Environmental Drivers of Aquatic Community Structures in a Shallow Eutrophic Lake of the Taihu Lake Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
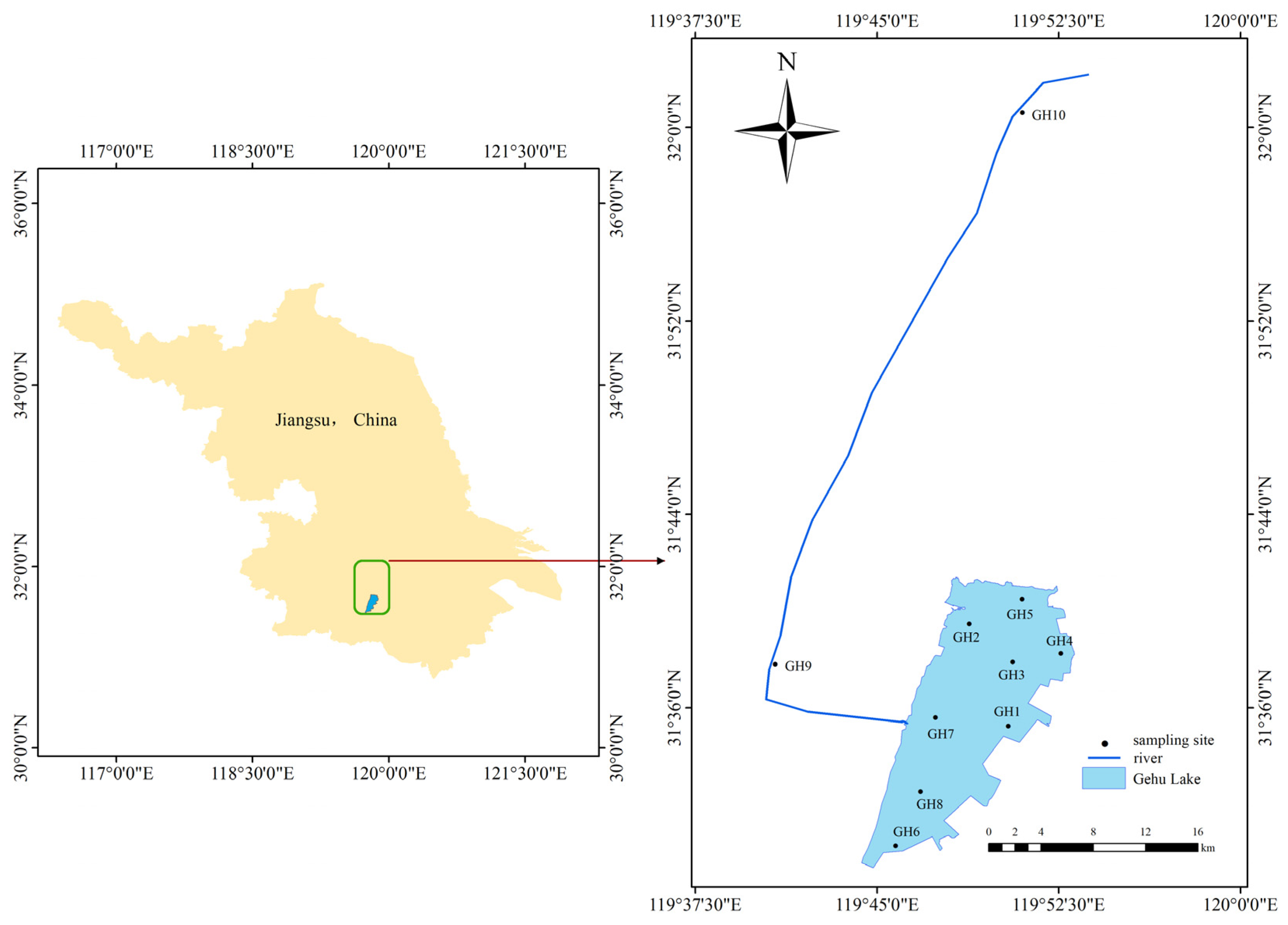
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Sample Collection
2.2.1. Water Sampling
2.2.2. Sample Collection and Identification
2.3. Data Processing and Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
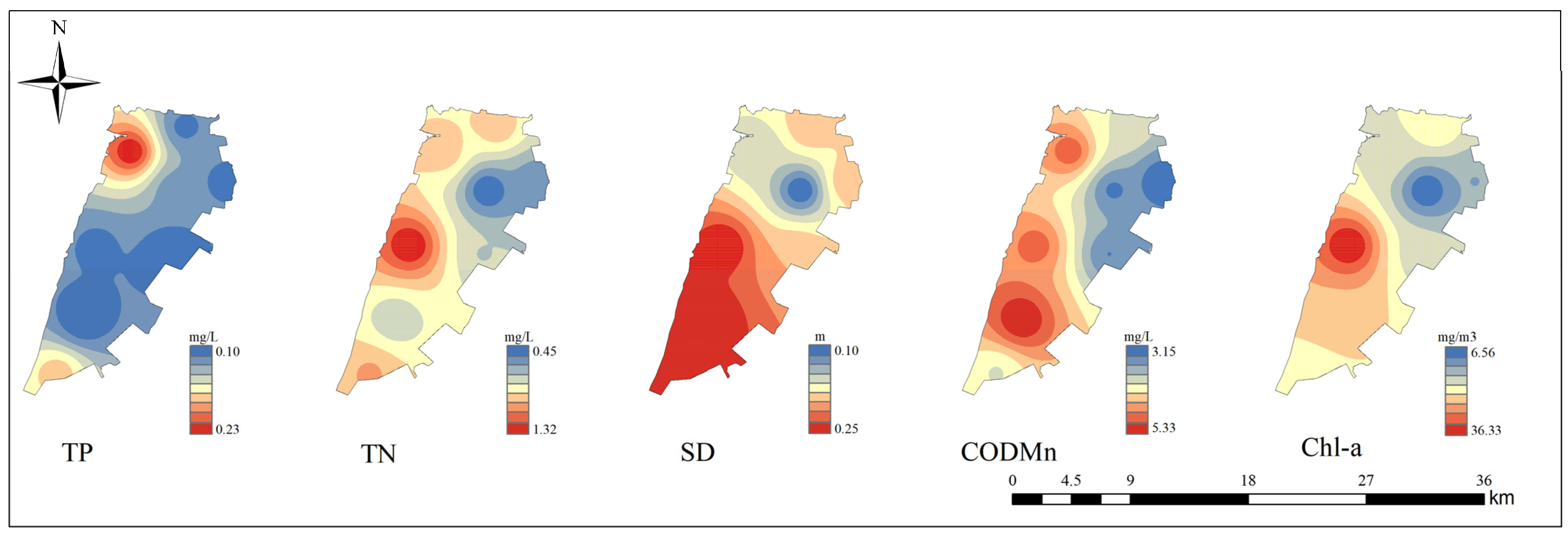
3.1. Characteristics of Environmental Factors
3.2. The Aquatic Biological Community Structure of the Lake
3.2.1. Composition of Species and Dominant Species
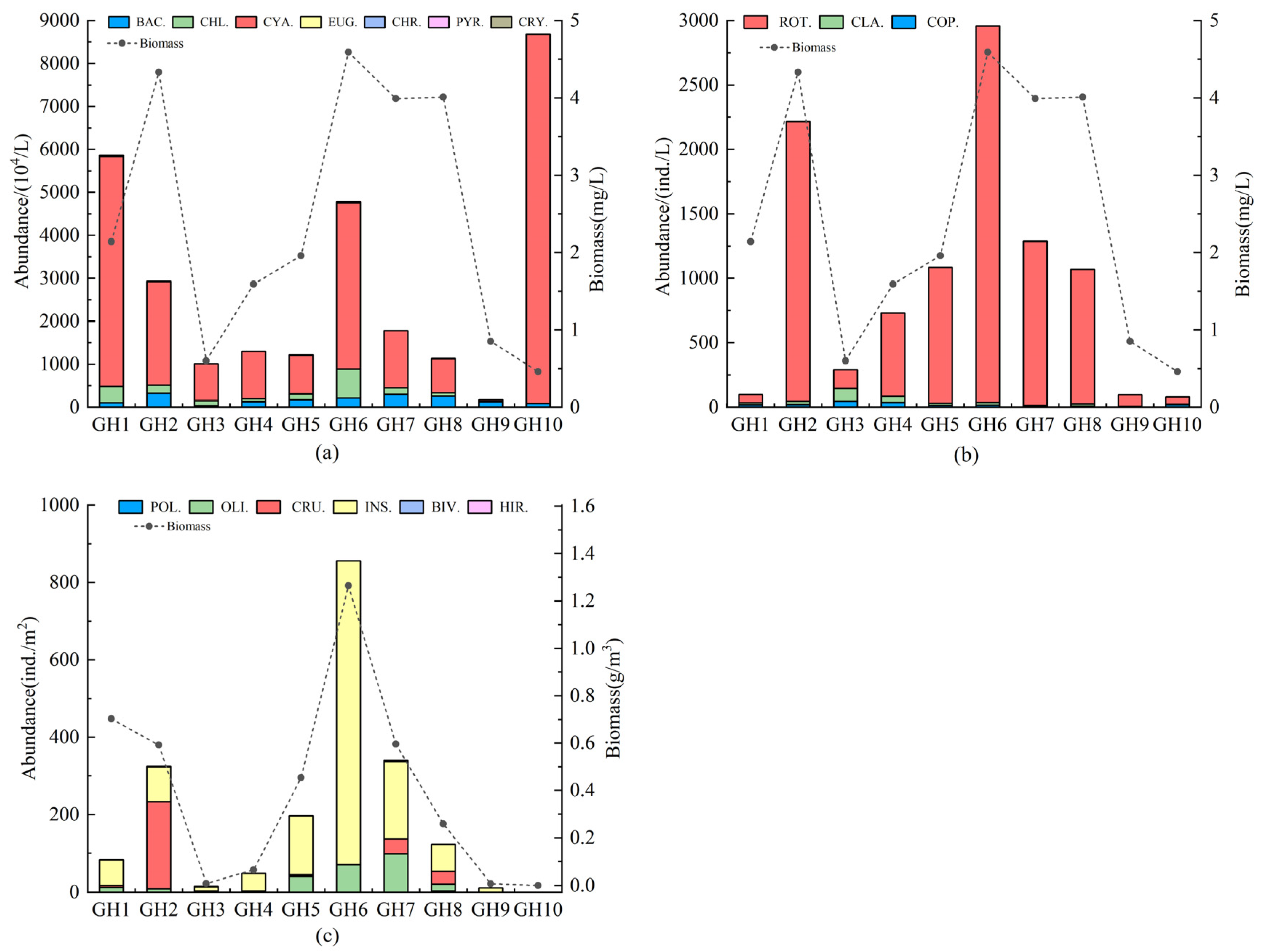
3.2.2. Spatial Variation in Abundance and Biomass
3.2.3. Evaluation of Biodiversity Indices
3.3. Pearson Correlation Analysis of Biomes with Environmental Factors
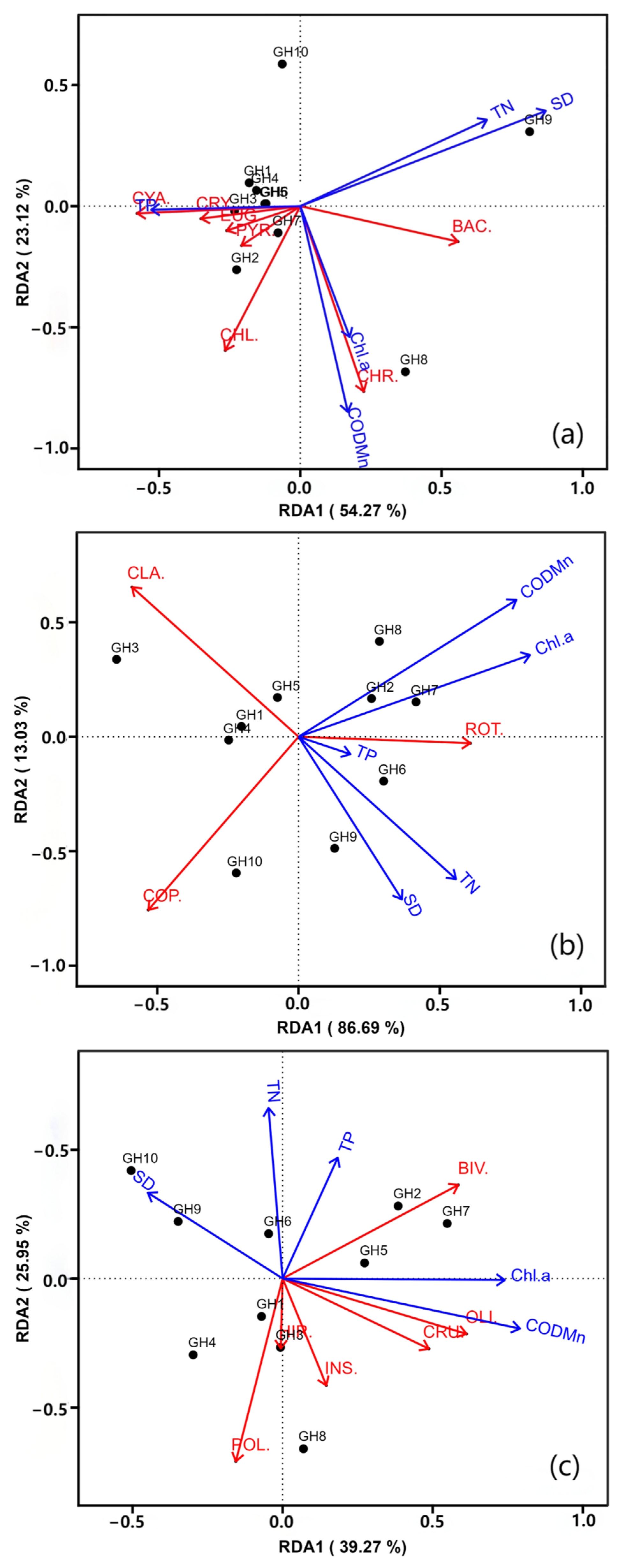
3.4. Relationships Between Aquatic Organisms and Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Water Quality in Gehu Lake
4.2. Characterizing the Spatial Distribution of Aquatic Abundance and Diversity
4.3. Factors Influencing Biome Structure
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reynolds, C.S. The Ecology of Phytoplankton; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Suthers, I.; Rissik, D.; Richardson, A. (Eds.) Plankton: A Guide to Their Ecology and Monitoring for Water Quality; CSIRO Publishing: Collingwood, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Bai, M.; Yao, L.; Ma, J.; He, F.; Bian, G.; Li, W. Phytoplankton and Zooplankton Community Dynamics in an Alpine Reservoir: Environmental Drivers and Ecological Implications in Daqing Reservoir, China. Water 2025, 17, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowski, P.G. The role of phytoplankton photosynthesis in global biogeochemical cycles. Photosynth. Res. 1994, 39, 235–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, K.R. Marine microorganisms and global nutrient cycles. Nature 2005, 437, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, E.; Morais, P.; Antunes, C.; Hoffman, J.C. The benthic food web connects the estuarine habitat mosaic to adjacent ecosystems. Food Webs 2023, 35, e00282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.K.; Park, H.J.; Choy, E.J.; Choi, K.S.; Hwang, K.; Kim, J.B. Linking intertidal and subtidal food webs: Consumer-mediated transport of intertidal benthic microalgal carbon. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil, J.; Attayde, J.L.; Vasconcelos, F.R.; Dantas, D.D.F.; Huszar, V.L. Drought-induced water-level reduction favors cyanobacteria blooms in tropical shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 2016, 770, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wu, N.; Tang, S.; Su, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Hecker, M.; et al. Factors associated with blooms of cyanobacteria in a large shallow lake, China. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.; Li, M.; Yu, R.; Sun, H.; Zhang, L.; Sun, L.; Lv, C.; Xu, J. Response of planktonic diversity and stability to environmental drivers in a shallow eutrophic lake. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borics, G.; Görgényi, J.; Grigorszky, I.; László-Nagy, Z.; Tóthmérész, B.; Krzsznai, e.; Várbíró, G. The role of phytoplankton diversity metrics in shallow lake and river quality assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 45, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.L.; Pan, J.Z.; Xu, L.G.; Lu, X.J.; Zhao, M.; Yang, H.S.; Wu, X.D. Ecological system health evaluation of lacustrine wetland in Taihu Basin. J. Lake Sci. 2019, 31, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Pan, J.Z.; Shen, Y.L.; Li, W.Z.; Huang, F. Overview and Degradation Reasons of Submerged Macrophytes of Gehu Lake. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 23, 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.N.; Zhang, H.G.; Zhou, W.; Shen, L.J. Analysis on the Relationship between the Distribution of Macrobenthos Community and Nitrogen-Phosphorus Factor in the Gehu Lake. Environ. Monit. Forew. 2016, 8, 45–50, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Pu, R.; Duan, H.; Ma, R.; Mao, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, L.; Xiao, Q. Evaluating the influences of harvesting activity and eutrophication on loss of aquatic vegetations in Taihu Lake, China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 87, 102038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Shi, Q.F.; Qu, J.Y.; He, M.X.; Liu, Q. A pollution risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in sediments: A case study of Lake Gehu, China. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2022, 50, 100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.M.; Yao, J.Y.; Yin, H.B. Occurrence characteristics and bioavailability of heavy metals in surface sediments of Lake Gehu, Taihu Basin. J. Lake Sci. 2016, 28, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.G.; Kwak, I.S. Evaluating the necessity of geographical locality for patterning biological integrity and its responses to multiple stressors in river systems. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Qin, H.; Wu, X.J.; Zhong, L. Study on the Optimization of Water Resources Regulation in Ecological Restoration of Gehu Lake in the New Period. Water Power 2023, 49, 12–16+28. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, C.H.; Zhang, R.L.; Wu, X.D.; Feng, L.H.; Wang, L.Q. Distribution and Pollution Assessment of Nutrient and Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments from Lake Gehu in Southern Jiangsu Province, China. Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 925–934. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, R.; Hu, M.; Xu, Y.X.; Xu, L.G.; Jiang, M.L. Modeling the inhibition effect of recreating submerged plants habitat on sediment resuspension in Lake Gehu. J. Lake Sci. 2024, 36, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Han, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Peng, S.; Pan, Y.; Li, A. Occurrence, distribution and potential environmental risks of pollutants in aquaculture ponds during pond cleaning in Taihu Lake Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 939, 173610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.P.; Nguyen, L.N.; Zdarta, J.; Nga, T.T.V.; Nghiem, L.D. Blue-green algae in surface water: Problems and opportunities. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2020, 6, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Ding, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.X.; Zhao, Y.F.; Fu, G. Eutrophication evolution trajectory influenced by human activities and climate in the shallow Lake Gehu, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 138, 108821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Technical Specifications for Surface Water Environmental Quality Monitoring: HJ 91.2-2022; Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China; Editorial Board of Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Methods (Eds.) Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Methods, 4th ed.; Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Technical Guidelines for Water Ecological Monitoring-Aquatic Organism Monitoring and Evaluation of Lakes and Reservoirs (On Trial): HJ 1296-2023; Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.J.; Wei, Y.X. (Eds.) Chinese Freshwater Algae—System, Classification and Ecology; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.X.; Chen, J.H. Atlas of Microbiology in Freshwater and Zoomacroinvertebrate, 2nd ed.; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Y. Atlas of Common Aquatic Organisms in Chinese River Basins; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, R.J.; Bahls, L.L. Rapid bioassessment protocols for use in streams and wadeable rivers: Periphyton, benthic macroinvertebrates and fish. In Periphyton Protocols, 2nd ed.; US EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; Volume 123. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.C.; Liu, X.Q. Evaluate method and Gradeification standard on lake eutrophication. Environ. Monit. China 2002, 18, 47–49. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Surface Water Environmental Quality Assessment Measures; Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.H.; Li, Y.F.; Zhang, M.Y.; Gao, J.T.; Li, W.P. Variation characteristics and trend analysis of water quality of typical lakes in Inner Mongolia based on long time series. J. Lake Sci. 2025, 37, 1249–1266. [Google Scholar]
- Bilgin, A. Trophic state and limiting nutrient evaluations using trophic state/level index methods: A case study of Borçka Dam Lake. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communications. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielou, E.C. Shannon’s formula as a measure of specific diversity: Its use and misuse. Am. Nat. 1966, 100, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalef, R. Temporal succession and spatial heterogeneity in phytoplankton. In Perspectives in Marine Biology; Buzzati-Traverson, A.A., Ed.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1958; pp. 323–349. [Google Scholar]
- Mcnaughton, S.J. Relationships among functional properties of Californian Grassland. Nature 1967, 216, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Wang, Q.; Wei, N.; Tang, C.; Sun, X.; Yang, Y. Biological indicators of ecological quality in typical urban river-lake ecosystems: The planktonicrotifer community and its response to environmental factors. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xie, Z.; Li, C.; Ye, C.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Wei, W.; Wang, H. Environmental factors affecting the phytoplankton composition in the lake of Tibetan Plateau. Diversity 2025, 17, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres-Neto, P.; Legendre, P.; Dray, S.; Borcard, D. Variation partitioning of species data matrices: Estimation and comparison of fractions. Ecology 2006, 87, 2614–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepš, J.; Šmilauer, P. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data Using CANOCO; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, V.H.; Tilman, G.D.; Nekola, J.C. Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 100, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmikandan, M.; Li, M.; Pan, B. Cyanobacterial blooms in environmental water: Causes and solutions. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2024, 10, 606–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H.; Schindler, D.W. Eutrophication science: Where do we go from here? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, R.H.; Wu, X.G.; Wang, Z.D.; Wang, B.Y.; Ke, F.; Han, C.; Zhou, Q.; Ren, J.H. Spatial distribution and pollution assessment on the main nutrients and heavy metals in sediments of Lake Gehu, Taihu Basin after removing the aquaculture net. J. Lake Sci. 2021, 33, 1436–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.X.; Zhu, G.W.; Qin, B.Q.; Pang, Y.; Gong, Z.J.; Zhang, Y.L. Effect of ecological engineering on the nutrient content of surface sediments in Lake Taihu, China. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 1624–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Cai, X.; Wang, S.; Yang, X. Analysis of the causes of cyanobacteria bloom: A review. J. Resour. Ecol. 2020, 11, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: Causes, consequences, and controls. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.C.; Michalak, A.M. Challenges in tracking harmful algal blooms: A synthesis of evidence from Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ger, K.A.; Urrutia-Cordero, P.; Frost, P.C.; Hansson, L.A.; Sarnelle, O.; Wilson, A.E.; Lürling, M. The interaction between cyanobacteria and zooplankton in a more eutrophic world. Harm. Alg. 2016, 54, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whatley, M.H.; Van Loon, E.E.; Cerli, C.; Arie Vonk, J.; Van Der Geest, H.G.; Admiraal, W. Linkages between benthic microbial and freshwater insect communities in degraded peatland ditches. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 46, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josefson, A.B.; Hansen, J.L.S.; Asmund, G.; Johansen, P. Threshold response of benthic macrofauna integrity to metal contamination in West Greenland. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, T.; Yang, W.; Li, X.; Ding, J.; Fu, X. Meta-analysis to identify inhibition mechanisms for the effects of submerged plants on algae. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 355, 120480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, B.B.; Antunes, S.C.; Pereira, R.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Gonçalves, F. Rotifer community structure in three shallow lakes: Seasonal fluctuations and explanatory factors. Hydrobiologia 2005, 543, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Rinaldi, S.; Gragnani, A.; Mur, L.R.; van Nes, E.H. On the dominance of filamentous cyanobacteria in shallow, turbid lakes. Ecology 1997, 78, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klausmeier, C.A.; Litchman, E.; Daufresne, T.; Mur, L.R.; Van Nes, E.H. Optimal nitrogen-to-phosphorus stoichiometry of phytoplankton. Nature 2004, 429, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejsmont-Karabin, J. The usefulness of zooplankton as lake ecosystem indicators: Rotifer trophic state index. Pol. J. Ecol. 2012, 60, 339–350. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.; Lundholm, N.; Friis, S.M.M.; Elledaard, M. Implications for photonic applications of Bacillariophyta growth and frustule nanostructure changes in response to different light wavelengths. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 2363–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaikova, E.; Walsh, D.A.; Stilwell, C.P.; Mohn, W.W.; Tortell, P.D.; Hallam, S.J. Microbial community dynamics in a seasonally anoxic fjord: Saanich Inlet, British Columbia. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 172–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilbert, T.; Couture, R.M.; Huser, B.J.; Salonen, K. Preface: Restoration of eutrophic lakes: Current practices and future challenges. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 4343–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, M.; Granéli, W.; Grimvall, A.; Hoffmann, C.C.; Mitsch, W.J.; Tonderski, K.S.; Verhoeven, J.T.A. How effective are created or restored freshwater wetlands for nitrogen and phosphorus removal? A systematic review. Environ. Evid. 2016, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Diversity Index | Evaluation Criteria | |
|---|---|---|
| Value | Water Quality Status | |
| Shannon–Wiener (H) | 0–1 | heavy pollution |
| 1–2 | α-moderate pollution | |
| 2–3 | β-moderate pollution | |
| >3 | light pollution or no pollution | |
| Margalef (D) | 0–1 | heavy pollution |
| 1–2 | α-moderate pollution | |
| 2–3 | β-moderate pollution | |
| >3 | light pollution or no pollution | |
| Pielou (J) | 0–0.3 | heavy pollution |
| 0.3–0.5 | moderate pollution | |
| 0.5–0.8 | light pollution | |
| >0.8 | no pollution | |
| Factor | GH1–GH8 | GH9–GH10 |
|---|---|---|
| Mean ± Std | Mean | |
| pH | 8.73 ± 0.36 | 8.43 |
| WT (°C) | 24.0 ± 0.6 | 27.35 |
| DO (mg/L) | 8.67 ± 2.05 | 7.16 |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.13 ± 0.05 | 0.12 |
| TN (mg/L) | 0.87 ± 0.30 | 1.505 |
| NH3-N (mg/L) | 0.18 ± 0.06 | 0.34 |
| NO3-N (mg/L) | 0.16 ± 0.15 | 0.71 |
| SD (m) | 0.24 ± 0.04 | 0.4 |
| Chl-a (mg/m3) | 19.8 ± 8.9 | 12.13 |
| EC (μS/cm) | 352.90 ± 4.48 | 416.1 |
| CODMn (mg/L) | 4.15 ± 0.83 | 3.12 |
| SS (mg/L) | 76.3 ± 18.5 | 23.5 |
| TLI | 58.20 ± 3.85 | 53.42 |
| Biology | Phylum | Dominant Species | Dominance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phytoplankton | Cyanophyta | Merismopedia punctata | 0.180 | ||
| Microcystis aeruginosa | 0.030 | ||||
| Aphanizomenon flos-aquae | 0.069 | ||||
| Aphanocapsa elachista | 0.028 | ||||
| Bacillariophyta | Melosira granulata | 0.024 | |||
| Zooplankton | Rotifera | Brachionus diversicornis | 0.531 | ||
| Brachionus calyciflorus | 0.243 | ||||
| Asplanchna priodonta | 0.055 | ||||
| Cladocera | Moina micrura | 0.022 | |||
| Macroinvertebrate | Outline | Dominant species | RD | RB | IV |
| Insecta | Microchironomus tabarui | 47.10 | 12.79 | 24.9 | |
| Chironomusflaviplumus | 6.42 | 30.66 | 16. 1 | ||
| Tanypus chinensis | 10. 11 | 20.37 | 13.2 | ||
| Crustacean | Grandidierella japonica | 12.70 | 12.72 | 12.2 | |
| Oligochaetes | Limnodrilus hofmeisteri | 11.82 | 5.69 | 10.2 | |
| Site | Phytoplankton | Zooplankton | Macroinvertebrate | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | J | D | H | J | D | H | J | D | |
| GH1 | 1.38 | 0.36 | 2.46 | 1.80 | 0.61 | 3.94 | 1.32 | 0.74 | 0.74 |
| GH2 | 2.44 | 0.62 | 2.97 | 1.55 | 0.46 | 3.51 | 1.13 | 0.54 | 0.87 |
| GH3 | 2.24 | 0.60 | 2.48 | 1.90 | 0.59 | 4.23 | 0.89 | 0.64 | 0.60 |
| GH4 | 1.88 | 0.65 | 1.04 | 1.34 | 0.43 | 3.19 | 0.87 | 0.54 | 0.65 |
| GH5 | 2.41 | 0.67 | 2.15 | 1.23 | 0.39 | 3.15 | 1.49 | 0.72 | 0.92 |
| GH6 | 2.44 | 0.60 | 3.28 | 1.17 | 0.36 | 3.13 | 1.29 | 0.72 | 0.55 |
| GH7 | 1.64 | 0.53 | 1.26 | 0.78 | 0.26 | 2.79 | 1.24 | 0.64 | 0.74 |
| GH8 | 2.06 | 0.67 | 1.29 | 0.82 | 0.29 | 2.44 | 1.75 | 0.84 | 0.98 |
| Average | 2.06 | 0.59 | 2.12 | 1.32 | 0.42 | 3.30 | 1.25 | 0.67 | 0.76 |
| GH9 | 0.76 | 0.34 | 0.56 | 1.53 | 0.60 | 2.63 | 0.26 | 0.37 | 0.21 |
| GH10 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.38 | 1.54 | 0.56 | 3.43 | _ | _ | _ |
| Phytoplankton | ||||
| Factor | RDA1 | RDA2 | R2 | p |
| TP | −0.99721 | 0.07462 | 0.2409 | 0.369 |
| TN | 0.89615 | 0.44374 | 0.4536 | 0.138 |
| SD | 0.93054 | 0.3662 | 0.7368 | 0.022 ** |
| CODMn | 0.26975 | −0.96293 | 0.7161 | 0.005 *** |
| Chl-a | 0.36461 | −0.93116 | 0.3127 | 0.293 |
| Zooplankton | ||||
| Factor | RDA1 | RDA2 | R2 | p |
| TP | 0.91828 | −0.39593 | 0.0327 | 0.901 |
| TN | 0.70165 | −0.71252 | 0.5684 | 0.054 * |
| SD | 0.51892 | −0.85482 | 0.5052 | 0.122 |
| CODMn | 0.82585 | 0.5639 | 0.6952 | 0.005 *** |
| Chl-a | 0.94449 | 0.32855 | 0.6043 | 0.051 * |
| Macroinvertebrates | ||||
| Factor | RDA1 | RDA2 | R2 | p |
| TP | 0.33506 | 0.9422 | 0.2208 | 0.41 |
| TN | −0.12674 | 0.99194 | 0.4002 | 0.194 |
| SD | −0.80228 | 0.59695 | 0.3018 | 0.306 |
| CODMn | 0.96076 | −0.27737 | 0.6288 | 0.027 ** |
| Chl-a | 0.99813 | −0.06105 | 0.5082 | 0.09 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C.; Ye, C.; Wang, Y. Environmental Drivers of Aquatic Community Structures in a Shallow Eutrophic Lake of the Taihu Lake Basin. Water 2025, 17, 2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162372
Ye Z, Zhang Q, Li C, Ye C, Wang Y. Environmental Drivers of Aquatic Community Structures in a Shallow Eutrophic Lake of the Taihu Lake Basin. Water. 2025; 17(16):2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162372
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Zishu, Qinghuan Zhang, Chunhua Li, Chun Ye, and Yang Wang. 2025. "Environmental Drivers of Aquatic Community Structures in a Shallow Eutrophic Lake of the Taihu Lake Basin" Water 17, no. 16: 2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162372
APA StyleYe, Z., Zhang, Q., Li, C., Ye, C., & Wang, Y. (2025). Environmental Drivers of Aquatic Community Structures in a Shallow Eutrophic Lake of the Taihu Lake Basin. Water, 17(16), 2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17162372






