Addition of Heterotrophic Nitrification and Aerobic Denitrification Bacterial Agents to Enhance Bio-Nests Treating Low Carbon-to-Nitrogen Ratio Municipal Wastewater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Seed Sludge, HN-AD Strains, and Wastewater
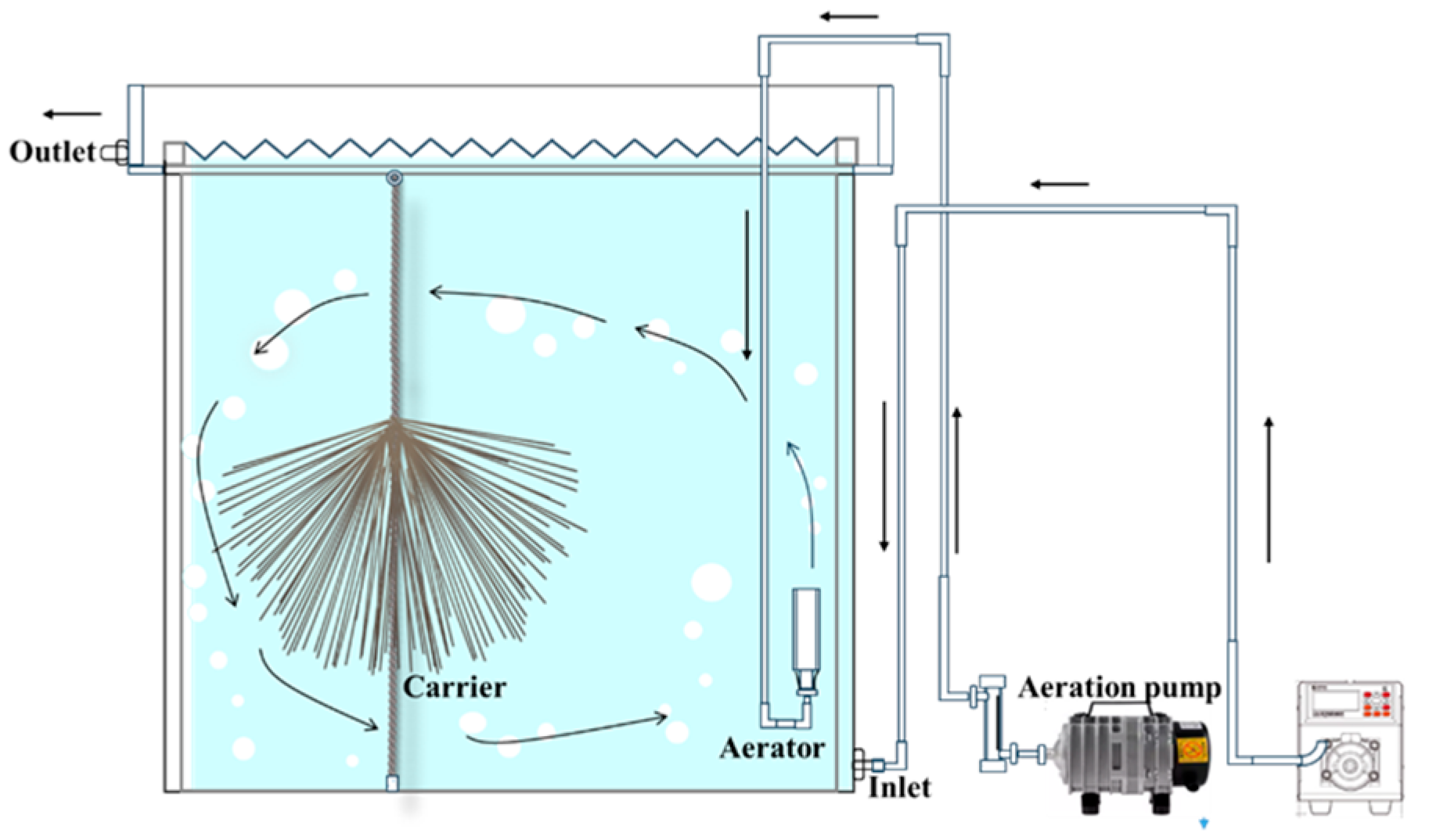
2.2. Experimental Reactor Setup and Operating Conditions
2.3. Biological Viability
2.4. Extracellular Polymeric Substance Extraction
2.5. DNA Extraction, Metagenomic Sequencing, and Analyses
2.6. Analytical Methods
3. Results
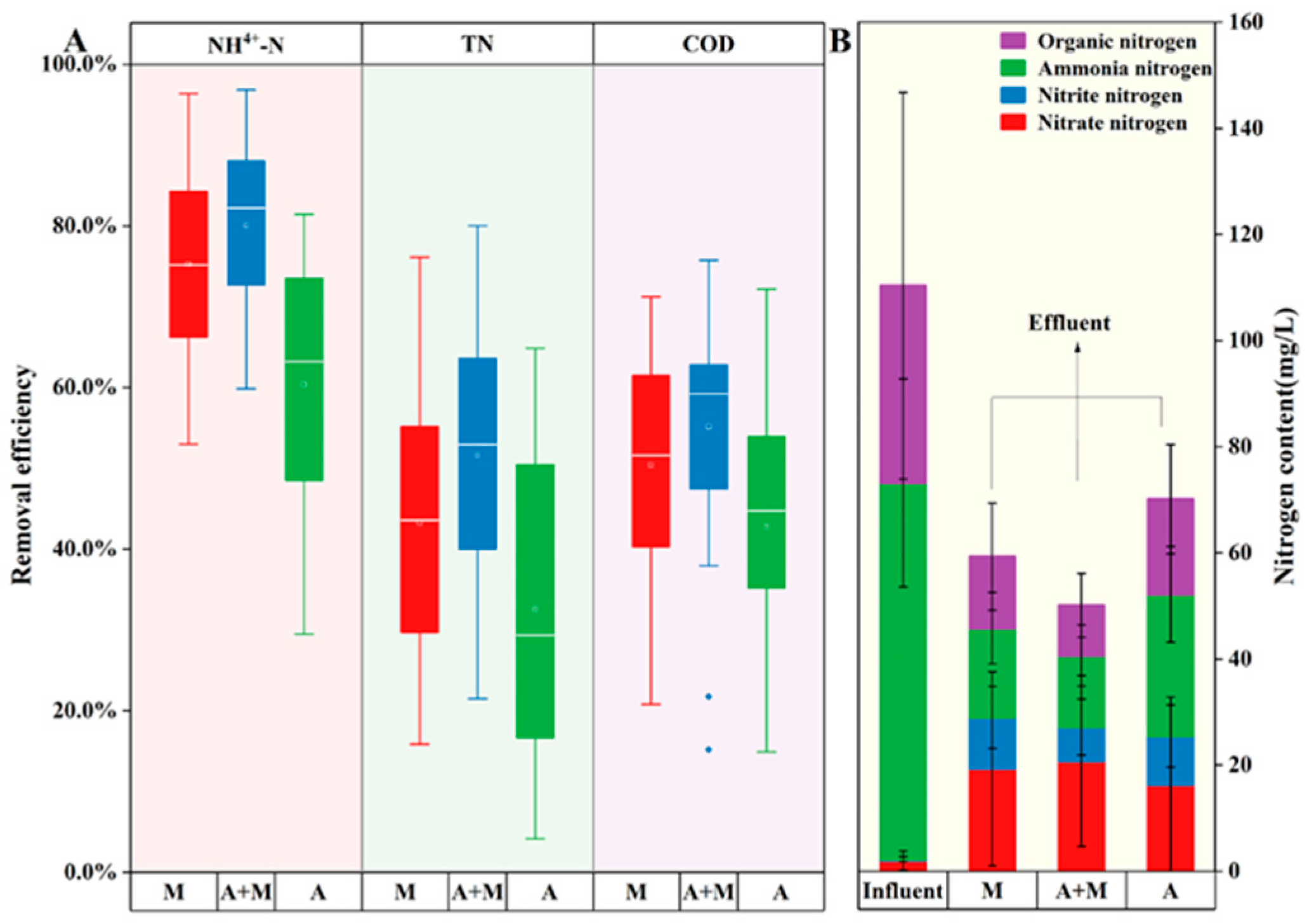
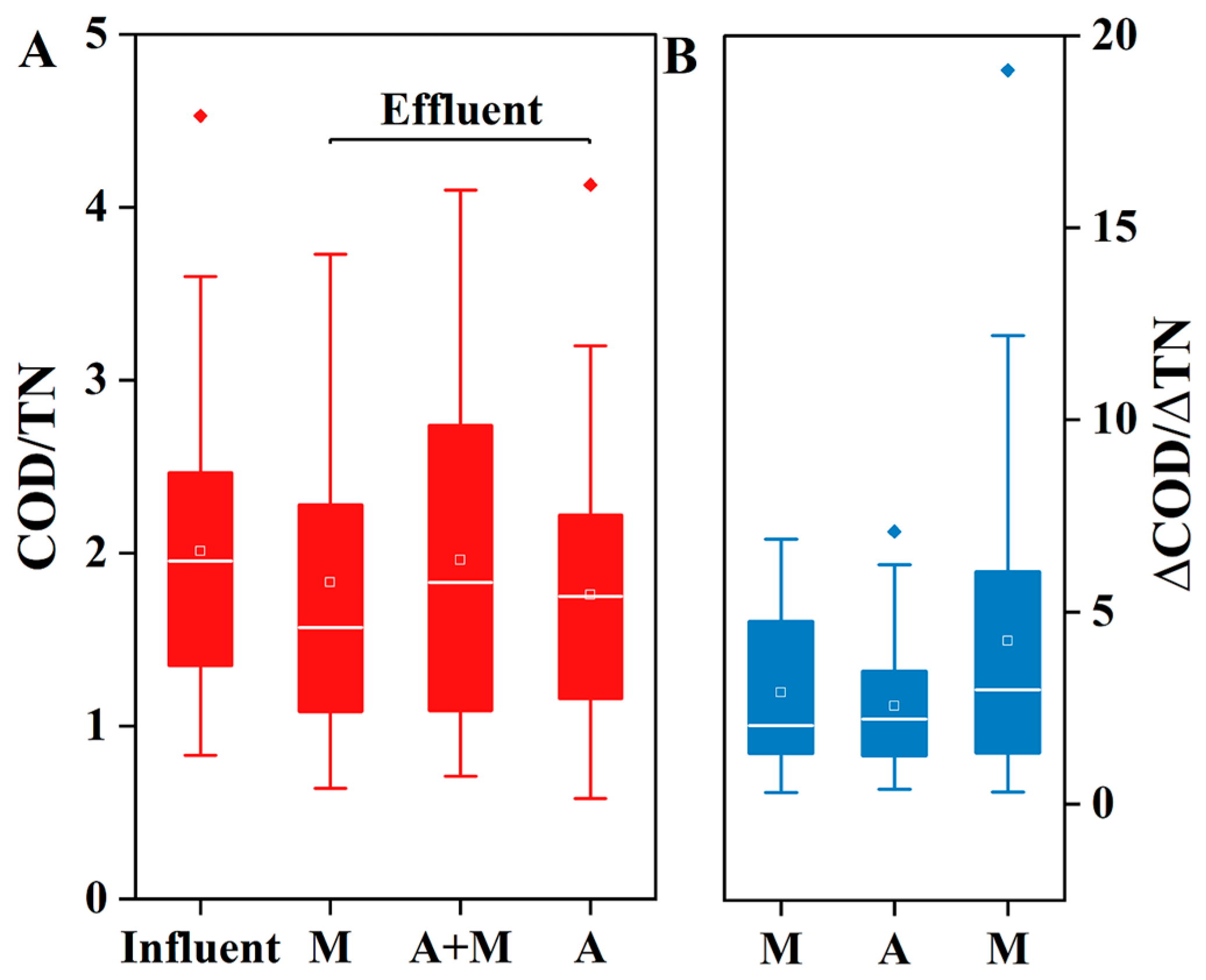
3.1. Pollutant Removal Capability and Carbon Source Utilization
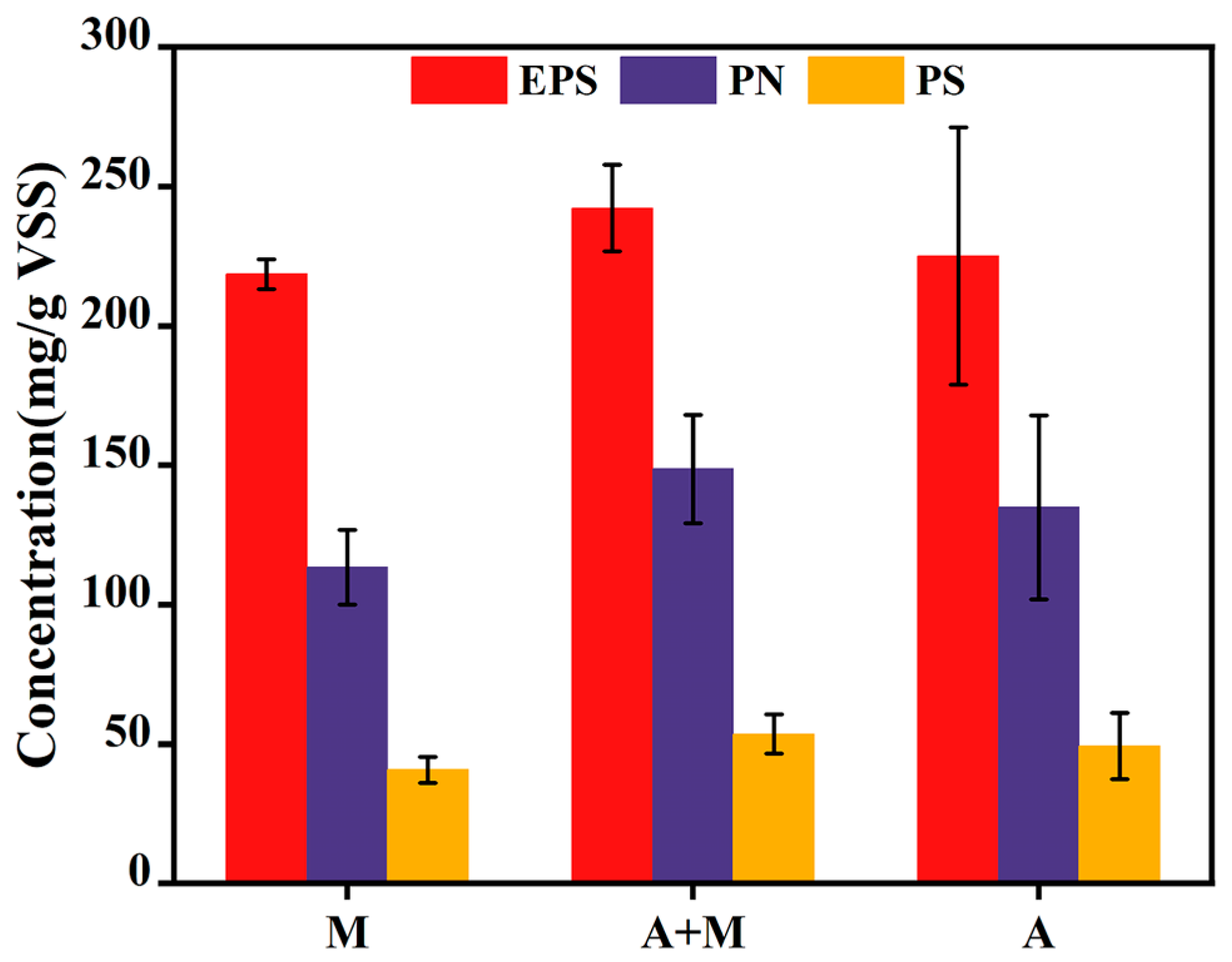
3.2. Influence of HN-AD Strain Agents on Biomass
3.3. Influence of HN-AD Strain Agents on Biological Viability
3.4. Microbial Community Differences in Reactors with and Without HN-AD Strains
3.5. Role of HN-AD Bacterial Stains in Nitrogen Conversion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Enhanced performance: the A+M reactor (HN-AD strains+activated sludge) achieved the highest removal efficiencies for NH4+-N (82.2%), TN (52.9%), and COD (51.6%), with a 40% reduction in carbon consumption per unit TN removed compared to conventional systems.
- Microbial synergy: dominance of Acinetobacter sp. Z1 (6.1%) and K. variicola L3 (1.1%) in the A+M reactor, alongside increased biodiversity (Proteobacteria, Bacteroidota), confirmed the synergistic role of HN-AD bacteria with native sludge communities.
- Biofilm robustness: high EPS content (242.26 mg/g-VSS) and PN/PS ratio (2.77) in the A+M reactor indicated stable biofilm activity, facilitated by modified basalt fiber carriers.
- Metabolic flexibility: gene annotation revealed complementary nitrogen pathways (nitrification, denitrification, DNRA) in the A+M system, explaining its superior performance under low C/N conditions.
- Future research directions include the following:
- Long-term stability: evaluate the reactor performance over extended periods (>1 year) to assess microbial community shifts and potential loss of HN-AD strains.
- Pathogen control: investigate disinfection strategies (e.g., UV, chlorination) to mitigate risks from pathogenic strains like K. variicola L3 in effluent reuse.
- Full-scale validation: test the technology in pilot-scale reactors with real wastewater to optimize carrier design, aeration, and operational parameters.
- Carbon source alternatives: explore low-cost carbon supplements (e.g., agricultural waste) to further improve denitrification efficiency.
- Mechanistic modeling: develop kinetic models integrating HN-AD bacterial growth and nitrogen pathways for process prediction and control.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, B.; Cui, Y.; Antwi, P.; Li, R.; Zhou, A.; Li, J.; Yue, X. Advancing the treatment of low carbon-to-nitrogen ratio municipal wastewater using a novel microaerobic sludge bed approach: Insights into enhanced performance and functional microbial community. Environ. Res. 2024, 258, 119461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Hao, Q.; Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liang, Z.; Jiang, C. Mitigating nitrous oxide emissions from low carbon to nitrogen ratio wastewater treatment: Utilizing sugarcane bagasse fermentation liquid for constructed wetlands. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 406, 131088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Li, Z.; Hu, Y.; Shi, L.; Liu, R.; Shi, L.; Chen, L.; Zhan, X. What’s the best way to achieve successful mainstream partial nitritation-anammox application? Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 1045–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Xue, T.; Li, B.; Dai, X.; Peng, Y. Treating low carbon/nitrogen (C/N) wastewater in simultaneous nitrification-endogenous denitrification and phosphorous removal (SNDPR) systems by strengthening anaerobic intracellular carbon storage. Water Res. 2015, 77, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, R.; Huang, M.; Liu, F.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Rittmann, B.E. How Comamonas testosteroni and Rhodococcus ruber enhance nitrification in the presence of quinoline. Water Res. 2023, 229, 119455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Li, D.; Liu, Q.; Tao, Y.; He, X.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Gao, P. Effect of organic carbon on nitriffication efficiency and community composition of nitrifying bioffilms. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, H.; Zhou, X.; Arslan, M.; Luo, Z.; Wei, J.; Wu, Z.; Gamal El-Din, M. Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification process: Promising but a long way to go in the wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, X.; Li, Q.; Ji, M.; Yan, G.; Guo, S. Isolation and niche characteristics in simultaneous nitrification and denitrification application of an aerobic denitrifier, Acinetobacter sp. YS2. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 302, 122799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shailaja, A.; Bruce, T.F.; Gerard, P.; Powell, R.R.; Pettigrew, C.A.; Kerrigan, J.L. Comparison of cell viability assessment and visualization of Aspergillus niger biofilm with two fluorescent probe staining methods. Biofilm 2022, 4, 100090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Fang, H.H.P. Extraction of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of sludges. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 95, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frølund, B.; Palmgren, R.; Keiding, K.; Nielsen, P.H. Extraction of extracellular polymers from activated sludge using a cation exchange resin. Water Res. 1996, 30, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Feng, J.; Ouyang, Z.; Yu, J.; Hou, H.; Chi, R. Dynamic elution of residual ammonium leaching agent from weathered crust elution-deposited rare earth tailings by magnesium chloride. Environ. Res. 2022, 210, 112935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Yin, H.; Jin, X.; Zhao, D.; Liu, Y.; Du, A.; Liu, X.; O’Mullane, A.P. A practical FeP nanoarrays electrocatalyst for efficient catalytic reduction of nitrite ions in wastewater to ammonia. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2023, 325, 122353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yun, H.; Peng, L.; Ji, J.; Wang, W.; Li, X. Deciphering the potential role of quorum quenching in efficient aerobic denitrification driven by a synthetic microbial community. Water Res. 2024, 251, 121162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odedishemi Ajibade, F.; Wang, H.-C.; Guadie, A.; Fausat Ajibade, T.; Fang, Y.-K.; Muhammad Adeel Sharif, H.; Liu, W.-Z.; Wang, A.-J. Total nitrogen removal in biochar amended non-aerated vertical flow constructed wetlands for secondary wastewater effluent with low C/N ratio: Microbial community structure and dissolved organic carbon release conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 322, 124430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Hou, J.; Wu, J.; Miao, L.; You, G.; Ao, Y. Intimately coupled photocatalysis and biodegradation for effective simultaneous removal of sulfamethoxazole and COD from synthetic domestic wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, X.; Liu, C.; Tang, S.-Q.; Guo, T.-T.; Pan, L.; Xue, Y.-P.; Zheng, Y.-G. Characterization of Acinetobacter indicus ZJB20129 for heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification isolated from an urban sewage treatment plant. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Ye, Q.; Wang, X.; Sheng, J.; Yu, X.; Zhao, S.; Zou, X.; Zhang, W.; Xue, G. Applying sludge hydrolysate as a carbon source for biological denitrification after composition optimization via red soil filtration. Water Res. 2024, 249, 120909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Wei, J.; Fang, Z.; Li, S.; Rong, X.; Luo, Z.; Liang, Z.; et al. Organic and inorganic nitrogen removals by an ureolytic heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification strain Acinetobacter sp. Z1: Elucidating its physiological characteristics and metabolic mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 362, 127792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phanwilai, S.; Kangwannarakul, N.; Noophan, P.; Kasahara, T.; Terada, A.; Munakata-Marr, J.; Figueroa, L.A. Nitrogen removal efficiencies and microbial communities in full-scale IFAS and MBBR municipal wastewater treatment plants at high COD:N ratio. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2020, 14, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, X.; Liu, J.F.; Huan, H.; Luo, Z.; Wu, Z. Feasibility of using basalt fiber as biofilm Carrier to construct bio-nest for wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2018, 212, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Hu, H.; Qiu, W.; Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Zhao, C.; Shi, X.; Xu, J. Community diversity and biofilm characteristic response to low temperature and low C/N ratio in a suspended carrier biofilm reactor. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 22212–22222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, G.-P.; Yu, H.-Q.; Li, X.-Y. Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, X.; Du, Q.; Gao, F.; Wang, Z.; Wu, G.; Guo, W.; Hao Ngo, H. Assessing the Long-Term performance of an integrated microbial fuel Cell-Anaerobic membrane bioreactor for swine wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 493, 152772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran-Bedolla, J.; Garza-Ramos, U.; Rodríguez-Medina, N.; Aguilar Vera, A.; Barrios-Camacho, H. Exploring the environmental traits and applications of Klebsiella variicola. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 2233–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, P.; Gong, S.; Wang, C.; Shu, Y.; Wu, X.; Tian, C.; Donde, O.O.; Cai, P.; Wu, H.; Xiao, B. Effects of organic carbon consumption on denitrifier community composition and diversity along dissolved oxygen vertical profiles in lake sediment surface. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2020, 38, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Gao, K.; Yang, L.; Lu, Y. Successional action of Bacteroidota and Firmicutes in decomposing straw polymers in a paddy soil. Environ. Microbiome 2023, 18, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laczi, K.; Bodor, A.; Kovács, T.; Magyar, B.; Perei, K.; Rákhely, G. Methanogenesis coupled hydrocarbon biodegradation enhanced by ferric and sulphate ions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIlroy, S.J.; Karst, S.M.; Nierychlo, M.; Dueholm, M.S.; Albertsen, M.; Kirkegaard, R.H.; Seviour, R.J.; Nielsen, P.H. Genomic and in situ investigations of the novel uncultured Chloroflexi associated with 0092 morphotype filamentous bulking in activated sludge. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2223–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.-J.; Ye, Y.-L.; Li, Y.-K.; Fu, G.-Y.; Wu, Y.-H.; Sun, C.; Xu, X.-W. Polysaccharide metabolic pattern of Cytophagales and Flavobacteriales: A comprehensive genomics approach. Front. Mar. Sci. 2025, 12, 1551618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Hanada, S.; Imachi, H.; Ohashi, A.; Harada, H.; Kamagata, Y. Anaerolinea thermolimosa sp. nov., Levilinea saccharolytica gen. nov., sp. nov. and Leptolinea tardivitalis gen. nov., sp. nov., novel filamentous anaerobes, and description of the new classes Anaerolineae classis nov. and Caldilineae classis nov. in the bacterial phylum Chloroflexi. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; He, Z.; Li, C.; Lichtfouse, E.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J. Nitrogen removal by heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification bacteria: A review. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 317, 100227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
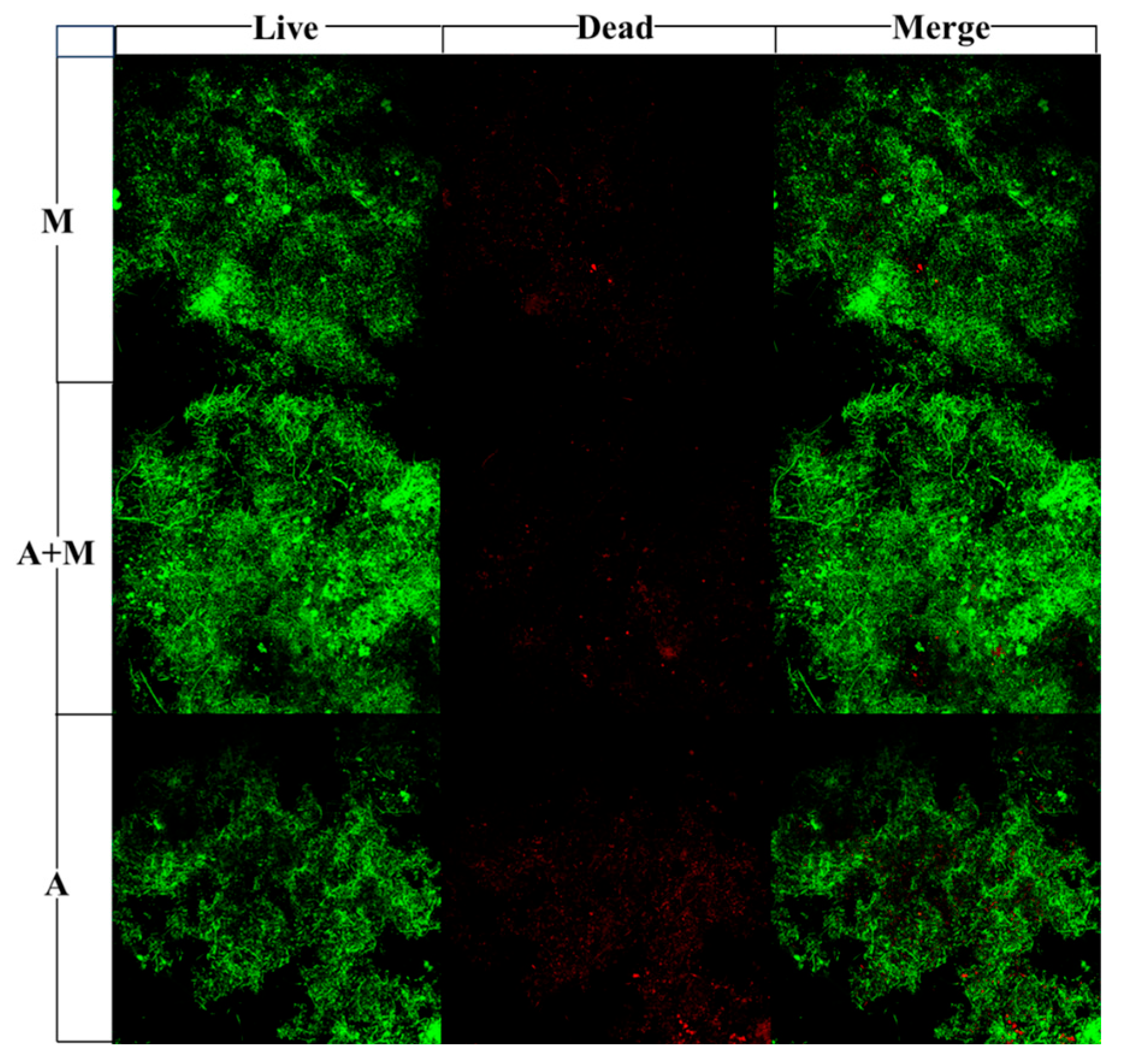
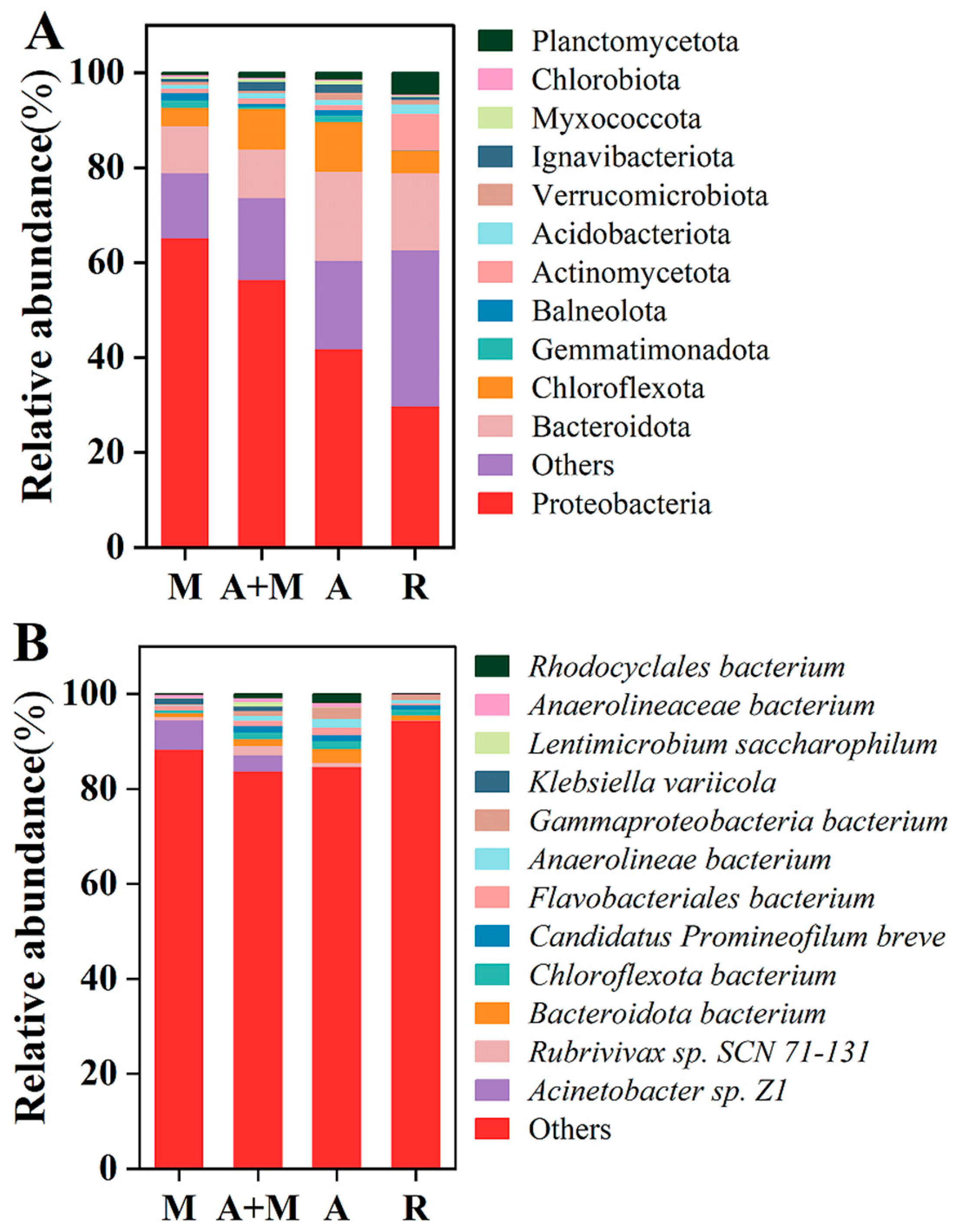
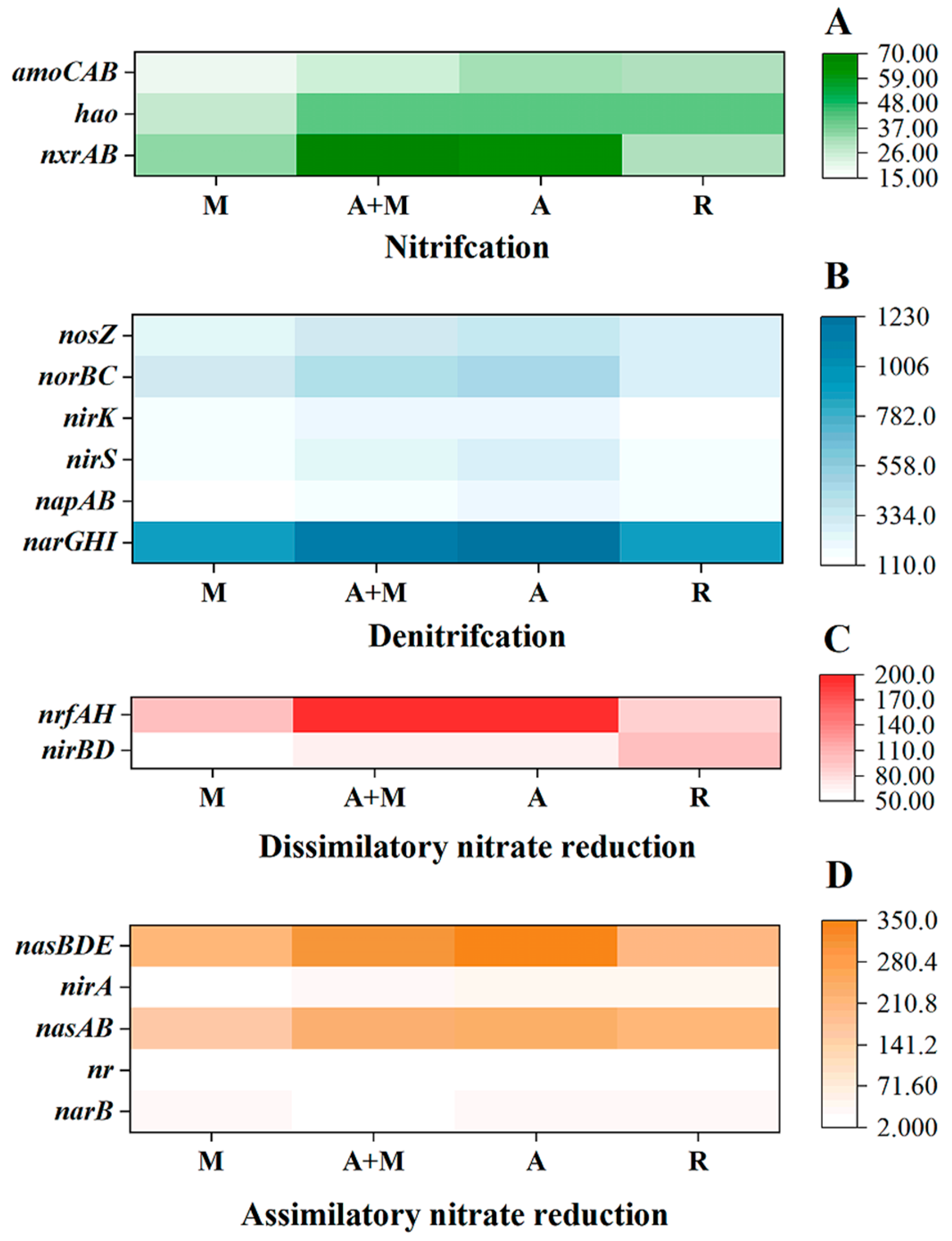
| Index | NH3+-N | NO3−-N | NO2−-N | TN | COD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mg/L) | 70.0 ± 19.6 | 2.0 ± 1.8 | 0.3 ± 0.5 | 110.3 ± 34.2 | 203.2 ± 57.8 |
| Group | SS (mg/L) | VSS (mg/L) | VSS/SS |
|---|---|---|---|
| RAW | 3698.00 ± 154.65 | 1928.00 ± 148.95 | 0.52 ± 0.02 |
| M | 6633.33 ± 560.39 | 4673.33 ± 181.47 | 0.71 ± 0.03 |
| A+M | 10,520.00 ± 1075.13 | 7395.00 ± 838.50 | 0.70 ± 0.01 |
| A | 12,916.67 ± 1173.90 | 8968.33 ± 1029.44 | 0.69 ± 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diao, Q.; Quan, C.; Li, W.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z.; Rong, X.; Liang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z. Addition of Heterotrophic Nitrification and Aerobic Denitrification Bacterial Agents to Enhance Bio-Nests Treating Low Carbon-to-Nitrogen Ratio Municipal Wastewater. Water 2025, 17, 2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162392
Diao Q, Quan C, Li W, Zhou X, Liu Z, Rong X, Liang Z, Wang X, Wu Z. Addition of Heterotrophic Nitrification and Aerobic Denitrification Bacterial Agents to Enhance Bio-Nests Treating Low Carbon-to-Nitrogen Ratio Municipal Wastewater. Water. 2025; 17(16):2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162392
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiao, Qingxin, Chaolin Quan, Wanmeng Li, Xiangtong Zhou, Zhigang Liu, Xinshan Rong, Zhishui Liang, Xiao Wang, and Zhiren Wu. 2025. "Addition of Heterotrophic Nitrification and Aerobic Denitrification Bacterial Agents to Enhance Bio-Nests Treating Low Carbon-to-Nitrogen Ratio Municipal Wastewater" Water 17, no. 16: 2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162392
APA StyleDiao, Q., Quan, C., Li, W., Zhou, X., Liu, Z., Rong, X., Liang, Z., Wang, X., & Wu, Z. (2025). Addition of Heterotrophic Nitrification and Aerobic Denitrification Bacterial Agents to Enhance Bio-Nests Treating Low Carbon-to-Nitrogen Ratio Municipal Wastewater. Water, 17(16), 2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162392








