Bacterial Communities Respond to Spatiotemporal Fluctuation in Water Quality and Microcystins at Lake Taihu
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
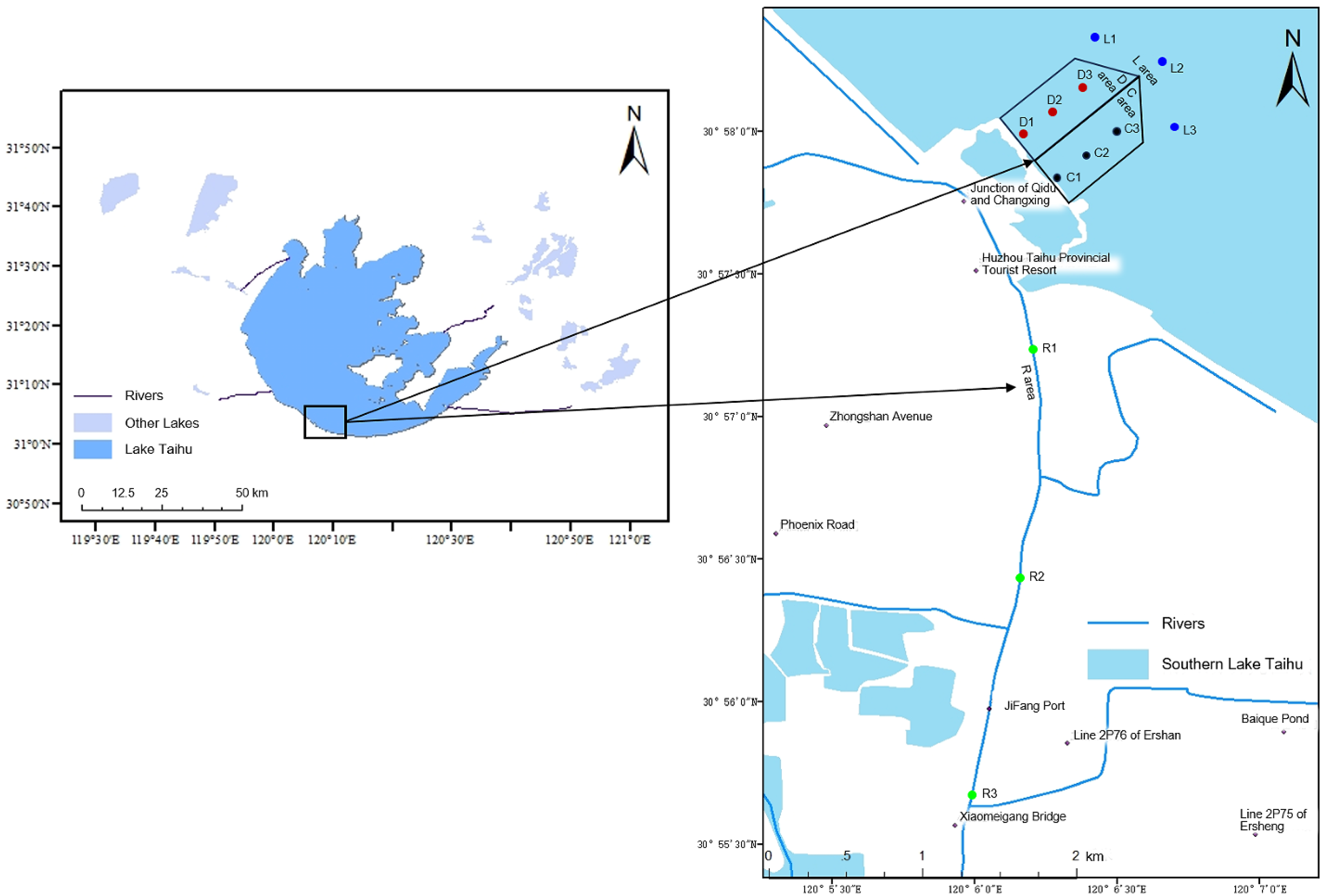
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Analysis of Physicochemical Properties
2.3. Analysis of Microcystins
2.4. DNA Extraction and Illumina Sequencing
2.5. Co-Occurrence Network Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
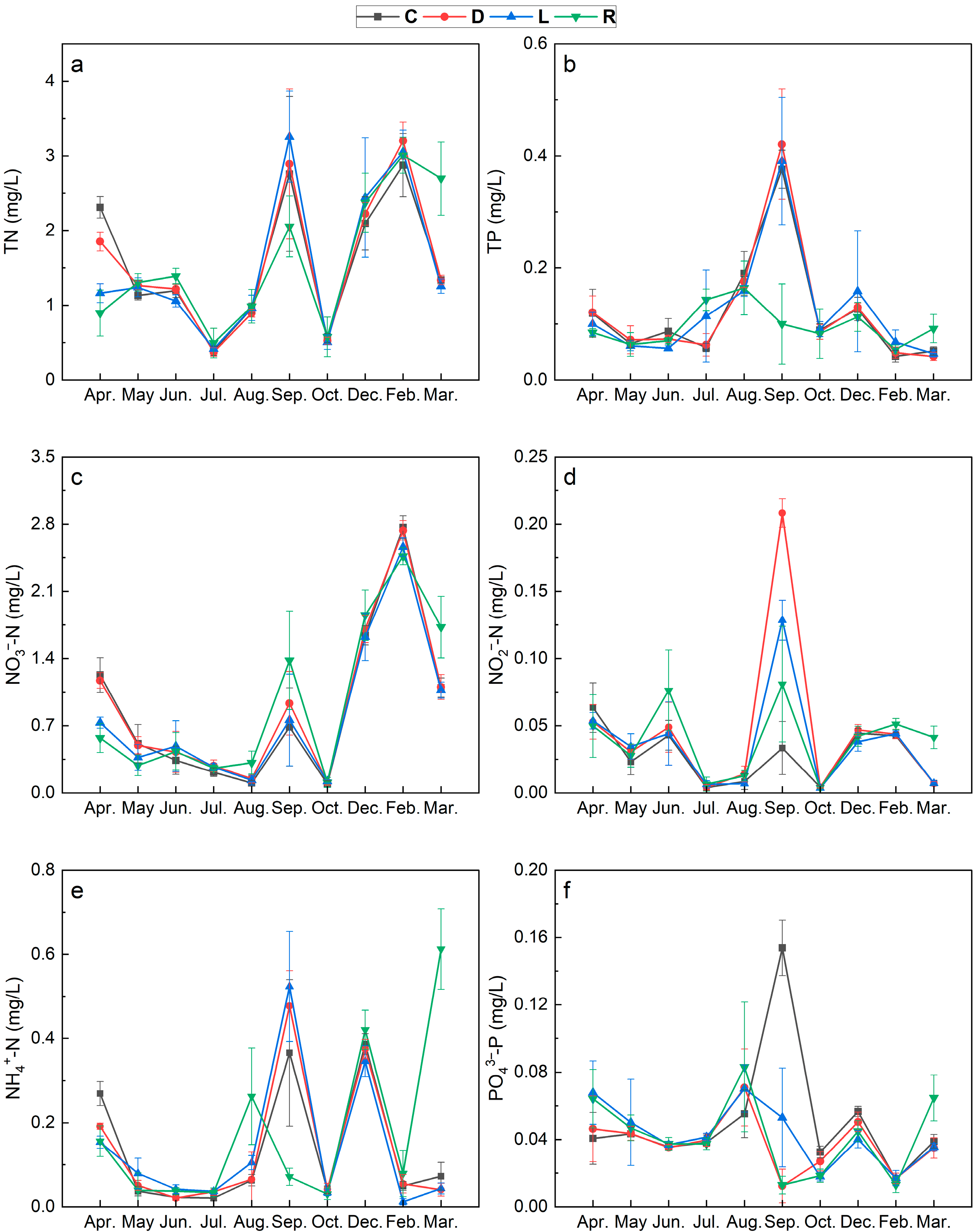
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variation in Environmental Factors in the Overlying Water
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variation in MC Concentrations of Overlying Water
3.3. Correlations Between MCs and Environmental Factors
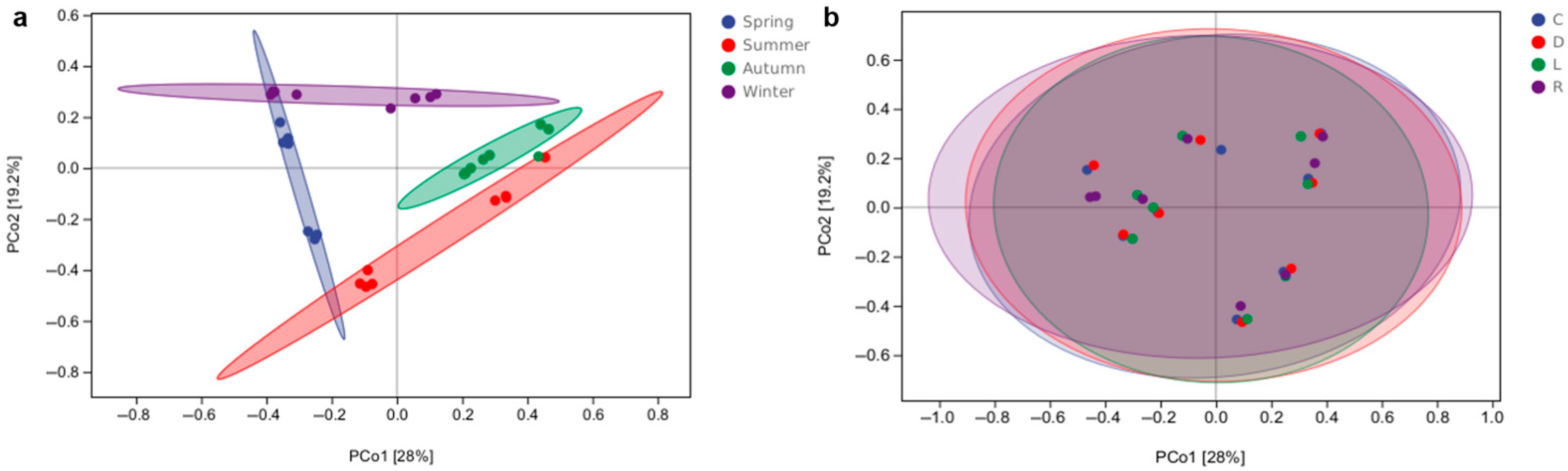
3.4. Alpha and Beta Diversity of Bacterial Communities in Overlying Water from Southern Lake Taihu
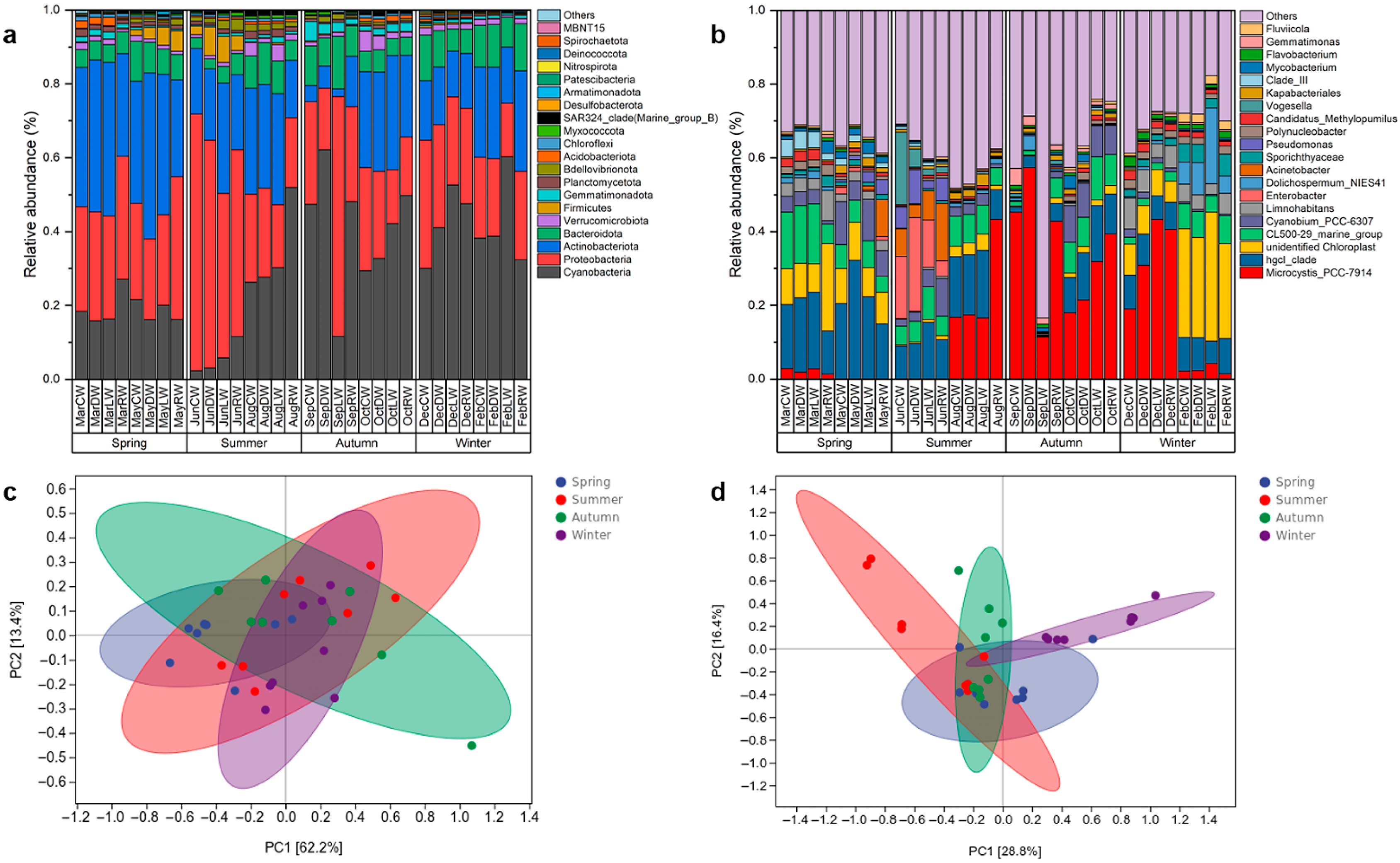
3.5. Composition of Bacterial Communities in Overlying Water
3.6. Analysis of Factors Influencing Bacterial Communities
3.7. Factors Influencing Bacterial Metabolic Functions
3.8. Seasonal Variation in Bacterial Co-Occurrence Networks
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Awual, M.R. An efficient composite material for selective lead(ii) monitoring and removal from wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubra, K.T.; Salman, M.S.; Hasan, M.N.; Islam, A.; Hasan, M.M.; Awual, M.R. Utilizing an alternative composite material for effective copper(ii) ion capturing from wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 336, 116325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.S.; Hasan, M.N.; Kubra, K.T.; Hasan, M.M. Optical detection and recovery of Yb(iii) from waste sample using novel sensor ensemble nanomaterials. Microchem. J. 2021, 162, 105868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awual, M.R. Novel conjugated hybrid material for efficient lead(ii) capturing from contaminated wastewater. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 101, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.M.; Shenashen, M.A.; Hasan, M.N.; Znad, H.; Salman, M.S.; Awual, M.R. Natural biodegradable polymeric bioadsorbents for efficient cationic dye encapsulation from wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 323, 114587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubra, K.T.; Salman, M.S.; Hasan, M.N.; Islam, A.; Teo, S.H.; Hasan, M.M.; Sheikh, M.C.; Awual, M.R. Sustainable detection and capturing of cerium(iii) using ligand embedded solid-state conjugate adsorbent. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 338, 116667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubra, K.T.; Salman, M.S.; Znad, H.; Hasan, M.N. Efficient encapsulation of toxic dye from wastewater using biodegradable polymeric adsorbent. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 329, 115541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chang, F.; Xie, P.; Liu, Q.; Duan, L.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; Peng, W.; Liu, F. In-situ responses of phytoplankton to graphene photocatalysis in the eutrophic lake Xingyun, southwestern China. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Dong, Y.; Kong, M.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, H.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z. Insights into the long-term pollution trends and sources contributions in Lake Taihu, China using multi-statistic analyses models. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Dai, S.; Wen, X.; Qian, C.; Luo, F.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Xi, Y. Chlorophyll-nutrient relationship changes with lake type, season and small-bodied zooplankton in a set of subtropical shallow lakes. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, X.; Guan, R.; Zhu, C.; Xu, C.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, Z.; Xue, Y.; Tu, J.; et al. Evaluation of different 16S rRNA gene V regions for exploring bacterial diversity in a eutrophic freshwater lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1254–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, R.; Li, P.; Bai, Q.; Li, Q.; Hao, Z.; Yu, S.; Cai, Y.; Liu, J. Spatial distribution, temporal variations and source of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in Taihu Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Lin, C.; Cao, Z.; Hu, M.; Xue, K.; Chen, X.; Ma, R. Development of remote sensing algorithm for total phosphorus concentration in eutrophic lakes: Conventional or machine learning? Water Res. 2022, 215, 118213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Zhu, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Xu, H. Seasonal dynamics of odor compounds concentration driven by phytoplankton succession in a subtropical drinking water reservoir, southeast China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 128056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Xu, C.; Yang, S.; Li, B. Investigating the effects of inflow river water quality on lake nutrient-concentration variations: A case study in Gehu Lake, China. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2023, 74, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Jin, H.; Wang, T.; Zhu, W.; Li, L. Underestimated nutrient from aquaculture ponds to Lake Eutrophication: A case study on Taihu Lake Basin. J. Hydrol. 2024, 630, 130749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Jiang, H. Coordinated photodegradation and biodegradation of organic matter from macrophyte litter in shallow lake water: Dual role of solar irradiation. Water Res. 2020, 172, 115516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Hou, J.; Suo, C.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Fu, R.; Wu, F. Molecular-level composition of dissolved organic matter in distinct trophic states in Chinese lakes: Implications for eutrophic lake management and the global carbon cycle. Water Res. 2022, 217, 118438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Luo, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhai, J.; Cao, Z.; Ma, J.; Qi, T.; Shen, M.; Gu, X.; Duan, H. Coordinated dynamics of aquaculture ponds and water eutrophication owing to policy: A case of Jiangsu province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 172194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Song, Z.; Xie, Z.; Li, L.; Song, L. Bioaccumulation of microcystins in two freshwater gastropods from a cyanobacteria-bloom plateau lake, Lake Dianchi. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 164, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, J.; Hu, L.; Shen, W.; Zeng, J.; Li, L.; Song, L.; Gan, N. The involvement of α—Proteobacteria Phenylobacterium in maintaining the dominance of toxic Microcystis blooms in lake Taihu, China. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 23, 1066–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yancey, C.E.; Mathiesen, O.; Dick, G.J. Transcriptionally active nitrogen fixation and biosynthesis of diverse secondary metabolites by dolichospermum and aphanizomenon-like cyanobacteria in western lake Erie microcystis blooms. Harmful Algae 2023, 124, 102408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanvir, R.U.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J. Cyanobacterial community succession and associated cyanotoxin production in hypereutrophic and eutrophic freshwaters. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Mao, M.; Feng, M.; Peng, T.; Long, X.; Yang, F. Fate, abundance and ecological risks of microcystins in aquatic environment: The implication of microplastics. Water Res. 2024, 251, 121121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Tu, Q. Survey Specification for Lake Eutrophication, 2nd ed.; China Environmental Science: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- GB3838-2002; The Surface Water Environmental Quality Standard. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese)
- Fadrosh, D.W.; Ma, B.; Gajer, P.; Sengamalay, N.; Ott, S.; Brotman, R.M.; Ravel, J. An improved dual-indexing approach for multiplexed 16S rRNA gene sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq platform. Microbiome 2014, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.; An, S. Identifying the biogeographic patterns of rare and abundant bacterial communities using different primer sets on the Loess Plateau. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, L.; Li, J.; Yin, L.; Luo, X.; Ahmad, M.; Fang, B.; Li, S.; Deng, Q.; Wang, P.; Li, W. Habitat-dependent prokaryotic microbial community, potential keystone species, and network complexity in a subtropical estuary. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, P.; Gao, H.; Zhang, B.; Feng, B. Nitrate input inhibited the biodegradation of erythromycin through affecting bacterial network modules and keystone species in lake sediments. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 355, 120530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Qiao, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, Z.; Yu, C. Microbial community succession in soils under long-term heavy metal stress from community diversity-structure to KEGG function pathways. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttigieg, P.L.; Ramette, A. A guide to statistical analysis in microbial ecology: A community-focused, living review of multivariate data analyses. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 90, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Liu, K.; Pedersen, M.W.; Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, C.; Liu, Y. Community assembly processes underlying the temporal dynamics of glacial stream and lake bacterial communities. Sci. Total Envrion. 2021, 761, 143178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Peres-Neto, P.R. Generalizing hierarchical and variation partitioning in multiple regression and canonical analyses using the rdacca.hp R package. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2022, 13, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edition, F. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; 4th edition incorporating the first and second addenda; World Health Organization: Genevan, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 430–433. [Google Scholar]
- Chorus, I.; Welker, M. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Li, Q.; Pang, Y.; Yang, X. Relationship between extra-cellular microcystin and intra-cellular microcystin. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2009, 40, 328–334. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Zhu, G.; Kong, F.; Li, S.; Shi, X.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Z.; Xu, H.; Zhu, M. Spatiotemporal characteristics of microcystin variants composition and associations with environmental parameters in Lake Chaohu, China. J. Lake Sci. 2019, 31, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Xie, L.; Wang, X.; Yao, L.; Xue, Q.; Li, J. Vertical distribution characteristics of microcystin concentration in water and sediment of Meiliang Bay, Lak Taihu. J. Lake Sci. 2019, 31, 976–987. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Lu, S.; Song, D.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, L. Spatial distribution, related environmental factors and health risk assessment of microcystins in Lake Qilu, a eutrophic plateau lake. J. Lake Sci. 2024, 36, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Z. The Temporal and Spatial Variation of Aquatic Phytoplankton and Microcystin in Dianchi Lake and the Removal of Microcystin with Bacteria. Master’s Thesis, Yunnan University, Kunming, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Yi, Q.; Liu, Z. Spatio-temporal distribution of microcystins and microcystin-producing cells in the Yanghe Reservoir. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2017, 37, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zou, H.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z. Spatial and temporal distribution of microcystin in Taihu Lake. Res. Environ. Sci. 2014, 27, 696–703. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.; Jiao, C.; Zhao, D.; Xu, H.; Huang, R.; Cao, X.; Yu, Z.; Wu, L. Patterns and assembly processes of planktonic and sedimentary bacterial community differ along a trophic gradient in freshwater lakes. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 106, 105491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhao, D.; Zeng, J.; Jiao, C.; Yu, Z.; Wu, Q.L. Distinct successional patterns and processes of free-living and particle-attached bacterial communities throughout a phytoplankton bloom. Freshw. Biol. 2020, 65, 1363–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Qin, B.; Paerl, H.W.; Brookes, J.D.; Hall, N.S.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, H.; et al. The persistence of cyanobacterial (Microcystis spp.) blooms throughout winter in Lake Taihu, China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowd, S.E.; Callaway, T.R.; Wolcott, R.D.; Sun, Y.; McKeehan, T.; Hagevoort, R.G.; Edrington, T.S. Evaluation of the bacterial diversity in the feces of cattle using 16S rDNA bacterial tag-encoded FLX amplicon pyrosequencing (bTEFAP). BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Gao, D.; Wang, Y.; He, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Du, X. Distribution of sediment microbial communities and their relationship with surrounding environmental factors in a typical rural river, Southwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 84206–84225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, T.; Liu, J.; Yao, Y.; Chen, K.; Mao, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, K.; Yang, P. Regulation and microbial response mechanism of nitric oxide to copper-containing swine wastewater treated by Pistia stratiotes. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 359, 124560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Hu, H.; Chow, A.T.; Chen, P.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Gong, Z.; Huang, S. Evaluation of organic matter and nitrogen removals, electricity generation and bacterial community responses in sediment microbial fuel cell coupled with Vallisneria natans. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Sun, N.; Li, L.; Zhou, H.; Yang, X.; Ai, J.; Yang, X.; Hu, C.; Wang, D.; Zhang, W. Enhanced removal of biolabile oxygen depleted dissolved organic matter by coagulation-adsorption process improves biological stability of reclaimed water. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 500, 157156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrana, J.M.; Li, B.; Watanabe, K. Cross-taxa assessment of species diversity and phylogenetic structure of benthic communities in a dam-impacted river undergoing habitat restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 958, 177886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Shen, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, R.; Niu, Y.; Cui, B. Quantitative effects of anthropogenic and natural factors on the spatial distribution of heavy metals and bacterial communities in sediments of the Pearl River Delta. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 35, 103648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Bi, R.; Liu, J.; Cui, J.; Fu, X.; Xiao, X.; Li, R.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, S.; Zhang, C.; et al. Spatial distribution of bacteria in response to phytoplankton community and multiple environmental factors in surface waters in Sanggou Bay. Mar. Environ. Res. 2025, 204, 106912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portas, A.; Carriot, N.; Ortalo-Magné, A.; Damblans, G.; Thiébaut, M.; Culioli, G.; Quillien, N.; Briand, J.F. Impact of hydrodynamics on community structure and metabolic production of marine biofouling formed in a highly energetic estuary. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 192, 106241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Niu, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L. Hydrodynamics-driven community coalescence determines ecological assembly processes and shifts bacterial networks stability in river bends. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Niu, L.; Zheng, J. Hydrodynamic disturbance and nutrient accumulation co-shape the depth-dependent prokaryotic community assembly in intertidal sediments of a mountainous river estuary. J. Hydrol. 2025, 651, 132580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



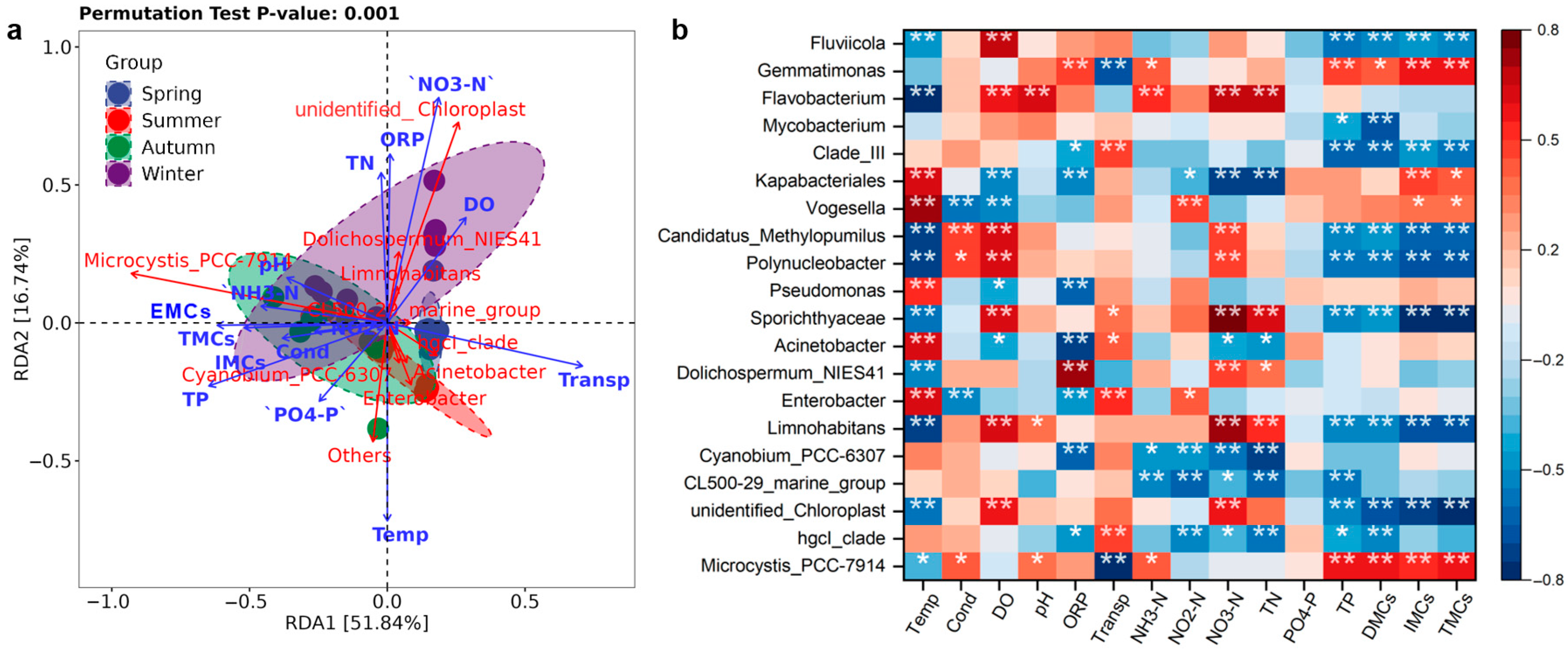
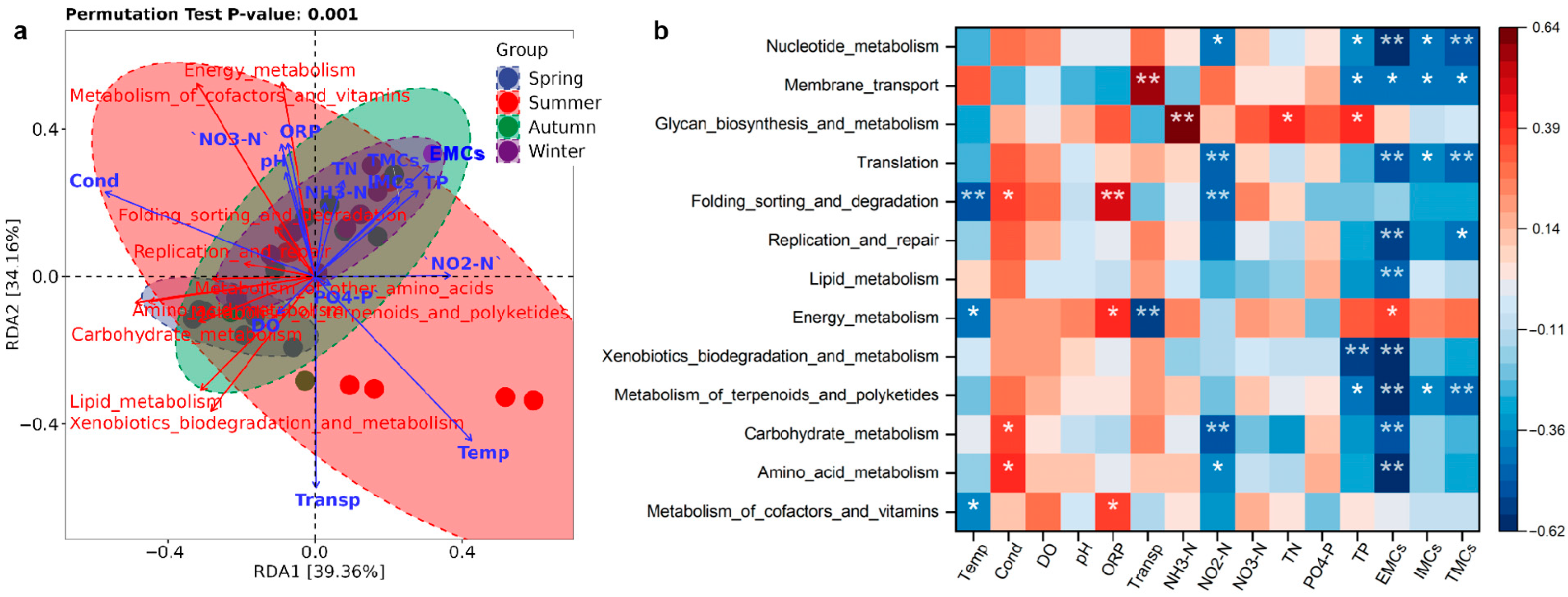

| Factors | TMCs | EMCs | IMCs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water temperature | 0.381 * | 0.345 * | 0.369 * |
| EC | 0.234 | 0.137 | 0.23 |
| DO | −0.327 * | −0.379 * | −0.316 * |
| pH | 0.087 | −0.117 | 0.104 |
| ORP | 0.11 | 0.205 | 0.057 |
| Water transparency | −0.335 * | −0.26 | −0.336 * |
| TN | −0.273 | −0.099 | −0.287 |
| TP | 0.613 ** | 0.624 ** | 0.574 ** |
| NO3−-N | −0.555 ** | −0.279 | −0.573 ** |
| NO2−-N | −0.135 | 0.015 | −0.146 |
| NH4+-N | 0.117 | 0.12 | 0.128 |
| PO43−-P | 0.134 | 0.137 | 0.159 |
| Topological Parameters | Topological Parameters | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Context | Total nodes | 60 | 54 | 76 | 64 |
| Total edges | 386 | 470 | 1166 | 816 | |
| Network overview | Average degree | 12.9 | 17.4 | 30.7 * | 25.5 * |
| Average weighted degree | 10.6 | 14.3 | 26.2 * | 21.3 * | |
| Network diameter | 7 | 5 | 8 | 6 | |
| Graph density | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 * | 0.4 * | |
| Connected components | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Community detection | Modularity | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| Statistical inference | 885.8 | 1125.7 | 2002.4 | 1654.2 | |
| Node overview | Average clustering coefficient | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 * | 0.7 * |
| Edge overview | Average path length | 2.4 | 1.9 | 2.0 | 1.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, A.; Xia, D.; Mou, X.; Kobayashi, S.; Haraguchi, T.; Iseri, Y.; Zhao, M. Bacterial Communities Respond to Spatiotemporal Fluctuation in Water Quality and Microcystins at Lake Taihu. Water 2025, 17, 2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152222
Hao A, Xia D, Mou X, Kobayashi S, Haraguchi T, Iseri Y, Zhao M. Bacterial Communities Respond to Spatiotemporal Fluctuation in Water Quality and Microcystins at Lake Taihu. Water. 2025; 17(15):2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152222
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Aimin, Dong Xia, Xingping Mou, Sohei Kobayashi, Tomokazu Haraguchi, Yasushi Iseri, and Min Zhao. 2025. "Bacterial Communities Respond to Spatiotemporal Fluctuation in Water Quality and Microcystins at Lake Taihu" Water 17, no. 15: 2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152222
APA StyleHao, A., Xia, D., Mou, X., Kobayashi, S., Haraguchi, T., Iseri, Y., & Zhao, M. (2025). Bacterial Communities Respond to Spatiotemporal Fluctuation in Water Quality and Microcystins at Lake Taihu. Water, 17(15), 2222. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152222






