Runoff Forecast Model Integrating Time Series Decomposition and Deep Learning for the Short Term: A Case Study in the Weihe River Basin, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data
2.2. Methodologies
2.2.1. Runoff Sequence Decomposition Methods
Variational Mode Decomposition
Seasonal-Trend Decomposition Procedures Based on Loess
2.2.2. Light Gradient Boosting Machine
2.2.3. Partial Autocorrelation Function
2.2.4. Integrated CNN-LSTM Forecasting Model
2.2.5. Decomposition Ensemble Models for Runoff Forecasting
2.2.6. Performance Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Comparative Analysis of CNN-LSTM and Standalone LSTM Performance
3.2. Comparative Analysis of VMD and STL Decomposition Performance
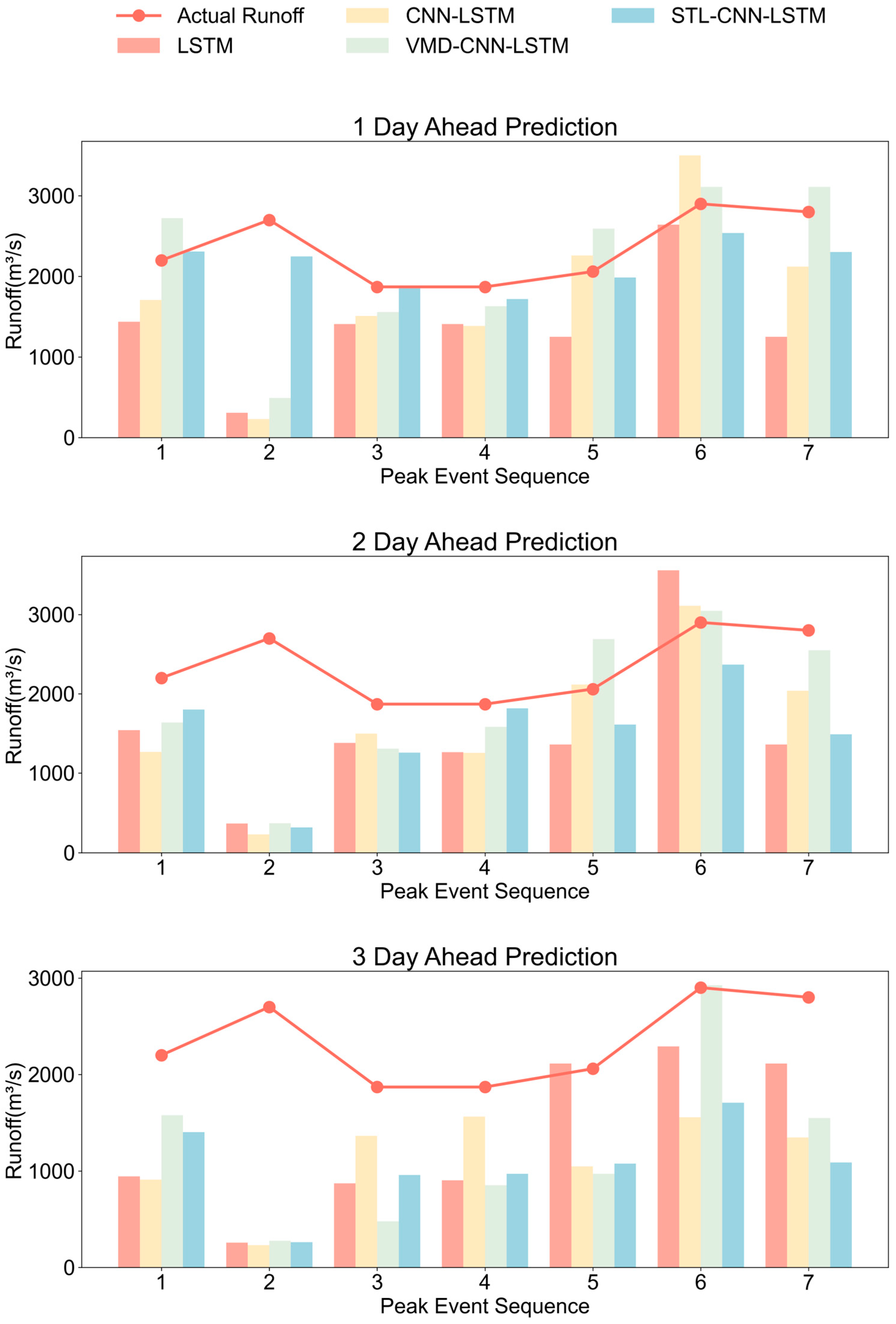
3.3. Comparative Predictive Performance Across Models
4. Discussion
4.1. Forecasting Performance Advantage Analysis of the Proposed Framework
4.2. Uncertainties and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, Z.; Niu, W.; Tang, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H. Monthly runoff time series prediction by variational mode decomposition and support vector machine based on quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.X.; Luo, J.G.; Zuo, G.G.; Xie, J.C. Daily Runoff Forecasting Using a Hybrid Model Based on Variational Mode Decomposition and Deep Neural Networks. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 1571–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiri, J.; Kisi, O. Short-term and long-term streamflow forecasting using a wavelet and neuro-fuzzy conjunction model. J. Hydrol. 2010, 394, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gupta, H.V. Uncertainty in hydrologic modeling: Toward an integrated data assimilation framework. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, W07401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzert, F.; Klotz, D.; Brenner, C.; Schulz, K.; Herrnegger, M. Rainfall–runoff modelling using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 6005–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Hu, C.; Wu, Q.; Jian, S.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S. Research on particle swarm optimization in LSTM neural networks for rainfall-runoff simulation. J. Hydrol. 2022, 608, 127553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeer, A.; Maskey, S.; Skaugen, T.; McClain, M.E. Simulating the hydrological regime of the snow fed and glaciarised Gilgit Basin in the Upper Indus using global precipitation products and a data parsimonious precipitation-runoff model. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Fang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhuo, S. Construction of three-dimensional mesoporous carbon nitride with high surface area for efficient visible-light-driven hydrogen evolution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 561, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, I.; Chang, L.; Chang, F. Exploring the spatio-temporal interrelation between groundwater and surface water by using the self-organizing maps. J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Luo, J.; Li, P.; Zuo, G.; Xie, J. A Hybrid Model Based on Variational Mode Decomposition and Gradient Boosting Regression Tree for Monthly Runoff Forecasting. Water Resour. Manag. 2020, 34, 865–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Yan, J.; Demir, I. A Rainfall-Runoff Model with LSTM-Based Sequence-to-Sequence Learning. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR025326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakoutian, M.M.A.; Samaei, S.Y.; Khaksar, M.; Malakoutian, Y. A prediction of future flows of ephemeral rivers by using stochastic modeling (AR autoregressive modeling). Sustain. Oper. Comput. 2022, 3, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, N.; Bao, X.; Wu, J.; Cui, X. Spatio-temporal deep learning model for accurate streamflow prediction with multi-source data fusion. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2024, 178, 106091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, G.; Luo, J.; Wang, N.; Lian, Y.; He, X. Decomposition ensemble model based on variational mode decomposition and long short-term memory for streamflow forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Peng, T.; Sun, N.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shahzad Nazir, M. Metaheuristic evolutionary deep learning model based on temporal convolutional network, improved aquila optimizer and random forest for rainfall-runoff simulation and multi-step runoff prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 229, 120616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, M.; Banihabib, M.E.; Behbahani, S.M.R. Comparison of the ARMA, ARIMA, and the autoregressive artificial neural network models in forecasting the monthly inflow of Dez dam reservoir. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chang, J.; Huang, Q.; Chen, Y. Monthly streamflow prediction using modified EMD-based support vector machine. J. Hydrol. 2014, 511, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, Y.; Yang, Q.; Shao, J.; Wang, G.; Bai, L.; Xue, Y. Enhanced LSTM Model for Daily Runoff Prediction in the Upper Huai River Basin, China. Engineering. 2023, 24, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, E.; Huang, S.; Huang, Q.; Fang, W.; Wu, L.; Wang, L. A robust method for non-stationary streamflow prediction based on improved EMD-SVM model. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 462–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Wu, J.; Chen, L. An ensemble CNN-LSTM and GRU adaptive weighting model based improved sparrow search algorithm for predicting runoff using historical meteorological and runoff data as input. J. Hydrol. 2023, 625, 129977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttarwar, S.B.; Lerch, S.; Avesani, D.; Majone, B. Performance assessment of neural network models for seasonal weather forecast postprocessing in the Alpine region. Adv. Water Resour. 2025, 204, 105061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachroo, R.K.; Natale, L. Non-linear modelling of the rainfall-runoff transformation. J. Hydrol. 1992, 135, 341–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liu, Y.; Zou, Q.; Ye, L.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, H. Study on optimization and combination strategy of multiple daily runoff prediction models coupled with physical mechanism and LSTM. J. Hydrol. 2023, 624, 129969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisouj, P.; Jun, C.; Bateni, S.M.; Heggy, E.; Band, S.S. Daily runoff forecasting using novel optimized machine learning methods. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 103319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Dong, Z.; Guzmán, S.M.; Conde, G.; Wang, W.; Zhu, S.; Shao, Y.; Meng, J. Two-step hybrid model for monthly runoff prediction utilizing integrated machine learning algorithms and dual signal decompositions. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 84, 102914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Singh, V.P. A Stepwise and Dynamic C-Vine Copula–Based Approach for Nonstationary Monthly Streamflow Forecasts. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2022, 27, 4021043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, B. Are hybrid models integrated with data preprocessing techniques suitable for monthly streamflow forecasting? Some experiment evidences. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, T.; Lu, C.; Yang, J.; Xie, Y. Variational mode decomposition coupled LSTM with encoder-decoder framework: An efficient method for daily streamflow forecasting. Earth Sci. Inform. 2024, 18, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xie, J.; Li, C. Daily reservoir inflow forecasting using multiscale deep feature learning with hybrid models. J. Hydrol. 2016, 532, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Dong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Shi, Q.; Han, Y. Research on stage-divided water level prediction technology of rivers-connected lake based on machine learning: A case study of Hongze Lake, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2021, 35, 2049–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Yuan, X.; Zhu, S.; Xu, Z.; Meng, L.; Peng, J. A hybrid support vector regression framework for streamflow forecast. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.; Gao, P.; Li, J. A Monthly Runoff Forecast Model Combining Time Series Decomposition and CNN-LSTM. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2023, 40, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Mo, L.; Zhou, J.; Fang, W.; Qin, H. Stepwise decomposition-integration-prediction framework for runoff forecasting considering boundary correction. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okkan, U.; Samui, P. Modeling of Watershed Runoff Using Discrete Wavelet Transform and Support Vector Machines. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2012, 21, 3971–3986. [Google Scholar]
- Parisouj, P.; Jun, C.; Bateni, S.M.; Heggy, E.; Band, S.S. Machine learning models coupled with empirical mode decomposition for simulating monthly and yearly streamflows: A case study of three watersheds in Ontario, Canada. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid. Mech. 2023, 17, 2242445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.P.; Qi, M. Neural network forecasting for seasonal and trend time series. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2005, 160, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Zhao, Y.; Lei, J. The incorrect usage of singular spectral analysis and discrete wavelet transform in hybrid models to predict hydrological time series. J. Hydrol. 2017, 552, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.S.K.Q. Examining the applicability of different sampling techniques in the development of decomposition-based streamflow forecasting models. J. Hydrol. 2019, 568, 534–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quilty, J.; Adamowski, J. Addressing the incorrect usage of wavelet-based hydrological and water resources forecasting models for real-world applications with best practices and a new forecasting framework. J. Hydrol. 2018, 563, 336–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Lei, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wen, X.; Ji, Y.; Kang, A. An adaptive middle and long-term runoff forecast model using EEMD-ANN hybrid approach. J. Hydrol. 2018, 567, 767–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, L. On practical challenges of decomposition-based hybrid forecasting algorithms for wind speed and solar irradiation. Energy. 2016, 112, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lu, H.; Lyu, F.; Lyu, H.; Gao, R.; Chen, Y.; Wu, M. Evolution of the proto-Weihe River system during the Eocene–Oligocene: Evidence from sediment provenance of the Weihe Basin. Geomorphology. 2025, 473, 109616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Ma, B.; Yao, R.; Wang, L. Evaluation of the water conservation capacity of the Weihe River Basin based on the Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Services and Tradeoffs model. Ecohydrology 2022, 15, e2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Rui, H. Exploration on Structural Characteristics of the Weihe Basin and Its Evolution. J. Geomech. 2018, 24, 60–69. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Yu, G.; Zhao, M.; Zong, H. Addressing multi-scale temporal variability: Deep integration and application of the CNN and transformer model in monthly streamflow prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 292, 128658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Wood, A.W.; Swenson, S. On Using AI-Based Large-Sample Emulators for Land/Hydrology Model Calibration and Regionalization. Water Resour. Res. 2025, 61, e2024WR039525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yang, K.; Tang, W.; Lu, H.; Qin, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, X. China Meteorological Forcing Dataset (1979–2018); National TPDC ed:National Tibetan Plateau Data Center: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Variational Mode Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, R.B.; Cleveland, W.S. STL: A seasonal-trend decomposition procedure based on Loess. J. Off. Stat. 1990, 6, 3–73. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, S.; Wang, H.; Qian, J.; Men, X. A novel combined model based on echo state network optimized by whale optimization algorithm for blast furnace gas prediction. Energy. 2023, 279, 128048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xu, Y.; Sun, M.; Xie, J. Multi-step-ahead forecast of reservoir water availability with improved quantum-based GWO coupled with the AI-based LSSVM model. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 125769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhao, W.; Lu, H.; Wang, J. Multi-step forecasting for wind speed using a modified EMD-based artificial neural network model. Renew. Energy. 2012, 37, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.Q.; Chen, W.J.; Huang, G.R. Deep insight into daily runoff forecasting based on a CNN-LSTM model. Nat. Hazards 2022, 113, 1675–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, L.; Wu, W. Extreme Short-Term Prediction of Unmanned Surface Vessel Nonlinear Motion Under Waves. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J. Application of a New Hybrid Deep Learning Model That Considers Temporal and Feature Dependencies in Rainfall–Runoff Simulation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, R.; Sun, T.; Gong, A.; Tian, F.; Khan, M.Y.A.; Ni, G. Improving LSTM hydrological modeling with spatiotemporal deep learning and multi-task learning: A case study of three mountainous areas on the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Hua, M.; Wu, X.U. A Hybrid CNN-LSTM Model for Forecasting Particulate Matter (PM2.5). IEEE Access 2020, 8, 26933–26940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Liew, M.W.V.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. ASABE. 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, W. Data Decomposition, Seasonal Adjustment Method and Machine Learning Combined for Runoff Prediction: A Case Study. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 37, 557–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xue, M.; Zhang, J.; Ou, R.; Zhang, Q.; Kuang, P. DetectDUI: An In-Car Detection System for Drink Driving and BACs. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2022, 30, 896–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Chen, Z.; Cai, C.; Luo, J.; Zhang, X. V2iFi: In-Vehicle Vital Sign Monitoring via Compact RF Sensing. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2020, 4, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gao, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, C. A hybrid rainfall-runoff model: Integrating initial loss and LSTM for improved forecasting. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1261239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Hu, D.; Shao, H.; Dai, X.; Liu, G.; Wu, S. Runoff simulation driven by multi-source satellite data based on hydrological mechanism algorithm and deep learning network. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 52, 101720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Zhou, L.; Du, J.; Zhou, C.; Nimai, S.; Wu, L.; Ao, T. Runoff Simulation in Data-Scarce Alpine Regions: Comparative Analysis Based on LSTM and Physically Based Models. Water 2024, 16, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 4768–4777. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Peng, H. Multiple spatio-temporal scale runoff forecasting and driving mechanism exploration by K-means optimized XGBoost and SHAP. J. Hydrol. 2024, 630, 130650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

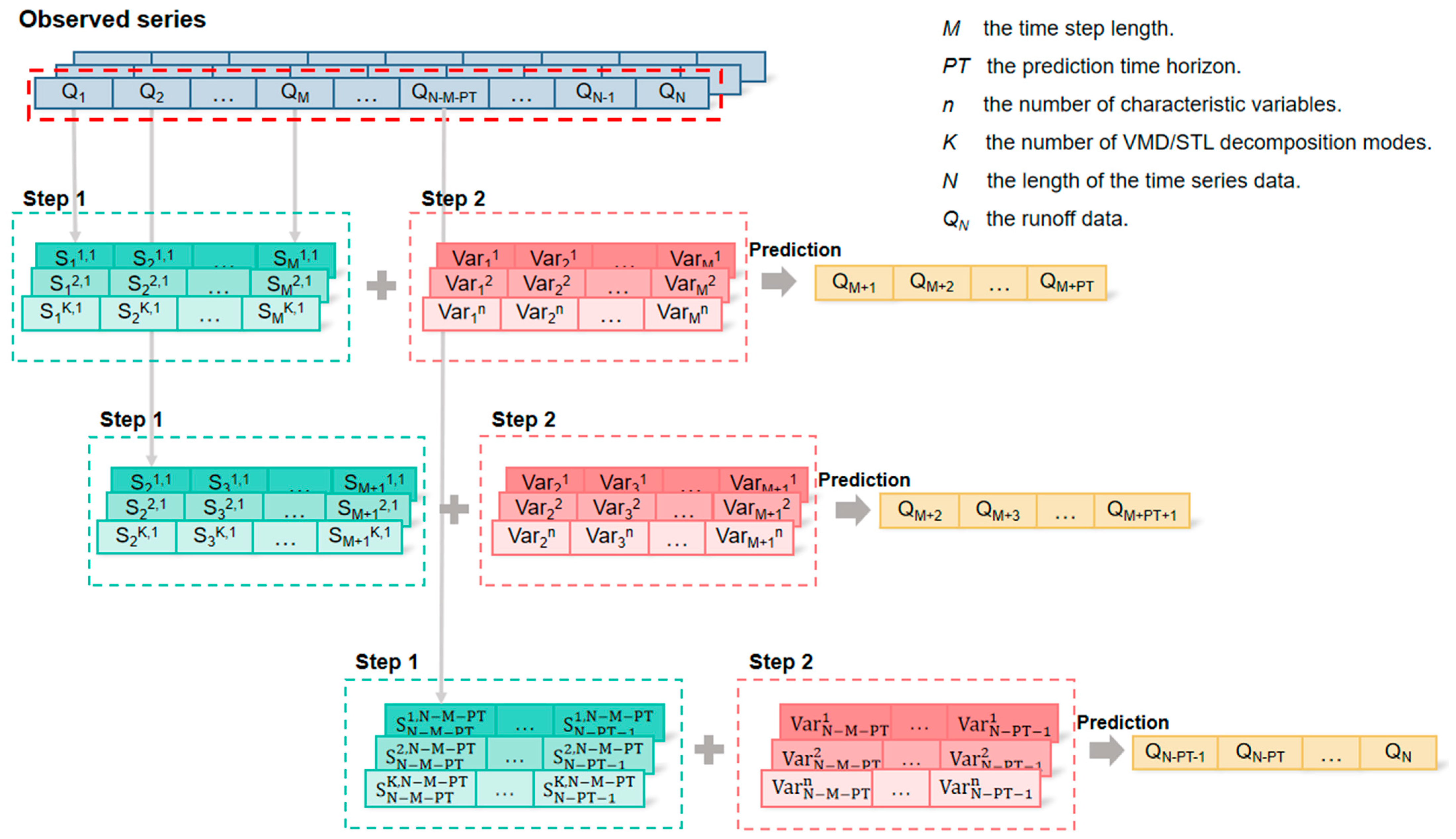
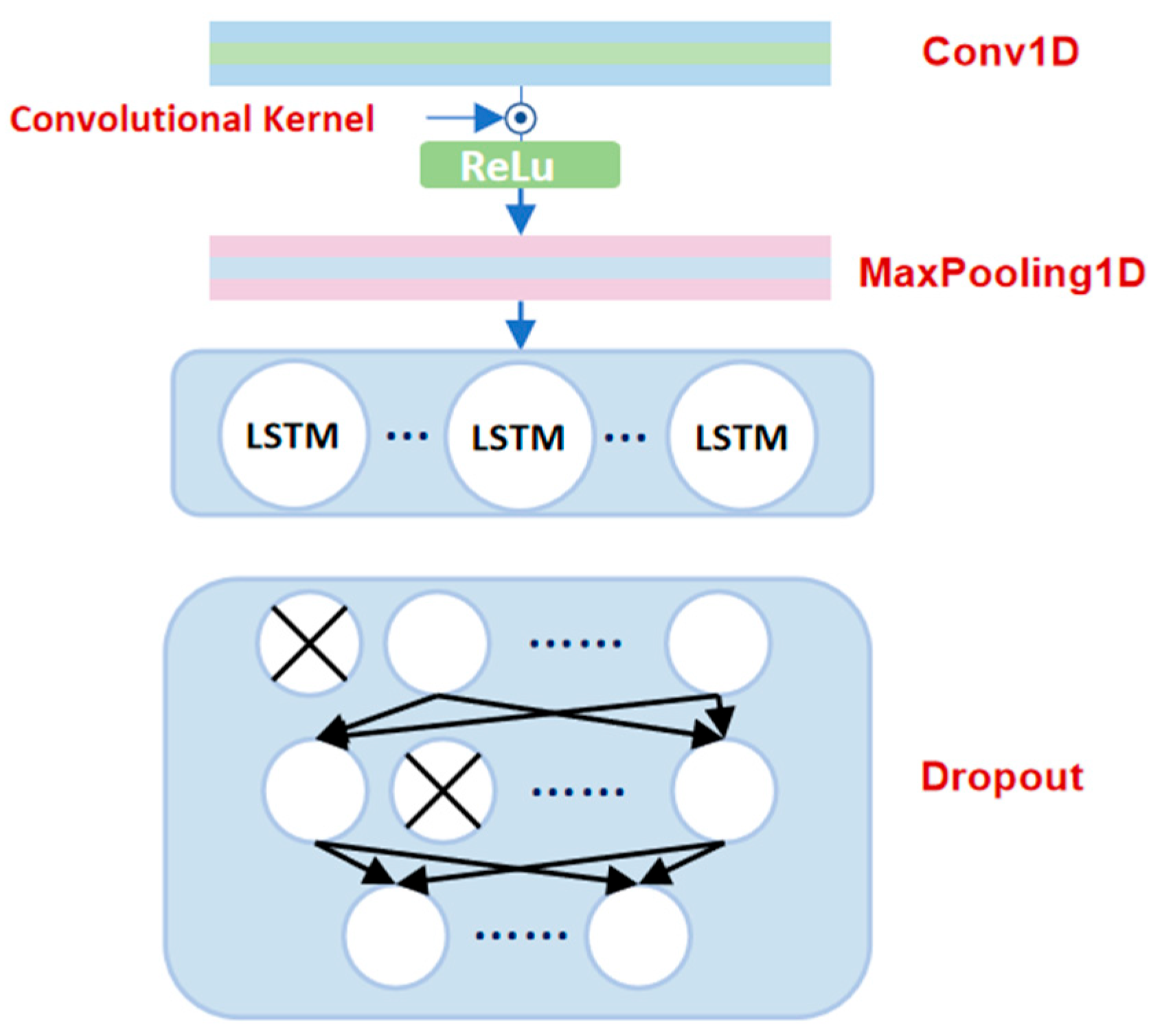

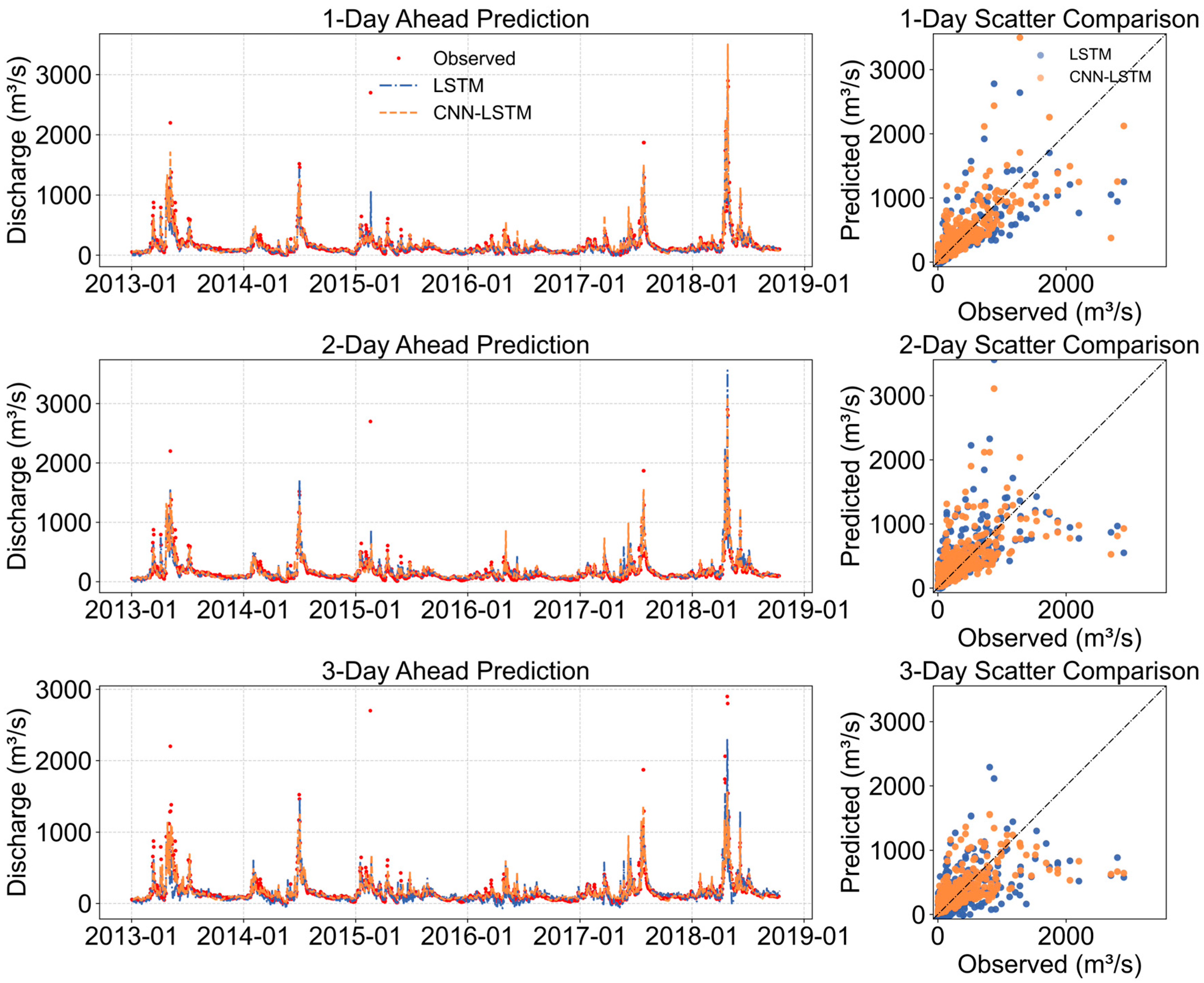
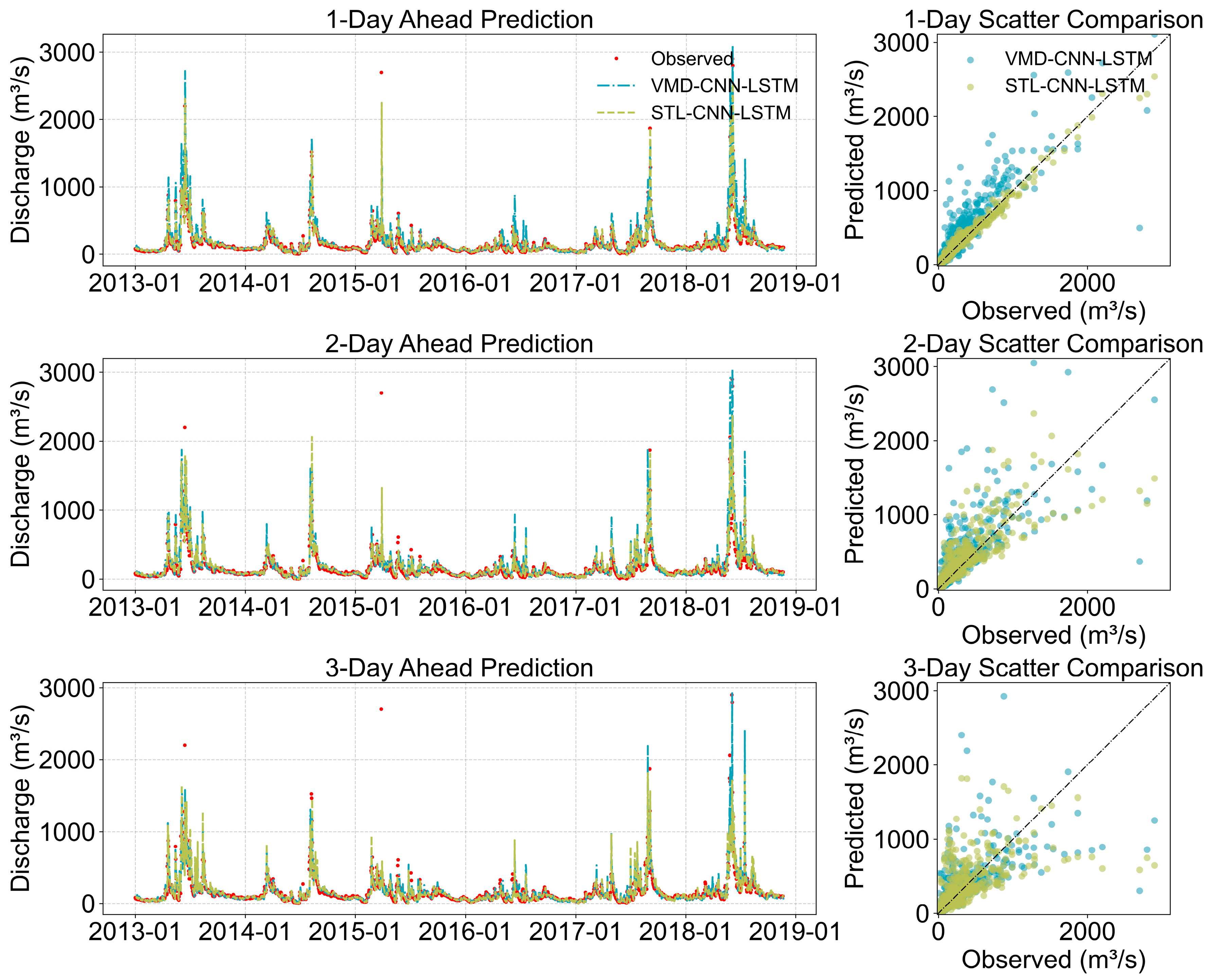

| Water Gauge ID | Water Gauge Name | Longitude (°E) | Latitude (°N) | Elevation (m a.s.l.) | Basin Area Controlled By Individual Water Gauge (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | Beidao | 105.97 | 34.62 | 1389 | 24,871 |
| W2 | Weijiabao | 107.70 | 34.30 | 496 | 37,012 |
| W3 | Xianyang | 108.70 | 34.32 | 387 | 46,827 |
| W4 | Lintong | 109.20 | 34.43 | 354 | 97,299 |
| W5 | Huaxian | 109.77 | 34.58 | 339 | 106,498 |
| Model Category | Performance Assessment | 1st-Day | 2nd-Day | 3rd-Day |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | MAE (m3/s) | 37.47 | 44.43 | 56.18 |
| RMSE (m3/s) | 101.06 | 104.84 | 120.56 | |
| NSE | 0.78 | 0.76 | 0.68 | |
| CNN-LSTM | MAE (m3/s) | 41.47 | 45.18 | 49.72 |
| RMSE (m3/s) | 92.16 | 97.98 | 117.75 | |
| NSE | 0.82 | 0.79 | 0.70 |
| Model Category | Performance Assessment | 1st-Day | 2nd-Day | 3rd-Day |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VMD-CNN-LSTM | MAE (m3/s) | 29.65 | 46.58 | 49.63 |
| RMSE (m3/s) | 65.18 | 96.98 | 112.63 | |
| NSE | 0.91 | 0.79 | 0.71 | |
| STL-CNN-LSTM | MAE (m3/s) | 19.01 | 32.45 | 34.01 |
| RMSE (m3/s) | 42.41 | 93.82 | 87.14 | |
| NSE | 0.96 | 0.83 | 0.80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, R.; An, Q.; Liu, L.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, X. Runoff Forecast Model Integrating Time Series Decomposition and Deep Learning for the Short Term: A Case Study in the Weihe River Basin, China. Water 2025, 17, 2718. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182718
Ma R, An Q, Liu L, Cheng Y, Liu X. Runoff Forecast Model Integrating Time Series Decomposition and Deep Learning for the Short Term: A Case Study in the Weihe River Basin, China. Water. 2025; 17(18):2718. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182718
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Ruijia, Qiang An, Liu Liu, Yongming Cheng, and Xingcai Liu. 2025. "Runoff Forecast Model Integrating Time Series Decomposition and Deep Learning for the Short Term: A Case Study in the Weihe River Basin, China" Water 17, no. 18: 2718. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182718
APA StyleMa, R., An, Q., Liu, L., Cheng, Y., & Liu, X. (2025). Runoff Forecast Model Integrating Time Series Decomposition and Deep Learning for the Short Term: A Case Study in the Weihe River Basin, China. Water, 17(18), 2718. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182718








