Simulation of Water Renewal Time in West Lake Based on Delft3D and Its Environmental Impact Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
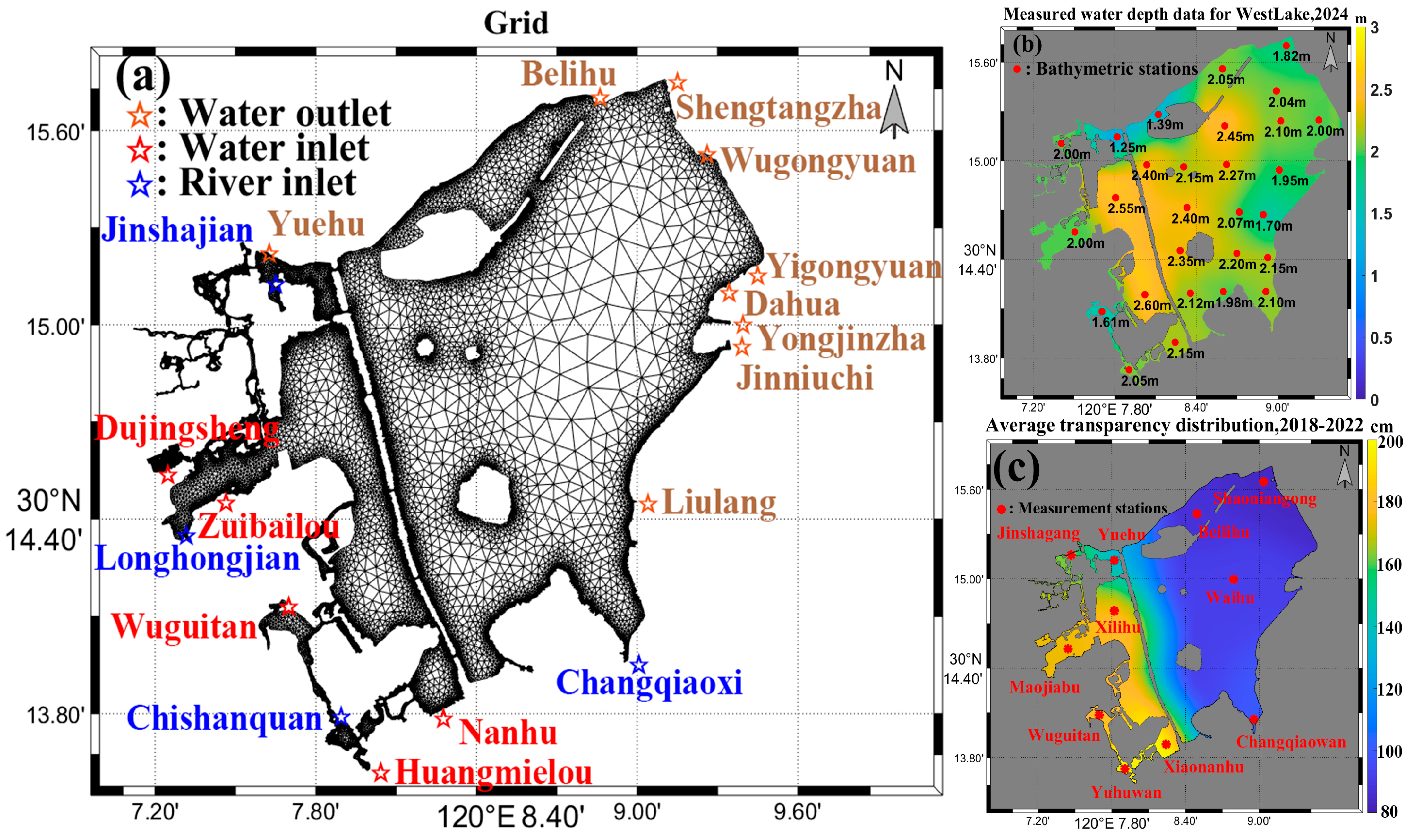
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Water Quality Parameters
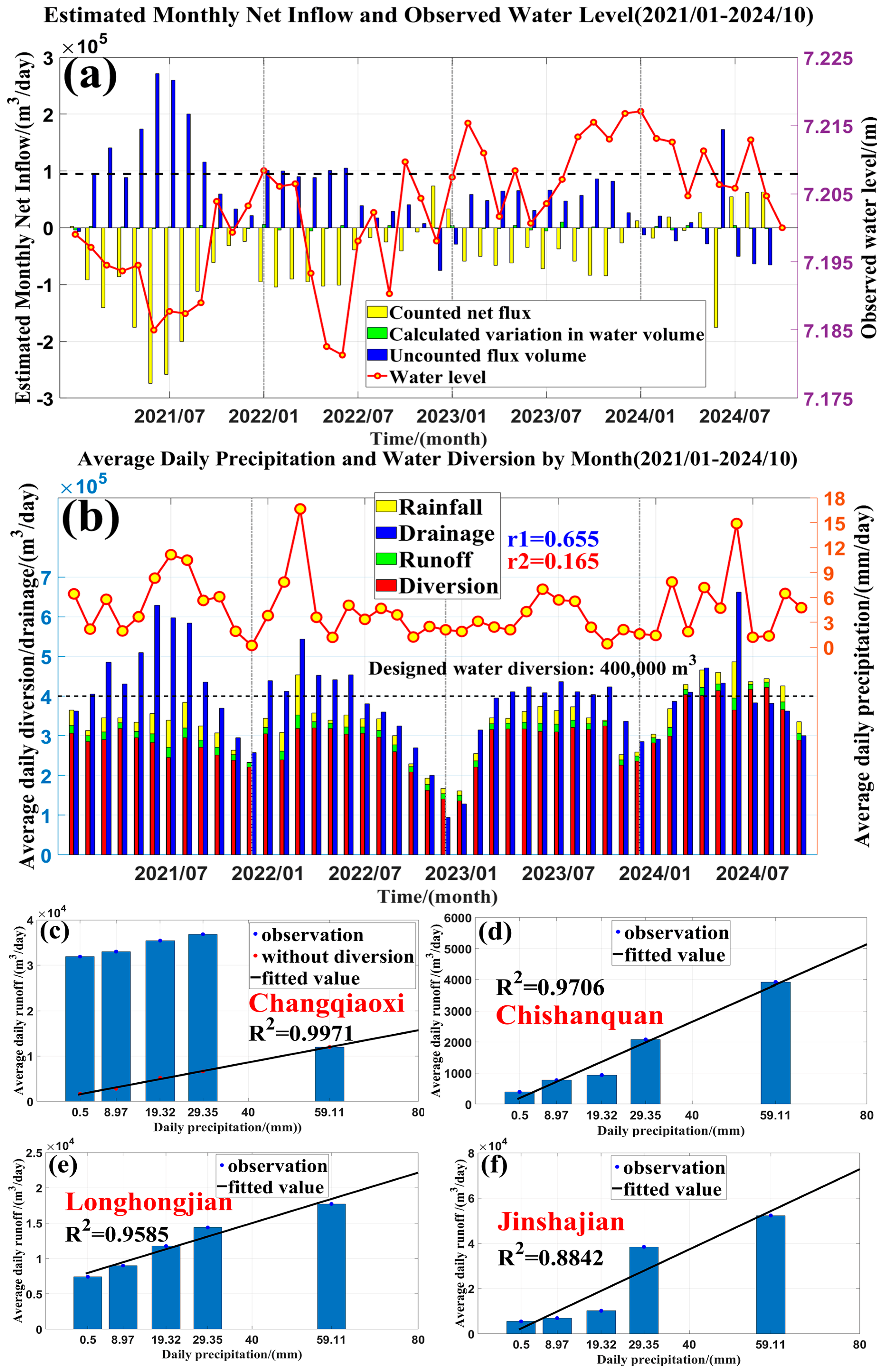
2.3. Hydrodynamic Model
2.4. Machine Learning Algorithms and Training Set Configuration Options
2.5. Water Renewal Time
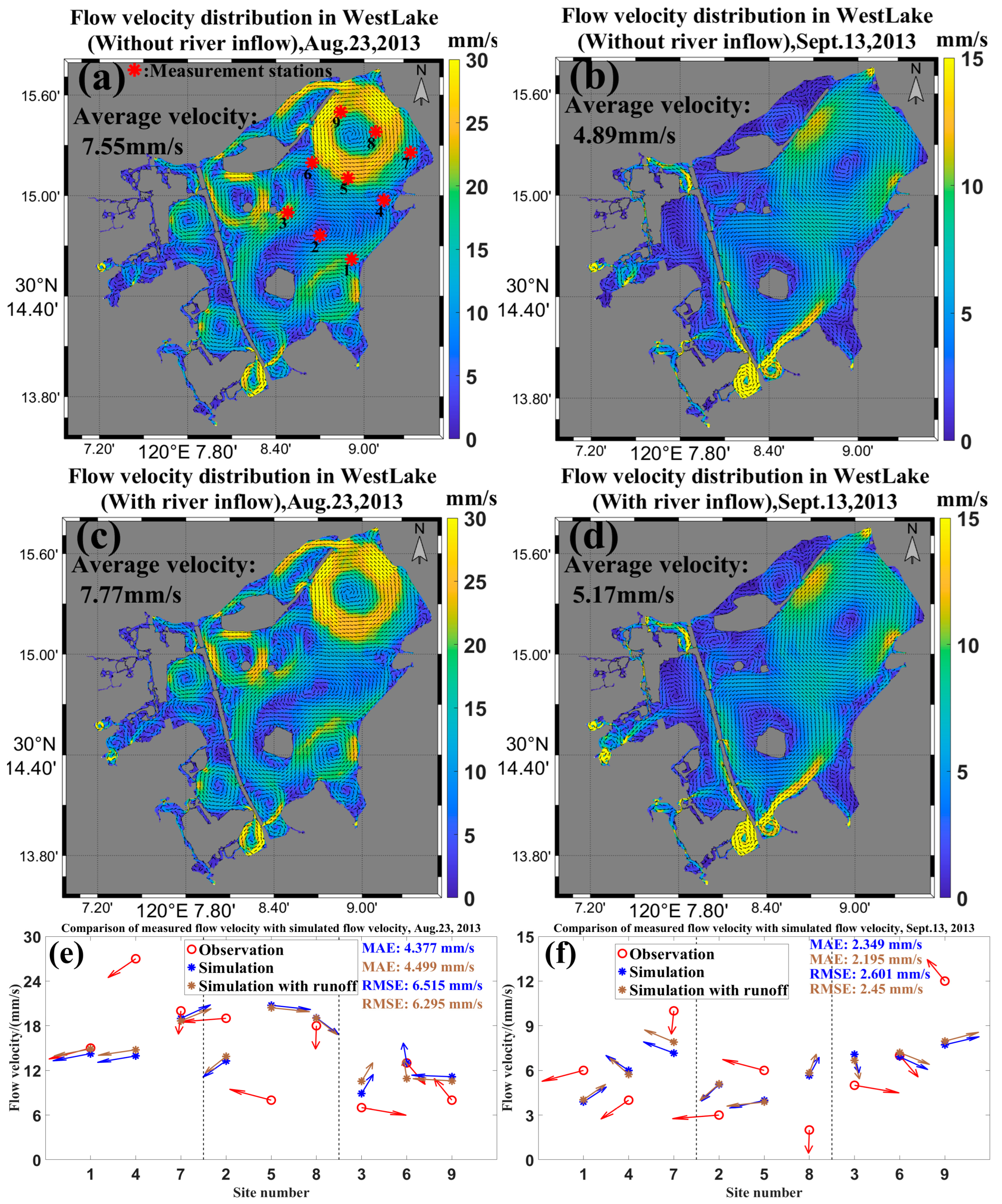
3. Model Validation
4. Results and Discussion
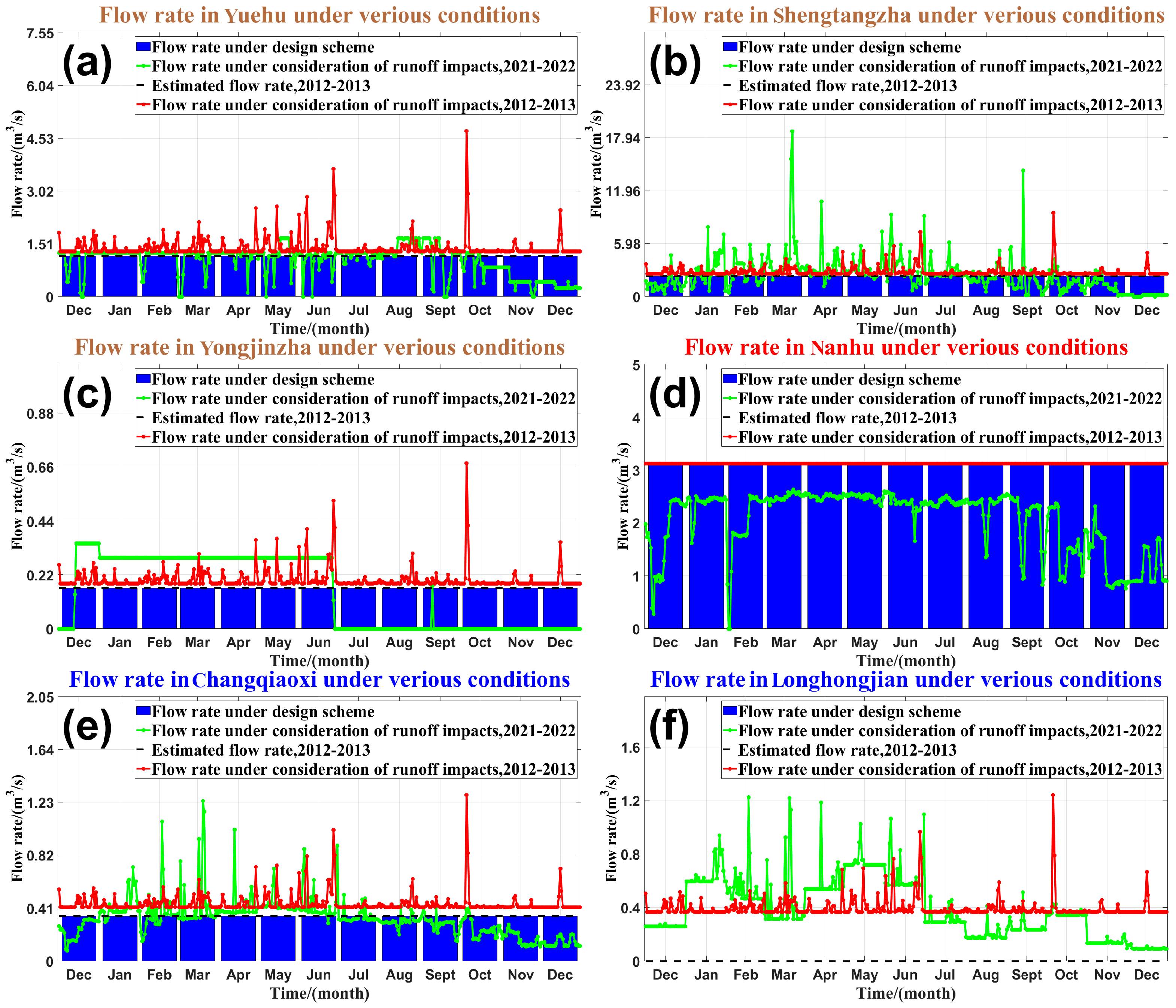
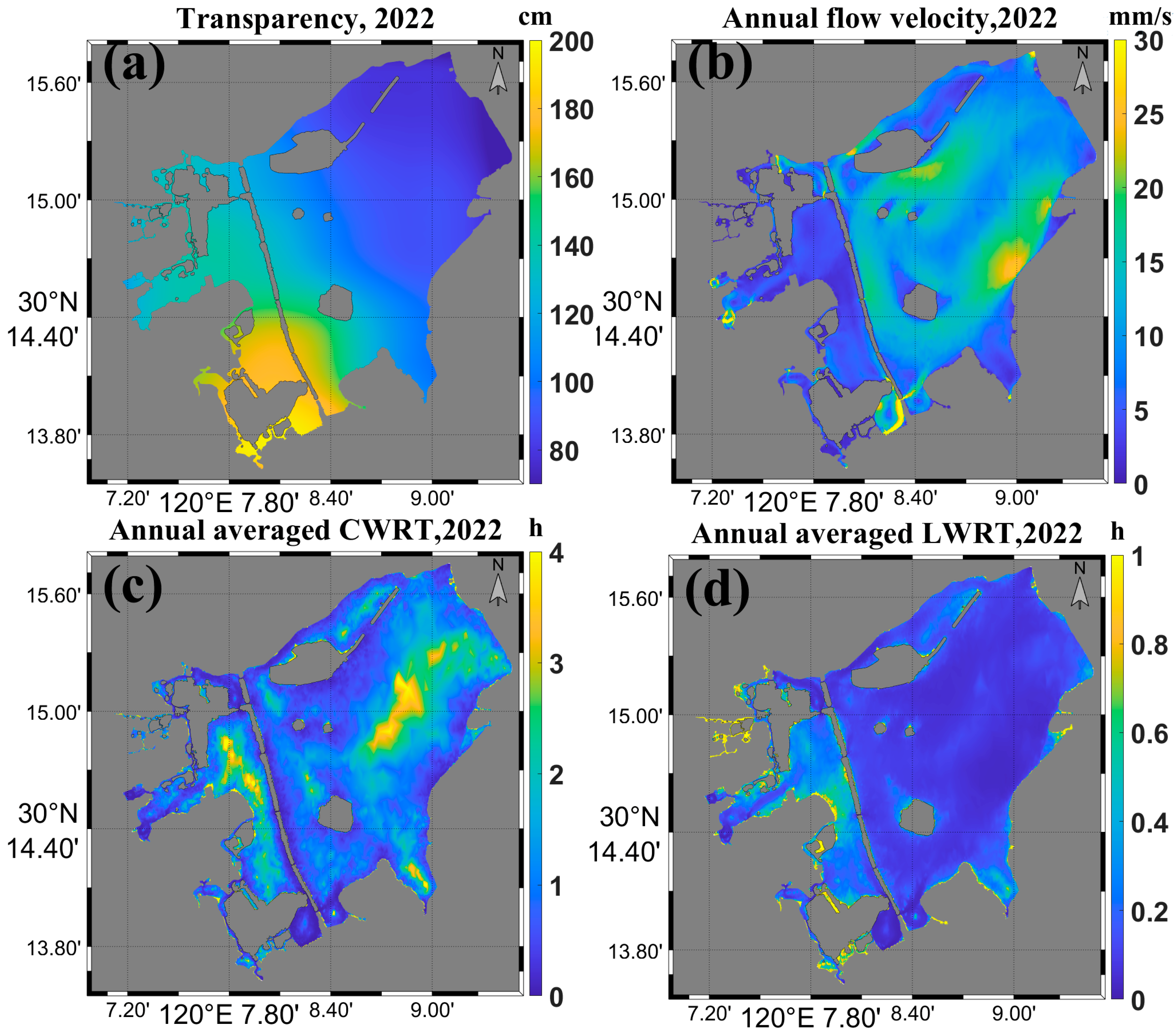
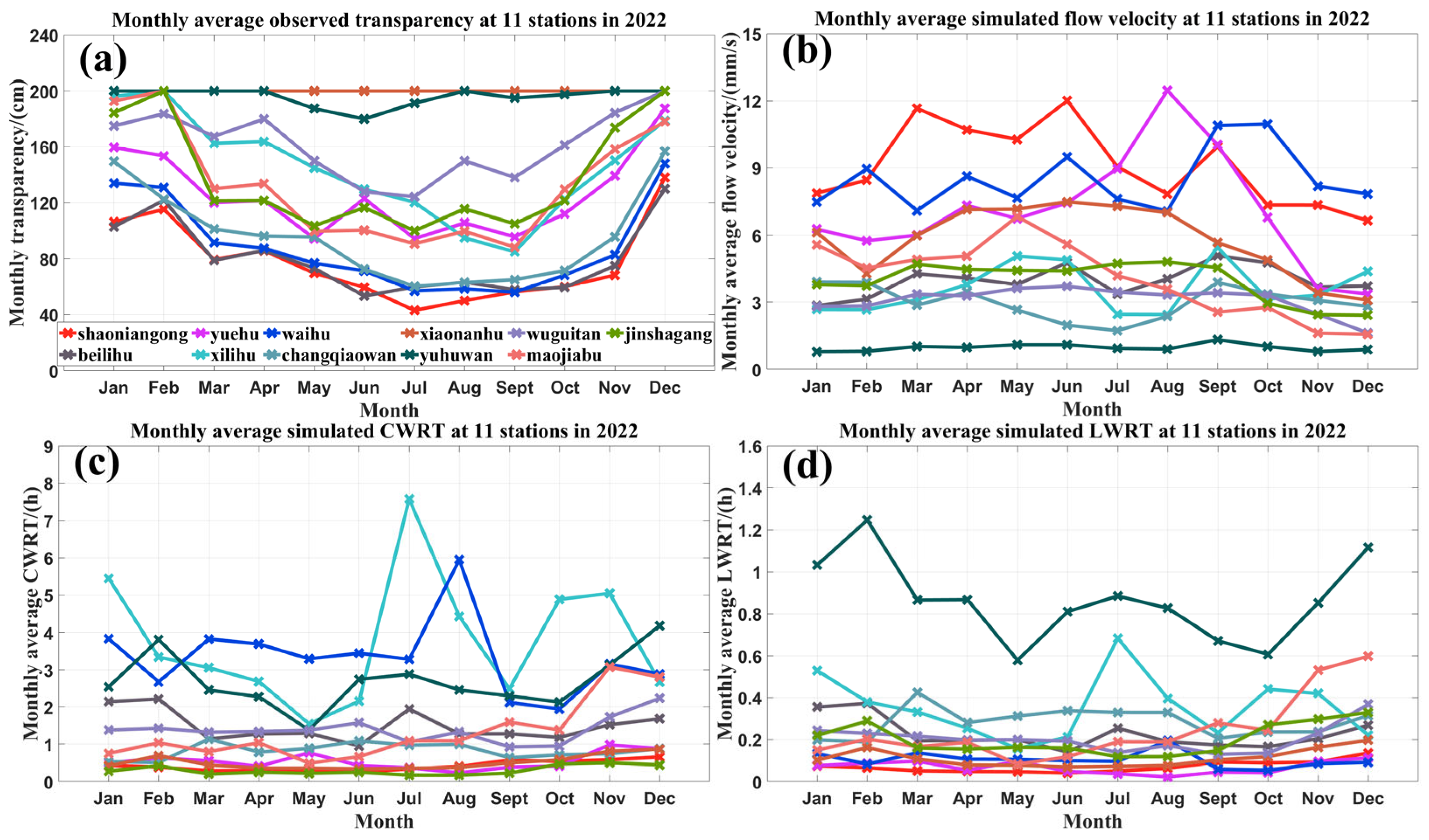
4.1. The Spatiotemporal Distribution of LWRT in West Lake
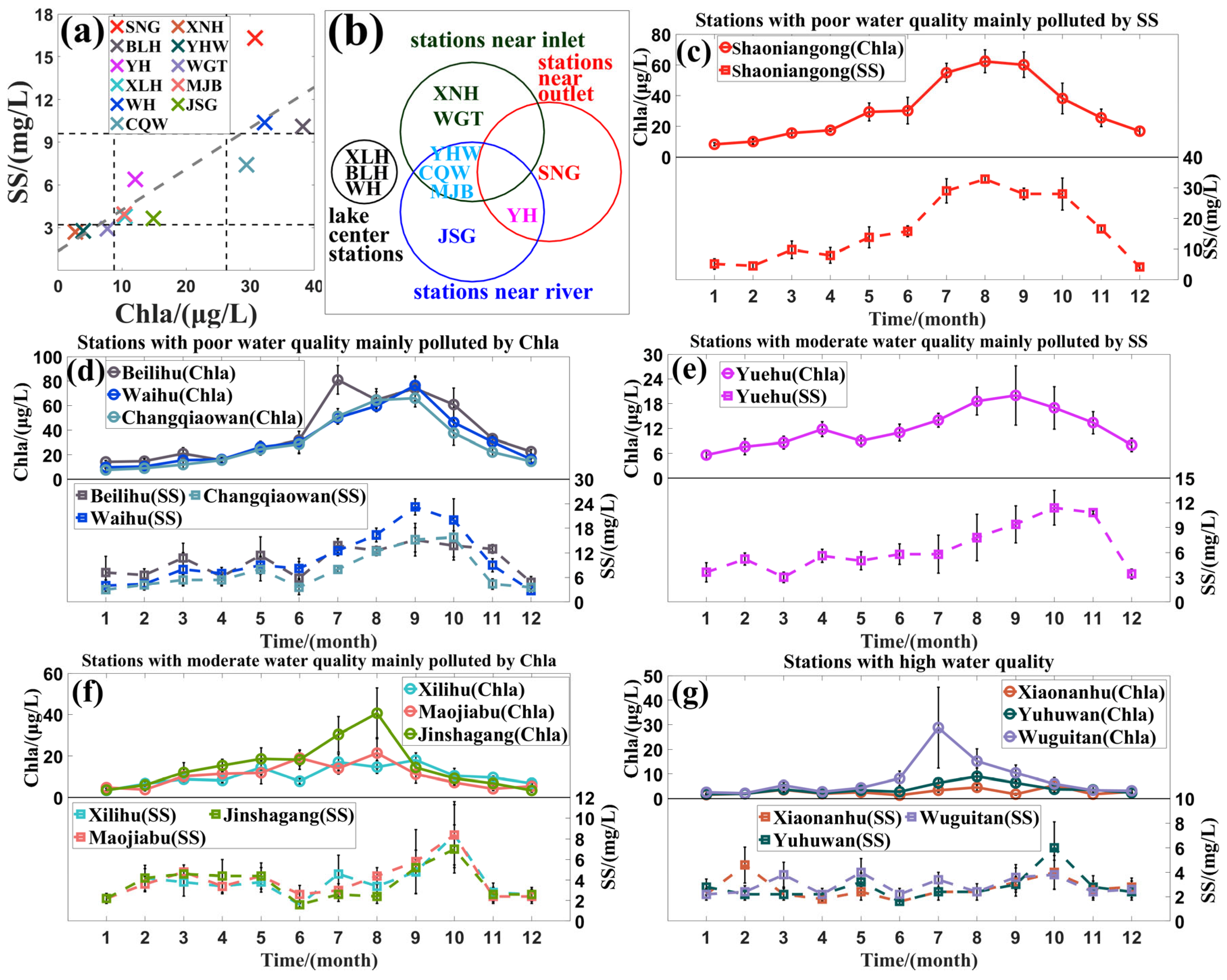
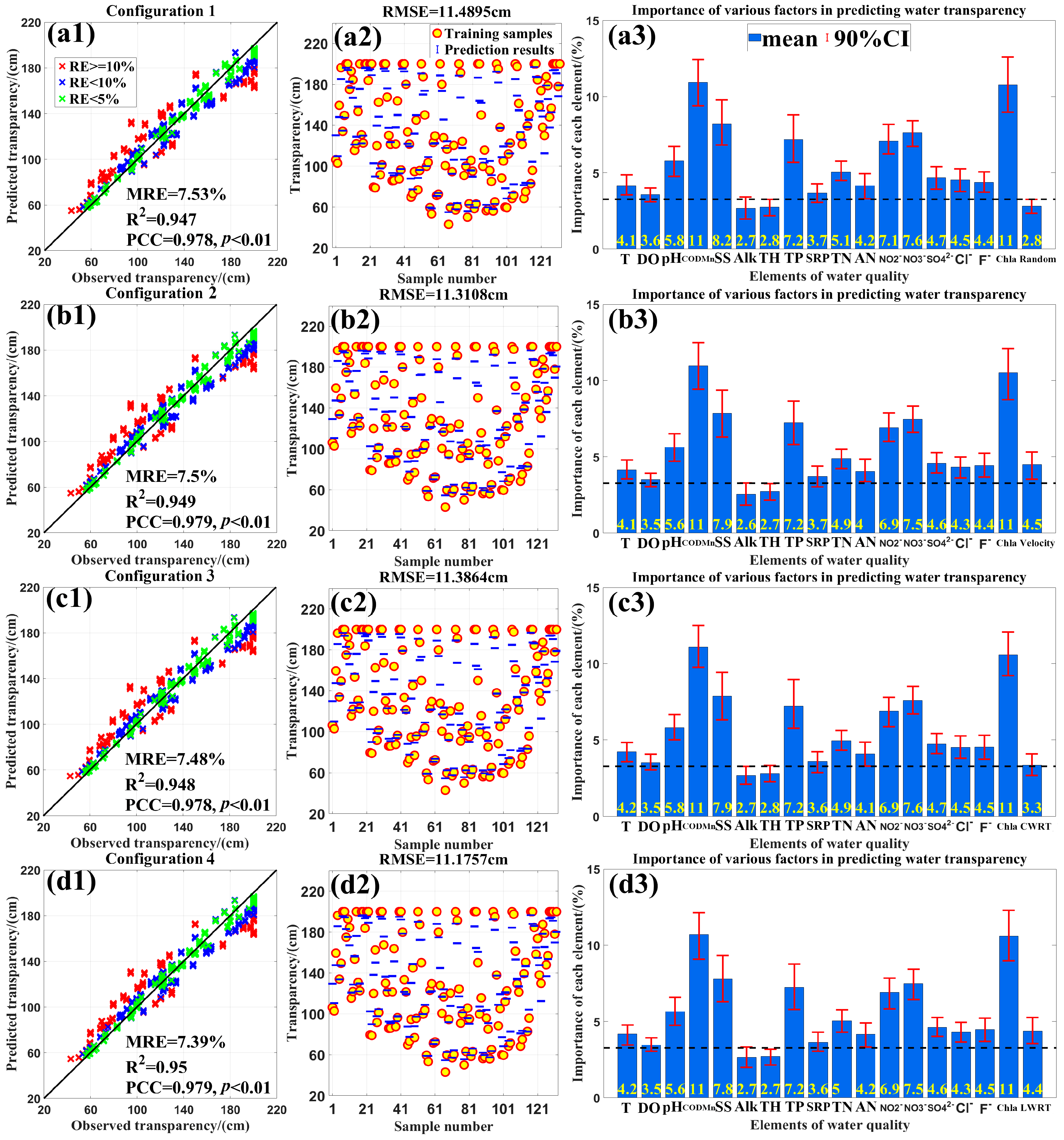
4.2. The Responsiveness of West Lake’s Transparency to LWRT and Other Parameters
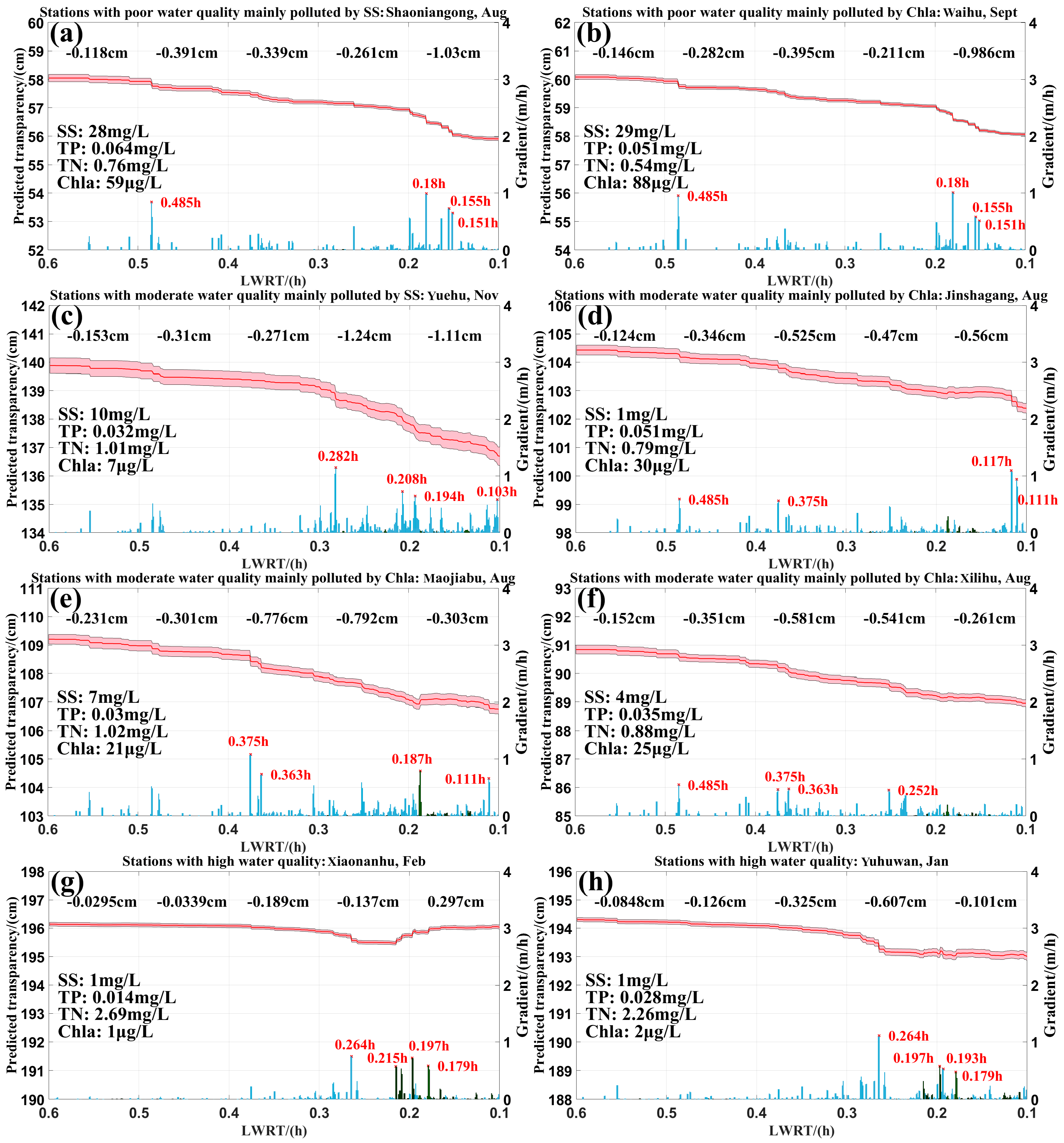
4.3. The Influence of LWRT on Transparency Under Varying Water Quality Conditions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dugener, N.M.; Stone, I.P.; Weinke, A.D.; Biddanda, B.A. Out of oxygen: Stratification and loading drove hypoxia during a warm, wet, and productive year in a Great Lakes estuary. J. Great Lakes Res. 2023, 49, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhu, R.; Zhou, Q.C.; Jeppesen, E.; Yang, K. Trophic status and lake depth play important roles in determining the nutrient-chlorophyll a relationship: Evidence from thousands of lakes globally. Water Res. 2023, 242, 120182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, R.J.; Li, X.H.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Q.Q. Water resource dynamics and protection strategies for inland lakes: A case study of Hongjiannao Lake. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 355, 120462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Li, S.; Sun, D.; Zhou, W.; Wei, J.; Fang, H.; Zhu, L.; Lu, Z.; Xu, J. Assessment and Comprehensive Evaluation of Large-Scale Reclaimed Water Reuse for Urban River Restoration and Water Resource Management: A Case Study in China. Water 2023, 15, 3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, K.; Yang, W.; Zhao, Y.-W. Ecological water replenishment through optimal allocation of lake water in water-scarce areas based on channel selection and replenishment period: A case study of China’s Baiyangdian Lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 956, 177340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yang, L.; Cui, C.; Wan, W.; Liang, S. Is water replenishment an effective way to improve lake water quality? Case study in Lake Ulansuhai, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1392768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Liu, S.; Li, R.; Sun, H.; Feng, J.; Cheng, X.; Yao, J. Research on the purification enhancement of ecological ponds: Integrating water cycle optimization and plants layout. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Xu, J.; Yang, J.; Mao, Y.; Jiang, H. Benifits of the restoration projects on West Lake: Evidence of chlorophyll-a change (1998–2007). Hupo Kexue 2009, 21, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, A.; Wu, Z.; Han, Z.; Yang, J.; Hua, L. Spatial and temporal distributions and variations of nutrients in the West Lake, Hangzhou, after the implementation of integrated water management program (1985–2013). Hupo Kexue 2015, 27, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Ye, X.; Jiao, L.; Wu, Z.; Yang, J.; Xu, J. Effects of comprehensive protection project to the ecological environment of West Lake in Hangzhou. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2007, 18, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Shi, X.; Sun, B.; Zhao, S.; Wang, S.; Yang, Z.; Han, Y.; Kang, R.; Chen, L. Effects of water replenishment on lake water quality and trophic status: An 11-year study in cold and arid regions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 281, 116621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, A.; Yu, W.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Long, X.; Du, Y.; Qu, D. Enhancing water quality and ecosystems of reclaimed water-replenished river: A case study of Dongsha River, Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 172024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, B.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Gao, X.; Han, Z.; Liu, X. Water quality evolution of water-receiving lakes under the impact of multi-source water replenishments. J. Hydrol.-Reg. Stud. 2024, 53, 101832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Luo, N.; Pei, H. Assessment of Spatio-Temporal Changes of Water Quality in West Lake, Hangzhou Using SOFM Neural Network. J. Biomath. 2007, 22, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Cheng, L.; Xue, Z.; Feng, G.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Hu, S. Changes of water exchange cycle in Lake Taihu (1986–2018) and its effect on the spatial pattern of water quality. Hupo Kexue 2021, 33, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P. Internal Circulation Scheme based on MIKE21 Hydrodynamic Model in Pipa Lake. Water Purif. Technol. 2018, 37, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, L.; You, A.; Han, Z.; Teng, H.; Zhu, J. Total Phosphorus Model Construction and Analysis of Internal Circulation Water Transfer in West Lake. J. China Hydrol. 2015, 35, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Hu, W.; Chen, Q.; Peng, Z.; Qin, H.; Luo, J. Hydrodynamic effects and water environment improvement of topographic reconstruction in shallow lakes. J. Hydrol. 2024, 634, 131125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Bei, C. Numerical simulation of water replenishment scheme in Lihu Lake based on EFDC model. Environ. Pollut. Control 2022, 44, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Li, Y.; Shu, J.; Wan, Z.; Jia, B.; Fan, Z. Water Transparency Prediction of Plain Urban River Network: A Case Study of Yangtze River Delta in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Yang, K.; Lee, M.Y.; Youn, S.H.; Son, M.; Park, S.R.; Kim, T.-H. Factors controlling massive green tide blooms on the coasts of Jeju Island, Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 186, 114446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Qi, P. Numerical Optimization Study of the Nanfei River Ecological Water Replenishment Plan. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2024, 23, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Xu, P.; Pan, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X. Reducing the water residence time is inadequate to limit the algal proliferation in eutrophic lakes. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lu, Y.; Hu, H.-Y. Replenishment of landscape water with reclaimed water: Threshold of hydraulic retention time employing transparency as a control indicator. Water Reuse 2024, 14, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, D.; Wei, L.; Pei, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, L. Simulation Study on the Optimisation of Replenishment of Landscape Water with Reclaimed Water Based on Transparency. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, H.; Cheng, B.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, B. A Study of the Effect of Lake Shape on Hydrodynamics and Eutrophication. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Li, R.; Qin, W.; Chen, B.; Wang, M.; Guan, W.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, M.; Ma, Z. Tidal water exchanges can shape the phytoplankton community structure and reduce the risk of harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a semi-closed lake. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2022, 40, 1868–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komita, B.; Weaver, R.; McClain, N.; Fox, A. Natural and Engineered Ocean Inflow Projects to Improve Water Quality Through Increased Exchange. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Duan, B.; He, S.; Lu, Y. Simulation study on the impact of ecological water replenishment on reservoir water environment based on Mike21--Taking Baiguishan reservoir as an example. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Lee, Z.; Spyrakos, E.; Feng, L.; Liu, C.; Zhao, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, L.; et al. Changes of water clarity in large lakes and reservoirs across China observed from long-term MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Luo, L.; Wang, X.C.; Xiong, J.; Han, J. Current status and characteristics of urban landscape lakes in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 135669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Yan, Z.; Wang, J.; Hao, S.; Liu, Y. Deep learning-based remote sensing estimation of water transparency in shallow lakes by combining Landsat 8 and Sentinel 2 images. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 4401–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; He, M. Long-term satellite records of water clarity suggest increasing human activity influence in an inland lake. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2025, 18, 2506491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.; Luo, L.; Wang, X.C.; Song, J.; Han, J.; Ao, D. A novel index for assessing the water quality of urban landscape lakes based on water transparency. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Sun, X.; Zhang, B. Water clarity changes in Lake Taihu over 36 years based on Landsat TM and OLI observations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lv, Y.; Dong, J.; Yuan, J.; Hui, X. Factors Influencing Transparency in Urban Landscape Water Bodies in Taiyuan City Based on Machine Learning Approaches. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lv, Y.; Dong, J.; Yuan, J.; Hui, X. Sensitivity Analysis of Urban Landscape Lake Transparency Based on Machine Learning in Taiyuan City. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, L.; You, A.; Han, Z.; Xu, H. Simulation analysis of the influence of heavy rainfall on urban lake. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Energy Engineering and Environmental Protection (EEEP), Sanya, China, 19–21 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Jin, J.; Shao, D.; Shao, Y. Application of Mathematical Modeling Method in Test Area of Hangzhou. China Water Wastewater 2013, 29, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Jiang, Y.-f.; Wang, C.-c.; Huang, X.-n.; Wu, Z.-y.; Chen, L. Characteristics of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Losses in Longhong Ravine Basin of Westlake in Rainstorm Runoff. Huanjing Kexue 2016, 37, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengül, R.; Nicodemus, U.; Rössler, O. The influence of specific external factors on an ADCP measurement. Wasserwirtschaft 2023, 113, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillenburger-Keenan, J.; Miller, C.; Sellar, B. On the Performance of a Horizontally Mounted ADCP in an Energetic Tidal Environment for Floating Tidal Turbine Applications. Sensors 2024, 24, 4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, A.; Hua, L.; Han, Z.; Zhang, J. Field observation and simulation study of three-dimensional flows in West Lake, Hangzhou. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2017, 36, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Han, Z. Response of Total Phosphorus Concentration to Water Diversion Allocation in West Lake. J. China Hydrol. 2013, 33, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Cao, F.; Lou, Z. A Study on the Numerical Simulation of Flow Field in West Lake in Response to Diversion Works. Shanghai Environ. Sci. 2008, 27, 99–103, 128. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.; Xu, W.; Yan, W.; Wu, T.; He, X.; Cheng, N. Comparison between Machine-Learning-Based Turbidity Models Developed for Different Lake Zones in a Large Shallow Lake. Water 2023, 15, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhi, W.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; et al. Improving remote sensing estimation of Secchi disk depth for global lakes and reservoirs using machine learning methods. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 1367–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Wang, G.; Chen, W.; Li, W.; Kong, F.; Li, N.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X. Integrated modeling framework to evaluate the impacts of multi-source water replenishment on lacustrine phytoplankton communities. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Liu, X.; Dong, F.; Peng, W.; Ma, B.; Han, Z.; Yang, X. Long-term variations in hydraulic residence time of floodplain lakes and their response to water conservancy projects. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 169, 112778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilboa, Y.; Friedler, E.; Talhami, F.; Gal, G. A novel approach for accurate quantification of lake residence time—Lake Kinneret as a case study. Water Res. X 2022, 16, 100149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhu, L.; Li, D.; Zu, Z.; Chen, K.; Wang, J.; Yi, Y. Role of hydraulic residence time in shaping phytoplankton community assembly in the upper yellow river cascade reservoirs. Front. Environ. Sci. 2025, 13, 1551988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Xu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, L.; Sun, Q. Tracer movement and residence time distribution simulation: An initiative to improve the wetland water environment in the Helan Mountain impact plain. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 82, 102682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; He, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L. Water exchange and pollutant diffusion law in Gangnan reservoir. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 12259–12269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCready, P.; McCabe, R.M.; Siedlecki, S.A.; Lorenz, M.; Giddings, S.N.; Bos, J.; Albertson, S.; Banas, N.S.; Garnier, S. Estuarine Circulation, Mixing, and Residence Times in the Salish Sea. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2021, 126, e2020JC016738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Shi, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Li, F.; Shao, Y. Response of Sea Water Exchange Processes to Monsoons in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, T.; Chen, C.; Cheng, Y. The inter relationship between the ecological environment parameters in the West Lake of Hangzhou. Environ. Monit. China 2002, 18, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Yu, X.; Shao, X. Study on the Annual variations of TN and TP and the Eutrophication in Hangzhou West Lake. J. Hydroecol. 2010, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Serra, T.; Font, E.; Soler, M.; Barcelona, A.; Colomer, J. Mean residence time of lagoons in shallow vegetated floodplains. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zhan, X.; Xu, H.; Zhu, G.; Zou, W.; Zhu, M.; Kang, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. New insights into eutrophication management: Importance of temperature and water residence time. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 111, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Seo, D.; Jones, J.R. Harmful algal bloom dynamics in a tidal river influenced by hydraulic control structures. Ecol. Model. 2022, 467, 109931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Mao, Z.; Rao, L.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Y. Simulation of Water Renewal Time in West Lake Based on Delft3D and Its Environmental Impact Analysis. Water 2025, 17, 2847. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192847
Xu P, Zhang L, Zhang X, Mao Z, Rao L, Yang J, Zhou Y. Simulation of Water Renewal Time in West Lake Based on Delft3D and Its Environmental Impact Analysis. Water. 2025; 17(19):2847. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192847
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Pinyan, Longwei Zhang, Xianliang Zhang, Zhihua Mao, Lihua Rao, Jun Yang, and Yinying Zhou. 2025. "Simulation of Water Renewal Time in West Lake Based on Delft3D and Its Environmental Impact Analysis" Water 17, no. 19: 2847. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192847
APA StyleXu, P., Zhang, L., Zhang, X., Mao, Z., Rao, L., Yang, J., & Zhou, Y. (2025). Simulation of Water Renewal Time in West Lake Based on Delft3D and Its Environmental Impact Analysis. Water, 17(19), 2847. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192847





