The Research on H2O Adsorption Characteristics of Lunar Regolith Simulants: Implications for the Development and Utilization of Lunar Water Resources
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
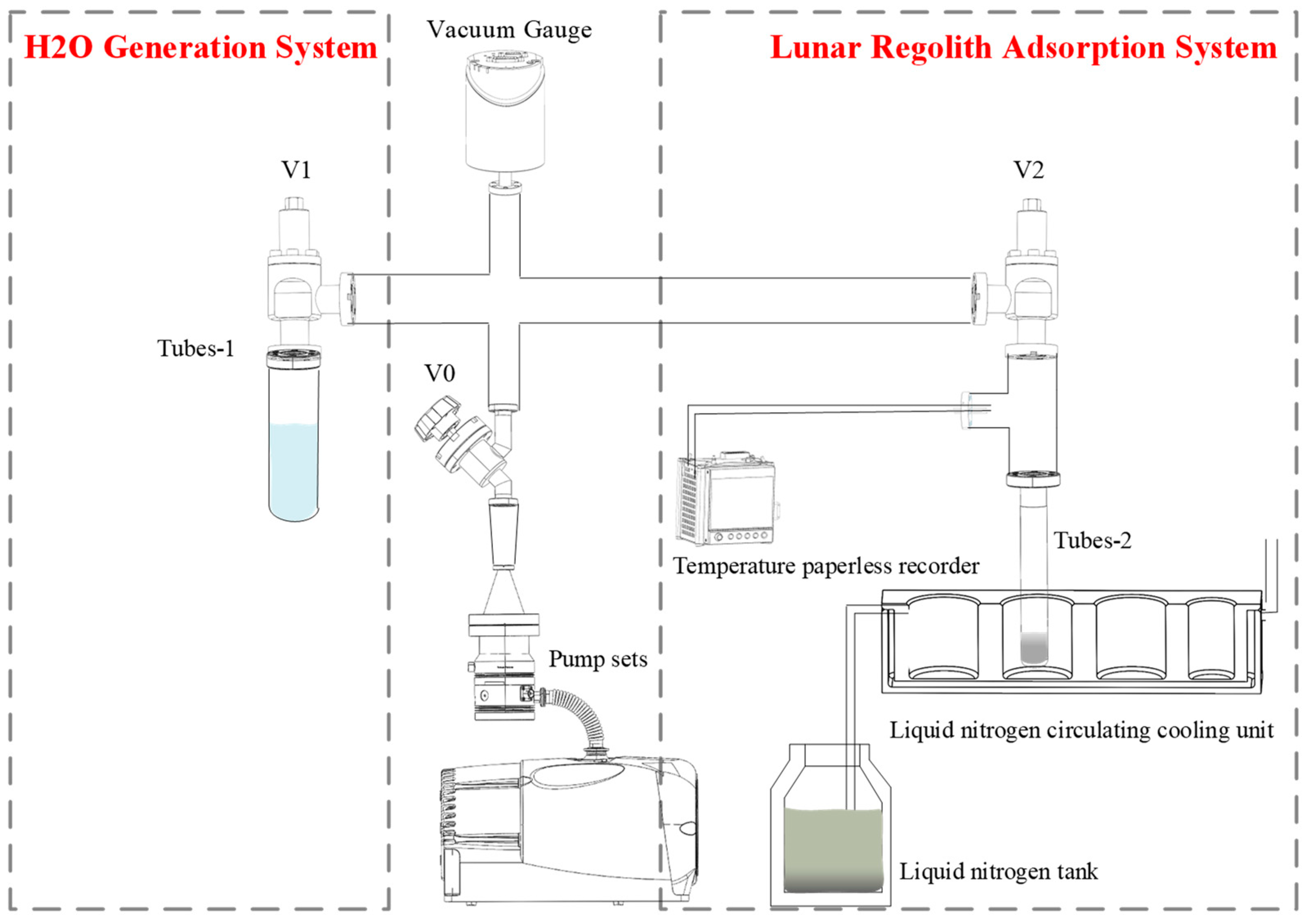
2.1. Ground-Based Simulation System of H2O Adsorption
2.2. Ground-Based Simulation Test Procedure
2.3. Sample Handling and H2O Release
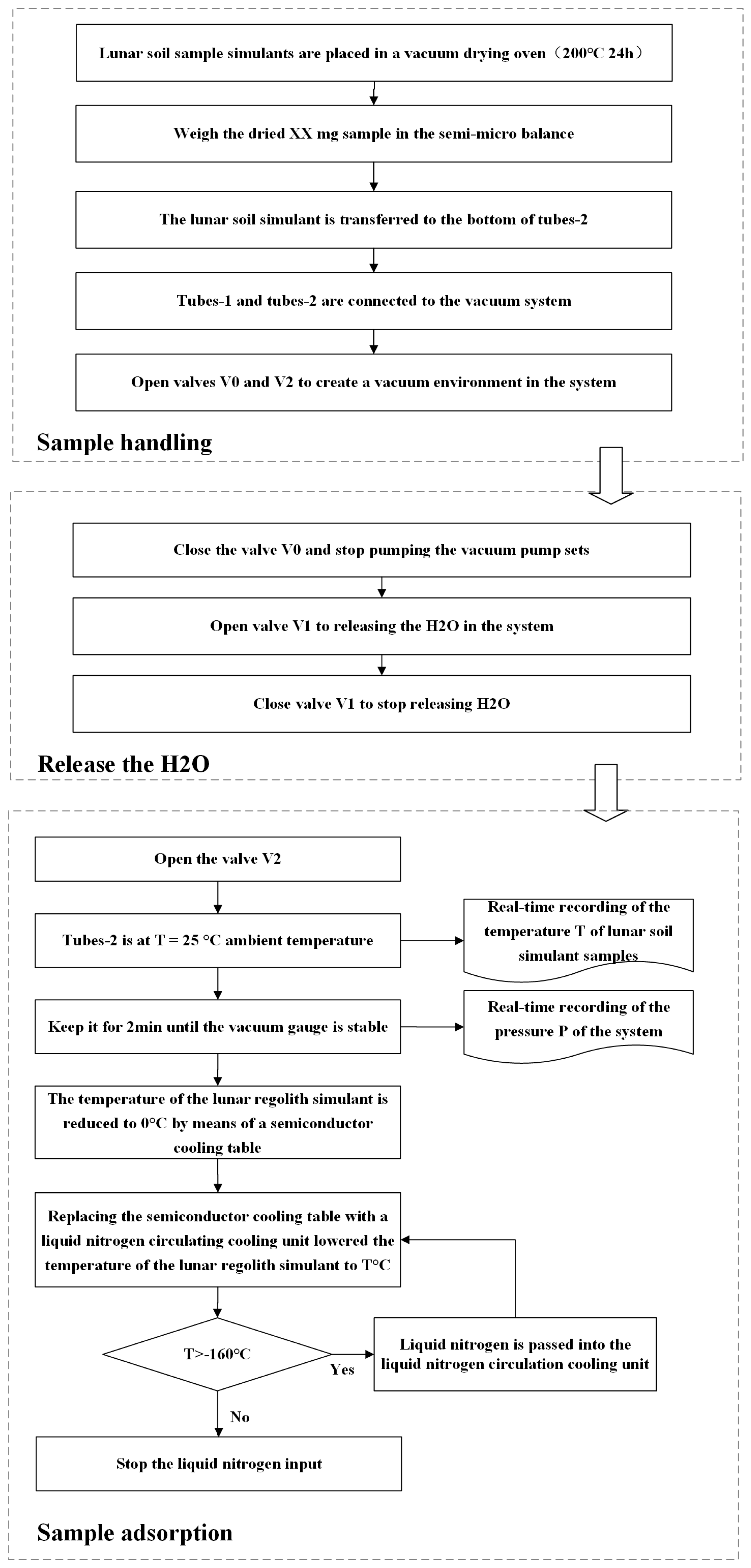
2.4. H2O Adsorption and Environmental Temperature Control
2.5. Representativeness of Samples and Characterization of H2O
3. Results and Discussion
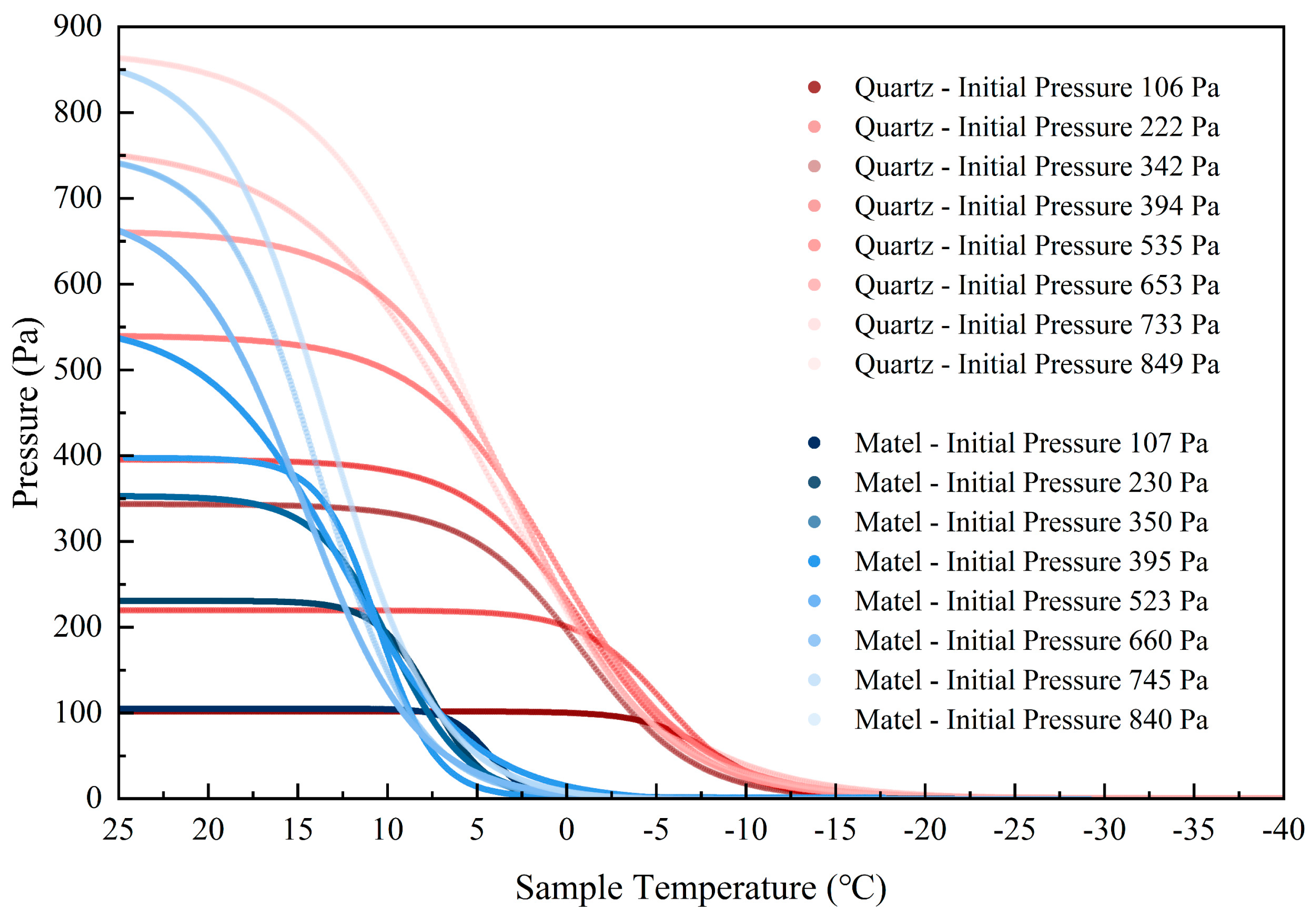
3.1. Selection of Material for Adsorption Vessels
3.2. Adsorption Thresholds of Polar Region Lunar Regolith Simulant at Different Temperatures
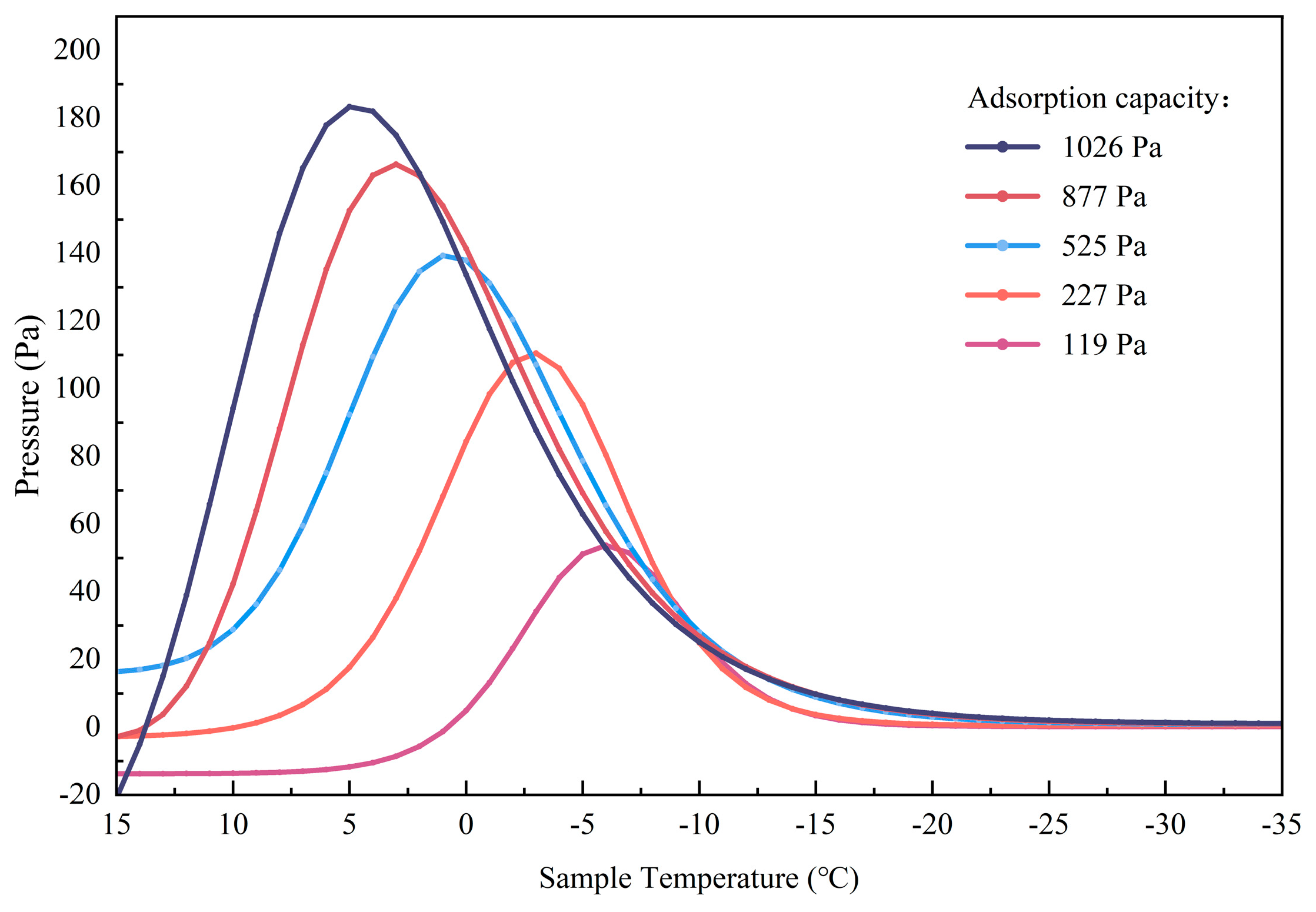
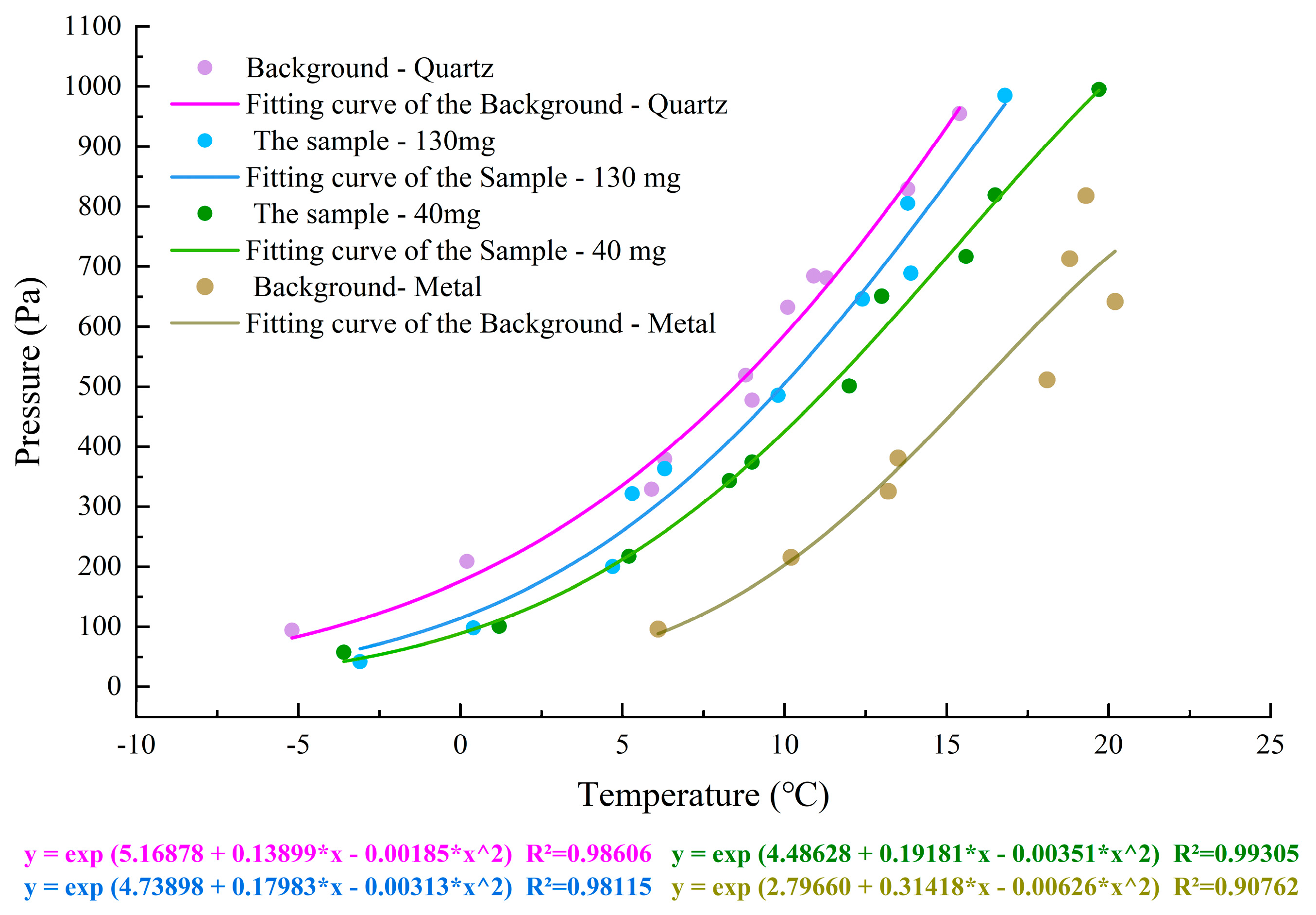
3.3. Effect of the Action of Other Substances on the Temperature of H2O Preservation
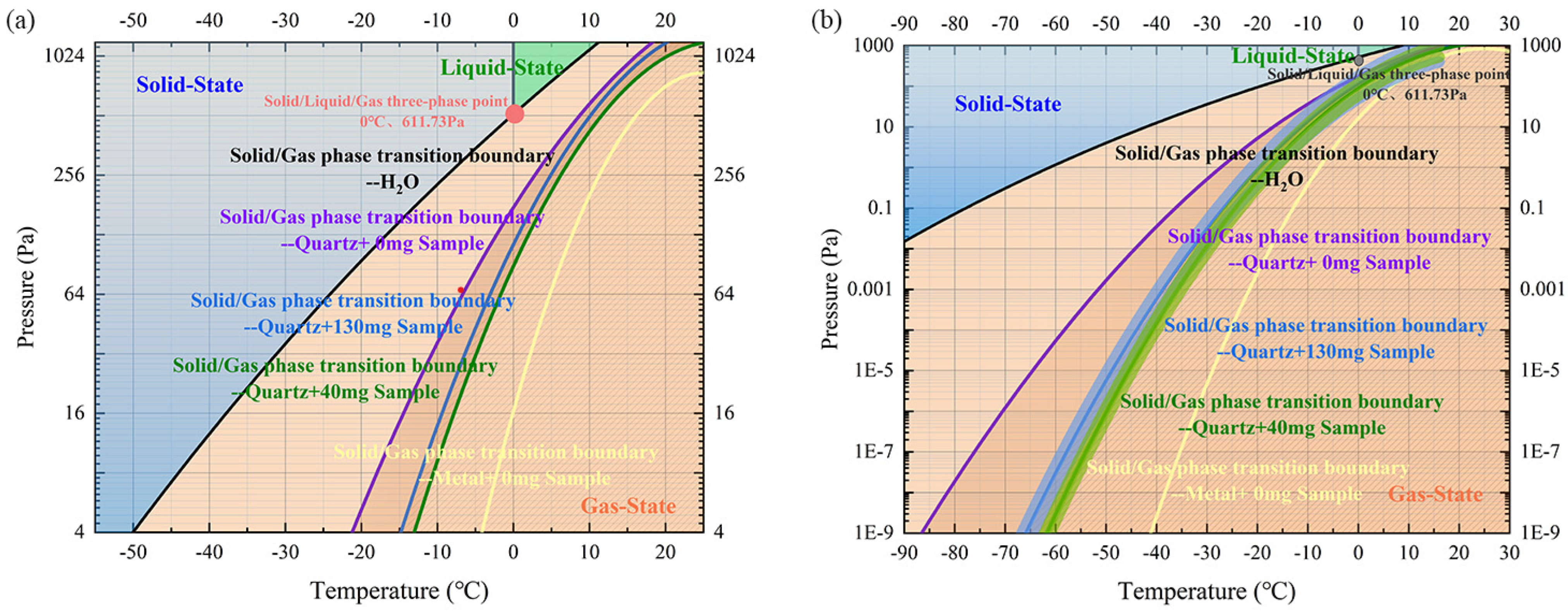
3.4. Prediction of Lunar Regolith Water Content on the Moon
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Witze, A. NASA’s Artemis Moon mission is set to launch: Here’s the science on board. Nature, 24 August 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Jia, Y.; Xue, C.; Lin, Y.; Liu, J.; Fu, X.; Xu, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y.; et al. Scientific objectives and payload configuration of the Chang’E-7 mission. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2024, 11, nwad329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacny, K.; Vendiola, V.; Morrision, P.; Paz, A. Robotics, Planetary Volatiles Extractor (PVEx) for Prospecting and In Situ Resource Utilization. Earth Space 2021, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Lin, H.; He, F.; Zhang, H. New frontier in race for deep space exploration: Lunar water resources. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2024, 39, 899–906. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, J.; Fisackerly, R.; Houdou, B. Establishing lunar resource viability. Space Policy 2016, 37, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.W.; Kliss, M.H. Exploration life support technology challenges for the Crew Exploration Vehicle and future human missions. Adv. Space Res. 2010, 45, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, C.R.; Salmeri, A.; Abbud-Madrid, A.; Carpenter, J.D.; Colaprete, A.; Hibbitts, K.A.; Kleinhenz, J.; Link, M.; Sanders, G. The Moon needs an international lunar resource prospecting campaign. Acta Astronaut. 2024, 214, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocks, F. Lunar Ice: Adsorbed Water on Subsurface Polar Dust. Icarus 2002, 160, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, R.R. Ice in the lunar polar regions revisited. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2002, 107, 5011. [Google Scholar]
- Grumpe, A.; Wöhler, C.; Berezhnoy, A.A.; Shevchenko, V.V. Time-of-day-dependent behavior of surficial lunar hydroxyl/water: Observations and modeling. Icarus 2019, 321, 486–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Milliken, R.E. Water on the surface of the Moon as seen by the Moon Mineralogy Mapper: Distribution, abundance, and origins. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wöhler, C.; Grumpe, A.; Berezhnoy, A.A.; Shevchenko, V.V. Time-of-day–dependent global distribution of lunar surficial water/hydroxyl. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poston, M.J.; Grieves, G.A.; Aleksandrov, A.B.; Hibbitts, C.A.; Dyar, M.D.; Orlando, T.M. Water interactions with micronized lunar surrogates JSC-1A and albite under ultra-high vacuum with application to lunar observations. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2013, 118, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbitts, C.A.; Grieves, G.A.; Poston, M.J.; Dyar, M.D.; Alexandrov, A.; Johnson, M.; Orlando, T. Thermal stability of water and hydroxyl on the surface of the Moon from temperature-programmed desorption measurements of lunar analog materials. Icarus 2011, 213, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goering, J.; Sah, S.; Burghaus, U.; Street, K.W. Adsorption of water on JSC-1A (simulated moon dust samples)—A surface science study. Surf. Interface Anal. 2008, 40, 1423–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sack, N.J.; Baragiola, R.A. Sublimation of vapor-deposited water ice below 170 K, and its dependence on growth conditions. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 48, 9973–9978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, R.; Yang, W.; Hao, J.; Guo, G. Oven Design for In-Situ Thermal Extraction of Volatiles from Lunar Regolith. Earth Space Sci. 2024, 11, e2024EA003556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Hao, M.; Guo, Z.; Yin, B.; Ma, Y.; Deng, L.; Chen, X.; Song, Y.; Cao, C.; Chai, C.; et al. Evidence of a hydrated mineral enriched in water and ammonium molecules in the Chang’e-5 lunar sample. Nat. Astron. 2024, 8, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wen, Z.; He, C.; Wei, Y.; Gao, Q. The Mechanism for the Barrier of Lunar Regolith on the Migration of Water Molecules. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2023, 128, e2022JE007254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Gao, S.; Cheng, S.; Guan, X. Mechanism research on radiation in the phase transition of water. Energy Res. Inf. 2021, 37, 40–45. Available online: https://eri.usst.edu.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20210107&flag=1 (accessed on 12 August 2025).
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Xue, L.; Zhu, S.Y. Physico-mechanical properties variation of rock with phase transformation under high temperature. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2013, 32, 935–942. [Google Scholar]
- Colaprete, A.; Schultz, P.; Goldstein, D.; Summy, D.; Bart, G.D.; Asphaug, E.; Korycansky, D.; Landis, D.; Sollitt, L.; Heldmann, J.; et al. Detection of Water in the LCROSS Ejecta Plume. Science 2010, 330, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; He, H.; Ji, J.; Lin, Y.; Hui, H.; Anand, M.; Tartèse, R.; Yan, Y.; Hao, J.; Li, R.; et al. A dry lunar mantle reservoir for young mare basalts of Chang’e-5. Nature 2021, 600, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Wang, S.; Zou, Y. Physical and Mechanical Properties of Lunar Regolith. Mineral. Petrol. 2004, 24, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, R.; Li, X.; Zou, M.; Wang, C.; Chen, L. JLU-H: A novel lunar highland regolith simulant for use in large-scale engineering experiments. Planet. Space Sci. 2022, 221, 105562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 50123-2019; Standard for Geotechnical Testing Method. Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- McKay, D.S.; Blacic, J.D. Workshop on Production and Uses of Simulated Lunar Materials; Lunar and Planetary Institute: Houston, TX, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Carrier, W.D., III; Olhoeft, G.R.; Mendell, W. Physical Properties of the Lunar Surface; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991; pp. 475–594. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Tang, J.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, W.; Pang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zou, M.; Wang, D. Lunar regolith water ice simulation method and characterization. Icarus 2024, 417, 116119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.H.; Hashim, M.A.; Mudhoo, A.; Debord, J. Beyond Freundlich and Langmuir: The Ruthven–virial equilibrium isotherm for aqueous-solid adsorption systems. Chem. Pap. 2023, 77, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayne, P.O.; Aharonson, O.; Williams, J.; Siegler, M.A.; Greenhagen, B.T.; Bandfield, J.; Vasavada, A.R.; Paige, D.A.; Diviner Lunar Radiometer Science Team. Small Scale Cold Traps on Airless Planetary Bodies; American Astronomical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Paige, D.A.; Siegler, M.A.; Zhang, J.A.; Hayne, P.O.; Foote, E.J.; Bennett, K.A.; Vasavada, A.R.; Greenhagen, B.T.; Schofield, J.T.; McCleese, D.J.; et al. Diviner Lunar Radiometer Observations of Cold Traps in the Moon’s South Polar Region. Science 2010, 330, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boazman, S.J.; Shah, J.; Gawronska, A.J.; Halim, S.H.; Satyakumar, A.V.; Gilmour, C.M.; Bickel, V.T.; Barrett, N.; Kring, D.A. The Distribution and Accessibility of Geologic Targets near the Lunar South Pole and Candidate Artemis Landing Sites. Planet. Sci. J. 2022, 3, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J. NASA’s Artemis I mission is testing a rocket and capsule that could return astronauts to the Moon after 50 years. Nature 2022. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-022-03831-0 (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- Rayal, I.; Thakur, P.K.; Chauhan, P.; Kumar, U. Multi-mission, multi-sensor study of the Shackleton Crater constrained for volatiles with emphasis on albedo distribution of the Lunar South Pole. Adv. Space Res. 2024, 73, 2277–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honniball, C.I.; Lucey, P.G.; Li, S.; Shenoy, S.; Orlando, T.M.; Hibbitts, C.A.; Hurley, D.M.; Farrell, W.M. Molecular water detected on the sunlit Moon by SOFIA. Nat. Astron. 2020, 5, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Yu, D.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zou, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Research on the main scientific and technological issues on lunar polar exploration. J. Deep. Space Explor. 2020, 7, 223–231+240. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, R.; Huang, X.; Li, J.; Tian, Y.; Tang, J.; Su, F.; He, H. The Research on H2O Adsorption Characteristics of Lunar Regolith Simulants: Implications for the Development and Utilization of Lunar Water Resources. Water 2025, 17, 2777. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182777
Zhang Y, Liu Z, Li R, Huang X, Li J, Tian Y, Tang J, Su F, He H. The Research on H2O Adsorption Characteristics of Lunar Regolith Simulants: Implications for the Development and Utilization of Lunar Water Resources. Water. 2025; 17(18):2777. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182777
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yanan, Ziheng Liu, Rongji Li, Xinyu Huang, Jiannan Li, Ye Tian, Junyue Tang, Fei Su, and Huaiyu He. 2025. "The Research on H2O Adsorption Characteristics of Lunar Regolith Simulants: Implications for the Development and Utilization of Lunar Water Resources" Water 17, no. 18: 2777. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182777
APA StyleZhang, Y., Liu, Z., Li, R., Huang, X., Li, J., Tian, Y., Tang, J., Su, F., & He, H. (2025). The Research on H2O Adsorption Characteristics of Lunar Regolith Simulants: Implications for the Development and Utilization of Lunar Water Resources. Water, 17(18), 2777. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182777






