climate shifts and drought regions in the central Indian river basins. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 29701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y. Climate change effect on hydrological processes over the Yangtze River Basin. Quatern. Int. 2011, 244, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xiao, W.; Hou, B.; Zhou, Y.; Hou, G.; Yi, L.; Cui, H. Hydrological projections in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River Basin from 2020 to 2050. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Morrison, R.R. Improved runoff forecasting performance through error predictions using a deep-learning approach. J. Hydrol. 2022, 608, 127653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaeh, N.; Pinthong, S.; Wipulanusat, W.; Weesakul, U.; Weekaew, J.; Pham, Q.B.; Ditthakit, P. Resampling-driven machine learning models for enhanced high streamflow forecasting. Water Cycle 2026, 7, 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Yu, J.; Paek, H. Impacts of four northern-hemisphere teleconnection patterns on atmospheric circulations over Eurasia and the Pacific. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 129, 815–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cheng, J.; Feng, G.; Zheng, Z.; Zhi, R.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, J.; Zuo, D. Dominant Role of Meridional Circulation in Regulating the Anomalous Subsidence of the Western Pacific Subtropical High in Early Summer 2020. Front. Phys. 2022, 10, 713087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, R.; Wang, X. Effect of Large-Scale Circulation Anomalies on Summer Rainfall over the Yangtze River Basin: Tropical versus Extratropical. J. Clim. 2023, 36, 4571–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.D.; Gao, S.T.; Liu, Y. Advances of research on polar vortex. Plateau Meteor. 2008, 27, 10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, B.Z.; Lian, Y.; Zhang, S.X.; Li, S.F. Impacts of arctic oscillation and polar vortex anomalies on winter temperature over Eurasian continent. Progress. Inquisitiones Mutat. Clim. 2012, 8, 434–439. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.H.; Zhou, B. Influences of the 11-yr Sunspot cycle and polar vortex oscillation on observed winter temperature variations in China. J. Meteorol. Res. 2018, 32, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Yu, R.; Zhang, J.; Drange, H.; Cassou, C.; Deser, C.; Hodson, D.L.R.; Sanchez-Gomez, E.; Li, J.; Keenlyside, N.; et al. Why the western Pacific subtropical high has extended westward since the late 1970s. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 2199–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Yang, X.; Sun, X. Zonal Oscillation of Western Pacific Subtropical High and Subseasonal SST Variations during Yangtze Persistent Heavy Rainfall Events. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 8929–8946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Gao, G.; Yao, L.; Yin, S.; Li, D.; Do, H.; Fu, B. Spatiotemporal variations of inter- and intra-annual extreme streamflow in the Yangtze River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2024, 629, 130634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Shen, H.; Xu, J. Seasonal Prediction of the Yangtze River Runoff Using a Partial Least Squares Regression Model. Atmos.-Ocean 2018, 56, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Qin, J.; Ren, H. The impact and mechanism analysis of preceding sea surface temperature anomalies on summer runoff in the Yangtze River basin and its southern region. Int. J. Climatol. 2024, 44, 1440–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Dong, J.; Huang, L.; Chen, L.; Li, Z.; You, N.; Singha, M.; Tao, F. Characterizing the 2020 summer floods in South China and effects on croplands. iScience 2023, 26, 107096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, F.; Sun, X.; Han, Z. Long-Term Runoff Prediction Using Large-Scale Climatic Indices and Machine Learning Model in Wudongde and Three Gorges Reservoirs. Water 2025, 17, 2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202942
Ma F, Sun X, Han Z. Long-Term Runoff Prediction Using Large-Scale Climatic Indices and Machine Learning Model in Wudongde and Three Gorges Reservoirs. Water. 2025; 17(20):2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202942
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Feng, Xiaoshan Sun, and Zihang Han. 2025. "Long-Term Runoff Prediction Using Large-Scale Climatic Indices and Machine Learning Model in Wudongde and Three Gorges Reservoirs" Water 17, no. 20: 2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202942
APA StyleMa, F., Sun, X., & Han, Z. (2025). Long-Term Runoff Prediction Using Large-Scale Climatic Indices and Machine Learning Model in Wudongde and Three Gorges Reservoirs. Water, 17(20), 2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202942




