Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment and Monitoring of Pesticide Residues in Soil, Surface Water, and Groundwater in Northwestern Tunisia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
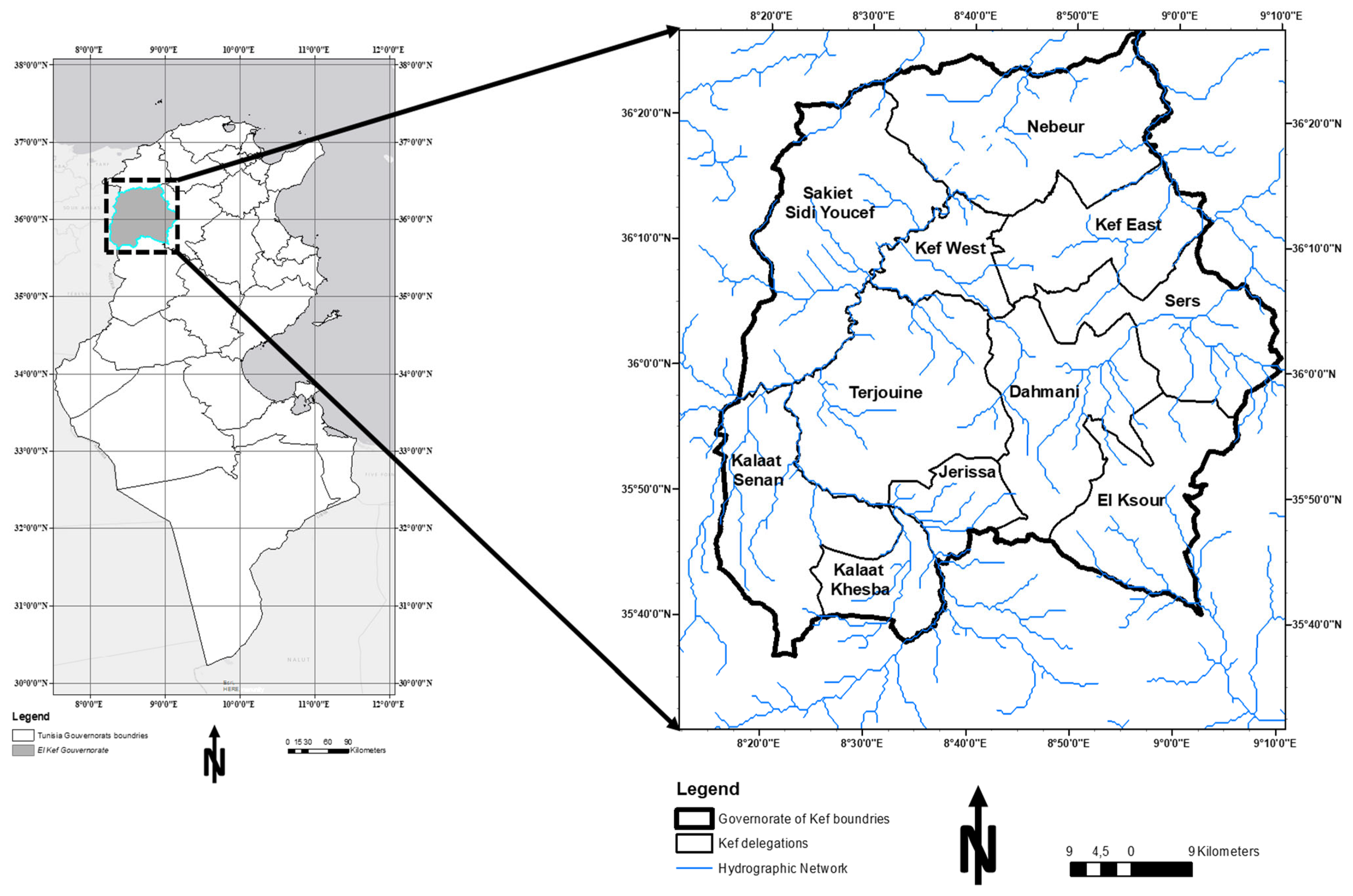
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Environmental Exposure Scenarios
2.3. Environmental Risk Assessment Methodology
2.3.1. Environmental Risk Perception of Studied Pesticide Residues
2.3.2. Monitoring of Pesticides in Soil and Water Samples
Water Sampling
Soil Sampling
2.3.3. Extraction and Analysis of Pesticide Residues in Water and Soil Samples
- A.
- Reagents and standards
- B.
- Pesticide residues in water samples
- C.
- Pesticide residues in soil samples
- D.
- LC-MS/MS
- E.
- Quality control
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Environmental Exposure Scenarios and Risks to the Environmental Compartments
3.1.1. Water Resources and Contamination Risks
3.1.2. Domestic Animals and the Poisoning Risk
3.1.3. Non-Target Organisms and the Toxicity Risk
3.1.4. Phytosanitary Practices and Attitudes Toward Environmental Risks
3.2. Potential Hazard Characterization of Studied Pesticide Residues
| Active Substances | Biological Activity a | Chemical Family | Toxicity Class (Who, 2020) b | CLP Classification c | DT50 d | Koc e | GUS f | Henry‘s Constant g | Kow h | LC50 Bees (mg/bee) | LC50 Worm (mg/kg) | LC50 Daphnia (mg/L) | EC50 Algae (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetamiprid | I | Neonicotinoid | II | Health: H302 Environment: H412 | 3 | 200 | 0.94 | 5.30 × 10−08 | 0.8 | 0.0089 | 9 | 49.8 | >98.3 |
| Chlorantraniliprole | I | Diamide | U | Health: H319, H335 Environment: H400, H410 | 204 | 362 | 3.51 | 3.2 × 10−09 | 2.86 | >0.004 | >1000 | 0.0116 | >2.0 |
| Chlorpyrifos | I | Organophosphate | II | Health: H301 Environment: H400, H410 | 27.6 | 5509 | 0.58 | 0.478 | 4.7 | 0 | 129 | 0.0001 | 0.48 |
| Chlorpyriphos Methyl | I, A | Organophosphate | III | Health: H317 Environment: H400, H410 | 1.24 | 4645 | 0.08 | 0.235 | 4.00 | 0 | 182 | 0.0006 | 0.57 |
| Cyflufenamid | F | Amide | NL | Health: H332 Environment: H400, H410, H411 | 25.3 | / | 1.12 | 2.81 × 10−02 | 4.7 | >0.1 | >500 | >1.73 | >0.828 |
| Cyprodinil | F | Anilinopyrimidine | III | Health: H317 Environment: H400, H410 | 45 | / | 1.06 | 6.60 × 10−03 | 4 | >0.075 | 192 | 0.22 | 2.6 |
| Dimethomorph | F | Morpholine | III | Environment: H411 | 44 | / | 2.26 | 2.5 × 10−05 | 2.68 | >0.102 | >500 | >20.1 | 29.2 |
| Epoxiconazole | F | Triazole | NL | Health: H351, H360Ddf Environment: H411 | 97.7 | 2.09 | 1.65 × 10−05 | 3.3 | >0.1 | >500 | >3.13 | >10.69 | |
| Flufenacet | H | Anilide | II | Health: H302, H317, H373 Environment: H400, H410 | 39 | 401 | 2.49 | 1.3 × 10−03 | 3.5 | >0.109 | 219 | 30.9 | 0.00204 |
| Fluopicolide | F | Benzamide | U | Environment: H400, H410 | 138.8 | / | 3.20 | 4.15 × 10−05 | 2.9 | >0.1 | >500 | >1.8 | 0.029 |
| Flupyradifurone | I | Organofluoride | II | Health: H302, H373 Environment: H400, H410, H412 | 130 | 98.4 | 4.24 | 8.2 × 10−08 | 1.2 | >0.2 | 185.6 | >77.6 | >100 |
| Imidacloprid | I | Neonicotinoid | II | Health: H302 Environment: H400, H410 | 174 | / | 3.69 | 1.7 × 10−10 | 0.57 | 0 | 10.7 | 85 | >10 |
| Isopropanil | H | Dinitroaniline | NL | Handling: H226 Environment: H400, H410 | / | 10,000 | 0.00 | 4.8 | 5.29 | / | / | >0.022 | / |
| Linuron | H | Urea | III | Health: H302, H351, H360Df, H373 Environment: H400, H410 | 48 | 842.8 | 2.11 | 2.00 × 10−04 | 3.0 | 0 | >500 | 0.31 | 0.016 |
| Metalaxyl | F | Anilide | II | Health: H302; H317 Environment: H412 | 14.1 | 162 | 2.06 | 1.60 × 10−05 | 1.75 | >0.2 | >1000 | 3.47 | 0.42 |
| Metalaxyl- M | F | Anilide | NL | Heath: H302, H318 | 14.1 | / | 2.64 | 3.50 × 10−05 | 1.71 | >0.1 | 830 | >100 | 36 |
| Metsulfuron methyl | H | Sulfonylurea | U | Environment: H400, H410 | 13.3 | / | 3.28 | 2.87 × 10−06 | −1.87 | 0 | >1000 | >43.1 | 0.113 |
| Penconazole | F | Triazole | III | H302, H361d, H400, H410 | 89.7 | / | 1.28 | 6.60 × 10−04 | 3.72 | >0.003 | >331.5 | 6.75 | 4.9 |
| Simazine | H | Triazine | U | Health: H351 Environment: H400, H410 | 90 | 130 | 2.20 | 5.60 × 10−05 | 2.3 | 0 | 1000 | 1.1 | 0.04 |
| S-metolachlor | H | Chloroacetamide | III | Health: H317 Environment: H400, H410 | 23.17 | / | 2.32 | 2.20 × 10−03 | 3.05 | >0.2 | 570 | 11.2 | 0.017 |
| Tetraconazole | F | Triazole | II | Health: H302, H332 Environment: H411 | 430 | / | 2.47 | 3.60 × 10−04 | 3.56 | 0.063 | 71 | 3 | 2.4 |
| Thiamethoxam | I | Neonicotinoid | NL | Health: H302 Environment: H400, H410 | 39 | 56.2 | 3.58 | 4.70 × 10−10 | −0.13 | 0 | >1000 | >100 | >100 |
| Triasulfuron | H | Sulfonylurea | U | Environment: H400, H410 | 38.5 | 60 | 4.59 | 8.00 × 10−05 | −0.59 | >0.1 | >1000 | >100 | 0.035 |
| Tribenuron-Methyl | H | Sulfonylurea | U | Health: H317, H373 Human: H400, H410 | 3.6 | 35 | 1.39 | 1.00 × 10−08 | 0.38 | 0 | >1000 | 894 | 0.11 |
3.3. Environmental Risk Assessment Using PERI Model
3.4. Monitoring of Pesticide Residues in Soil and Water (Surface and Groundwater)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chebbi, H.E.; Pellissier, J.P.; Rolland, J.P.; Khechimi, W.; Projet D’appui à L’initiative ENPARD Méditerranée. Rapport de Synthèse sur L’agriculture en Tunisie Pages 22–24. 2019. Available online: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-02137636 (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- ITES (Institut Tunisien des Études Stratégiques). 2020. Available online: https://www.ites.tn/home (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- ONAGRI (Observatoire National de l’Agriculture). 2017. Available online: http://www.onagri.nat.tn/ (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- MIEM (Ministère de l’Industrie, de l’Energie et des Mines). 2018. Available online: https://www.energiemines.gov.tn/fr/accueil/ (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- GIZ. Etude de la Filière des Céréales Dans le Gouvernorat du Kef, Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusam-Menarbeit, page 9. 2014. Available online: http://www.onagri.nat.tn/uploads/filieres/cereales%20/cereales-kef.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- FAOSTAT. 2016. Available online: http://faostat.fao.org/site/291/default.aspx (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- ITES (Institut Tunisien des Études Stratégiques). 2017. Available online: https://www.ites.tn/home (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- Singh, N.S.; Sharma, R.; Parween, T.; Patanjali, P.K. Pesticide Contamination and Human Health Risk Factor. In Modern Age Environmental Problems and Their Remediation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 49–68. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-64501-8_3#citeas (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Yatoo, A.M.; Ali, N.; Zaheen, Z.; Baba, Z.A.; Ali, S.; Rasool, S.; Sheikh, T.A.; Sillanpää, M.; Gupta, P.K.; Hamid, B.; et al. Assessment of pesticide toxicity on earthworms using multiple biomarkers: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2573–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vryzas, Z. Pesticide fate in soil-sediment-water environment in relation to contamination preventing actions. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 4, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, G.; Atreya, K.; Scheepers, P.T.; Geissen, V. Concentration and distribution of pesticide residues in soil: Non-dietary human health risk assessment. Chemosphere 2020, 253, 126594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudh, S.; Singh, J.S. Pesticide Contamination: Environmental Problems and Remediation Strategies. In Emerging and Eco-Friendly Approaches for Waste Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 245–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suciu, N.; Farolfi, C.; Marsala, R.Z.; Russo, E.; De Crema, M.; Peroncini, E.; Tomei, F.; Antolini, G.; Marcaccio, M.; Marletto, V.; et al. Evaluation of groundwater contamination sources by plant protection products in hilly vineyards of Northern Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudi, M.; Ruan, H.D.; Wang, L.; Lyu, J.; Sadler, R.; Connell, D.; Chu, C.; Phung, D.T. Agriculture Development, Pesticide Application and Its Impact on the Environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaeed, R.D.; Aldarwish, A.Q.; Khouri, L.; Kolluru, V. Response surface modeling of sodium hypochlorite-based manganese oxidation in drinking water. DYSONA Appl. Sci. 2025, 6, 334–342. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, S.P.; Mohanty, B. The neonicotinoid pesticide imidacloprid and the dithiocarbamate fungicide mancozeb disrupt the pituitary–thyroid axis of a wildlife bird. Chemosphere 2015, 122, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, R.L.; Morrissey, C.A.; Clark, R.G. Analysis of trends and agricultural drivers of farmland bird declines in North America: A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 254, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siviter, H.; Muth, F. Do novel insecticides pose a threat to beneficial insects? Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2020, 287, 20201265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main, A.R.; Hladik, M.L.; Webb, E.B.; Goyne, K.W.; Mengel, D. Beyond neonicotinoids–Wild pollinators are exposed to a range of pesticides while foraging in agroecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, C.; Barot, S.; Capowiez, Y.; Hedde, M.; Vandenbulcke, F. Pesticides and earthworms. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 34, 199–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANCSEP (Agence Nationale de Contrôle Sanitaire et Environnemental des Produits). 2017. Available online: http://www.ancsep.rns.tn/ (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- Toumi, K. Exposition des Travailleurs Aux Résidus de Pesticides Sur Les Fleurs Coupées et Sur les Produits Horticoles. Ph.D. Thesis, University de Liege, Liege, Belgium, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Toumi, K.; Joly, L.; Tarchoun, N.; Souabni, L.; Bouaziz, M.; Vleminckx, C.; Schiffers, B. Risk assessment of Tunisian consumers and farm workers exposed to residues after pesticide application in chili peppers and tomatoes. Tunis. J. Plant Prot. 2018, 13, 127–143. [Google Scholar]
- Toumi, K.; Laure, J.; Nafissa, S.; Abdelkarim, A.; Bruno, S.; Habiba, G.-G. Pesticide Use in Market Gardening and Perceived Risk of Consumers Exposed to Pesticide Residues. Turk. J. Agric. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 10, 1072–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CRDA Kef. 2017. Available online: https://catalog.agridata.tn/organization/crda-kef (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Samaali, H.; Mjejra, M. Essai typologique des périmètres irrigués du Gouvernorat d’El Kef (Nord-ouest de la Tunisie): Un outil pour diagnostiquer et juger les performances des exploitations agricoles. Rev. Marocaine Des Sci. Agron. Vétérinaires 2020, 8. Available online: https://agrimaroc.org/index.php/Actes_IAVH2/article/view/863/1188 (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- ESRI, Inc. ArcGIS Desktop (Version 10.7.0) (10.7.0) [Windows]. Environmental Systems Research. 2019. Available online: https://desktop.arcgis.com/en/system-requirements/10.7/arcgis-desktop-system-requirements.htm (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Muhammetoglu, A.; Durmaz, S.; Uslu, B. Evaluation of the Environmental Impact of Pesticides by Application of Three Risk Indicators. Environ. Forensics 2010, 11, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soudani, N.; Belhamra, M.; Ugya, A.Y.; Patel, N.; Carretta, L. Environmental risk assessment of pesticide use in Algerian agriculture. J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsala, R.Z.; Capri, E.; Russo, E.; Bisagni, M.; Colla, R.; Lucini, L.; Gallo, A.; Suciu, N.A. First evaluation of pesticides occurrence in groundwater of Tidone Valley, an area with intensive viticulture. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, G.-F.; Fan, C.-L.; Liu, Y.-M.; Cao, Y.-Z.; Zhang, J.-J.; Fu, B.-L.; Li, X.-M.; Li, Z.-Y.; Wu, Y.-P. Multi-residue method for the determination of 450 pesticide residues in honey, fruit juice and wine by double-cartridge solid-phase extraction/gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Addit. Contam. 2006, 23, 777–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado-Sánchez, M.; Romero-González, R.; Rodríguez-Cáceres, M.; Durán-Merás, I.; Frenich, A.G. Rapid and sensitive on-line solid phase extraction-ultra high performance liquid chromatography–electrospray-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of pesticides in surface waters. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1305, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubirola, A.; Boleda, M.R.; Galceran, M.T. Multiresidue analysis of 24 Water Framework Directive priority substances by on-line solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry in environmental waters. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1493, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazić, S.; Sunjkai, D.; Jovanov, P.; Vukovic, S.; Guzsvany, V. LC-MS/MS determination of acetamiprid residues in sweet cherries. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2018, 23, 13317–13326. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, N.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, Z.; Liang, S.; Wang, B.; Lu, Z.; Economou, A.S. Determination of the Novel Insecticide Flupyradifurone and Its Two Metabolites in Traditional Chinese Herbal Medicines Using Modified QuEChERS and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2020, 2020, 8812797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Luo, J.; Bu, C.; Zhang, W.; Ma, L. Efficacy of a large-scale integrated constructed wetland for pesticide removal in tail water from a sewage treatment plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomgnimbou, A.P.; Savadogo, P.W.; Nianogo, A.J.; Millogo-Rasolodimby, J. Usage des intrants chimiques dans un agrosystème tropical: Diagnostic du risque de pollution environnementale dans la région cotonnière de l’est du Burkina Faso. BASE 2009, 13. Available online: https://popups.uliege.be/1780-4507/index.php?id=4524 (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Caloni, F.; Cortinovis, C.; Rivolta, M.; Davanzo, F. Suspected poisoning of domestic animals by pesticides. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahmar, R.; Berny, P.; Mahjoub, T.; Ben Youssef, S. Animal Pesticide Poisoning in Tunisia. Front. Veter. Sci. 2019, 6, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decourtye, A.; Vidau, C.; Rollin, O.; Requier, F.; Rüger, C.; Allier, F.; Le Féon, V.; Kretzschmar, A.; Devillers, J.; Henry, M.; et al. Fréquentation des cultures par les abeilles mellifères et sauvages: Synthèse des connaissances pour réduire le risque d’intoxication aux pesticides. Cah. Agric. 2016, 25, 44001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadlikova, K.; Vaclavikova, M.; Halesova, T.; Kamler, M.; Markovic, M.; Erban, T. The investigation of honey bee pesticide poisoning incidents in Czechia. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouzel, J.N. Pesticides. Comment Ignorer ce Que l’on Sait. Presses de Sciences Po, 264 p. 2019. Available online: https://sciencespo.hal.science/hal-02959871/ (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- Zhang, D.H.; Wu, X.F.; Fu, L. Determination of Security of the Natural Enemy Ladybug by Several Pesticides. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. 2007, 44, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Damalas, C.A.; Telidis, G.K.; Thanos, S.D. Assessing farmers’ practices on disposal of pesticide waste after use. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 390, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Tao, S. Environmental and human health challenges of industrial livestock and poultry farming in China and their mitigation. Environ. Int. 2017, 107, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, E.; Turrero, N.; Kolia, M.; Konaté, Y.; de Alencastro, L.F. Dietary risk assessment of pesticides from vegetables and drinking water in gardening areas in Burkina Faso. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calliera, M.; Capri, E.; Marsala, R.Z.; Russo, E.; Bisagni, M.; Colla, R.; Marchis, A.; Suciu, N. Multi-actor approach and engagement strategy to promote the adoption of best management practices and a sustainable use of pesticides for groundwater quality improvement in hilly vineyards. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 142251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasha, A.M.; Mulume, D.A.; Mwisha, S.W.; Fyama, J.N.M.; Kalumbu, J.T. Utilisation des pesticides en cultures maraîchères sur l’île d’Idjwi à l’est de la République démocratique du Congo: Connaissances et pratiques des agriculteurs. Cah. Agric. 2023, 32, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesesew, H.A.; Woldemichael, K.; Massa, D.; Mwanri, L.; Spanoghe, P. Farmers Knowledge, Attitudes, Practices and Health Problems Associated with Pesticide Use in Rural Irrigation Villages, Southwest Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, D.; Somda, I.; Legreve, A.; Schiffers, B. Pratiques phytosanitaires des producteurs de tomates du Burkina Faso et risques pour la santé et l’environnement. Cah. Agric. 2017, 26, 25005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loha, K.M.; Lamoree, M.; Weiss, J.M.; de Boer, J. Import, disposal, and health impacts of pesticides in the East Africa Rift(EAR) zone: A review on management and policy analysis. Crop. Prot. 2018, 112, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai, M.V.S.; Revati, G.D.; Ramya, R.; Swaroop, A.M.; Maheswari, E.; Kumar, M.M. Knowledge and perception of farmers regarding pesticide usage in a rural farming village, Southern India. Indian J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2019, 23, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekei, E.; Ngowi, A.V.; Kapeleka, J.; London, L. Acute pesticide poisoning amongst adolescent girls and women in northern Tanzania. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. The WHO Recommended Classification of Pesticides by Hazard and Guidelines to Classification 2019; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; p. 92. [Google Scholar]
- PPDB—Pesticides Properties Database. 2023. Available online: http://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/ppdb/ (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- SAgE Pesticides Database. Pesticides Database. 2023. Available online: http://www.sagepesticides.qc.ca/ (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- Classification Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on the classification, labeling, and packaging of substances and mixtures, amending and repealing Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32008R1272 (accessed on 5 August 2025).
- Cruz, R.; Andrades, M.S.; Sánchez Martín, M.J.; Sánchez Camazano, M. Efecto de la Aplicación de Lodos de Aguas Residuales al Suelo en la Persistencia Del Herbicida Linuron En Condiciones De Campo; Instituto Tecnológico Agrario de Castilla y León: Valladolid, Spain, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cycoń, M.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z.; Kozdrój, J. Linuron effects on microbiological characteristics of sandy soils as determined in a pot study. Ann. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medo, J.; Maková, J.; Medová, J.; Lipková, N.; Cinkocki, R.; Omelka, R.; Javoreková, S. Changes in soil microbial community and activity caused by application of dimethachlor and linuron. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, F.B.; Muñoz, S.R.; Smith, P.N. Laboratory Determination of Particulate-Matter–Bound Agrochemical Toxicity among Honeybees, Mason Bees, and Painted Lady Butterflies. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2023, 42, 2642–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, D.A.; Garratt, M.P.D.; Wickens, J.B.; Wickens, V.J.; Potts, S.G.; Raine, N.E. Neonicotinoid pesticide exposure impairs crop pollination services provided by bumblebees. Nature 2015, 528, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, D.G. A Neonicotinoid Insecticide at a Rate Found in Nectar Reduces Longevity but Not Oogenesis in Monarch Butterflies, Danaus plexippus (L.). (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae). Insects 2019, 10, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prouty, C.; Barriga, P.; Davis, A.K.; Krischik, V.; Altizer, S. Host Plant Species Mediates Impact of Neonicotinoid Exposure to Monarch Butterflies. Insects 2021, 12, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, J.; Dong, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zheng, Y. Effect of tetraconazole application on the soil microbial community. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 8323–8332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sułowicz, S.; Cycoń, M.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. Non-target impact of fungicide tetraconazole on microbial communities in soils with different agricultural management. Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 1047–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubrod, J.P.; Bundschuh, M.; Feckler, A.; Englert, D.; Schulz, R. Ecotoxicological impact of the fungicide tebuconazole on an aquatic decomposer-detritivore system. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 2718–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubrod, J.P.; Englert, D.; Feckler, A.; Koksharova, N.; Konschak, M.; Bundschuh, R.; Schnetzer, N.; Englert, K.; Schulz, R.; Bundschuh, M. Does the Current Fungicide Risk Assessment Provide Sufficient Protection for Key Drivers in Aquatic Ecosystem Functioning? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, D.L.; Voiculescu, D.I.; Filip, M.; Ostafe, V.; Isvoran, A. Effects of Triazole Fungicides on Soil Microbiota and on the Activities of Enzymes Found in Soil: A Review. Agriculture 2021, 11, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, D.L.; Voiculescu, D.I.; Ostafe, V.; Ciorsac, A.; Isvoran, A. A review of the toxicity of triazole fungicides approved to be used in European Union to the soil and aqueous environment. Ovidius Univ. Ann. Chem. 2022, 33, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, J.; Preetha, G. Pesticide Toxicity to Microorganisms: Exposure, Toxicity and Risk Assessment Methodologies. In Pesticide Toxicity to Non-Target Organisms; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 351–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recchia, L.; Sarri, D.; Rimediotti, M.; Boncinelli, P.; Cini, E.; Vieri, M. Towards the environmental sustainability assessment for the viticulture. J. Agric. Eng. 2018, 49, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjarres-López, D.P.; Andrades, M.S.; Sánchez-González, S.; Rodríguez-Cruz, M.S.; Sánchez-Martín, M.J.; Herrero-Hernández, E. Assessment of pesticide residues in waters and soils of a vineyard region and its temporal evolution. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, T.; Sinha, A.K. Pesticides in Agricultural Run Offs Affecting Water Resources: A Study of Punjab (India). Agric. Sci. 2019, 10, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saeid, M.H.; Alghamdi, A.G. Identification of Pesticide Residues and Prediction of Their Fate in Agricultural Soil. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczak, D.; Kondzielski, I.; Kijeńska, M.; Gworek, B. Influence of the selected physicochemical properties of the active substances of plant protection products on the results of their model exposure assessment in the surface water compartment. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 234, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, B.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, F.; Sui, Q.; Chen, Z.; Xu, D.; et al. Occurrence, source and ecotoxicological risk assessment of pesticides in surface water of Wujin District (northwest of Taihu Lake), China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Tran, T.M.; Nguyen, V.T.; Wang, A.; Wang, J.; Kannan, K. Neonicotinoids, fipronil, chlorpyrifos, carbendazim, chlorotriazines, chlorophenoxy herbicides, bentazon, and selected pesticide transformation products in surface water and drinking water from northern Vietnam. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Zhang, H.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Li, Q. Pesticides in surface waters of tropical river basins draining areas with rice–vegetable rotations in Hainan, China: Occurrence, relation to environmental factors, and risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 283, 117100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaçikoç, M.; Censur, M. Environmental monitoring of pesticide residues in surface waters of Buyuk Menderes River. Sigma J. Eng. Nat. Sci. 2022, 40, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutshekwa, T.; Mugwedi, L.; Moyo, B.; Madala, N.E.; Wasserman, R.J.; Dondofema, F.; Dalu, T. Assessing acetamiprid and chlorpyrifos pesticide concentrations in water and sediments across macadamia orchard and communal area small reservoirs. Chem. Ecol. 2023, 39, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, J.; Liu, P.; Qi, A.; Jin, H.; Jia, R.; Zheng, Z.; Yan, C.; Cai, M. Contamination characteristics, spatial distribution and ecological-health risk assessment of legacy and current-use pesticides: A case study in the Beibu Gulf. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1167712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvie, M.; Sosan, M.; Africa, A.; Cairncross, E.; London, L. Environmental monitoring of pesticide residues from farms at a neighbouring primary and pre-school in the Western Cape in South Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466–467, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero-Hernández, E.; Pose-Juan, E.; Sánchez-Martín, M.J.; Andrades, M.S.; Rodríguez-Cruz, M.S. Intra-annual trends of fungicide residues in waters from vineyard areas in La Rioja region of northern Spain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 22924–22936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, M.B.; Munitz, M.S.; Resnik, S.L. Validation and expanded uncertainty determination of pesticides in water; and their survey on paddy rice irrigation water from Argentina. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2020, 55, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, M.; Djaneye-Boundjou, G.; Wala, K.; Gnandi, K.; Batawila, K.; Sanni, A.; Akpagana, K. Assessment of pesticide residues and trace element contamination in market gardens of Togo. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 6, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukul, P.; Spiteller, M. Metalaxyl: Persistence, degradation, metabolism, and analytical methods. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 164, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Zhou, T.; Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Du, Z.; Li, B. Effects of successive metalaxyl application on soil microorganisms and the residue dynamics. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 103, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celis, R.; Gámiz, B.; Adelino, M.; Hermosín, M.; Cornejo, J. Environmental behavior of the enantiomers of the chiral fungicide metalaxyl in Mediterranean agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 444, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pose-Juan, E.; Sánchez-Martín, M.J.; Andrades, M.S.; Rodríguez-Cruz, M.S.; Herrero-Hernández, E. Pesticide residues in vineyard soils from Spain: Spatial and temporal distributions. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 514, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.A.; Tzilivakis, J.; Warner, D.J.; Green, A. An international database for pesticide risk assessments and management. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2016, 22, 1050–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemolin, C.; Avila, L.; Cassol, G.; Massey, J.; Camargo, E. Environmental fate of S-Metolachlor: A review. Planta Daninha 2014, 32, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.H.; Li, R.T.; Wu, X.M. Degradation of S-metolachlor in soil as affected by environmental factors. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2014, 14, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasmi, O.; Louati, M.; Chekirbane, A.; Menchen, A.; Twihri, A.; Alday, J.J.G.; Mlayah, A. Assessment of groundwater quality and pesticide distribution in Mornag aquifer using GIS-based technique (Northeast Tunisia). Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondhia, S. Persistence of Metsulfuron-Methyl in Paddy Field and Detection of Its Residues in Crop Produce. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 83, 799–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necibi, M.; Saadaoui, H.; Atayat, A.; Mzoughi, N. Determination of Triazole Pesticides in the Surface Water of the Medjerda River, Tunisia. Anal. Lett. 2020, 54, 742–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maznah, Z.; Ismail, B.S.; Eng, O.K. Residue and Dissipation Kinetics of Metsulfuron-Methyl Herbicide in Soil: A Field Assessment at an Oil Palm Plantation. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, B.S.; Tet-Vun, C. A field study on persistence and mobility of metsulfuron-methyl in three tropical agricultural soils. Soil Res. 2003, 41, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zheng, W.; Ma, Y.; Liu, K.K. Sorption and Degradation of Imidacloprid in Soil and Water. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2006, 41, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didović, M.P.; Kowalkowski, T.; Broznić, D. Emerging Contaminant Imidacloprid in Mediterranean Soils: The Risk of Accumulation Is Greater than the Risk of Leaching. Toxics 2022, 10, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajeer, M.A.; Nizamani, S.M.; Sherazi, S.T.H.; Bhanger, M.I. Adsorption and Leaching Potential of Imidacloprid Pesticide through Alluvial Soil. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2012, 03, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bošković, N.; Brandstätter-Scherr, K.; Sedláček, P.; Bílková, Z.; Bielská, L.; Hofman, J. Adsorption of epoxiconazole and tebuconazole in twenty different agricultural soils in relation to their properties. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaziem, A.E.; Gao, B.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; He, Z.; Wen, Y.; Wang, M.-H. Enantioselective bioactivity, toxicity, and degradation in different environmental mediums of chiral fungicide epoxiconazole. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, F.B. First survey of agricultural pesticides used for crops in Ichkeul Lake–Bizerte lagoon watershed (Tunisia). Environ. Sci. Indian J. 2017, 13, 156. [Google Scholar]
- Mhadhbi, T.; Pringault, O.; Nouri, H.; Spinelli, S.; Beyrem, H.; Gonzalez, C. Evaluating polar pesticide pollution with a combined approach: A survey of agricultural practices and POCIS passive samplers in a Tunisian lagoon watershed. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 26, 342–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pap, S.M.; Popović, B.; Stojić, N.; Danojević, D.; Pucarević, M.; Červenski, J.; Šperanda, M. The environmental issue of pesticide residues in agricultural soils in Serbia. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 20, 7263–7276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šunjka, D.; Pucarević, M.; Lazić, S.; Stojić, N.; Milošević, L.; El Bilali, H.; Bošković, D.; Vuković, S.; Mitrić, S.; Berjan, S.; et al. Monitoring of Herbicide Residues in Agricultural Soils in Vojvodina Province (Northern Serbia). Land 2024, 13, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passeport, E.; Benoit, P.; Bergheaud, V.; Coquet, Y.; Tournebize, J. Epoxiconazole degradation from artificial wetland and forest buffer substrates under flooded conditions. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; He, H.; Zhou, L.; Dong, F.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Y. Different biodegradation potential and the impacted soil functions of epoxiconazole in two soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vašíčková, J.; Hvězdová, M.; Kosubová, P.; Hofman, J. Ecological risk assessment of pesticide residues in arable soils of the Czech Republic. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nélieu, S.; Delarue, G.; Ollivier, E.; Awad, P.; Fraillon, F.; Pelosi, C. Evaluation of epoxiconazole bioavailability in soil to the earthworm Aporrectodea icterica. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 23, 2977–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, S.-I.; Hwang, I.-S.; Lee, H.-S.; Ki, S.-J.; Son, M.-H. Development and application of an advanced algorithm for environmental risk assessment and safety management of pesticide residues in agricultural soils: Monitoring of currently used pesticide in upland soils. Environ. Int. 2024, 190, 108865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.L.; Wu, X.M.; Li, S.N.; Fang, H.; Zhan, H.Y.; Yu, J.Q. An exploration of the relationship between adsorption and bioavailability of pesticides in soil to earthworm. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 141, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boithias, L.; Sauvage, S.; Srinivasan, R.; Leccia, O.; Sánchez-Pérez, J.-M. Application date as a controlling factor of pesticide transfers to surface water during runoff events. Catena 2014, 119, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, M.; Murugan, T.; Wins, J. Antimicrobial Activity and Phytochemical Constituents of Leaf Extracts of Cassia auriculata. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 75, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Water Source Categories | Number of Water Points | Distance (m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–50 | 51–500 | 501–1000 | >1000 | ||
| Source | 2 | 1 (50%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (50%) |
| Majel | 6 | 6 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| River | 18 | 8 (44%) | 5 (28%) | 1 (6%) | 4 (22%) |
| Valve | 29 | 29 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Borehole | 55 | 50 (91%) | 3 (5%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (4%) |
| Well | 103 | 94 (91%) | 6 (6%) | 2 (2%) | 1 (1%) |
| Active Substances | GUS Score | Kh Score | Kow Score | B Score | W Score | D Score | A Score | ER Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linuron | 4 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 5.50 |
| Tetraconazole | 4 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 5.50 |
| Chlorantraniliprole | 5 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 5.30 |
| Flupyradifurone | 5 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 5.28 |
| Imidacloprid | 5 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 5.28 |
| Fluopicolide | 5 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 5.25 |
| Epoxiconazole | 4 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 5.25 |
| Thiamethoxam | 5 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 5.25 |
| Metsulfuron methyl | 5 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 5.23 |
| Triasulfuron | 5 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5.18 |
| Flufenacet | 4 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 5.13 |
| S-metolachlor | 4 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 5.13 |
| Cypridonil (cyprodinil) | 3 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 4.63 |
| Isopropanil (isopropalin) | 1 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 4.50 | |||
| Penconazole | 3 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 4.38 |
| Cyflufenamid | 3 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 4.25 |
| Simazine | 4 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 4.25 |
| Dimethomorph | 4 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 4.23 |
| Metalaxyl | 4 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 4.23 |
| Metalaxyl- M | 4 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4.20 |
| Chlorpyrifos | 2 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 3.63 |
| Chlorpyriphos methyl | 2 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 3.63 |
| Tribenuron-methyl | 3 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3.20 |
| Acetamiprid | 2 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2.30 |
| Sample | Water | Soil | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth (m) | Number of Active Substances Detected (Quantified) | Total Pesticide Concentration (µg/L) | Number of Active Substances Detected (Quantified) | Total Pesticide Concentration (µg/kg) | ||
| Wells | 1 | 80 | 13 (7) | 2.81 | 1 (1) | 166.60 |
| 2 | 100 | 13 (7) | 1.08 | 4 (0) | 0.00 | |
| 3 | 24 | 9 (4) | 1.04 | 0 (0) | 0.00 | |
| 4 | 25 | 10 (4) | 0.58 | 3 (3) | 16.25 | |
| 5 | 90 | 11 (5) | 1.50 | 9 (4) | 78.16 | |
| 6 | 20 | 5 (3) | 7.87 | 7 (5) | 256.82 | |
| 7 | 80 | 8 (6) | 4.94 | 9 (6) | 284.43 | |
| 8 | 6 | 6 (3) | 0.95 | 3 (1) | 0.93 | |
| 9 | 7 | 9 (5) | 9.37 | 4 (1) | 1718.42 | |
| 10 | 26 | 8 (6) | 2.73 | 3 (0) | 0.00 | |
| Rivers | 11 | - | 8 (4) | 7.62 | 1 (0) | 0.00 |
| 12 | - | 7 (5) | 8.28 | 5 (1) | 3.87 | |
| 13 | - | 3 (3) | 0.38 | 1 (0) | 0.00 | |
| 14 | - | 4 (4) | 0.12 | 3 (0) | 0.00 | |
| 15 | - | 9 (8) | 0.16 | 5 (1) | 1.07 | |
| BA | Pesticide Residues | Water Samples (n = 15) | Soil Samples (n = 15) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N(F) | R in µg/L | N(F) | R in µg/kg | |||
| Rivers (n = 5) | Wells (n = 10) | |||||
| F | Cyflufenamid | 5 (100%) | 8 (80%) | [<LOD–0.012] | 3 (20%) | [<LOD–1.500] |
| Cypridonil | 3 (60%) | 8 (80%) | [<LOD–0.008] | 4 (27%) | [<LOD–3.600] | |
| Dimethomorph | 1 (20%) | 7 (70%) | [<LOD–0.013] | - | - | |
| Epoxiconazol | 0 | 2 (20%) | [<LOD–<LOQ] | 1 (7%) | [<LOD–2.777] | |
| Fluopicolide | 0 | 1 (10%) | [<LOD–<LOQ] | 1 (7%) | [<LOD–<LOQ] | |
| Metalaxyl | 0 | 9 (90%) | [<LOD–<LOQ] | 7 (47%) | [<LOD–<LOQ] | |
| Metalaxyl- M | 1 (20%) | 10 (100%) | [<LOD–<LOQ] | 10 (67%) | [<LOD–<LOQ] | |
| Penconazole | 4 (80%) | 9 (90%) | [<LOD–0.053] | 4 (27%) | [<LOD–7.300] | |
| Tetraconazole | - | - | - | - | - | |
| H | Flufenacet | - | - | - | 4 (27%) | [<LOD–<LOQ] |
| Isopropanil | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Linuron | 3 (60%) | 4 (40%) | [<LOD–7.795] | 6 (40%) | [<LOD–1718.424] | |
| Metsulfuron-Methyl | - | - | - | 2 (13%) | [<LOD–2.628] | |
| Simazine | 2 (40%) | 0 | [<LOD–<LOQ] | 3 (20%) | [<LOD–0.934] | |
| S-Metolachlor | 3 (60%) | 6 (60%) | [<LOD–<LOQ] | 6 (40%) | [<LOD–<LOQ] | |
| Triasulfuron | 0 | 1 (10%) | [<LOD–<LOQ] | - | - | |
| Tribenuron-Methyl | 1 (20%) | 0 | [<LOD–0.014] | - | - | |
| I | Acetamiprid | 5 (100%) | 9 (90%) | [<LOD–3.405] | - | - |
| Chlorantraniliprole | 0 | 1 (10%) | [<LOD–<LOQ] | - | - | |
| Chlorpyrifos | 0 | 2 (20%) | [<LOD–0.007] | 3 (20%) | [<LOD–<LOQ] | |
| Chlorpyriphos Methyl | 0 | 1 (10%) | [<LOD–<LOQ] | - | - | |
| Flupyradifurone | 2 (40%) | 9 (90%) | [<LOD–7.821] | 2 (13%) | [<LOD–231.100] | |
| Imidacloprid | - | - | - | 2 (13%) | [<LOD–1.071] | |
| Thiamethoxam | - | - | - | - | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toumi, K.; Arbi, A.; Soudani, N.; Lomadze, A.; Haouas, D.; Bertuzzi, T.; Cardinali, A.; Lamastra, L.; Capri, E.; Suciu, N.A. Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment and Monitoring of Pesticide Residues in Soil, Surface Water, and Groundwater in Northwestern Tunisia. Water 2025, 17, 2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162387
Toumi K, Arbi A, Soudani N, Lomadze A, Haouas D, Bertuzzi T, Cardinali A, Lamastra L, Capri E, Suciu NA. Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment and Monitoring of Pesticide Residues in Soil, Surface Water, and Groundwater in Northwestern Tunisia. Water. 2025; 17(16):2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162387
Chicago/Turabian StyleToumi, Khaoula, Abir Arbi, Nafissa Soudani, Anastasia Lomadze, Dalila Haouas, Terenzio Bertuzzi, Alessandra Cardinali, Lucrezia Lamastra, Ettore Capri, and Nicoleta Alina Suciu. 2025. "Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment and Monitoring of Pesticide Residues in Soil, Surface Water, and Groundwater in Northwestern Tunisia" Water 17, no. 16: 2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162387
APA StyleToumi, K., Arbi, A., Soudani, N., Lomadze, A., Haouas, D., Bertuzzi, T., Cardinali, A., Lamastra, L., Capri, E., & Suciu, N. A. (2025). Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment and Monitoring of Pesticide Residues in Soil, Surface Water, and Groundwater in Northwestern Tunisia. Water, 17(16), 2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162387









