Activation of Peracetic Acid by Ozone for Recalcitrant Pollutant Degradation: Accelerated Kinetics, Byproduct Mitigation, and Microbial Inactivation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. DBP Formation Potential
2.5. Ecotoxicity Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
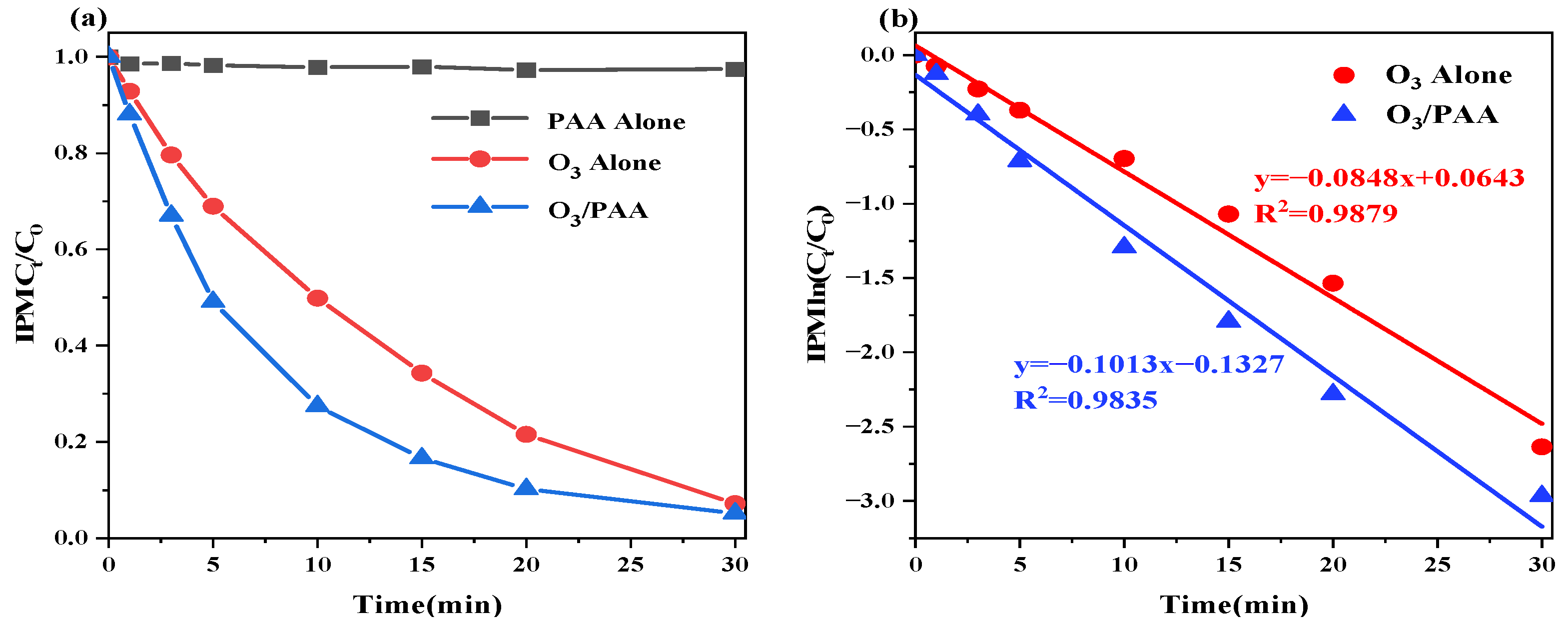
3.1. IPM Degradation in Various Systems
3.2. Effects of Crucial Factors via O3/PAA System
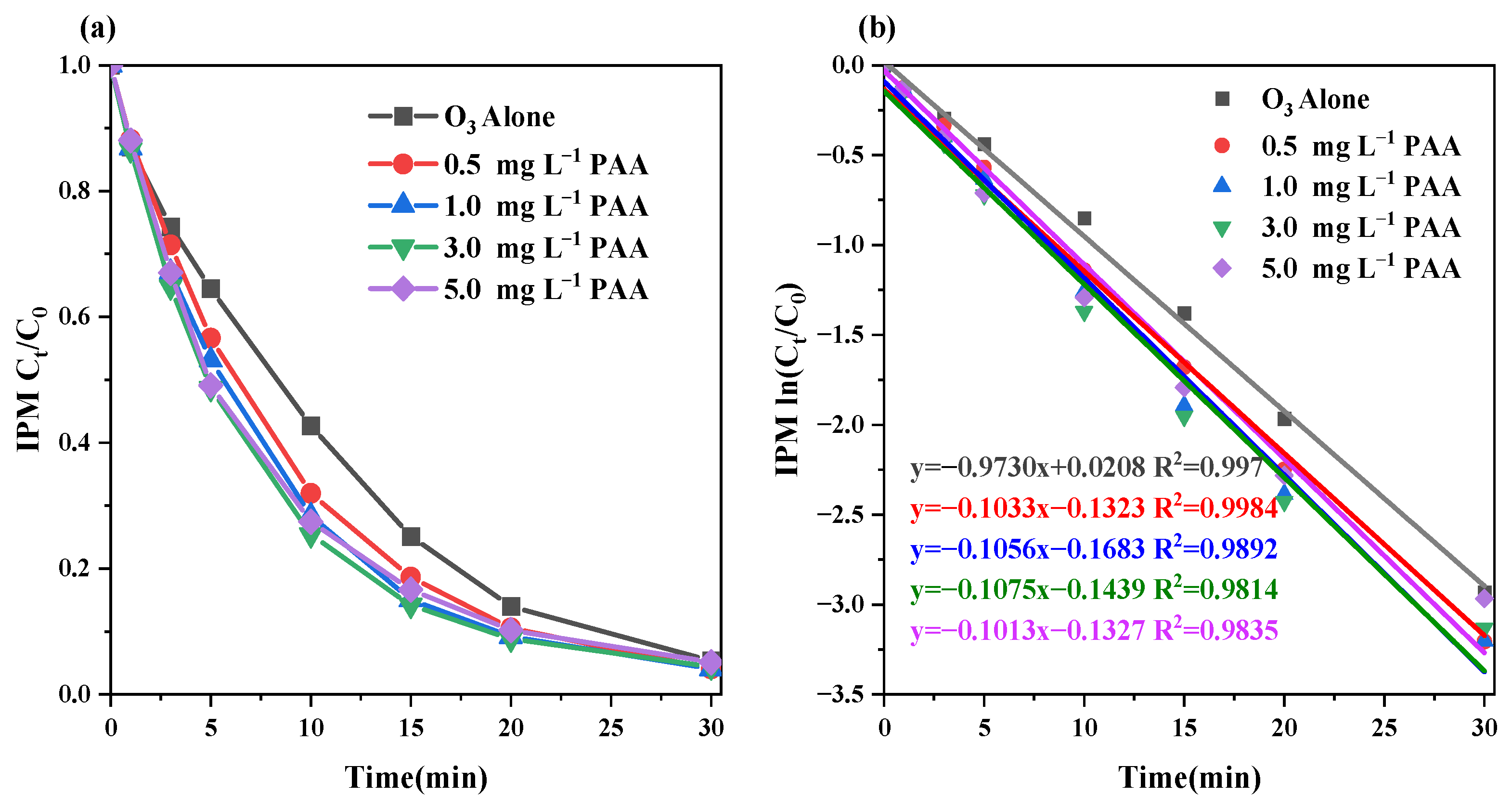
3.2.1. O3 and PAA Dose
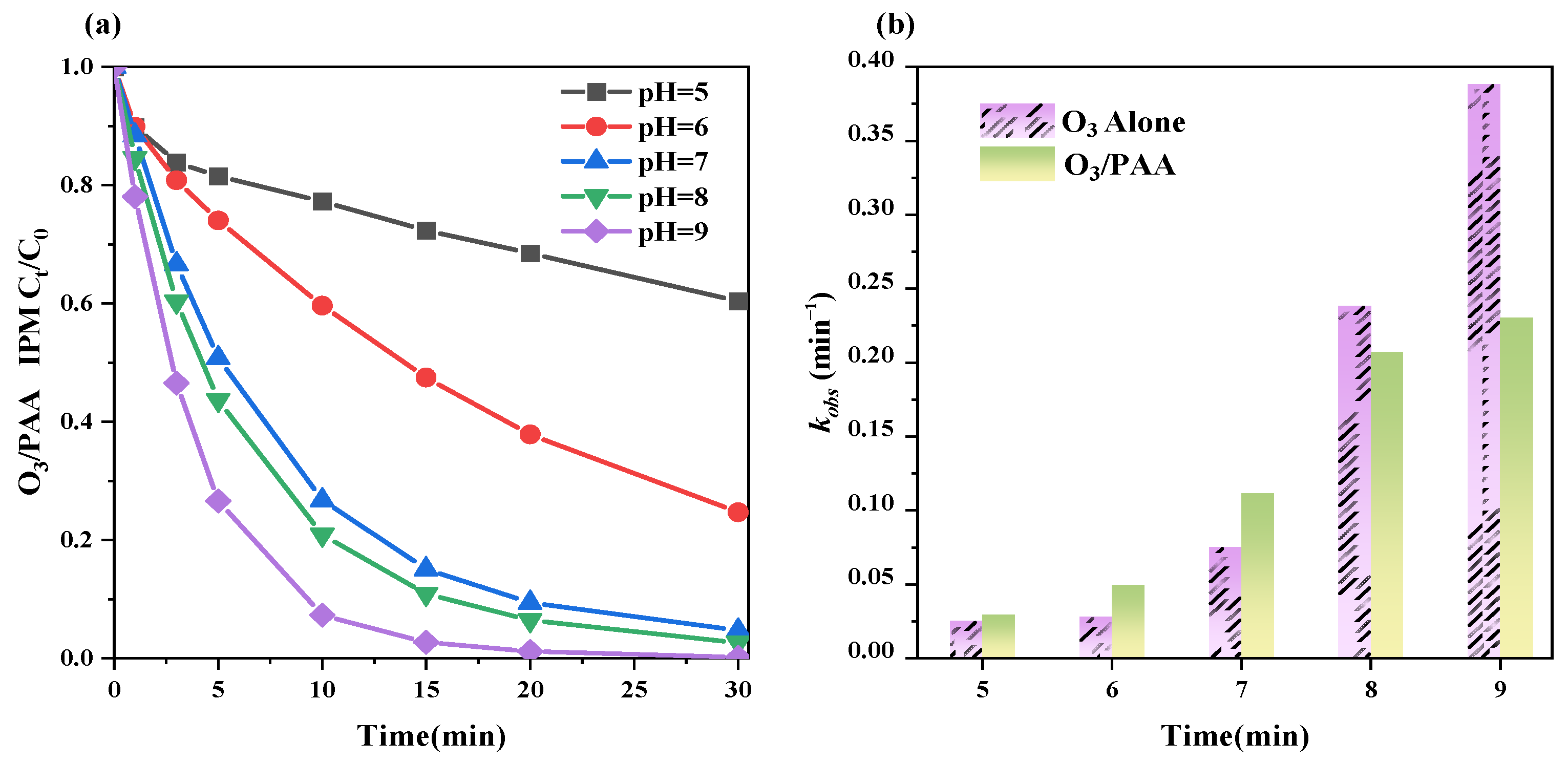
3.2.2. Solution pH
3.2.3. Water Matrix
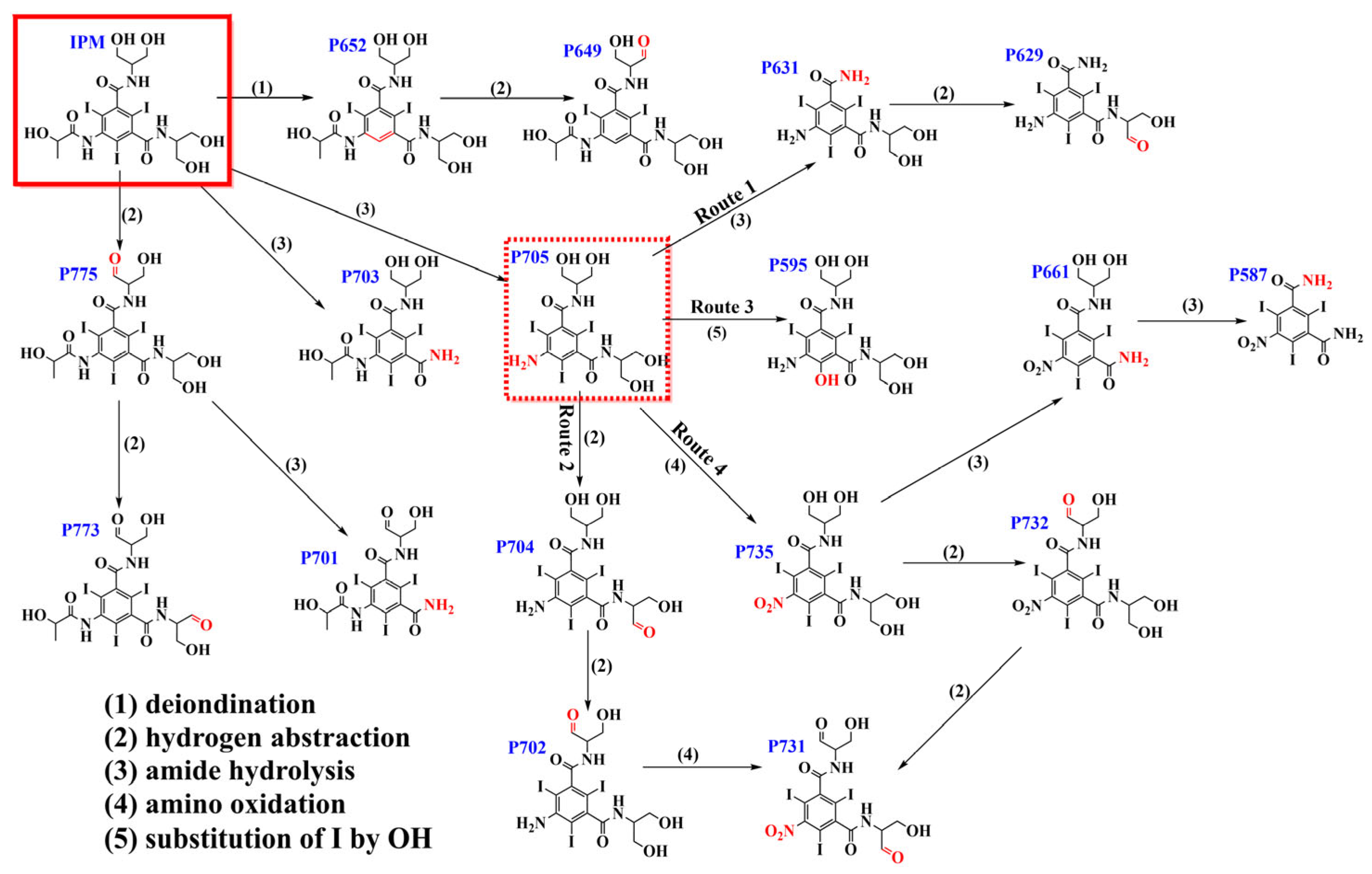
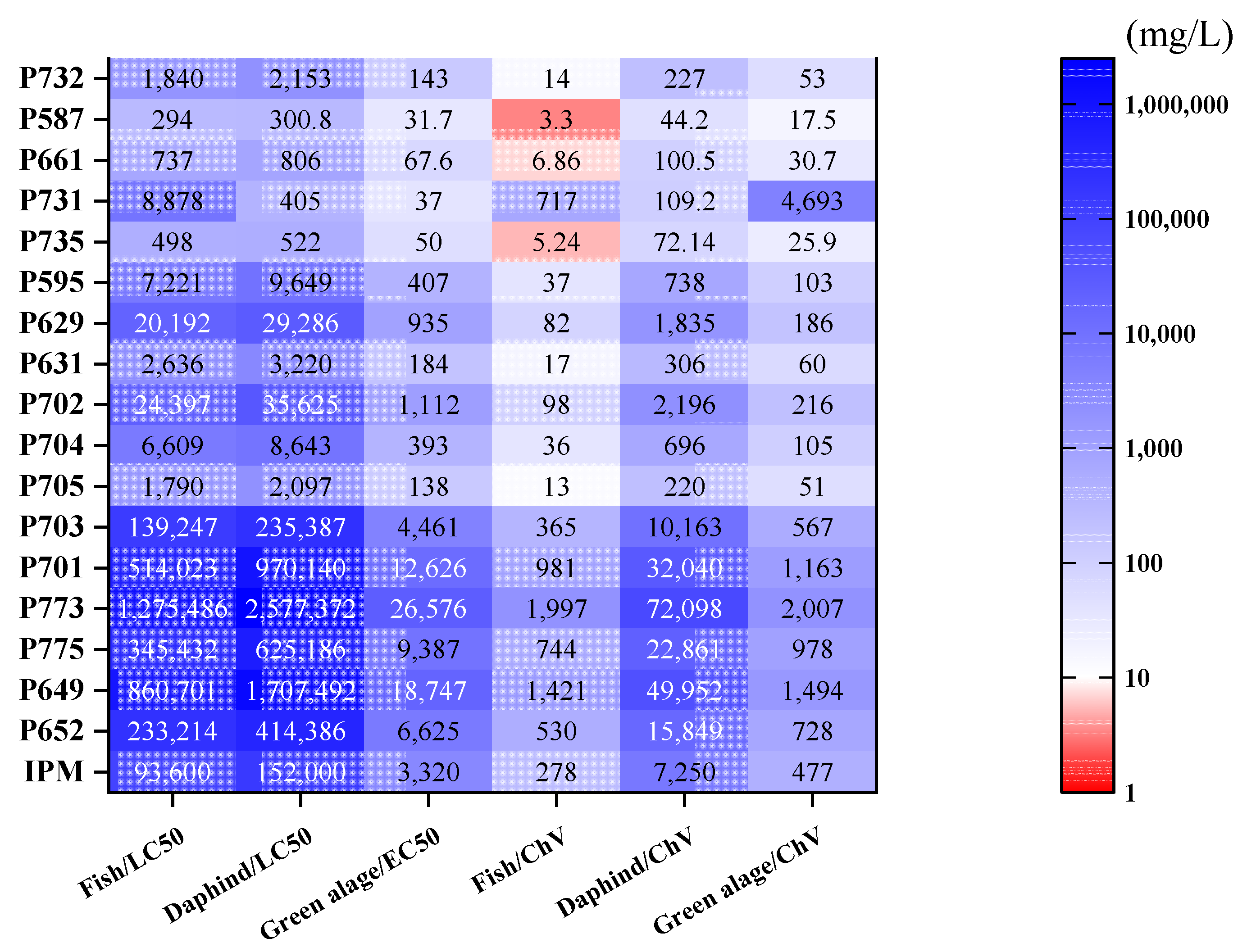
3.3. Degradation Pathways and Ecotoxicity Evaluation
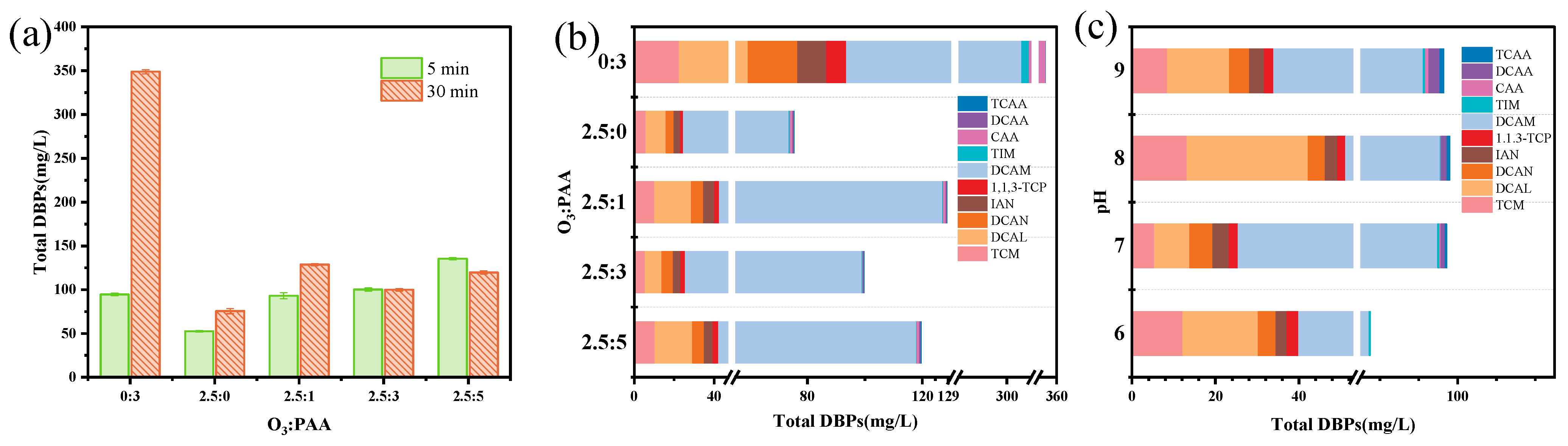
3.4. DBPs Formation
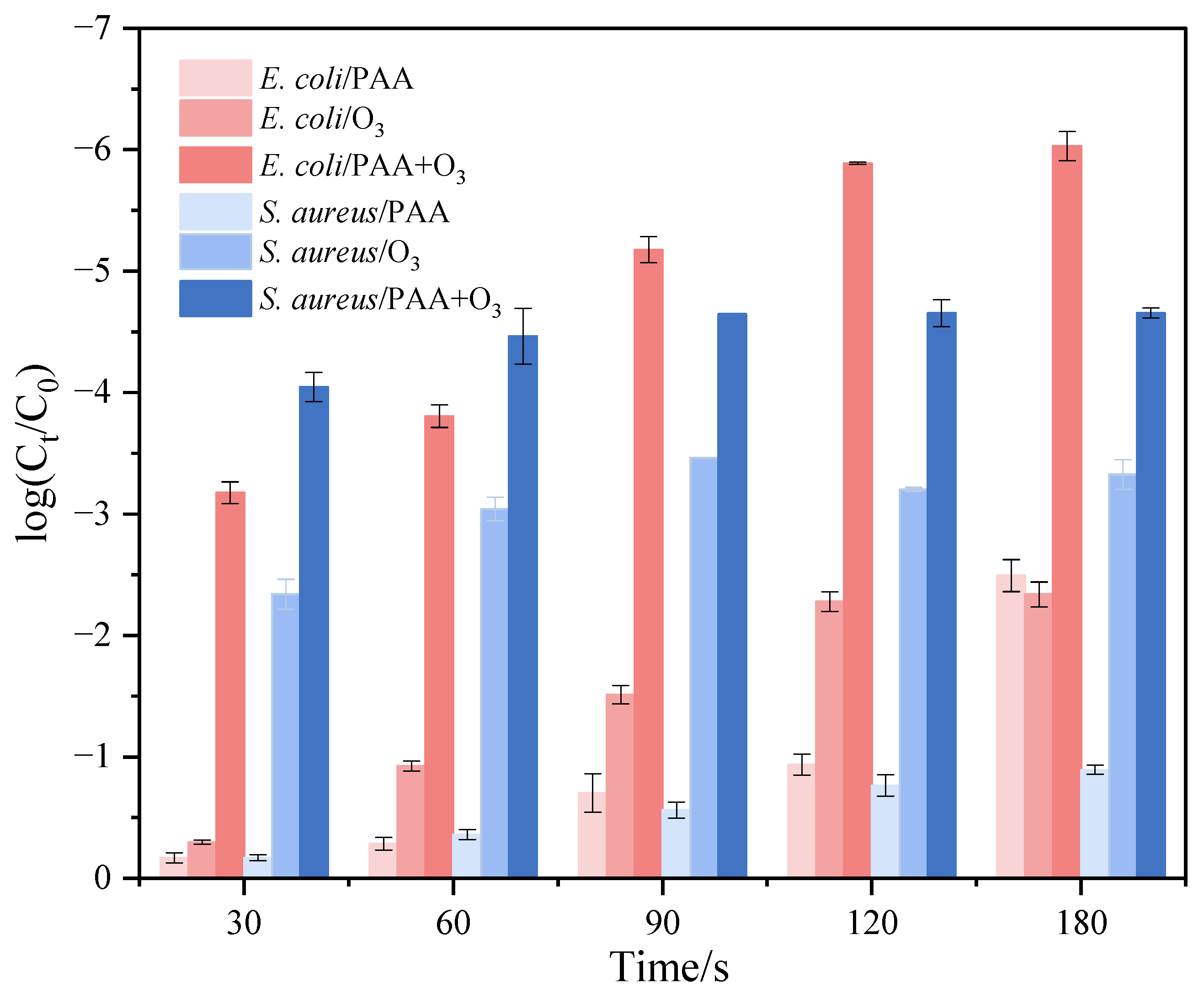
3.5. Sterilization Performance Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rook, J. Formation of Haloform during Chlorination of Natural Water. Water Treat. Exam. 1974, 23, 234–243. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, S.D.; Plewa, M.J.; Wagner, E.D.; Schoeny, R.; DeMarini, D.M. Occurrence, Genotoxicity, and Carcinogenicity of Regulated and Emerging Disinfection By-products in Drinking Water: A Review and Roadmap for Research. Mutat. Res. 2007, 636, 178–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Yang, M.; Tan, C.; Chu, W. The Occurrence, Characteristics, Transformation and Control of Aromatic Disinfection By-products: A Review. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, B.; Shen, L.; Liu, Z.; Tang, L.; Tan, X.; Wang, D.; Zeng, W.; Wu, T.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Disinfection Byproducts Formation from Emerging Organic Micropollutants during Chlorine-Based Disinfection Processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.M.; Plewa, M.J.; Wagner, E.D.; Wei, X.; Bokenkamp, K.; Hur, K.; Jia, A.; Liberatore, H.K.; Lee, C.-F.T.; Shirkhani, R.; et al. Drivers of Disinfection Byproduct Cytotoxicity in U.S. Drinking Water: Should Other DBPs be Considered for Regulation? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendel, F.M.; Ternes, T.A.; Richardson, S.D.; Duirk, S.E.; Pals, J.A.; Wagner, E.D.; Plewa, M.J. Comparative Toxicity of High-Molecular Weight Iopamidol Disinfection Byproducts. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2016, 3, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternes, T.A.; Hirsch, R. Occurrence and Behavior of X-ray Contrast Media in Sewage Facilities and the Aquatic Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 2741–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.-X.; Xu, B.; Lin, Y.-L.; Hu, C.-Y.; Zhang, T.-Y.; Gao, N.-Y. Photodegradation Kinetics of Iopamidol by UV Irradiation and Enhanced Formation of Iodinated Disinfection By-products in Sequential Oxidation Processes. Water Res. 2014, 58, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duirk, S.E.; Lindell, C.; Cornelison, C.C.; Kormos, J.; Ternes, T.A.; Attene-Ramos, M.; Osiol, J.; Wagner, E.D.; Wagner, M.J.; Plewa, S.D. Richardson, Formation of Toxic Iodinated Disinfection By-products from Compounds Used in Medical Imaging. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 6845–6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, J.L.; Bukhari, Z.; Hargy, T.M.; Bolton, J.R.; Dussert, B.W.; Marshall, M.M. Using UV to Inactivate Cryptosporidium. J. Am. Water Works Ass. 2000, 92, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Kazama, F.; Hu, J.; Ray, A.K. Ray, Ferrates (iron(VI) and iron(V)): Environmentally Friendly Oxidants and Disinfectants. J. Water Health 2005, 3, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Li, L.; Chen, W.; Pan, S. Effect and Mechanism of Preoxidation Using Potassium Permanganate in an Ultrafiltration Membrane System. Desalination 2012, 286, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yao, S.; Lin, K.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, C. Removal of Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Control of Horizontal Transfer Risk by UV, Chlorination and UV/Chlorination Treatments of Drinking Water. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manousaridis, G.; Nerantzaki, A.; Paleologos, E.; Tsiotsias, A.; Savvaidis, I.; Kontominas, M. Effect of Ozone on Microbial, Chemical and Sensory Attributes of Shucked Mussels. Food Microbiol. 2005, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Prieto, I.J.; Pérez-Pastenes, H.; Núñez-Correa, S.; Cuevas-Díaz, M.C.; Guzmán-López, O.; Rodríguez-Ramírez, T.E. Multivariate Analysis of Ozonation as a Control for the Formation of Iodinated Disinfection By-products from Iopamidol Oxidation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 22, 2931–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasim, M.F.; Bao, Y.; Elgarahy, A.M.; Osman, A.I.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Rooney, D.W.; Yap, P.-S.; Oh, W.-D. Peracetic Acid Activation Using Heterogeneous Catalysts for Environmental Decontamination: A Review. Catal. Commun. 2023, 180, 106702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Hu, Y.; Xiao, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, M.; Yang, H.; Zou, J.; Yuan, B.; Ma, J. Enhanced Diclofenac Elimination in Fe(II)/Peracetic Acid Process by Promoting Fe(III)/Fe(II) Cycle with ABTS as Electron Shuttle. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 129692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wei, J.; Li, Y.; Huo, J.; Ji, W.; Cui, N.; Li, J.; Niu, X.; Jiang, Z.; Cui, X.; et al. A State-of-the-art Review on Heterogeneous Catalysts-mediated Activation of Peracetic Acid for Micropollutants Degradation: Classification of Reaction Pathways, Mechanisms, Influencing Factors and DFT Calculation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 477, 147051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Cheng, Y.; Dong, H.; Sun, L.; Pan, F.; Yuan, X. Insights into the Novel Oxidation Process of Ozone/Peracetic Acid: Kinetics Evaluation, Degradation Pathways, and Toxicity Assessment. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Much, J.W.; Hautman, D.P. Determination of Chlorination Disinfection By-products, Chlorinated Solvents, and Halogenated Pesticides/herbicides in Drinking Water by Liquid–Liquid Extraction and Gas Chromatograph with Electron-capture Detection (Revision 1.0); U.S.EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1995.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency, Ecological Structure Activity Relationships (ECOSAR) Predictive Model. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/tsca-screening-tools/ecological-structure-activity-relationships-ecosar-predictive-model (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Liu, B.; Guo, W.; Jia, W.; Wang, H.; Zheng, S.; Si, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Luo, H.; Jiang, J.; Ren, N. Insights into the oxidation of organic contaminants by Co(II) activated peracetic acid: The overlooked role of high-valent cobalt-oxo species. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosjean, D.; Williams, E.L. Environmental persistence of organic compounds estimated from structure-reactivity and linear free-energy relationships. Unsaturated aliphatics, Atmos. Environ. A Gen. Top. 1992, 26, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wei, C.; Hu, Y.; Wu, H. Zinc Ferrite Catalysts for Ozonation of Aqueous Organic Contaminants: Phenol and Bio-Treated Coking Wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Ji, Q.; Li, T.; He, H.; Song, H.; Yang, S.; Li, S.; Yan, S.; et al. Identifying the Role of Oxygen Vacancy on Cobalt-based Perovskites towards Peroxymonosulfate Activation for Efficient Iohexol Degradation. Appl. Catal. B 2022, 319, 121901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dong, H.; Li, H.; Sun, L.; Pan, F.; Yuan, X. Unraveling the Catalytic Ozonation Mechanisms with ZnO Decorated rGO Composite: Structural Properties and Reactive Oxygen Species Evolution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 324, 124590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Sun, P.; Zhang, L.; Huang, C.-H. UV/Peracetic Acid for Degradation of Pharmaceuticals and Reactive Species Evaluation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 14217–14224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boncz, M.A.; Bruning, H.; Rulkens, W.H.; Zuilhof, H.; Sudhölter, E.J.R. The Effect of Salts on Ozone Oxidation Processes. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2005, 27, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Kim, J.; Huang, C.-H. Mechanistic insight for Disinfection Byproduct Formation Potential of Peracetic Acid and performic acid in Halide-Containing Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 18898–18908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinelli, G.; Coha, M.; Vione, D.; Minella, M.; Tiraferri, A. Tiraferri, Formation of Halogenated Byproducts upon water Treatment with Peracetic Acid. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 5123–5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.-m.; Yuan, J.-m. Advanced Treatment of Sodium Acetate in Water by Ozone Oxidation. Water Environ. Res. 2014, 86, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.M.; Macedo, G.; Pedrosa, M.; Becerra-Castro, C.; Castro-Silva, S.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Silva, A.M.T.; Nunes, O.C.; Manaia, C.M. Ozonation and UV254nm Radiation for the Removal of Microorganisms and Antibiotic Resistance Genes from Urban Wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Li, N.; Xiao, S.; Chen, J.; Ji, R.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y. Revisiting Iodide Species Transformation in Peracetic Acid Oxidation: Unexpected Role of Radicals in Micropollutants Decontamination and Iodate Formation. Water Res. 2024, 265, 122270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, D.; Liu, C.; Zhang, S.; Dong, H.; Sun, L.; Yuan, X. Activation of Peracetic Acid by Ozone for Recalcitrant Pollutant Degradation: Accelerated Kinetics, Byproduct Mitigation, and Microbial Inactivation. Water 2025, 17, 2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152240
Bai D, Liu C, Zhang S, Dong H, Sun L, Yuan X. Activation of Peracetic Acid by Ozone for Recalcitrant Pollutant Degradation: Accelerated Kinetics, Byproduct Mitigation, and Microbial Inactivation. Water. 2025; 17(15):2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152240
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Dihao, Cong Liu, Siqing Zhang, Huiyu Dong, Lei Sun, and Xiangjuan Yuan. 2025. "Activation of Peracetic Acid by Ozone for Recalcitrant Pollutant Degradation: Accelerated Kinetics, Byproduct Mitigation, and Microbial Inactivation" Water 17, no. 15: 2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152240
APA StyleBai, D., Liu, C., Zhang, S., Dong, H., Sun, L., & Yuan, X. (2025). Activation of Peracetic Acid by Ozone for Recalcitrant Pollutant Degradation: Accelerated Kinetics, Byproduct Mitigation, and Microbial Inactivation. Water, 17(15), 2240. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152240






