Optimizing Drip Irrigation and Nitrogen Fertilization for Sustainable Wheat Production in Arid Soils: Water–Nitrogen Use Efficiency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
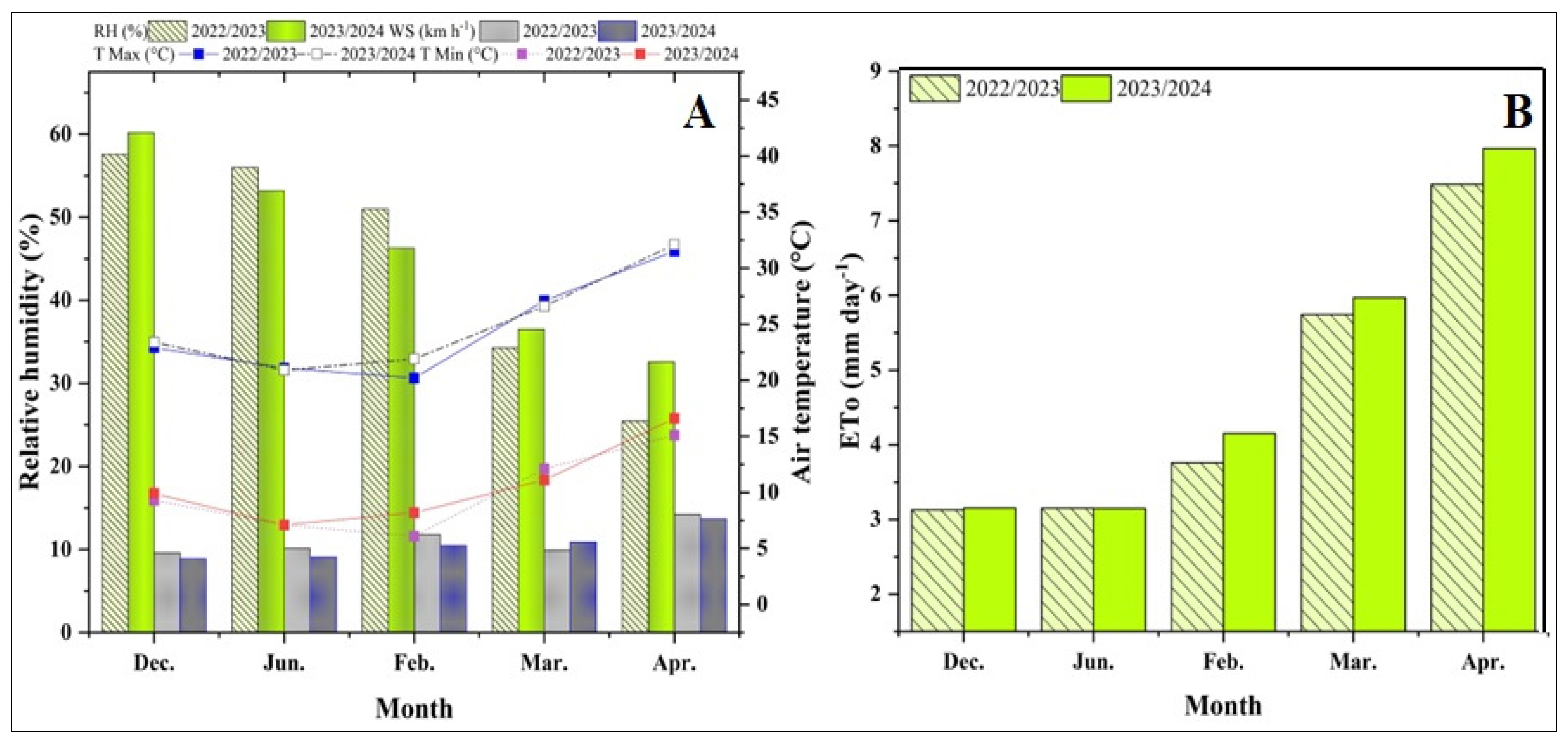
2.1. Weather Conditions
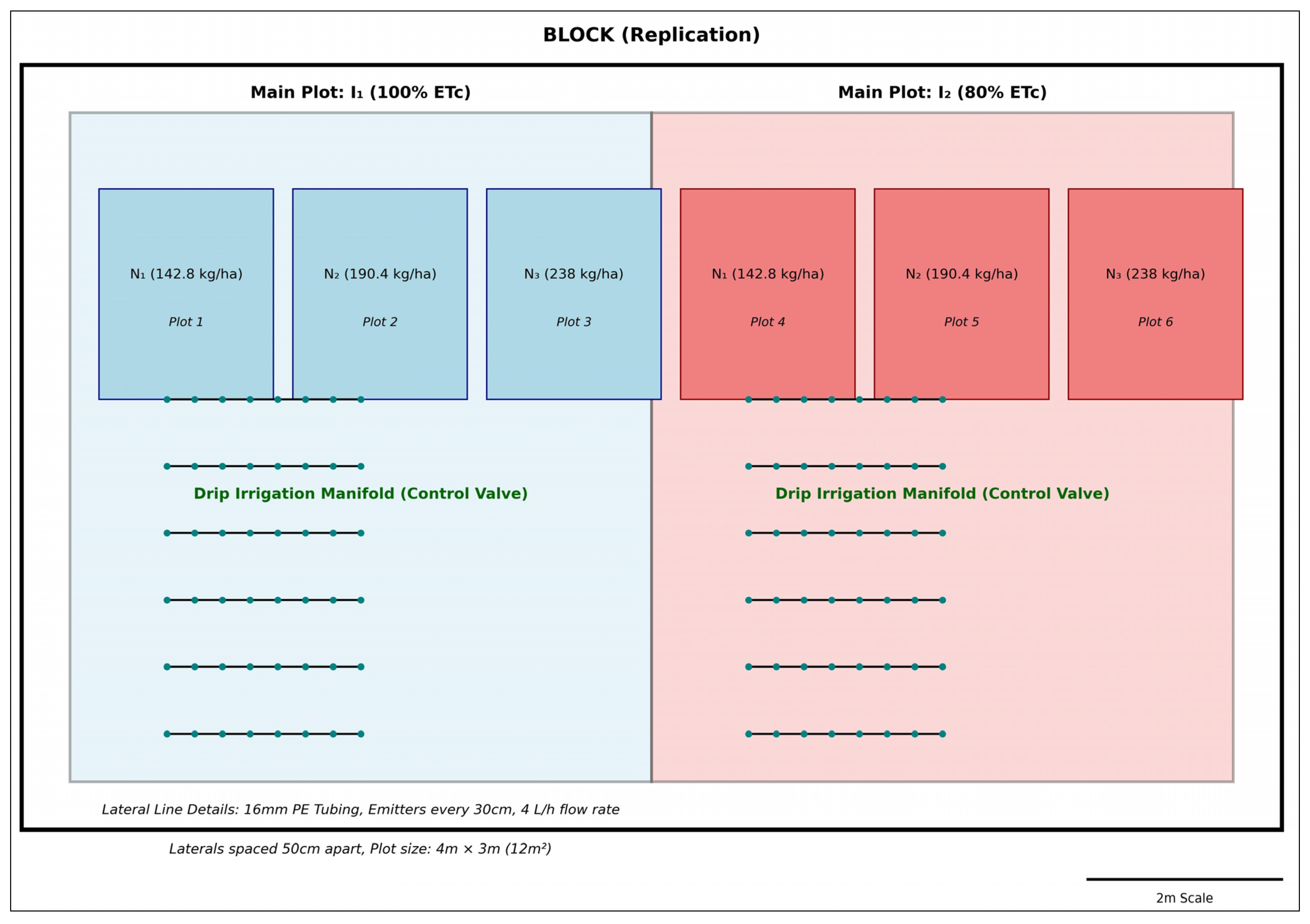
2.2. Experimental Site, Design, and Field Management
2.3. Crop Evapotranspiration (ETc)
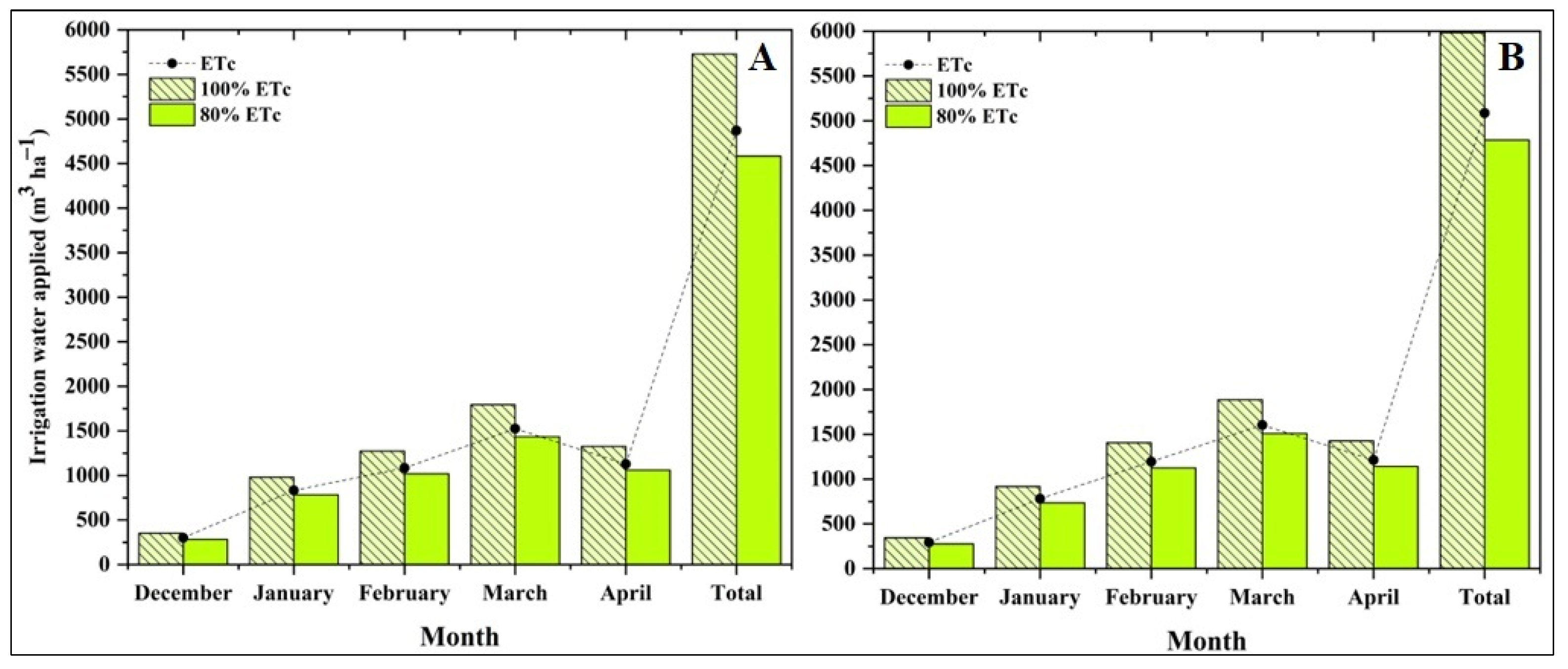
2.4. Actual Irrigation Water Applied (AIWA)
2.5. Nitrogen Fertilizer Use Efficiency (NUE)
2.6. Productivity of Applied Water (PAW)
2.7. Crop Water Productivity (CWP)
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Crop Evapotranspiration (ETc) and Actual Irrigation Water Applied (AIWA)
3.2. Wheat Traits and Yield
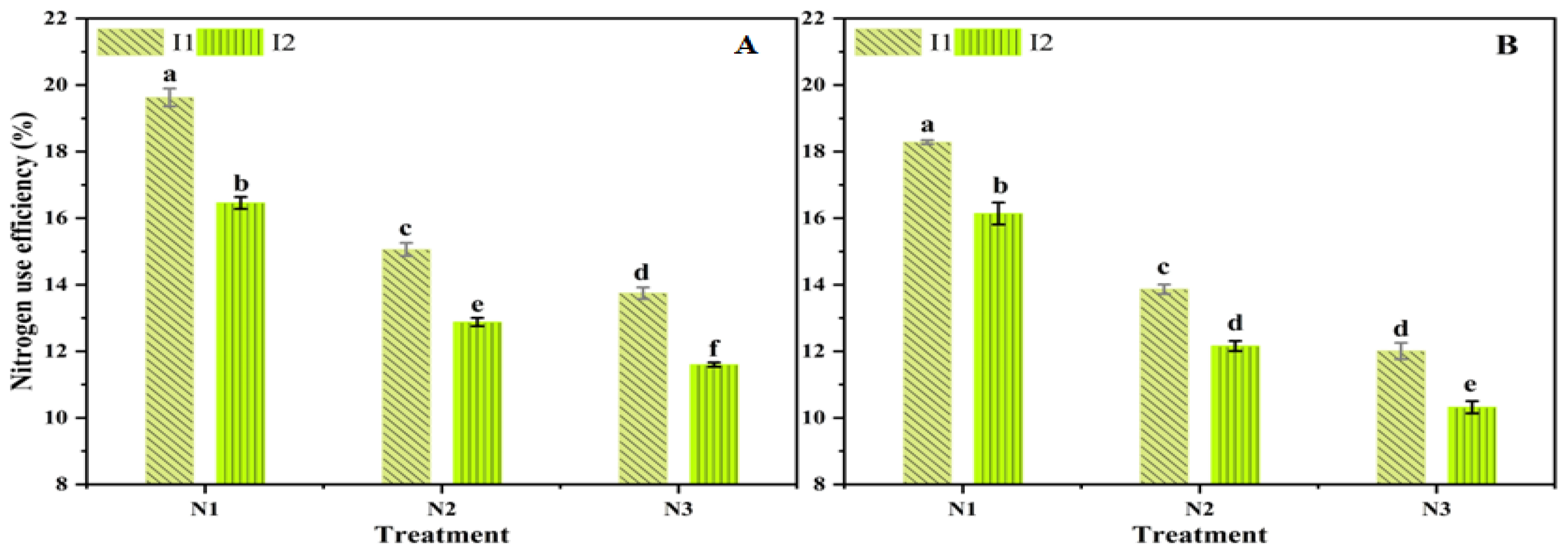
3.3. Water and Nitrogen Efficiency
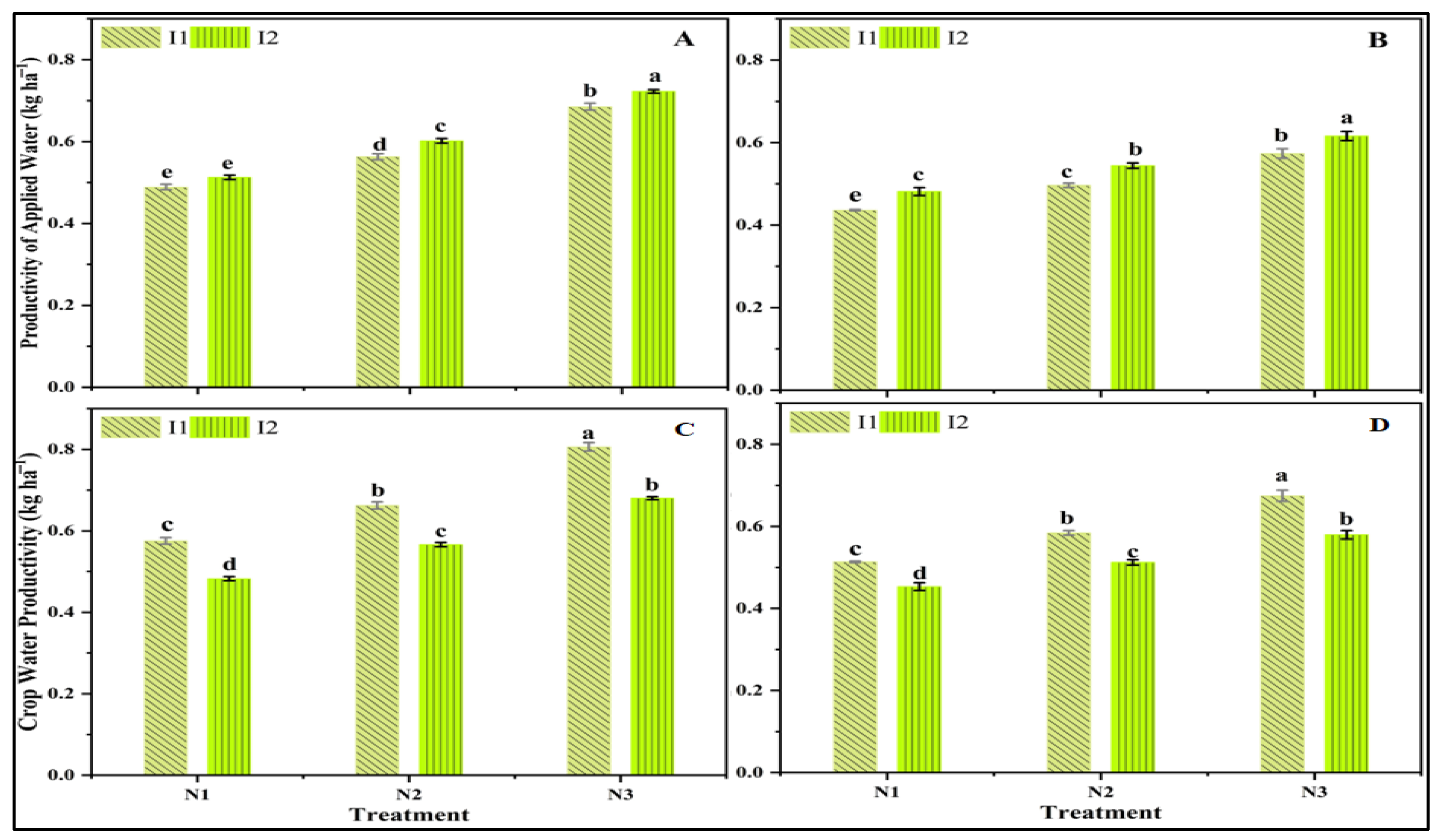
3.4. Productivity of Applied Water (PAW) and Crop Water Productivity (CWP)
3.5. Optimizing Crop Water Productivity
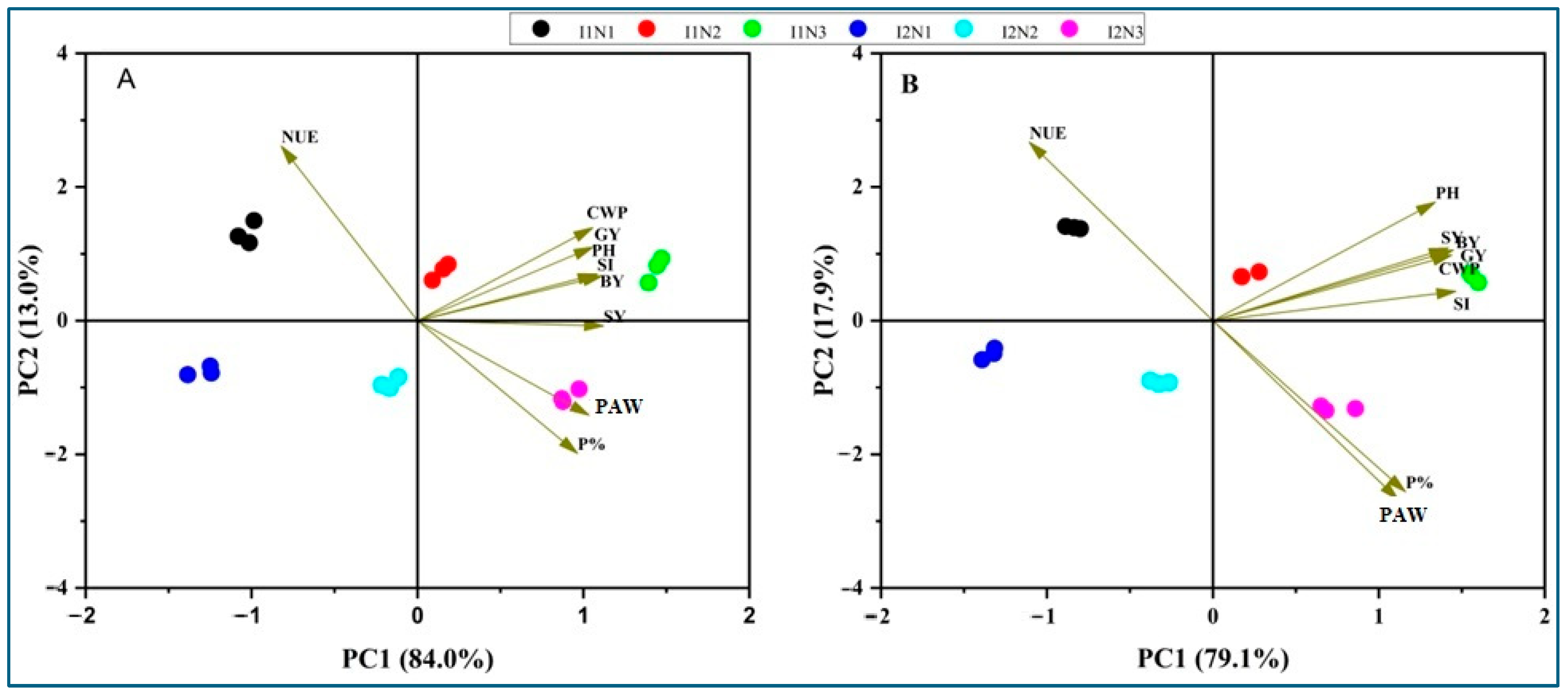
3.6. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shehata, G.; Zahran, H.; Srour, A. Egyptian food security of wheat in light of new challenges. Proc. Syst. Dyn. Innov. Food Netw. 2023, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadl, M.E.; AbdelRahman, M.A.E.; El-Desoky, A.I.; Sayed, Y.A. Assessing soil productivity potential in arid region using remote sensing vegetation indices. J. Arid Environ. 2024, 222, 105166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awaad, M.S.; Deshesh, T.H. Wheat growth and nitrogen use efficiency under drip irrigation on semi-arid region. Eurasian J. Soil Sci. 2019, 8, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, M.L.; Elkot, A.F.; Noreldin, T.; Richard, B.; Qi, A.; Shabana, Y.M.; Saleh, S.M.; Fitt, B.D.; Kheir, A.M. Optimizing wheat yield and water productivity under water scarcity: A modeling approach for irrigation and cultivar selection across different agro-climatic zones of Egypt. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 317, 109668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noreldin, T.; Ouda, S.; Mounzer, O.; Abdelhamid, M.T. CropSyst model for wheat under deficit irrigation using sprinkler and drip irrigation in sandy soil. J. Water Land Dev. 2015, 26, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, A.; Becker, M.; Stellmacher, T. The contribution of agronomic management to sustainably intensify Egypt’s wheat production. Agriculture 2023, 13, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouda, S.; Noreldin, T.; Alarcón, J.J.; Ragab, R.; Caruso, G.; Sekara, A.; Abdelhamid, M.T. Response of spring wheat (Triticum aestivum) to deficit irrigation management under the semi-arid environment of egypt: Field and modeling study. Agriculture 2021, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadl, M.E.; Sayed, Y.A.; El-Desoky, A.I.; Shams, E.M.; Zekari, M.; Abdelsamie, E.A.; Drosos, M.; Scopa, A. Irrigation practices and their effects on soil quality and soil characteristics in arid lands: A comprehensive geomatic analysis. Soil Syst. 2024, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Water footprint benchmarks for crop production: A first global assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 46, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiel, C.A.; Eltahir, E.A.B. Past and future trends of Egypt’s water consumption and its sources. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, Y.A.; Fadl, M.E. Agricultural sustainability evaluation of the new reclaimed soils at Dairut Area, Assiut, Egypt using GIS modeling. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Sp. Sci. 2021, 24, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabr, M.E.S. Management of irrigation requirements using FAO-CROPWAT 8.0 model: A case study of Egypt. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 3127–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.-D.; Leghari, S.J.; Guan, X.-K.; Ma, S.-C.; Ding, C.-M.; Mei, F.-J.; Wei, L.; Wang, T.-C. Deficit Subsurface Drip Irrigation Improves Water Use Efficiency and Stabilizes Yield by Enhancing Subsoil Water Extraction in Winter Wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Aty, M.A.; Gad, K.; Hefny, Y.; Shehata, M. Performance of some wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genotypes and their drought tolerance indices under normal and water stress. Egypt. J. Soil Sci. 2024, 64, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzad, M.A. Impact of nitrogen nutrition and moisture deficits on growth, yield and radiation use efficiency of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 13980–13987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, A.M.; Elhabbak, A.K.; Mohamed, I.; AbdelRahman, M.A.; Scopa, A.; Bassouny, M.A. Can deficit irrigations be an optimum solution for increasing water productivity under arid conditions? A case study on wheat plants. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 30, 103537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, O.; Gupta, R.; Thind, H.; Jat, M.; Sidhu, H.; Singh, Y. Yadvinder-Singh Drip irrigation and nitrogen management for improving crop yields, nitrogen use efficiency and water productivity of maize-wheat system on permanent beds in north-west India. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 219, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonen, B.M.; Moges, M.F.; Gelagl, D.B. Innovative irrigation water-saving strategies to improve water and yield productivity of onions. Int. J. Res. Agric. Sci. 2022, 9, 37–2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, Q.; Gan, Y.; Zhao, C.; Xu, H.-L.; Waskom, R.M.; Niu, Y.; Siddique, K.H. Regulated deficit irrigation for crop production under drought stress. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Fu, P.; Lu, J.; Ma, F.; Sun, X.; Fang, Y. Regulated deficit irrigation: An effective way to solve the shortage of agricultural water for horticulture. Stress Biol. 2022, 2, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asmamaw, D.K.; Janssens, P.; Dessie, M.; Tilahun, S.A.; Adgo, E.; Nyssen, J.; Walraevens, K.; Assaye, H.; Yenehun, A.; Nigate, F.; et al. Effect of deficit irrigation and soil fertility management on wheat production and water productivity in the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 277, 108077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, M.A.; Rekaby, S.A.; Hegab, S.A.; Ragheb, H.M. Effect of deficit irrigation on drip-irrigated wheat grown in semi-arid conditions of Upper Egypt. J. Plant Nutr. 2018, 41, 1576–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadl, M.E.; ElFadl, D.M.A.; Hussien, E.A.A.; Zekari, M.; Shams, E.M.; Drosos, M.; Scopa, A.; Megahed, H.A. Irrigation Water Quality Assessment in Egyptian Arid Lands, Utilizing Irrigation Water Quality Index and Geo-Spatial Techniques. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhen, W.; Wang, G. Interaction Effects of Water and Nitrogen Practices on Wheat Yield, Water and Nitrogen Productivity under Drip Fertigation in Northern China. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, R.; Balasaheb, K.S. Optimizing water use efficiency and yield of wheat crops through integrated irrigation and nitrogen management: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Environ. Clim. Change 2023, 13, 4059–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamani, A.K.M.; Abubakar, S.A.; Fu, Y.; Kpalari, D.F.; Wang, G.; Duan, A.; Gao, Y.; Ju, X. The coupled effects of various irrigation scheduling and split nitrogen fertilization modes on post-anthesis grain weight variation, yield, and grain quality of drip-irrigated winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in the North China Plain. J. Integr. Agric. 2024, 24, 2123–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobnitch, S.T.; Donovan, T.C.; Wenz, J.A.; Flynn, N.E.; Schipanski, M.E.; Comas, L.H. Can nitrogen availability impact plant performance under water stress? A review of traits, mechanisms, and whole plant effects. Plant Soil 2024, 511, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bwambale, E.; Abagale, F.K.; Anornu, G.K. Smart irrigation monitoring and control strategies for improving water use efficiency in precision agriculture: A review. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 260, 107324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.; Arshad, M.A.; Akbar, B.A.; Bibi, A.; Ain, Q.U.; Bilal, A.; Arqam, S.M.; Asif, M.; Ishtiaq, M.H.; Rasheed, H.U.; et al. Integrated nitrogen and irrigation management strategies for sustainable wheat production: Enhancing yield and environmental efficiency. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2024, 13, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hütsch, B.W.; Schubert, S. Maize harvest index and water use efficiency can be improved by inhibition of gibberellin biosynthesis. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2018, 204, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Lian, H.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y.; Cai, H.; Zhang, S. The role of root size and root efficiency in grain production, and water-and nitrogen-use efficiency in wheat. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 7083–7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Mak-Mensah, E.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Huang, L.; Song, S.; Zhi, K.; Zhang, J. Interactive effects of drip irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on wheat and maize yield: A meta-analysis. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 1547–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; She, D.; Ding, J.; Abulaiti, A.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R.; Wang, F.; Shan, J.; Xia, Y. Coping with groundwater pollution in high-nitrate leaching areas: The efficacy of denitrification. Environ. Res. 2024, 250, 118484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhiar, I.A.; Yan, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, G.; He, B.; Hao, B.; Han, Y.; Wang, B.; Bao, R.; Syed, T.N.; et al. A review of precision irrigation water-saving technology under changing climate for enhancing water use efficiency, crop yield, and environmental footprints. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL-Sayed, M.M.; Khalifa, Y.A.M.; Elglaly, A.M.M. Effect of Water Irrigation Management and Nitrogen Fertilizer Sources on Water Productivity and Quality of Some Egyptian Cotton Cultivar. Misr J. Agric. Eng. 2020, 37, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanardağ, A.B. Damage to Soil and Environment Caused by Excessive Fertilizer Use; Agriculture, Forestry and Aquaculture Sciences; Serüven Publishing: Ankara, Turkey, 2024; p. 203. [Google Scholar]
- Akram, M.; Iqbal, R.M.; Jamil, M. The response of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to integrating effects of drought stress and nitrogen management. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 20, 275–286. [Google Scholar]
- Si, Z.; Zain, M.; Mehmood, F.; Wang, G.; Gao, Y.; Duan, A. Effects of nitrogen application rate and irrigation regime on growth, yield, and water-nitrogen use efficiency of drip-irrigated winter wheat in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 231, 106002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, G.; Chen, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, Q.; Xu, X.; Huo, Z. Effects of irrigation and fertilization on grain yield, water and nitrogen dynamics and their use efficiency of spring wheat farmland in an arid agricultural watershed of Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 260, 107277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, S.; Felemban, A.; Abdelrahim, A.; Al-Dakhil, M. Agricultural and Technology-based strategies to improve water-use efficiency in Arid and Semiarid areas. Water 2024, 16, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N. CROPWAT Model for ETo Calculation Using Penman Monteith Method; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1991; pp. 112–140. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements—FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; Volume 300, p. D05109. [Google Scholar]
- James, L.G. Principles of Farm Irrigation Systems Design; John Willey & Sons. Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Zwart, S.J.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. Review of measured crop water productivity values for irrigated wheat, rice, cotton and maize. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 69, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghih, H.; Behmanesh, J.; Rezaie, H.; Khalili, K. Climate and rainfed wheat yield. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 144, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvnjak, J.; Katanic, Z.; Sarcevic, H.; Spanic, V. Analysis of the Photosynthetic Parameters, Grain Yield, and Quality of Different Winter Wheat Varieties over a Two-Year Period. Agronomy 2024, 14, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamian, S.; Khordadi, M.J.; Abedi-Koupai, J. Effects of variations in climatic parameters on evapotranspiration in the arid and semi-arid regions. Glob. Planet. Change 2011, 78, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, M.; Matsuno, A.; El-Kilani, R.M.M.; Abdel-Fattah, A.; Mahmoud, M.A. Crop evapotranspiration in the Nile Delta under different irrigation methods. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2017, 62, 1618–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouk, A.S.; Abdelghany, A.M.; Shehab, A.A.; Alwakel, S.E.; Makled, K.M.; Naif, E.; Ren, H.; Lamlom, S.F. Optimizing wheat productivity through integrated management of irrigation, nutrition, and organic amendments. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djaman, K.; O’neill, M.; Owen, C.; Smeal, D.; West, M.; Begay, D.; Allen, S.; Koudahe, K.; Irmak, S.; Lombard, K. Long-term winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seasonal irrigation amount, evapotranspiration, yield, and water productivity under semiarid climate. Agronomy 2018, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tari, A.F. The effects of different deficit irrigation strategies on yield, quality, and water-use efficiencies of wheat under semi-arid conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 167, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashisth, A.; Goyal, A.; Krishanan, P. Effect of weather variability on growth and yield of wheat crop under semi-arid region of india. J. Agrometeorol. 2020, 22, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faloye, O.T.; Ajayi, A.E.; Oguntunde, P.G.; Kamchoom, V.; Fasina, A. Modeling and Optimization of Maize Yield and Water Use Efficiency under Biochar, Inorganic Fertilizer and Irrigation Using Principal Component Analysis. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, G.; Zhu, D.; Yan, Y. Effects of water deficit and high N fertilization on wheat storage protein synthesis, gluten secondary structure, and breadmaking quality. Crop J. 2022, 10, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Niu, W.; Sun, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, E.; Wang, J. Soil moisture and nitrogen content influence wheat yield through their effects on the root system and soil bacterial diversity under drip irrigation. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 3062–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashmawy, F.; Abo-Warda, A.M.A. Response of some wheat cultivars to different seeding rates and nitrogen fertilization levels in sandy soil. Egypt. J. Appl. Sci. 2002, 17, 136–157. [Google Scholar]
- Pouri, K.; Mardeh, A.S.-S.; Sohrabi, Y.; Soltani, A. Crop phenotyping for wheat yield and yield components against drought stress. Cereal Res. Commun. 2019, 47, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafoor, I.; Habib-Ur-Rahman, M.; Ali, M.; Afzal, M.; Ahmed, W.; Gaiser, T.; Ghaffar, A. Slow-release nitrogen fertilizers enhance growth, yield, NUE in wheat crop and reduce nitrogen losses under an arid environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 43528–43543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Akmal, M. Wheat Growth, Yield, and Quality Under Water Deficit and Reduced Nitrogen Supply. A Review. Gesunde Pflanz. 2022, 74, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M.; Tian, Z.; Ata-Ul-Karim, S.T.; Cui, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zahoor, R.; Jiang, D.; Dai, T. Nitrogen nutrition improves the potential of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to alleviate the effects of drought stress during vegetative growth periods. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, I.; Yang, L.; Ahmad, S.; Farooq, S.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Khan, A.; Zeeshan, M.; Elshikh, M.S.; Abbasi, A.M.; Zhou, X.-B. Nitrogen fertilizer modulates plant growth, chlorophyll pigments and enzymatic activities under different irrigation regimes. Agronomy 2022, 12, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.-Z.; Ma, T.; Huang, J.-S.; Wu, J.-W. Nitrogen transportation and transformation under different soil water and salinity conditions. Ecol. Chem. Eng. 2016, 23, 677–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Anwar, S.; Shaobo, Y.; Gao, Z.; Sun, M.; Ashraf, M.Y.; Ren, A.; Yang, Z. Soil water consumption, water use efficiency and winter wheat production in response to nitrogen fertilizer and tillage. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, Z.; Hussain, K.; Iqbal, I.; Nawaz, K.; Siddiqui, E.H.; Javeria, M.; Nazeer, A.; Ali, S.S. Improvements of crop productivity in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by the applications of phytohormones. Pak. J. Bot. 2021, 53, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yu, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Effects of nitrogen rate and ratio of base fertilizer and topdressing on uptake, translocation of nitrogen and yield in wheat. Front. Agric. China 2007, 1, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochieng’, I.O.; Gitari, H.I.; Mochoge, B.; Rezaei-Chiyaneh, E.; Gweyi-Onyango, J.P. Optimizing Maize Yield, Nitrogen Efficacy and Grain Protein Content under Different N Forms and Rates. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 1867–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Dugo, V.; Durand, J.-L.; Gastal, F. Water deficit and nitrogen nutrition of crops. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Palta, J.A.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y.; Deng, X. Nitrogen fertilization improved water-use efficiency of winter wheat through increasing water use during vegetative rather than grain filling. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 197, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, A.J.; Armstrong, R.D.; Grace, P.R.; Scheer, C.; Partington, D.L. Nitrogen use efficiency of 15N urea applied to wheat based on fertiliser timing and use of inhibitors. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2020, 116, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Chen, Y.; Pan, J.; Ye, Y.; Miao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Cui, Z. Improved crop management achieved high wheat yield and nitrogen use efficiency. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2021, 15, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorburn, P.J.; Biggs, J.S.; Puntel, L.A.; Sawyer, J.E.; Everingham, Y.L.; Archontoulis, S.V. The nitrogen fertilizer conundrum: Why is yield a poor determinant of crops’ nitrogen fertilizer requirements? Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 44, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.A.; Mason, K.E.; Bleeker, A.; Hicks, W.K.; Masso, C.; Raghuram, N.; Reis, S.; Bekunda, M. Just enough nitrogen: Summary and synthesis of outcomes. In Just Enough Nitrogen: Perspectives on How to Get There for Regions with Too Much and Too Little Nitrogen; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Howell, T.A. Irrigation efficiency. Encycl. Water Sci. 2003, 467, 500. [Google Scholar]
| Property | Unit | Mean Value | Property | Unit | Mean Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gravel | % | 30.4 | Soluble cations | Ca | mmol L−1 | 1.43 |
| Sand | % | 90.9 | Mg | 1.16 | ||
| Silt | % | 7.1 | Na | 0.19 | ||
| Clay | % | 3.0 | K | 0.75 | ||
| Texture class | - | Sandy | Soluble anions | CO3 + HCO3 | 1.68 | |
| Saturation percentage | w% | 23.3 | Cl | 1.47 | ||
| Field capacity | w% | 10.9 | SO4 | 0.35 | ||
| Wilting point | w% | 4.50 | Available N | mg kg−1 | 32.47 | |
| Available water | w% | 6.50 | Available P | 8.31 | ||
| Bulk density | Mg cm−3 | 1.62 | Available K | 37.24 | ||
| CaCO3 | % | 30.0 | - | - | - | - |
| Organic matter (OM) | % | 0.10 | - | - | - | - |
| pH (1:1) | - | 8.37 | - | - | - | - |
| EC (soil past extract) | ds m−1 | 0.33 | - | - | - | - |
| 2022–2023 | 2023–2024 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | 100% ETc | 80% ETc | Mean | 100% ETc | 80% ETc | Mean |
| Plant height (cm) | ||||||
| N1 | 89.88 ± 0.31 d | 83.93 ± 0.92 e | 86.90 ± 1.40 c | 88.20 ± 0.07 d | 83.40 ± 0.14 f | 85.55 ± 1.0756 c |
| N2 | 95.72 ± 0.10 b | 92.60 ± 0.32 c | 94.16 ± 0.71 b | 89.75 ± 0.03 c | 85.61 ± 0.06 e | 87.55 ± 0.9253 b |
| N3 | 100.72 ± 0.36 a | 95.45 ± 0.07 b | 98.08 ± 1.19 a | 96.34 ± 0.14 a | 89.10 ± 0.16 b | 92.55 ± 1.6207 a |
| Mean | 95.24 ± 1.57 a | 90.24 ± 1.75 b | 91.43 ± 1.25 a | 86.04 ± 0.83 b | ||
| F | P | F | P | |||
| IR | 128.64 | 0.008 | ** | 3888.02 | 0.000 | *** |
| N | 335.86 | 0.000 | *** | 3600.73 | 0.000 | *** |
| IR × N | 5.71 | 0.028 | * | 182.44 | 0.000 | *** |
| Straw yield (kg ha−1) | ||||||
| N1 | 6077.20 ± 25.70 d | 6043.89 ± 42.82 d | 6060.54 ± 23.54 c | 5704.79 ± 11.02 c | 5132.16 ± 38.01 d | 5418.55 ± 129.26 c |
| N2 | 6710.87 ± 23.82 c | 6617.71 ± 28.07 c | 6664.29 ± 26.55 b | 6087.14 ± 17.69 b | 5646.49 ± 35.46 c | 5866.55 ± 100.11 b |
| N3 | 7458.89 ± 50.18 a | 7057.68 ± 38.93 b | 7258.28 ± 94.10 a | 6628.91 ± 94.31 a | 6086.06 ± 71.57 b | 6357.55 ± 132.42 a |
| Mean | 6748.24 ± 200.44 a | 6573.24 ± 147.92 a | 6140.28 ± 136.91 a | 5621.57 ± 140.17 b | ||
| F | P | F | P | |||
| IR | 46.12 | 0.021 | * | 137.02 | 0.007 | ** |
| N | 528.03 | 0.000 | *** | 130.90 | 0.000 | *** |
| IR × N | 14.34 | 0.002 | ** | 0.71 | 0.520 | NS |
| Biological yield (kg ha−1) | ||||||
| N1 | 8880.04 ± 38.06 e | 8394.27 ± 17.38 f | 8637.15 ± 110.22 c | 8316.14 ± 11.19 c | 7436.95 ± 29.90 d | 7876.55 ± 197.11 c |
| N2 | 9936.65 ± 64.95 c | 9376.46 ± 35.17 d | 9656.55 ± 129.55 b | 9057.23 ± 12.37 b | 8251.58 ± 3.37 c | 8654.55 ± 180.24 b |
| N3 | 11,385.03 ± 30.03 a | 10,370.85 ± 58.05 b | 10,877.94 ± 228.65 a | 10,059.43 ± 29.33 a | 9033.86 ± 57.22 b | 9546.55 ± 231.11 a |
| Mean | 10,067.24 ± 363.79 a | 9380.24 ± 286.01 b | 9144.27 ± 252.75 a | 8240.80 ± 231.26 b | ||
| F | P | F | P | |||
| IR | 1434 | 0.000 | *** | 1559.93 | 0.000 | *** |
| N | 1616.66 | 0.000 | *** | 2177.30 | 0.000 | *** |
| IR × N | 26.27 | 0.000 | *** | 9.76 | 0.007 | ** |
| 2022–2023 | 2023–2024 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | 100% ETc | 80% ETc1 | Mean | 100% ETc2 | 80% ETc3 | Mean |
| Grain yield (kg ha−1) | ||||||
| N1 | 2802.84 ± 38.36 c | 2350.38 ± 25.52 d | 2576.61 ± 103.25 c | 2611.36 ± 8.65 c | 2304.80 ± 46.78 d | 2458.55 ± 71.77 c |
| N2 | 3225.78 ± 41.96 b | 2758.74 ± 26.70 c | 2992.26 ± 106.77 b | 2970.09 ± 29.91 b | 2605.09 ± 32.10 c | 2787.55 ± 83.94 b |
| N3 | 3926.14 ± 50.12 a | 3313.17 ± 19.12 b | 3619.66 ± 139.15 a | 3430.52 ± 69.82 a | 2947.80 ± 52.80 b | 3189.55 ± 114.81 a |
| Mean | 3318.24 ± 165.23 a | 2807.24 ± 140.01 b | 3003.99 ± 120.58 a | 2619.23 ± 95.53 b | ||
| F | P | F | P | |||
| IR | 1957.47 | 0.000 | *** | 174.04 | 0.006 | ** |
| N | 357.20 | 0.000 | *** | 120.13 | 0.000 | *** |
| IR × N | 2.55 | 0.139 | NS | 1.80 | 0.226 | NS |
| Seed index (%) | ||||||
| N1 | 45.23 ± 0.29 c | 44.07 ± 0.25 d | 44.65 ± 0.31 c | 42.28 ± 0.34 c | 40.58 ± 0.34 d | 41.55 ± 0.44 c |
| N2 | 47.28 ± 0.12 b | 45.88 ± 0.18 c | 46.58 ± 0.33 b | 44.70 ± 0.47 b | 43.16 ± 0.28 c | 43.55 ± 0.42 b |
| N3 | 48.55 ± 0.24 a | 47.70 ± 0.21 b | 48.12 ± 0.24 a | 47.84 ± 0.38 a | 45.26 ± 0.36 b | 46.55 ± 0.62 a |
| Mean | 47.24 ± 0.50 a | 45.24 ± 0.53 b | 44.94 ± 0.83 a | 43.00 ± 0.70 b | ||
| F | P | F | P | |||
| IR | 62.12 | 0.015 | * | 130.67 | 0.008 | ** |
| N | 107.42 | 0.000 | *** | 91.55 | 0.000 | *** |
| IR × N | 0.66 | 0.54 | NS | 1.09 | 0.381 | NS |
| Protein content (%) | ||||||
| N1 | 10.77 ± 0.08 e | 12.09 ± 0.10 d | 11.43 ± 0.30 c | 11.42 ± 0.08 e | 12.85 ± 0.14 d | 12.55 ± 0.33 c |
| N2 | 12.25 ± 0.02 d | 13.01 ± 0.03 c | 12.63 ± 0.17 b | 13.05 ± 0.03 d | 13.76 ± 0.06 c | 13.55 ± 0.16 b |
| N3 | 14.28 ± 0.08 b | 14.97 ± 0.07 a | 14.63 ± 0.16 a | 15.04 ± 0.17 b | 15.78 ± 0.06 a | 15.55 ± 0.18 a |
| Mean | 12.24 ± 0.51 b | 13.24 ± 0.43 a | 13.17 ± 0.53 b | 14.13 ± 0.44 a | ||
| F | P | F | P | |||
| IR | 698.86 | 0.001 | ** | 969.20 | 0.001 | ** |
| N | 748.16 | 0.000 | *** | 386.08 | 0.000 | *** |
| IR × N | 8.28 | 0.011 | * | 5.86 | 0.027 | * |
| Treatment | 2022–2023 | 2023–2024 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE%) | ||||||
| F | P | F | P | |||
| IR | 31.41 | 0.031 | * | 128.10 | 0.008 | ** |
| N | 6526.45 | 0.000 | *** | 445.39 | 0.000 | *** |
| IR × N | 4.59 | 0.047 | * | 0.80 | 0.482 | NS |
| Productivity of Applied Water (PAW kg ha−1) | ||||||
| F | P | F | P | |||
| IR | 64.69 | 0.015 | * | 67.24 | 0.015 | * |
| N | 491.61 | 0.000 | *** | 102.32 | 0.000 | *** |
| IR × N | 1.35 | 0.313 | Ns | 0.15 | 0.864 | NS |
| Crop Water Productivity (CWP kg ha−1) | ||||||
| F | P | F | P | |||
| IR | 1289.29 | 0.000 | *** | 165.14 | 0.006 | ** |
| N | 420.30 | 0.000 | *** | 125.21 | 0.000 | *** |
| IR × N | 2.98 | 0.11 | NS | 2.13 | 0.181 | NS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelrhman, A.A.; Abdel-Fattah, I.M.; Mostafa, M.O.; Fadl, M.E.; Drosos, M.; Scopa, A. Optimizing Drip Irrigation and Nitrogen Fertilization for Sustainable Wheat Production in Arid Soils: Water–Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Water 2025, 17, 2708. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182708
Abdelrhman AA, Abdel-Fattah IM, Mostafa MO, Fadl ME, Drosos M, Scopa A. Optimizing Drip Irrigation and Nitrogen Fertilization for Sustainable Wheat Production in Arid Soils: Water–Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Water. 2025; 17(18):2708. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182708
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelrhman, Ahmed A., Ibrahim M. Abdel-Fattah, Mostafa O. Mostafa, Mohamed E. Fadl, Marios Drosos, and Antonio Scopa. 2025. "Optimizing Drip Irrigation and Nitrogen Fertilization for Sustainable Wheat Production in Arid Soils: Water–Nitrogen Use Efficiency" Water 17, no. 18: 2708. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182708
APA StyleAbdelrhman, A. A., Abdel-Fattah, I. M., Mostafa, M. O., Fadl, M. E., Drosos, M., & Scopa, A. (2025). Optimizing Drip Irrigation and Nitrogen Fertilization for Sustainable Wheat Production in Arid Soils: Water–Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Water, 17(18), 2708. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182708










