Hydrochemical Characteristics and Evolution of Underground Brine During Mining Process in Luobei Mining Area of Lop Nur, Northwestern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
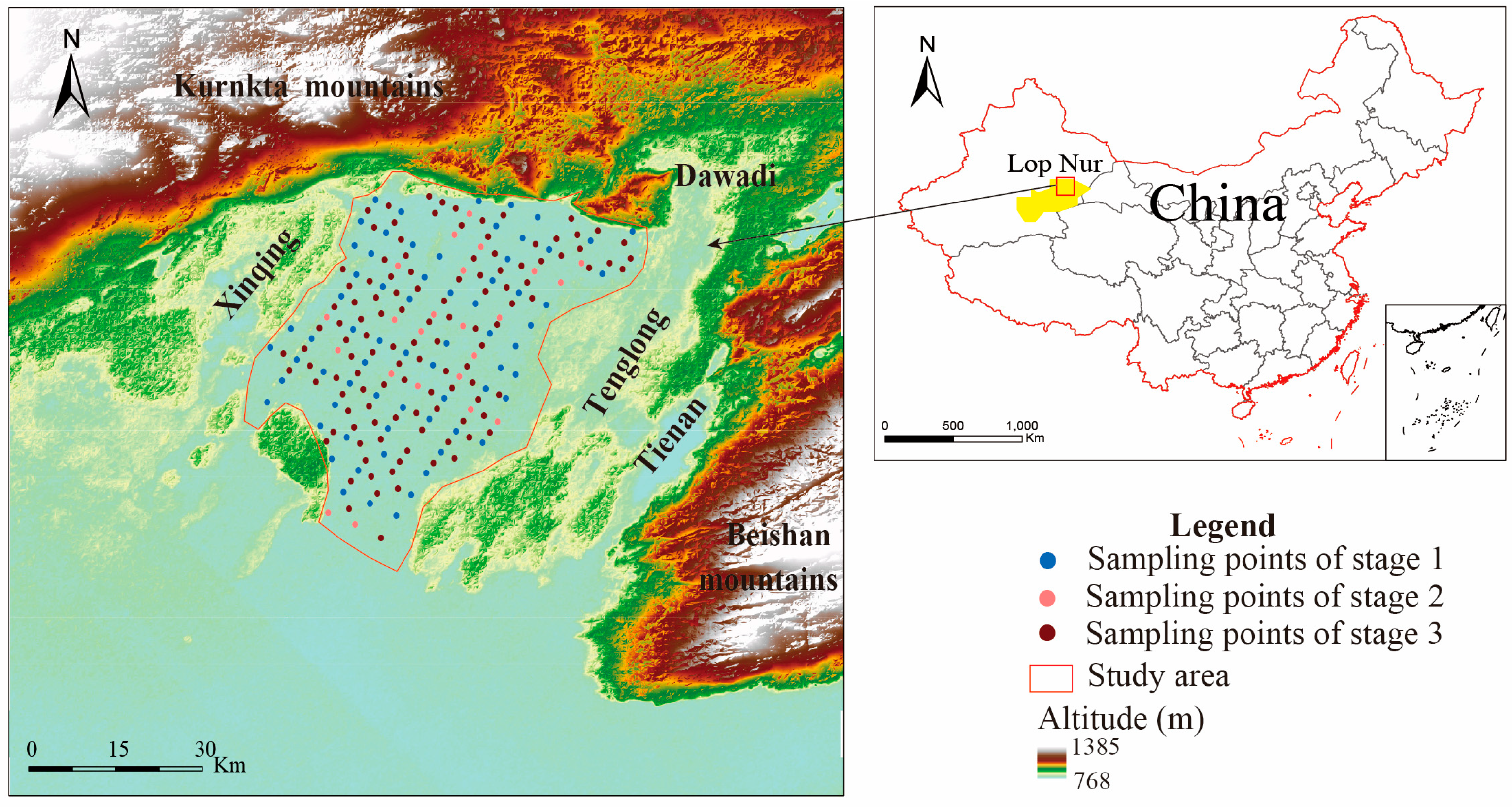
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Testing
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Hydrochemical Components in the Luobei Depression
3.2. Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of Mg2+ Concentration in the Luobei Depression
4. Discussion
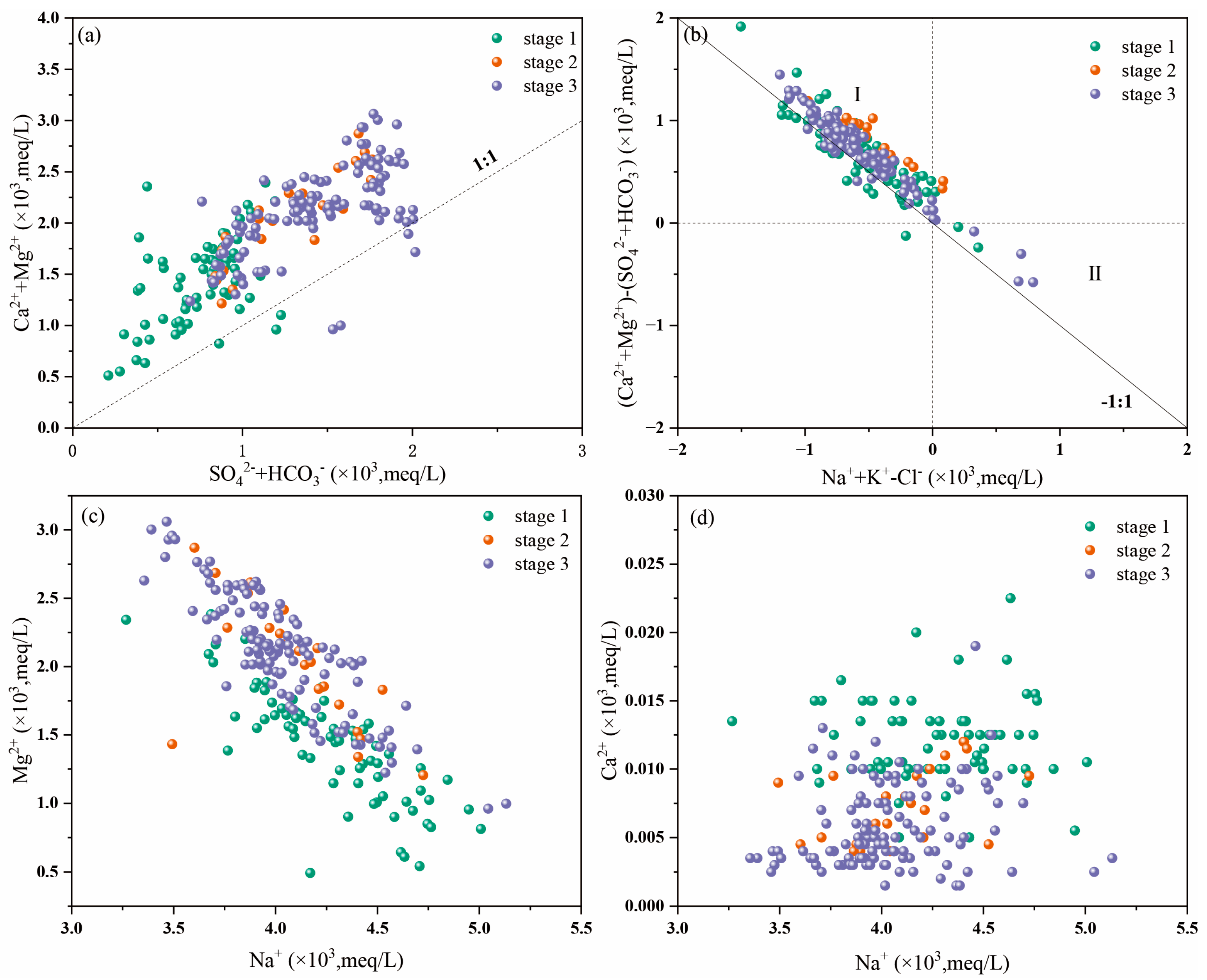
4.1. Salt Sources of Underground Brine
4.2. Water-Rock Interactions
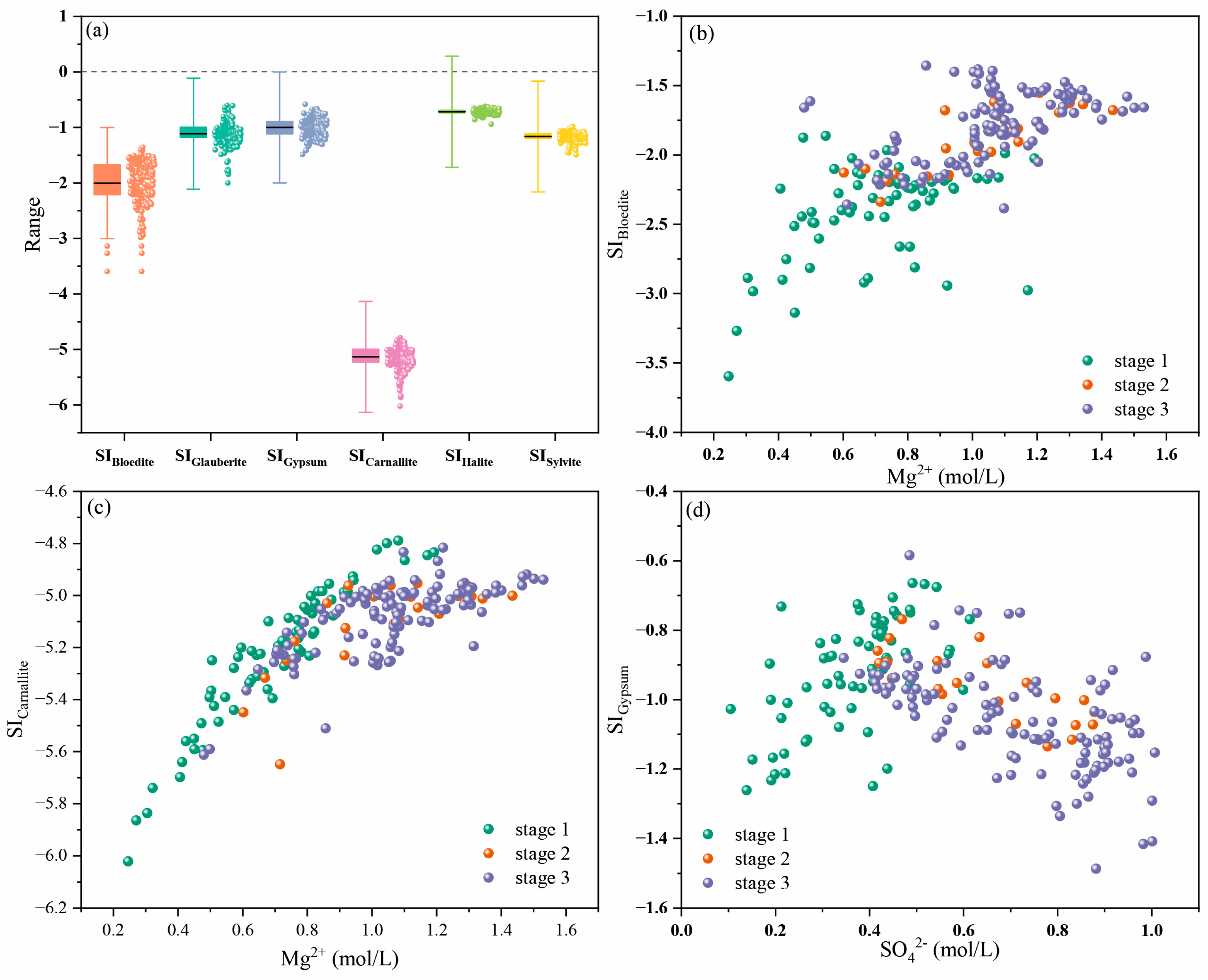
4.2.1. Saturation Index (SI) of Minerals
4.2.2. Ratios of Major Ions
4.2.3. Basinal Fluid Line for Diagenesis
4.3. Mixing Effect
4.4. Evolution of Brine and Indicative Implications
5. Conclusions
- The ionic composition of the Luobei phreatic brine was predominantly characterized by Na+ and Cl−, with SO42−, Mg2+, and K+ following in sequence. During the mining process, the Mg2+ concentrations have been gradually increasing, and the correlation coefficient between Mg2+ and total dissolved solids (TDS) has changed significantly. This indicated that the content of Mg2+ has been markedly influenced by environmental changes. Consequently, Mg2+ was identified as a crucial indicator for analyzing hydrochemical evolution.
- The findings regarding the spatial distribution characteristics of Mg2+ concentration reveal that from stage 1 to stage 3, the high-value area of Mg2+ concentration within the mining area has gradually migrated from its original southern location towards the east. Moreover, with the ongoing exploitation of brine, the high–value area of Mg2+ concentration has gradually expanded from the east towards the central part of the mining area.
- There were three primary factors contributing to the increase in Mg2+ concentration within the mining area. Firstly, the brine in the mining area has undergone long–term dissolution and evaporation-concentration processes. The dissolution of magnesium–bearing minerals has augmented the Mg2+ content in the brine. Secondly, reverse cation exchange has occurred, where in Na+ in the brine displaces Mg2+ in the aquifer medium, leading to elevated Mg2+ levels. Thirdly, brine mining has accelerated the flow of groundwater in the mining area and simultaneously intensified the recharge of peripheral groundwater to the mining area. The mixed recharge of groundwater rich in Mg2+ from the Tenglong Platform, Tienan fault depression and confined brine in Luobei depression was also one of the contributing factors to the increase in Mg2+ content in the mining area.
- The increase in Mg2+ content in underground brine significantly restricts the extraction processes of potassium (K) and lithium (Li) from the brine. In view of this, it is suggested that during the brine extraction operation, real-time dynamic monitoring of Mg2+ concentration in underground brine should be conducted, so as to provide scientific support for the rational and efficient utilization of underground brine resources.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, W.J.; Sheng, Y.Z.; Wang, G.C.; Shi, Z.M.; Liu, F.T.; Zhang, J.; Chen, D.L. Cl, Br, B, Li, and noble gases isotopes to study the origin and evolution of deep groundwater in sedimentary basins, a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 1497–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.S.; Lowenstein, T.K.; Wei, H.C.; Yuan, Q.; Qin, Z.J.; Shan, F.S.; Ma, H.Z. Sr isotope and major ion compositional evidence for formation of Qarhan salt lake, western China. Chem. Geol. 2018, 497, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.P.; Zhang, Y.S.; Liu, X.F.; Qi, W.; Kong, F.J.; Nie, Z.; Pu, L.Z.; Hou, X.H.; Wang, H.L.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Progress and prospect of salt lake research in China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2016, 90, 2123–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.R.; Fan, Q.S.; Li, Q.K.; Du, Y.S.; Qin, Z.; Wei, H.C.; Shan, F. The Source, Distribution, and Sedimentary Pattern of K-Rich Brines in the Qaidam Basin, Western China. Minerals 2019, 9, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Jiao, P.C.; Sun, X.H.; Lu, F.L.; Zhang, H. Research on potash forming and exploration progress in potash deposits in the Lop Nur Salt Lake. Acta Geol. Sin. 2018, 92, 1551–1570. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Han, J.; Ma, L.; Zheng, M.; Wu, Y.; Yang, B. Distribution and Genesis of Potassium-Bearing Minerals in Lop Nor Playa, Xinjiang, China. Minerals 2023, 13, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Zheng, M.P.; Qi, W. Sources of Ore-Forming Materials of the Superlarge B and Li Deposit in Zabuye Salt Lake, Tibet, China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2007, 81, 1709–1715. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, Z.; Bu, L.Z.; Zheng, M.P. Lithium Resources Industrialization of Salt Lakes in China: A Case Study of the Xitaijinaier Salt Lake and the Zabuye Salt Lake. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2010, 31, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- François, R.; Bertrand, F. Bromine geochemistry of salar de Uyuni and deeper salt crusts, Central Altiplano, Bolivia. Chem. Geol. 2000, 167, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehlert, A.M. Physical, chemical, and microbial feedbacks controlling brine geochemistry and lake morphology in polyextreme salar environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.H.; Liu, C.L.; Jiao, P.C.; Yan, H.; Chen, Y.Z.; Ma, L.C.; Zhang, Y.M.; Wang, C.L.; Li, W.X. A further discussion on genesis of potassium-rich brine in Lop Nur: Evaporating experiments for brine in gypsum-bearing clastic strata. Miner. Depos. 2016, 35, 1190–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.L.; Wang, M.L.; Jiao, P.C.; Chen, Y.Z. The probing of regularity and controlling factors of potash deposits distribution in Lop Nur salt lake, Xinjiang. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2009, 30, 796–802. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Feng, J. Hydrochemical Dynamic Characteristics and Evolution of Underground Brine in the Mahai Salt Lake of the Qaidam Basin Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Geol. Sin-Engl. 2018, 92, 1981–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.J.; Hu, S.Y.; Zhao, Q.S.; Li, B.; Lu, L.J. Hydrochemical evolution characteristics of underground brine in Mahai Salt Lake under mining conditions. World Geol. 2019, 39, 693–699. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Jiao, P.C.; Liu, C.L.; Yan, H.; Zhang, F.K.; Li, W.X.; Yu, Y.M.; Wang, L.S.; Hu, Y.F.; Wang, L.C.; et al. Discovery of the Ca-Cl type brine in deep aquifers and implications for the shallow giant glauberite deposits in the Lop Nur playa, Tarim Basin, NW China. China Geol. 2021, 04, 364–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.X.; Zhao, L.L.; Ma, B.C. Study on dynamic characteristics and influencing factorsof potassium brine in Lop Nor salt lake. Geol. Chem. Miner. 2017, 39, 163–167. [Google Scholar]
- Han, G.; Han, J.B.; Liu, J.B.; Hou, X.H.; Chen, J.N.; Cao, Y.Z. Variation characteristics of LiCl deposit under condition of mining in East Taijnar Salt Lake, Qaidam Basin. Inorg. Chem. Ind. 2020, 12, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.K.; Han, J.B.; Wang, J.P. Study on driving factors for changes in the subsidence funnel area of brine-bearing layers in the eastern mining area of the Qarhan salt lake. J. Salt Lake Res. 2025, 33, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.H.; Wang, G.C.; Li, Q.Y.; Zhao, Q.S.; Hu, S.Y.; Lu, L.J. Dynamic characteristics and evolution laws of underground brine in Mahai salt lake of Qaidam Basin during mining process. Sci. Rep. 2024, 01, 10778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, F.F.; Shi, D.Y.; Sun, Z.W. Brif Introduction on Structure and Water Control in Northern Lop Nur, Xinjiang. West-China Explor. Eng. 2013, 25, 174–176. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.Y.; Zhang, F.K.; Deng, Y.F.; Yu, Y.M.; Dong, L.B.; Li, W.X.; Wang, L.F.; Ma, B.C. Geological Characteristics and Genesis of the Solid Potash Salt Deposit in the NO.3 Fault Depression Zone in Northwest Lop Nur. J. Salt Lake Res. 2022, 30, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Sun, M.G.; Ma, L.C.; Tang, Q.F.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Y. Spatial variability in the geochemical characteristics of the k-rich brines in the Lop Nor. Acta Geol. Sin. 2020, 94, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H. Distribution Characteristics of the Main Ions in Luobei Area of Lop Nur Salt Lake. Master’s Thesis, Qingdao University, Qingdao, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.C.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Q.F.; Sun, M.G. Abnormal Enrichment Mechanism of Potassium-Rich Brine Deposit in Lop Nor Basin of Xinjiang. Earth Sci. Rev. 2022, 47, 72–81. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.L.; Bai, M.; Huang, F.X.; Li, M.; Lv, G.H.; Tang, P.H.; Han, F.F.; Ding, G.F.; Xu, M.; Bian, T.Z.; et al. Xinjiang Ruoqiang County Luobei Concave Potash Mine Detailed Investigation Report; Ruoqiang County Natural Resources Bureau, Bayingolin Mongol Autonomous Prefecture: Ruoqiang, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.P.; Weng, H.C.; Guo, H.M. Unraveling influences of nitrogen cycling on arsenic enrichment in groundwater from the Hetao Basin using geochemical and multi-isotopic approaches. J. Hydrol. 2021, 595, 125981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordstrom, D.K.; Ball, J.W.; Donahoe, R.J. Groundwater chemistry and water-rock interactions at Stripa. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 1727–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.R.; Wang, G.C.; Rao, Z.; Liao, F.; Shi, Z.M.; Huang, X.J.; Chen, X.L.; Yang, Y. Deciphering spatial pattern of groundwater chemistry and nitrogen pollution in Poyang Lake Basin (eastern China) using self-organizing map and multivariate statistics. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 329, 0959–6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, X.C.; Han, J.J.; Cao, Q.; Jiang, C.L.; Guo, J.; Zhou, H.Y. Evolution of the Subsurface K-Rich Brines in the Triassic Carbonates in the Sichuan Basin of China. Groundwater 2018, 56, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.J.; Sheng, Y.Z.; Shi, Z.M.; Guo, H.M.; Chen, X.L.; Mao, H.R.; Liu, F.T.; Ning, H.; Liu, N.N.; Wang, G.C. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and evolution of formation water in the continental sedimentary basin: A case study in the Qaidam Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Q.S.; Ma, H.Z.; Tan, H.B.; Xu, X.J.; Li, W.T. Characteristics and origin of brines in western aidam Basin. Geochimica 2007, 36, 633–637. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.M. Geochemical Characteristics and Genesis of Brine from Hadahexiu Salt Lake. Master’s Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.S.; Li, T.W.; Peng, X.M.; Han, Y.H.; Li, Z.P.; Ma, H.Z. Hydrogeochemical behaviors of oilfield water in the Tertiary in western Qaidam Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 2014, 35, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Zhang, F.K.; Li, B.Y.; Deng, Y.F.; Wang, L.F.; Yu, Y.M.; Li, W.X.; Li, X.N. Study on the spatial distribution and enrichment regularity of lithium and boron in potassium-rich brine in Luobei depression. J. Salt Lake Res. 2024, 32, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, S.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Zhang, K.Y.; Wang, J.L.; Li, M.H.; Yang, X.; Ren, X.H.; Hao, Y.L.; Yu, R.H. Multi-isotopes (δD, δ18Owater, 87Sr/86Sr, δ34S and δ18Osulfate) as indicators for groundwater salinization genesis and evolution of a large agricultural drainage lake basin in Inner Mongolia, Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Zhang, G.R.; Apps, J.; Zhu, C. Comparison of thermodynamic data files for PHREEQC. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 225, 103888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Y.; Liu, C.L.; Jiao, P.C.; Lü, F.L. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Evolution of Underground Brine in Lop Nur, Northwestern China. Acta Geol. Sin-Engl. 2024, 98, 786–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Zhao, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Gao, Z. Hydrochemical Characteristics, Controlling Factors and Strontium Enrichment Sources of Groundwater in the Northwest Plain of Shandong Province, China. Water-Sui. 2024, 16, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, F.; Jiang, W.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Niu, X.; Cao, W.; Shan, Q. Quantifying the factors controlling groundwater fluoride and associated health risks in the coastal river delta, northern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2024, 259, 105929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.J.; Sheng, Y.Z.; Liu, H.W.; Ma, Z.; Song, Y.X.; Liu, F.T.; Chen, S.M. Groundwater quality assessment and hydrogeochemical processes in typical watersheds in Zhangjiakou region, northern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 3521–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.C.; Gao, X.B.; Wang, Y.X. Hydrogeochemistry of high-fluoride groundwater at Yuncheng Basin, northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 508, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, I.C.; Johnson, J.T.E.; Kuang, L.; Naylor, S.; Subak, T.; Koleszar, A.M.; Levy, J.S. Brine formation in cold desert, shallow groundwater systems: Antarctic Ca-Cl brine chemistry controlled by cation exchange, microclimate, and organic matter. GSAB. 2024, 136, 3591–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.T.; Ma, T.; Du, Y.; Chen, L.Z. Genesis of formation water in the northern sedimentary basin of South China Sea: Clues from hydrochemistry and stable isotopes (D, 18O, 37Cl and 81Br). J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 196, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labotka, D.M.; Panno, S.V.; Locke, R.A.; Freiburg, J.T. Isotopic and geochemical characterization of fossil brines of the Cambrian Mt. Simon Sandstone and Ironton-Galesville Formation from the Illinois Basin, USA. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 165, 342–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davisson, M.; Criss, R. Na-Ca-Cl relations in basinal fluids. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 2743–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCaffrey, M.A.; Lazar, B.; Holland, H.D. The evaporation path of seawater and the coprecipitation of Br− and K+ with halite. J. Sediment. Petrol. 1987, 57, 928–937. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.C.; Wang, C.L.; Huang, H.; Yan, K. Origin of lithium in oilfield brines in continental petroliferous basin: Insights from Li and Sr isotopes in the Jianghan Basin, central China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2024, 160, 106576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, R.; Nadri, A.; Raeisi, E.; Shariati, A.; Mirbagheri, M.; Bahadori, F. Chemical evolution of a gas-capped deep aquifer, southwest of Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 3171–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschetti, T.; Toscani, L.; Shouakar, O.; Iacumin, P.; Venturelli, G.; Mucchino, C.; Frape, S.K. Salt Waters of the Northern Apennine Foredeep Basin (Italy): Originm and Evolution. Aquat. Geochem. 2011, 17, 71–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschetti, T.; Awadh, S.M.; Al-Mimar, H.S.; Iacumin, P.; Toscani, L.; Selmo, E.; Yaseen, Z.M. Chemical and isotope composition of the oilfield brines from Mishrif Formation (southern Iraq): Diagenesis and geothermometry. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 122, 104637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L. Study on Characteristics and Evolution of Underground Brine Chemical Field in Platform of TengLong, XinJiang Province. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, N.; Qin, X.W.; Ma, Y.L.; Pan, T.; Chen, J.Z.; Ding, C.W.; Jiang, Z.W.; Zhang, D.; Liu, C.L.; Li, Q.K.; et al. Origin and mineralization potential evaluation of intercrystalline brine formation of the Balun Mahai Basin, Qaidam. J. Lake Sci. 2025, 38, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Mahlknecht, J.; Merch´an, D.; Rosner, M.; Meixner, A.; Ledesma-Ruiz, R. Assessing seawater intrusion in an arid coastal aquifer under high anthropogenic influence using major constituents, Sr and B isotopes in groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 587–588, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, Z.F.; Liu, W.J.; Moon, S.; Zhao, T.; Zhou, X.D.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, H.; et al. Hydro-geochemical and Sr isotope characteristics of the Yalong River basin, eastern Tibetan plateau: Implications for chemical weathering and controlling factors. Geochem. Geophy. Geosy. 2019, 20, 1221–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Wang, M.L.; Jiao, P.C. Hydrogen, oxygen, strontium and sulfur isotope geochemistry and source of potassium ore-forming materials in Lop Nur Salt Lake, Xinjiang. Miner. Depos. 1999, 18, 268–276. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.L.; Jiao, P.C.; Wang, M.L.; Yan, H.; Chen, Y.Z.; Sun, X.H.; Bo, Y.; Xuan, Z.Q.; Lv, F.L.; Zhang, H.; et al. Formation Conditions and Laws of Potash Deposits in Lop Nur Salt Lake; Scientific Press: Beijing, China, 2020; pp. 123–134. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Yu, Y.; Su, Q.; Yang, L.; Fu, T.F.; Liu, W.Q.; Chen, G.Q.; Lyu, W.Z. The Study on the Genesis of Underground Brine in Laizhou Bay Based on Hydrochemical Data. Water 2023, 21, 3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| K+ (g/L) | Na+ (g/L) | Ca2+ (g/L) | Mg2+ (g/L) | Cl− (g/L) | SO42− (g/L) | HCO3− (g/L) | TDS (g/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 1 (2006) | Number of samples: 68 | |||||||
| Max | 13.35 | 115.18 | 0.45 | 28.60 | 196.80 | 58.84 | 0.42 | 371.85 |
| Minimum | 5.14 | 75.14 | 0.10 | 5.90 | 155.14 | 10.06 | 0 | 273.50 |
| Mean | 9.40 | 98.24 | 0.24 | 16.97 | 179.23 | 35.32 | 0.19 | 339.87 |
| Standard deviation | 1.98 | 8.01 | 0.06 | 5.06 | 6.74 | 11.10 | 0.13 | 17.15 |
| Coefficient of variation | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.04 | 0.31 | 0.68 | 0.05 |
| Stage 2 (2019) | Number of samples: 23 | |||||||
| Max | 11.88 | 108.67 | 0.24 | 34.43 | 181.47 | 84.31 | 0.48 | 383.73 |
| Minimum | 7.47 | 80.34 | 0.08 | 14.46 | 137.54 | 40.07 | 0.14 | 283.62 |
| Mean | 9.87 | 94.14 | 0.15 | 24.62 | 170.26 | 60.76 | 0.31 | 360.52 |
| Standard deviation | 1.14 | 6.96 | 0.06 | 5.55 | 9.26 | 15.92 | 0.10 | 20.83 |
| Coefficient of variation | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.40 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.06 |
| Stage 3 (2023) | Number of samples: 116 | |||||||
| Max | 13.07 | 118.04 | 0.38 | 36.73 | 184.59 | 96.66 | 0.38 | 394.19 |
| Minimum | 7.19 | 77.19 | 0.03 | 11.52 | 147.83 | 33.14 | 0.08 | 339.01 |
| Mean | 9.79 | 92.78 | 0.12 | 25.38 | 171.88 | 68.11 | 0.20 | 368.41 |
| Standard deviation | 0.83 | 7.27 | 0.06 | 5.20 | 7.49 | 17.58 | 0.07 | 13.79 |
| Coefficient of variation | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.50 | 0.20 | 0.04 | 0.26 | 0.35 | 0.04 |
| K+ (g/L) | Na+ (g/L) | Ca2+ (g/L) | Mg2+( g/L) | Cl− (g/L) | SO42− (g/L) | TDS (g/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tenglong Platform | 9.65 | 99.70 | 0.12 | 22.78 | 165.55 | 67.25 | 365.70 |
| Tienan Fault Depression | 9.44 | 89.37 | 0.13 | 22.18 | 169.40 | 56.67 | 347.40 |
| Confined brine in Luobei Depression | 9.87 | 94.07 | 0.13 | 26.73 | 165.96 | 74.32 | 371.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, X.; Deng, Y.; Geng, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Sun, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, M.; et al. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Evolution of Underground Brine During Mining Process in Luobei Mining Area of Lop Nur, Northwestern China. Water 2025, 17, 2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152192
Han X, Deng Y, Geng H, Zhao L, Zhang J, Wang L, Wang L, Sun X, Zhou Z, Wang M, et al. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Evolution of Underground Brine During Mining Process in Luobei Mining Area of Lop Nur, Northwestern China. Water. 2025; 17(15):2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152192
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Xu, Yufei Deng, Hao Geng, Liangliang Zhao, Ji Zhang, Lingfen Wang, Lei Wang, Xiaohong Sun, Zihao Zhou, Meng Wang, and et al. 2025. "Hydrochemical Characteristics and Evolution of Underground Brine During Mining Process in Luobei Mining Area of Lop Nur, Northwestern China" Water 17, no. 15: 2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152192
APA StyleHan, X., Deng, Y., Geng, H., Zhao, L., Zhang, J., Wang, L., Wang, L., Sun, X., Zhou, Z., Wang, M., & Liu, Z. (2025). Hydrochemical Characteristics and Evolution of Underground Brine During Mining Process in Luobei Mining Area of Lop Nur, Northwestern China. Water, 17(15), 2192. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152192





