Assessment of the Surface Water Quality of Ibrahim River (Lebanon): A Spatio-Temporal Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
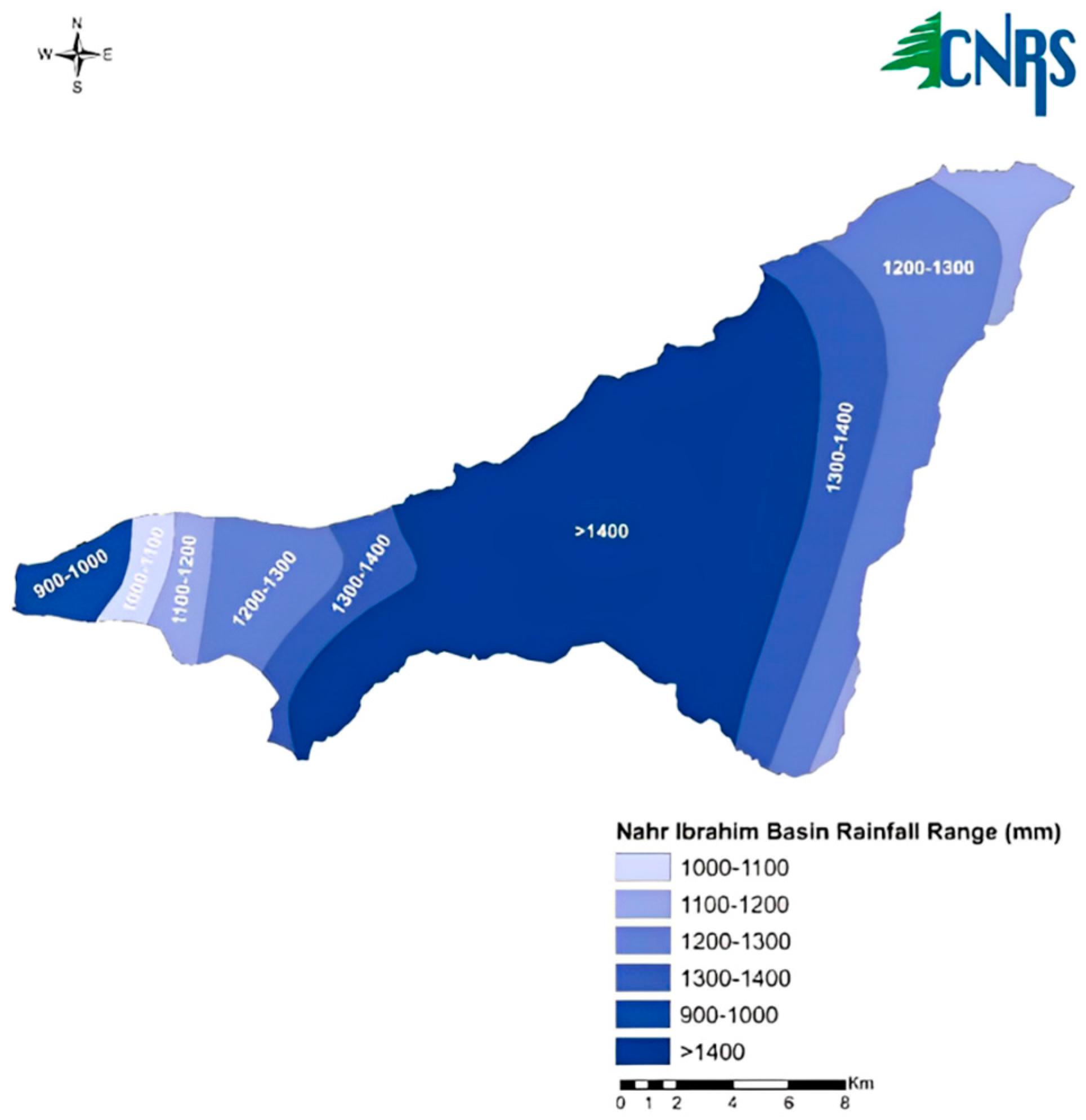
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Pretreatment
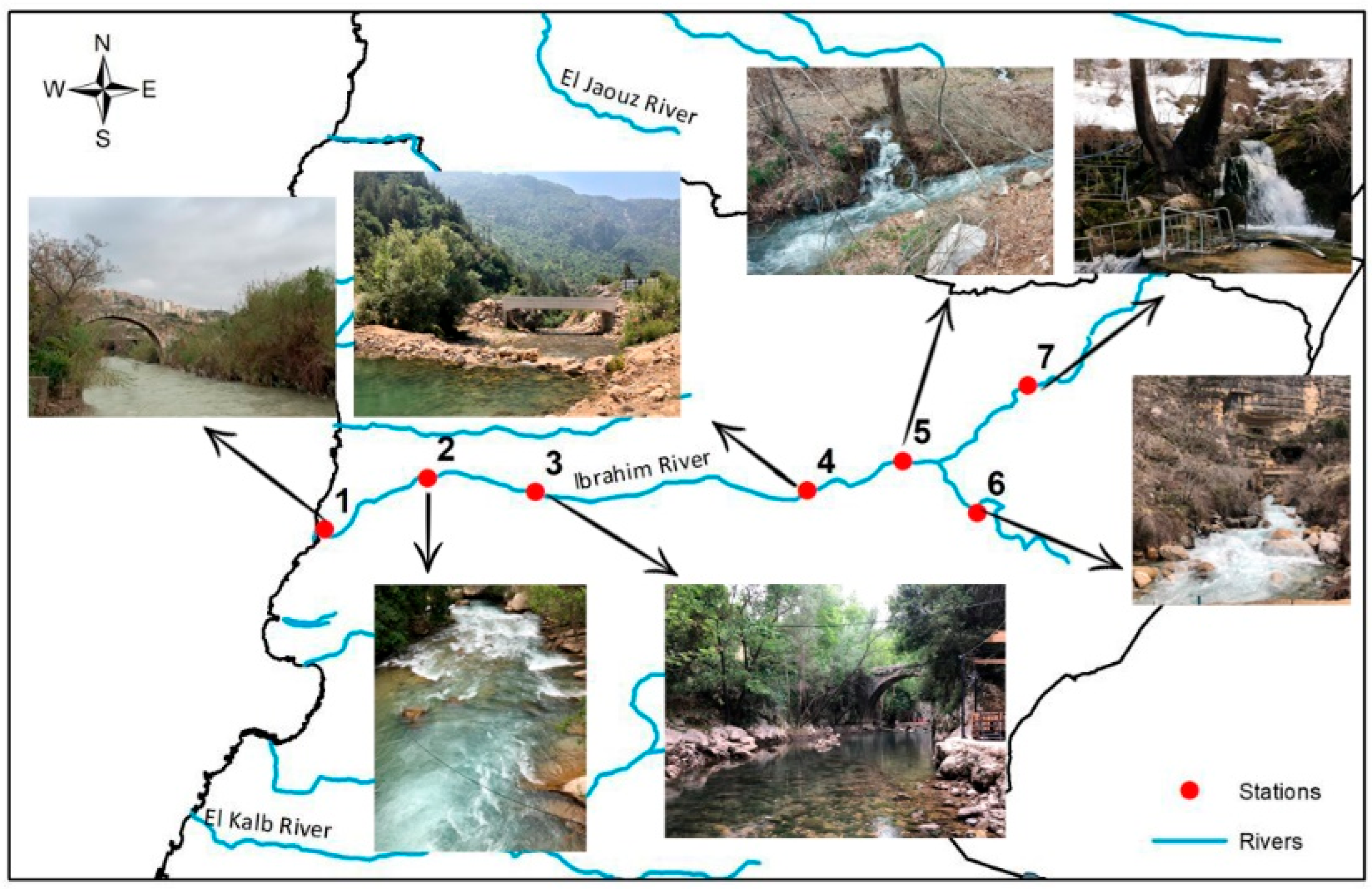
2.2.1. Characteristics of the Stations
2.2.2. Initial Processing
2.3. Physicochemical Analysis
2.4. Microbiological Analysis
2.5. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
2.6. Water Quality Index (WQI)
3. Results and Discussion
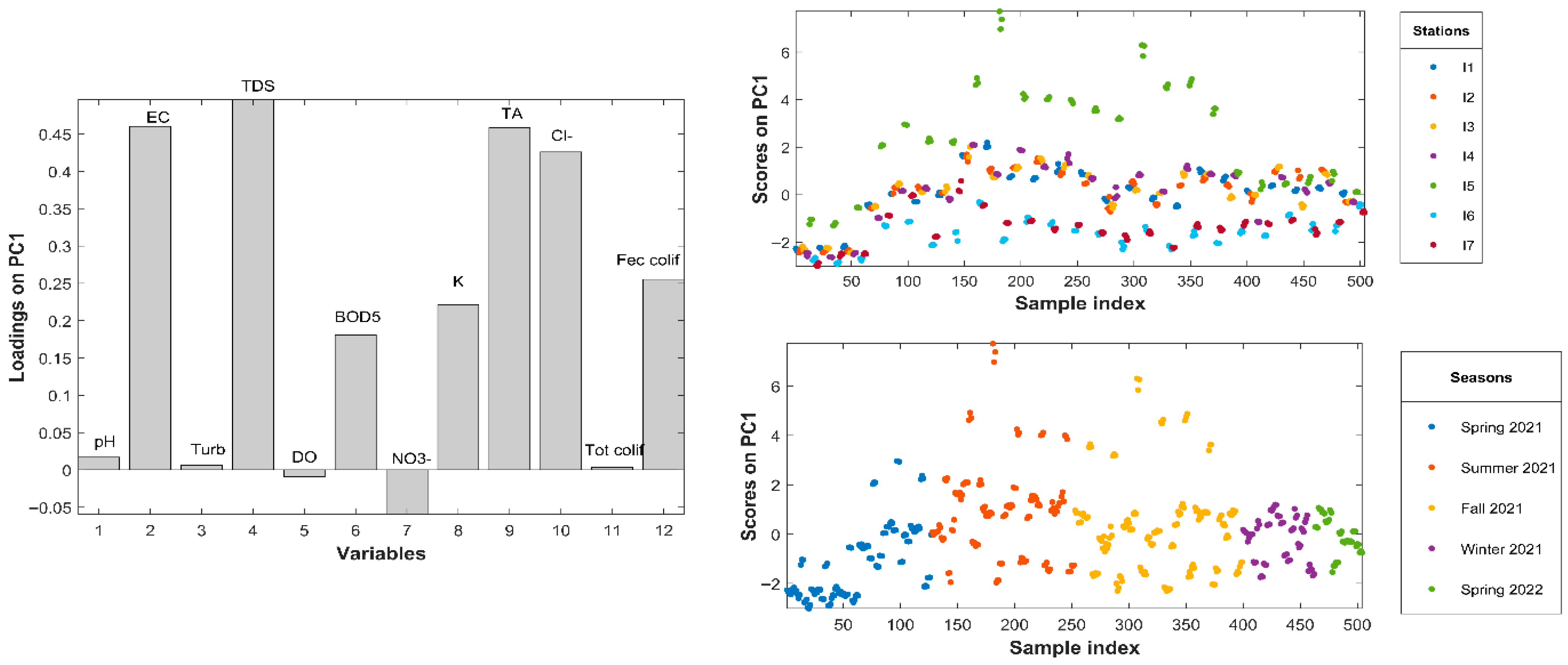
3.1. Spatial Variation
3.2. Temporal Variation
3.3. Water Quality Index
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Liermann, C.R.; et al. Global Threats to Human Water Security and River Biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, S.; Sharma, B.; Singh, P.; Dobhal, R. Water Quality Assessment in Terms of Water Quality Index. Am. J. Water Resour. 2013, 1, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şener, Ş.; Şener, E.; Davraz, A. Evaluation of Water Quality Using Water Quality Index (WQI) Method and GIS in Aksu River (SW-Turkey). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, D.W.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapra, S.C.; Hecky, R.E.; Orihel, D.M. Reducing Phosphorus to Curb Lake Eutrophication Is a Success. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8923–8929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidiac, S.; El Najjar, P.; Ouaini, N.; El Rayess, Y.; El Azzi, D. A Comprehensive Review of Water Quality Indices (WQIs): History, Models, Attempts and Perspectives. Rev. Env. Sci Biotechnol. 2023, 22, 349–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Najjar, P.; Kassouf, A.; Probst, A.; Probst, J.-L.; Ouaini, N.; Daou, C.; El Azzi, D. High-Frequency Monitoring of Surface Water Quality at the Outlet of the Ibrahim River (Lebanon): A Multivariate Assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, A.; Ebeid, M.; Soliman, A.; Halim, A.A.; Ali, A.E.; Fahmy, M. Evaluation of the Water Quality and the Eutrophication Risk in Mediterranean Sea Area: A Case Study of the Port Said Harbour, Egypt. Environ. Chall. 2022, 7, 100484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, M.; Wang, Z.; Liang, X.; Huang, T.; Huang, H. Analyses on the Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Water Quality in a Seagoing River Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques: A Case Study in the Duliujian River, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, D.; Wu, H.; Lin, A.; He, L. Using Principal Components Analysis and IDW Interpolation to Determine Spatial and Temporal Changes of Surface Water Quality of Xin’anjiang River in Huangshan, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, A. Groundwater Model of the Nahr Ibrahim Valley, Lebanon. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; p. 58.
- Assaker, A. Hydrologie et Biogéochimie Du Bassin Versant Du Fleuve Ibrahim: Un Observatoire Du Fonctionnement de La Zone Critique Au Liban. Diploma Thesis, Institut National Polytechnique de Toulouse (INP Toulouse), Toulouse, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Saab, B.H.; Nassif, N.; Samrani, A.G.E.; Daoud, R.; Medawar, S.; Ouaïni, N. Suivi de la qualité bactériologique des eaux de surface (rivière Nahr Ibrahim, Liban). Rev. Des Sci. De L’eau 2007, 20, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daou, C.; Salloum, M.; Legube, B.; Kassouf, A.; Ouaini, N. Characterization of Spatial and Temporal Patterns in Surface Water Quality: A Case Study of Four Major Lebanese Rivers. Env. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Amil, R.; Oudwane, J. Les Ressources En Eau et En Matières Minérales Du Bassin Versant Du Nahr Ibrahim. In Mémoire de Fin D’études En Maîtrise de Biologie; Faculté des Sciences II, Université Libanaise: Fanar, Liban, 2000; p. 42. [Google Scholar]
- Daou, C.; Salloum, M.; Mouneimne, A.H.; Legube, B. Multidimensionnal Analysis of Two Lebanese Surface Water Quality: Ibrahim And El-Kalb Rivers. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2013, 9, 2777–2787. [Google Scholar]
- Korfali, S.I.; Davies, B.E. Seasonal Variations of Trace Metal Chemical Forms in Bed Sediments of a Karstic River in Lebanon: Implications for Self-Purification. Env. Geochem. Health 2005, 27, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodier, J.; Legube, B.; Merlet, N.; Brunet, R. L’analyse de: Eaux Naturelles, Eaux Résiduaires, Eau de Mer, 9th ed.; Environnement; Dunod: Paris, France, 2009; ISBN 978-2-10-054179-9. [Google Scholar]
- Hébert, S.; Légaré, L. Suivi de la Qualité de L’eau des Rivières et Petits Cours d’eau, Québec, Direction du Suivi de L’état de L’environnement; Envirodoq no ENV-2001-0141; Ministère de L’environnement: Paris, France, 2000; Available online: https://www.environnement.gouv.qc.ca/eau/eco_aqua/rivieres/GuidecorrDernier.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- NL ISO 9308-1:2012; Water Quality—Enumeration of Escherichia coli and Coliform Bacteria—Part 1: Membrane Filtration Method for Waters with Low Bacterial Background Flora. NEN–Netherlands Standardization Institute: Delft, The Netherlands, 2012.
- ISO 7899-2:2000(E); Water Quality—Detection and Enumeration of Intestinal Enterococci—Part 2: Membrane Filtration Method. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2000.
- Braga, F.H.R.; Dutra, M.L.S.; Lima, N.S.; Silva, G.M.; Miranda, R.C.M.; Firmo, W.C.A.; Moura, A.R.L.; Monteiro, A.S.; Silva, L.C.N.; Silva, D.F.; et al. Study of the Influence of Physicochemical Parameters on the Water Quality Index (WQI) in the Maranhão Amazon, Brazil. Water 2022, 14, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhong, M.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Huang, H. The Water Quality Evaluation in Balihe Lake Based on Principal Component Analysis. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2019, 07, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Esbensen, K.; Geladi, P. Principal Component Analysis (PCA): Concept, Geometrical Intrepretation, Mathematical Background, Algorithms, History. In Comprehensive Chemometrics; Brown, S., Taulor, R., Walczak, R., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2009; Volume 2, pp. 211–226. ISBN 978-0-444-52701-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Mora-Orozco, C.; Flores-Lopez, H.; Rubio-Arias, H.; Chavez-Duran, A.; Ochoa-Rivero, J. Developing a Water Quality Index (WQI) for an Irrigation Dam. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannel, P.R.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kanel, S.R.; Khan, S.P. Application of Water Quality Indices and Dissolved Oxygen as Indicators for River Water Classification and Urban Impact Assessment. Env. Monit. Assess. 2007, 132, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, S.F.; Wunderlin, D.A. Use of Water Quality Indices to Verify the Impact of Córdoba City (Argentina) on Suquía River. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2915–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saalidong, B.M.; Aram, S.A.; Otu, S.; Lartey, P.O. Examining the Dynamics of the Relationship between Water pH and Other Water Quality Parameters in Ground and Surface Water Systems. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmanian, N.; Ali, S.H.B.; Homayoonfard, M.; Ali, N.J.; Rehan, M.; Sadef, Y.; Nizami, A.S. Analysis of Physiochemical Parameters to Evaluate the Drinking Water Quality in the State of Perak, Malaysia. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 716125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emenike, C.P.; Tenebe, I.T.; Jarvis, P. Fluoride Contamination in Groundwater Sources in Southwestern Nigeria: Assessment Using Multivariate Statistical Approach and Human Health Risk. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 156, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kothari, V.; Vij, S.; Sharma, S.; Gupta, N. Correlation of Various Water Quality Parameters and Water Quality Index of Districts of Uttarakhand. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2021, 9, 100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusydi, A.F. Correlation between Conductivity and Total Dissolved Solid in Various Type of Water: A Review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 118, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, M.S.; Hamid, A.; Bhat, S.U.; Rashid, I.; Kuniyal, J.C. Impact Evaluation of the Run-of-River Hydropower Projects on the Water Quality Dynamics of the Sindh River in the Northwestern Himalayas. Env. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanoranga; Khalid, S. An Assessment of Groundwater Quality for Irrigation and Drinking Purposes around Brick Kilns in Three Districts of Balochistan Province, Pakistan, through Water Quality Index and Multivariate Statistical Approaches. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 197, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, R.; Siddiqui, S. Application of Water Quality Index and Multivariate Statistical Techniques for Assessment of Water Quality around Yamuna River in Agra Region, Uttar Pradesh, India. Water Supply 2022, 22, 3399–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoderao, S.B.; Meshram, S.G.; Meshram, C. Development and Evaluation of a Water Quality Index for Groundwater Quality Assessment in Parts of Jabalpur District, Madhya Pradesh, India. Water Supply 2022, 22, 6002–6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, J. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Assessment of Water Quality in the Al-Saad Lake, Abha Saudi Arabia. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2869–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Maniar, K.; Pillai, A.; Siddiqui, S.; Bambhrolia, M.; Shah, M.; Panchal, J. Geothermal Water in Bakreshwar-Tantoli Region in West Bengal, India: Implications on Water Quality for Irrigation and Drinking Purposes. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 18, 100773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Bojjagani, S.; Maurya, A.; Kisku, G.C. Spatial Distribution of Physicochemical-Bacteriological Parametric Quality and Water Quality Index of Gomti River, India. Env. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.; Ullah, I. Spatial and Seasonal Variation of Water Quality Indices in Gomal Zam Dam and Its Tributaries of South Waziristan District, Pakistan. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 29141–29151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghildyal, D. Statistical Analysis of Coliforms and Bod Levels in Hindon River at Meerut: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Lakes Rivers 2018, 11, 13–28. [Google Scholar]
- Maity, S.; Maiti, R.; Senapati, T. Evaluation of Spatio-Temporal Variation of Water Quality and Source Identification of Conducive Parameters in Damodar River, India. Env. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Azzi, D.; Probst, J.L.; Teisserenc, R.; Merlina, G.; Baqué, D.; Julien, F.; Payre-Suc, V.; Guiresse, M. Trace Element and Pesticide Dynamics During a Flood Event in the Save Agricultural Watershed: Soil-River Transfer Pathways and Controlling Factors. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2016, 227, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Yu, Y.; Dong, M.; Li, Y. Temporal Trends and Source Apportionment of Water Pollution in Honghu Lake, China. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 60130–60144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Ishak, M.I.S.; Ahmad, M.I.; Umar, K.; Md Yusuff, M.S.; Anees, M.T.; Qadir, A.; Ali Almanasir, Y.K. Modification of the Water Quality Index (WQI) Process for Simple Calculation Using the Multi-Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM) Method: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedim Godoy, R.F.; Crisiogiovanni, E.L.; Trevisan, E.; Dias Radomski, F.A. Spatial and Temporal Variation of Water Quality in a Watershed in Center-West Paraná, Brazil. Water Supply 2021, 21, 1718–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ye, C. Evaluation and Prediction of Water Quality in the Dammed Estuaries and Rivers of Taihu Lake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 12832–12844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, E. A Holistic Framework of Water Quality Evaluation Using Water Quality Index (WQI) in the Yihe River (China). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 80937–80951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Niu, C.; Wang, H. Spatiotemporal Patterns in River Water Quality and Pollution Source Apportionment in the Arid Beichuan River Basin of Northwestern China Using Positive Matrix Factorization Receptor Modeling Techniques. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calmuc, M.; Calmuc, V.; Arseni, M.; Topa, C.; Timofti, M.; Georgescu, L.P.; Iticescu, C. A Comparative Approach to a Series of Physico-Chemical Quality Indices Used in Assessing Water Quality in the Lower Danube. Water 2020, 12, 3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.M.; Marcionilio, S.M.L.D.O.; Morais, W.A.; Alves, W.D.S.; Oliveira, L.D.; Teixeira, M.B.; Oliveira, D.M.D.S. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Water Quality Indicators in a Watershed in Brazilian Cerrado. Water Supply 2023, 23, 1161–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| WQI | General Information | Parameters | Weights | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSFWQI | Developed by the National Sanitation Foundation in the U.S.; widely used globally | 9 core parameters | Fixed weights | Summarized in a single index value in an objective, rapid, and reproducible manner | General water quality, therefore, does not represent specific use of water; loss of data during handling; lack of dealing with uncertainty and subjectivity present in complex environmental issues |
| CCMEWQI | Created by the Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment; guideline-based | User-defined parameters | No weights | Easy to understand and calculate; tolerance to missing data; adaptability to different legal requirements and different water uses | Loss of information and interaction among variables; same importance given to all parameters |
| OWQI | Developed by Oregon Department of Environmental Quality; consumption-oriented | Specific to local use | Equal weights | Simple; availability of required quality parameters; formula is sensitive to changing conditions and to significant impacts on water quality | Exclude stressors; data is representative of sampling site |
| Sampling Stations | Latitude | Longitude | Elevation (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 34°03′48.5″ N | 35°38′42.4″ E | 4 |
| L2 | 34°04′58.0″ N | 35°41′01.5″ E | 111 |
| L3 | 34°04′39.0″ N | 35°43′26.7″ E | 274 |
| L4 | 34°04′41.2″ N | 35°49′33.5″ E | 743 |
| L5 | 34°05′59.9″ N | 35°51′35.1″ E | 1063 |
| L6 | 34°04′05.1″ N | 35°53′33.1″ E | 1213 |
| L7 | 34°06′32.4″ N | 35°54′29.1″ E | 1268 |
| Parameters | Unit | Analytical Method |
|---|---|---|
| pH | - | Hanna Instruments Portable Analog pH Meter HI-8314 AOAC 973.41 |
| Conductivity (EC) | μS/cm | Hanna Instruments Portable EC/TDS/Temperature Meter HI-99300 NF EN 27888 |
| Turbidity (Turb) | NTU | Turbidimeter TB1 Velp Scientifica NF EN ISO 7027 (March 2007) |
| Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) | mg/L | Hanna Instruments Portable EC/TDS/Temperature Meter HI-99300 AOAC 920.193 |
| Dissolved Oxygen (DO) | mg/L | Oxygen meter Lutron DO5510 NF EN 25814 (March 1993) |
| Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD5) | mg/L | Lovibond BD 600 OxiDirect NF EN 1899-2 (May 1998) |
| Dissolved Nitrate (NO3−) | mg/L | Spectrometry Helios Alpha Thermo NF T 90-045 ISO 7890-3:1988 |
| Dissolved Potassium (K+) | mg/L | Flame photometry M410 Sherwood Scientific NF T 90-019 |
| Total Alkalinity (TA) | mg/L CaCO3 | Titrimetry NF T 90-036 ISO 9963-1:1994 |
| Dissolved Chloride (Cl−) | mg/L | Titrimetry NF T 90-014 ISO 9297-1989 |
| Total Coliforms (Tot Colif) | CFU/100 mL | NL ISO 9308-1:2012 and ISO 7899-2:2000(E) |
| Fecal Coliforms (Fec Colif) | CFU/100 mL | NL ISO 9308-1:2012 and ISO 7899-2:2000(E) |
| Stations | pH | EC (μS/cm) | Turb (NTU) | TDS (mg/L) | DO (mg/L) | BOD5 (mg/L) | NO3− (mg/L) | K+ (mg/L) | TA (mg CaCO3/L | Cl− (mg/L) | Tot Colif (CFU/100 mL) | Fec Colif (CFU/100 mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 8.13 ± 0.51 | 270.68 ± 36.69 | 12.83 ± 26.72 | 134.64 ± 17.71 | 13.32 ± 9.60 | 2.48 ± 3.61 | 1.54 ± 084 | 1.26 ± 2.31 | 182.47 ± 31.60 | 8.68 ± 3.23 | 4257.17 ± 2814.20 | 440.69 ± 568.13 |
| L2 | 8.14 ± 0.41 | 280.18 ± 38.21 | 22.68 ± 57.86 | 138.71 ± 18.37 | 12.24 ± 7.95 | 1.98 ± 3.04 | 1.46 ± 0.59 | 1.31 ± 2.45 | 196.92 ± 38.86 | 8.25 ± 3.03 | 6152.42 ± 14,355.76 | 140.94 ± 118.87 |
| L3 | 8.13 ± 0.43 | 282.90 ± 39.97 | 12.67 ± 26.77 | 139.63 ± 17.92 | 12.89 ± 9.69 | 2.27 ± 3.30 | 1.38 ± 0.77 | 1.19 ± 2.34 | 200.13 ± 39.98 | 7.86 ± 2.96 | 4300.52 ± 9238.88 | 117.35 ± 135.24 |
| L4 | 8.13 ± 0.44 | 287.88 ± 42.36 | 7.19 ± 16.15 | 141.00 ± 20.39 | 13.99 ± 10.12 | 2.18 ± 3.17 | 1.57 ± 0.83 | 1.26 ± 2.41 | 202.28 ± 40.86 | 7.33 ± 3.02 | 5498.92 ± 14,404.14 | 127.21 ± 121.99 |
| L5 | 8.06 ± 0.43 | 359.58 ± 66.88 | 1.33 ± 1.19 | 177.10 ± 29.78 | 12.89 ± 8.72 | 1.94 ± 3.29 | 1.53 ± 0.97 | 1.33 ± 2.57 | 269.79 ± 55.91 | 11.2 ± 4.82 | 12,308.40 ± 20,917.54 | 406.13 ± 1029.64 |
| L6 | 8.04 ± 0.45 | 225.72 ± 37.67 | 0.88 ± 1.10 | 107.81 ± 9.47 | 13.43 ± 9.14 | 1.77 ± 2.71 | 1.48 ± 0.67 | 0.47 ± 0.93 | 151.71 ± 23.68 | 5.99 ± 2.70 | 4470.48 ± 10,312.26 | 60.83 ± 134.73 |
| L7 | 8.00 ± 0.41 | 231.03 ± 45.38 | 0.81 ± 0.97 | 109.81 ± 10.08 | 13.24 ± 8.58 | 1.67 ± 2.67 | 1.09 ± 0.74 | 0.62 ± 1.17 | 162.40 ± 28.80 | 6.77 ± 3.78 | 13,911.7 ± 24,083.49 | 1.50 ± 4.40 |
| WHO Standards | 6.5–8.5 | 250 | <5 | <600 | - | - | 10 | - * | 200 | <250 | <10 | 0 |
| Seasons | pH | EC | Turb | TDS | DO | BOD5 | NO3− | K+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring 2021 | 7.84 ± 0.46 | 258.11 ± 76.52 | 4.62 ± 7.05 | 117.48 ± 26.40879 | 7.86 ± 3.23 | 0.55 ± 0.70 | 1.41 ± 0.55 | 0.02 ± 1.39 × 10−17 |
| Summer 2021 | 8.25 ± 0.22 | 267.29 ± 49.97 | 0.64 ± 0.74 | 133.86 ± 2497 | 8.01 ± 3.87 | 6.78 ± 2.61 | 1.11 ± 0.48 | 3.66 ± 2.84 |
| Fall 2021 | 8.00 ± 0.48 | 297.39 ± 61.17 | 5.14 ± 30.56 | 148.59 ± 69.14 | 17.92 ± 9.59 | 0.70 ± 1.26 | 1.17 ± 0.73 | 0.47 ± 1.00 |
| Winter 2021 | 8.37 ± 0.46 | 284.41 ± 38.58 | 3.63 ± 1.79 | 142.27 ± 19.22 | 11.44 ± 4.18 | 0 ± 0 | 2.37 ± 1.03 | 0.02 ± 1.04 × 10−17 |
| Spring 2022 | 8.21 ± 0.08 | 278.57 ± 33.84 | 60.86 ± 72.36 | 138.78 ± 17.14 | 30.21 ± 6.55 | 0 ± 0 | 2.03 ± 0.53 | 0.02 ± 1.04 × 10−17 |
| Parameter | Weight (Pi) |
|---|---|
| pH | 2 |
| EC | 3 |
| Turb | 2 |
| TDS | 2 |
| DO | 4 |
| BOD5 | 3 |
| NO3− | 1 |
| K+ | 2 |
| TA | 3 |
| Cl− | 3 |
| Tot Colif | 3 |
| Fec Colif | 3 |
| Date | WQI per Sampling Campaign | Months | WQI per Month | Stations | WQI per Station | Date | WQI During High Flow | Date | WQI During Low Flow |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 March 2021 | 87.73 ± 3.62 | Mar-21 | 87.73 ± 3.62 | L1 | 80.10 ± 6.37 | 21 March 2021 | 87.73 ± 3.62 | 26 May 2021 | 85.36 ± 3.66 |
| 8 April 2021 | 94.73 ± 2.32 | Apr-21 | 91.56 ± 3.11 | L2 | 82.69 ± 5.24 | 8 April 2021 | 94.73 ± 2.32 | 13 June 2021 | 82.06 ± 3.52 |
| 25 April 2021 | 88.39 ± 3.44 | May-21 | 83.37 ± 3.64 | L3 | 83.16 ± 5.09 | 25 April 2021 | 79.63 ± 3.44 | 27 June 2021 | 75.48 ± 3.26 |
| 9 May 2021 | 81.38 ± 2.35 | Jun-21 | 78.77 ± 4.72 | L4 | 83.90 ± 5.73 | 9 May 2021 | 71.98 ± 2.35 | 12 July 2021 | 71.90 ± 1.91 |
| 26 May 2021 | 85.36 ± 3.66 | Jul-21 | 74.64 ± 5.59 | L5 | 80.62 ± 7.33 | 9 January 2022 | 89.62 ± 2.82 | 25 July 2021 | 77.37 ± 1.91 |
| 13 June 2021 | 82.06 ± 3.52 | Aug-21 | 79.75 ± 4.92 | L6 | 87.30 ± 5.54 | 13 February 2022 | 90.61 ± 1.68 | 4 August 2021 | 78.97 ± 6.68 |
| 27 June 2021 | 75.48 ± 3.26 | Sep-21 | 78.98 ± 3.97 | L7 | 86.90 ± 5.25 | 27 February 2022 | 90.51 ± 1.86 | 28 August 2021 | 80.54 ± 4.86 |
| 12 July 2021 | 71.90 ± 1.91 | Oct-21 | 83.67 ± 3.50 | - | 27 March 2022 | 84.55 ± 5.87 | 11 September 2021 | 76.94 ± 4.17 | |
| 25 July 2021 | 77.37 ± 1.91 | Nov-21 | 84.09 ± 4.57 | - | 3 April 2022 | 85.05 ± 5.71 | 26 September 2021 | 81.01 ± 2.49 | |
| 4 August 2021 | 78.97 ± 6.68 | Dec-21 | 85.49 ± 6.20 | - | - | 10 October 2021 | 84.22 ± 3.63 | ||
| 28 August 2021 | 80.54 ± 4.86 | Jan-22 | 89.62 ± 2.82 | - | - | 24 October 2021 | 83.12 ± 3.37 | ||
| 11 September 2021 | 76.94 ± 4.17 | Feb-22 | 90.56 ± 1.75 | - | - | 7 November 2021 | 83.23 ± 4.19 | ||
| 26 September 2021 | 81.01 ± 2.49 | Mar-22 | 84.55 ± 5.87 | - | - | 21 November 2021 | 84.95 ± 4.86 | ||
| 2 October 2021 | 84.22 ± 3.63 | Apr-22 | 85.05 ± 5.71 | - | - | 5 December 2021 | 86.10 ± 5.12 | ||
| 24 October 2021 | 83.12 ± 3.37 | - | - | - | 19 December 2021 | 84.88 ± 7.20 | |||
| 7 November 2021 | 83.23 ± 4.19 | - | - | - | - | ||||
| 21 November 2021 | 84.95 ± 4.86 | - | - | - | - | ||||
| 5 December 2021 | 86.10 ± 5.12 | - | - | - | - | ||||
| 19 December 2021 | 84.88 ± 7.20 | - | - | - | - | ||||
| 9 January 2022 | 89.62 ± 2.82 | - | - | - | - | ||||
| 13 February 2022 | 90.61 ± 1.68 | - | - | - | - | ||||
| 27 February 2022 | 90.51 ± 1.86 | - | - | - | - | ||||
| 27 March 2022 | 84.55 ± 5.87 | - | - | - | - | ||||
| 3 April 2022 | 85.05 ± 5.71 | - | - | - | - | ||||
| Average | 83.70 ± 4.97 | 84.13 ± 4.28 | 83.53 ± 5.79 | 86.05 ± 6.84 | 81.08 ± 4.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chidiac, S.; El Najjar, P.; Kassouf, A.; Ouaini, N.; El Rayess, Y.; El Azzi, D. Assessment of the Surface Water Quality of Ibrahim River (Lebanon): A Spatio-Temporal Analysis. Water 2025, 17, 2483. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162483
Chidiac S, El Najjar P, Kassouf A, Ouaini N, El Rayess Y, El Azzi D. Assessment of the Surface Water Quality of Ibrahim River (Lebanon): A Spatio-Temporal Analysis. Water. 2025; 17(16):2483. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162483
Chicago/Turabian StyleChidiac, Sandra, Paula El Najjar, Amine Kassouf, Naïm Ouaini, Youssef El Rayess, and Desiree El Azzi. 2025. "Assessment of the Surface Water Quality of Ibrahim River (Lebanon): A Spatio-Temporal Analysis" Water 17, no. 16: 2483. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162483
APA StyleChidiac, S., El Najjar, P., Kassouf, A., Ouaini, N., El Rayess, Y., & El Azzi, D. (2025). Assessment of the Surface Water Quality of Ibrahim River (Lebanon): A Spatio-Temporal Analysis. Water, 17(16), 2483. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162483







