Sludge-Derived Hercynite–Carbon as a Low-Cost Catalyst for Efficient Degradation of Refractory Pollutants in Wastewater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Catalyst Preparation Methods
2.3. Catalytic Performance Test
2.4. Amperometric Experiments
2.5. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
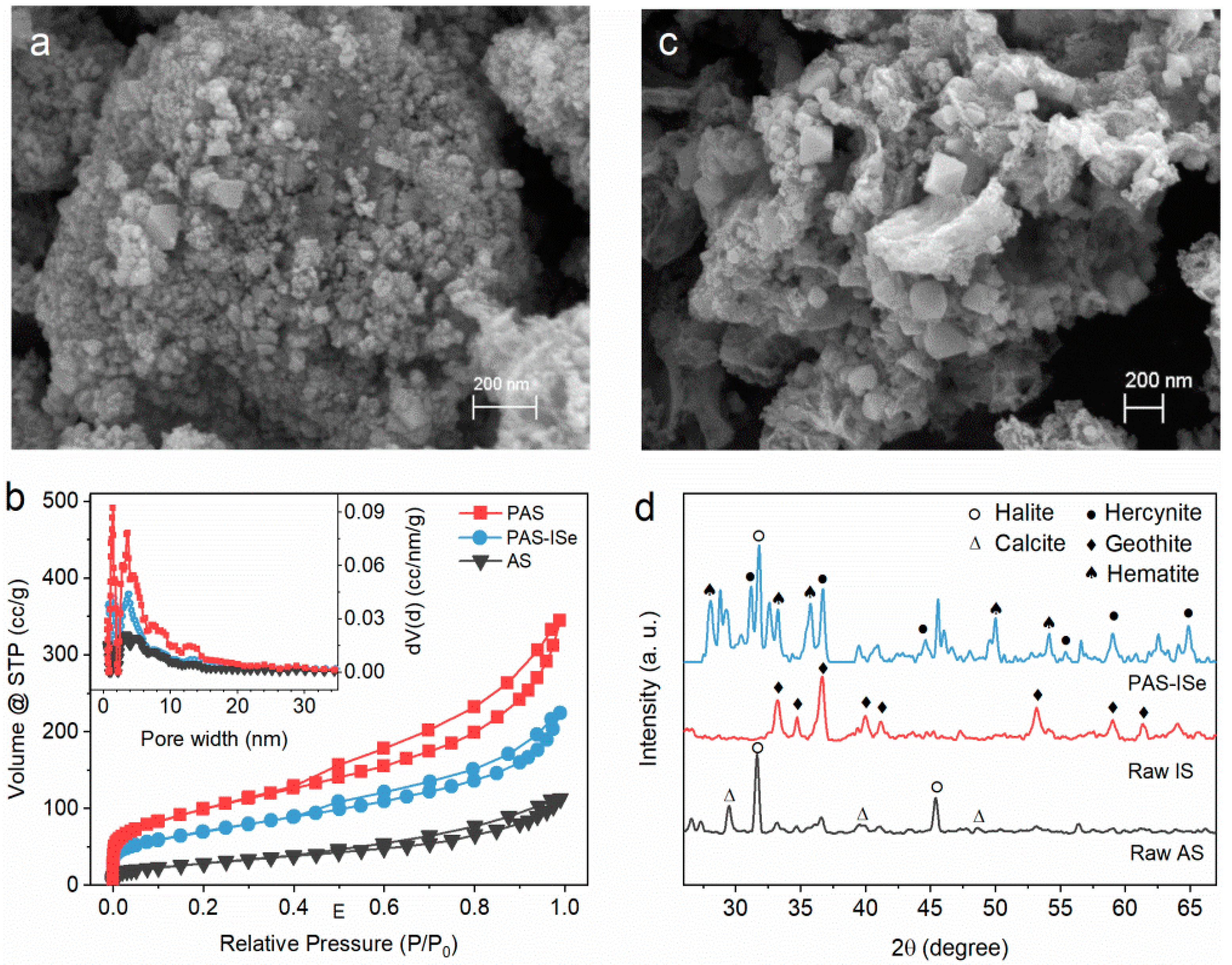
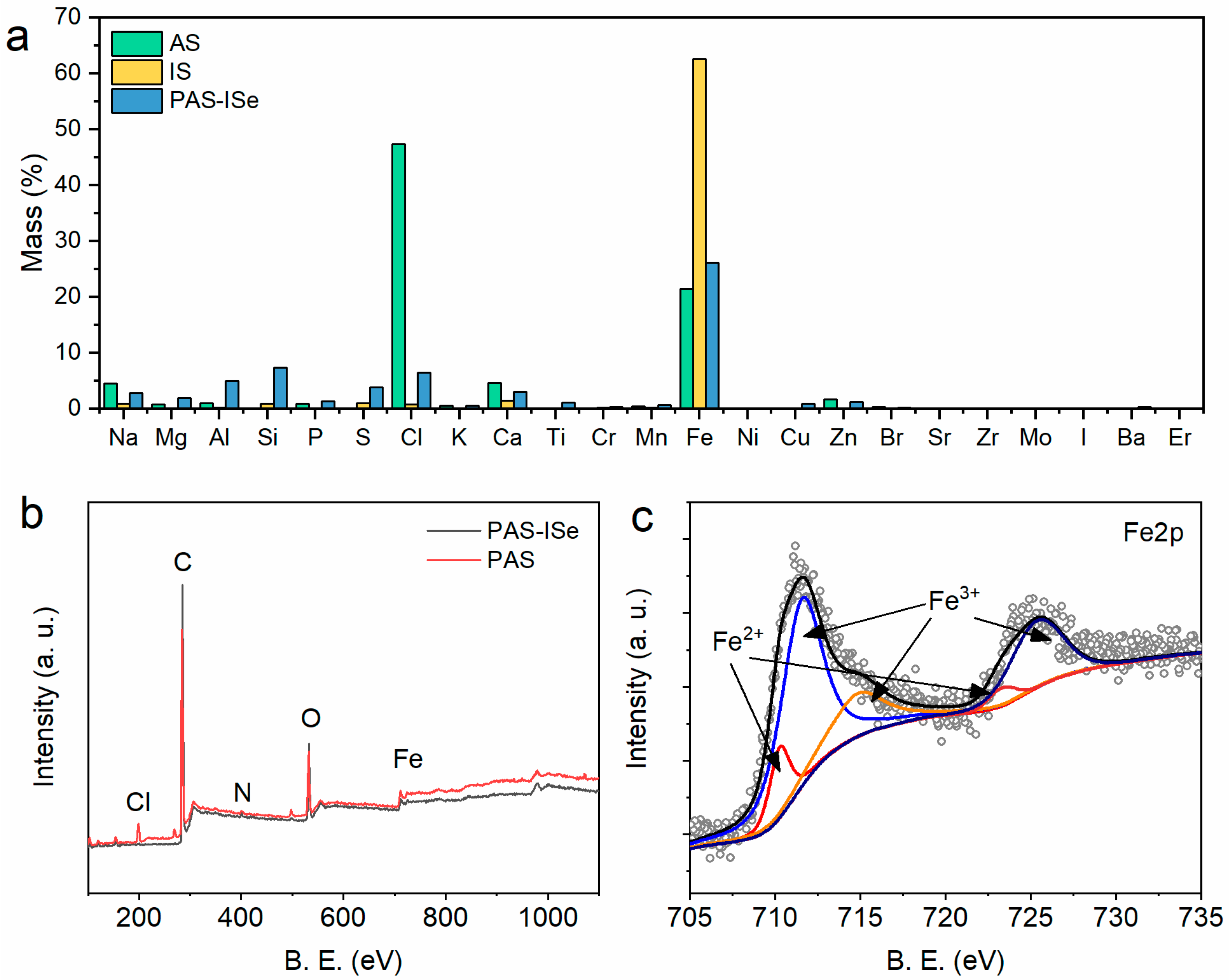
3.1. Catalysts Characterization
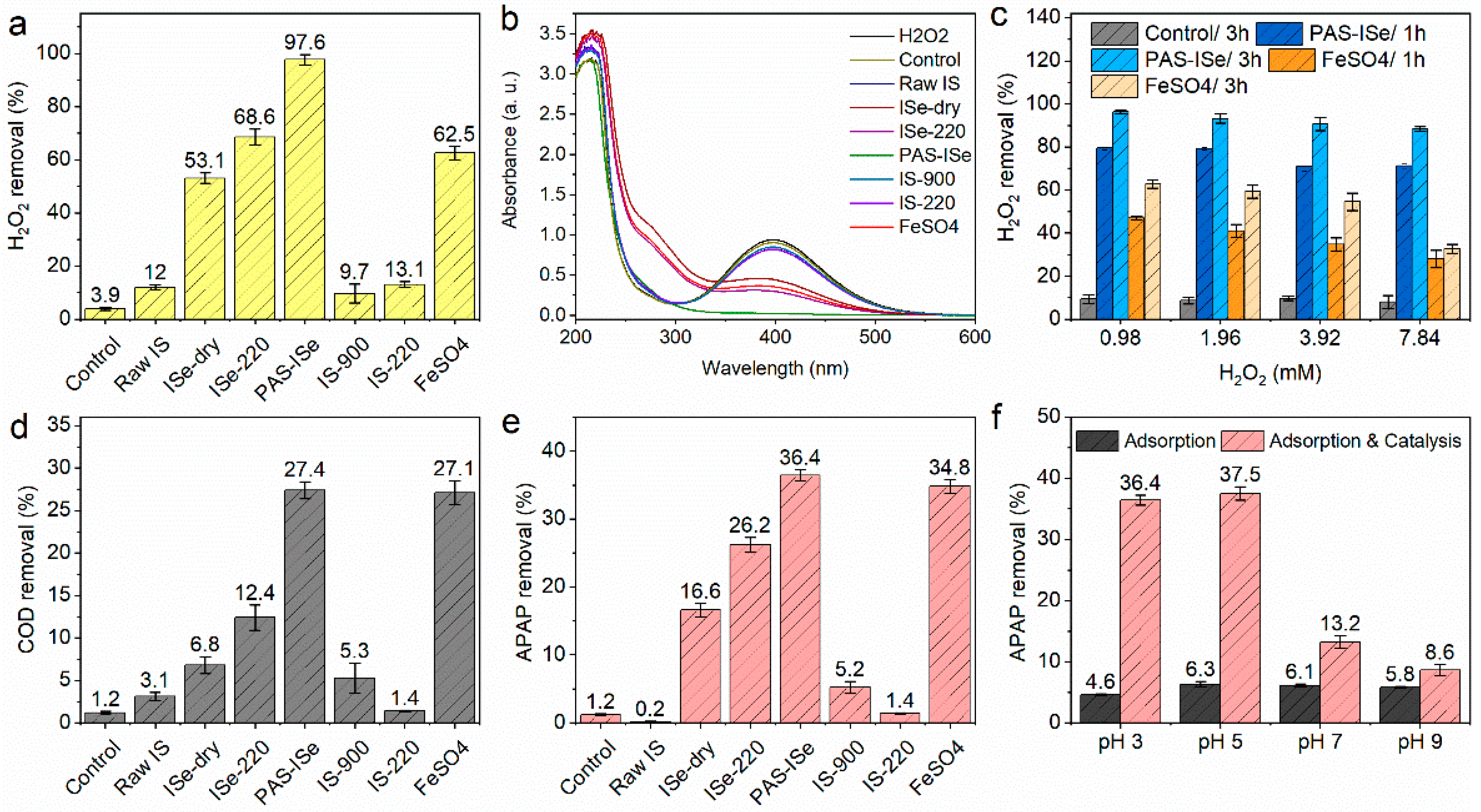
3.2. Catalytic Performances
3.2.1. Catalytic Performance Comparison
3.2.2. Effect of pH
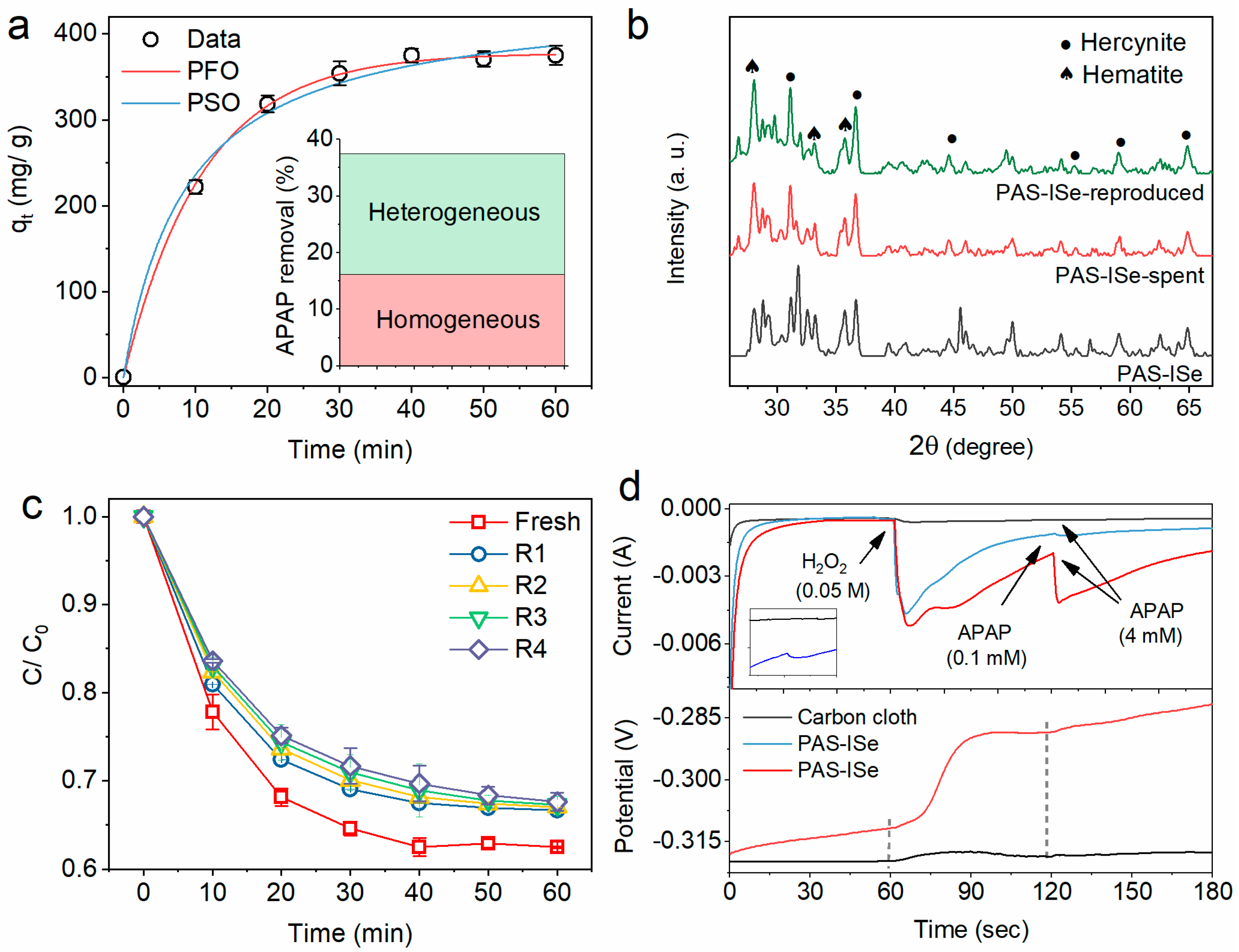
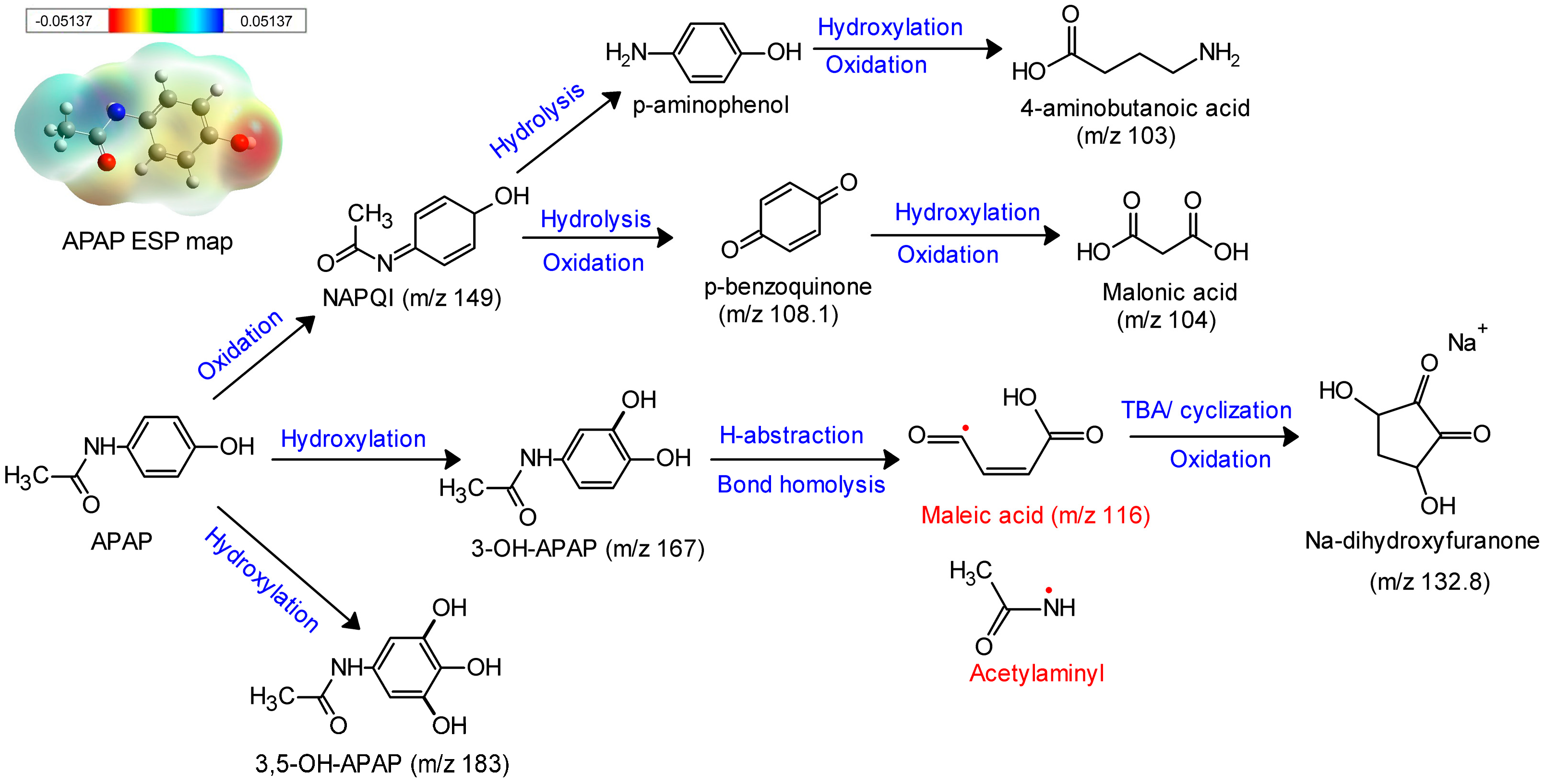
3.2.3. Catalytic Reaction Path
3.2.4. Catalyst Stability
3.2.5. Electron Transfer Potential
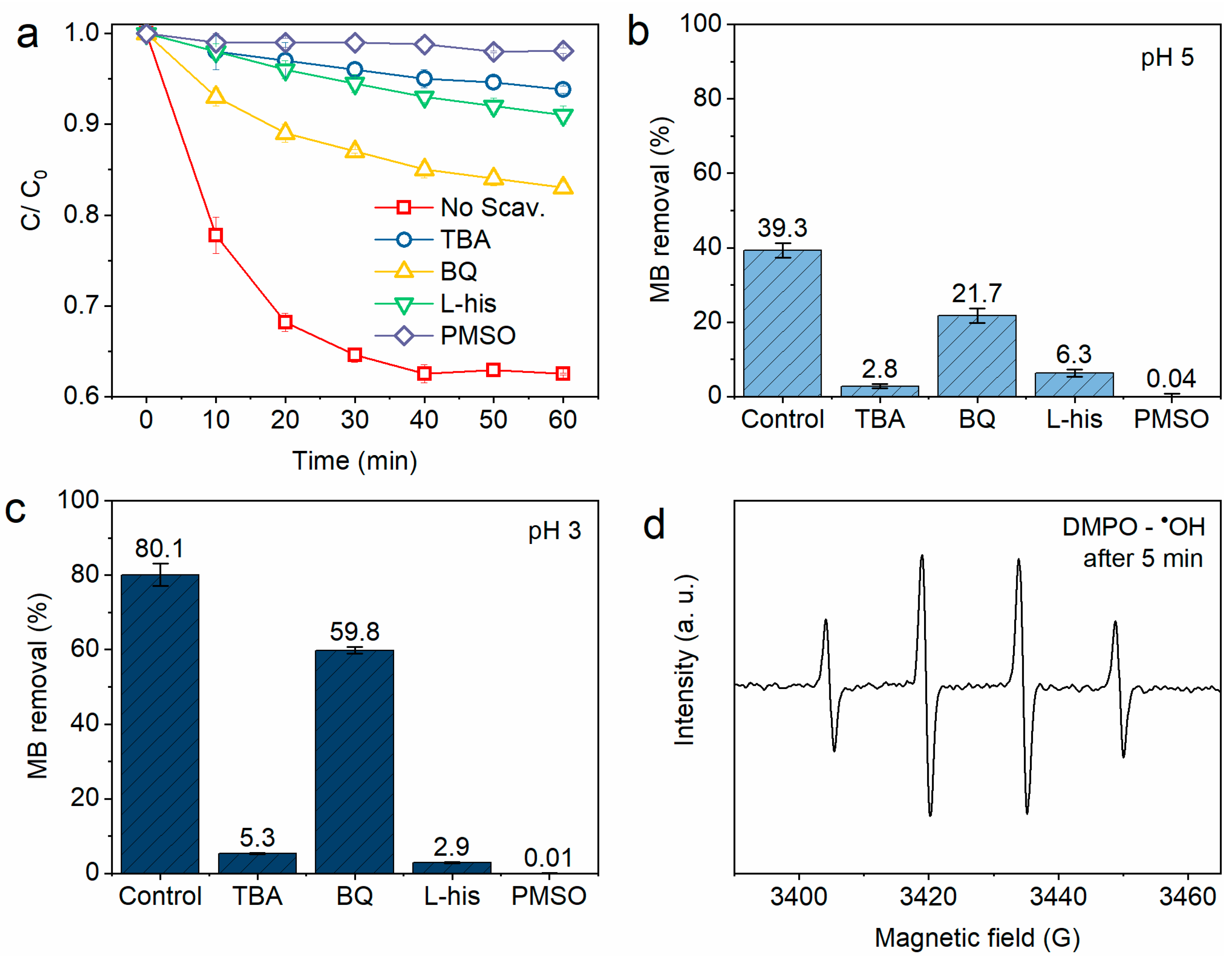
3.3. Catalytic Mechanisms
3.4. Techno-Economic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, C.; Su, Y.; Quan, X.; Sharma, V.K.; Chen, S.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, J. Electronic Modulation of Iron-Bearing Heterogeneous Catalysts to Accelerate Fe(III)/Fe(II) Redox Cycle for Highly Efficient Fenton-like Catalysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 276, 119016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez-Medrano, R.; Prato-Garcia, D.; Vedrenne, M. Chapter 4—Ferrioxalate-Mediated Processes. In Advanced Oxidation Processes for Waste Water Treatment; Ameta, S.C., Ameta, R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 89–113. ISBN 978-0-12-810499-6. [Google Scholar]
- Mian, M.M.; Liu, G.; Fu, B. Conversion of Sewage Sludge into Environmental Catalyst and Microbial Fuel Cell Electrode Material: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, J.P.; Marques, C.C.; Neves, M.C.; Gomes, H.G.M.F.; Sarinho, L.; Tarelho, L.A.C.; Nunes, M.I. Catalytic Performance of Thermochemically Treated Sludge Generated in the Fenton Process for AOX Degradation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2025, 144, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Q.; Hou, H.; Liang, S.; Qiu, J.; Tao, S.; Yang, L.; Yu, W.; Xiao, K.; Liu, B.; Hu, J.; et al. Sludge-Derived Biochar with Multivalent Iron as an Efficient Fenton Catalyst for Degradation of 4-Chlorophenol. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Chen, N.; Ben, H.; Zhan, G.; Sun, H.; Li, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhang, L. Hydroxylamine Enables Rapid Heterogeneous-Homogeneous Coupled Fenton Sulfamethazine Degradation on Ferric Phosphate. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 312, 121410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhu, W.; Liu, J.; Lin, P.; Zhang, J.; Huang, T.; Liu, K. Mesoporous Sulfur-Doped CoFe2O4 as a New Fenton Catalyst for the Highly Efficient Pollutants Removal. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 295, 120273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, P.; Ye, Z.; Zhao, L.; Xue, Q.; Lanzalaco, S.; He, Q.; Qi, X.; Sirés, I. Tailoring Single-Atom FeN4 Moieties as a Robust Heterogeneous Catalyst for High-Performance Electro-Fenton Treatment of Organic Pollutants. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2023, 322, 122116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.-C.; Li, L.; Huang, G.-X.; Pan, X.-Q.; Yu, H.-Q. Heterogeneous Fenton Water Purification Catalyzed by Iron Phosphide (FeP). Water Res. 2023, 241, 120151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Fang, G.; Liu, P.; Zhou, D.; Ma, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhan, J. Fe3O4@β-CD Nanocomposite as Heterogeneous Fenton-like Catalyst for Enhanced Degradation of 4-Chlorophenol (4-CP). Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 188, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Zhu, Y.; Xian, H.; Yan, L.; Fu, H.; Zhu, G.; Xi, Y.; Zhu, J.; He, H. CNTs/Ferrihydrite as a Highly Efficient Heterogeneous Fenton Catalyst for the Degradation of Bisphenol A: The Important Role of CNTs in Accelerating Fe(III)/Fe(II) Cycling. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 270, 118891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.-H.; Du, M.; Han, R.-Y.; Zhang, A.-Y.; Yu, H.-Q.; Xing, M. Ultrafast Water Purification by Template-Free Nanoconfined Catalysts Derived from Municipal Sludge. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202423629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mian, M.M.; Ao, W.; Deng, S. Sludge-Based Biochar Adsorbent: Pore Tuning Mechanisms, Challenges, and Role in Carbon Sequestration. Biochar 2023, 5, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L.; Ye, B.; Wang, L. Antibiotics in Soil and Water in China–a Systematic Review and Source Analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Shen, X.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, Y.; Yin, D. Rsearch Progress on Biochar Materials for New Pollutants Removal in the Aquatic Environment: A Mini-Review. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2024, 19, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikala, S.P.; Nibila, T.A.; Babitha, K.B.; Mohamed, A.A.P.; Solaiappan, A. Competitive Photo-Degradation Performance of ZnO Modified Bentonite Clay in Water Containing Both Organic and Inorganic Contaminants. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2019, 29, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchithra, P.S.; Carleer, R.; Ananthakumar, S.; Yperman, J. A Hybridization Approach to Efficient TiO2 Photodegradation of Aqueous Benzalkonium Chloride. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 293, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.T.; Kwon, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, C.; Yang, G.G.; San Lee, G.; Lee, C.W.; Kim, J.G.; Cha, S.; Jung, H.-T.; et al. Sunlight-Driven Self-Cleaning Ultrafine Particulate Matter Filter with Antibacterial Activity. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 6387–6397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mian, M.M.; Ao, W.; Xiao, L.; Xiao, J.; Deng, S. Preparation of Low-Cost Sludge-Based Highly Porous Biochar for Efficient Removal of Refractory Pollutants from Agrochemical and Pharmaceutical Wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 478, 135572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mian, M.M.; Alam, N.; Ahommed, M.S.; He, Z.; Ni, Y. Emerging Applications of Sludge Biochar-Based Catalysts for Environmental Remediation and Energy Storage: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 360, 132131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Mansouri, G. Synthesis and Characterization of a Hercynite-Supported Copper(II) Complex Based on 1,10-Phenanthroline-5,6-Dione and Acetylacetone Building Blocks and Its Catalytic Application in Annulation Reactions. Langmuir 2024, 40, 22773–22786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mian, M.M.; Liu, G.; Fu, B.; Song, Y. Facile Synthesis of Sludge-Derived MnOx-N-Biochar as an Efficient Catalyst for Peroxymonosulfate Activation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 255, 117765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhang, T.; Xing, J.; Xu, C. Hierarchical Porous Fe3O4/Co3S4 Nanosheets as an Efficient Electrocatalyst for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 9210–9216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mian, M.M.; Liu, G. Activation of Peroxymonosulfate by Chemically Modified Sludge Biochar for the Removal of Organic Pollutants: Understanding the Role of Active Sites and Mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 392, 123681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Wang, D.; He, D.; Sun, J.; Pan, X.; Zeng, Y.; Luo, H. Sustainable and Energy-Efficient Degradation of Acetaminophen in Water Using an Optimized Fenton-like System with Iron-Doped Graphitic Carbon Nitride Catalyst. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, R.; Meraji, S.H.; Mahmoudi, A.; Sanati, A.M.; Ramavandi, B. Enhanced Catalytic Degradation of Acetaminophen Using Magnesium Oxide-Infused Clay with Ultrasonic Activation of Hydrogen Peroxide. Arab. J. Chem. 2024, 17, 106047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 8978-1996; Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1998.
- Zhou, X.; Ke, M.-K.; Huang, G.-X.; Chen, C.; Chen, W.; Liang, K.; Qu, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; et al. Identification of Fenton-like Active Cu Sites by Heteroatom Modulation of Electronic Density. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2119492119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yi, Z.; Wong, L.W.; Tang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhou, C.; He, Y.; Xiong, W.; Wang, G.; et al. Oxygen Doping Cooperated with Co-N-Fe Dual-Catalytic Sites: Synergistic Mechanism for Catalytic Water Purification within Nanoconfined Membrane. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2404278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.-P.; Wu, W.D.; Wu, Z. Nanostructured Semiconductor Supported Iron Catalysts for Heterogeneous Photo-Fenton Oxidation: A Review. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 15513–15546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Shao, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Shao, B.; Xu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, W.; Wu, D. Enhanced Oxidation of Organic Contaminants by Iron(II)-Activated Periodate: The Significance of High-Valent Iron–Oxo Species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 7634–7642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhang, C.; Waite, T.D. Hydroxyl Radicals in Anodic Oxidation Systems: Generation, Identification and Quantification. Water Res. 2022, 217, 118425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Peng, H.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, G.; Wang, S.; Hong, L. Degradation of Acetaminophen in Aqueous Solution under Visible Light Irradiation by Bi-Modified Titanate Nanomaterials: Morphology Effect, Kinetics and Mechanism. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 5906–5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.-L.; Hung, J.-C.; Kuo, Y.-M. Electrochemical Co-Degradation of Acetaminophen and Bisphenol A in Aqueous Solutions: Degradation Competition and Pathways. Processes 2024, 12, 2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Brigante, M.; Dong, W.; Wu, Z.; Mailhot, G. Degradation of Acetaminophen via UVA-Induced Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs). Involvement of Different Radical Species: HO, SO4− and HO2/O2−. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Qiu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Küppers, S. Fenton-Like Catalysis and Oxidation/Adsorption Performances of Acetaminophen and Arsenic Pollutants in Water on a Multimetal Cu–Zn–Fe-LDH. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 25343–25352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Ge, L.; Peng, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W. Enhanced Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole by a Novel Fenton-like System with Significantly Reduced Consumption of H2O2 Activated by g-C3N4/MgO Composite. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Wang, J. Fenton-like Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole Using Fe-Based Magnetic Nanoparticles Embedded into Mesoporous Carbon Hybrid as an Efficient Catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 351, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.-X.; Qiu, F.; Wang, P.; Li, H.; Wang, C.-C. Magnetic MgFe2O4/MIL-88A Catalyst for Photo-Fenton Sulfamethoxazole Decomposition under Visible Light. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 301, 121965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, S.; Ren, J.; Wang, A.; Cheng, R.; Liang, H.; Liu, H.; Chen, F.; Tsiakaras, P. An Efficient Photo-Fenton In2O3@FeIn2S4 Composite Catalyst for Tetracycline Degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 491, 151549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Li, S.; Wu, G.; Ma, J. Recycling Waste Iron-Rich Algal Flocs as Cost-Effective Biochar Activator for Heterogeneous Fenton-like Reaction towards Tetracycline Degradation: Important Role of Iron Species and Moderately Defective Structures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 460, 132377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Peng, Q.; Liu, K.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, J. Building Cu0/CuFe2O4 Framework to Efficiently Degrade Tetracycline and Improve Utilization of H2O2 in Fenton-like System. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Wang, D.; Chang, Y.; Feng, Q.; Liu, Z.; Pang, M.; Meng, D.; Feng, Y.; Fan, C. Anchoring Single-Atom Cu on Tubular g-C3N4 with Defect Engineering for Enhanced Fenton-like Reactions to Efficiently Degrade Carbamazepine: Performance and Mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 479, 147841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Hu, Y.; Xu, M.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z. Photo-Fenton Degradation of Carbamazepine and Ibuprofen by Iron-Based Metal-Organic Framework under Alkaline Condition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, C.; Chunrui, Z.; Li, T.; Jiang, J.; Han, Z.; Zhang, C.; Sun, H.; Dong, S. Citric Acid-Modified MIL-88A(Fe) for Enhanced Photo-Fenton Oxidation in Water Decontamination. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 308, 122945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mian, M.M.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, X.; Deng, S. Sludge-Derived Hercynite–Carbon as a Low-Cost Catalyst for Efficient Degradation of Refractory Pollutants in Wastewater. Water 2025, 17, 2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192908
Mian MM, Zhu J, Jiang X, Deng S. Sludge-Derived Hercynite–Carbon as a Low-Cost Catalyst for Efficient Degradation of Refractory Pollutants in Wastewater. Water. 2025; 17(19):2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192908
Chicago/Turabian StyleMian, Md Manik, Jiaxin Zhu, Xiangzhe Jiang, and Shubo Deng. 2025. "Sludge-Derived Hercynite–Carbon as a Low-Cost Catalyst for Efficient Degradation of Refractory Pollutants in Wastewater" Water 17, no. 19: 2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192908
APA StyleMian, M. M., Zhu, J., Jiang, X., & Deng, S. (2025). Sludge-Derived Hercynite–Carbon as a Low-Cost Catalyst for Efficient Degradation of Refractory Pollutants in Wastewater. Water, 17(19), 2908. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192908






