Trophic Ecology of Slender Snipe Eel Nemichthys scolopaceus Richardson, 1848 (Anguilliformes: Nemichthyidae) in the Central Mediterranean Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Samples Collection
2.2. Laboratory Analysis
2.3. Trophic Indexes
3. Results
3.1. Fish Metrics
3.2. Trophic Ecology
3.3. Feeding Strategy
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bilecenoglu, M.; Kaya, M.; Irmak, E. First records of the slender snipe eel, Nemichthys scolopaceus (Nemichthyidae), and the robust cusk-eel, Benthocometes robustus (Ophidiidae), from the Aegean Sea. Acta Ichthyol. Piscat. 2006, 36, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.G.; Smith, D.G. The eel family Nemichthyidae (Pisces, Anguilliformes). Dana Rep. 1978, 88, 1–71. [Google Scholar]
- Fishelson, L. Comparative morphology of deep-sea eels, with particular emphasis on gonads and gut structure. J. Fish. Biol. 1994, 44, 75–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.G.; Tighe, K.A. Snipe eels. Family Nemichthyidae. In Fishes of the Gulf of Maine, 3rd ed.; Collette, B.B., Klein-MacPhee, G., Eds.; Smithsonian Institute Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; pp. 100–101. [Google Scholar]
- Karmovskaya, E.S. Systematics and some ecology of the snipe eels of the family Nemichthyidae. Proc. Shirshov. Inst. Oceanol. 1982, 118, 151–161. [Google Scholar]
- Feagans-Bartow, J.N.; Sutton, T.T. Ecology of the oceanic rim: Pelagic eels as key ecosystem components. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 502, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, J.V., Jr.; Sulak, K.J.; Ross, S.W.; Necaise, A.M. Persistent near-bottom aggregations of mesopelagic animals along the North Carolina and Virginia continental slopes. Mar. Biol. 2008, 153, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.G.; Nielsen, J.G. Family Nemichthyidae: Snipe eels. In Fishes of the Western North Atlantic; Part 9; Böhlke, E.B., Ed.; Sears Foundation for Marine Research: New Haven, CT, USA, 1989; Volume 1, pp. 441–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charter, S.R. Nemichthyidae: Snipe eels. In The Early Stages of Fishes in the California Current Region; Moser, H.G., Ed.; California Cooperative Oceanic Fisheries Investigations (CalCOFI) Atlas: La Jolla, CA, USA, 1996; Volume 33, pp. 122–129. [Google Scholar]
- Bayhan, Y.K.; Ergüden, D.; Ayas, D. The first occurrence of male specimen of Nemichthys scolopaceus (Richardson, 1848) from Eastern Mediterranean. Turk. J. Marit. Mar. Sci. 2020, 6, 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.; Koyama, S.; Mochioka, N.; Aoyama, J.; Watanabe, S.; Tsukamoto, K. Vertical body orientation by a snipe eel (Nemichthyidae, Anguilliformes) in the deep mesopelagic zone along the West Mariana Ridge. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2014, 47, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, J.V., Jr.; Crabtree, R.E.; Sulak, K.J. Feeding at depth. In Deep-Sea Fishes; Marine and Freshwater Behaviour and Physiology; Randall, D.J., Farrell, A.P., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 271, pp. 115–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrett, N.R. Biogeography and the oceanic rim: A poorly known zone of ichthyofaunal interaction. UNESCO Tech. Pap. Mar. Sci. 1986, 49, 201–209. [Google Scholar]
- Bucklin, A.; Batta-Lona, P.G.; Questel, J.M.; McMonagle, H.; Wojcicki, M.; Llopiz, J.K.; Wiebe, P.H. Metabarcoding and morphological analysis of diets of mesopelagic fishes in the NW Atlantic Slope Water. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1411996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feagans, J.N. Trophic Ecology of the Slender Snipe eel, Nemichthys scolopaceus (Anguilliformes: Nemichthyidae). Master’s Thesis, Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Giordano, D.; Profeta, A.; Busalacchi, B.; Minutoli, R.; Guglielmo, L.; Bergamasco, A.; Granata, A. Summer larval fish assemblages in the Southern Tyrrhenian Sea (Western Mediterranean Sea). Mar. Ecol. 2015, 36, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falciai, L.; Minervini, R. Guida ai Crostacei Decapodi d’Europa, 2nd ed.; Ricca editore: Rome, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Tuset, V.M.; Lombarte, A.; Assis, C.A. Otolith atlas for the western Mediterranean, north and central eastern Atlantic. Sci. Mar. 2008, 72, 7–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.M.; Inada, T.; Iwamoto, T.; Scialabba, N. Gadiform Fishes of the World. FAO Fish. Synop. 1990, 125, 453. [Google Scholar]
- Bräger, Z.; Moritz, T. A scale atlas for common Mediterranean teleost fishes. Vertebr. Zool. 2016, 66, 275–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apollonio, S. Breeding Fecundity of the Glass Shrimp, Pasiphaea multidentata (Decapoda, Caridea), in the Gulf of Maine. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1969, 26, 1969–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Company, J.B.; Sardà, F. Growth parameters of deep-water decapod crustaceans in the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea: A comparative approach. Mar. Biol. 2000, 136, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilari, A.; Thessalou-Legaki, M.; Petrakis, G. Population structure and reproduction of the deep-water shrimp Plesionika martia (decapoda: Pandalidae) from the eastern Ionian Sea. J. Crustac. Biol. 2005, 25, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başusta, N.; Başusta, A. Length-Weight Relationship and Condition Factor of Hollowsnout grenadier (Coelorinchus caelorhincus, (Rinso, 1810) From Iskenderun Bay, northeastern Mediterranean, Turkey. International Marine & Freshwater Sciences Symposium Proceedings (MARFRESH2018). In Proceedings of the Book, International Marine & Freshwater Sciences Symposium, Kemer-Antalya, Turkey, 18–21 October 2018; pp. 300–302. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, R.; Gouveia, L.; Pinto, A.R.; Timóteo, V.; Delgado, J.; Henriques, P. Weight-length relationships of six shrimp species caught off the Madeira Archipelago, Northeastern Atlantic. Braz. J. Biol. 2018, 79, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra-Marrero, A.; Caballero-Méndez, C.; Espino-Ruano, A.; Couce-Montero, L.; Jiménez-Alvarado, D.; Castro, J.J. Length-weight relationships of 15 mesopelagic shrimp species caught during exploratory surveys off the Canary Islands (central eastern Atlantic). Sci. Mar. 2024, 88, e081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkas, L.; Oliphant, M.S.; Iverson, I.L.K. Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna and bonito in California waters. Calif. Dep. Fish Game’s Fish Bull. 1971, 152, 1–105. [Google Scholar]
- Hyslop, E.J. Stomach content analysis: A review of methods and their application. J. Fish Biol. 1980, 17, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacunda, J.S. Trophic relationships among demersal fishes in a coastal area of the Gulf of Maine. Fish. Bull. 1981, 79, 775–788. [Google Scholar]
- Costello, M.J. Predator feeding strategy and prey importance: A new graphical analysis. J. Fish Biol. 1990, 36, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundsen, P.A.; Gabler, H.M.; Staldvik, F.J. A new approach to graphical analysis of feeding strategy from stomach contents data modification of the Costello (1990) method. J. Fish. Biol. 1996, 48, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D.; Christensen, V. Primary production required to sustain global fisheries. Nature 1995, 374, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D.; Trites, A.W.; Capuli, E.V.; Christensen, V. Diet composition and trophic levels of marine mammals. ICES J. Mar. Sci 1998, 55, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D.; Froese, R.; Sa-a, P.; Palomares, M.; Christensen, V.; Rius, J. TrophLab Manual; ICLARM: Manila, Philippines, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Pauly, D.; Palomares, M.L. Approaches for dealing with three sources of bias when studying the fishing down marine food web phenomenon. CIESM Work. Ser. 2000, 12, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Piccinetti, C.; Murenu, M.; Cau, A. Risorse alieutiche profonde dell’Arcipelago delle Eolie. In Caratterizzazione Ambientale Marina del Sistema Eolie e dei Bacini Limitrofi di Cefalù e Gioia (EOCUMM94); Data Rep.; Faranda, F.M., Ed.; CoNISMa: Rome, Italy, 1995; pp. 363–368. [Google Scholar]
- Pandian, T.J. Intake, digestion, absorption, and conversion of food in the fishes Megalops cyprinoides and Ophiocephalus striatus. Mar. Biol. 1967, 1, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandian, T.J. Transformation of food in the fish Megalops cyprinoides. I. Influence of quality of food. Mar. Biol. 1967, 1, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froglia, C. Osservazioni Sull’alimentazione del Merluzzo (Merluccius merluccius L.) nel Medio Adriatico; Atti V Congresso SIBM: Nardò, Italy, 1973; pp. 327–341. [Google Scholar]
- Froglia, C. Observations on the feeding of Helicolenus dactylopterus (Delaroche) (Pisces, Scorpaenidae) in the Mediterranean Sea. Rapp. Comm. Int. Mer Méditerranée 1976, 23, 47–48. [Google Scholar]
- Battaglia, P.; Pagano, L.; Consoli, P.; Esposito, V.; Granata, A.; Guglielmo, L.; Pedá, C.; Romeo, T.; Zagami, G.; Vicchio, T.M.; et al. Consumption of mesopelagic prey in the Strait of Messina, an upwelling area of the central Mediterranean Sea: Feeding behaviour of the blue jack mackerel Trachurus picturatus (Bowdich, 1825). Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2020, 155, 103158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, P.; Andaloro, F.; Esposito, V.; Granata, A.; Guglielmo, L.; Guglielmo, R.; Musolino, S.; Romeo, T.; Zagami, G. Diet and trophic ecology of the lanternfish Electrona risso (Cocco 1829) in the Strait of Messina (central Mediterranean Sea) and potential resource utilization from the Deep Scattering Layer (DSL). J. Mar. Syst. 2016, 159, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmo, L.; Zagami, G. Role of euphausiids in DSL of Western Mediterranean Sea. Mem. Di Biol. Mar. E Di Oceanogr. 1985, 15, 191–206. [Google Scholar]
- Sardou, J.; Etienne, M.; Andersen, V. Seasonal abundance and vertical distributions of macroplankton and micronekton in the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Oceanol. Acta 1996, 19, 645–656. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, V.; François, F.; Sardou, J.; Picheral, M.; Scotto, M.; Nival, P. Vertical distributions of macroplankton and micronekton in the ligurian and tyrrhenian seas (northwestern mediterranean). Oceanol. Acta 1998, 21, 655–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, V.; Nival, P.; Caparroy, P.; Gubanova, A. Zooplankton community during the transition from spring bloom to oligotrophy in the open NW Mediterranean and effects of wind events. 1. Abundance and specific composition. J. Plankton Res. 2001, 23, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiebe, P.H.; D’Abramo, L. Distribution of euphausiid assemblages in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Biol. 1972, 15, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, J.D.; Demer, D.A.; McGehee, D.E.; Di Mento, R.; Borsani, J.F. Zooplankton in the Ligurian Sea: Part II. Exploration of their physical and biological forcing functions during summer 2000. J. Plankton Res. 2004, 26, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, W.D.; Nival, P.; Choe, S.M.; Picheral, M.; Gorsky, G. Vertical distribution and nutritional behaviour of Cyclothone braueri, Nematoscelis megalops, Meganyctiphanes norvegica and Salpa fusiformis in the NW Mediterranean mesopelagic zone. Int. Counc. Explor. Sea CM 2007, 3, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Guglielmo, L.; Costanzo, G.; Berdar, A. Ulteriore contributo alla conoscenza dei crostacei spiaggiati lungo il litorale messinese dello Stretto. Atti Soc. Peloritana 1973, 19, 129–156. [Google Scholar]
- Brancato, G.; Minutoli, R.; Granata, A.; Sidoti, O.; Guglielmo, L. Diversity and vertical migration of euphausiids across the Straits of Messina area. In Mediterranean Ecosystem: Structures and Processes; Faranda, F.M., Guglielmo, L., Spezie, G., Eds.; Springer: Milano, Italy, 2001; pp. 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Minutoli, R.; Guglielmo, L. Mesozooplankton carbon requirement in the Tyrrhenian Sea: Its vertical distribution, diel variability and its relation to particle flux. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 446, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartes, J.E. Diets of deep-water pandalid shrimps on the Western Mediterranean slope. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1993, 96, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartes, J.E. Feeding habits of pasiphaeid shrimps close to the bottom on the western Mediterranean slope. Mar. Biol. 1993, 117, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, G.W.; Earle, S.A. Notes on the natural history of snipe eels. Proc. Calif. Acad. Sci. 1970, 38, 99–103. [Google Scholar]





| Campaign | Fishing Area | Local Date | Lat. N | Long. E | Sampling Depth (m) | Local Time (Start–Finish) | Specimens Caught (Per Time) | Specimen ID Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial fishing | Gulf of Patti (ME) | May–June 2022 | 38°14.346′ | 15°7.818′ | 300–700 | - | 11 | 7CB, 13CB, 14CB, 15CB, 18CB, 21CB, 22CB, 23CB, 24CB, 25CB, 26CB |
| May–June 2023 | - | 12 | 34CB, 35CB, 36CB, 37CB, 38CB, 39CB, 40CB, 41CB, 42CB, 47CB, 48CB, 49CB | |||||
| NAUCRATES22 | Pa-Ca Canyon | 12/10/2022 | 38°25.91′ | 10°42.24′ | 309–305 | 12:53–17:35 | 1 | 28CB |
| 19/10/2022 | 38°13.65′ | 10°37.32′ | 323–358 | 22:20–1:47 | 1 | 31CB | ||
| 14/10/2022 | 38°15.00′ | 10°37.32′ | 370–311 | 12:30–16:33 | 2 | 32CB, 33CB | ||
| MEDINEA22 | Pa-Ca Canyon | 14/10/2022 | 38°03.60′ | 10°47.28′ | 332–349 | 19:07–23:07 | 2 | 29CB, 30CB |
| MEDITS24 | GSA10 | 21/06/2024 | 39°28.24′ | 15°44.27′ | 583–626 | 07:13–08:13 | 2 | 44CB, 45CB |
| 22/06/2024 | 39°13.18′ | 16°02.19′ | 83–86 | 06:51–07:21 | 1 | 50CB | ||
| 22/06/2024 | 39°06.21′ | 15°55.49′ | 634–619 | 14:46–15:46 | 1 | 46CB | ||
| 25/06/2024 | 38°10.56′ | 14°51.02′ | 26–18 | 12:00–12:30 | 1 | 51CB | ||
| 26/06/2024 | 38°07.70′ | 13°38.44′ | 568–529 | 16:15–17:15 | 1 | 43CB |
| Phylum/ | Family | Species/Taxa | %IRIi | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subphylum/ | Frequency | Number | Weight | ||||||
| Class/Order | n | % | n | % | n | % | |||
| CRUSTACEA/ | |||||||||
| Malacostraca/ | |||||||||
| Decapoda | |||||||||
| Pandalidae | Plesionika martia | 2 | 6.45 | 2 | 5.88 | 11.51 | 9.32 | 2.15 | |
| Plesionika sp. | 1 | 3.23 | 1 | 2.94 | 10.3 | 8.34 | 0.8 | ||
| Pasiphaeidae | Pasiphaea multidentata | 1 | 3.23 | 1 | 2.94 | 5.75 | 4.65 | 0.54 | |
| Sergestidae | Robustosergia robusta | 1 | 3.23 | 1 | 2.94 | 0.97 | 0.79 | 0.26 | |
| Penaeidae | Funchalia woodwardi | 1 | 3.23 | 1 | 2.94 | 0.29 | 0.23 | 0.22 | |
| Funchalia sp. | 3 | 9.68 | 3 | 8.82 | 0.53 | 0.43 | 1.96 | ||
| Decapoda unid. | 5 | 12.9 | 5 | 14.71 | 16.3 | 13.19 | 7.88 | ||
| Crustacea unid. | 6 | 19.35 | 6 | 17.65 | 19.55 | 15.82 | 14.17 | ||
| CHORDATA | |||||||||
| VERTEBRATA | |||||||||
| Teleostei | |||||||||
| Stomiiformes | Stomiidae | Stomias boa | 1 | 3.23 | 1 | 2.94 | 0.89 | 0.72 | 0.26 |
| Gadiformes | Macrouridae | Macrouridae unid. | 1 | 3.23 | 1 | 2.94 | 13.66 | 11.06 | 11.85 |
| 2 | |||||||||
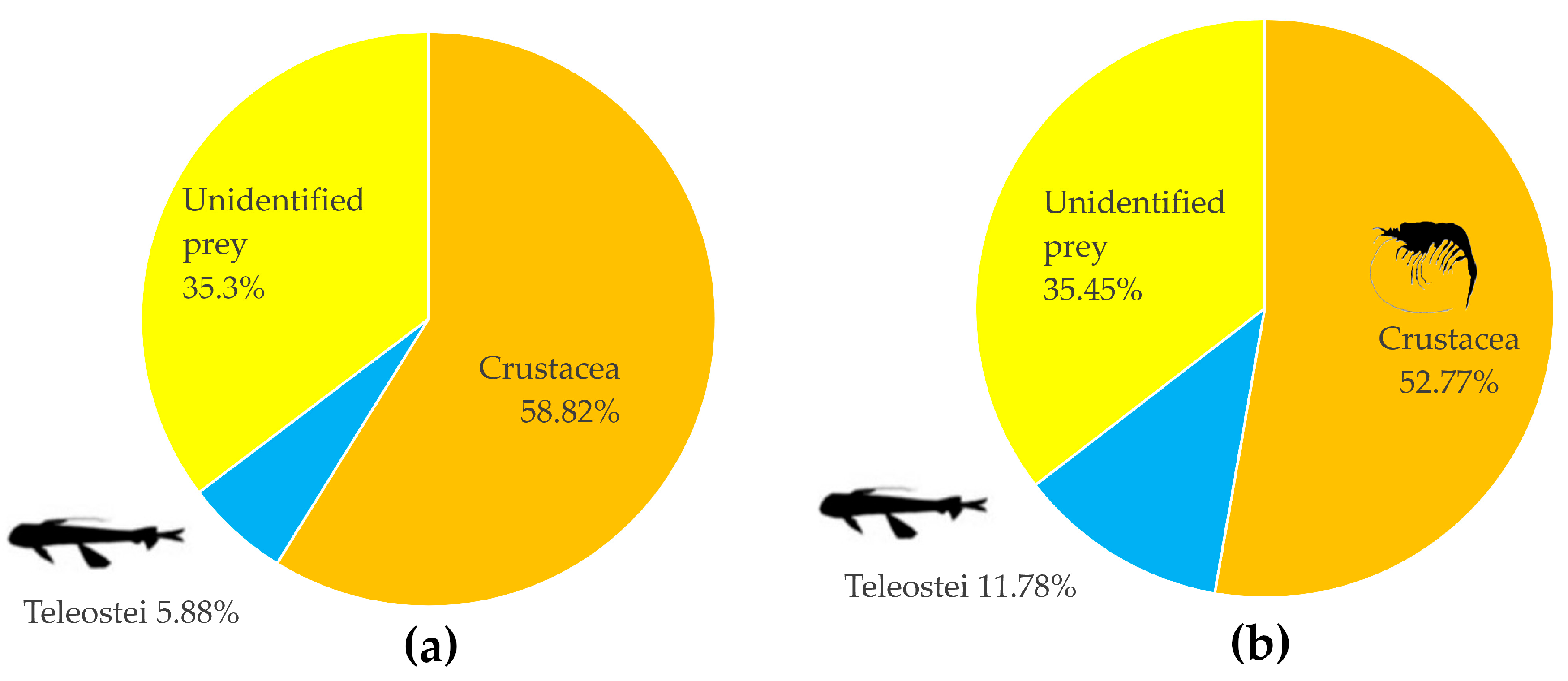
| Unidentified | 12 | 38.71 | 12 | 35.3 | 43.8 | 35.45 | 59.91 | ||
| Totals | 31 | 34 | 100 | 123.55 | 100 | 100 | |||
| This Paper | Faegans-Bartow, Sutton, 2014 [6] | Bucklin et al., 2024 [14] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Visual Method Only) | |||
| Examined specimens | 35 | 164 | 7 |
| Macrocrustacea | N = 20 (%N = 58.82%) | N = 131 (%N = 100%) | N = ~1 (%N = ~50%) |
| Amphipoda | N = 0 (%N = 0%) | N = 0 (%N = 0%) | N = ~1 (%N = ~20%) |
| Teleostei | N = 2 (%N = 5.88%) | N = 0 (%N = 0%) | N = 0 (%N = 0%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geraci, A.; Scipilliti, A.; Guglielmo, Y.; Lauritano, C.; Profeta, A.; Minutoli, R.; Veneziano, F.; Di Paola, D.; Massi, D.; Guglielmo, L.; et al. Trophic Ecology of Slender Snipe Eel Nemichthys scolopaceus Richardson, 1848 (Anguilliformes: Nemichthyidae) in the Central Mediterranean Sea. Water 2025, 17, 2405. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162405
Geraci A, Scipilliti A, Guglielmo Y, Lauritano C, Profeta A, Minutoli R, Veneziano F, Di Paola D, Massi D, Guglielmo L, et al. Trophic Ecology of Slender Snipe Eel Nemichthys scolopaceus Richardson, 1848 (Anguilliformes: Nemichthyidae) in the Central Mediterranean Sea. Water. 2025; 17(16):2405. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162405
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeraci, Andrea, Andrea Scipilliti, Ylenia Guglielmo, Chiara Lauritano, Adriana Profeta, Roberta Minutoli, Francesca Veneziano, Davide Di Paola, Daniela Massi, Letterio Guglielmo, and et al. 2025. "Trophic Ecology of Slender Snipe Eel Nemichthys scolopaceus Richardson, 1848 (Anguilliformes: Nemichthyidae) in the Central Mediterranean Sea" Water 17, no. 16: 2405. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162405
APA StyleGeraci, A., Scipilliti, A., Guglielmo, Y., Lauritano, C., Profeta, A., Minutoli, R., Veneziano, F., Di Paola, D., Massi, D., Guglielmo, L., Carbonara, P., & Granata, A. (2025). Trophic Ecology of Slender Snipe Eel Nemichthys scolopaceus Richardson, 1848 (Anguilliformes: Nemichthyidae) in the Central Mediterranean Sea. Water, 17(16), 2405. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162405










