Evaluating the Effects of Irrigation Water Quality and Compost Amendment on Soil Health and Crop Productivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
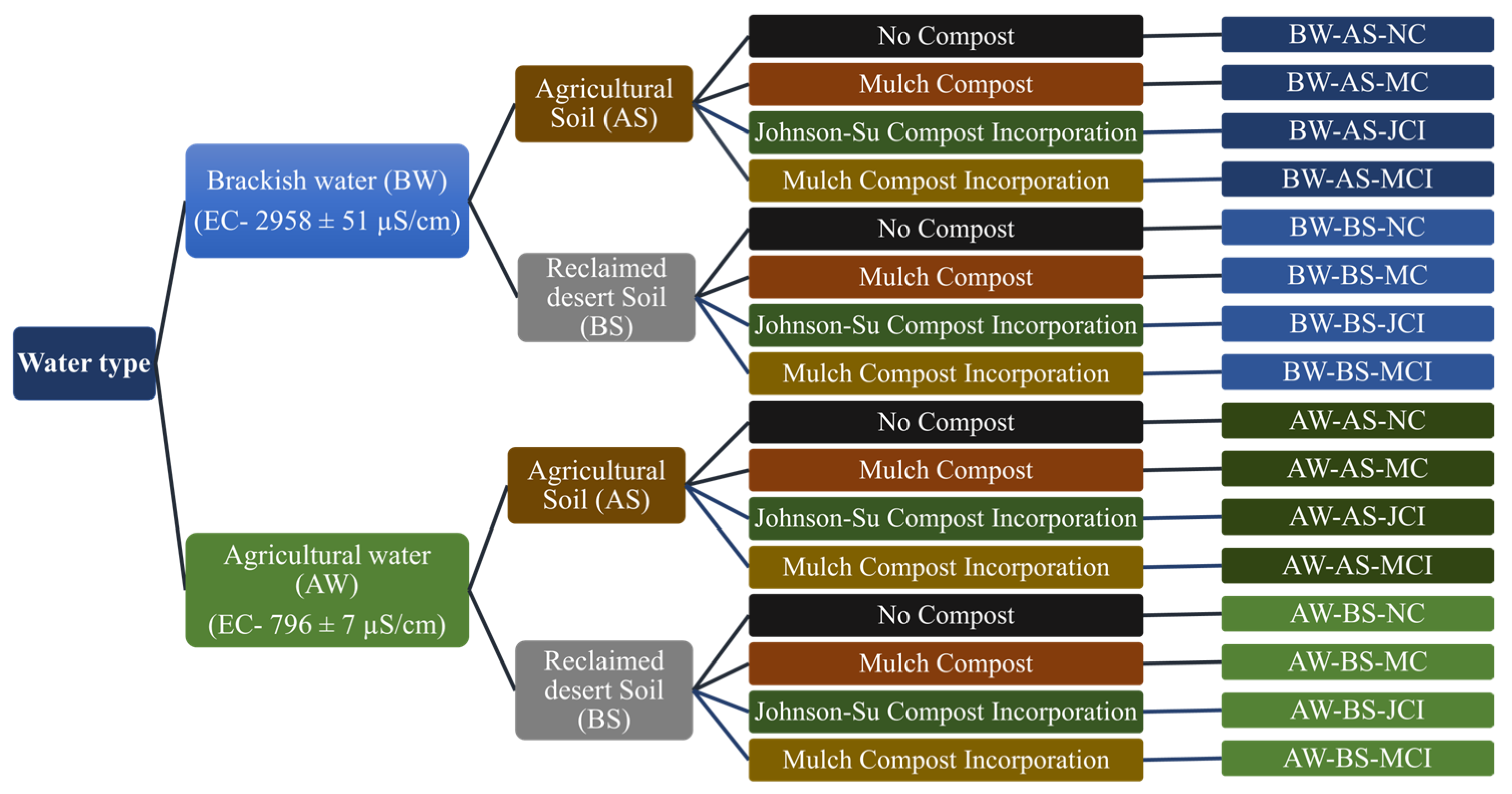
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Soil and Compost Preparation
2.3. Irrigation and Monitoring
2.4. Flood Irrigation and Leachate Collection
2.5. Plant Harvest and Biomass Measurement
2.6. Calculations, Data Quality, and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Impact of Irrigation Water Quality, Soil, and Compost Quality
3.2. Combined Impact of Irrigation Water Quality and Compost Treatment
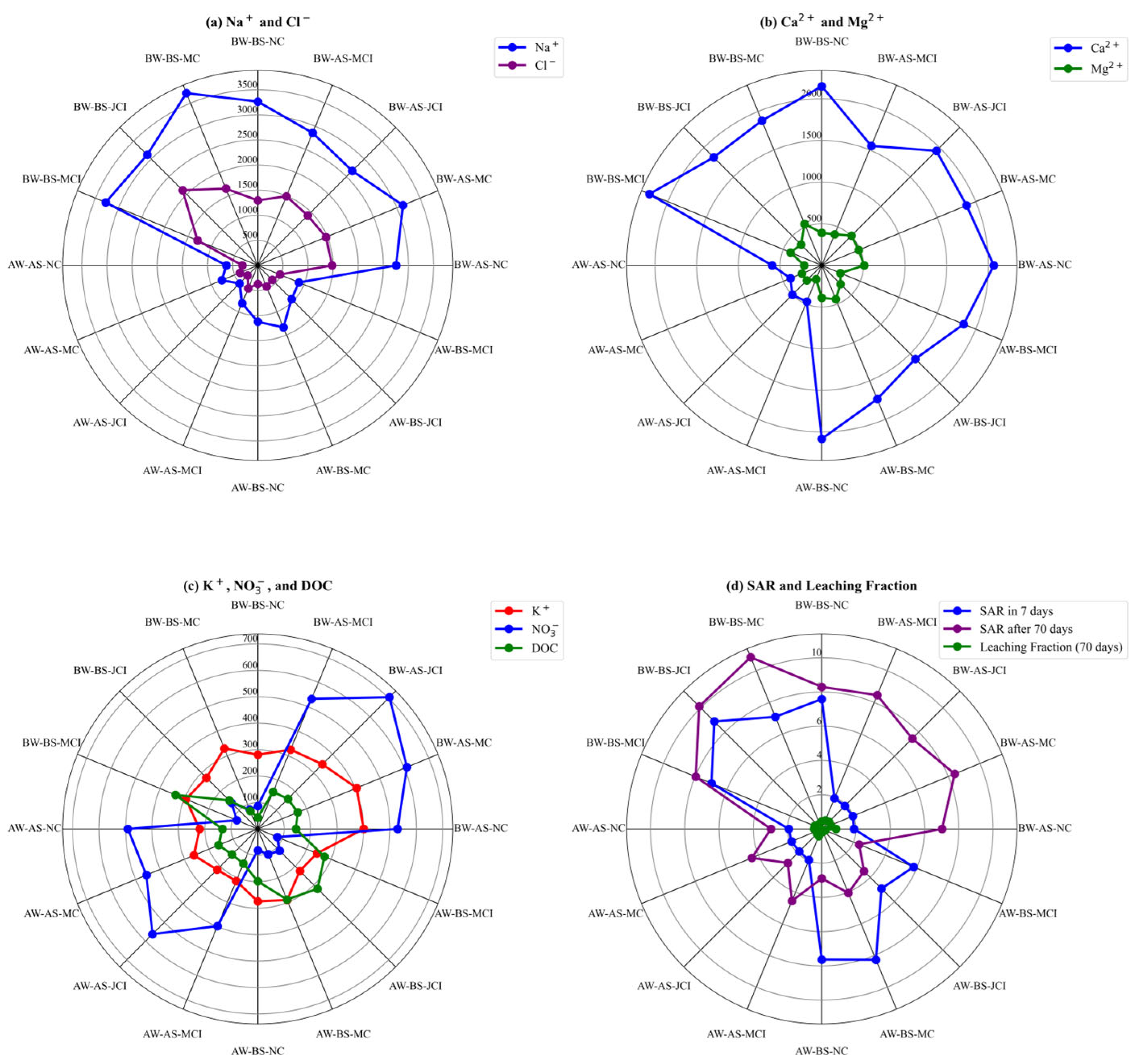
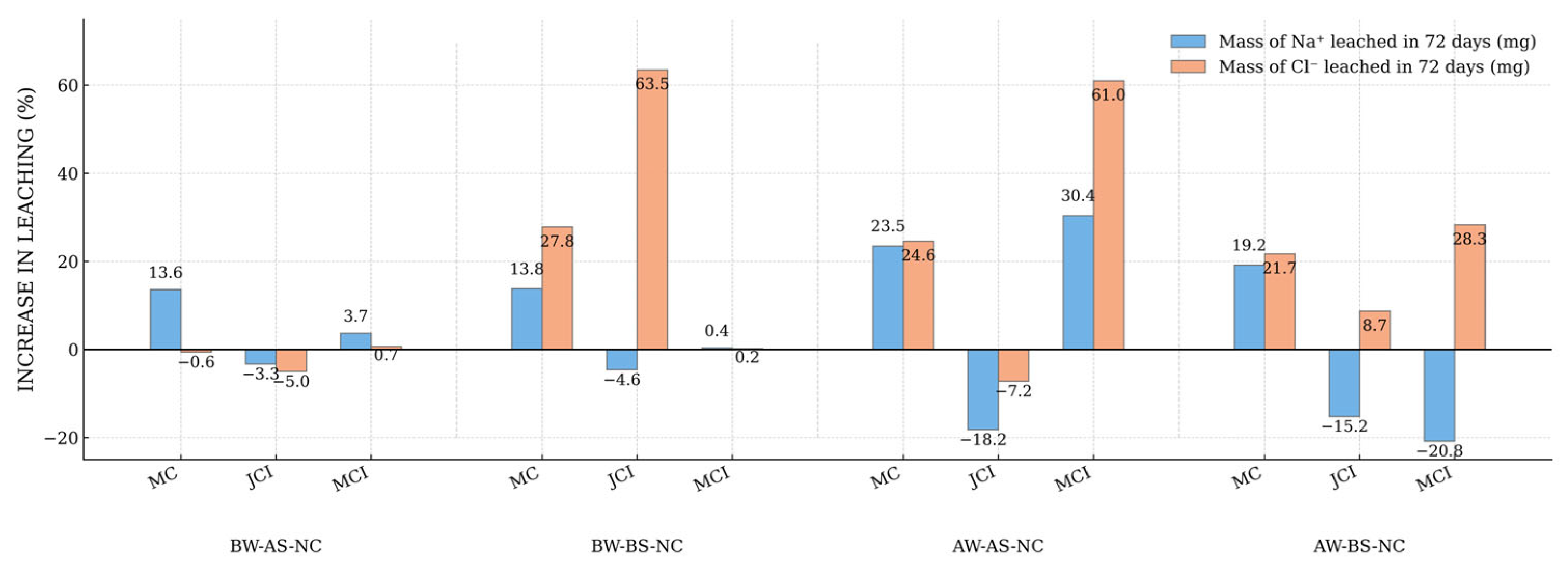
3.3. Impact on Soil Leaching of Ions and Organics
3.4. Impact of Irrigation Water, Soil, and Compost Treatment on the Leaching of Ions Driving Soil Sodicity
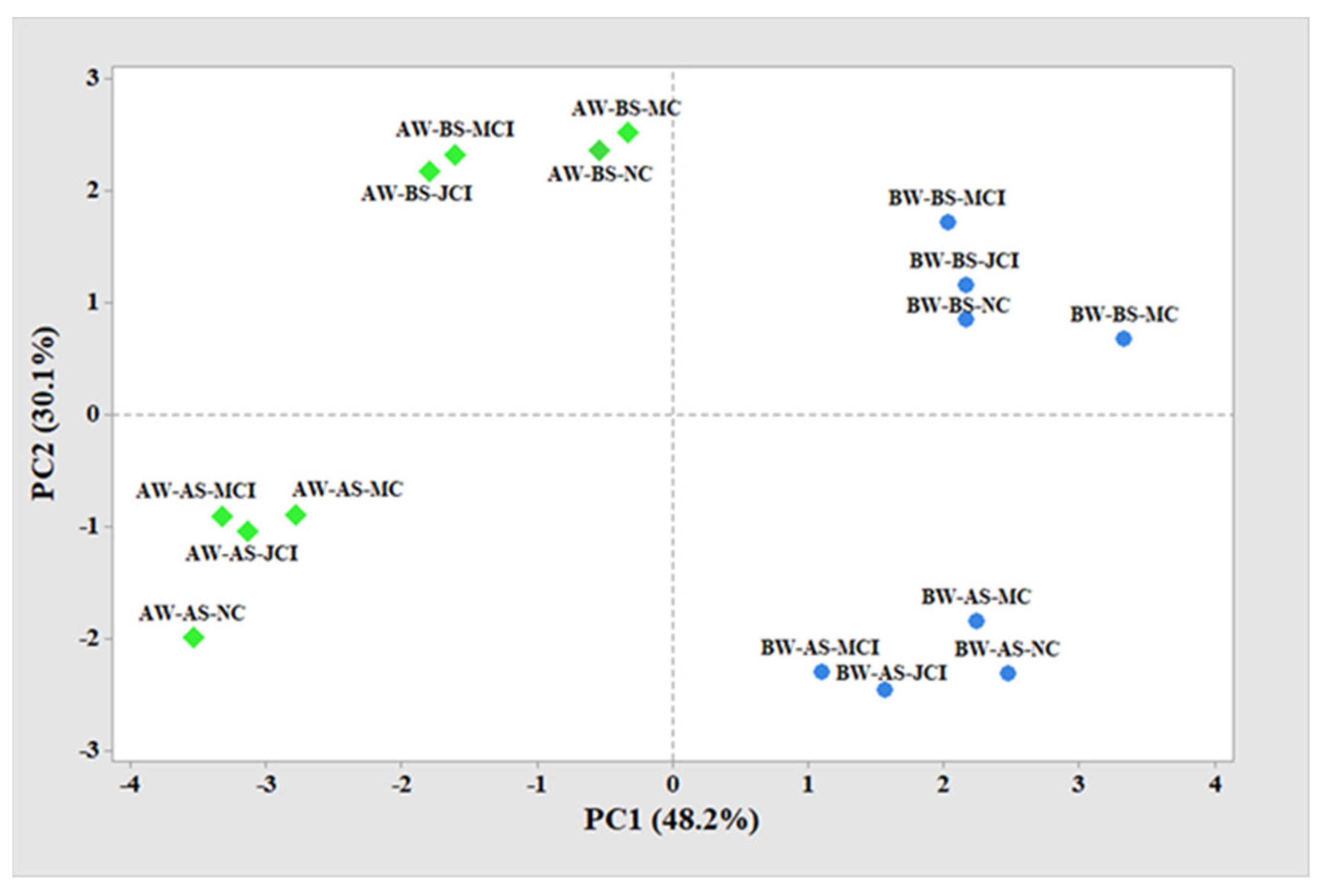
3.5. Principal Component Analysis of Ion Leaching and Sodicity Under Irrigation, Soil, and Compost Treatments
3.6. Impact on Plant Growth Parameters
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sekaran, U.; Kotlar, A.M.; Kumar, S. Soil health and soil water. In Soil Hydrology in a Changing Climate; CSIRO Publishing: Clayton South, Australia, 2022; Volume 39, pp. 39–57. [Google Scholar]
- Doran, J.W.; Zeiss, M.R. Soil health and sustainability: Managing the biotic component of soil quality. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2000, 15, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monther, M.T.; Kholoud, M.A.; Yahia, A.O.; DanielI, I.L. Soil health and sustainable agriculture. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarafdar, J. Role of soil biology on soil health for sustainable agricultural production. In Structure and Functions of Pedosphere; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 67–81. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Siddique, K.H.; Liu, K. Cropping systems in agriculture and their impact on soil health—A review. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 23, e01118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytenew, M.; Bore, G. Effects of organic amendments on soil fertility and environmental quality: A review. Plant Sci 2020, 8, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, L.; Bauddh, K. Sustainable agricultural approaches for enhanced crop productivity, better soil health, and improved ecosystem services. In Ecological and Practical Applications for Sustainable Agriculture; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Mathur, S. Water Scarcity: Root Causes, Effects, and Possible Solutions. Ascent Int. J. Res. Anal. 2015, VI, 32.1–32.7. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolaou, G.; Neocleous, D.; Christou, A.; Kitta, E.; Katsoulas, N. Implementing sustainable irrigation in water-scarce regions under the impact of climate change. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanka-Pedige, H.; Cheng, X.; Munasinghe-Arachchige, S.; Bandara, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, P.; Schaub, T.; Nirmalakhandan, N. Conventional vs. algal wastewater technologies: Reclamation of microbially safe water for agricultural reuse. Algal Res. 2020, 51, 102022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gao, X.; Li, S.; Bundschuh, J. A review of the distribution, sources, genesis, and environmental concerns of salinity in groundwater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 41157–41174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, P.; Kumar, R. Soil salinity: A serious environmental issue and plant growth promoting bacteria as one of the tools for its alleviation. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Shaukat, M.; Ashraf, M.; Zhu, C.; Jin, Q.; Zhang, J. Salinity stress in arid and semi-arid climates: Effects and management in field crops. Clim. Change Agric. 2019, 13, 201–226. [Google Scholar]
- Katerji, N.; Van Hoorn, J.; Hamdy, A.; Mastrorilli, M. Salt tolerance classification of crops according to soil salinity and to water stress day index. Agric. Water Manag. 2000, 43, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asana, R.; Kale, V. A study of salt tolerance of four varieties of wheat. Indian J. Plant Physiol. 1965, 8, 5–22. [Google Scholar]
- Sonneveld, C.; Van der Burg, A. Sodium chloride salinity in fruit vegetable crops in soilless culture. Neth. J. Agric. Sci. 1991, 39, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, T.; Feng, H. A revised saline water quality assessment method considering including Mg2+/Na+ as a new indicator for an arid irrigated area. J. Hydrol. 2024, 639, 131619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture. In FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Tomaz, A.; Palma, P.; Fialho, S.; Lima, A.; Alvarenga, P.; Potes, M.; Costa, M.J.; Salgado, R. Risk assessment of irrigation-related soil salinization and sodification in Mediterranean areas. Water 2020, 12, 3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demo, A.H.; Gemeda, M.K.; Abdo, D.R.; Guluma, T.N.; Adugna, D.B. Impact of soil salinity, sodicity, and irrigation water salinity on crop production and coping mechanism in areas of dryland farming. Agrosystems Geosci. Environ. 2025, 8, e70072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorsandi, F.; Anagholi, A. Reproductive compensation of cotton after salt stress relief at different growth stages. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2009, 195, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, E.A.; Mohanan, K. A study on the effect of salinity stress on the growth and yield of some native rice cultivars of Kerala state of India. Agric. Fish 2013, 2, 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zheng, C.; Ning, S.; Cao, C.; Li, K.; Dang, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J. Impacts of long-term saline water irrigation on soil properties and crop yields under maize-wheat crop rotation. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 286, 108383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleick, P.H. Roadmap for sustainable water resources in southwestern North America. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21300–21305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Nawaz, T.; Beaudry, J. Nitrogen and phosphorus recovery from wastewater. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.T.T. Compost Effects on Soil Properties and Plant Growth. Ph.D. Thesis, School of Agriculture, Food and Wine, The University of Adelaide, Adelaide, Australia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- El Hasini, S.; De Nobili, M.; Azim, K.; Douaik, A.; Laghrour, M.; El Idrissi, Y.; El Alaoui El Belghiti, M.; Zouahri, A. The influence of compost humic acid quality and its ability to alleviate soil salinity stress. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2020, 9, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadshirazi, F.; Brown, V.; Heitman, J.; McLaughlin, R. Effects of tillage and compost amendment on infiltration in compacted soils. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 71, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.B.; Ali, A.; Prasad, M.; Yadav, A.; Shrivastav, P.; Goyal, D.; Dantu, P.K. Role of organic fertilizers in improving soil fertility. In Contaminants in Agriculture: Sources, Impacts and Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 61–77. [Google Scholar]
- Lakhdar, A.; Rabhi, M.; Ghnaya, T.; Montemurro, F.; Jedidi, N.; Abdelly, C. Effectiveness of compost use in salt-affected soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, A.; Glaser, B. Meta-analysis on how manure application changes soil organic carbon storage. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvendran, S.; Johnson, D.; Acevedo, M.; Smithers, B.; Xu, P. Effect of Irrigation Water Quality and Soil Compost Treatment on Salinity Management to Improve Soil Health and Plant Yield. Water 2024, 16, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvendran, S.; Johnson, D.; Acevedo, M.; Smithers, B.; Xu, P. Electromagnetic Water Treatment and Soil Compost Incorporation to Alleviate the Impact of Soil Salinization. Water 2024, 16, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Beltagi, H.S.; Basit, A.; Mohamed, H.I.; Ali, I.; Ullah, S.; Kamel, E.A.; Shalaby, T.A.; Ramadan, K.M.; Alkhateeb, A.A.; Ghazzawy, H.S. Mulching as a sustainable water and soil saving practice in agriculture: A review. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmina, M.; Rahmanb, M.; Shikhac, F.; Rahmand, M.; Rahmane, J.; Tipuf, M. Effect of mulch on soil temperature, soil moisture conservation and yield of chilli. J. Clean WAS (JCleanWAS) 2020, 4, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.D.; Lal, B.R. Effect of mulching on crop production under rainfed condition: A review. Int. J. Res. Chem. Environ. 2012, 2, 8–20. [Google Scholar]
- Nehela, Y.; Mazrou, Y.S.; Alshaal, T.; Rady, A.M.; El-Sherif, A.M.; Omara, A.E.-D.; El-Monem, A.M.A.; Hafez, E.M. The integrated amendment of sodic-saline soils using biochar and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria enhances maize (Zea mays L.) resilience to water salinity. Plants 2021, 10, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mawof, A.; Prasher, S.; Bayen, S.; Nzediegwu, C. Effects of biochar and biochar-compost mix as soil amendments on soil quality and yield of potatoes irrigated with wastewater. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 2600–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omara, A.E.-D.; Hafez, E.M.; Osman, H.S.; Rashwan, E.; El-Said, M.A.; Alharbi, K.; El-Moneim, D.A.; Gowayed, S.M. Collaborative impact of compost and beneficial rhizobacteria on soil properties, physiological attributes, and productivity of wheat subjected to deficit irrigation in salt affected soil. Plants 2022, 11, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, M.; Brinton, W.; Shields, F.; West, J.; Thompson, W. Compost Maturity Index; California Integrated Waste Management Board (CIWMB): Sacramento, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Suvendran, S.; Acevedo, M.F.; Smithers, B.; Walker, S.J.; Xu, P. Soil Fertility and Plant Growth Enhancement Through Compost Treatments Under Varied Irrigation Conditions. Agriculture 2025, 15, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D. Johnson Su Bioreactor. 2016 March 2016 [cited 2022]. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DxUGk161Ly8 (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- Baath, G.S.; Shukla, M.K.; Bosland, P.W.; Walker, S.J.; Saini, R.K.; Shaw, R. Water use and yield responses of chile pepper cultivars irrigated with brackish groundwater and reverse osmosis concentrate. Horticulturae 2020, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, R.; Thapa, V.R.; Acosta-Martinez, V.; Schipanski, M.; Slaughter, L.C.; Fonte, S.J.; Shukla, M.K.; Bista, P.; Angadi, S.V.; Mikha, M.M. Soil health assessment and management framework for water-limited environments: Examples from the Great Plains of the USA. Soil Syst. 2023, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Cao, H.-X.; Liu, X.; Li, H.-T.; Hu, Q.-Y.; Xue, W.-K. By increasing infiltration and reducing evaporation, mulching can improve the soil water environment and apple yield of orchards in semiarid areas. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 253, 106936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Malhi, G.S.; Kaur, M.; Singh, G.; Jatav, H.S. Use of organic soil amendments for improving soil ecosystem health and crop productivity. In Ecosystem Services; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Suite N Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Aggelides, S.; Londra, P. Effects of compost produced from town wastes and sewage sludge on the physical properties of a loamy and a clay soil. Bioresour. Technol. 2000, 71, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, Z.; Malik, N.; Noor, I.; Kamran, M.; Parveen, A.; Ali, M.; Sabir, F.; Elansary, H.O.; El-Abedin, T.K.Z.; Mahmoud, E.A. Combined Effect of Rice-Straw Biochar and Humic Acid on Growth, Antioxidative Capacity, and Ion Uptake in Maize (Zea mays L.) Grown Under Saline Soil Conditions. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 42, 3211–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beecher, H. Effect of saline water on rice yields and soil properties in the Murrumbidgee Valley. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 1991, 31, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, N.T.K.; Khoi, C.M.; Ritz, K.; Linh, T.B.; Minh, D.D.; Duc, T.A.; Sinh, N.V.; Linh, T.T.; Toyota, K. Influence of rice husk biochar and compost amendments on salt contents and hydraulic properties of soil and rice yield in salt-affected fields. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Feng, H. Cation composition of saline water affects soil structure by altering the formation of macropores and cracks in illite soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 239, 106052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyaswamy, G. A Super-Ion Called Magnesium: The Unsung Hero of Vitality and Well-Being; Notion Press: Chennai, India, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X.; Yang, Y.; Guan, P.; Geng, L.; Ma, L.; Di, H.; Liu, W.; Li, B. Remediation of organic amendments on soil salinization: Focusing on the relationship between soil salts and microbial communities. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 239, 113616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manohar, A.; Kathula, K. Role of Sulphur Nutrition in Enhancing the Productivity of Pulses and Oilseeds. Indian J. Nat. Sci. 2022, 13, 43172–43182. [Google Scholar]
- Likus-Cieślik, J.; Pietrzykowski, M.; Chodak, M. Chemistry of sulfur-contaminated soil substrate from a former Frasch extraction method sulfur mine leachate with various forms of litter in a controlled experiment. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wu, Y.; Gao, L.; Ma, J.; Li, C.Y.; Xiang, C.B. Sulfur nutrient availability regulates root elongation by affecting root indole-3-acetic acid levels and the stem cell niche. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2014, 56, 1151–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y. Saline-alkali soil applied with vermicompost and humic acid fertilizer improved macroaggregate microstructure to enhance salt leaching and inhibit nitrogen losses. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 156, 103705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, S.; Zhou, B.; Wang, Q.; Tao, W. Evaluation of irrigation water salinity and leaching fraction on the water productivity for crops. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2020, 13, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Rashti, M.R.; Dougall, A.; Esfandbod, M.; Van Zwieten, L.; Chen, C. Subsoil application of compost improved sugarcane yield through enhanced supply and cycling of soil labile organic carbon and nitrogen in an acidic soil at tropical Australia. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 180, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-Z.; Wang, F.; Suo, D.-R.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Du, M.-W. Long-term effect of fertilizer and manure application on soil-carbon sequestration and soil fertility under the wheat–wheat–maize cropping system in northwest China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2006, 75, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaragamage, D.; Warren, J.; Spiers, G. Soil chemistry. In Digging into Canadian Soils: Soil Chemistry; Canadian Society of Soil Science: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.; Chowdhury, N. Effects of leaching on the reclamation of saline soils as affected by different organic and inorganic amendments. J. Environ. Sci. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 3, 329–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.; Crohn, D.M. Compost induced soil salinity: A new prediction method and its effect on plant growth. Compos. Sci. Util. 2012, 20, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodabadi, M.; Yazdanpanah, N.; Sinobas, L.R.; Pazira, E.; Neshat, A. Reclamation of calcareous saline sodic soil with different amendments (I): Redistribution of soluble cations within the soil profile. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 120, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Irrigation Water | pH | EC | Alkalinity | SAR | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Na+ | K+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (µS/cm) | (mg/L as CaCO3) | (mg/L) | |||||||||
| Brackish water | 8.65 ± 0.17 | 2958 ± 51 | 480 | 11.7 | 120.9 | 1.1 | 1229 | 107.5 | 26.8 | 522.5 | 12.15 |
| Agricultural water | 7.61 ± 0.25 | 796 ± 7 | 155 | 6.1 | 29.4 | 0.2 | 262 | 28.2 | 6.6 | 139.0 | 3.55 |
| Treatment | Soil Moisture Content (m3/m3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–15 cm | 15–30 cm | 30–45 cm | ||
| BW-AS-NC | 0.250 ± 0.02 bcde | 0.292 ± 0.03 ab | 0.300 ± 0.03 bc | * |
| BW-AS-MC | 0.264 ± 0.03 abc | 0.302 ± 0.02 a | 0.329 ± 0.02 ab | ** |
| BW-AS-JCI | 0.271 ± 0.02 ab | 0.314 ± 0.02 a | 0.325 ± 0.03 ab | ** |
| BW-AS-MCI | 0.260 ± 0.02 abcd | 0.292 ± 0.02 ab | 0.307 ± 0.03 ab | * |
| BW-BS-NC | 0.242 ± 0.02 cde | 0.252 ± 0.02 c | 0.254 ± 0.03 d | * |
| BW-BS-MC | 0.237 ± 0.02 de | 0.256 ± 0.03 c | 0.256 ± 0.03 d | * |
| BW-BS-JCI | 0.236 ± 0.01 de | 0.251 ± 0.02 c | 0.241 ± 0.01 d | ** |
| BW-BS-MCI | 0.241 ± 0.02 cde | 0.249 ± 0.02 c | 0.252 ± 0.02 d | * |
| AW-AS-NC | 0.263 ± 0.02 abc | 0.302 ± 0.03 a | 0.313 ± 0.03 ab | * |
| AW-AS-MC | 0.268 ± 0.03 ab | 0.315 ± 0.02 a | 0.335 ± 0.03 ab | ** |
| AW-AS-JCI | 0.275 ± 0.03 ab | 0.314 ± 0.02 a | 0.343 ± 0.02 a | ** |
| AW-AS-MCI | 0.284 ± 0.02 a | 0.299 ± 0.03 a | 0.328 ± 0.02 ab | * |
| AW-BS-NC | 0.242 ± 0.02 cde | 0.258 ± 0.02 c | 0.256 ± 0.02 d | * |
| AW-BS-MC | 0.229 ± 0.01 e | 0.267 ± 0.02 bc | 0.255 ± 0.02 d | ** |
| AW-BS-JCI | 0.235 ± 0.01 de | 0.250 ± 0.02 c | 0.260 ± 0.02 cd | ** |
| AW-BS-MCI | 0.241 ± 0.02 cde | 0.252 ± 0.02 c | 0.248 ± 0.02 d | * |
| p-value IW | 0.069 | 0.034 | 0.015 | |
| S | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| C | 0.095 | 0.020 | 0.054 | |
| IW × S | 0.011 | 0.633 | 0.176 | |
| IW × C | 0.209 | 0.476 | 0.463 | |
| S × C | 0.013 | 0.046 | 0.028 | |
| IW × S × C | 0.562 | 0.100 | 0.650 | |
| Treatment | Soil Electrical Conductivity (mS/cm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–15 cm | 15–30 cm | 30–45 cm | ||
| BW-AS-NC | 0.777 ± 0.11 abc | 0.866 ± 0.11 abcd | 0.944 ± 0.11 bcd | n.s |
| BW-AS-MC | 0.905 ± 0.10 a | 0.926 ± 0.09 ab | 1.104 ± 0.10 a | ** |
| BW-AS-JCI | 0.876 ± 0.11 ab | 1.016 ± 0.08 a | 1.073 ± 0.09 ab | * |
| BW-AS-MCI | 0.828 ± 0.09 ab | 0.933 ± 0.09 ab | 1.017 ± 0.11 abc | * |
| BW-BS-NC | 0.818 ± 0.08 ab | 0.964 ± 1.13 a | 0.879 ± 0.11 def | n.s |
| BW-BS-MC | 0.751 ± 0.09 bcd | 0.875 ± 0.12 abcd | 0.852 ± 0.10 defg | * |
| BW-BS-JCI | 0.776 ± 0.07 bc | 0.825 ± 0.08 abcde | 0.786 ± 0.08 efgh | n.s |
| BW-BS-MCI | 0.863 ± 0.07 ab | 0.887 ± 0.08 abc | 0.919 ± 0.09 cde | n.s |
| AW-AS-NC | 0.553 ± 0.07 e | 0.643 ± 0.10 e | 0.782 ± 0.09 fgh | ** |
| AW-AS-MC | 0.586 ± 0.10 e | 0.683 ± 0.13 cde | 0.870 ± 0.10 def | ** |
| AW-AS-JCI | 0.602 ± 0.09 e | 0.722 ± 0.08 bcde | 0.849 ± 0.08 defg | ** |
| AW-AS-MCI | 0.596 ± 0.08 e | 0.740 ± 0.08 bcde | 0.852 ± 0.12 defg | ** |
| AW-BS-NC | 0.644 ± 0.10 de | 0.680 ± 0.06 cde | 0.691 ± 0.07 h | n.s |
| AW-BS-MC | 0.664 ± 0.11 cde | 0.697 ± 0.08 cde | 0.707 ± 0.08 h | n.s |
| AW-BS-JCI | 0.614 ± 0.06 e | 0.671 ± 0.09 de | 0.727 ± 0.09 gh | ** |
| AW-BS-MCI | 0.619 ± 0.07 e | 0.688 ± 0.08 cde | 0.696 ± 0.13 h | * |
| p-value IW | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| S | 0.794 | 0.149 | 0.000 | |
| C | 0.328 | 0.825 | 0.016 | |
| IW × S | 0.000 | 0.408 | 0.103 | |
| IW × C | 0.670 | 0.782 | 0.471 | |
| S × C | 0.007 | 0.024 | 0.002 | |
| IW × S × C | 0.009 | 0.355 | 0.014 | |
| Treatment | Compost Type | Chlorophyll | Plant Height (cm) | Wet Biomass (g) | Root Length (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impact of compost soil treatment (Type of compost/NC) on increase in plant growth in % (values of change) | |||||
| BW-AS-NC | MC | −4.8 (36 → 34.3) | −25.2 (14.7 → 11) | −3.6 (4.7 → 4.5) | 1.5 (15.3 → 15.5) |
| JCI | 19.9 (36 → 43.2) | 58.4 (14.7 → 23.3) | 364.3 (4.7 → 21.8) | 111.3 (15.3 → 32.3) | |
| MCI | −20.9 (36 → 28.5) | −60.9 (14.7 → 5.7) | −58.6 (4.7 → 1.9) | −30.3 (15.3 → 10.7) | |
| BW-BS-NC | MC | 15.5 (32.8 → 37.9) | 38.1 (12.9 → 17.8) | 154.5 (3.7 → 9.4) | 35.1 (30.5 → 41.2) |
| JCI | 30.9 (32.8 → 42.9) | 85.5 (12.9 → 23.9) | 709.1 (3.7 → 29.9) | 47.5 (30.5 → 45.0) | |
| MCI | −7.0 (32.8 → 30.5) | −20.5 (12.9 → 10.3) | −22.7 (3.7 → 2.9) | −32.2 (30.5 → 20.7) | |
| AW-AS-NC | MC | 42.7 (26.3→ 37.5) | 110.2 (8.2→ 17.2) | 600.0 (1.3 → 9.1) | 58.3 (10.5 → 16.6) |
| JCI | 41.6 (26.3 → 37.2) | 213.5 (8.2→ 25.7) | 1400.0 (1.3 → 19.5) | 166.2 (10.5 → 28.0) | |
| MCI | 16.9 (26.3 → 30.7) | −2.0 (8.2→ 8.0) | 50.0 (1.3 → 2.0) | 41.4 (10.5 → 14.8) | |
| AW-BS-NC | MC | 7.9 (36.3 → 30) | −0.1 (17.6 → 17.6) | 70.0 (6.0 → 10.2) | −5.9 (45.0–42.3) |
| JCI | 24.5 (36.3 → 45.2) | 56.0 (17.6 → 27.5) | 350.0 (6.0 → 27.0) | 0.0 (45.0–45.0) | |
| MCI | −21.4 (36.3 → 28.5) | −43.9 (17.6 → 9.9) | −56.5 (6.0 → 2.6) | −63.9 (45.0 → 16.2) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suvendran, S.; Acevedo, M.F.; Smithers, B.; Walker, S.J.; Xu, P. Evaluating the Effects of Irrigation Water Quality and Compost Amendment on Soil Health and Crop Productivity. Water 2025, 17, 2927. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202927
Suvendran S, Acevedo MF, Smithers B, Walker SJ, Xu P. Evaluating the Effects of Irrigation Water Quality and Compost Amendment on Soil Health and Crop Productivity. Water. 2025; 17(20):2927. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202927
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuvendran, Subanky, Miguel F. Acevedo, Breana Smithers, Stephanie J. Walker, and Pei Xu. 2025. "Evaluating the Effects of Irrigation Water Quality and Compost Amendment on Soil Health and Crop Productivity" Water 17, no. 20: 2927. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202927
APA StyleSuvendran, S., Acevedo, M. F., Smithers, B., Walker, S. J., & Xu, P. (2025). Evaluating the Effects of Irrigation Water Quality and Compost Amendment on Soil Health and Crop Productivity. Water, 17(20), 2927. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17202927









