Spatiotemporal Patterns and Atmospheric Drivers of Anomalous Precipitation in the Taihu Basin, Eastern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Datasets
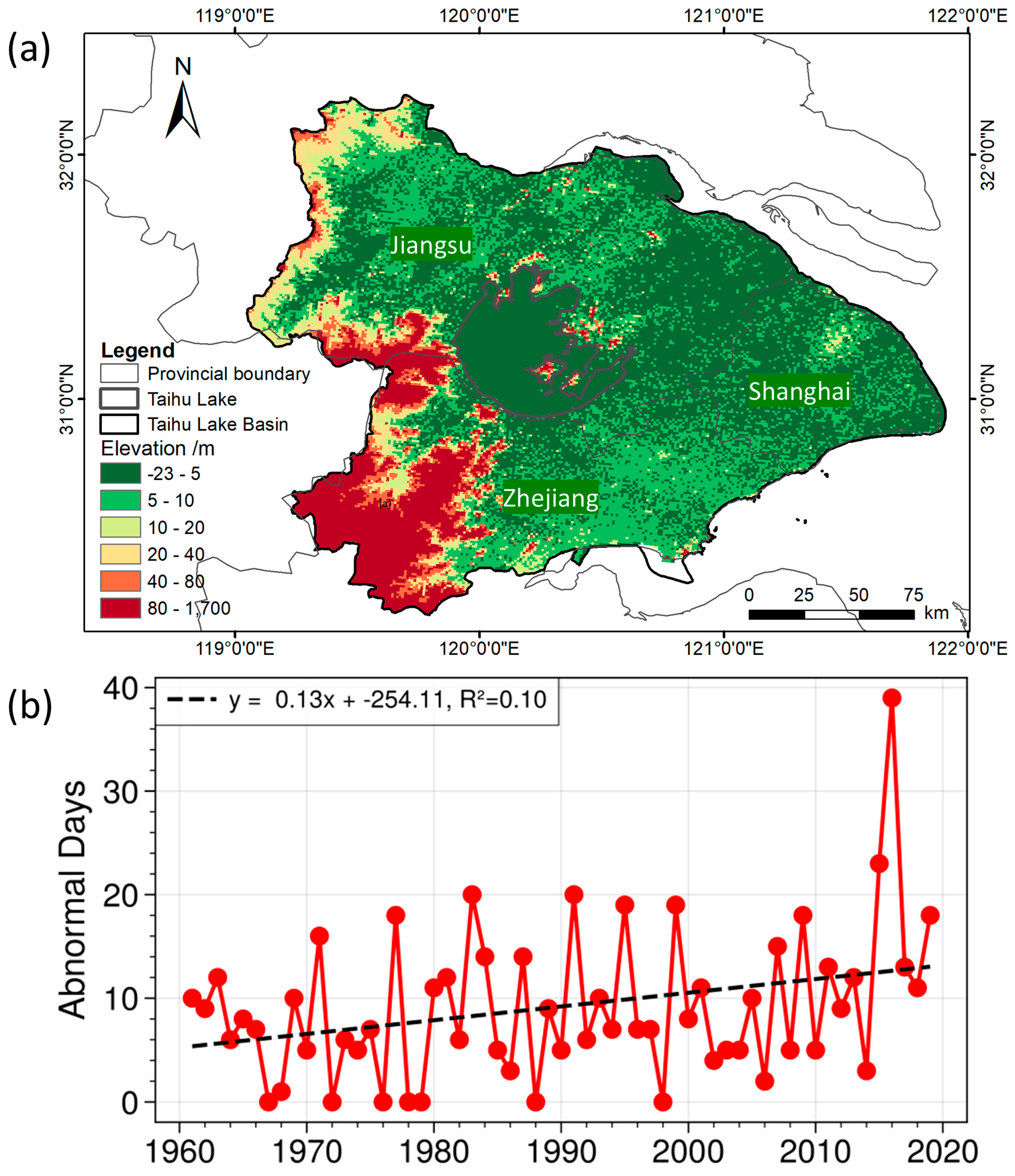
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. Rainfall Dataset
2.2.2. RA5 Reanalysis Dataset
3. Methodology
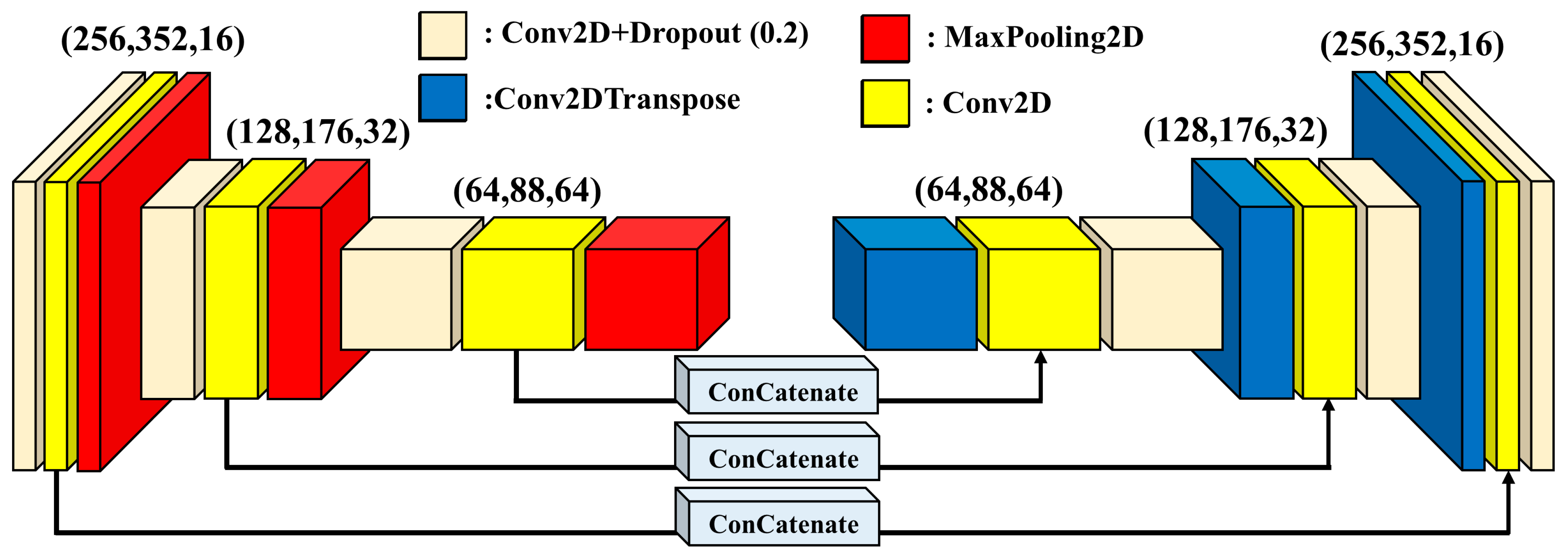
3.1. Autoencoder-Based Identification of Anomalous Precipitation Events
3.2. SOM-Based Clustering of Precipitation Spatial Patterns
3.3. WNPSH and EAJ Circulation Indices
4. Results
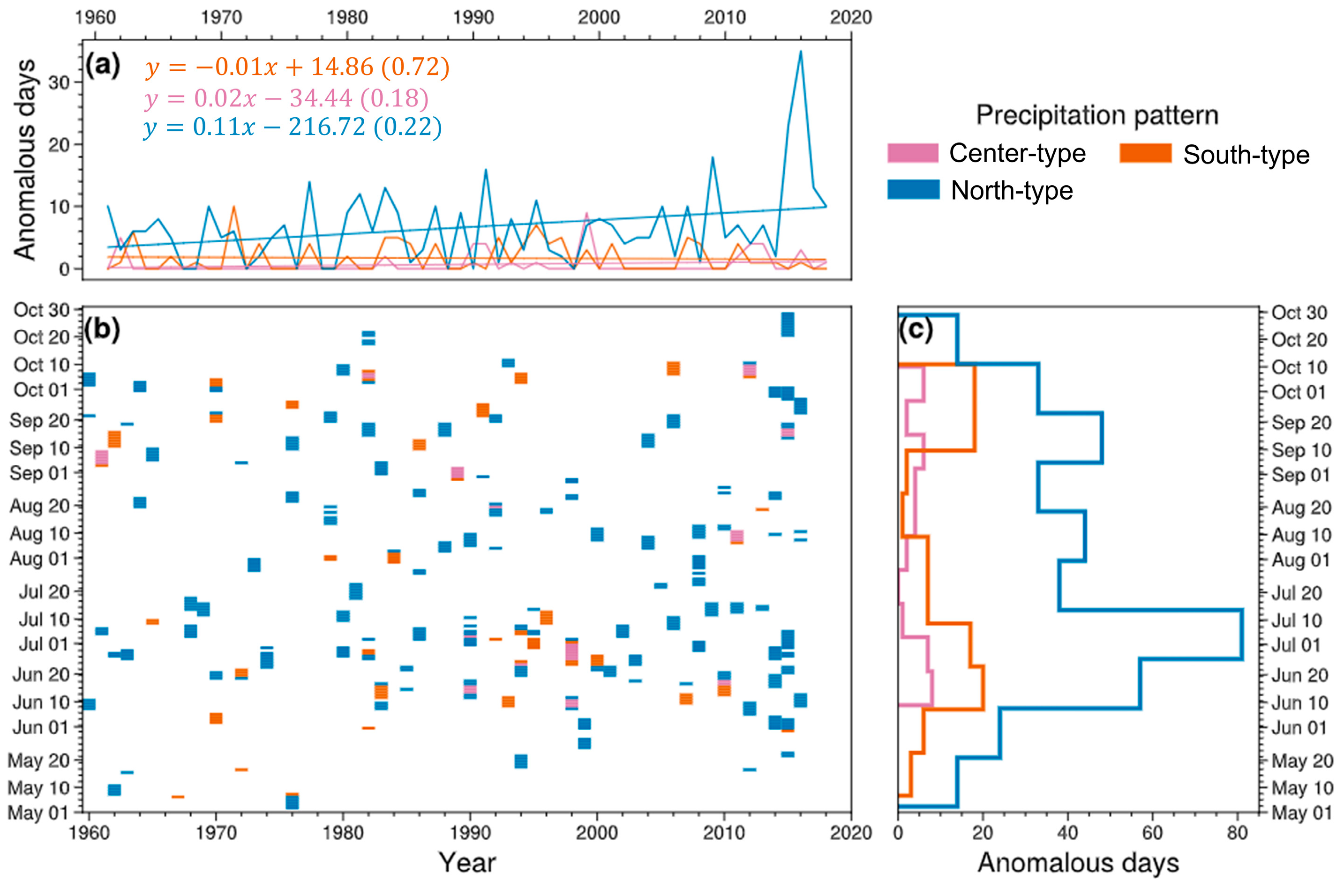
4.1. Classified Anomalous Precipitation Patterns
4.2. Temporal Variability of Anomalous Precipitation Patterns
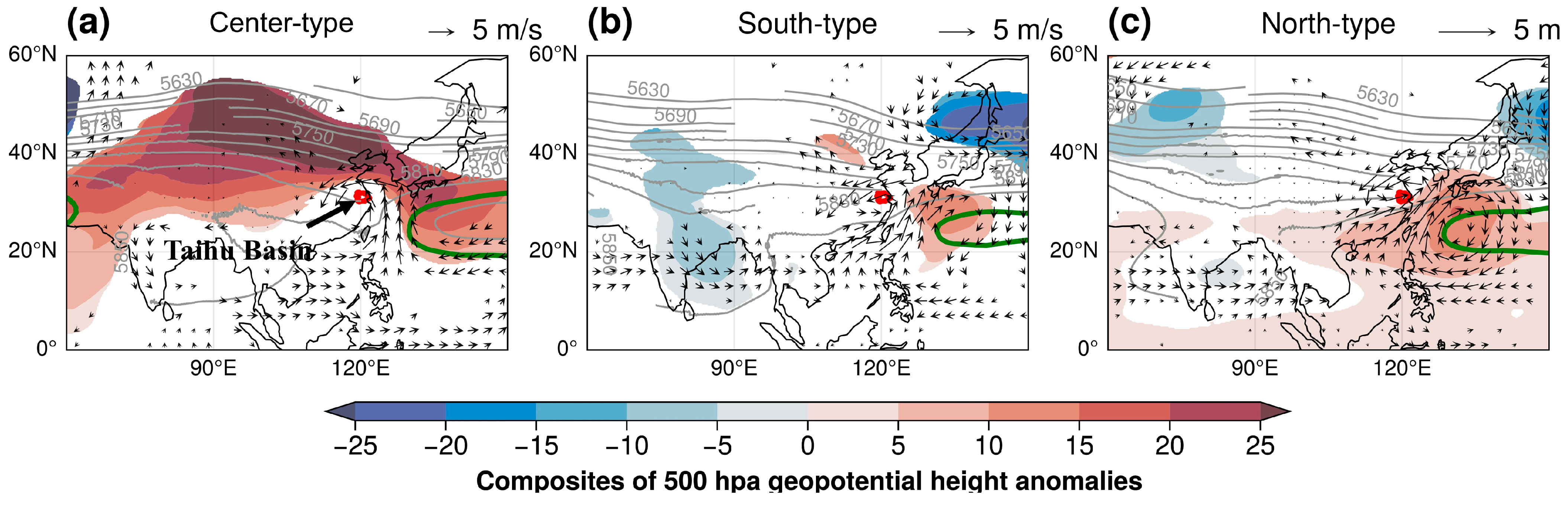
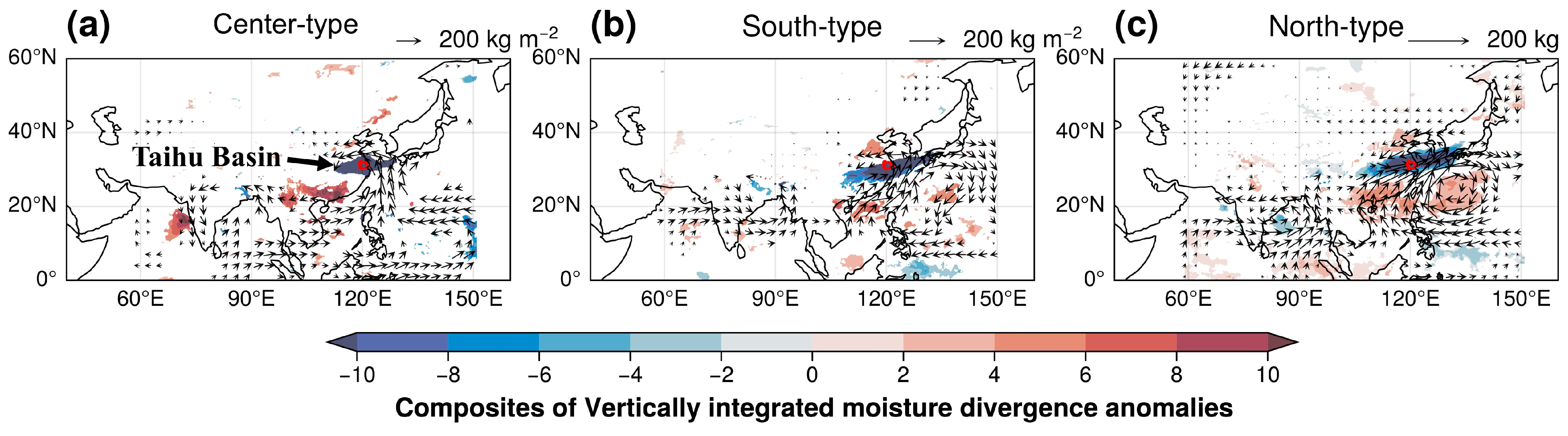
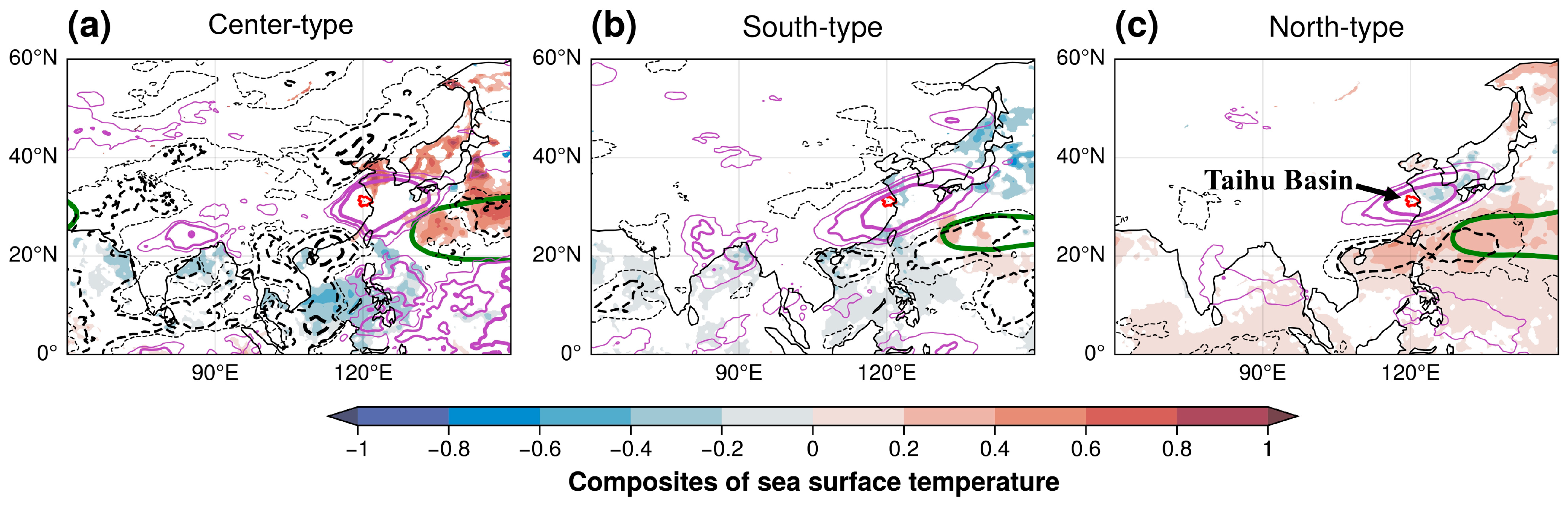
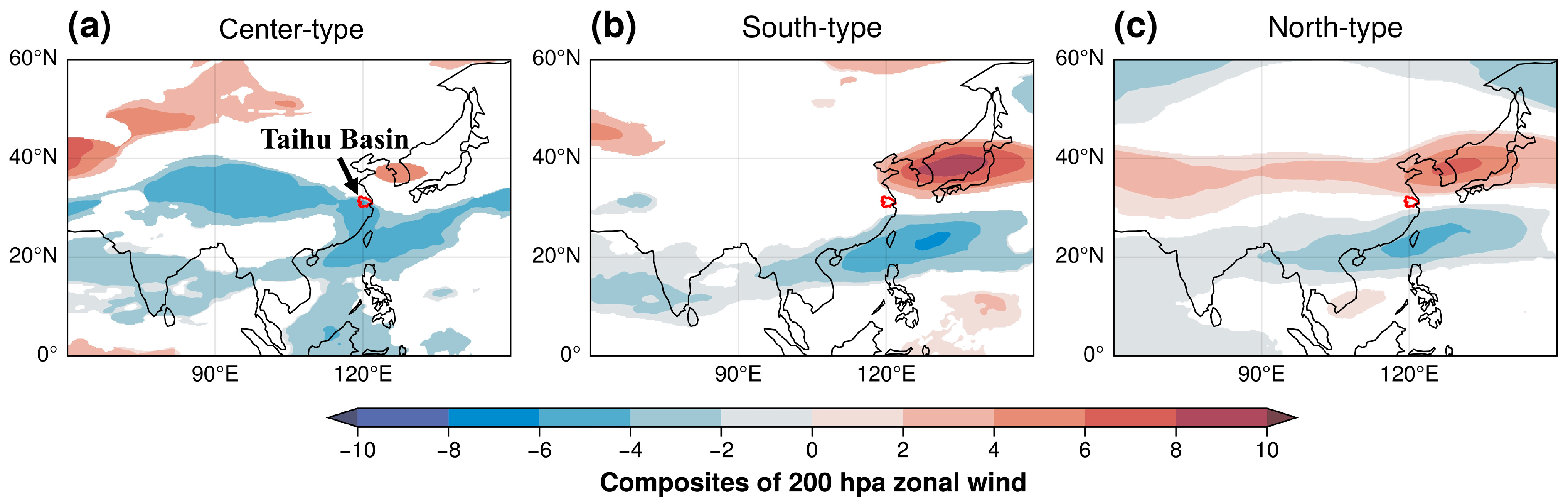
4.3. Underlying Synoptic-Scale Circulation Patterns
5. Discussion and Implication
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murakami, H.; Delworth, T.L.; Cooke, W.F.; Kapnick, S.B.; Hsu, P.-C. Increasing frequency of anomalous precipitation events in Japan detected by a deep learning autoencoder. Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wada, Y.; Wanders, N.; Sheffield, J. Intensification of hydrological drought in California by human water management. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Li, J.; Lee, T.; Tse, W.P.; Chan, F.; Chen, Y.D.; Gu, X. A 131-year evidence of more extreme and higher total amount of hourly precipitation in Hong Kong. Environ. Res. Lett. 2024, 19, 034008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Kinouchi, T.; Nguyen, H.Q. A framework for projecting future intensity-duration-frequency (IDF) curves based on CORDEX Southeast Asia multi-model simulations: An application for two cities in Southern Vietnam. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, T.; Miyoshi, T. Predictability of the July 2018 heavy rain event in Japan associated with Typhoon Prapiroon and southern convective disturbances. Sci. Online Lett. Atmos. SOLA 2021, 17, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athira, K.; Singh, S.; Abebe, A. Rising risk and localized patterns of Indian summer monsoon rainfall extremes. Atmos. Res. 2024, 309, 107554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erpicum, S.; Poppema, D.; Burghardt, L.; Benet, L.; Wüthrich, D.; Klopries, E.-M.; Dewals, B. A dataset of floating debris accumulation at bridges after July 2021 flood in Germany and Belgium. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Xing, A. History must not repeat itself—Urban geological safety assessment is essential. Nat. Hazards 2022, 111, 2141–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ming, Y.; Gao, L. Distribution characteristics of POC and DOC at the Yangtze River Estuary during the 2020 summer flood. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2022, 41, 653–659. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Tao, Q.; Qiu, J.; Pueppke, S.G.; Gao, G.; Ou, W. Integrating water quantity- and quality-related ecosystem services into water scarcity assessment: A multi-scenario analysis in the Taihu Basin of China. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 160, 103101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, K.; Wu, Y.; Gao, C. Detection of flood trends drivers in the Taihu Basin China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 56, 101990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Guo, H. Circulation differences and mechanisms of summer anomalous precipitation events in the Yangtze-Huaihe River Basin. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 38, 656–669. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Zhu, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Li, X. Analysis of rainfall and water level elements of typical floods in the Taihu Basin. J. Hydraul. Waterw. Eng. 2022, 40–49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Wang, T.; Li, F. Moisture transport characteristics of anomalous autumn rainfall in Jinhua, Zhejiang. Sci. Bull. 2023, 39, 13–22. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cai, W.; Campbell, E.P. Statistical Modeling of Extreme Rainfall in Southwest Western Australia. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, J.; Sheffield, J.; Wood, E.F. Changes in drought risk over the contiguous United States (1901–2012): The influence of the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 5897–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Yao, J.; He, Q.; Chen, J. Changes in precipitation amounts and extremes across Xinjiang (northwest China) and their connection to climate indices. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Huang, C.; Tang, Y.; Peng, J. Precipitation Variations in the Flood Seasons of 1910–2019 in Hunan and Its Association With the PDO, AMO, and ENSO. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Guo, S.; Yin, J.; Yang, G.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, D. On the event-based extreme precipitation across China: Time distribution patterns trends return levels. J. Hydrol. 2018, 562, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All You Need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762 (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Luo, W.; Li, Y.; Urtasun, R.; Zemel, R. Understanding the Effective Receptive Field in Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1701.04128. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1701.04128 (accessed on 10 March 2025). [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhong, L.; Sha, P.; Wu, X.; Liu, Z. Analysis of typical rainfall and flood characteristics in the western Taihu Basin. Water Resour. Plan. Des. 2024, 53–56+62. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Yan, Y.; Zou, X. Spatiotemporal characteristics of heavy rainfall in the Taihu Basin. J. Nat. Resour. 2012, 27, 766–777. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Y. Analysis of the spatiotemporal distribution of rainfall in the Taihu Basin. Haihe Water Resour. 2003, 33–35. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Sang, Y.F. Precipitation complexity and its spatial difference in the Taihu Lake Basin, China. Entropy 2019, 21, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Abhishek, T.; Takhellambam, B.S.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Kinouchi, T. Spatiotemporal variability of current and future sub-daily rainfall in Japan using state-of-the-art high-quality data sets. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2022WR034305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z. The impact of the spatiotemporal structure of rainfall on flood frequency over a small urban watershed: An approach coupling stochastic storm transposition and hydrologic modeling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 4701–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.B.; Smith, J.A.; Baeck, M.L. Flood frequency analysis using radar rainfall fields and stochastic storm transposition. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 1592–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Abhishek, L.; Gong, Y.; Wu, X.; Sheng, B.; Zhao, W. Variations in present and future hourly extreme rainfall: Insights from high-resolution data and novel temporal disaggregation model. Water 2024, 16, 3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douinot, A.; Roux, H.; Garambois, P.-A.; Larnier, K.; Labat, D.; Dartus, D. Accounting for rainfall systematic spatial variability in flash flood forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, N.; Blumensaat, F.; Molnar, P.; Fatichi, S.; Burlando, P. Partitioning the impacts of spatial and climatological rainfall variability in urban drainage modeling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 1559–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendergrass, A.G.; Knutti, R.; Lehner, F.; Deser, C.; Sanderson, B.M. Precipitation variability increases in a warmer climate. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Lu, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, L. Integrated protection and restoration of mountains, rivers, forests, farmlands, lakes, and grasslands in the Taihu Basin. Environ. Monit. Manag. Technol. 2024, 36, 1–6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Du, Q.; Huang, X.; She, D. Spatiotemporal characteristics of water quality and its relationship with landscape patterns in the Jiangsu section of the Taihu Basin. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2025, 39, 361–370. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, J.; Ye, J.-S.; Li, F.-M.; Zhang, F. HRLT: A high-resolution (1 d, 1 km) and long-term (1961–2019) gridded dataset for surface temperature and precipitation across China. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 4793–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Guo, S.; Abhishek, Y.; Yin, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, J.; Guo, J. Variation and attribution of probable maximum precipitation of China using a high-resolution dataset in a changing climate. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2024, 28, 1873–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Dong, X.; Ma, Y.; Gou, J.; Li, L.; Bo, H.; Yu, D.; Su, B. Applicability comparison of various precipitation products of long-term hydrological simulations and their impact on parameter sensitivity. J. Hydrol. 2023, 618, 129187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yang, K.; Tang, W.; Lu, H.; Qin, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, X. The first high-resolution meteorological forcing dataset for land process studies over China. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Pu, C.; Peng, T. Batch image encryption using generated deep features based on stacked autoencoder network. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2017, 2017, 3675459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Tan, X.; Wu, X.; Tan, X.; Fu, J.; Liu, B. Long-term changes, synoptic behaviors, and future projections of large-scale anomalous precipitation events in China detected by a deep learning autoencoder. J. Clim. 2023, 36, 1237–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, R.; Kinouchi, T.; Zhao, W. Sediment load estimation using a novel regionalization sediment-response similarity method for ungauged catchments. J. Hydrol. 2023, 618, 129198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, R.; Li, G. Different configurations of interannual variability of the Western North Pacific Subtropical High and East Asian Westerly Jet in summer. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Hu, H.; Ren, X.; Yang, X.-Q. Subseasonal zonal variability of the western Pacific subtropical high in summer: Climate impacts and underlying mechanisms. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 3325–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xue, H.; Song, J. Tropical cyclone potential hazard in Southeast China and its linkage with the East Asian westerly jet. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 53, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basconcillo, J.; Moon, I.J. Increasing activity of tropical cyclones in East Asia during the mature boreal autumn linked to long-term climate variability. Npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Jin, K. Flood and drought disaster prevention in the Taihu Basin in 2024. China Flood Drought Manag. 2024, 34, 32–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y. Analysis of rainstorm characteristics and causes in the Taihu Basin. In Proceedings of the S2 Session: Monitoring 2013, Analysis and Forecasting of Severe Weather, China Meteorological Society, Beijing, China, 3 November 2014; Shanxi Meteorological Decision-Making Service Center: Taiyuan, China, 2014; pp. 2757–2766. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, M. Spatiotemporal characteristics and heavy rain frequency analysis of precipitation in the Taihu Basin. China Flood Drought Manag. 2025, 35, 24–30. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Randel, J.W.; Fu, R. Relationships between outgoing longwave radiation and diabatic heating in reanalyses. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 49, 2911–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T. Influence of spatiotemporal distribution of design storms on flood levels in the Taihu Basin. J. Lake Sci. 2022, 34, 1308–1318. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Meng, L.; Yan, C.; Zhuang, W.; Zhang, W.; Yan, X. Reconstruction of Three-Dimensional Temperature Salinity Fields From Satellite Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2021, 126, 17966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, G.V.; Le, X.-H.; Nguyen Van, L.; May, D.T.T.; Jung, S.; Lee, G. Machine learning approaches for reconstructing gridded precipitation based on multiple source products. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 48, 101475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, F.; Zhu, S.; Luo, H.; Zhi, X.; Wang, H. Future changes in precipitation extremes over Southeast Asia: Insights from CMIP6 multi-model ensemble. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 024013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, P.; Schaefli, B.; Kauzlaric, M. Why do we have so many different hydrological models? A review based on the case of Switzerland. WIREs Water 2022, 9, 129187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Abhishek; Zhao, W.; Zhou, C.; Liang, S.; Long, B.; Xu, Y.; Ma, S. Spatiotemporal Patterns and Atmospheric Drivers of Anomalous Precipitation in the Taihu Basin, Eastern China. Water 2025, 17, 2442. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162442
Hu J, Zhang J, Abhishek, Zhao W, Zhou C, Liang S, Long B, Xu Y, Ma S. Spatiotemporal Patterns and Atmospheric Drivers of Anomalous Precipitation in the Taihu Basin, Eastern China. Water. 2025; 17(16):2442. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162442
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jingwen, Jian Zhang, Abhishek, Wenpeng Zhao, Chuanqiao Zhou, Shuoyuan Liang, Biao Long, Ying Xu, and Shuping Ma. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Patterns and Atmospheric Drivers of Anomalous Precipitation in the Taihu Basin, Eastern China" Water 17, no. 16: 2442. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162442
APA StyleHu, J., Zhang, J., Abhishek, Zhao, W., Zhou, C., Liang, S., Long, B., Xu, Y., & Ma, S. (2025). Spatiotemporal Patterns and Atmospheric Drivers of Anomalous Precipitation in the Taihu Basin, Eastern China. Water, 17(16), 2442. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162442





