Ferric Tannate-Enhanced Electrochemical Conditioning Process for Improving Sludge Dewaterability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.1.1. Sludge Sample and Chemicals
2.1.2. Preparation of Ferric Tannate
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
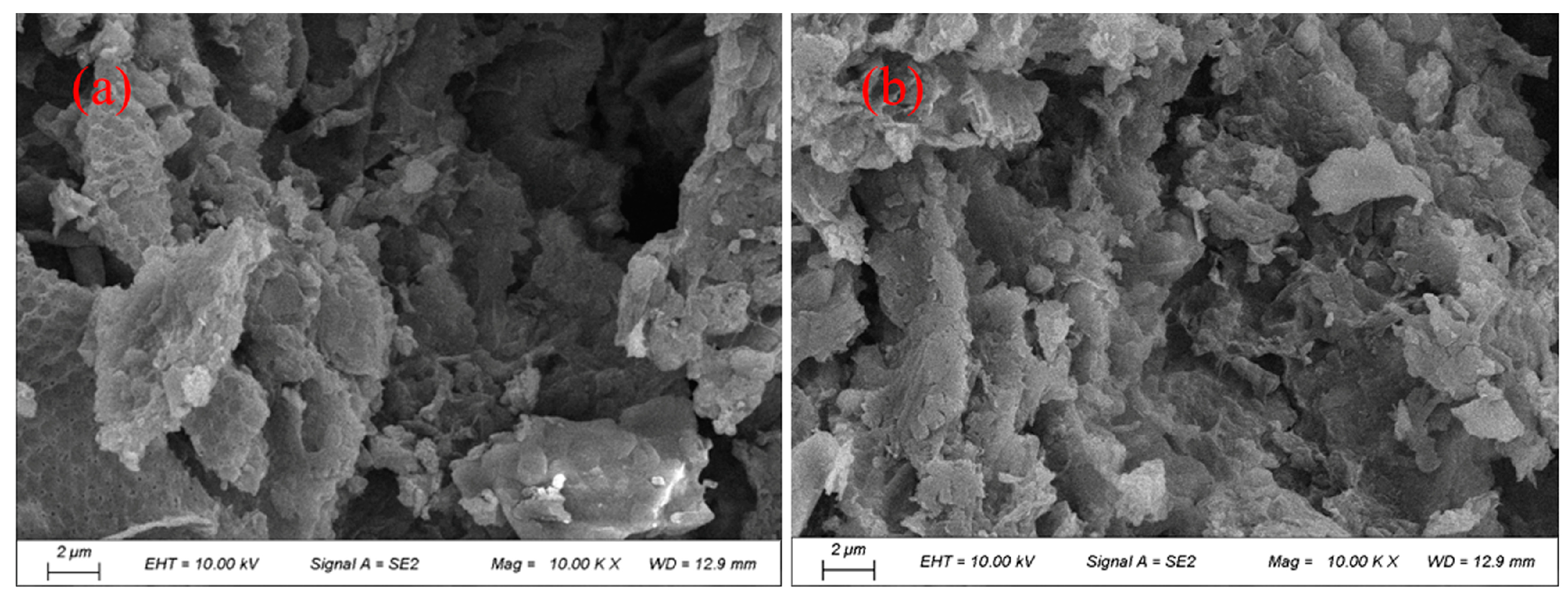
3.1. Physicochemical Characteristics of the Prepared Ferric Tannate
3.2. Effects of Process Parameters on Sludge Dewaterability
3.3. Effects of Ferric Tannate-Enhanced Electrochemical Process on Sludge Properties
3.3.1. Viscosity
3.3.2. Zeta Potential
3.3.3. Particle Size
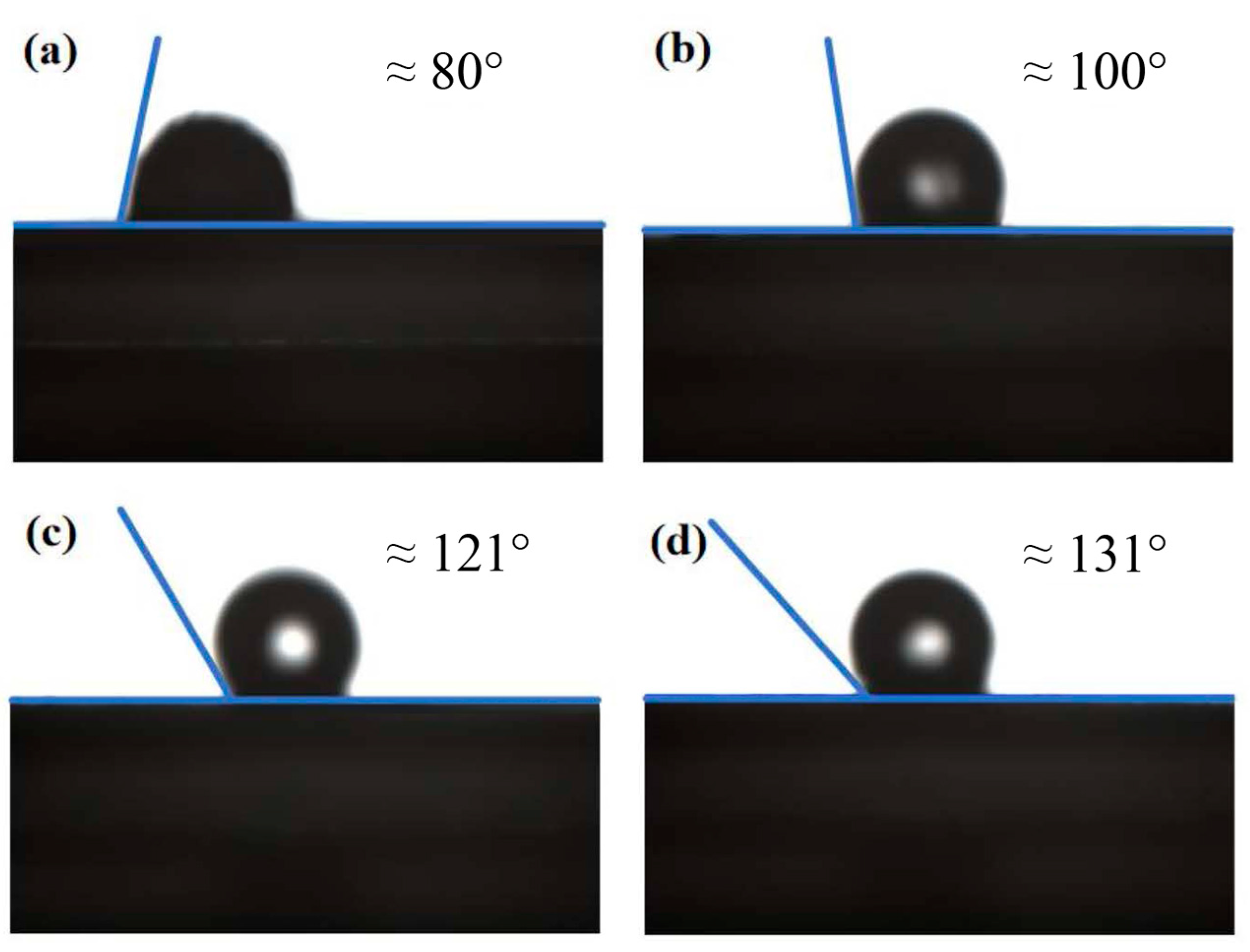
3.3.4. Contact Angle
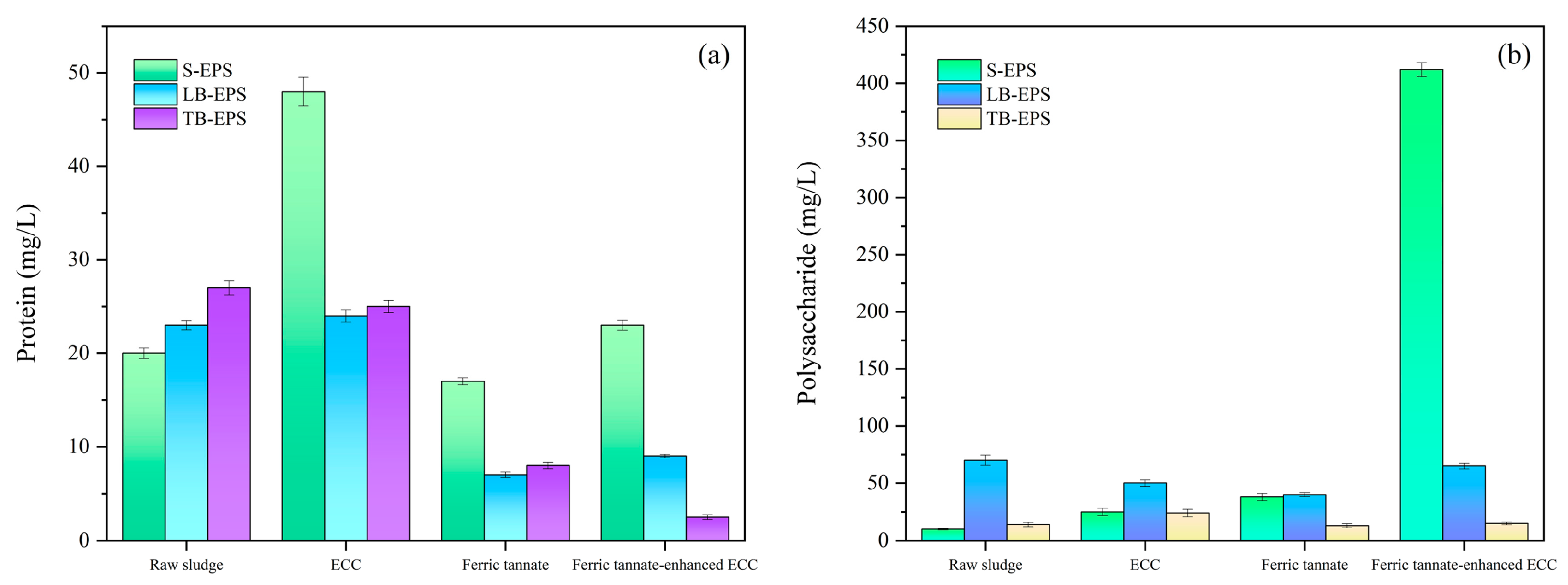
3.3.5. EPS Contents
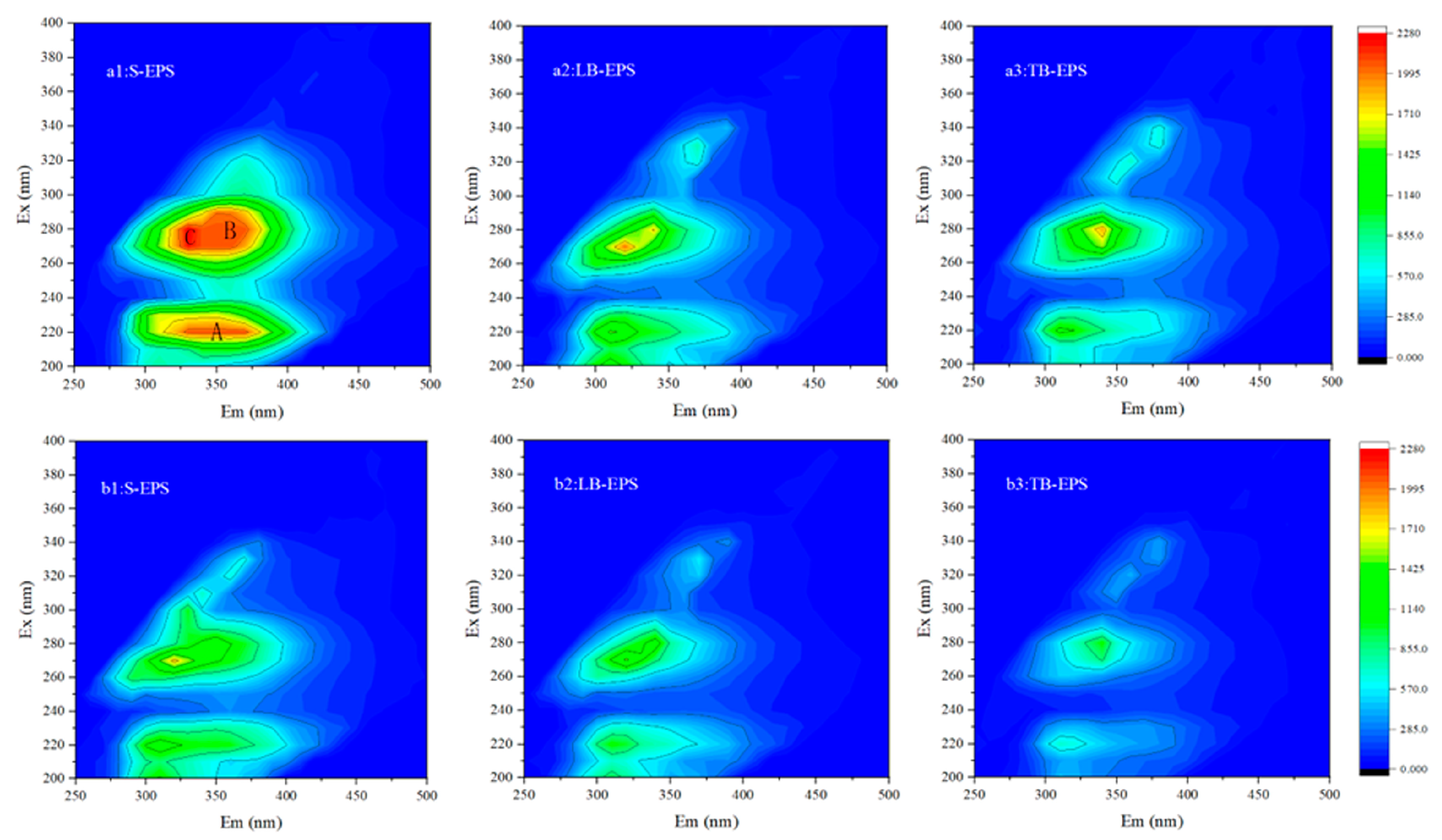
3.3.6. Fluorescence Components
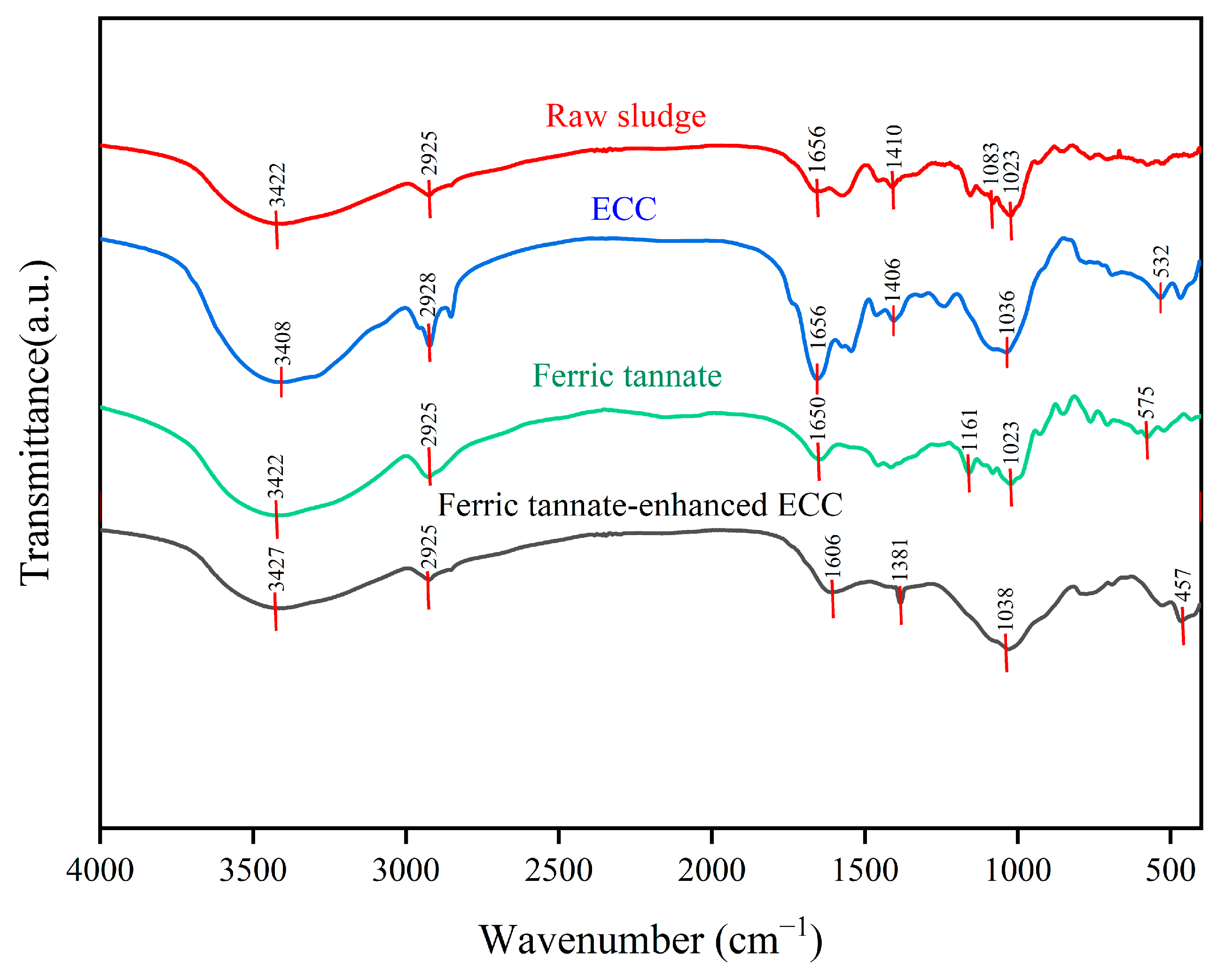
3.3.7. Functional Groups
3.3.8. Morphological Structure
3.3.9. Chemical Components
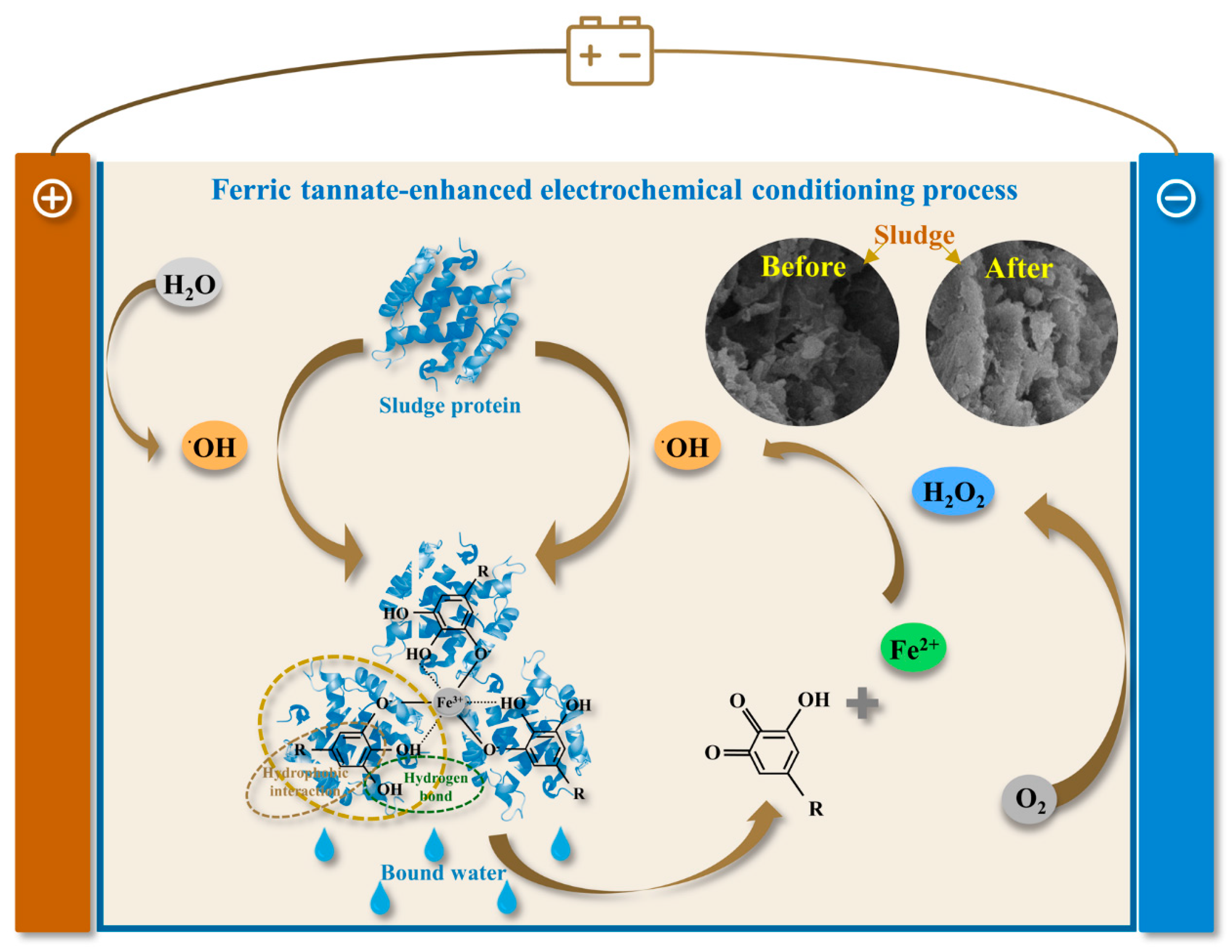
3.4. Mechanism Exploration
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EPS | Extracellular polymeric substances |
| ECC | Electrochemical conditioning |
| CST | Capillary suction time |
| SRF | Specific resistance to filtration |
| Wc | Water content |
| •OH | Hydroxyl radical |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| TS | Total solid |
| VS | Volatile solid |
| S-EPS | Slime EPS |
| LB-EPS | Loosely bound EPS |
| TB-EPS | Tightly bound EPS |
| 3D-EEM | Three-dimensional excitation emission matrix |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TA | Tannic acid |
| PPC | Polyphenolic compound |
| ORR | Oxygen reduction reaction |
| Q | Quinine |
| SQ• | Semiquinone radical |
References
- Hernández-Chover, V.; Bellver-Domingo, Á.; Hernández-Sancho, F. Efficiency of wastewater treatment facilities: The influence of scale economies. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 228, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Feng, L.; Zhao, W.; Li, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wei, L. Composition and molecular structure analysis of hydrophilic/hydrophobic extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) with impacts on sludge dewaterability. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 462, 142234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mądzielewska, W.I.; Jachimowicz, P.; Otieno, J.O.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A. Impact of Tire-Derived Microplastics on Microbiological Activity of Aerobic Granular Sludge. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Yu, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhu, N.; Mojiri, A.; Ge, D. Tannic acid as a green chemical for the removal of various heavy metals: A critical review of recent developments. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 375, 124390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Hasaer, B.; Bai, Y.; Liu, R.; Hu, C.; Qu, J. Using activated peroxymonosulfate by electrochemically generated FeII for conditioning and dewatering of anaerobically digested sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Zhu, N.; Song, L. Conditioning of sewage sludge with electrolysis: Effectiveness and optimizing study to improve dewaterability. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4285–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Zhao, W.; Hu, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, D.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, J.; Hou, H. Integration of electrochemical and calcium hypochlorite oxidation for simultaneous sludge deep dewatering, stabilization and phosphorus fixation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masihi, H.; Gholikandi, G.B. Employing Electrochemical-Fenton process for conditioning and dewatering of anaerobically digested sludge: A novel approach. Water Res. 2018, 144, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Wang, Q.; Wells, G.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Song, Z.; Jin, M.; Hu, J.; Ho, S.-H.; Xiao, R.; Wei, Z. Improving dewaterability and filterability of waste activated sludge by electrochemical Fenton pretreatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Zhang, H.; Guo, J.; Yu, S.-Y.; Luo, M.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, P.; He, C.-S. Boosted H2O2 utilization and selective hydroxyl radical generation for water decontamination: Synergistic roles of dual active sites in H2O2 activation. Water Res. 2024, 267, 122453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Jiang, X.-h.; Wang, M.; Fan, Z.-n.; Gu, Y.-l.; Zou, R.-h.; Zhao, L.-l.; Liu, L. Catalase catalyzed tannic acid-Fe3+ network coating: A theranostic strategy for intestinal barrier restoration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 274, 133304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Huang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Y.; Xu, K. Preparation and characterization of high mechanical strength chitosan/oxidized tannic acid composite film with Schiff Base and hydrogen bond crosslinking. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.-L.; Tian, P.-X.; Li, Y.-D.; Zeng, J.-B. Biobased covalent adaptable networks: Towards better sustainability of thermosets. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 4363–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liu, B.; Han, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, F.; Wang, T.; Yu, D. Tannic acid/non-covalent interaction-mediated modification of hemp seed proteins: Focused on binding mechanisms, oil-water interface behavior, and rheological properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 157, 110483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuliani, L.; Frison, N.; Jelic, A.; Fatone, F.; Bolzonella, D.; Ballottari, M. Microalgae cultivation on anaerobic digestate of municipal wastewater, sewage sludge and agro-waste. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Guan, Q.; Jiang, J.; Khan, M.S. Tannin complexation with metal ions and its implication on human health, environment and industry: An overview. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Thi, K.-S.; Fareed, H.; Le-Thi, A.-D.; Lee, Y.; Kang, S.; Kim, I.S. Leveraging tannic acid-ferric iron (TA/Fe3+) complexation in polyamide selective layer for synthesizing robust thin film composite reverse osmosis (TFC-RO) hollow fiber membranes for saline water treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 348, 127669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.; López-Maldonado, J.; Cárdenas, J.; Orozco, G.; Bustos, E.; Rivera, F. Design of an electrochemical flow reactor prototype to the electro-oxidation of amoxicillin in aqueous media using modified electrodes with transition metal oxides. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Zhong, Y.; Li, X.; Deng, Y.; Wang, L.; Yi, K.; Zeng, G. Enhanced dewaterability of waste activated sludge by Fe (II)-activated peroxymonosulfate oxidation. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 206, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemfira, T.; Milanovskiy, E. The contact angle of wetting of the solid phase of soil before and after chemical modification. Eurasian J. Soil Sci. 2015, 4, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Song, L.; Han, B.; Song, H.; Bai, R.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Lin, Z.; Hu, W. Highly efficient enhancement of municipal sludge dewaterability using persulfate activation with nZVI/HA. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 79, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Wan, Y.; Yu, H. Fast start-up of partial nitrification for high-ammonia wastewater treatment using zeolite with in-situ bioregeneration. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 59, 105077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-H.; Wu, J.; Weng, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wu, A. An improved phenol-sulfuric acid method for the determination of carbohydrates in the presence of persulfate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 227, 115332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Yang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, M.; Long, M.; Fang, F.; Guo, J. The differences in characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances of flocs and anammox granules impacted aggregation. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 44, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divjak, B.; Franko, M.; Novič, M. Determination of iron in complex matrices by ion chromatography with UV–Vis, thermal lens and amperometric detection using post-column reagents. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 829, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Liu, P.; Ma, Z.; Xue, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Sun, X.; Mu, Y. High H2O2 concentrations observed during haze periods during the winter in Beijing: Importance of H2O2 oxidation in sulfate formation. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Ge, D.; Bai, L.; Dong, Y.; Bian, C.; Xu, J.; Zhu, N.; Yuan, H. Insight into the roles of electrolysis-activated persulfate oxidation in the waste activated sludge dewaterability: Effects and mechanism. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Chen, R. Study of complexes of tannic acid with Fe (III) and Fe (II). J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2019, 2019, 3894571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Li, L.; Liu, J. Synthesis and characterization of ferric tannate as a novel porous adsorptive-catalyst for nitrogen removal from wastewater. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 40785–40791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimune-Moriya, S.; Nagata, Y. Tough polyimide nanocomposites with high thermal resistance at extremely low filler content. Polym. Compos. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomma, J.; Abbas, S.; Al-Dujaili, A. New Quinolin-2-one, Indazole, and Benzisoxazole Derivatives Derived from Chalcones: Synthesis, Characterization, and Biological Activity. Russ. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 59, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamimed, M.Y.; Belfilali, I.; Guenfoud, F.; Roisnel, T. Efficient heavy metal removal from water using a novel thiosemicarbazone-based ligand. J. Coord. Chem. 2025, 78, 1284–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januário, E.F.D.; Vidovix, T.B.; Araújo, L.A.d.; Bergamasco Beltran, L.; Bergamasco, R.; Vieira, A.M.S. Investigation of Citrus reticulata peels as an efficient and low-cost adsorbent for the removal of safranin orange dye. Environ. Technol. 2022, 43, 4315–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drescher, D.; Büchner, T.; McNaughton, D.; Kneipp, J. SERS reveals the specific interaction of silver and gold nanoparticles with hemoglobin and red blood cell components. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 5364–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, F.; Qin, S.; Huang, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Wu, C.; Shao, L. Deprotonated tannic acid regulating pyrrole polymerization to enhance nanofiltration performance for molecular separations under both aqueous and organic solvent environments. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 298, 121647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, M. Review of recent trends in capillary suction time (CST) dewaterability testing research. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 8157–8163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobbledick, J.; Nguyen, A.; Latulippe, D.R. Demonstration of FBRM as process analytical technology tool for dewatering processes via CST correlation. Water Res. 2014, 58, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Luo, F.; He, L.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Z. Physical conditioning methods for sludge deep dewatering: A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 360, 121207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu’azu, N.D.; Zubair, M.; Jarrah, N.; Alagha, O.; Al-Harthi, M.A.; Essa, M.H. Sewage sludge ZnCl2-activated carbon intercalated MgFe–LDH nanocomposites: Insight of the sorption mechanism of improved removal of phenol from water. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Zeng, S.; Chen, Z.; Lv, M.; Tang, X.; He, X.; Chen, Y.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, J. Synergistic effect of organic matter-floc size-bound water and multifactorial quantitative model of optimal reagent demand in sewage sludge conditioning process prior to dewatering. Water Res. 2024, 251, 121108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Gao, F.; Zhang, N.; Li, J.; Xu, M.; Jiang, Y. Dehydration performance of municipal sludge and its dewatering conditioning methods: A review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 11337–11357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Chen, N.; Feng, C.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F. Treatment of polluted river sediment by electrochemical oxidation: Changes of hydrophilicity and acute cytotoxicity of dissolved organic matter. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Dai, X.; Dong, B.; Dai, L. New insights into the effect of sludge proteins on the hydrophilic/hydrophobic properties that improve sludge dewaterability during anaerobic digestion. Water Res. 2020, 173, 115503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Hao, Z.; Liu, X.; Tian, X.; Wang, D. Molecular mechanisms of interaction between protease and humic acid of waste activated sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 389, 126229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wei, Q.; Chen, Y.; Feng, A.; Zhang, W. Enhancement of hydrogen bonds between proteins and polyphenols through magnetic field treatment: Structure, interfacial properties, and emulsifying properties. Food Res. Int. 2024, 192, 114822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Yuan, H.; Ge, D.; Zhu, N. A novel conditioning approach for amelioration of sludge dewaterability using activated carbon strengthening electrochemical oxidation and realized mechanism. Water Res. 2022, 220, 118704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhai, Y.; Xu, Z.; Liu, L.; Ren, W.; Xie, Y.; Li, C.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, M. Unraveling the impacts of Cu+-based treatments on sludge dewaterability: The overlooked role of Cu3+. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 457, 141106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Liang, M.; Xia, Y.; Li, C.; Huang, M.; Peng, S.; Huang, Y. Reduction mechanisms of V5+ by vanadium-reducing bacteria in aqueous environments: Role of different molecular weight fractionated extracellular polymeric substances. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.-p.; Cheng, X.-b.; Chen, S.-p.; Zhu, N.-w.; Zhou, Z.-y. New sludge pretreatment method to improve dewaterability of waste activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5659–5664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.-H.; He, P.-J.; Shao, L.-M. Novel insights into sludge dewaterability by fluorescence excitation–emission matrix combined with parallel factor analysis. Water Res. 2010, 44, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Pan, L.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, D.; Yang, G.; Yuan, X.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, J. How does zero valent iron activating peroxydisulfate improve the dewatering of anaerobically digested sludge? Water Res. 2019, 163, 114912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Westerhoff, P.; Leenheer, J.A.; Booksh, K. Fluorescence excitation− emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5701–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, D.; Wang, F.; Yang, J.; Wu, X.; Zhang, W.; Dai, X. Effects of temperature variation on wastewater sludge electro-dewatering. J. Cleaner Prod. 2019, 214, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Seow, W.Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, D.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, Y. Effects of thermal-Fe (II) activated oxone treatment on sludge dewaterability. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 322, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Zhao, K.; Zhao, J.; Liang, H.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.-Y.; Hu, C.; Qu, J. Enzyme-enhanced acidogenic fermentation of waste activated sludge: Insights from sludge structure, interfaces, and functional microflora. Water Res. 2024, 249, 120889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Wen, Q.; Yang, J.; Xiao, K.; Zhu, Y.; Tao, S.; Lv, Y.; Liang, S.; Fan, W.; Zhu, S. Unraveling oxidation behaviors for intracellular and extracellular from different oxidants (HOCl vs. H2O2) catalyzed by ferrous iron in waste activated sludge dewatering. Water Res. 2019, 148, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, M.O. Bond characterization in cementitious material binders using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, H.K.J.; Taylor, M.C. Interactions of iron (II) and iron (III) with gallic acid and its homologues: A potentiometric and spectrophotometric study. Aust. J. Chem. 1982, 35, 739–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Li, C.; Xu, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Z.; Sun, H.; Liang, J.; Ma, P.a.; Yang, P. Natural Tannin and Upconversion Photons Co-Potentiate Fe Fenton Anticancer Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 2503641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Sun, X.; Bai, S.; Wang, N.; Liang, J.; Zhou, L. The coupling reaction of Fe2+ bio-oxidation and resulting Fe3+ hydrolysis drastically improve the formation of iron hydroxysulfate minerals in AMD. Environ. Technol. 2021, 42, 2325–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolobajev, J.; Trapido, M.; Goi, A. Interaction of tannic acid with ferric iron to assist 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol catalytic decomposition and reuse of ferric sludge as a source of iron catalyst in Fenton-based treatment. Appl. Catal. B 2016, 187, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, K.; Fujii, S.; Yamano, S.; Cho, A.K.; Kamisuki, S.; Nakai, Y.; Sugawara, F.; Froines, J.R.; Kumagai, Y. An approach to evaluate two-electron reduction of 9, 10-phenanthraquinone and redox activity of the hydroquinone associated with oxidative stress. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, L.; Lu, F.; Zhong, D. Ultrafast dynamics of nonequilibrium short-range electron transfer in semiquinone flavodoxin. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 3202–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, D.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, H.; Zhu, N. A novel Fe2+/persulfate/tannic acid process with strengthened efficacy on enhancing waste activated sludge dewaterability and mechanism insight. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Freitas, V.; Mateus, N. Protein/polyphenol interactions: Past and present contributions. Mechanisms of astringency perception. Curr. Org. Chem. 2012, 16, 724–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
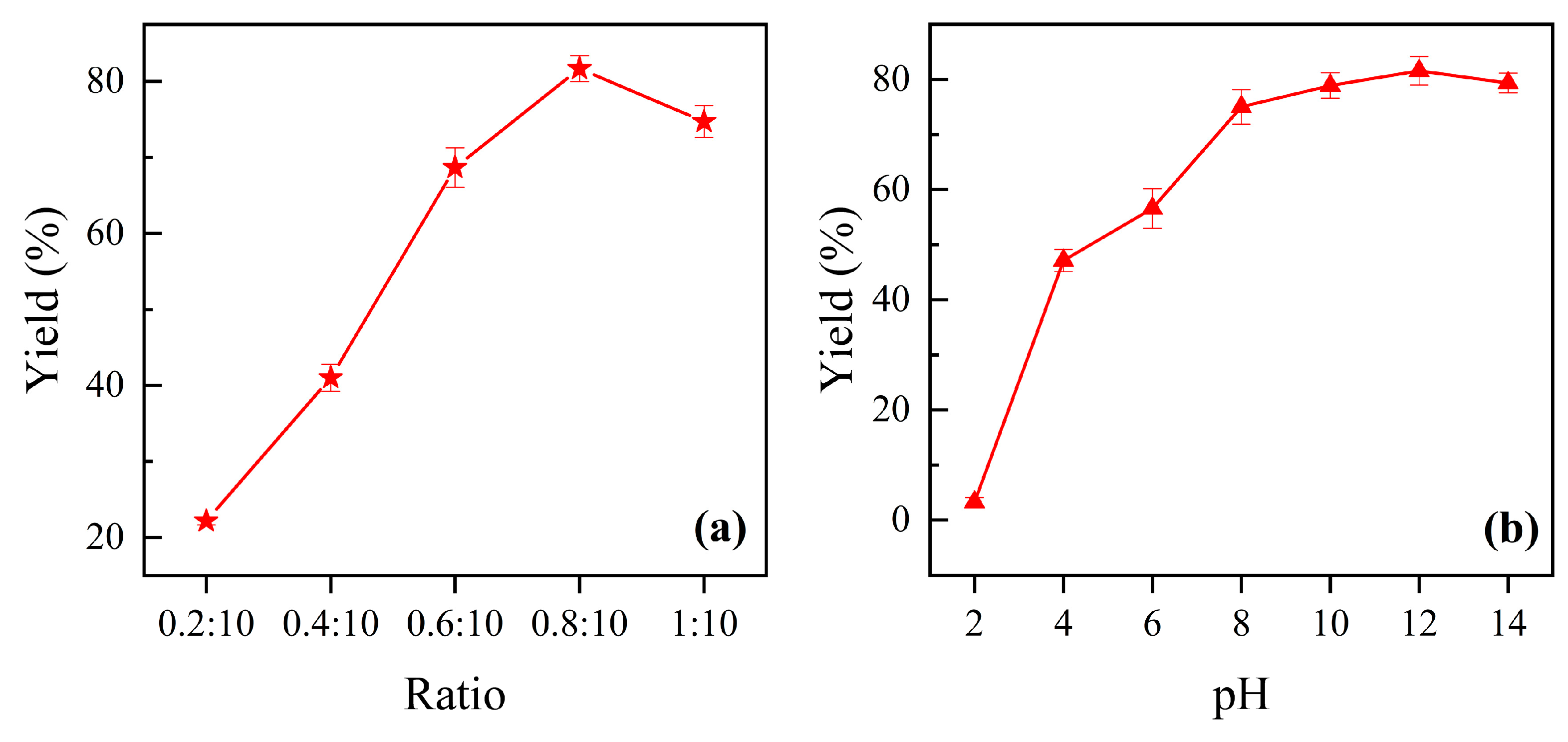
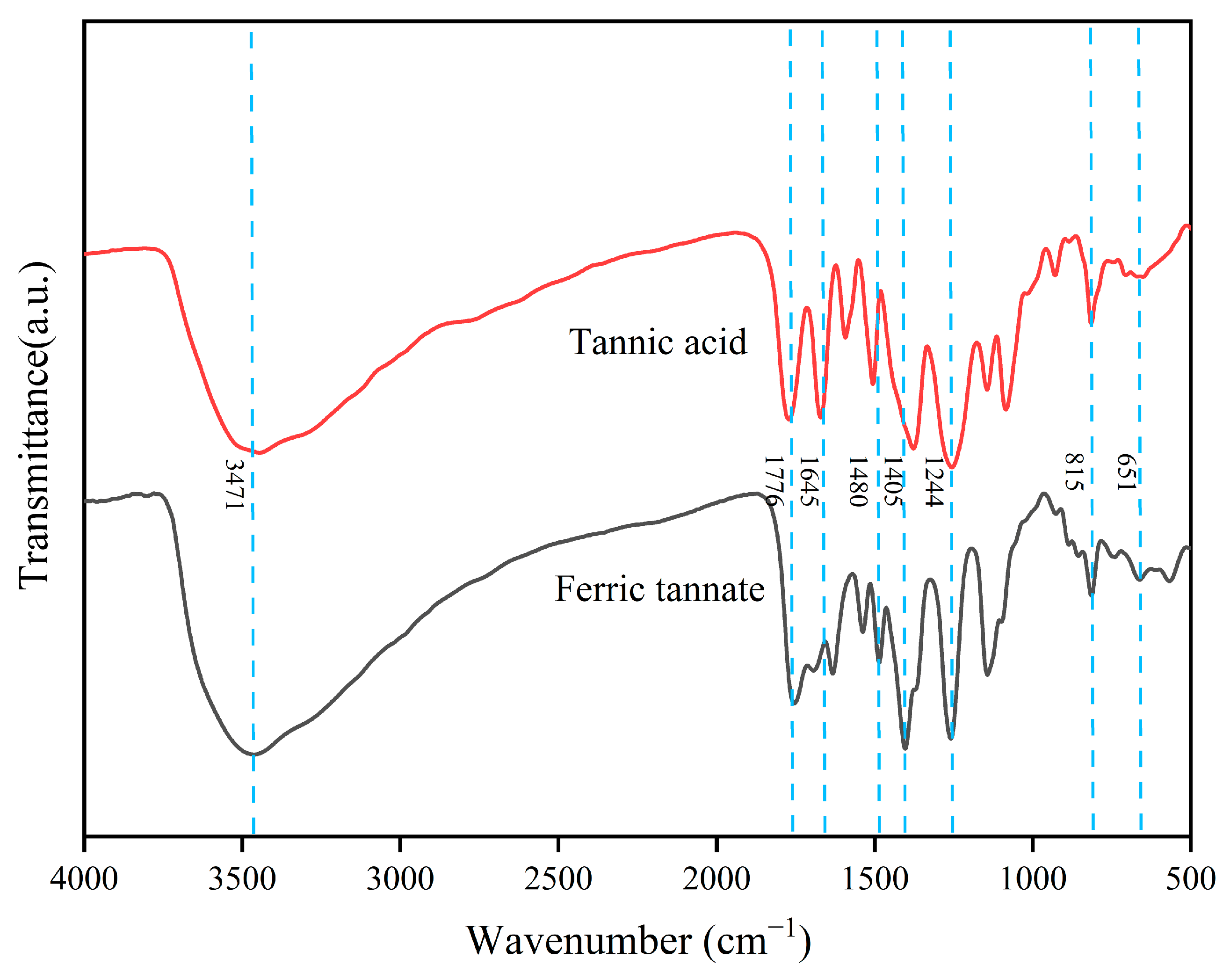
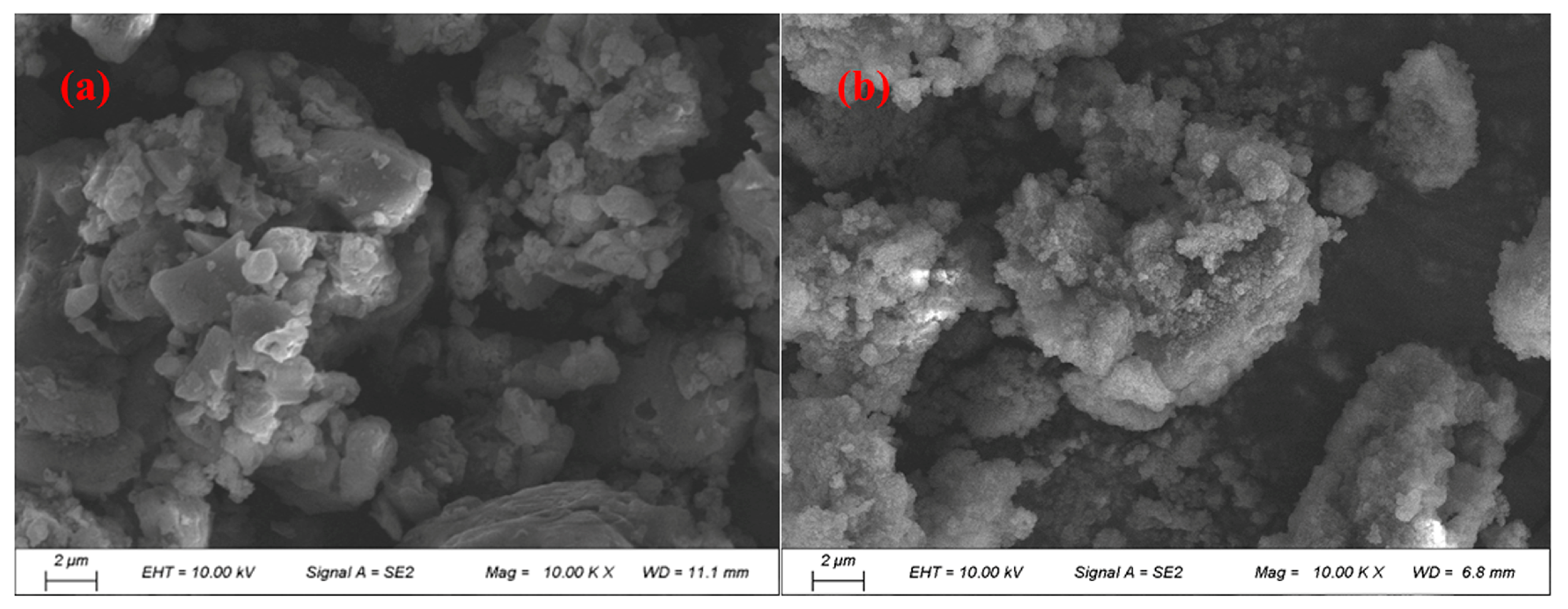
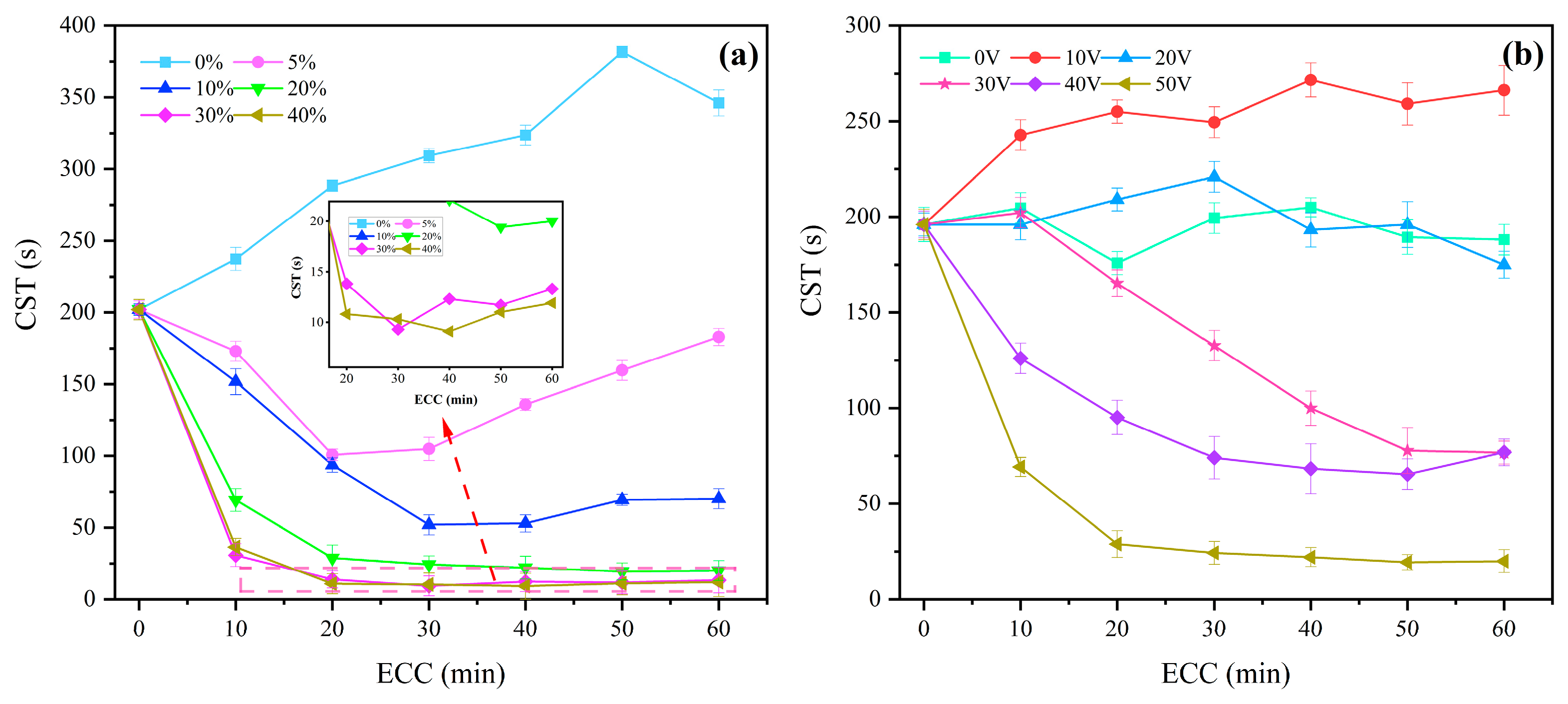
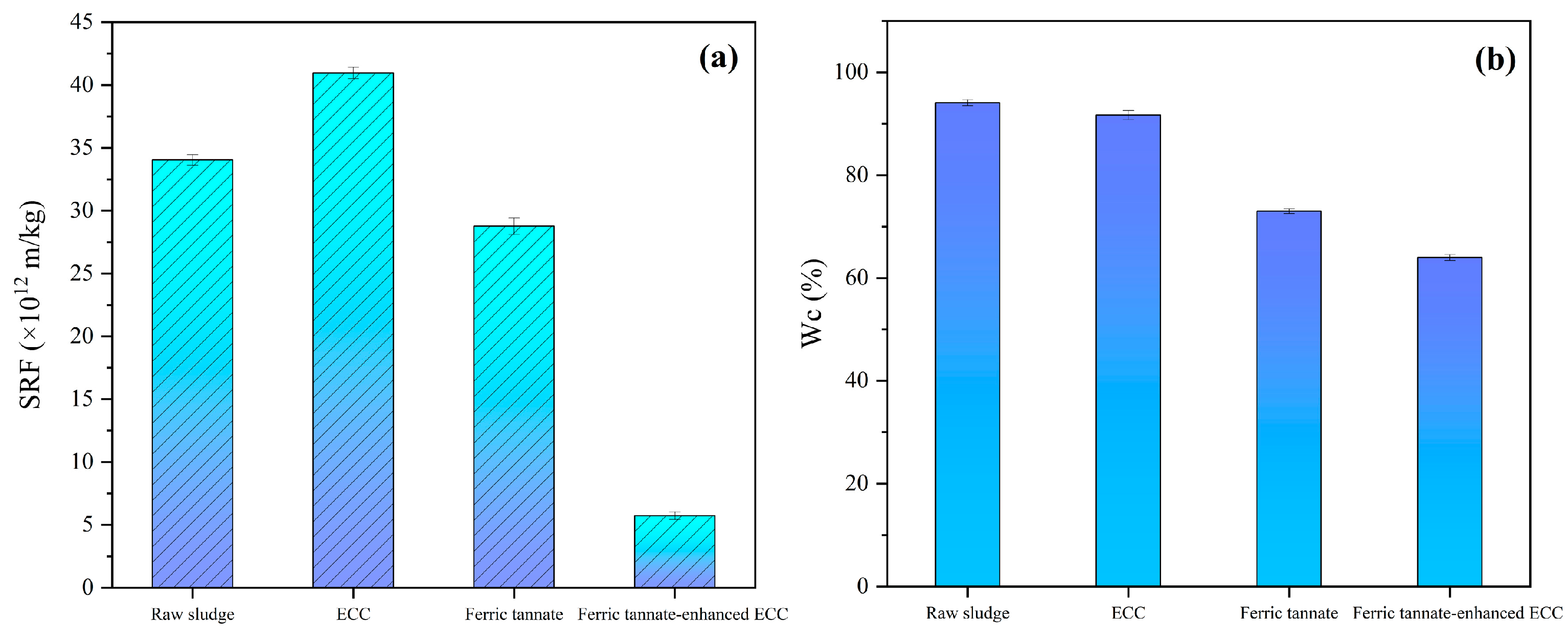
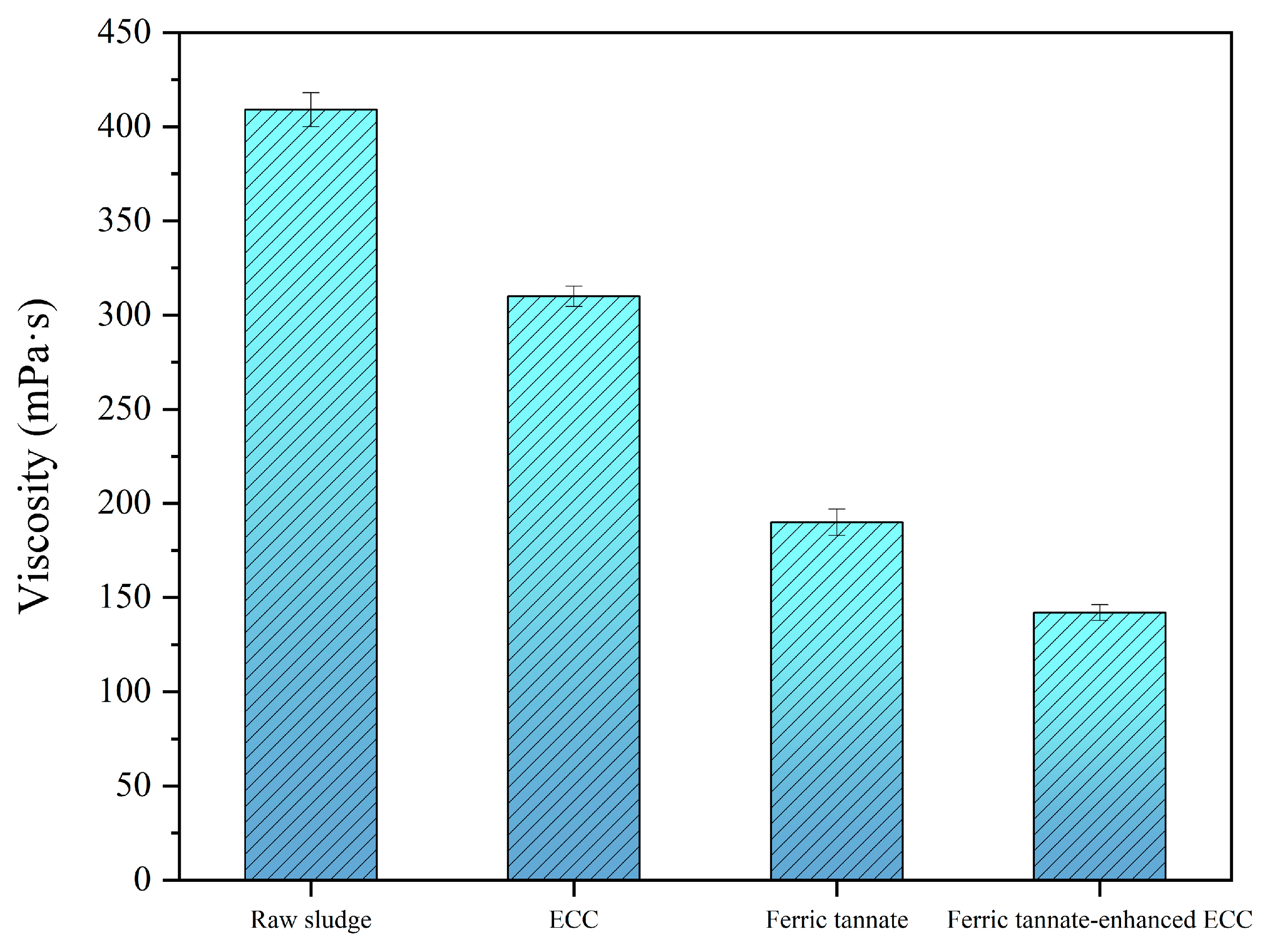
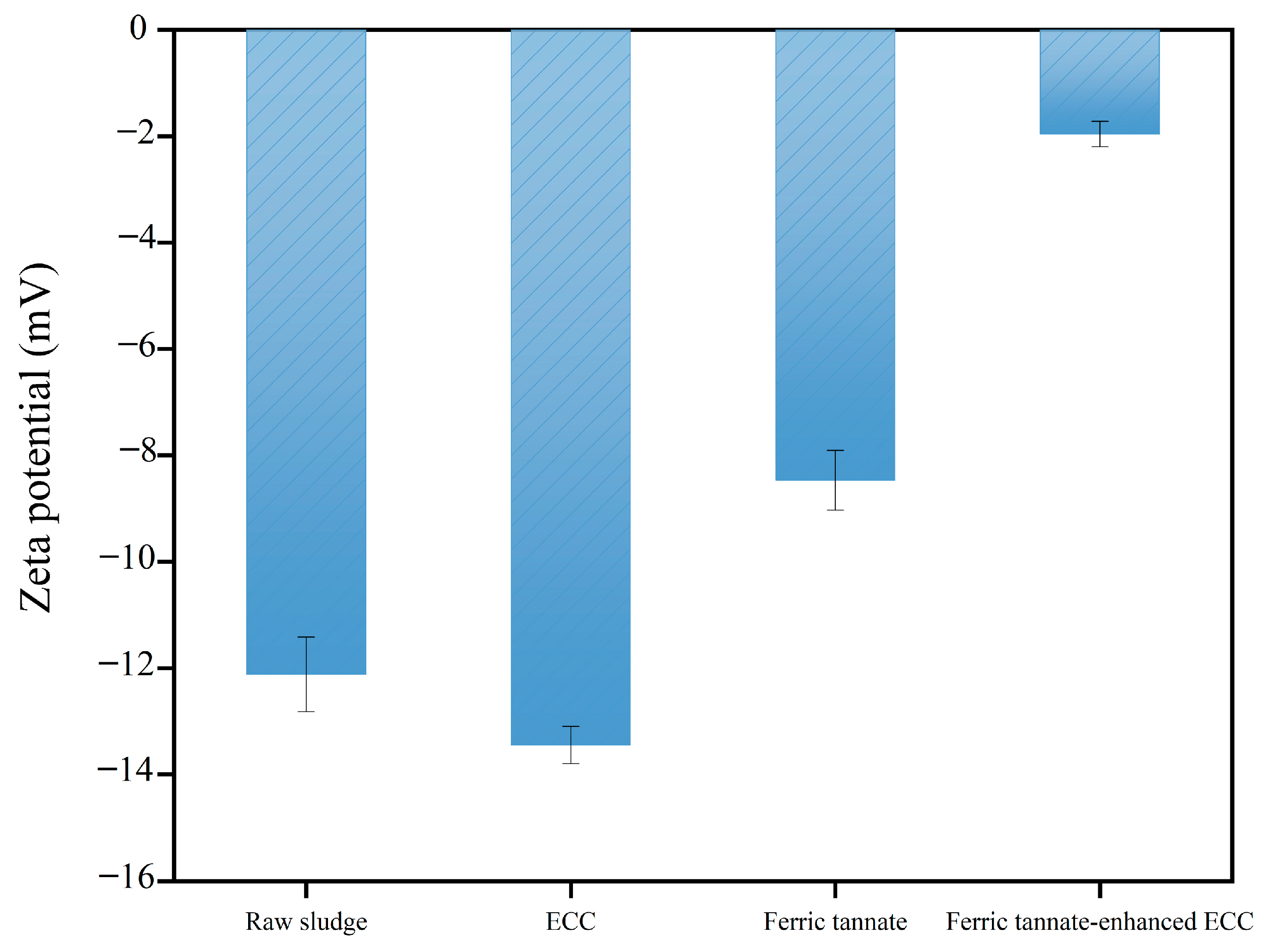
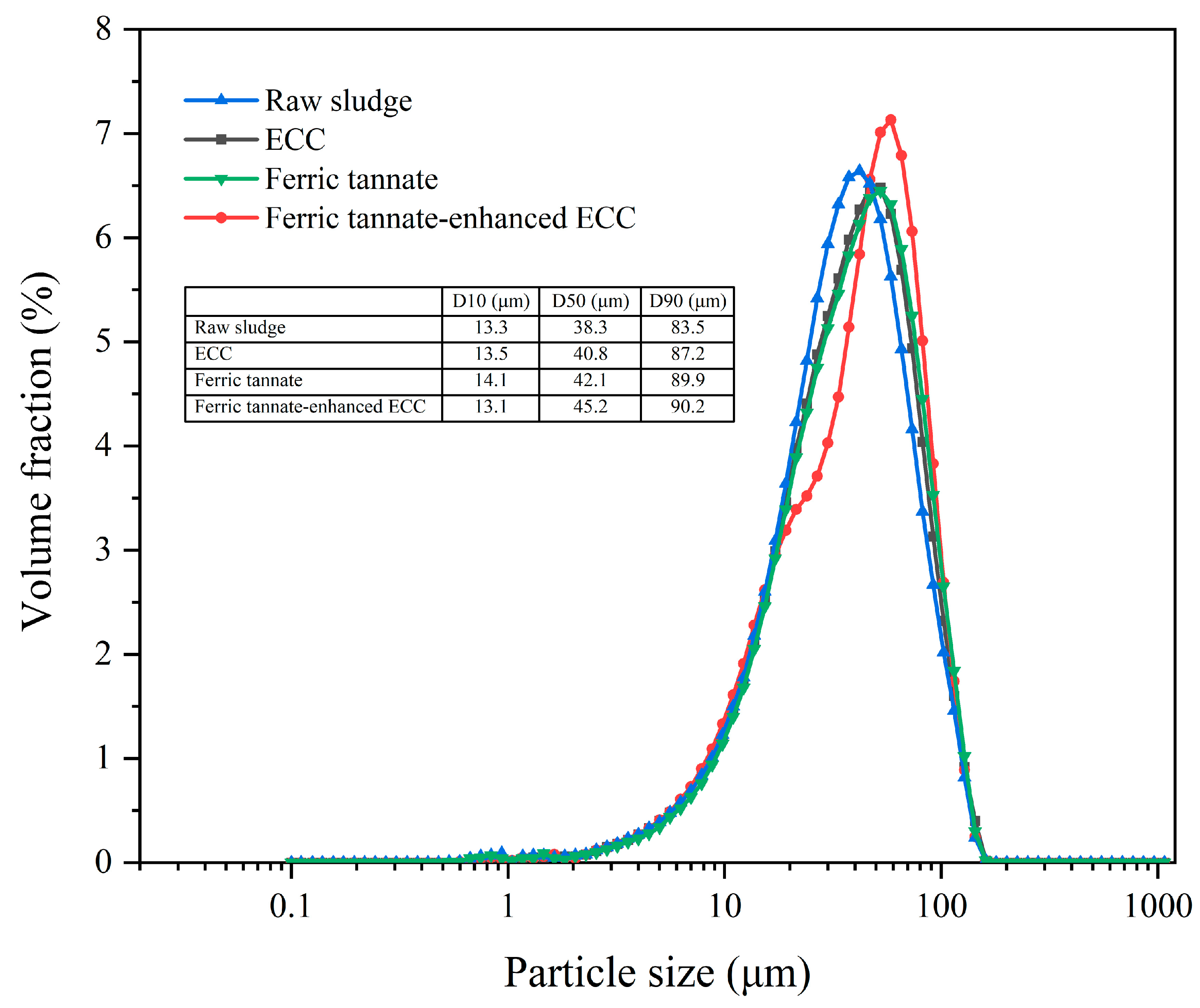

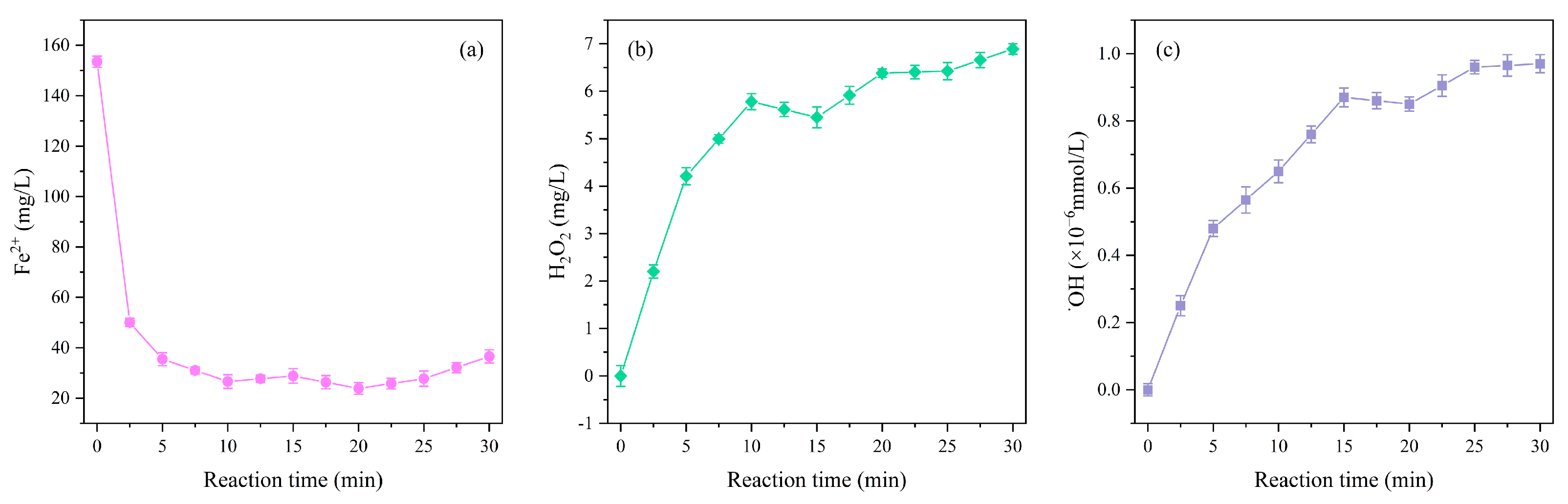
| Sample | TS (g/L) | VS (g/L) | CST (S) | SRF (m/kg) | pH | Wc of Dewatered Sludge Cake (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw sludge | 32.0 ± 0.4 | 20.1 ± 0.4 | 183 ± 3.5 | 34.6 ± 0.2 | 6.98 ± 0.03 | 94.6 ± 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhu, N.; Ge, D. Ferric Tannate-Enhanced Electrochemical Conditioning Process for Improving Sludge Dewaterability. Water 2025, 17, 2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162424
Yu Y, Feng J, Zhu N, Ge D. Ferric Tannate-Enhanced Electrochemical Conditioning Process for Improving Sludge Dewaterability. Water. 2025; 17(16):2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162424
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Yalin, Junkun Feng, Nanwen Zhu, and Dongdong Ge. 2025. "Ferric Tannate-Enhanced Electrochemical Conditioning Process for Improving Sludge Dewaterability" Water 17, no. 16: 2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162424
APA StyleYu, Y., Feng, J., Zhu, N., & Ge, D. (2025). Ferric Tannate-Enhanced Electrochemical Conditioning Process for Improving Sludge Dewaterability. Water, 17(16), 2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162424





