Synthesis of Zirconium-Based MOF–Biochar Composites for Efficient Congo Red Removal from Industrial Wastewater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. The Preparation of BY, UIO-66@BY, and UIO-67@BY
2.3. Characterization Techniques
2.4. Batch Adsorption Experiment
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of BY, UIO-66@BY, and UIO-67@BY
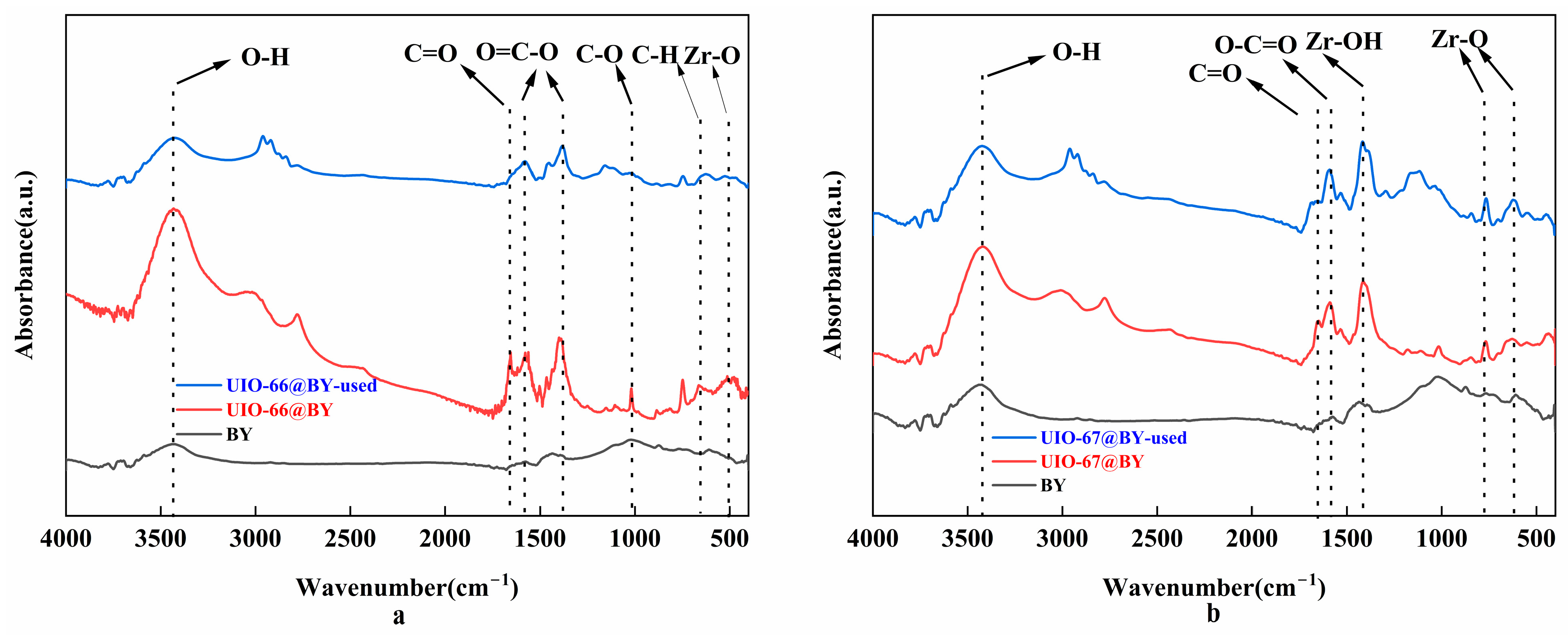
3.1.1. FTIR Analysis
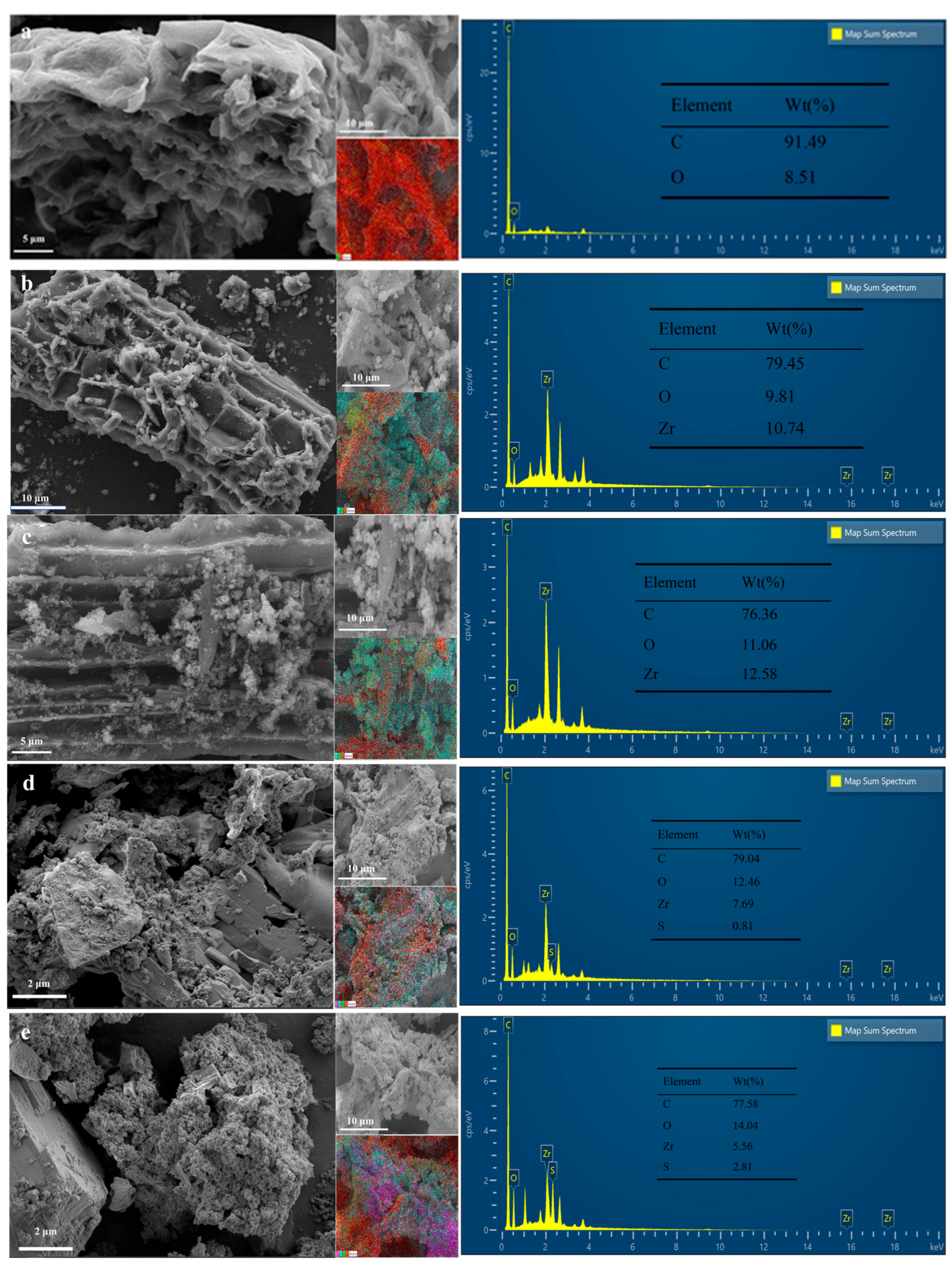
3.1.2. SEM and EDS Analysis
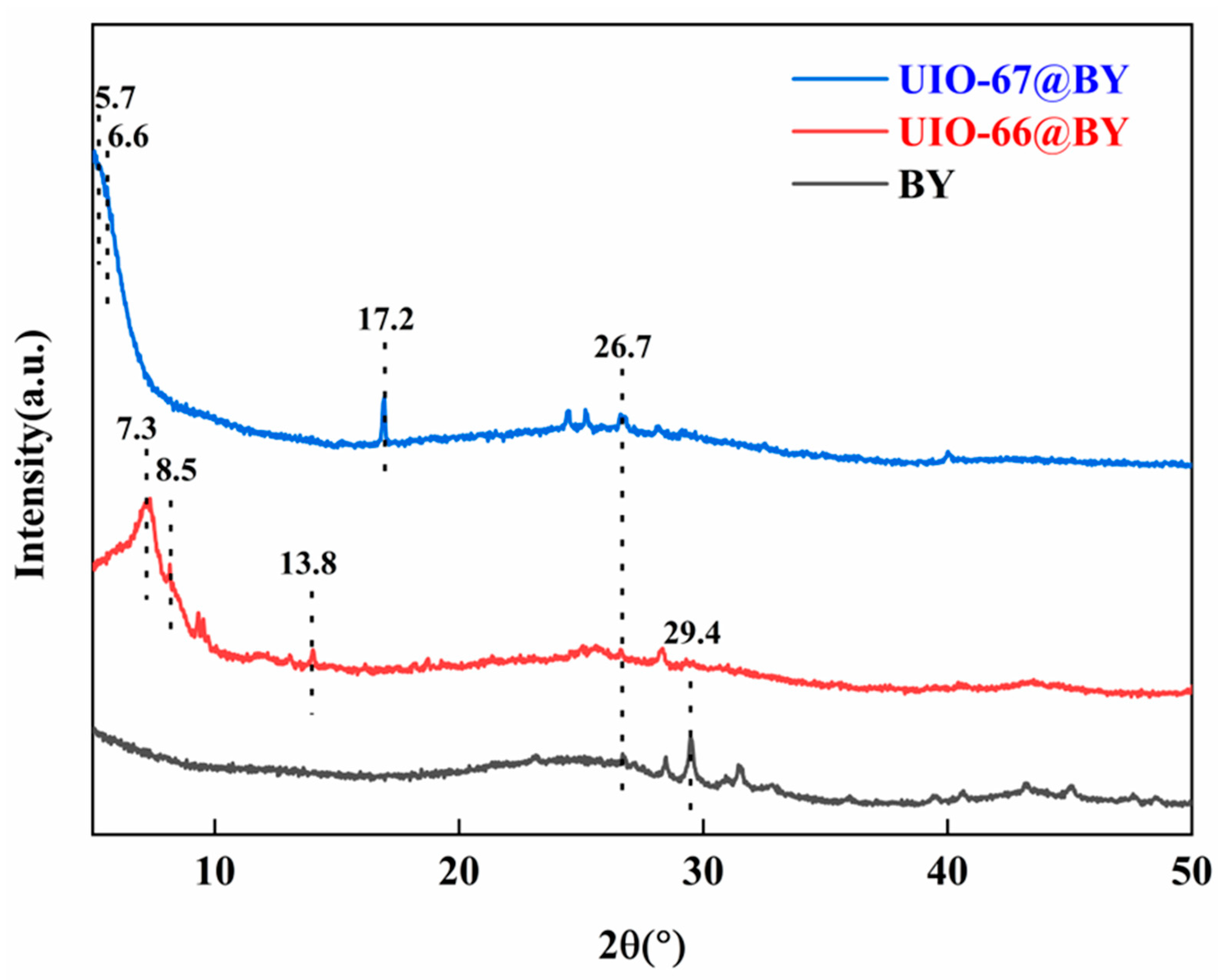
3.1.3. XRD Analysis
3.1.4. BET Analysis
3.1.5. XPS Analysis
3.2. BY, UIO-66@BY, and UIO-67@BY Study on Adsorption Performance
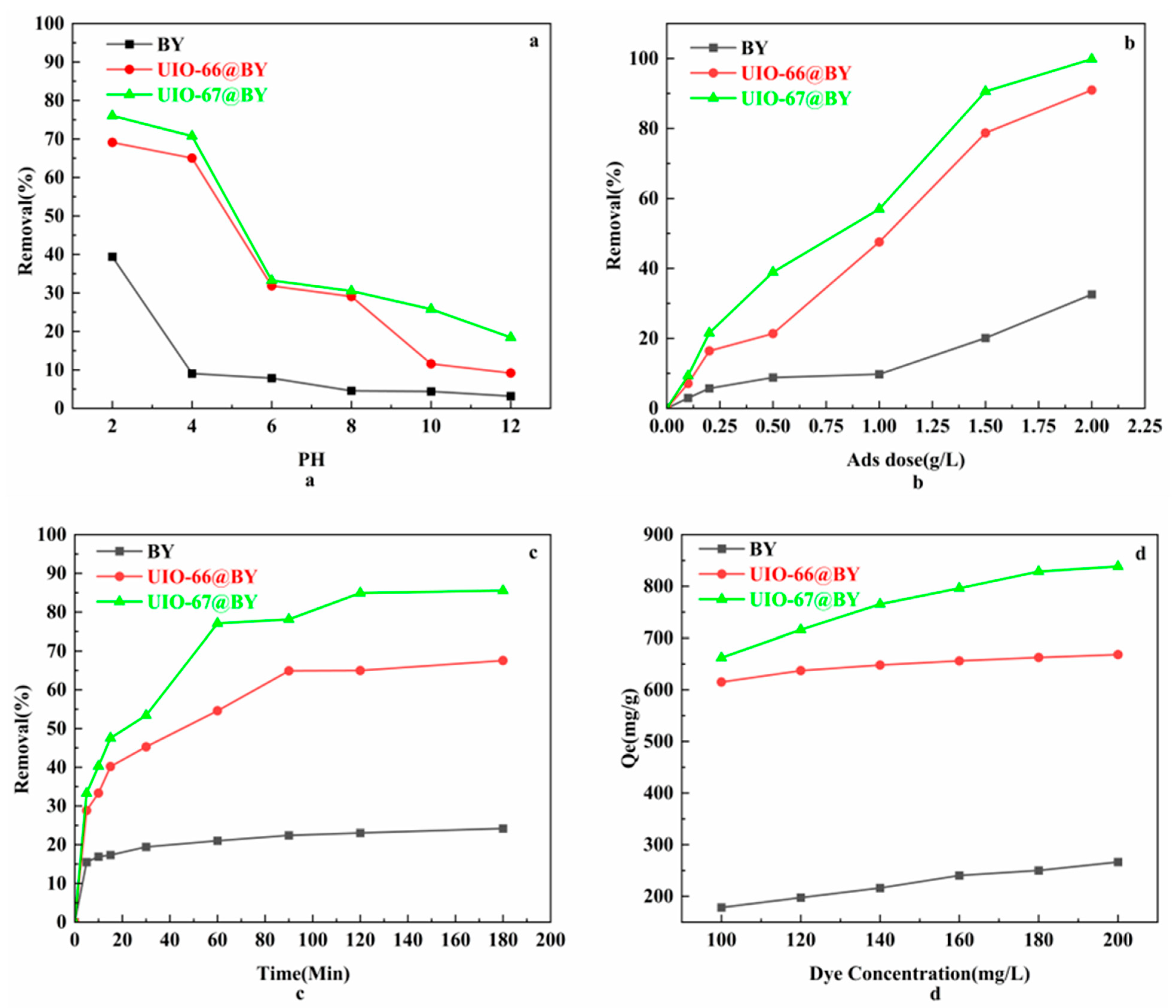
3.2.1. The Impact of pH
3.2.2. The Impact of Adsorbent Dose
3.2.3. The Influence of Contact Time and Initial Concentration
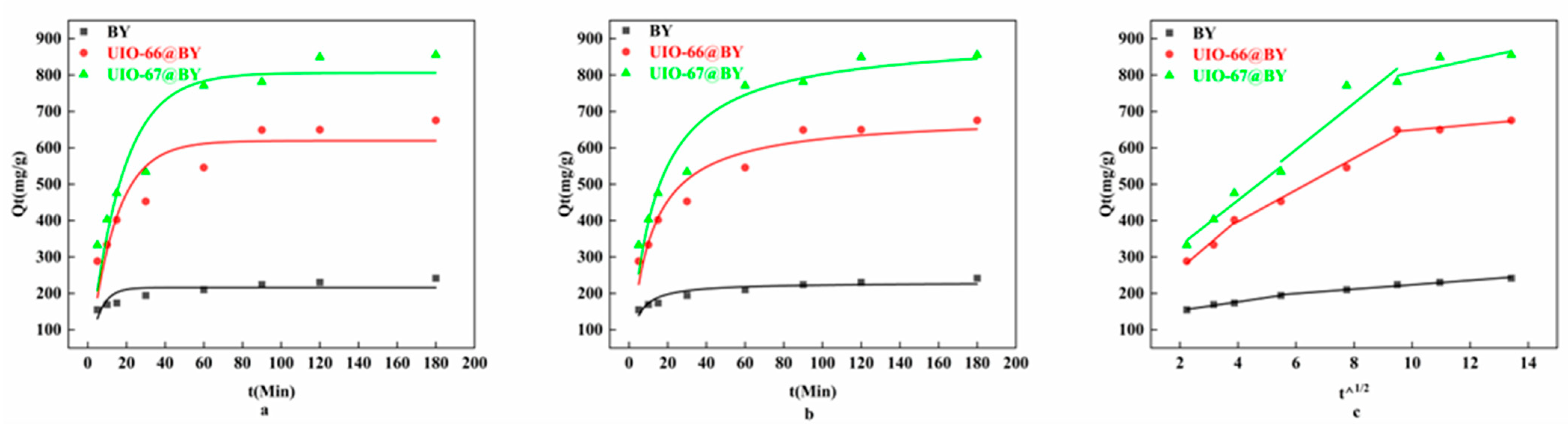
3.3. Study on Adsorption Kinetics
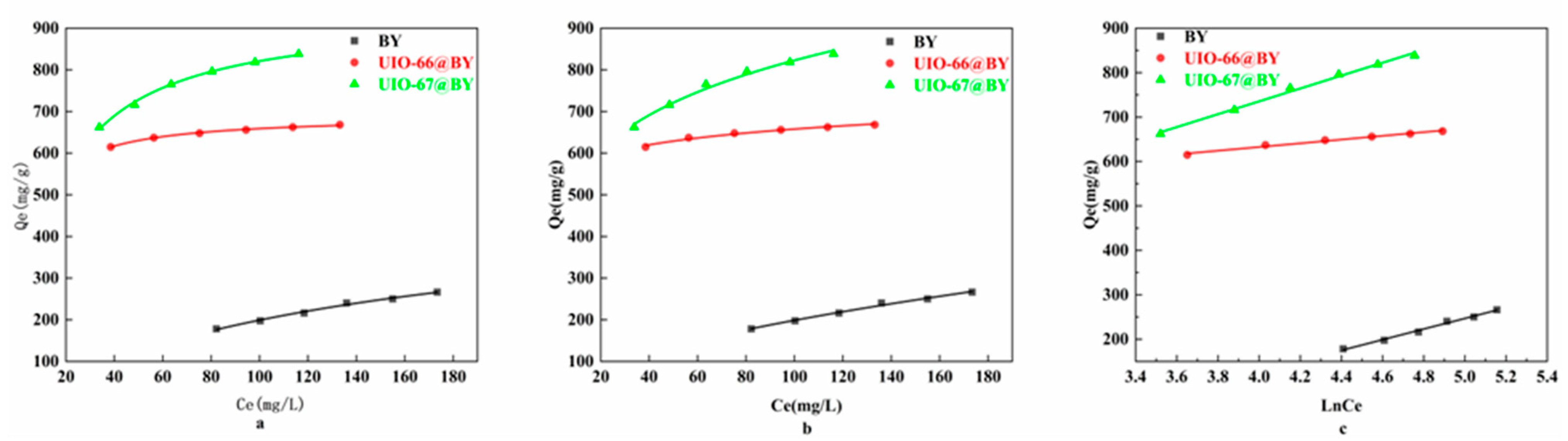
3.4. Study on Adsorption Isotherms
3.5. Thermodynamic Research
3.6. Study on Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, W.; Tong, J.; Li, G. Graphene oxide intercalated Alk-MXene adsorbents for efficient removal of Malachite green and Congo red from aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2024, 360, 142376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Qiao, W.; Li, D.; Wang, L.-j. Dual cross-linked magnetic gelatin/carboxymethyl cellulose cryogels for enhanced Congo red adsorption: Experimental studies and machine learning modelling. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 678, 619–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajab, H.; Nayab, D.; Mannan, A.; Waseem, A.; Jafry, A.T.; Yaqub, A. Comparative analysis of the equilibrium, kinetics, and characterization of the mechanism of rapid adsorption of Congo red on nano-biosorbents based on agricultural waste in industrial effluents. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 358, 120863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Dang, Q.; Liu, C.; Niu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Sang, F.; Su, J.; Zhang, B.; Cha, D. Novel versatile 5-aminoisophthalic acid modified chitosan nanofiber pads for adsorption toward Congo red, methyl orange, crystal violet, and methylene blue. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 500, 156804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.-R.; Xu, S.; Han, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, K.-Y.; Huang, Z.; Rushlow, J.; Cai, P.; Samorì, P.; Zhou, H.-C. Exceptionally High Perfluorooctanoic Acid Uptake in Water by a Zirconium-Based Metal–Organic Framework through Synergistic Chemical and Physical Adsorption. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 9811–9818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, A.; Popa, I.-M.; Markeb, A.A.; Moral-Vico, J.; Naughton, E.M.; Eckhardt, H.-G.; Ayllón, J.A.; López-Periago, A.M.; Domingo, C.; Negahdar, L. Multifunctionalized zirconium-based MOF as a novel support for dispersed copper: Application in CO2 adsorption and catalytic conversion. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 21758–21771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Hu, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, L.-Y. Highly Defective Zirconium-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks for the Efficient Adsorption and Detection of Sugar Phosphates in the Biological Sample. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 37641–37655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Gu, H.; Lam, S.S.; Peng, W.; Li, H.; Yan, L. Enhanced Biochar as a Game-Changer in Heavy Metal and Organic Pollutant Remediation. Eng. Sci. 2025, 36, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.; Liu, F. Preparation of potassium hydroxide-modified poplar biochar via pyrolysis and its adsorption performance for five pesticides. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2025, 27, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedi, S.; Rajabi, H.; Hadi Mosleh, M.; Babakhani, P.; Sedighi, M. UiO-67 metal-organic framework loaded on hardwood biochar for sustainable management of environmental boron contaminations. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Naqvi, S.R.; Ali, I.; Farooq, W.; Anjum, M.W.; AlMohamadi, H.; Lam, S.S.; Verma, M.; Ng, H.S.; Liew, R.K. Algal biochar: A natural solution for the removal of Congo red dye from textile wastewater. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2025, 166, 105312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Tan, W.; Li, J.; Su, D.; Wang, H.; Yang, M. A study on the performance of a novel adsorbent UiO-66 modified by a nickel on removing tetracycline in wastewater. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Ye, Z.; Xiong, G. Efficient removal of anionic dye congo red by Chitosan/Poly (dimethyl diallyl ammonium chloride-co-acrylamide) composite hydrogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 294, 139462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ye, P.; Zhang, T.; Huang, X.; Wang, M.; Gao, H. Enhanced adsorption of Congo red from urea/calcium chloride co-modified biochar: Performance, mechanisms and toxicity assessment. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 388, 129783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Hou, H.-M.; Zhang, G.-L.; Hao, H.; Zhu, B.-w.; Bi, J. Defective UiO-66/cellulose nanocomposite aerogel for the adsorption of heterocyclic aromatic amines. Food Chem. 2024, 449, 139225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, P.; Zheng, Q.; Hameed, M.U.; Raza, S. Synthesis of cellulose cotton-based UiO-66 MOFs for the removal of rhodamine B and Pb(II) metal ions from contaminated wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shi, R.; Yin, W. Fabrication of a corn stalk derived cellulose-based bio-adsorbent to remove Congo red from wastewater: Investigation on its ultra-high adsorption performance and mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 241, 124545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Li, B.; Cui, Z.; Tang, Y.; Hu, X. Distinct property of biochar from pyrolysis of poplar wood, bark, and leaves of the same origin. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 202, 117001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Fang, S.; Li, G. Magnetic Fe3O4/bamboo-based activated carbon/UiO-66 composite as an environmentally friendly and effective adsorbent for removal of Bisphenol A. Chemosphere 2023, 340, 139696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, N.; Wang, H.; Cui, P.; Xu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhou, X.; Amirkhanian, S. Environmental hazard reduction and anti-aging enhancement of steel slag powder-asphalt mastic based on TiO2@UiO-67 composites. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 419, 138331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshgar, H.; Sojdeh, S.; Salehi, G.; Edrisi, M.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Rabiee, N. Comparative study of synthesis methods and pH-dependent adsorption of methylene blue dye on UiO-66 and NH2-UiO-66. Chemosphere 2024, 353, 141543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhao, L.; He, D.; Sun, J.; Yang, J.; Tang, W.; Yu, H.; Lou, C.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; et al. Preparation of Zirconium-Based MOF-Derived Phosphide on GO/MXene Double Substrates for High-Performance Asymmetric Supercapacitors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 47751–47762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Li, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Yin, L.; Du, Q.; Pi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Metal framework functionalized with nitro groups and chitosan composite adsorption of Congo red. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 305, 141140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, K.; Du, Q.; Wang, Y.; Pi, X.; et al. Efficient adsorption of Congo red by micro/nano MIL-88A (Fe, Al, Fe-Al)/chitosan composite sponge: Preparation, characterization, and adsorption mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Yu, H.; He, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, D.; Cheng, F. Ce-UiO-66-F4-based composites decorated with green carbon dots for universal adsorption of organic pollutants containing hydrogen bond donors and its application exploration. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 486, 150266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashda; Liu, Y.; Gao, H.; Li, Z.; Han, R. Magnetic bio-composite based on zirconium and chitosan modified activated carbon from peanut husk with enhanced antibacterial and adsorptive potential for alizarin red and congo red in wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 273, 132995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, F.; Hu, N.; Pei, H.; Yang, W.; Li, Z.; Suo, Y.; Wang, J. High effective adsorption/removal of illegal food dyes from contaminated aqueous solution by Zr-MOFs (UiO-67). Food Chem. 2018, 254, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, S.; Kannan, P.; Balasubramani, K.; Rajamohan, N.; Rajasimman, M. Sustainable remediation of toxic congo red dye pollution using bio based carbon nanocomposite: Modelling and performance evaluation. Chemosphere 2023, 343, 140206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tati, A.; Ahmadipouya, S.; Molavi, H.; Mousavi, S.A.; Rezakazemi, M. Efficient removal of organic dyes using electrospun nanofibers with Ce-based UiO-66 MOFs. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 266, 115584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Fu, S.; Meng, W.; He, G.; Cao, W.; Zhang, W. Adsorption kinetics and mechanisms of carbohydrate/UiO-66 composites for cationic/anionic dye removal. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 75, 108017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Mao, H.; Chang, Z.; Guo, H.; Tian, L.; Du, W.; Wu, D.; Zhang, P.; Li, H.; Yu, Y. Adsorption-desorption properties and control mechanism of aromatic organophosphate esters on biochar-mineral complexes. Ecotoxicol. Env. Saf. 2025, 292, 117979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Shen, Y.; Wu, J.; Hao, C. Effective removal of Congo red and hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by guar gum/sodium alginate/Mg/Al-layered double hydroxide composite microspheres. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 293, 139385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhaimi, A.; Jawad, A.H.; Yusoff, M.Z.M.; Wilson, L.D.; Alothman, Z.A. Design of composite chitosan/algae/zeolite by freeze- or air-drying: A comparative adsorbent analysis for optimized removal of brilliant green dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 288, 138650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Guan, Y.; Ji, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, H. Efficient removal of Congo red and methylene blue using biochar from Medulla Tetrapanacis modified by potassium carbonate. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 376, 128912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, V.; Uthappa, U.T.; Mane, P.; Ji, S.M.; Suneetha, M.; Wang, B.; Altalhi, T.; Subrahmanya, T.M.; Kurkuri, M.D. Design of low-cost natural casein biopolymer based adsorbent for efficient adsorption of multiple anionic dyes and diclofenac sodium from aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2024, 353, 141571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, P.; Dai, X.; Guan, H.; Wang, X. Carboxylated lamellar wood sponge enables high loading and uniform dispersion of MIL-53(Al) for efficient organic dye adsorption. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 356, 123400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanthamathee, C.; Chantarangkul, C.; Jakkrawhad, C.; Payaka, A.; Dechatiwongse, P. Fine-tuning the dye adsorption capacity of UiO-66 by a mixed-ligand approach. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, L.; Solomon, M.B.; D’Alessandro, D.M.; Donald, W.A. Dual-functional metal-organic frameworks for adsorptive removal and ultra-trace quantitation of 50 per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 494, 138679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Zhao, J.; Song, H.; Yang, F.; Shen, L.; Zhu, L.; Zeng, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, G. Enhanced adsorption of dyes by functionalized UiO-66 nanoparticles: Adsorption properties and mechanisms. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1292, 136111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshta, B.E.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Yi, H.; Jian, S.; Uddin, M.D.A.; Ouyang, C.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Preparation of unsaturated MIL-101(Cr) with Lewis acid sites for the extraordinary adsorption of anionic dyes. npj Clean Water 2025, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Y.; Liu, R.; Lan, J.; Sun, T.; Xu, A. Recyclable chitosan adsorbent: Facile functionalization strategy, excellent removal capacity of dyes and adsorption mechanism. Chemosphere 2024, 359, 142291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Sample | SBET (m2·g−1) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| BY | 22.93 | 7.38 |
| UIO-66@BY | 183.10 | 6.06 |
| UIO-67@BY | 135.21 | 5.27 |
| BY | UIO-66@BY | UIO-67@BY | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe exp (mg∙g−1) | 245.6 | 684.5 | 865.2 | |
| PFO | Qecal (mg·g−1) | 215.898 | 619.258 | 806.283 |
| K1 (min−1) | 0.185 | 0.073 | 0.059 | |
| R2 | 0.572 | 0.822 | 0.869 | |
| PSO | Qecal (mg·g−1) | 230.031 | 688.875 | 905.231 |
| K2 (min−1) | 0.001 | 0.0001 | 0.00008 | |
| R2 | 0.853 | 0.931 | 0.942 | |
| IPD 1st stage | C1 (mg·g−1) | 129.533 | 129.995 | 206.809 |
| Ki (mg·g−1·min−1/2) | 11.823 | 68.379 | 62.268 | |
| R2 | 0.987 | 0.963 | 0.951 | |
| 2nd stage | C2 (mg·g−1) | 163.678 | 222.234 | 212.890 |
| Ki (mg·g−1·min−1/2) | 6.009 | 43.673 | 63.752 | |
| R2 | 0.982 | 0.984 | 0.840 | |
| 3rd stage | C3 (mg·g−1) | 577.725 | 634.691 | |
| Ki (mg·g−1·min−1/2) | 7.126 | 17.196 | ||
| R2 | 0.881 | 0.686 |
| BY | UIO-66@BY | UIO-67@BY | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | Qmax (mg·g−1) | 489.632 | 690.257 | 940.701 |
| KL (L·mg−1) | 0.0069 | 0.211 | 0.069 | |
| R2 | 0.993 | 0.996 | 0.996 | |
| Freundlich | KF (g·mg−1·min−1) | 16.356 | 488.464 | 343.158 |
| 1/n | 0.542 | 0.065 | 0.190 | |
| R2 | 0.992 | 0.983 | 0.987 | |
| Temkin | A | 0.053 | 69,870 | 2.93 |
| B | 20.711 | 59.371 | 16.570 | |
| R2 | 0.992 | 0.986 | 0.993 |
| ΔS° (Kj·mol−1) | ΔH° (kJ/mol) | ΔG° (Kj·Mol−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 °C | 40 °C | 50 °C | 60 °C | |||
| BY | 53.276 | 16.270 | −0.069 | −0.305 | −0.800 | −1.708 |
| UIO-66@BY | 50.582 | 11.448 | −3.875 | −4.397 | −4.917 | −5.385 |
| UIO-67@BY | 70.370 | 17.005 | −4.289 | −5.109 | −5.705 | −6.432 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; He, Y. Synthesis of Zirconium-Based MOF–Biochar Composites for Efficient Congo Red Removal from Industrial Wastewater. Water 2025, 17, 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192814
Zhang Y, He Y. Synthesis of Zirconium-Based MOF–Biochar Composites for Efficient Congo Red Removal from Industrial Wastewater. Water. 2025; 17(19):2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192814
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yufei, and Yifeng He. 2025. "Synthesis of Zirconium-Based MOF–Biochar Composites for Efficient Congo Red Removal from Industrial Wastewater" Water 17, no. 19: 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192814
APA StyleZhang, Y., & He, Y. (2025). Synthesis of Zirconium-Based MOF–Biochar Composites for Efficient Congo Red Removal from Industrial Wastewater. Water, 17(19), 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17192814





