Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Metals and Metalloids in Surface Drinking Water Sources of the Pearl River Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Assessment of MMP Pollution Levels
2.4. Method of Health Risk Assessment
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Analysis and Discussion
3.1. Water Chemical Parameters
3.2. Overall Pollution Level of MMPs
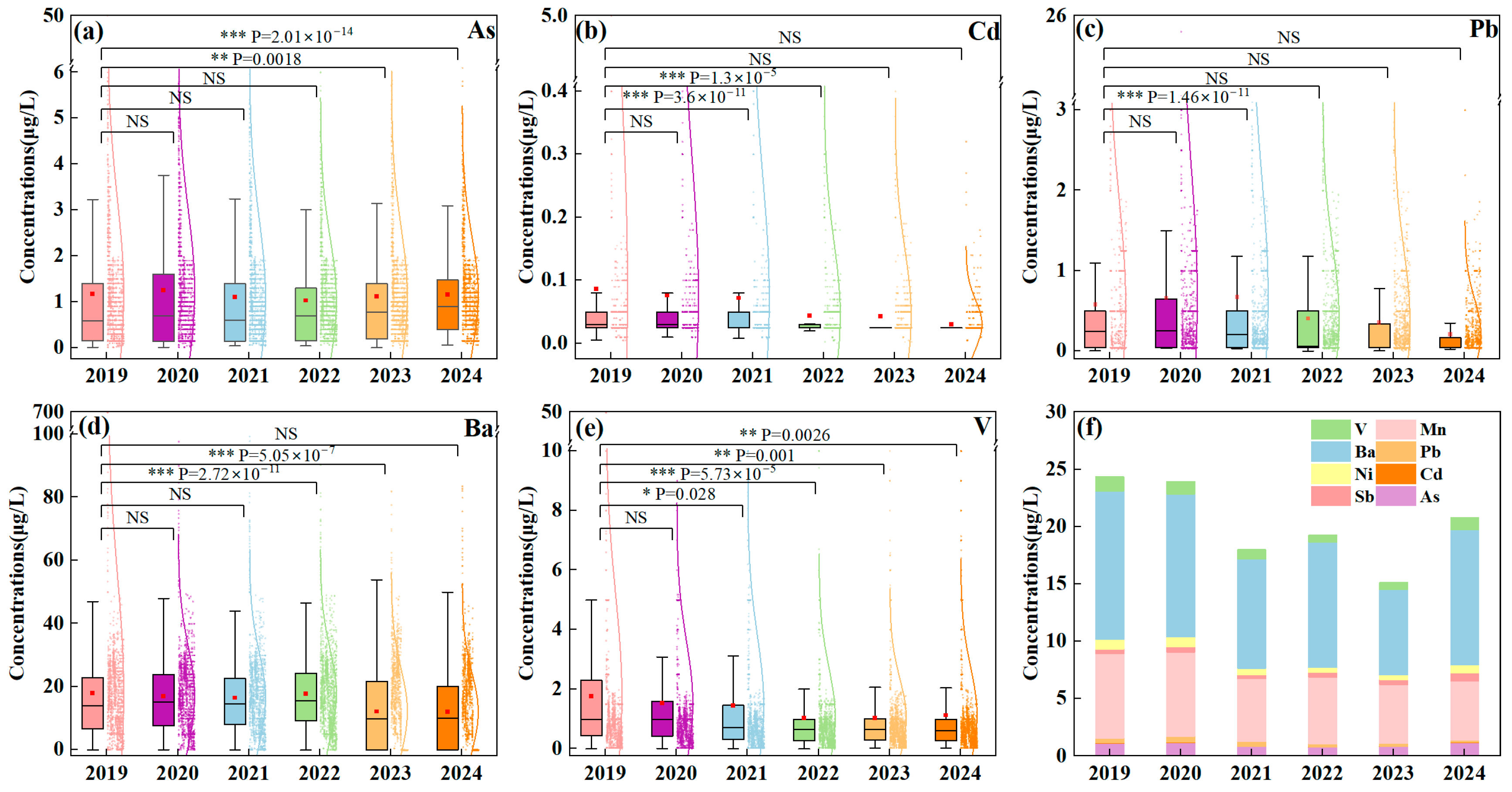
3.3. Temporal Variations in MMPs
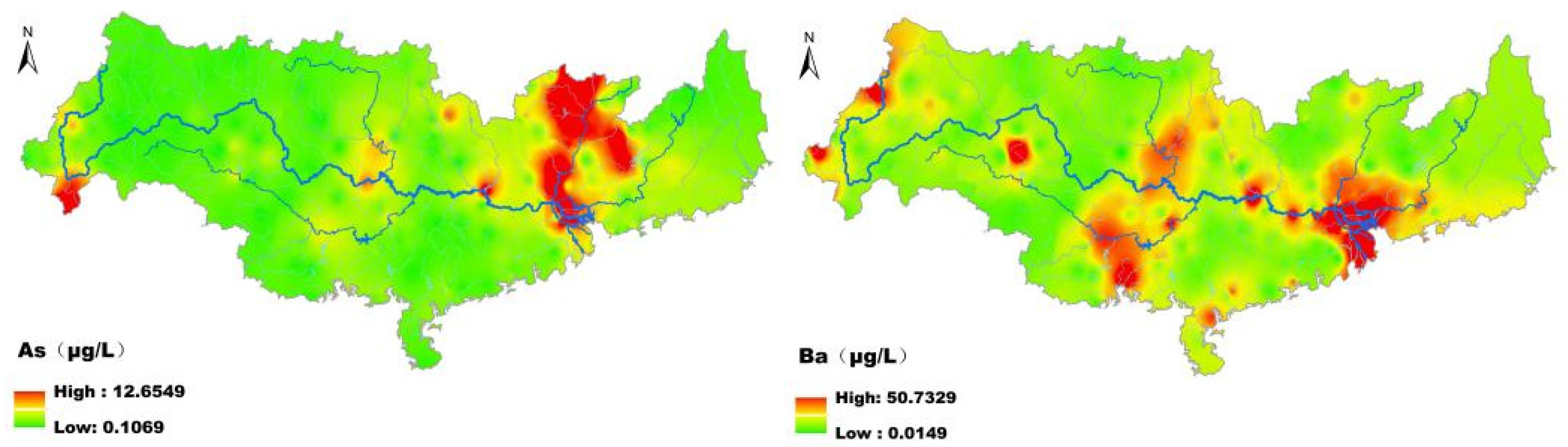
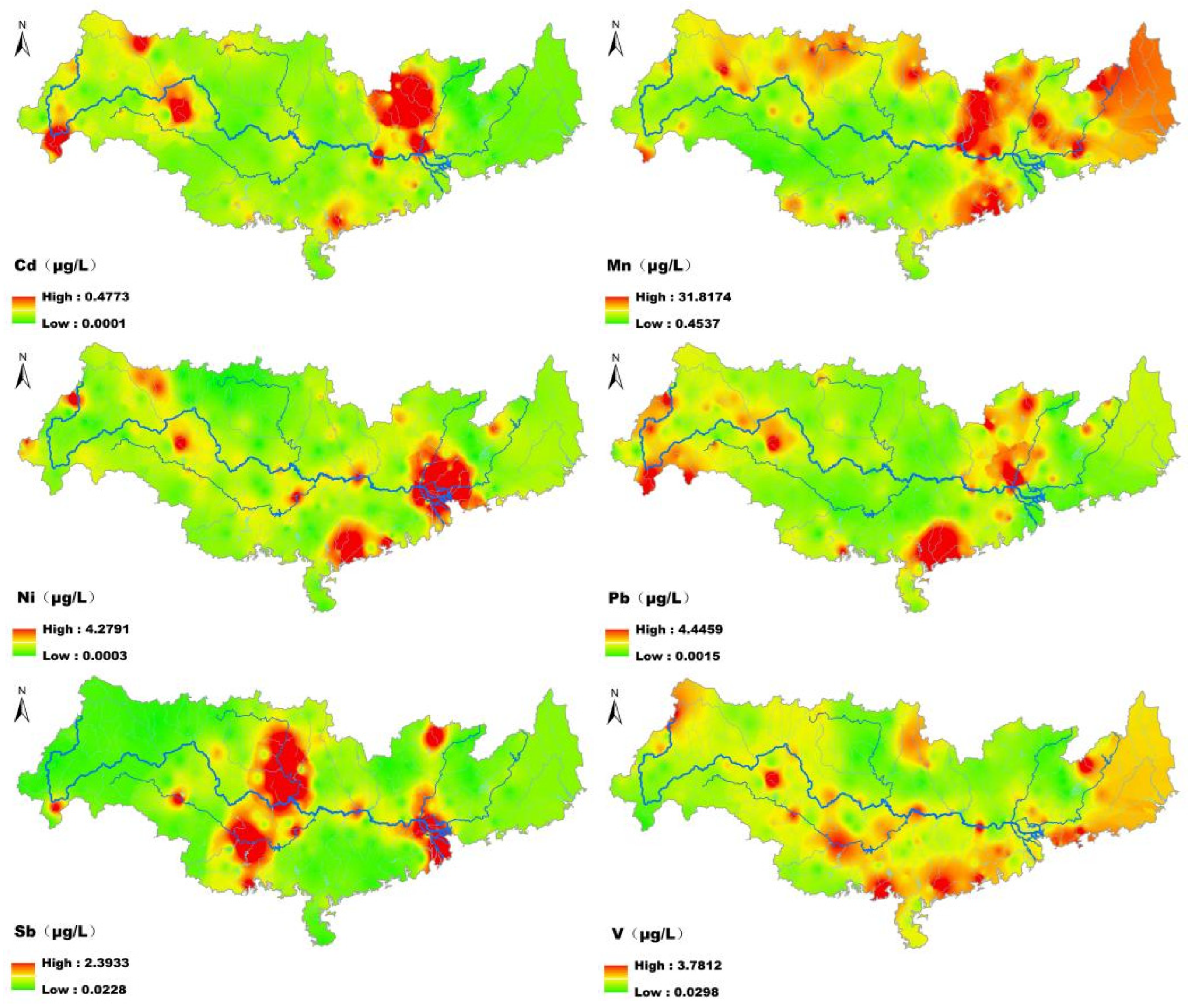
3.4. Spatial Distribution of MMPs
3.5. Health Risk Assessment
3.5.1. Non-Carcinogenic Risk
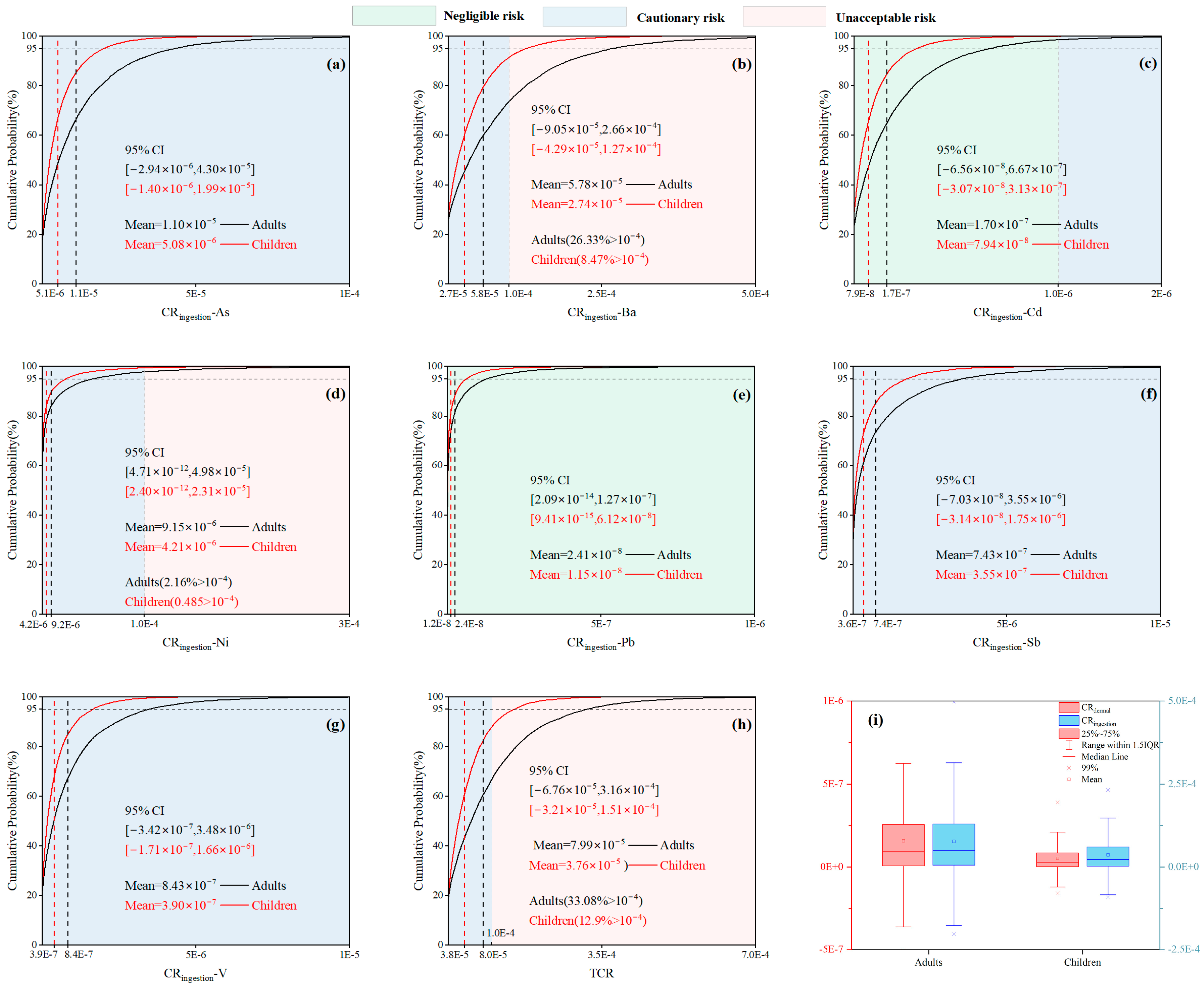
3.5.2. Carcinogenic Risk
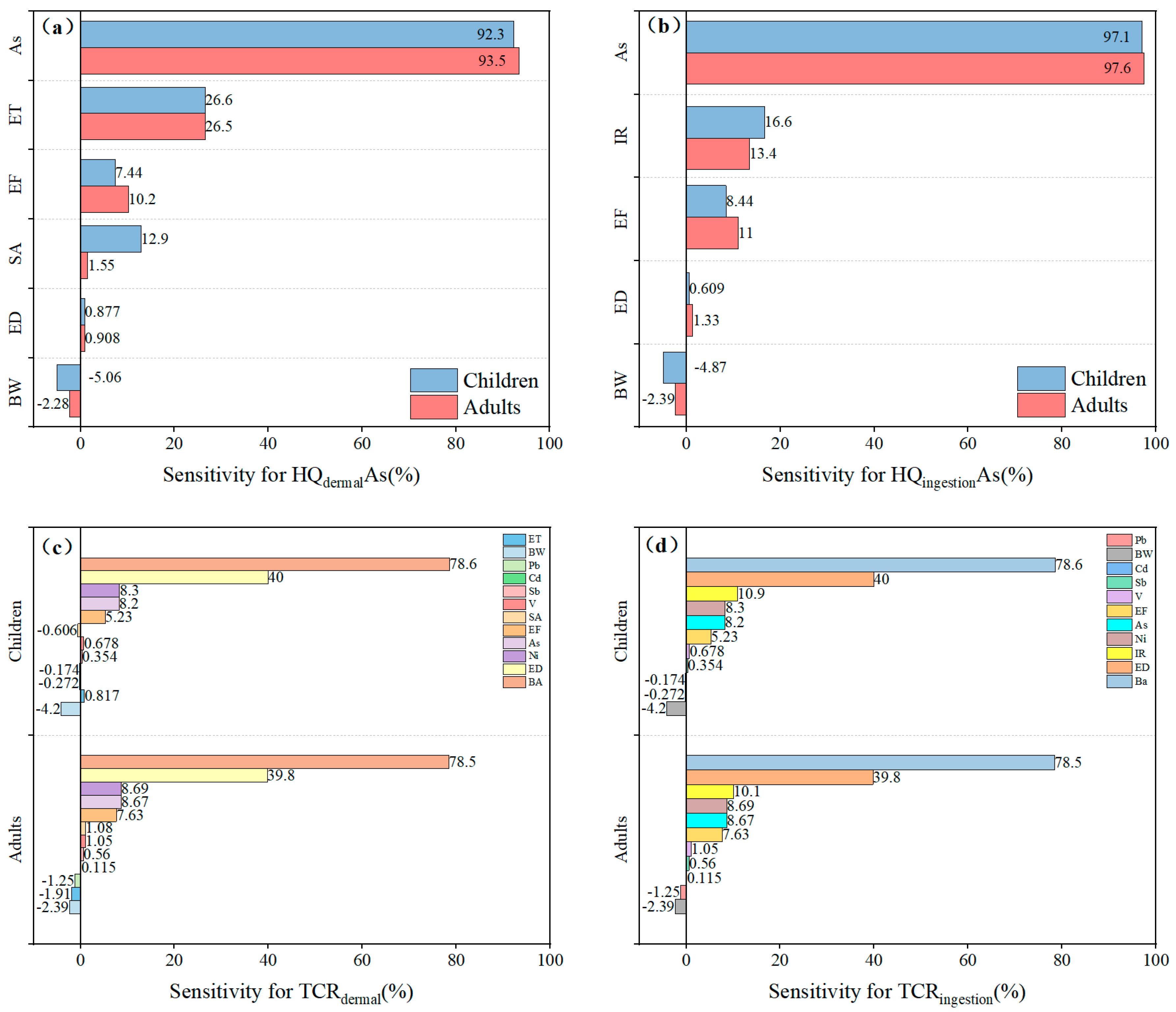
3.5.3. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, V.; Pandita, S.; Singh, S.; Bhardwaj, R.; Varol, M.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. A global meta-analysis of toxic metals in continental surface water bodies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.; Muhammad, S.; Fatima, H. Evaluation and risks assessment of potentially toxic elements in water and sediment of the Dor River and its tributaries, Northern Pakistan. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S. Water quality prospective in Twenty First Century: Status of water quality in major river basins, contemporary strategies and impediments: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, M.A.; Khatun, B.; Jewel, M.A.S.; Ara, J.; Islam Kazal, M.S.; Hasan, J. Assessment of water quality and heavy metal indices in a tropical freshwater river for aquatic life and public health standard. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 169, 112862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulke, A.B.; Ratanpal, S.; Sonker, S. Understanding heavy metal toxicity: Implications on human health, marine ecosystems and bioremediation strategies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 206, 116707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Tareq, A.M.; Emran, T.B.; Nainu, F.; Khusro, A.; Idris, A.M.; Khandaker, M.U.; Osman, H.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; et al. Impact of heavy metals on the environment and human health: Novel therapeutic insights to counter the toxicity. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustaoğlu, F.; Islam, M.S. Potential toxic elements in sediment of some rivers at Giresun, Northeast Turkey: A preliminary assessment for ecotoxicological status and health risk. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.B. Levels of heavy metals (Fe, Cu, Ni, Cr, Pb, and Zn) in tissue of Mugil cephalus and Trachurus mediterraneus from Iskenderun Bay, Turkey. Environ. Res. 2003, 92, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Luo, P.; Li, S.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, D. Distributions of Heavy Metals in Rice and Corn and Their Health Risk Assessment in Guizhou Province. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 108, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balali-Mood, M.; Naseri, K.; Tahergorabi, Z.; Khazdair, M.R.; Sadeghi, M. Toxic Mechanisms of Five Heavy Metals: Mercury, Lead, Chromium, Cadmium, and Arsenic. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 643972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Liu, D.; Bu, T.; Zhang, M.; Peng, J.; Ma, J. Assessment of pollution and health risks from exposure to heavy metals in soil, wheat grains, drinking water, and atmospheric particulate matter. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 376, 124448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asefa, E.M.; Damtew, Y.T.; Mengistu, D.A.; Tolera, S.T.; Dugasa, F.F.; Berhanu, A.; Enoe, J.; Ober, J.; Teklu, B.M.; Weldemariam, E.D. Heavy metals in Ethiopian drinking water and public health risks: Insights from nationwide and regional analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.; Wang, C.; Florkowski, W.J.; Yang, Z. Determinants of urban consumer expenditure on aquatic products in Shanghai, China. Aquac. Econ. Manag. 2023, 27, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.K.; Jain, C.K.; Singhal, D.C.; Choubey, V.K. Kinetics of sorption of lead on bed sediments of River Hindon, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 157, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Huang, G.; Liu, L.; Zhai, M.; Guan, Y. Metabolism of urban wastewater: Ecological network analysis for Guangdong Province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 217, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Qu, S.; Nel, W.; Ji, J. The impact of natural weathering and mining on heavy metal accumulation in the karst areas of the Pearl River Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, G.; Li, Y.; Tong, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W. Temporal variation and regional transfer of heavy metals in the Pearl (Zhujiang) River, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 8410–8420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, A.; Gong, L.; Ding, H.; Wang, M. Cancer Mortality and Long-Term Environmental Exposure of Cadmium in Contaminated Community Based on a Third Retrospective Cause of Death Investigation of Residents Living in the Guangdong Province from 2004 to 2005. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 4504–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Jia, X. Oyster arsenic, cadmium, copper, mercury, lead and zinc levels in the northern South China Sea: Long-term spatiotemporal distributions, combined effects, and risk assessment to human health. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 12706–12719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, H.M.; Duzgoren-Aydin, N.S.; Au, C.K.; Krupanidhi, S.; Fung, K.Y.; Cheung, K.C.; Wong, Y.K.; Peng, X.L.; Ye, Z.H.; Yung, K.K.L.; et al. Monitoring and assessment of heavy metal contamination in a constructed wetland in Shaoguan (Guangdong Province, China): Bioaccumulation of Pb, Zn, Cu and Cd in aquatic and terrestrial components. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 24, 9079–9088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, R.; Cui, J.; Gan, S.; Pan, J.; Guo, P. Improvement of water quality in the Pearl River Estuary, China: A long-term (2008–2017) case study of temporal-spatial variation, source identification and ecological risk of heavy metals in surface water of Guangzhou. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 21084–21097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, J.; Wang, Y.; Luo, H. Distribution, sources, and fluxes of heavy metals in the Pearl River Delta, South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lao, X.; Tam, N.F.Y.; He, H.; Su, X.; Zhong, M.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Wei, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Distribution Characteristics and Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Sediments of Fengyuan River, Guangdong. Environ. Forensics 2025, 26, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Han, Z.; Lu, H.; Zhao, R.; Wen, M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, B. Spatial-temporal variation, source apportionment and risk assessment of lead in surface river sediments over ~20 years of rapid industrialisation in the Pearl River Basin, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 464, 132981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 91.2-2022; Technical Specifications for Surface Water Environmental Quality Monitoring. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Sheng, D.; Meng, X.; Wen, X.; Wu, J.; Yu, H.; Wu, M. Contamination characteristics, source identification, and source-specific health risks of heavy metal(loid)s in groundwater of an arid oasis region in Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Al-Hilali, A.A.; Ahmed, A.M.; Mussa, Z.H.; Falah, M.W.; Abed, S.A.; Deo, R.; Jawad, A.H.; Abdul Maulud, K.N.; Latif, M.T.; et al. Statistical and spatial analysis for soil heavy metals over the Murray-Darling river basin in Australia. Chemosphere 2023, 317, 137914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Li, Q.; Ma, X.; Han, M. Assessment of heavy metals contamination and water quality characterization in the Nanming River, Guizhou Province. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 43, 1273–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Ariyan, T.N.; Quraishi, S.B.; Nur E Alam, M.; Khan, M.S.R.; Faria, F.F.; Kabir, A. Comprehensive analysis and human health risk assessment of tap water quality in Dhaka City, Bangladesh: Integrating source identification, index-based evaluation, and heavy metal assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 485, 136837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Bai, Y.; Wang, E.; Zhang, M.; Fu, Q.; Wei, L.; Yu, Y. Heavy metals in influent and effluent from 146 drinking water treatment plants across China: Occurrence, explanatory factors, probabilistic health risk, and removal efficiency. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 450, 131003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, M.H.; Tamma, A.A.; Saeed, O.; Székács, A.; Abukhadra, M.R.; El-Sherbeeny, A.M.; Bence, C.; Mikita, V.; Kovács, A.; Szűcs, P. Advanced approach combines integrated weight water quality index and potential toxic elements for environmental and health risk assessment supported by simulation technique in Oued Souf, Algeria. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.B.; Reza, A.H.M.S.; Siddique, M.A.B.; Akbor, M.A.; Nahar, A.; Hasan, M.; Uddin, M.R.; Zaman, M.N.; Islam, I. Origin, spatial distribution, sediment contamination, ecological and health risk evaluation of trace metals in sediments of ship breaking area of Bangladesh. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Cao, R.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Geng, N. A nationwide investigation on the characteristics and health risk of trace elements in surface water across China. Water Res. 2024, 250, 121076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Qadeer, A.; Chang, S.; Tu, X.; Shang, H.; Khan, M.A.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, Q.; Yu, Y.; Feng, Y. Short-chain PFASs dominance and their environmental transport dynamics in urban water systems: Insights from multimedia transport analysis and human exposure risk. Environ. Int. 2025, 202, 109602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Brookes, J.; Wang, X.; Han, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, G.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, S.; Qin, B. Water quality improvement and existing challenges in the Pearl River Basin, China. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 55, 104184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sun, S. Assessing trace element-related health risks in urban centralized drinking water sources in China. Water Res. 2025, 285, 124118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Chang, S.; Tu, X.; Yu, Y.; Shang, H.; Wang, E.; Fu, Q. A comprehensive study of heavy metals in centralized drinking water sources of the Yangtze River Basin: Levels, sources, and probabilistic health risk. Water 2024, 16, 3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Yu, M.; Yuan, Q.; Meng, Y.; Qie, Y.; Shang, Z.; Luan, F.; Zhang, D. Spatial distribution, pollution assessment, and source identification of heavy metals in the Yellow River. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ding, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. Characterizing the changes in the source apportionment of metal in surface waters by an integrated approach. ACS EST Water 2023, 3, 2041–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Routh, J.; Luo, D.; Wei, L.; Liu, Y. Arsenic in the Pearl River Delta and its related waterbody, South China: Occurrence and sources, a review. Geosci. Lett. 2021, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.W.; Huang, P.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Xie, K.Z.; Wang, X.H.; He, G.X. Water quality of a tributary of the Pearl River, the Beijiang, Southern China: Implications from multivariate statistical analyses. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 172, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Deng, C.; Huang, N.; Huang, X. Multivariate statistical approach to identify heavy metal sources in agricultural soil around an abandoned Pb–Zn mine in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 68, 1331–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Luyen, N.; Savichev, O.G. Assessing the Influence of the Mining Operations on the State of Streams in the Northern Part of the Red River Basin (Viet Nam). Geogr. Nat. Resour. 2018, 39, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Song, N.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; He, L.; Yang, R.; Yang, L.; He, D. Assessment of health risk and identification of pollution sources of heavy metals in water in Chongqing’s wastewater treatment plants based on ICP-MS. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 373, 126193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, S.; Lu, W.; Yang, W.; Li, S. Water quality assessment, possible origins and health risks of toxic metal(loid)s in five cascade reservoirs in the upper Mekong. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 441, 141049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, I.A.; Ghosh, P.; Bhattacharaya, A.; Baalousha, M. Origin, distribution, fate, and risks of potentially toxic elements in the aquatic environment of Bengaluru metropolis, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Xiao, X.; Zou, H.; Yang, Z.; Ahmad, U.M.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, G.; Liu, G.; Duan, X.; et al. Levels, origins and probabilistic health risk appraisal for trace elements in drinking water from Lhasa, Tibet. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 45, 3405–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Oyola, S.; Valverde-Armas, P.E.; Romero-Crespo, P.; Capa, D.; Valdivieso, A.; Coronel-León, J.; Guzmán-Martínez, F.; Chavez, E. Heavy metal(loid)s contamination in water and sediments in a mining area in Ecuador: A comprehensive assessment for drinking water quality and human health risk. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 4929–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, N.; Rahman, M.S. Groundwater hydrogeochemistry and probabilistic health risk assessment through exposure to arsenic-contaminated groundwater of Meghna floodplain, central-east Bangladesh. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleem, E.M.; Mostafa, A.; Mokhtar, M.; Salman, S.A. Risk assessment of heavy metals in drinking water on the human health, Assiut City, and its environs, Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Li, H.; Tudi, M.; Yuan, X.; Yang, L. Comparison of characteristics, water quality and health risk assessment of trace elements in surface water and groundwater in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 219, 112283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Yang, G.; Lei, T.; Mei, S.; Yang, H.; Liu, L.; Yang, H.; et al. Heavy Metals in the Mainstream Water of the Yangtze River Downstream: Distribution, Sources and Health Risk Assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, L.; Rishi, M.S.; Siddiqui, A.U. Deterministic and probabilistic health risk assessment techniques to evaluate non-carcinogenic human health risk (NHHR) due to fluoride and nitrate in groundwater of Panipat, Haryana, India. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Fu, X.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Xie, F. Source-specific probabilistic health risk assessment of heavy metals in surface water of the Yangtze River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahmardeh Behrooz, R.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Grivas, G.; Mihalopoulos, N. Human health risk assessment for toxic elements in the extreme ambient dust conditions observed in Sistan, Iran. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Chang, S.; Tu, X.; Wang, E.; Yu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Fu, Q. Heavy metals in centralized drinking water sources of the Yangtze River: A comprehensive study from a basin-wide perspective. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 133936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Yin, H.; Dong, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Lu, C. Analysis and probabilistic health risk assessment of vertical heavy metal pollution in the water environment of reservoir in the west coast new area of Qingdao, China. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 362, 125021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippong, T.; Resz, M.-A.; Tănăselia, C.; Cadar, O. Assessing microbiological and heavy metal pollution in surface waters associated with potential human health risk assessment at fish ingestion exposure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Symbol | Parameters | Units | Distribution | Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adults | Children | ||||
| MEC | Measured Environmental Concentration | mg/L | - | Data value | Data value |
| IR | Ingestion Rate | L/da | Log-normal | (1.23, 0.27) | (1.12, 0.27) |
| EF | Exposure Frequency | d/a | Triangular | 345 (180–365) | 345 (180–365) |
| ED | Exposure Duration | years | Uniform | (0, 70) | (0, 10) |
| AT | Averaging time—non-carcinogen | days | Constant | 365 × ED | |
| Averaging time—carcinogen | Constant | 365 × 70 | |||
| BW | Body Weight | kg | Log-normal | (59.78, 1.07) | (16.68, 1.48) |
| SA | Skin Surface Area | cm2 | Log-normal | LN (17,900, 339.93) | LN (11,493, 2296) |
| ET | Exposure Time | hours/days | Triangular | 0.11 (0.03–0.33) | |
| As | Arsenic | µg/L | Weibull | (0.00066, 0.00063) | |
| Cd | Cadmium | µg/L | Gumbel | (0.00002, 0.00003) | |
| Pb | Lead | µg/L | Log-normal | (0.00101, 0.02875) | |
| Mn | Manganese | µg/L | Gamma | (0.02661, 0.00023) | |
| Sb | Antimony | µg/L | Log-normal | (0.00347, 0.2317) | |
| Ni | Nickel | µg/L | Gamma | (0.00501, 0.00012) | |
| Ba | Barium | µg/L | Gamma | (0.05683, 0.00019) | |
| V | Vanadium | µg/L | Gumbel | (0.00037, 0.00071) | |
| KP | Dermal Permeability Coefficient | cm/h | - | As = 0.001; Cd = 0.001; Pb = 0.001; Sb = 0.001; Ni = 0.0002; Ba = 0.001; V = 0.001 | |
| RfD | Reference Dose | mg/(kg·day) | - | As = 0.0003; Cd = 0.0001; Pb = 0.0035; Mn = 0.024; Sb = 0.0004; Ni = 0.02; Ba = 0.2; V = 0.007 | |
| SF | Slope Factor | kg·day/mg | - | As = 1.5; Cd = 0.63; Pb = 0.0085; Sb = 0.207; Ni = 1.7; Ba = 0.851; V = 0.122 | |
| Parameters | As | Cd | Pb | Mn | Sb | Ni | Ba | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detection Rate (%) | 81.98 | 66.83 | 70.51 | 80.83 | 67.67 | 61.96 | 68.39 | 68.20 |
| Mean Concentration (µg/L) | 1.14 | 0.06 | 0.48 | 7.43 | 0.65 | 0.98 | 15.55 | 1.32 |
| CV (%) | 144.6 | 329.5 | 249.6 | 167.7 | 113.6 | 167.4 | 130.4 | 165.6 |
| Median Concentration (µg/L) | 0.70 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 5.05 | 0.31 | 0.46 | 13.50 | 0.74 |
| Pollution Level Index | Max. | Min. | Mean | Median | 90th Percentile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPI | 87.08 | 1.37 × 10−6 | 4.81 | 2.28 | 11.93 |
| NI | 1.28 | 3.75 × 10−6 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.29 |
| CD | 5.20 | 5.0 × 10−6 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 0.51 |
| Risk | MMPs | Mean (Median) | Std. Deviation | Min−Max | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adults | Children | Adults | Children | Adults | Children | ||
| HQ | As | 4.85 × 10−2 (3.45 × 10−2) | 1.59 × 10−1 (1.12 × 10−1) | 5.94 × 10−2 | 1.95 × 10−1 | −7.58 × 10−2–6.39 × 10−1 | −1.87 × 10−1–2.35 |
| Ba | 6.84 × 10−4 (6.47 × 10−4) | 2.25 × 10−3 (2.10 × 10−3) | 1.14 × 10−3 | 3.79 × 10−3 | −5.83 × 10−3–7.97 × 10−3 | −2.10 × 10−2–2.75 × 10−2 | |
| Cd | 5.37 × 10−3 (4.05 × 10−3) | 1.76 × 10−2 (1.33 × 10−2) | 6.37 × 10−3 | 2.12 × 10−2 | −9.33 × 10−3–5.83 × 10−2 | −3.63 × 10−2–2.36 × 10−1 | |
| Mn | 3.78 × 10−3 (1.71 × 10−3) | 1.25 × 10−2 (5.53 × 10−3) | 7.12 × 10−3 | 2.42 × 10−2 | −9.75 × 10−4–1.66 × 10−1 | −3.62 × 10−3–6.84 × 10−1 | |
| Ni | 5.32 × 10−4 (5.74 × 10−6) | 1.73 × 10−3 (1.83 × 10−5) | 1.62 × 10−3 | 5.22 × 10−3 | 8.92 × 10−11–2.92 × 10−2 | 3.65 × 10−10–8.50 × 10−2 | |
| Pb | 1.63 × 10−3 (7.91 × 10−5) | 5.42 × 10−3 (2.63 × 10−4) | 4.16 × 10−3 | 1.42 × 10−2 | −4.16 × 10−10–5.60 × 10−2 | −1.35 × 10−9–3.33 × 10−1 | |
| Sb | 1.81 × 10−2 (5.71 × 10−3) | 5.93 × 10−2 (1.86 × 10−2) | 2.93 × 10−2 | 9.58 × 10−2 | −2.51 × 10−3–3.05 × 10−1 | −1.37 × 10−2–8.41 × 10−1 | |
| V | 1.96 × 10−3 (1.29 × 10−3) | 6.45 × 10−3 (4.20 × 10−3) | 2.73 × 10−3 | 8.91 × 10−3 | −2.79 × 10−3–4.33 × 10−2 | −9.14 × 10−3–9.82 × 10−2 | |
| THI | All MMPs | 8.06 × 10−2 (6.61 × 10−2) | 2.64 × 10−1 (2.14 × 10−1) | 6.72 × 10−2 | 2.21 × 10−1 | −4.07 × 10−2–6.75 × 10−1 | −1.63 × 10−1–2.64 |
| CR | As | 1.10 × 10−5 (5.45 × 10−6) | 5.08 × 10−6 (2.56 × 10−6) | 1.69 × 10−5 | 7.63 × 10−6 | −1.78 × 10−5–2.59 × 10−4 | −9.17 × 10−6–9.47 × 10−5 |
| Ba | 5.78 × 10−5 (3.57 × 10−5) | 2.74 × 10−5 (1.65 × 10−5) | 1.18 × 10−4 | 5.54 × 10−5 | −7.17 × 10−4–1.02 × 10−3 | −3.87 × 10−4–4.63 × 10−4 | |
| Cd | 1.70 × 10−7 (9.01 × 10−8) | 7.94 × 10−8 (4.20 × 10−8) | 2.54 × 10−7 | 1.21 × 10−7 | −4.61 × 10−7–2.71 × 10−6 | −2.96 × 10−7–1.42 × 10−6 | |
| Ni | 9.15 × 10−6 (6.86 × 10−8) | 4.21 × 10−6 (3.14 × 10−8) | 3.25 × 10−5 | 1.49 × 10−5 | 1.30 × 10−14–5.65 × 10−4 | 1.12 × 10−15–3.01 × 10−4 | |
| Pb | 2.41 × 10−8 (8.32 × 10−10) | 1.15 × 10−8 (3.76 × 10−10) | 7.47 × 10−8 | 3.70 × 10−8 | −9.69 × 10−15–1.48 × 10−6 | −2.42 × 10−15–1.12 × 10−6 | |
| Sb | 7.43 × 10−7 (1.52 × 10−7) | 3.55 × 10−7 (7.03 × 10−8) | 1.44 × 10−6 | 7.01 × 10−7 | −1.72 × 10−7–1.56 × 10−5 | −1.02 × 10−7–9.19 × 10−6 | |
| V | 8.43 × 10−7 (3.85 × 10−7) | 3.90 × 10−7 (1.76 × 10−7) | 1.43 × 10−6 | 6.49 × 10−7 | −2.10 × 10−6–2.40 × 10−5 | −9.61 × 10−7–9.44 × 10−6 | |
| CR | All MMPs | 7.79 × 10−5 (4.97 × 10−5) | 3.66 × 10−5 (2.30 × 10−5) | 1.27 × 10−4 | 5.91 × 10−5 | −7.59 × 10−4–1.65 × 10−3 | −3.54 × 10−4–6.12 × 10−4 |
| Risk | MMPs | Mean (Median) | Std. Deviation | Min−Max | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adults | Children | Adults | Children | Adults | Children | ||
| HQ | As | 1.11 × 10−4 (7.21 × 10−5) | 2.58 × 10−4 (1.61 × 10−4) | 1.44 × 10−4 | 3.53 × 10−4 | −1.50 × 10−4–1.60 × 10−3 | −5.62 × 10−4–4.59 × 10−3 |
| Ba | 1.60 × 10−6 (1.32 × 10−6) | 3.65 × 10−6 (2.92 × 10−6) | 2.77 × 10−6 | 6.76 × 10−6 | −1.89 × 10−5–1.97 × 10−5 | −4.08 × 10−5–9.10 × 10−5 | |
| Cd | 1.22 × 10−5 (8.39 × 10−6) | 2.87 × 10−5 (1.86 × 10−5) | 1.57 × 10−5 | 3.87 × 10−5 | −3.00 × 10−5–1.68 × 10−4 | −9.44 × 10−5–4.52 × 10−4 | |
| Ni | 2.40 × 10−7 (2.34 × 10−9) | 5.53 × 10−7 (5.34 × 10−9) | 7.88 × 10−7 | 1.77 × 10−6 | 2.25 × 10−14–1.90 × 10−5 | 6.06 × 10−14–2.86 × 10−5 | |
| Pb | 3.67 × 10−6 (1.72 × 10−7) | 8.80 × 10−6 (3.80 × 10−7) | 9.86 × 10−6 | 2.46 × 10−5 | −1.01 × 10−12–1.51 × 10−4 | −2.07 × 10−12–4.87 × 10−4 | |
| Sb | 4.20 × 10−5 (1.18 × 10−5) | 9.54 × 10−5 (2.70 × 10−5) | 7.31 × 10−5 | 1.67 × 10−4 | −7.43 × 10−6–7.63 × 10−4 | −2.05 × 10−5–2.06 × 10−3 | |
| V | 4.50 × 10−6 (2.65 × 10−6) | 1.04 × 10−5 (5.87 × 10−6) | 6.65 × 10−6 | 1.59 × 10−5 | −7.34 × 10−6–8.30 × 10−5 | −1.55 × 10−5–2.74 × 10−4 | |
| THI | All MMPs | 1.74 × 10−4 (1.29 × 10−4) | 4.04 × 10−4 (2.90 × 10−4) | 1.69 × 10−4 | 4.09 × 10−4 | −1.12 × 10−4–1.68 × 10−3 | −3.13 × 10−4–5.62 × 10−3 |
| CR | As | 2.50 × 10−8 (1.14 × 10−8) | 8.28 × 10−9 (3.71 × 10−9) | 4.00 × 10−8 | 1.37 × 10−8 | −5.06 × 10−8–4.99 × 10−7 | −2.68 × 10−8–1.74 × 10−7 |
| Ba | 1.35 × 10−7 (7.35 × 10−8) | 4.44 × 10−8 (2.33 × 10−8) | 2.81 × 10−7 | 9.87 × 10−8 | −2.07 × 10−6–2.64 × 10−6 | −8.86 × 10−7–1.10 × 10−6 | |
| Cd | 3.83 × 10−10 (1.87 × 10−10) | 1.30 × 10−10 (6.06 × 10−11) | 6.12 × 10−10 | 2.19 × 10−10 | −1.52 × 10−9–8.72 × 10−9 | −5.72 × 10−10–2.64 × 10−9 | |
| Ni | 4.09 × 10−9 (2.87 × 10−11) | 1.36 × 10−9 (8.88 × 10−12) | 1.53 × 10−8 | 5.24 × 10−9 | 4.31 × 10−18–2.98 × 10−7 | 3.00 × 10−19–1.32 × 10−7 | |
| Pb | 5.36 × 10−11 (1.78 × 10−12) | 1.90 × 10−11 (5.73 × 10−13) | 1.70 × 10−10 | 6.46 × 10−11 | −2.06 × 10−17–2.86 × 10−9 | −4.11 × 10−18–1.77 × 10−9 | |
| Sb | 1.73 × 10−9 (3.14 × 10−10) | 5.69 × 10−10 (1.04 × 10−10) | 3.61 × 10−9 | 1.22 × 10−9 | −5.06 × 10−10–4.87 × 10−8 | −2.29 × 10−10–2.18 × 10−8 | |
| V | 1.93 × 10−9 (7.99 × 10−10) | 6.30 × 10−10 (2.50 × 10−10) | 3.52 × 10−9 | 1.16 × 10−9 | −5.01 × 10−9–5.85 × 10−8 | −1.62 × 10−9–2.02 × 10−8 | |
| CR | All MMPs | 1.59 × 10−7 (9.20 × 10−8) | 5.40 × 10−8 (2.99 × 10−8) | 2.87 × 10−7 | 9.93 × 10−8 | −1.63 × 10−6–2.86 × 10−6 | −5.20 × 10−7–1.19 × 10−6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Tu, X.; Huo, S.; Fu, Q.; Chang, S.; Zhang, K. Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Metals and Metalloids in Surface Drinking Water Sources of the Pearl River Basin. Water 2025, 17, 2873. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192873
Li B, Hu Y, Zhu Y, Yang Y, Tu X, Huo S, Fu Q, Chang S, Zhang K. Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Metals and Metalloids in Surface Drinking Water Sources of the Pearl River Basin. Water. 2025; 17(19):2873. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192873
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bin, Yang Hu, Yinying Zhu, Yubo Yang, Xiang Tu, Shouliang Huo, Qing Fu, Sheng Chang, and Kunfeng Zhang. 2025. "Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Metals and Metalloids in Surface Drinking Water Sources of the Pearl River Basin" Water 17, no. 19: 2873. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192873
APA StyleLi, B., Hu, Y., Zhu, Y., Yang, Y., Tu, X., Huo, S., Fu, Q., Chang, S., & Zhang, K. (2025). Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Metals and Metalloids in Surface Drinking Water Sources of the Pearl River Basin. Water, 17(19), 2873. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192873





