A Novel Multimodal Large Language Model-Based Approach for Urban Flood Detection Using Open-Access Closed Circuit Television in Bandung, Indonesia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
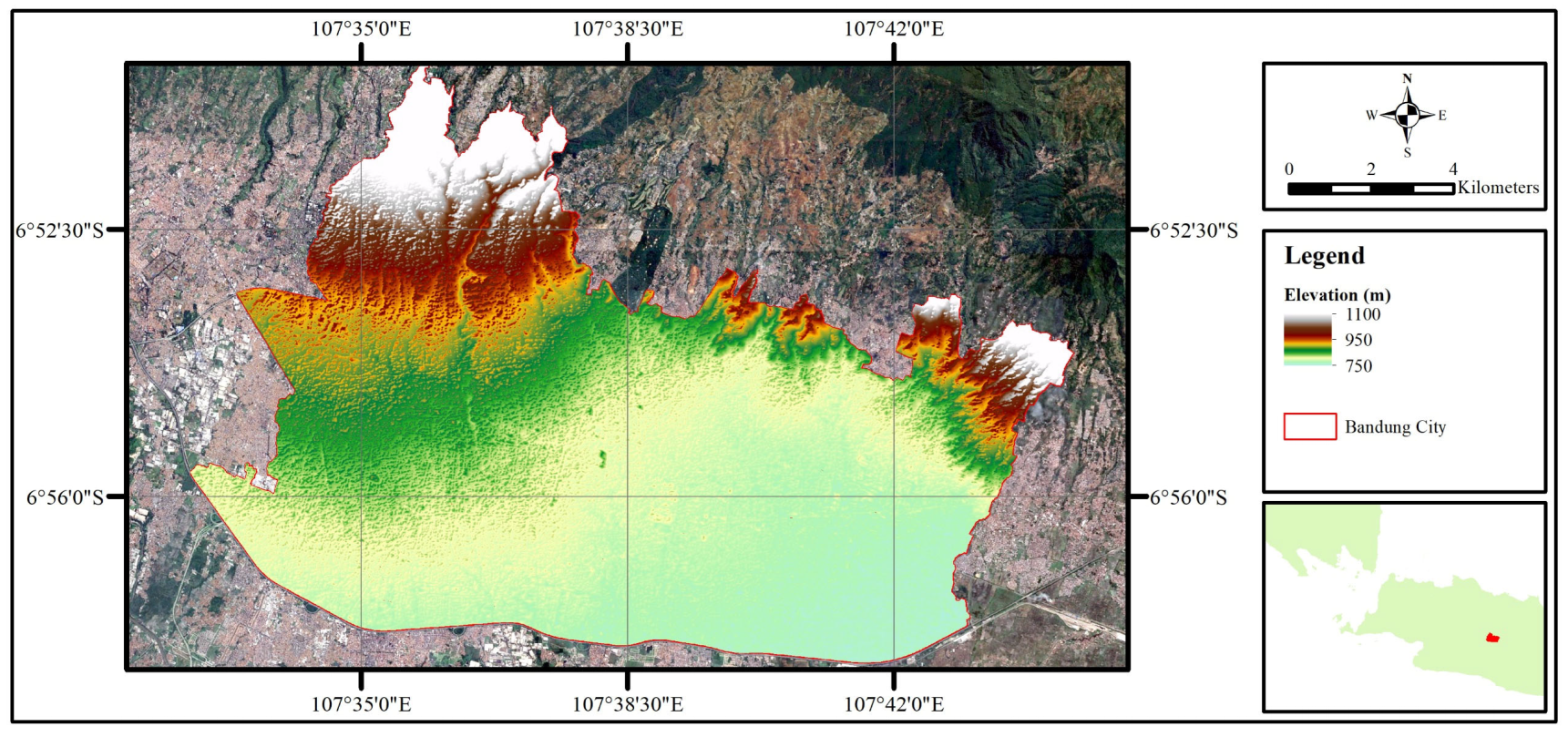
2.1. Study Area
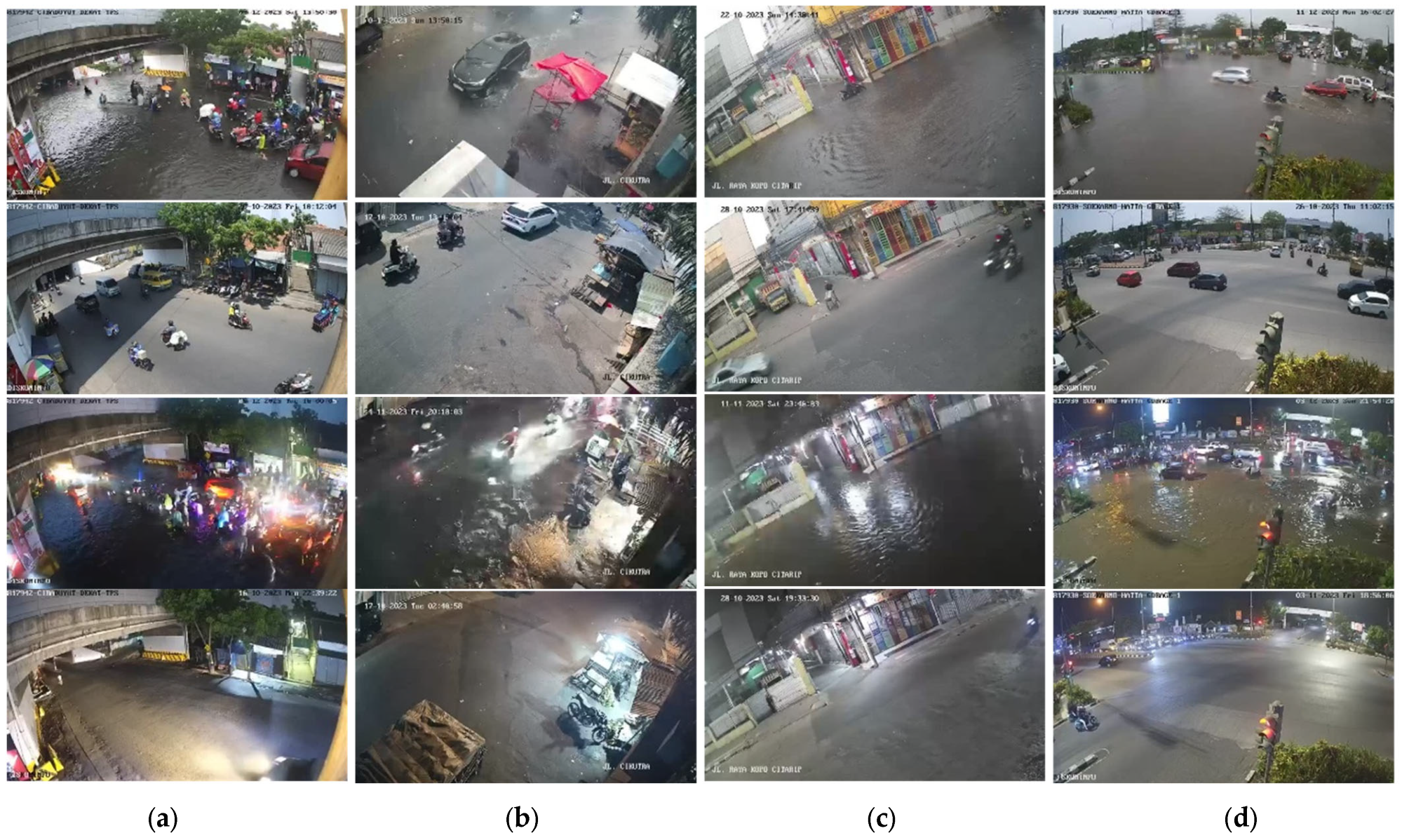
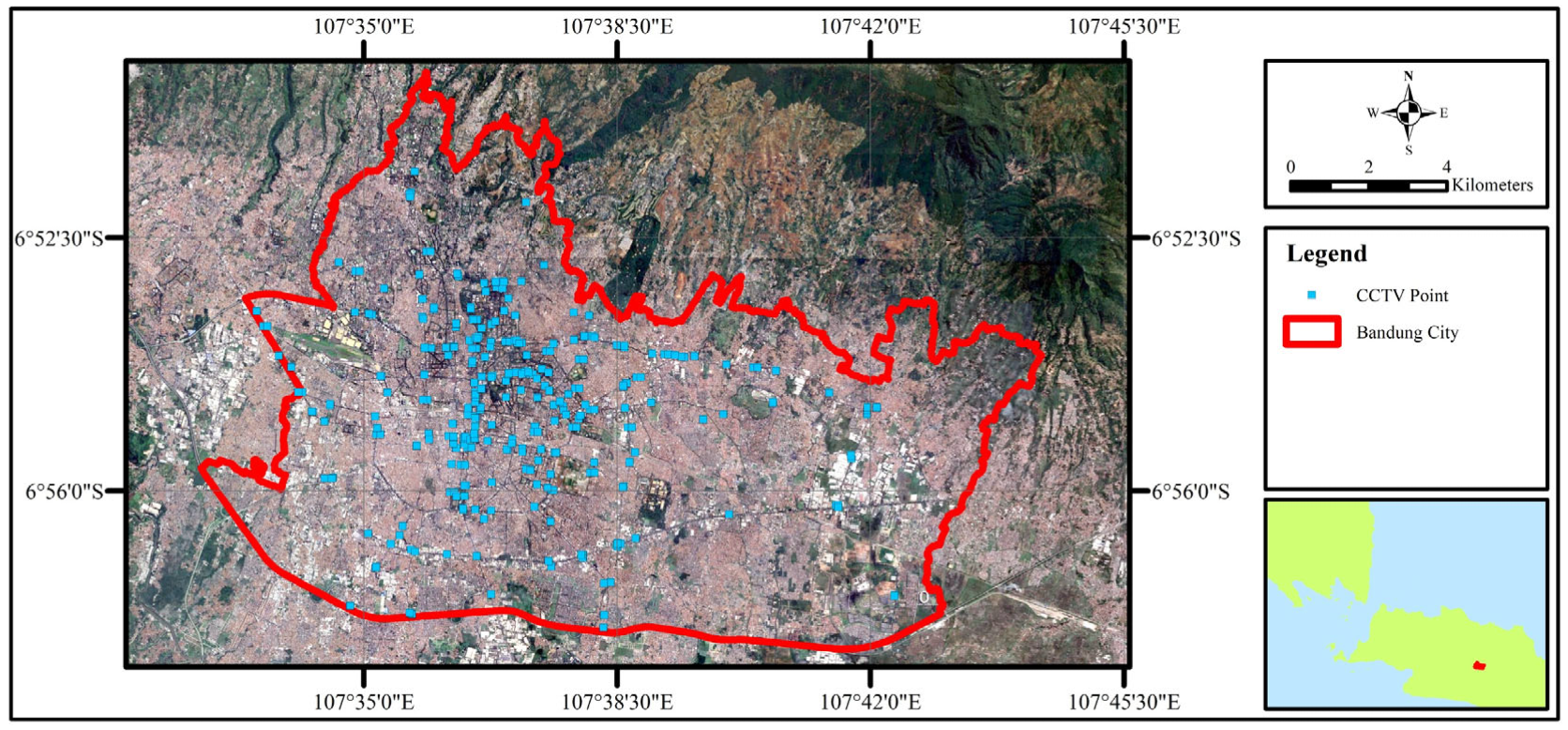
2.2. CCTV Data
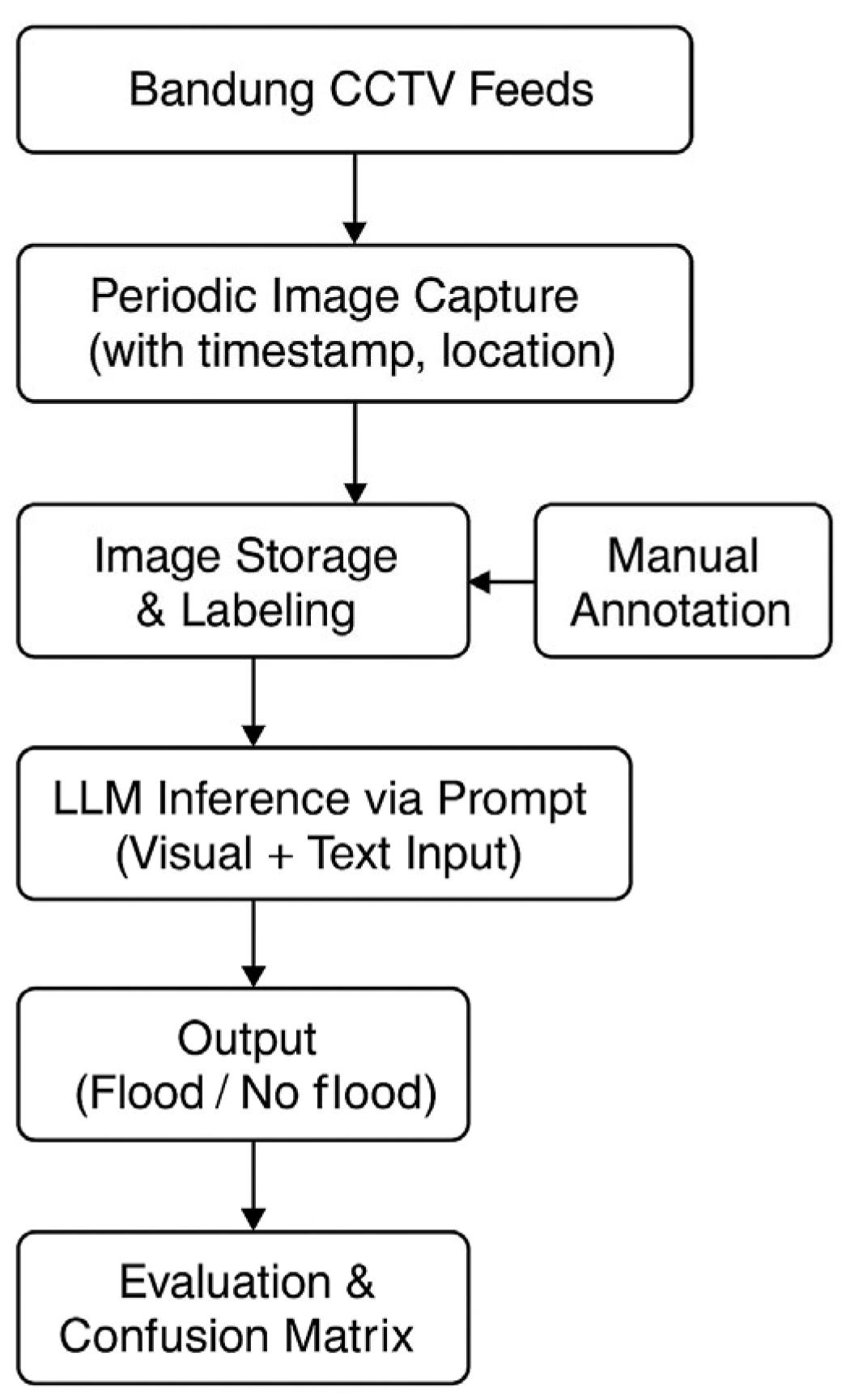
2.3. Model Framework
- Step 1. Image Acquisition from Open-Access CCTV
- Step 2. Labeling of Visual Conditions
- Step 3. Visual Prediction using LLMs
2.4. Objective Functions
3. Results
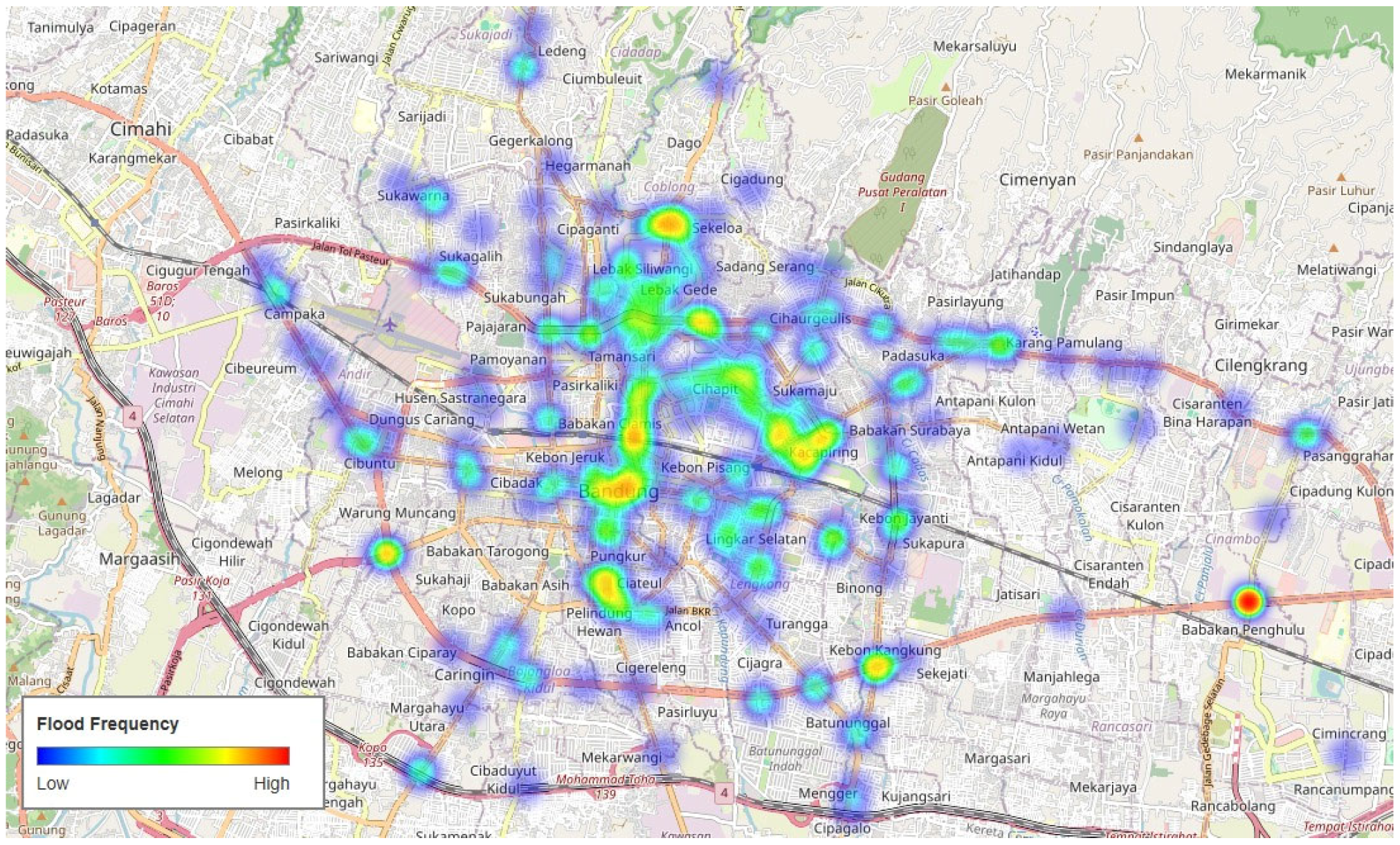
3.1. Overall Accuracy
3.2. Various Image Setting Analyses
3.3. Detailed Prompt Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Challenges
4.2. Opportunities
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rincón, D.; Khan, U.T.; Armenakis, C. Flood risk mapping using GIS and multi-criteria analysis: A greater toronto area case study. Geosciences 2018, 8, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moel, H.; Jongman, B.; Kreibich, H.; Merz, B.; Penning-Rowsell, E.; Ward, P.J. Flood risk assessments at different spatial scales. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2015, 20, 865–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.W.; Abid, S.K.; Sulaiman, N.; Nazir, U.; Azam, K. A systematic review of the flood vulnerability using geographic information system. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q.; Mostafavi, A. Unraveling the Temporal Importance of Community-Scale Human Activity Features for Rapid Assessment of Flood Impacts. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 1138–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpino, S.; Albano, R.; Cantisani, A.; Mancusi, L.; Sole, A.; Milillo, G. Article multitemporal SAR data and 2D hydrodynamic model flood scenario dynamics assessment. ISPRS Int. J. Geoinf. 2018, 7, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedin, S.J.H.; Stephen, H. GIS framework for spatiotemporal mapping of urban flooding. Geosciences 2019, 9, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamiru, H.; Dinka, M.O. Application of ANN and HEC-RAS model for flood inundation mapping in lower Baro Akobo River Basin, Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 36, 100855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyangadze, T.; Mavhura, E.; Mudavanhu, C.; Pedzisai, E. Flood inundation mapping in data-scarce areas: A case of Mbire District, Zimbabwe. Geo 2022, 9, e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, O.T.; Yang, T.H. A novel hybrid approach based on cellular automata and a digital elevation model for rapid flood assessment. Water 2021, 13, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, O.T.; Yang, T.H.; Hsu, H.M.; Gourbesville, P. A rapid flood inundation model for urban flood analyses. Methods X 2023, 10, 102202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, T.; Rogerson, R.; Barnacle, M. A comparison between the cost effectiveness of CCTV and improved street lighting as a means of crime reduction. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2018, 68, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, M.P.J. The Value of CCTV Surveillance Cameras as an Investigative Tool: An Empirical Analysis. Eur. J. Crim. Pol. Res. 2017, 23, 441–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, B.C.; Piza, E.L.; Thomas, A.L.; Farrington, D.P. Private Security and Closed-Circuit Television (CCTV) Surveillance: A Systematic Review of Function and Performance. J. Contemp. Crim. Justice 2020, 36, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piza, E.L.; Welsh, B.C.; Farrington, D.P.; Thomas, A.L. CCTV surveillance for crime prevention: A 40-year systematic review with meta-analysis. Criminol. Public Policy 2019, 18, 135–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leem, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Yoon, J. Linking Data and Converging Systems for Smarter Urban Services: Two Cases of U-City Service in Korea. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2014, 22, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, M.; Shen, L.; Zhan, C.; Xiao, Y.; Corbin, S.; Chen, D. Operation data for evaluating benefits and costs of advanced traffic management components. Transp. Res. Rec. 2008, 2086, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhokarkar Vaidya, R.; Kulkarni, S.; Didore, V. Intelligent transportation system using IOT: A Review. Int. J. Res. Trends Innov. 2021, 6, 80–87. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, M.; Azarmi, M.; Mohammad Pour Mir, F. 3D-Net: Monocular 3D object recognition for traffic monitoring. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 227, 120253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.F.; Liao, Y.T.; Wang, P.C. Development and Deployment of a Virtual Water Gauge System Utilizing the ResNet-50 Convolutional Neural Network for Real-Time River Water Level Monitoring: A Case Study of the Keelung River in Taiwan. Water 2024, 16, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.S.; You, H. A Digital Twin Dam and Watershed Management Platform. Water 2023, 15, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-B.; Lee, F.-Z.; Chang, K.-C.; Lai, J.-S.; Lo, S.-W.; Wu, J.-H.; Lin, T.-K. The Artificial Intelligence of Things Sensing System of Real-Time Bridge Scour Monitoring for Early Warning during Floods. Sensors 2021, 21, 4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzhizhanovskaya, V.V.; Shirshov, G.S.; Melnikova, N.B.; Belleman, R.G.; Rusadi, F.I.; Broekhuijsen, B.J.; Gouldby, B.P.; Lhomme, J.; Balis, B. Bubak, Flood early warning system: Design, implementation and computational modules. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2011, 4, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhadi, N.A.; Abdullah, A.F.; Bejo, S.K.; Mahadi, M.R.; Mijic, A. Image segmentation methods for flood monitoring system. Water 2020, 12, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cai, R.; Tan, Y.; Zhou, H.; Sadick, A.-M.; Shou, W.; Wang, X. Automatic detection of actual water depth of urban floods from social media images. Measurement 2023, 216, 112891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Salahshour, B.; Cetin, M.; Iftekharuddin, K.; Tahvildari, N.; Huang, G.; Harris, D.K.; Ampofo, K.; Goodall, J.L. Urban flood extent segmentation and evaluation from real-world surveillance camera images using deep convolutional neural network. Environ. Model. Softw. 2024, 173, 105939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pally, R.J.; Samadi, S. Application of image processing and convolutional neural networks for flood image classification and semantic segmentation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2022, 148, 105285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, N.H.; Lee, H.; Kim, N.; Kim, G. Real-time flash flood detection employing the YOLOv8 model. Earth Sci. Inform. 2024, 17, 4809–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utomo, S.B.; Irawan, J.F.; Alinra, R.R. Early warning flood detector adopting camera by Sobel Canny edge detection algorithm method. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2021, 22, 1796–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Jin, S. Rapid flood mapping and evaluation with a supervised classifier and change detection in Shouguang using Sentinel-1 SAR and Sentinel-2 optical data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humaira, N.; Samadi, V.S.; Hubig, N.C. DX-FloodLine: End-To-End Deep Explainable Pipeline for Real Time Flood Scene Object Detection from Multimedia Images. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 110644–110655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelindung—Pemantauan Lingkungan Kota Bandung [Internet]. Available online: https://pelindung.bandung.go.id/ (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Tanim, A.H.; McRae, C.B.; Tavakol-davani, H.; Goharian, E. Flood Detection in Urban Areas Using Satellite Imagery and Machine Learning. Water 2022, 14, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ChatGPT|OpenAI [Internet]. Available online: https://openai.com/chatgpt/overview/ (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Gemini API|Google AI for Developers [Internet]. Available online: https://ai.google.dev/gemini-api/docs (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Frontier AI LLMs, Assistants, Agents, Services|Mistral AI [Internet]. Available online: https://mistral.ai/ (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Janus Pro AI [Internet]. Available online: https://janusai.pro/#google_vignette (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Roboflow [Internet]. Available online: https://universe.roboflow.com/alumatngdetect/flood-iqlub/dataset/1 (accessed on 22 August 2025).



| LLM Model | Version | Total Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT [33] | OpenAI GPT-4.1 | ~1.76T * |
| Gemini [34] | Gemini 2.5 Pro | ~1.76T * |
| Mistral [35] | Mistral Pixtral Large | 124B |
| DeepSeek [36] | DeepSeek Janus | 671B |
| LLM Model | Overall Accuracy | Avg. Cost/Image | Avg. Speed/Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| OpenAI GPT-4.1 | 0.8506 | ~USD 0.0050 | 3 s |
| Gemini 2.5 Pro | 0.8413 | ~USD 0.0047 | 3 s |
| Mistral P. Large | 0.8322 | ~USD 0.0067 | 1 s |
| DeepSeek JANUS | 0.7918 | ~USD 0.0019 | 2 s |
| Image Setting | GPT-4.1-Nano | GPT-4.1-Mini | GPT-4.1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Day | 0.9128 | 0.9553 | 0.9679 |
| Night | 0.6972 | 0.7298 | 0.7332 |
| Overall | 0.8050 | 0.8426 | 0.8506 |
| Avg. Cost/Image | ~USD 0.00068 | ~USD 0.0026 | ~USD 0.0050 |
| Prompts | GPT-4.1 Nano | GPT-4.1 Mini | GPT-4.1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified | 0.7269 | 0.7523 | 0.7894 |
| Detailed | 0.8050 | 0.8426 | 0.8506 |
| Test Image | DeepSeek Janus | Mistral P Large | Gemini 2.5. Pro | ChatGPT 4.1. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nano | Mini | Standard | ||||
| Standard Case | ||||||
 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Day (NF) | ||||||
 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✖ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Day (F) | ||||||
 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Night (NF) | ||||||
 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Night (F) | ||||||
| Hard Case | ||||||
 | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ✖ | ✓ |
| Light Obstruction (F) | ||||||
 | ✖ | ✖ | ✓ | ✖ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Partial Image Defect (NF) | ||||||
 | ✖ | ✓ | ✓ | ✖ | ✖ | ✓ |
| Blurred Image | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, T.-H.; Wijaya, O.T.; Ardianto, S.; Christian, A.B. A Novel Multimodal Large Language Model-Based Approach for Urban Flood Detection Using Open-Access Closed Circuit Television in Bandung, Indonesia. Water 2025, 17, 2739. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182739
Yang T-H, Wijaya OT, Ardianto S, Christian AB. A Novel Multimodal Large Language Model-Based Approach for Urban Flood Detection Using Open-Access Closed Circuit Television in Bandung, Indonesia. Water. 2025; 17(18):2739. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182739
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Tsun-Hua, Obaja Triputera Wijaya, Sandy Ardianto, and Albert Budi Christian. 2025. "A Novel Multimodal Large Language Model-Based Approach for Urban Flood Detection Using Open-Access Closed Circuit Television in Bandung, Indonesia" Water 17, no. 18: 2739. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182739
APA StyleYang, T.-H., Wijaya, O. T., Ardianto, S., & Christian, A. B. (2025). A Novel Multimodal Large Language Model-Based Approach for Urban Flood Detection Using Open-Access Closed Circuit Television in Bandung, Indonesia. Water, 17(18), 2739. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17182739







