Abstract
Traditional intensive agricultural system impedes ecological functions, such as nutrient cycling and biodiversity conservation, resulting in excessive nitrogen discharge, CH4 emission, and ecosystem service losses. To enhance critical ecosystem services and mitigate environmental externalities in paddy fields, we developed a multi-objective agricultural system (MIA system), which combines two eco-functional units: paddy wetlands and Beitang (irrigation water collection pond). Pilot study results demonstrated that the MIA system enhanced biodiversity and inhibited pest outbreak, with only a marginal reduction in rice production compared with the control. Additionally, the paddy wetland effectively removed nitrogen, with removal rates of total nitrogen and dissolved inorganic nitrogen ranging from 0.06 to 0.65 g N m−2 d−1 and from 0.02 to 0.22 g N m−2 d−1, respectively. Continuous water flow in the paddy wetland reduced the CH4 emission by 84.4% compared with the static water conditions. Furthermore, a simulation experiment indicated that tide flow was more effective in mitigating CH4 emission, with a 68.3% reduction compared with the drying–wetting cycle treatment. The emergy evaluation demonstrated that the MIA system outperformed the ordinary paddy field when considering both critical ecosystem services and environmental externalities. The MIA system exhibited higher emergy self-sufficiency ratio, emergy yield ratio, and emergy sustainable index, along with a lower environmental load ratio. Additionally, the system required minimal transformation, thus a modest investment. By presenting the case of the MIA system, we provide a theoretical foundation for comprehensive management and assessment of agricultural ecosystems, highlighting its significant potential for widespread application.
1. Introduction
Paddy fields are essential for grain production while also serving important functions, such as nutrient cycling and biodiversity conservation [1]. However, excessive use of synthetic fertilizer and agrochemicals in paddy fields impedes these functions, resulting in external environmental degradation and ecosystem service losses [2,3]. Nevertheless, paddy fields are a significant source of methane (CH4), contributing approximately 11% to total global CH4 emissions. To meet food demands, CH4 emissions from paddy fields are projected to increase by at least 25% over the next few decades [4].
Various approaches have been developed to mitigate the environmental externalities of paddy fields and address ecosystem service losses, such as paddy eco-ditch and wetland systems that reduce nitrogen losses by 87.8% [5]; biodiversity conservation through reduced pesticide use [6]; and genetically modified SUSIBA2rice, which incorporates SUSIBA2, a transcription factor gene from barley that suppresses CH4 production [7]. However, these solutions often address specific issues without integrally improving ecosystem functions [8]. For instance, biological weed control can promote rice growth but may disrupt pollination and pest control by displacing natural enemies [9].
Accordingly, it is critical to develop approaches that can fulfill multiple objects so as to comprehensively improve critical ecosystem services and mitigate environmental externalities [10]. However, few studies have comprehensively explored how systems can simultaneously enhance multiple ecosystem services while maintaining agricultural productivity. The work of Garbach et al. [11] on agroecological intensification (AEI) systems has demonstrated the potential for multi-functional approaches to increase both crop yields and ecosystem services. Yet, a holistic approach that integrates biodiversity, nitrogen efficiency, and methane reduction in paddy fields remains underexplored. This gap highlights the need for integrated systems, like the proposed MIA system, that can holistically address these challenges and improve overall ecological and agricultural performance in paddy fields.
One promising yet underexplored approach involves revisiting traditional ecological practices that inherently embody principles of multifunctionality, such as the Beitang. Beitang, a traditional water conservation measure originated from the ancient Chinese ecological wisdom of biological symbiosis and nutrient recycling, can provide irrigation and cultural functions along with other ecosystem services, such as pollutants removal and soil, water, and biodiversity conservation. It is essentially a pond with irrigation water ways leading toward it for water collection and storage [12]. Regardless, at present, traditional Beitang has never been introduced to the modern intensive agricultural systems probably because of its occupation of farmland areas and low pollutants purification capacity.
Here, we proposed a multi-objective integrated agricultural system (MIA system) consisting of paddy wetland and Beitang. We expect that the MIA system can simultaneously prevent nitrogen discharge, reduce CH4 emissions, and create multiple habitats, while maintaining the grain yield. Agroecosystems often focus on a limited set of ecosystem services, typically optimizing one or two aspects, such as nutrient cycling or pest management, alongside maintaining or slightly improving crop yields [11]. In contrast, the MIA system simultaneously targets several environmental goals: it aims to reduce nitrogen discharge, mitigate methane (CH4) emissions, conserve biodiversity, and maintain the grain yield. Since water management strategies strongly influence CH4 dynamics in paddy fields [13], we further hypothesized that applying a tidal circulation flow regime can enhance methane mitigation by promoting soil aeration and suppressing methanogenesis. This approach aims to provide an alternative solution that addresses both economic and ecological demands [14]. Therefore, the objectives of this study are (1) to construct and implement a pilot-scale MIA system; (2) to evaluate its ecological performance through nitrogen removal, CH4 emission reduction, and biodiversity enhancement; and (3) to assess its environmental sustainability using emergy analysis. By achieving these goals, we aim to demonstrate the feasibility and advantages of multifunctional systems that introduces two key innovations: (1) the integration of the traditional Beitang into a modern agroecological framework and (2) the application of emergy analysis to jointly assess ecosystem services and environmental externalities.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The field experiment was conducted from June to November 2021 at Qingan Farm, Shanghai (121°28′28.682″ N, 31°2′16.811″ E). The site includes a 710 m2 depressed pond and a 9800 m2 ordinary rice field, managed under an alternating wet and dry irrigation system in a sole cropping pattern. The local climate is subtropical humid monsoon with a daily average temperature of 14.0 °C and annual precipitation of 1660.8 mm. By 2021, Shanghai’s urbanization rate reached 89.3%, resulting in a shortage of agricultural land, with 109,000 ha of paddy fields intensively cultivated. High-intensity farming in this agricultural area has led to many ecological and environmental issues, such as CH4 emissions, water quality deterioration, and habitat degradation.
2.2. Experimental System Design
2.2.1. Construction and Operation of the MIA System
The MIA system consisted of a paddy wetland and a Beitang (Figure 1). The degree of agricultural non-point source pollution is related to surface runoff caused by rainfall and tailwater during the farming period, which are characterized by uneven spatial and temporal distribution. To effectively regulate and store runoff and tailwater, a 710 m2 Beitang (about 1.5 m deep) was constructed, integrating the topography of the experimental site with design principles from the traditional Beitang. Zizania latifolia was the main emergent plant in the Beitang.
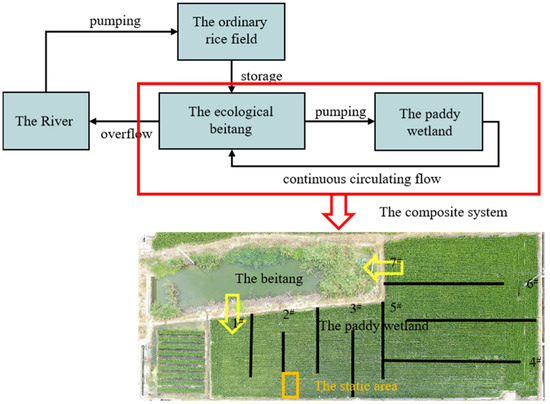
Figure 1.
The MIA system design (aerial view), including a 710 m2 depressed pond (Beitang) and a 1,960 m2 paddy wetland. Water sampling sites included the influent, effluent, and 5 sampling sites in the middle of the paddy wetland, indicated as 1#, 2#, …, 7#.
To ensure comparability, the experimental setup included both a treatment and control condition within the same rice field. Specifically, a 1960 m2 section of the rice field adjacent to the Beitang was modified to create the paddy wetland, forming part of the MIA system. The remaining area of the 9800 m2 rice field was maintained under conventional practices and served as the control. This layout allowed both systems to be cultivated under identical soil, climatic, and management conditions, except for the interventions specific to the MIA system.
The 1960 m2 paddy wetland was modified to support engineered water circulation between the wetland and the adjacent Beitang. A 6 m PVC pipe, equipped with a row of perforations for water inflow and a plastic baffle to direct water distribution, ensured full and uniform water flow into the paddy wetland. Water was pumped from the Beitang into the paddy wetland, while the outflow of the paddy wetland was discharged into the Beitang via water collection pipes, creating a continuous water circulation between the two systems. The river served as the primary source of irrigation for the ordinary rice field, and when the water level in the Beitang exceeded capacity, it overflowed into the river.
Moreover, a static area (3 m × 4 m) was established in the middle of the paddy wetland using the plastic baffle. A gap in the plastic baffle, positioned just below the water surface, allowed the static area to be replenished with water.
The experiment commenced with the transplantation of young rice plants (Oryza sativa L. cultivar ‘Nanjing 46’) on 9 June 2021. On 24 June, the paddy wetland started operation but was shut down on 10 October for drying the fields, while the rice was harvested on 24 October. The surface water level in the paddy wetland was maintained at 5 cm throughout this study, except during the period from 25 to 30 July when Typhoon In-Fa swept across Shanghai. The inflow rate of the paddy wetland was maintained at 2–3 m3 h−1, and the outflow rate ranged from 0.13 to 0.47 m3 h−1.
The total fertilizer application in the MIA system was reduced by half compared with the ordinary rice field. Specifically, in the paddy wetland (MIA system), 209.9 kg/ha of urea (N > 46%) and 93.7 kg/ha of bulk blending fertilizer (BB fertilizer, 15–15–15 (N–P–K)) were applied. No pesticides were applied in the MIA system, while the ordinary rice field normally utilized pesticides. When necessary, the remaining weeds in the paddy wetland were manually removed during the rice-growing seasons.
2.2.2. Simulation Experiment for Verifying the Paddy Wetland’s Purification Capacity
Excessive nitrogen fertilizer is often applied to meet the demand of rice plants prior to the booting stage, resulting in significant nitrogen runoff that can negatively impact surrounding environments. A simulation experiment was conducted to assess the purification capacity of the paddy wetland under high nitrogen load, mimicking nitrogen runoff entering the Beitang. Nitrogen concentrations in agricultural runoff typically range between 2 and 20 mg L−1 [15]. To simulate real-world runoff conditions, approximately 15 kg of urea fertilizer was added to the Beitang (area: 710 m2, average depth: 1.5 m) in a single application to simulate runoff from the surrounding farmland during the flowering stage. To evaluate the system’s purification performance, changes in total nitrogen (TN), ammonia nitrogen (NH4+–N), nitrate nitrogen (NO3−–N), and nitrite nitrogen (NO2−–N) in the paddy wetland’s water were measured on Days 1, 2, 4, 6, and 9 after urea application.
2.2.3. Enclosure Experiment for Verifying the Effect of the Tide Flow on Reducing CH4 Emissions
To test the hypothesis that the tidal circulation flow can further reduce CH4 emissions, an experiment was conducted in the vicinity of the paddy wetland. The young rice plants (Oryza sativa L. cultivar ‘Nanjing 46’) were transplanted in the growth chambers (e.g., 57 (length, cm) × 39 (width, cm) × 30 (depth, cm), Figure S1) on 15 May. Six rice plants were planted per growth chamber under alternating wet and dry irrigation conditions. Fertilizer and pesticide application rates per unit area in each growth chamber matched those used in the ordinary rice field.
The experiment started on 29 August (blooming stage) and continued for 14 days. In tidal flow treatment, overlying water continuously circulated, alternating between wet and dry conditions on a daily basis. Water was injected at 08:00 every day, with circulation maintained by a peristaltic pump at a flow rate of 16 mL min−1. Nitrogen (0.19 g N m−2) was added at 11:00, and the circulation stopped at 16:00, with complete drainage by 20:00. In drying–wetting cycle treatment, the overlying water remained static, with irrigation occurring only after the water had naturally evaporated. Furthermore, 2.7 g N m−2 was applied at 11:00 on the first day. Both treatments were conducted in 4 replicates. CH4 emission fluxes of all sets were monitored on Days 1, 2, 3, 6, and 14.
2.3. Sampling and Analysis
2.3.1. Measurement of Grain Growth and Rice Quality
In both the paddy wetland and the ordinary rice field, three 1 × 1 m sampling sites were placed at fixed locations representing the upper, middle, and lower reaches along the water flow direction to capture spatial variability in plant growth. The rice plant height and chlorophyll content were continuously monitored, with mean values calculated for comparison. At the maturation stage, rice was harvested and the total yield was calculated. Concentrations of pesticides and heavy metals in rice were analyzed by ICAS Testing Technology Service (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
2.3.2. Measurement of Arthropod and Amphibian Community
For amphibians, surveys were conducted on three consecutive days starting from 12 October. Each day at 10:00, a 50 m transect along the field ridges of both the paddy wetland and ordinary rice field was inspected, with species and abundance of amphibians recorded through visual inspection. The morphology of the amphibians was documented with photographs.
For arthropods, seven equidistant sampling sites were selected on the east side of both the paddy wetland and the ordinary rice field at 8:00 on 12 October, on the west side at 15: 00 on 13 October, and again on the east side at 20:00 on 14 October. A comprehensive survey of arthropod species and numbers was conducted in the morning, midday, and evening. At each sampling site, we started 2 m from the field ridge and systematically swept toward the center using a net for 5 min. This approach minimized the impact of human disturbance on arthropods. The collected specimens were preserved in 75% alcohol for further analysis.
According to the investigation results, the identified arthropods and amphibians were divided into three functional groups: natural enemies, pests, and neutral groups for rice [16,17]. Richness was calculated as the total number of species observed across the surveyed area. The Shannon–Wiener index (H’) was calculated using the formula
whereby i is the index of species in the community, and Pi is the proportion of the total number of individuals in the community that belongs to species i.
2.3.3. Measurement of Water Quality
Water samples were collected from the 7 sampling sites (Figure 1) in the paddy wetland, immediately placed in a cooler and analyzed within a week. The samples were first filtered using a glass fiber filter and then analyzed for NH4+–N, NO3−–N + NO2−–N, and TN using an ultraviolet–visible spectrophotometer (UV-7504, Xinmao Co. Ltd., Shanghai, China). The analysis methods followed those described by Chen et al. [18].
2.3.4. Measurement of CH4
Three random CH4 measurement sites were selected in the paddy wetland, the ordinary rice field, and the static area. CH4 fluxes were measured in situ using an Ultra-Portable GHG Analyzer (Los Gatos Inc., Santa Ana, CA, USA). The measurement and calculation method followed the protocols outlined by Yang et al. [19].
2.4. Emergy Evaluation
In this study, a global emergy baseline 1.20 × 1025 sej yr−1 (solar emjoules per year) was applied [20], with all cited unit emergy values (UEVs) converted to this baseline [21]. Also the emergy transformity coefficient used in this study primarily referenced research findings from Lan Shengfang et al. [22], Wang et al. [23], and Chen et al. [24]. The emergy flow diagrams for the three scenarios (OR, ordinary rice fields; MIA1, ordinary rice paddy, paddy wetland, and Beitang equal to 10:4:1; MIA2, ordinary rice paddy, paddy wetland, and Beitang equal to 10:1:1) are shown in Figure S2. The inputs considered here were of both natural inputs and economic inputs for grain production up to the harvest gate. In detail, the natural inputs included rain, wind, sun radiation, and soil; the economic inputs included labor, seed, machinery, diesel oil, fertilizer, agrochemicals, and electricity purchased for the production (Table S1). In this study, rain and wind were regarded as derivatives of sun radiation in emergy analysis, and thus, only the flow with the highest renewable can be calculated [25]. Outputs were the sum of critical ecosystem service and environmental externalities. The critical ecosystem service included rice production, water regulation, biodiversity, micro-climate regulation, as well as recreational and cultural values. We further used environmental externalities to characterize the factors that negatively affect the external environment. In this study, the environmental externalities included N discharge and CH4 emission.
Based on energy input and output analysis, environmental efficiency and sustainability of the three paddy cropping systems were evaluated using four emergy indices: (1) emergy self-sufficiency ratio (ESR), which indicates the proportion of renewable resources in total inputs; (2) emergy yield ratio (EYR), reflecting the capacity to generate output relative to imported inputs; (3) environmental load ratio (ELR), which assesses the pressure exerted on the environment; and (4) emergy sustainable index (ESI), which combines EYR and ELR to reflect overall system sustainability. The formulas were provided by Yong et al. [26]. and are given as follows: ESR = (R + N)/U; EYR = Y/(R + T); ELR = (F + N)/(R + T); and ESI = EYR/ELR, where N is the topsoil loss, representing non-renewable natural resources; F is the non-renewable industrial auxiliary energy including mechanical energy, diesel, fertilizer, pesticides, and electricity; T is the renewable biological auxiliary energy including labor and seeds; and (Y) is the total output including key ecosystem services and environmental externalities.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Rice Growth and Biodiversity Conservation of the MIA System
The mean of the grain yield and chlorophyll content of each treatment are shown in Figure 2. The results suggest that the paddy wetland provided excellent growing conditions for the rice, as no significant (p > 0.05) differences in plant height and chlorophyll content were observed compared with the ordinary rice field. The rice produced by the MIA system had no pesticide residues, and the heavy metal concentrations were below China’s maximum levels for contaminants in foods.
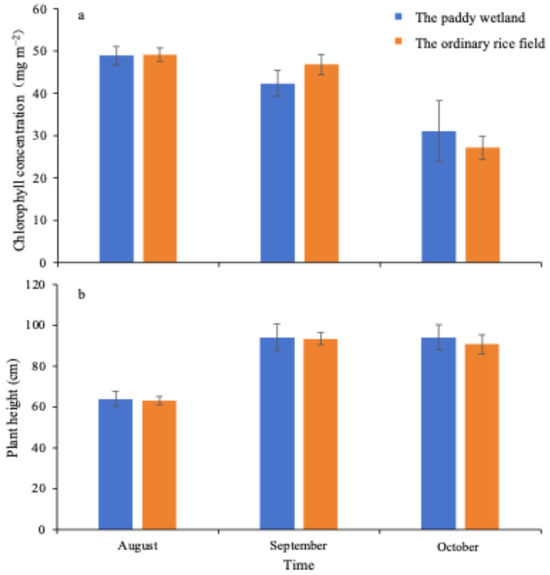
Figure 2.
Rice growth under different treatments. (a): chlorophyll content; (b): plant height. Error bars presented standard deviations.
However, the yield of the paddy wetland was 7.89 t hm−2, approximately 6.3% lower than that of the ordinary rice field. This decrease may be attributed to insufficient nutrients during the booting stage, which is necessary for glume development and increase in sink capacity, ultimately affecting the thousand-grain weight [27]. The low inflow concentration of TN and DIN at the booting stage (August) resulted from the application of only half of the amount of fertilizer used for the paddy wetland compared with the control, thereby inadequately meeting the nitrogen demand. Although, in the current experiment, the nitrogen supplied by circulating water flow did not fully compensate for the amount of chemical fertilizer that the paddy wetland needed, the overall impact on the yield was minimal, with an insignificant reduction of merely 6.3%.
The composition of the arthropod and amphibian community in the paddy wetland and the control is presented in Table 1. Overall, the paddy wetland contained 26 species and 116 individuals, surpassing the biodiversity of the ordinary rice field. The paddy wetland inhibited pest outbreak, improved biodiversity, and supported a greater variety of species compared with the control. Although the richness and richness ratio for pests were much higher in the MIA system compared with those in the ordinary rice field, the abundance and abundance ratio of pests were lower. The richness and richness ratio for neutral insects in the MIA system were lower compared with those in the ordinary rice field, while the abundance and abundance ratio were higher.

Table 1.
Composition of arthropod and amphibian community in the MIA system and the ordinary rice field.
Regarding the arthropod community, the dominant species in the paddy wetland was the neutral insect Musca domestica with its dominance index of 0.13. In contrast, the ordinary rice field had Leptocorisa chinensis Dallas (pests), Nezara viridula (pests), and Paederus fuscipes Curtis (natural enemies) as dominant species, with dominance indexes of 0.13, 0.13, and 0.11, respectively. The Shannon–Wiener index of the paddy wetland and the ordinary rice field was 3.12 and 2.98, respectively. For the amphibian community (natural enemies), the density in the paddy wetland was 12 times higher than in the control. These findings suggested that although there was no pesticide application, pest populations were lower in the paddy wetland likely due to the increased presence of natural enemies.
Amphibians are extremely sensitive to environmental quality, especially water quality [28]. The current research suggests that an excessive application of pesticides in the ordinary rice field had poisoned soil and water, which negatively impacted amphibian survival and reproduction [29,30]. Contrarily, the paddy wetland maintained a stable water layer, with no application of pesticides, thus maintaining a healthy habitat, which is conducive to the survival and reproduction of amphibians. Amphibians play a crucial role in pest control, as the majority of their prey are pests [28]. The reduction in the number of individuals of Leptocorisa chinensis Dallas and Nezara viridula in the paddy wetland may primarily be attributed to amphibian predation. Numerous studies suggested that change in management practices initiated a trophic cascade in the rice–pest–predator interactions, where an increased abundance in predators leads to pests’ reduction, positively impacting grain yield [31]. Subsequently, the integration of the paddy wetland with the Beitang enlarged the ecological niche, which can lead to an increase in the species richness and provide multiple habitats for natural enemies. Therefore, without the application of pesticides, the arthropod and amphibian community protected the paddy wetland and helped to maintain the yield. Nevertheless, the incorporation of Beitang increases the diversity of landscape patterns and creates additional landscape patches, thereby providing habitats for wildlife. Moreover, it can be utilized for aquaculture, such as fish farming and the cultivation of aquatic vegetables, offering opportunities for economic gain.
3.2. The Nitrogen Removal Capacity of the MIA System
The results showed that the MIA system can effectively remove nitrogen under both low and high nitrogen loading conditions. The nitrogen reduction of the MIA system under low nitrogen loading is shown in Figure 3. The concentrations of TN and dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) at sampling site 3# were significantly lower compared with those closer to the inlet. The removal capacity of TN and DIN in sections 1#–3# of the paddy wetland was 0.11–0.15 g N m−2 d−1 and 0.02–0.05 g N m−2 d−1, respectively. In October, the concentration of DIN abnormally increased for sampling sites 4# to 7# (end), which was caused by the second high nitrogen pollutant simulation experiment (Figure 3b). Nevertheless, the concentration of DIN in the effluent remained lower compared with that in the influent, and the TN concentration at the end of the flow remained low, indicating the paddy wetland’s robust nitrogen purification capacity, even after exposure to two higher nitrogen loading events.
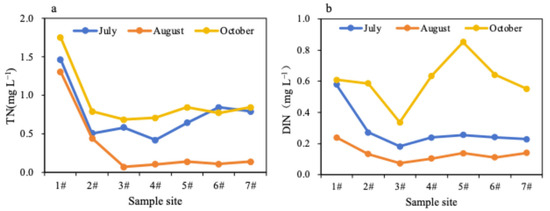
Figure 3.
Changes in the concentration of TN (a) and DIN (b) along the flow direction of the paddy wetland under low nitrogen loading.
The nitrogen reduction performance of the paddy wetland under high nitrogen loading is presented in Figure 4. On Day 6 following urea application in the Beitang, the concentration of TN and DIN in sampling site 3# decreased to 0.92 and 0.20 mg L−1 respectively. TN concentration at the inlet peaked at 9.11 mg L−1 on Day 1 after urea application and decreased to 1.06 mg L−1 on Day 9. Similarly, DIN concentration reached a peak of 3.71 mg L−1 on Day 2 and decreased to 0.54 mg L−1 on Day 9. The removal capacities of TN and DIN in sections 1#–3# of the paddy wetland were 0.06–0.65 g N m−2 d−1 and 0.02–0.22 g N m−2 d−1, respectively.
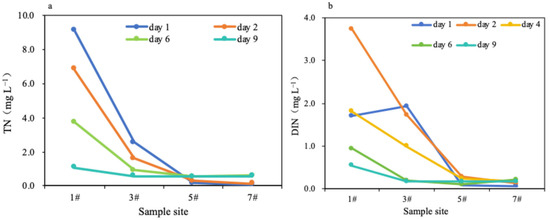
Figure 4.
Changes in the concentration of TN (a) and DIN (b) along the flow direction of the paddy wetland under high nitrogen loading. The legend indicates the days of urea fertilizer application in the Beitang.
The removal capacity of DIN and TN in sections 1#–3# was affected by the concentration of DIN and TN at the inlet, with a positive correlation (R2 = 0.9907 and 0.9852, respectively; n = 7), indicating that the full removal potential of the paddy wetland was not entirely utilized (Figure 5). The nitrogen removal capacity was efficient in sections 1#–3# in both low and high nitrogen loading conditions. Given the circulating water flow, sections 1#–3# of the paddy wetland were sufficient for effective nitrogen removal.
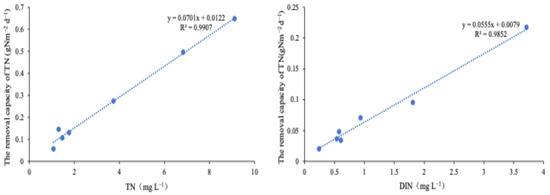
Figure 5.
The positive correlation between the removal capacity in sections 1#–3# and the concentration at the inlet.
Previous studies conducted regarding nitrogen reduction by rice paddy reported removal capacities ranging from 0.023 to 0.14 gNm−2 d−1, which were lower than those of the current study [32,33]. As reported by Xue and Yang [33], traditional flooding-overflow systems where water enters a designated site and overflows in a 20 m × 12.5 m rice paddy often result in incomplete water flow throughout the field. This limited flow can reduce the system’s efficiency in nitrogen removal. Contrarily, the full water flow within the paddy wetland might be the reason for the higher removal capacity. Muramatsu et al. [32] used an enclosure experiment, with a plant density of 22 plants m−2, to simulate continuous water circulation in paddy fields for nitrogen removal. As nitrogen uptake by rice plants is one of the primary removal pathways, the lower plant density (35% lower) compared with the current study might be the reason for a reduced removal capacity.
3.3. The CH4 Emissions of Rice Paddy
The average CH4 emission of each treatment is shown in Figure 6. The results suggest that the CH4 emissions in paddy wetlands gradually increased from 1487.9 to 3962.9 mg m−2 d−1, with an average CH4 emission of 2403.9 mg m−2 d−1. To study the effect of the continuous circulating flow on CH4 reduction, a static area was established within the paddy wetland. The results showed that at the mature stage, the CH4 emission in the continuous flowing area was 84.4% lower compared with the static area. Therefore, continuous circulating flow proves to be effective in mitigating CH4 emissions when compared with static water level control.
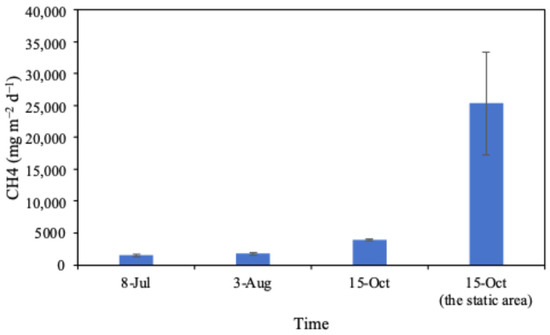
Figure 6.
The CH4 emissions of the paddy wetland.
However, the CH4 emission in the paddy wetland was significantly (p < 0.05) higher compared with the control site, in total approximately three times, regardless of the flood period (July) or drying–wetting cycles period (August) (Figure S3). In July, 6 days prior to CH4 measurements, the control was drained and dried for 2 days for herbicide application. This might be the reason for lower CH4 emissions in the control. Furthermore, the drying–wetting cycles enhance soil permeability and soil redox potential, inhibiting the activity of methanogenic bacteria while promoting the activity of methanotrophic bacteria that oxidize CH4, thereby greatly reducing CH4 emissions [13].
According to the field investigations, we suggested that a paddy wetland with a continuous drying–wetting cycle may be a better solution for CH4 emission reduction. Therefore, an enclosure experiment simulating tidal flow was carried out adjacent to the MIA system. The results, as shown in Figure 7, proved that the total mean of CH4 emissions of the tidal flow treatment decreased by 68.3% compared with the drying–wetting cycle treatment.
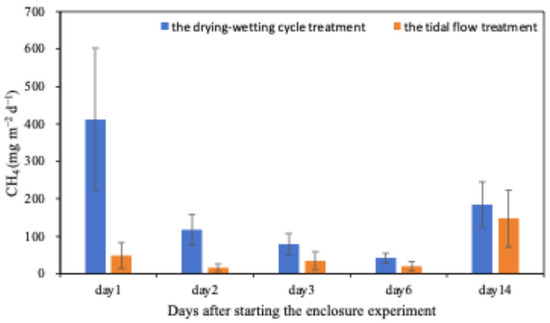
Figure 7.
The CH4 emissions of the enclosure experiment.
3.4. The Emergy Analysis
Emergy is defined as the sum of solar energy required, indirectly or directly, to produce a product or provide a service, expressed in solar emjoules [25]. It has been effectively used to evaluate resource utilization, environmental impact, and overall sustainability for the productivity of agricultural systems, especially for the integrated crop and livestock co-culture systems [34,35]. In this study, we developed the emergy analysis as a systematic tool to conduct an integrated assessment of environmental externalities and critical ecosystem services across three scenarios: ordinary rice fields (OR), MIA1 (ordinary rice paddy, paddy wetland, and Beitang at a ratio of 10:4:1), and MIA2 (ordinary rice paddy, paddy wetland, and Beitang at a ratio of 10:1:1). Emergy inputs and outputs of these three systems are shown in Table S1. MIA1 had the highest total input (9.42 × 1015 sej ha−1) followed by the OR (8.03 × 1015 sej ha−1) and MIA2 (8.02 × 1015 sej ha−1). The elevated total input for MIA1 can be attributed to higher costs associated with the depreciation of the water pump, electricity for irrigation, and labor for the manual weeding, all of which surpassed those of the OR and MIA2. The critical ecosystem services and the total output for MIA1 were far higher compared with those for OR, while those for MIA2 were the highest. However, the rice production and the environmental externalities were the highest in the OR and lowest in MIA2.
To further evaluate the economic and ecological efficiencies [36], we calculated the emergy indices of the three scenarios (Table S2). The ESR of both MIA1 and MIA2 was slightly higher than that of the OR. This suggests a greater proportion of renewable resources applied to MIA1 and MIA2, reducing the reliance on fossil fuels and chemicals. The EYR of MIA2 was 31.8 and 76.0% higher compared with that of MIA1 and the OR, respectively. Among the three scenarios, MIA2 was better to exploit available local resources by investing outside resources. Compared with the OR’s ELR, that of MIA1 and MIA2 decreased by 21.3 and 13.6%, respectively. Conversely, MIA1’s and MIA2’s ESI increased by 69.5 and 103.7%, respectively, compared with that of the OR. These results suggested that MIA1 had the lowest environmental stress, while MIA2 had the best sustainable development potential. Above all, both MIA1 and MIA2 outperformed the OR regarding the output, critical ecosystem services, and environmental externalities, as well as ESR, EYR, ELR, and ESI, with MIA2 particularly excelling in reducing inputs. Therefore, the integrated system was a feasible mean for the comprehensive improvement of paddy field ecosystem services, with MIA2 emerging as the best among the three scenarios.
3.5. Limitations and Future Direction for Practice and Research
The implementation of the MIA system has an advantage over other treatment systems as it directly incorporates a portion of existing paddy fields, requiring only minimal transformation and investment. Although constructed wetlands are commonly employed to mitigate agricultural non-point source pollution [18,37], they require complex and extensive construction. Moreover, the MIA system can simultaneously remove nitrogen pollutants and produce grain, and has the potential to reduce CH4 emission. Nevertheless, as the MIA system is free of pesticides, the market value of its rice should be much higher than that of conventional varieties.
However, several limitations affect the scalability and generalization of the findings from this study. Firstly, the relatively small size of the pilot-scale 1960 m2 paddy wetland can limit the extrapolation of findings to larger-scale applications. The small plot size may affect certain system functions, such as water retention, nutrient cycling, and biodiversity dynamics. As the MIA system was integrated into the existing rice field, the results observed provide a foundation for scaling up the system. Future studies should focus on larger-scale implementations to assess how the system performs under different field sizes and management intensities. It is anticipated that scaling up may require adjustments in irrigation strategies, water management, and plant density. Additionally, long-term studies are needed to evaluate the system’s sustainability over multiple seasons, particularly in terms of soil health, water management efficiency, and the continued effectiveness in methane reduction.
Another limitation of this study is the labor demands associated with manual weeding in the MIA system, which resulted in significantly higher labor input. Reducing weeding frequency and selectively removing only those weeds that affect rice photosynthesis can decrease labor costs. Furthermore, maintaining a limited proportion of weeds might enhance rice growth by serving as a temporary nutrients pool, while the diverse weed community might promote biodiversity conservation. These optimization strategies should be explored in future research.
Moreover, the MIA system’s integration with an aquaculture tank (e.g., shrimp cultivation) offers an opportunity to improve the overall system (Figure 8). The energy used to pump water from the Beitang into the paddy wetland can first be utilized to pump water into the aquaculture tank, facilitating shrimp cultivation. This not only generates an additional output in the form of shrimp, which can financially contribute to offset the energy cost of the pump, but also allows for a more efficient use of resources. Water flow from the aquaculture tank to the paddy field would require no additional energy, relying instead on gravitational force. Furthermore, incorporating this aquaculture tank would facilitate more efficient application of tidal flow in the paddy wetland, which, in turn, would contribute to the mitigation of methane emissions.
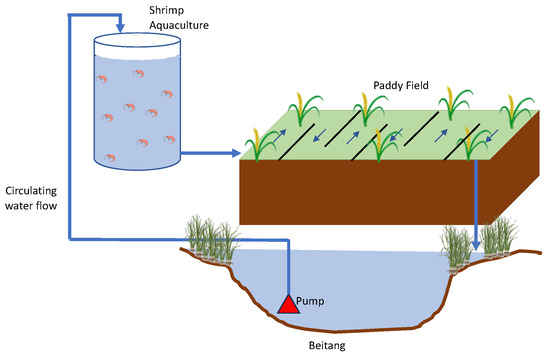
Figure 8.
Schematic overview of the incorporation of a shrimp aquaculture tank.
4. Conclusions
The MIA system improved biodiversity and inhibited pest outbreak, with slightly lower rice production than that in control. The excessive nitrogen can be effectively removed by the paddy wetland, with the TN and DIN removal rate of 0.06–0.65 g N m−2 d−1 and 0.02–0.22 g N m−2 d−1, respectively. The CH4 emission in the paddy wetland was reduced by 84.4% with continuous water flow compared with that with static water. The tidal flow was a better choice for preventing CH4 emission, as CH4 emissions in the tidal flow treatment decreased by 68.3% compared with that in the drying–wetting cycle treatment. The emergy evaluation suggested that the MIA system surpassed the ordinary paddy field, as it had higher ESR, EYR, and ESI and lower ELR while taking both critical ecosystem services and environmental externalities into account. In addition, the output of the MIA system significantly exceeded that of the ordinary paddy field, reinforcing its potential as a more sustainable agriculture practice that benefits both farmers and the environment.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w17152244/s1, Figure S1: Diagram of the growth chamber setup for tidal circulation treatment; Figure S2: Resumed diagram of agricultural production system; Figure S3: The CH4 emission of the paddy wetland and the ordinary rice field; Table S1: Emergy inputs and outputs of the three scenarios; Table S2: Emergy indices of the three scenarios.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.R., H.Z., M.F. and X.C.; formal analysis, S.S., M.F. and R.D.; funding acquisition, Y.H. and X.C.; investigation, N.R., H.Z., Y.W., R.D. and P.X.; methodology, N.R., H.Z., Y.C. and P.X.; software, N.R. and H.Z.; supervision, Y.H. and X.C.; visualization, N.R. and H.Z.; writing—original draft, N.R. and H.Z.; writing—review and editing, S.S., M.F., Y.H., Y.C., Y.W., R.D., P.X. and X.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Scientific Research Plan Project of Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (No. 22dz1202600).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Conflicts of Interest
Author Hongshuo Zou was employed by the company Shanghai International Airport Co., Ltd. Pudong International Airport. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be constructed as a potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Natuhara, Y. Ecosystem services by paddy fields as substitutes of natural wetlands in Japan. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 56, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Xie, H.; Yuan, X.; Pei, E.; Wang, T. Effects of landscape heterogeneity and breeding habitat diversity on rice frog abundance and body condition in agricultural landscapes of Yangtze River Delta, China. Curr. Zool. 2020, 66, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ouyang, X.; Shen, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, W.; Jiang, W.; Wu, J. Nitrogen and phosphorus runoff losses were influenced by chemical fertilization but not by pesticide application in a double rice-cropping system in the subtropical hilly region of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.W.; Lim, J.Y.; Bhuiyan, M.S.I.; Das, S.; Khan, M.I.; Kim, P.J. Investigating the arable land that is the main contributor to global warming between paddy and upland vegetable crops under excessive nitrogen fertilization. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 346, 131197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Peng, S.; Luo, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, S. A paddy eco-ditch and wetland system to reduce non-point source pollution from rice-based production system while maintaining water use efficiency. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 4406–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, N.; Osada, Y.; Mashiko, M.; Baba, Y.G.; Tanaka, K.; Kusumoto, Y.; Okubo, S.; Ikeda, H.; Natuhara, Y. Organic farming and associated management practices benefit multiple wildlife taxa: A large-scale field study in rice paddy landscapes. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 56, 1970–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Hu, C.; Yan, X.; Jin, Y.; Chen, Z.; Guan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, D.; Jansson, C.; Wang, F.; et al. Expression of barley SUSIBA2 transcription factor yields high-starch low-methane rice. Nature 2015, 523, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremen, C.; Miles, A. Ecosystem Services in Biologically Diversified versus Conventional Farming Systems. Ecol. Soc. 2012, 17, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ani, O.; Onu, O.; Okoro, G.; Uguru, M. Overview of Biological Methods of Weed Control. In Biological Approaches for Controlling Weeds; Radhakrishnan, R., Ed.; InTech: Nappanee, IN, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-1-78923-654-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraresi de Araujo, G.J.; Ronquim Filho, A.; Cezarino, L.O.; Liboni, L.B. Sugar-energy bioelectricity in energy trading environments: Reasons for the lack of competitiveness. Int. J. Energy Sect. Manag. 2023, 17, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbach, K.; Milder, J.C.; DeClerck, F.A.J.; de Wit, M.M.; Driscoll, L.; Gemmill-Herren, B. Examining multi-functionality for crop yield and ecosystem services in five systems of agroecological intensification. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2017, 15, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, R.; Huang, J. Ecological engineering for traditional Chinese agriculture—A case study of Beitang. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 76, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagomarsino, A.; Agnelli, A.E.; Linquist, B.; Adviento-Borbe, M.A.; Agnelli, A.; Gavina, G.; Ravaglia, S.; Ferrara, R.M. Alternate Wetting and Drying of Rice Reduced CH4 Emissions but Triggered N2O Peaks in a Clayey Soil of Central Italy. Pedosphere 2016, 26, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Xu, D.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Z. Measuring residents’ perceptions of multifunctional land use in peri-urban areas of three Chinese megacities: Suggestions for governance from a demand perspective. Cities 2022, 126, 103703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Jin, L.; Wu, J.; Pang, M.; Wei, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, T.; Yang, Z.; et al. Rainfall Runoff and Nitrogen Loss Characteristics on the Miyun Reservoir Slope. Water 2024, 16, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar Escobar, N.; Castro, J.M.; Baquero, G.Y.; Hoyos Benjumea, D. Identification of functional groups of insects associated with family agricultural production systems in the province of Sumapaz, Colombia. Bol. Científico Cent. Mus. Mus. Hist. Nat. 2022, 26, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; de Kraker, J.; Bianchi, F.J.J.A.; Xiao, H.; Huang, J.; Deng, X.; Hou, L.; van der Werf, W. Do diverse landscapes provide for effective natural pest control in subtropical rice? J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 57, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Yang, H.; Pan, L.; Perry, D.C.; Xu, P.; Tang, J.; You, W.; He, X.; Wen, Q. Restoring wetlands outside of the seawalls and to provide clean water habitat. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Tang, J.; Zhang, C.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, C.; Xu, P.; Perry, D.C.; Chen, X. Enhanced Carbon Uptake and Reduced Methane Emissions in a Newly Restored Wetland. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2020, 125, e2019JG005222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.T.; Campbell, D.E.; Vilbiss, C.D.; Ulgiati, S. The geobiosphere emergy baseline: A synthesis. Ecol. Model. 2016, 339, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Campbell, D.E.; Qin, P.; Cui, L. Integrated water quality, emergy and economic evaluation of three bioremediation treatment systems for eutrophic water. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 69, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.; Qin, P. Emergy analysis of ecosystems. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2001, 12, 129–131. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, L.; Cheng, K.; Ji, C.; Yue, Q.; Bian, R.; Pan, G. An assessment of emergy, energy, and cost-benefits of grain production over 6 years following a biochar amendment in a rice paddy from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 9683–9696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, J.; Hu, N.; Zhu, L. Evaluation on environmental consequences and sustainability of three rice-based rotation systems in Quanjiao, China by an integrated analysis of life cycle, emergy and economic assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 310, 127493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odum, H.T. Environmental Accounting: Emergy and Environmental Decision Making; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; ISBN 978-0-471-11442-0. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Ya, X.-Y.; Gong, S.-L.; Li, C.-W.; Zhu, R.; Zhu, B.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Wang, X.-L.; Cao, P. Changes in paddy cropping system enhanced economic profit and ecological sustainability in central China. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 566–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chu, G.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Mid-season nitrogen application strategies for rice varieties differing in panicle size. Field Crops Res. 2013, 150, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, K.D. The Ecology and Behavior of Amphibians; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-226-89334-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kidera, N.; Kadoya, T.; Yamano, H.; Takamura, N.; Ogano, D.; Wakabayashi, T.; Takezawa, M.; Hasegawa, M. Hydrological effects of paddy improvement and abandonment on amphibian populations; long-term trends of the Japanese brown frog, Rana japonica. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 219, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingaraj, V.K.; Nitin, K.S.; Rajendra Prasad, B.S. Arthropod Community on Rice: A Blend of Aquatic and Terrestrial Species. In Economic and Ecological Significance of Arthropods in Diversified Ecosystems: Sustaining Regulatory Mechanisms; Chakravarthy, A.K., Sridhara, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 147–167. ISBN 978-981-10-1524-3. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, N.-F.; Cai, Y.-M.; Shen, Y.-J.; Ji, X.-Y.; Wu, X.-W.; Zheng, X.-R.; Cheng, W.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y.-P.; Chen, X.; et al. Increasing plant diversity with border crops reduces insecticide use and increases crop yield in urban agriculture. eLife 2018, 7, e35103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, A.; Ito, H.; Sasaki, A.; Kajihara, A.; Watanabe, T. Cultivation of rice for animal feed with circulated irrigation of treated municipal wastewater for enhanced nitrogen removal: Comparison of cultivation systems feeding irrigation water upward and downward. Water Sci. Technol. J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Res. 2015, 72, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.H.; Yang, L.Z. Purification of Water with Low Concentrations of N and P in Paddy Wetlands in Taihu Lake Region. Res. Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.-F.; Cai, C.-J.; Zeng, X.-S.; Campbell, D.E.; Fan, S.-H.; Liu, G.-L. Bamboo vs. crops: An integrated emergy and economic evaluation of using bamboo to replace crops in south Sichuan Province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 177, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Li, M.; Deng, S.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, H. Emergy evaluation of an integrated livestock wastewater treatment system. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 92, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.-F.; Kang, W.-L.; Campbell, D.E.; Ren, H.; Tan, Y.-W.; Feng, R.-X.; Luo, J.-T.; Chen, F.-P. Emergy and economic evaluations of four fruit production systems on reclaimed wetlands surrounding the Pearl River Estuary, China. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 1743–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messer, T.L.; Moore, T.L.; Nelson, N.; Ahiablame, L.; Bean, E.Z.; Boles, C.; Cook, S.L.; Hall, S.G.; McMaine, J.; Schlea, D. Constructed Wetlands for Water Quality Improvement: A Synthesis on Nutrient Reduction from Agricultural Effluents. Trans. ASABE 2021, 64, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).