Sustainable Greywater Treatment in Jordan: The Role of Constructed Wetlands as Nature-Based Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
- High greywater generation: Frequent ablution generates a steady greywater flow.
- Community engagement potential: As religious and social hubs, mosques are effective platforms for promoting water reuse awareness.
- Institutional backing: Being public facilities managed by the Jordanian government, mosques offer a supportive environment for piloting and scaling NbS-CW systems.
- To establish an alternative water source for mosque irrigation that can serve as a model for other facilities.
- To enhance public awareness and acceptance of treated greywater reuse via NbS-CWs, promoting water conservation as a climate change adaptation measure.
- Physical processes, such as sedimentation and filtration.
- Chemical processes, including precipitation and adsorption.
- Biological processes involving microbial degradation and plant uptake [7].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Onsite Assessment
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Design and Preparation
- Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT)
- The Hydraulic Loading Rate (HLR) is expressed as (m/d)
- Mass Loading Rates (ML) [kg/m2d] represent the amount of mass loaded into the CW daily and can be calculated as
- The Cross-Sectional Organic Loading Rate (CSL) (gBOD5/m2d) is fundamental to avoiding clogging problems during the operation. It is measured as
2.4. Filter Media Selection
2.5. Monitoring
3. Results
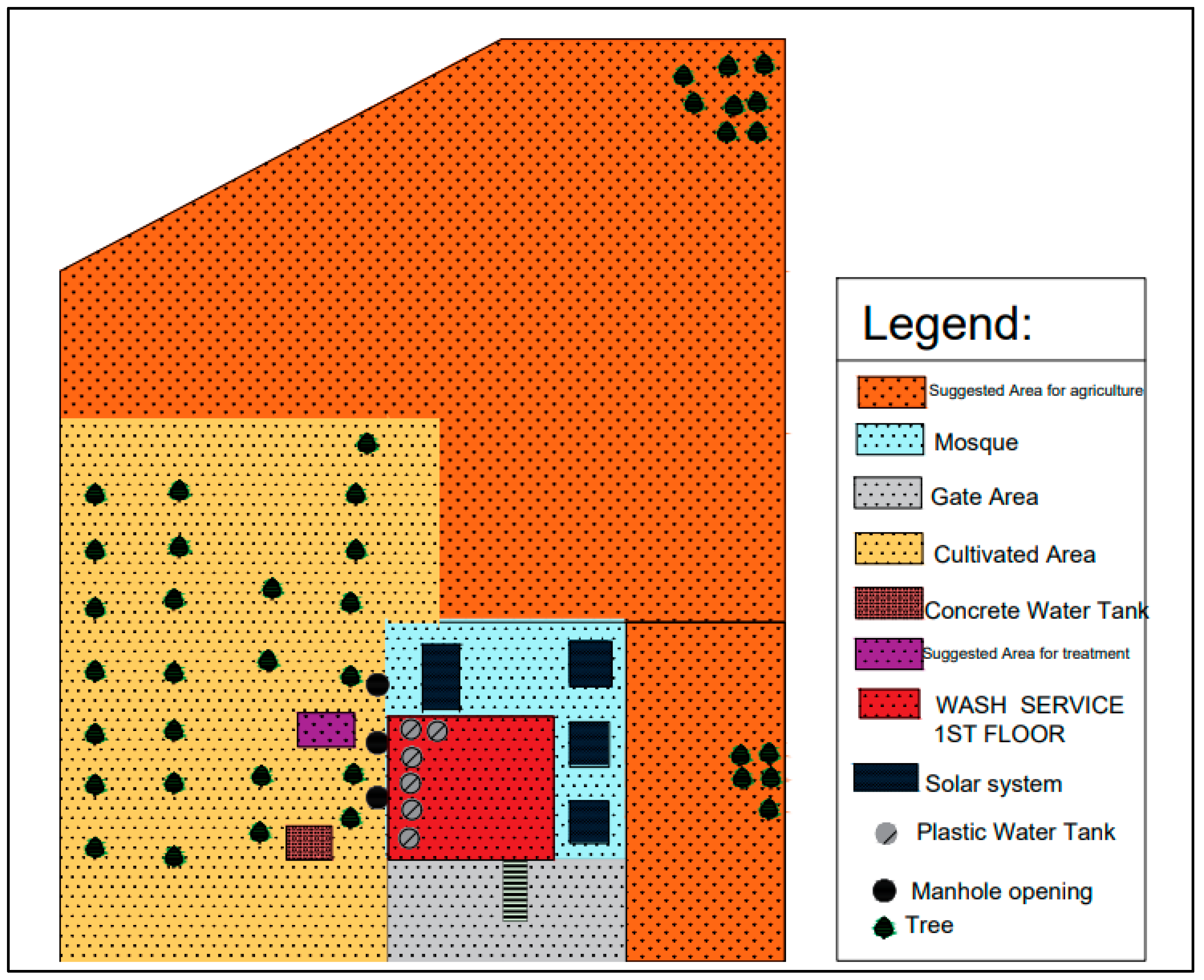
3.1. Assessment and Mosque Selection
3.2. Data Collections
3.3. Detailed Design
3.3.1. Raw Greywater Characterization
3.3.2. Design Targets and Reuse Standards
3.3.3. Flow Assumptions
- The first tank serves as a collection/sedimentation unit for the raw greywater.
- The second tank receives the treated greywater from the HFCW.
- The third tank fully stores the treated greywater, which is connected to the irrigation network.
- The first and last 40 cm of the tank length were filled with coarse volcanic tuff, with a diameter of 4 cm.
- The central 3.2 m were filled with tuff of 2 cm in diameter.
- It dilutes raw greywater with treated greywater.
- It maximizes reuse, enabling the storage and recirculation of treated water when direct reuse is not required.
- It maintains water levels in the CW, supporting optimal performance.
- The first tank has an overflow connection to the sewer system, ensuring smooth discharge by gravity in case of overloading or pump failure.
- The second tank includes an overflow outlet that directs excess treated greywater to irrigate trees, as the quality at this stage is suitable for reuse.
- An additional overflow from the final collection tank on the rooftop is connected to the first collection tank, completing the recirculation loop.
3.4. Monitoring Plan, Laboratory Details
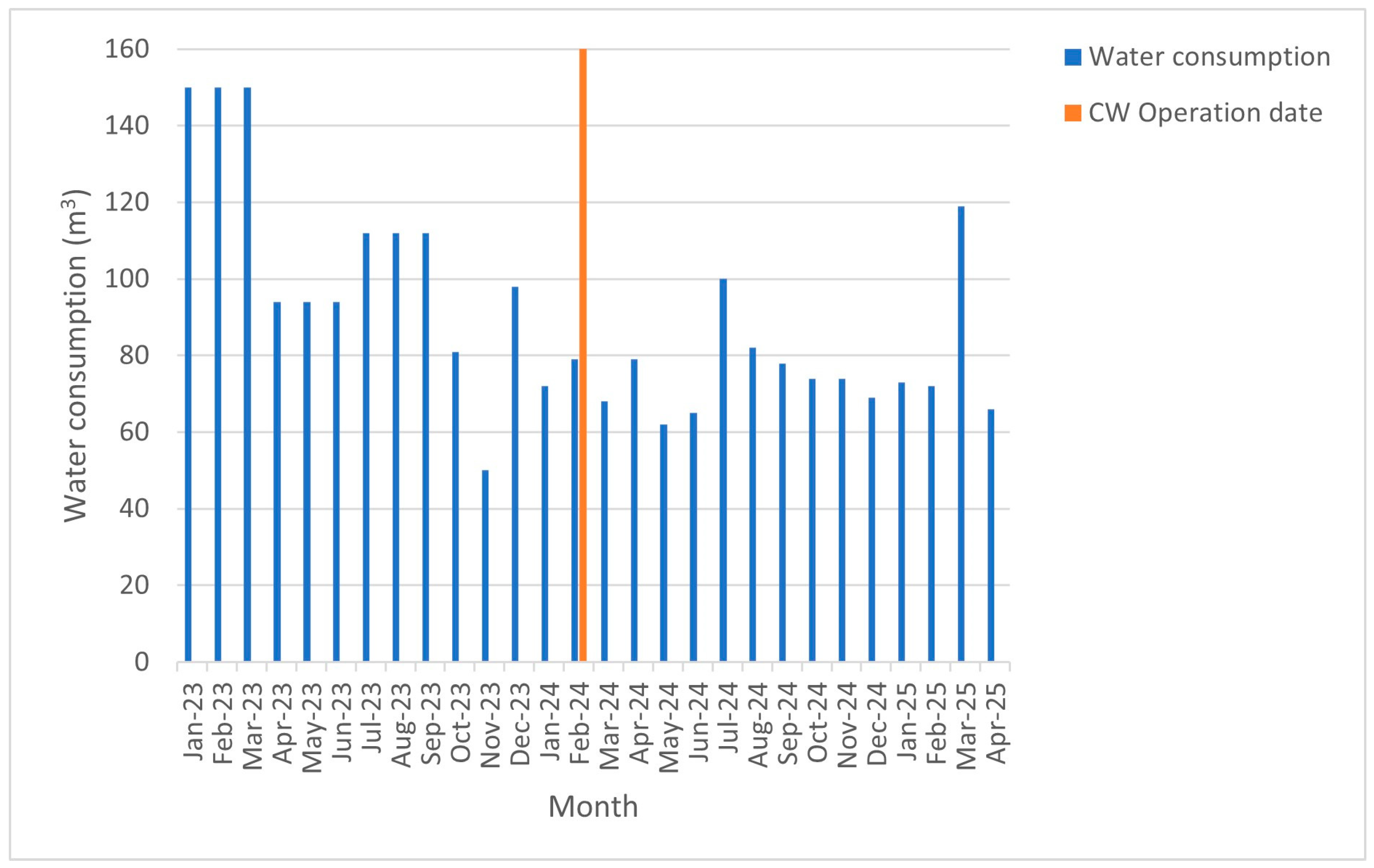
3.5. Water Saving
4. Discussion and Conclusions
- Long-term monitoring to understand seasonal and operational variability;
- Quantification of sludge generation and its management;
- Consideration of advanced treatment (e.g., UV, chlorination) for sensitive reuse applications;
- Design refinement for nitrogen and phosphorus removal.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdelhay, A.; Abunaser, S.G. Modeling and Economic Analysis of Greywater Treatment in Rural Areas in Jordan Using a Novel Vertical-Flow Constructed Wetland. Environ. Manag. 2021, 67, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Arni, S.; Elwaheidi, M.; Salih, A.A.M.; Ghernaout, D.; Matouq, M. Greywater Reuse: An Assessment of the Jordanian Experience in Rural Communities. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 85, 1952–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JS 1776/2013; JSMO Reclaimed Graywater. JSMO: Amman, Jordan, 2013.
- Al-Mashaqbeh, O.A.; Ghrair, A.M.; Megdal, S.B. Grey Water Reuse for Agricultural Purposes in the Jordan Valley: Household Survey Results in Deir Alla. Water 2012, 4, 580–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, A.M.N.; Belotti, M.; Alfarra, A.; Sorlini, S. Multi-Criteria Analysis for Evaluating Constructed Wetland as a Sustainable Sanitation Technology, Jordan Case Study. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qdais, H.A.; Abdulla, F.; Kurbatova, A. Wastewater Reuse in Jordan and Its Potential as an Adaptation Measure to Climate Change. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2019, 14, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boano, F.; Caruso, A.; Costamagna, E.; Ridolfi, L.; Fiore, S.; Demichelis, F.; Galvão, A.; Pisoeiro, J.; Rizzo, A.; Masi, F. A Review of Nature-Based Solutions for Greywater Treatment: Applications, Hydraulic Design, and Environmental Benefits. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Miino, M.C.; Hernan Gomez, F.; Torretta, V.; Rada, E.C.; Sorlini, S. Horizontal Flow Constructed Wetland for Greywater Treatment and Reuse: An Experimental Case. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boopathi, N.; Kadarkarai, R. A Laboratory-Scale Study of Residential Greywater Treatment with Sugarcane in a Constructed Wetland. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 61178–61186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qomariyah, S.; Utomo, B.; Wahyudi, A.H. Constructed Wetlands with Cyperus Alternifolius as a Sustainable Solution for Household Greywater Treatment. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1065, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachicha, R.; Fersi, M.; Jedidi, N.; Mechichi, T.; Hassen, A.; Hachicha, R. Graywater Treatment with Two Planted Vertical Constructed Wetlands in Series: A Pilot Study. Clean 2022, 50, 2100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, F.; Rizzo, A.; Regelsberger, M. The Role of Constructed Wetlands in a New Circular Economy, Resource Oriented, and Ecosystem Services Paradigm. J Environ. Manag. 2018, 216, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arden, S.; Ma, X. Constructed Wetlands for Greywater Recycle and Reuse: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadlec, R.H.; Wallace, S.D. Treatment Wetlands; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; ISBN 9781566705264. [Google Scholar]
- MWI. Jordan Water Sector, FACTS and Figures; MWI: Amman, Jordan, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Masoud, A.M.N.; Alfarra, A.; Sorlini, S. Constructed Wetlands as a Solution for Sustainable Sanitation: A Comprehensive Review on Integrating Climate Change Resilience and Circular Economy. Water 2022, 14, 3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanakis, A.I. The Role of ConstructedWetlands as Green Infrastructure for Sustainable Urban Water Management. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, L.M.; Frazer-Williams, R.A.D.; Winward, G.; Shirley-Smith, C.; Liu, S.; Memon, F.A.; Jefferson, B. Constructed Wetlands for Grey Water Treatment. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2007, 7, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotro, G.; Langergraber, G.; Molle, P.; Nivala, J.; Puigagut, J.; Stein, O.; von Sperling, M. Biological Wastewater Treatment Series, Volume 7: Treatment Wetlands; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2017; Volume 7, ISBN 9781780408774. [Google Scholar]
- UN-HABITAT UN-HABITAT. Constructed Wetlands Manual. In UN-HABITAT Water for Asian Programme Nepal, Kathmandu; United Nations Human Settlements Programme: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2008; ISBN 9789211319637. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanakis, A.; Akratos, C.S.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. Vertical Flow Constructed Wetlands: Eco-Engineering Systems for Wastewater and Sludge Treatment, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Arias, C.A.; Amin, L.; Ananthatmula, R.; Andrews, L.; Baxpehler, H.; Behrends, L.L.; Bresciani, R.; Brodnik, U.; Buttiglier, G.; Castañares, L.; et al. Nature-Based Solutions for Wastewater Treatment; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, R.B.; Rice, C.E.W.; Eaton, A.D. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water Works Association (AWWA), Water Environment Federation (WEF): Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- MWI. Jordan Water Sector—Facts and Figures; MWI: Amman, Jordan, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zidan, A.R.A.; Hady, M.A.A. Constructed Subsurface Wetlands Case Study and Modeling; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; ISBN 9781315365893. [Google Scholar]
- Merriman, L.S.; Hathaway, J.M.; Burchell, M.R.; Hunt, W.F. Adapting the Relaxed Tanks-in-Series Model for Stormwaterwetland Water Quality Performance. Water 2017, 9, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Dwairi, R.A.; Al Saqarat, B.; Shaqour, F.; Sarireh, M. Characterization of Jordanian Volcanic Tuff and Its Potential Use as Lightweight Aggregate. Jordan J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 9, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Mara, D. Domestic Wastewater Treatment in Developing Countries; Routledge: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- MWI. National Water Strategy 2016–2025; MWI: Amman, Jordan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Environment Programme Nature-Based Solutions for Wastewater Management; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2021.
- Al-Mashaqbeh, O.; Alsalhi, L.; Salaymeh, L.; Dotro, G.; Lyu, T. Treatment of Pharmaceutical Industry Wastewater for Water Reuse in Jordan Using Hybrid Constructed Wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 939, 173634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abunaser, S.G.; Abdelhay, A. Performance of a Novel Vertical Flow Constructed Wetland for Greywater Treatment in Rural Areas in Jordan. Environ. Technol 2020, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammari, T.G.; Al-Zu’bi, Y.; Al-Balawneh, A.; Tahhan, R.; Al-Dabbas, M.; Ta’any, R.A.; Abu-Harb, R. An Evaluation of the Re-Circulated Vertical Flow Bioreactor to Recycle Rural Greywater for Irrigation under Arid Mediterranean Bioclimate. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 70, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Free Water Surface CW | Vegetated Submerged CW |
|---|---|---|
| Organic loading rate (kg BOD/ha day) | 5–110 | 10–200 |
| Nitrogen loading rate, kg N/ha. day (Kg/ha day) | 0.5–60 | 2–80 |
| HRT (d) | 3–10 | 2–7 |
| HLT (cm/d) | 2.5–10 | 2.5–20 |
| Water depth from the surface (cm) | 20–50 | 2–10 |
| L:W | 4:1–6:1 | 2:1 |
| Bed depth (cm) | - | 30–90 |
| Year | Duration | Water Consumption (m3) | Cost (JOD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | First Quarter | 45 | 23.0 |
| Second quarter | 200 | 409.3 | |
| Third quarter | 68 | 53.5 | |
| Fourth quarter | 217 | 462.4 | |
| 2021 | First Quarter | 108 | 141.7 |
| Second quarter | 97 | 113.6 | |
| Third quarter | 326 | 791.6 | |
| Fourth quarter | 99 | 118.7 | |
| 2022 | First Quarter | 147 | 251.0 |
| Year | Duration | Water Consumption (m3) | Cost (JOD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | First Quarter | - | - |
| Second quarter | 165 | 305.4 | |
| Third quarter | 155 | 275.2 | |
| Fourth quarter | - | - | |
| 2022 | First Quarter | 122 | 177.4 |
| Second quarter | 178 | 344.6 | |
| Third quarter | 173 | 329.5 | |
| Fourth quarter | 235 | 515.8 | |
| 2023 | First Quarter | 235 | 515.8 |
| Second quarter | 282 | 658.7 | |
| Third quarter | 336 | 821.78 | |
| Fourth quarter | 50 | 86.7 |
| Parameter | Unit | Raw Greywater Abdulla Al Azab | Raw Greywater Roqayya Bent Al Rasoul |
|---|---|---|---|
| BOD | mg/L | 100 | 100 |
| COD | mg/L | 170 | 153 |
| TSS | mg/L | 200 | 195 |
| NH4 | mg/L | less than 4.4 | less than 5 |
| NO3− | mg/L | 12.96 | 13 |
| Turbidity | NTU | 15.9 | 16 |
| Temperature | C | 25 | 25 |
| Parameter | Cooked Vegetables, Parks, Playgrounds, and Roadsides Within Cities | Food Crops Intended for Human Consumption, Including Raw Consumption | Toilet Flushing |
|---|---|---|---|
| BOD5 (mg/L) | 60 | 60 | <10 |
| COD (mg/L) | 120 | 120 | <20 |
| TSS (mg/L) | 100 | 100 | <10 |
| pH | 6–9 | 6–9 | 6–9 |
| NO3− (mg/L) | 70 | 70 | 70 |
| TN (mg/L) | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Parameter | K20 (m/y) | Q (m3/day) | T (°C) | Kt (m/y) | Cin (mg/L) | C* (mg/L) | Cout (mg/L) | A (m2) | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BOD | 37 | 1.1 | 25 | 37.0 | 100.0 | 8.8 | 60.0 | 6.3 | 40 |
| TSS | 30 | 1.1 | 25 | 48.3 | 200.0 | 37.1 | 100.0 | 7.9 | 50 |
| HF-CW Tank Size | |
|---|---|
| High (m) (including 0.3 m free board) | 0.8 |
| Width (m) | 2.0 |
| Length (m) | 4.0 |
| Area (m2) | 8.0 |
| Volume (m3) | 6.4 |
| AREA (m2) | Saturated Depth (m) | (porosity) | HRT (d) | HLR (m3/d) | ML—BOD (kg/ha.d) | CSL Rate (gBOD5/m2d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.00 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 1.8 | 0.14 | 13.75 | 137.5 |
| Parameter | 1 August | 2 September | 5 October | 12 November | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw | Treated | Efficiency | Raw | Treated | Efficiency | Raw | Treated | Efficiency | Raw | Treated | Efficiency | |
| BOD5 (mg/L) | 100 | 30 | 70% | 57 | 4 | 93% | 91 | 9 | 90% | 84 | 10.1 | 88% |
| COD (mg/L) | 146 | 17 | 88% | 160 | 12 | 93% | 139 | 11.3 | 92% | |||
| TSS (mg/L) | 200 | 6 | 97% | 183 | 12 | 93% | 156 | 5 | 97% | 138.7 | 0 | 100% |
| pH | 8 | 7.3 | 8.3 | 7.1 | 7.8 | 7.2 | 7.6 | |||||
| NO3− (mg/L) | 13 | 12.28 | 6% | 36 | 24 | 33% | 31 | 23 | 26% | 39 | 27 | 31% |
| TN (mg/L) | 39 | 30 | 23% | 36 | 26 | 28% | 41 | 29 | 29% | |||
| Turbidity NTU | 16 | 7 | 56% | 57 | 3 | 95% | 16 | 0 | 100% | 17 | 0 | 100% |
| E. coli (MPN/100 mL) | <1 | 763 | 213 | 72% | 661 | 190 | 71% | 310 | 146 | 53% | ||
| Helminth eggs (egg/L) | NA | NA | - | NA | NA | NA | NA | |||||
| FOG (mg/L) | NA | NA | - | NA | NA | NA | NA | |||||
| Parameter | Treated Greywater | Food Crops Intended for Human Consumption, Including Raw Consumption | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 August | 2 September | 5 October | 12 November | ||
| BOD5 (mg/L) | 30 | 4 | 9 | 10.1 | 60 |
| COD (mg/L) | 17 | 12 | 11.3 | 120 | |
| TSS (mg/L) | 6 | 12 | 5 | 0 | 100 |
| pH | 8 | 8.3 | 7.8 | 7.6 | 6–9 |
| NO3− (mg/L) | 12.28 | 24 | 23 | 27 | 70 |
| TN (mg/L) | 30 | 26 | 29 | 50 | |
| Turbidity NTU | 7 | 3 | 0 | 0 | undefined |
| E. coli (CFU/100 mL) | <1 | 213 | 190 | 146 | 1000 |
| Helminth eggs (egg/L) | NA | NA | NA | <1 | |
| Fat, Oil, & Grease (FOG) (mg/L) | NA | NA | NA | 8 | |
| Parameter | 1 March 2024 | 2 July 2024 | 5 October 2024 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw | Treated | Efficiency | Raw | Treated | Efficiency | Raw | Treated | Efficiency | |
| BOD5 (mg/L) | 397 | 20 | 95% | 458 | 16 | 97% | 186 | 16 | 91% |
| COD (mg/L) | 496 | 43 | 91% | 610 | 24 | 96% | 243 | 22 | 91% |
| TSS (mg/L) | 23 | 0 | 100% | 64 | 18 | 72% | 13 | 0 | 100% |
| pH | 7.22 | 8 | 7.31 | 7.39 | 6.9 | 7.7 | |||
| NO3− (mg/L) | |||||||||
| TN (mg/L) | |||||||||
| Turbidity NTU | 12 | 0 | 100% | 14 | 0 | 100% | 13 | 0 | 100% |
| E. coli (MPN/100 mL) | 2310 | 163 | 93% | ||||||
| Helminth eggs (egg/L) | NA | NA | - | NA | NA | ||||
| FOG (mg/L) | NA | NA | - | NA | NA | ||||
| Parameter | 1 March | 2 July | 5 October | Food Crops Intended for Human Consumption, Including Raw Consumption |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BOD5 (mg/L) | 20 | 16 | 16 | 60 |
| COD (mg/L) | 43 | 24 | 22 | 120 |
| TSS (mg/L) | 0 | 18 | 0 | 100 |
| pH | 8 | 7.39 | 7.7 | 6–9 |
| NO3− (mg/L) | 70 | |||
| TN (mg/L) | 50 | |||
| Turbidity NTU | 0 | 0 | 0 | undefined |
| E. coli (CFU/100 mL) | 163 | 1000 | ||
| Helminth eggs (egg/L) | NA | NA | <1 | |
| Fat, Oil, & Grease (FOG) (mg/L) | NA | NA | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masoud, A.M.N.; Alfarra, A.; Al-Shurafat, A.W.; Sorlini, S. Sustainable Greywater Treatment in Jordan: The Role of Constructed Wetlands as Nature-Based Solutions. Water 2025, 17, 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162497
Masoud AMN, Alfarra A, Al-Shurafat AW, Sorlini S. Sustainable Greywater Treatment in Jordan: The Role of Constructed Wetlands as Nature-Based Solutions. Water. 2025; 17(16):2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162497
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasoud, Ahmed M. N., Amani Alfarra, Alham W. Al-Shurafat, and Sabrina Sorlini. 2025. "Sustainable Greywater Treatment in Jordan: The Role of Constructed Wetlands as Nature-Based Solutions" Water 17, no. 16: 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162497
APA StyleMasoud, A. M. N., Alfarra, A., Al-Shurafat, A. W., & Sorlini, S. (2025). Sustainable Greywater Treatment in Jordan: The Role of Constructed Wetlands as Nature-Based Solutions. Water, 17(16), 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162497








