Experimental Measurements on the Influence of Inlet Pipe Configuration on Hydrodynamics and Dissolved Oxygen Distribution in Circular Aquaculture Tank
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Device
2.2. Experimental Design
2.2.1. Experimental Scheme
2.2.2. Velocity Measurements
2.2.3. Dissolved Oxygen Measurements
2.3. Data Processing
3. Results
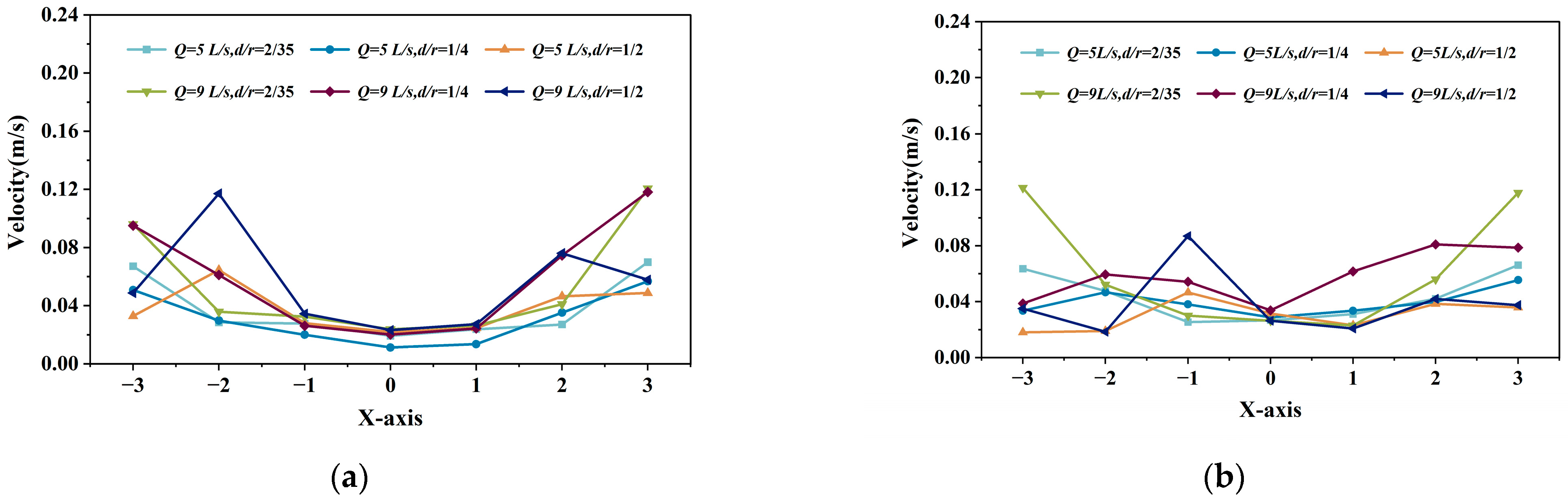
3.1. Influence of Inlet Structure on Velocity Distribution Along the Aquaculture Tank X-Axis
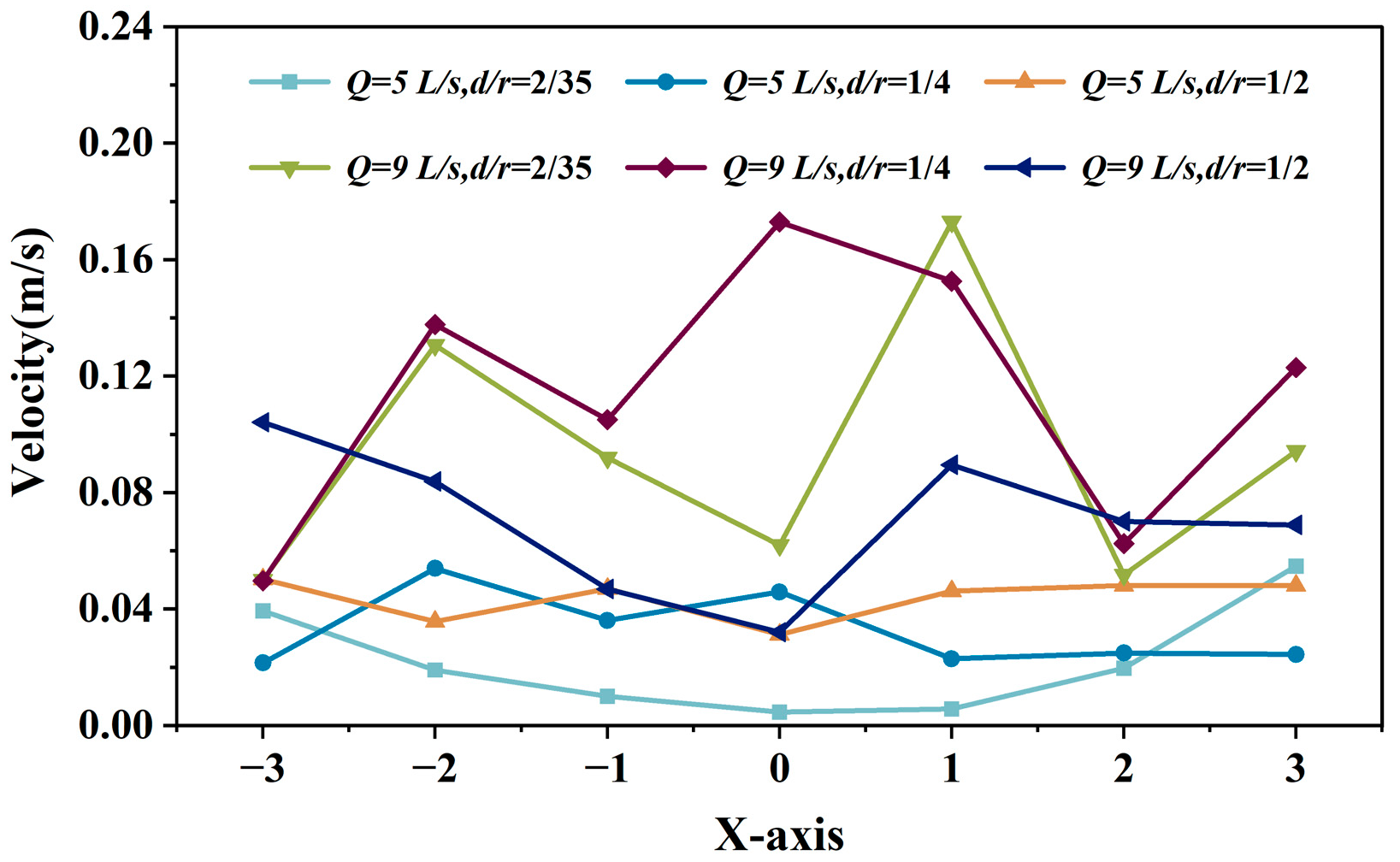
3.1.1. Influence of Horizontal Single-Pipe Single-Hole Inlet on Flow Velocity Variation Along the Aquaculture Tank X-Axis
3.1.2. Influence of Vertical Single-Pipe Porous Inlet on Flow Velocity Variation Along the Aquaculture Tank X-Axis
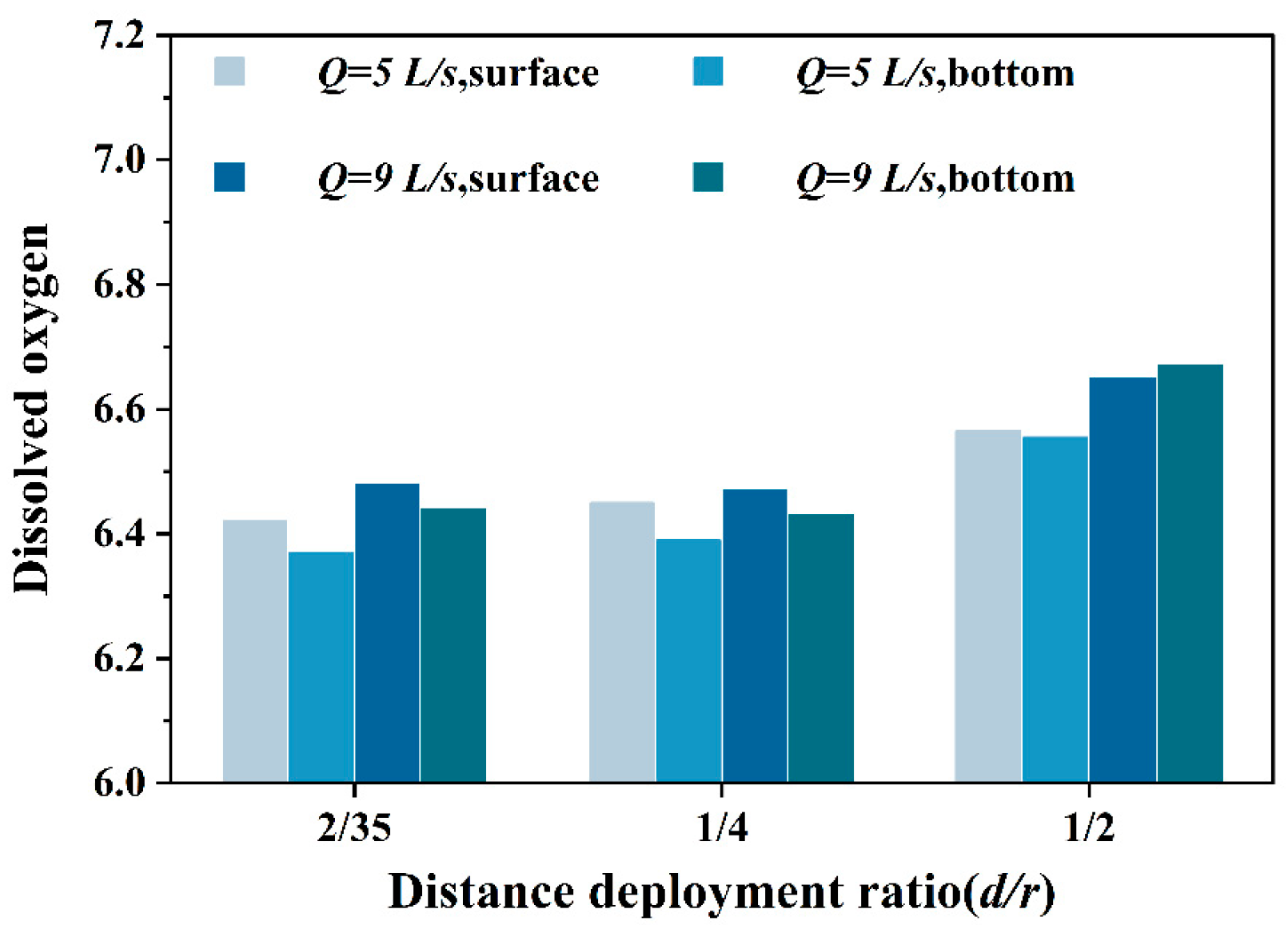
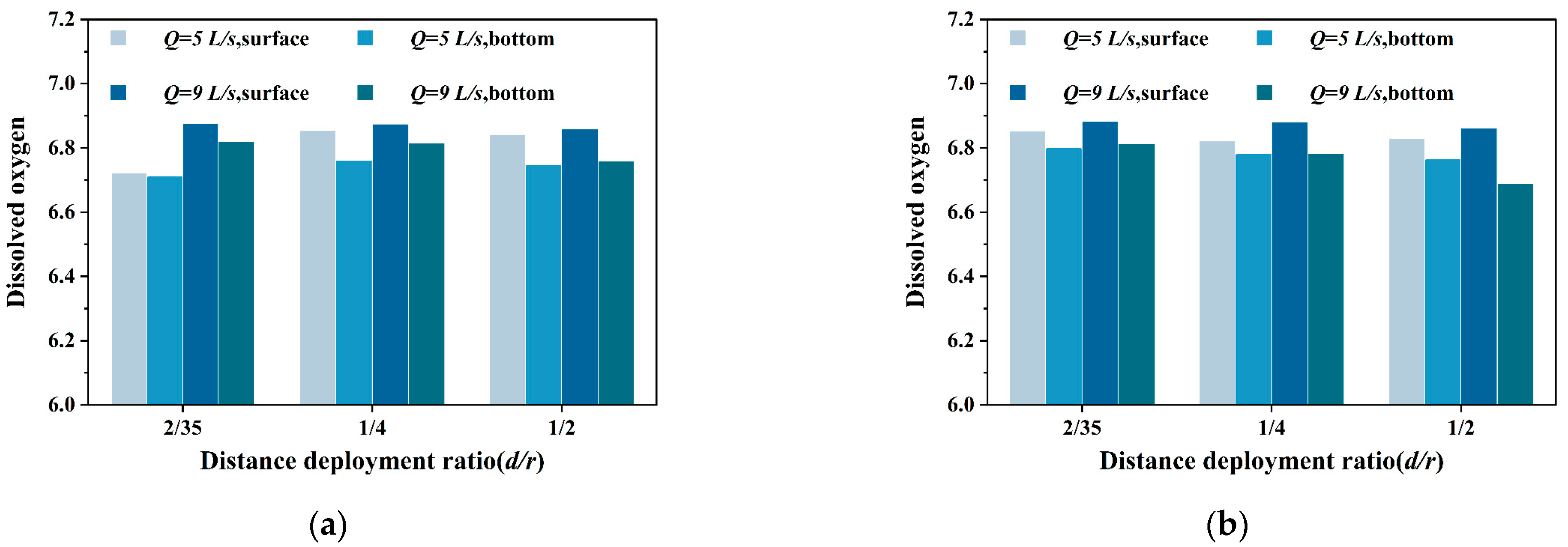
3.2. Influence of Inlet Structure on Dissolved Oxygen in Different Water Layers
3.2.1. Influence of Horizontal Single-Pipe Single-Hole Inlet on Dissolved Oxygen in Different Water Layers
3.2.2. Influence of Vertical Single-Pipe Porous Inlet on Dissolved Oxygen in Different Water Layers
3.3. Influence of Inlet Structure on Hydrodynamic Characteristics in Circular Aquaculture Tanks
3.3.1. Average Velocity in Circular Aquaculture Tanks
3.3.2. Uniformity Coefficient of the Velocity Field in Circular Aquaculture Tanks
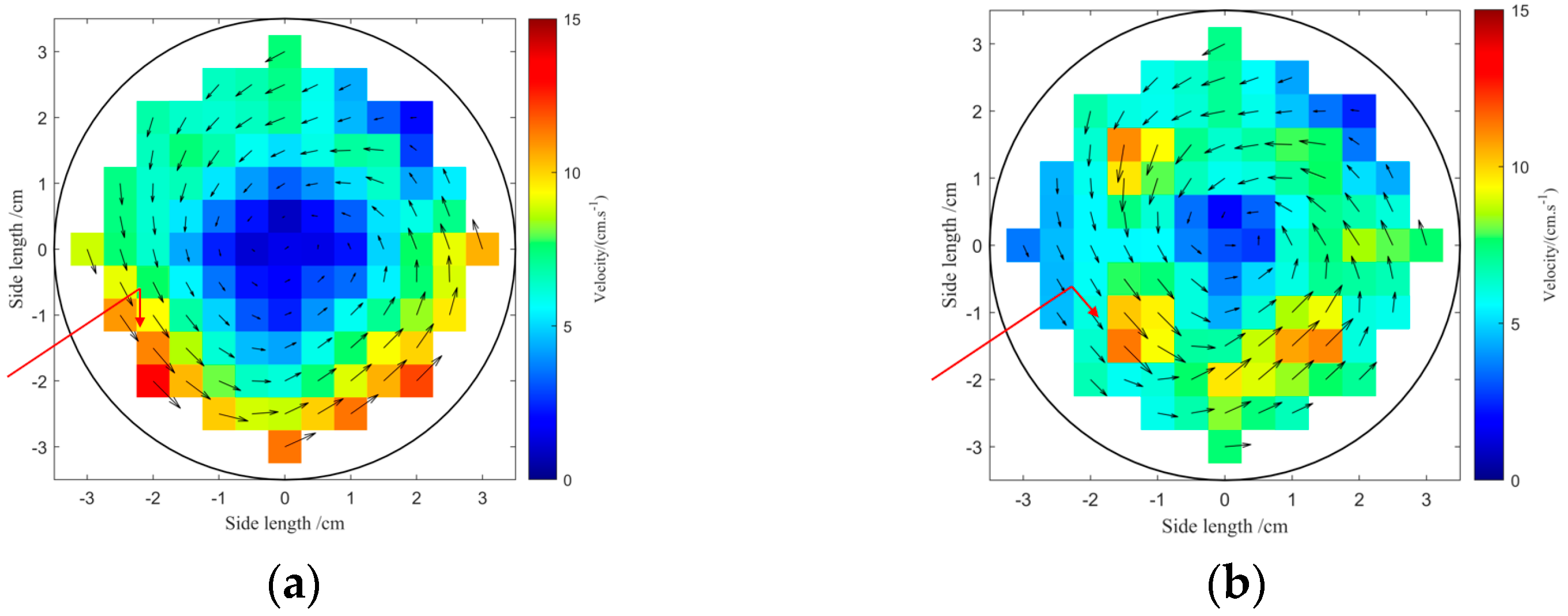
3.4. Influence of Inlet Structure on Flow Field Distribution Characteristics in Circular Aquaculture Tanks
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fisheries and Fishery Administration Bureau of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Zones; National Aquatic Technology Promotion Center; China Fisheries Association. China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Che, X.; Chen, C.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, N.; Maidaibieke, D.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Z. Hydrodynamics of waste collection in a recirculating aquaculture tank with different numbers of inlet pipes. Aquac. Eng. 2023, 101, 102324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xue, B.; Bi, C.; Ren, X.; Liu, Y. Influence mechanisms of macro-infrastructure on micro-environments in the recirculating aquaculture system and biofloc technology system. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 15, 991–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Rebollar, B.M.; Salinas-Tapia, H.; García-Pulido, D.; Durán-García, M.D.; Gallego-Alarcón, I.; Fonseca-Ortiz, C.R.; García-Aragón, J.A.; Díaz-Delgado, C. Performance study of annular settler with gratings in circular aquaculture tank using computational fluid dynamics. Aquac. Eng. 2021, 92, 102143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Rebollar, B.M.; García-Pulido, D.; Diaz-Delgado, C.; Gallego-Alarcón, I.; García-Aragón, J.A.; Salinas-Tapia, H. Sedimentation efficiency evaluation of an aquaculture tank through experimental floc characterization and CFD simulation. Aquac. Eng. 2023, 102, 102343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jia, G.; Wang, M.; Cao, S.; Mkumbuzi, S.G. Hydrodynamics of recirculating aquaculture tanks with different spatial utilization. Aquac. Eng. 2022, 96, 102217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, N.; Wang, M.; Chen, C.; Gao, Y.; Cao, S.; Liu, X.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Z. Hydrodynamics of waste collection in a recirculating aquaculture tank with different flow-guide discs. Aquac. Eng. 2024, 106, 102395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Hu, J.; Qu, X.; Feng, D.; Gui, F.; Zhu, F. Effect of inlet pipe design on self-cleaning ability of a circular tank in RAS. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1120205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ren, X.; Xue, B.; Bi, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y. Systematic optimization of the square arc angle aquaculture tank combining CFD methodology and multi-objective genetic algorithm. Aquac. Eng. 2023, 101, 102326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labatut, R.A.; Ebeling, J.M.; Bhaskaran, R.; Timmons, M.B. Modeling hydrodynamics and path/residence time of aquaculture-like particles in a mixed-cell raceway (MCR) using 3D computational fluid dynamics (CFD). Aquac. Eng. 2015, 67, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, J.; Summerfelt, S. Solids flushing, mixing, and water velocity profiles within large (10 and 150 m3) circular ‘Cornell-type’ dual-drain tanks. Aquac. Eng. 2004, 32, 245–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oca, J.; Masaló, I.; Reig, L. Comparative analysis of flow patterns in aquaculture rectangular tanks with different water inlet characteristics. Aquac. Eng. 2004, 31, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oca, J.; Masaló, I. Design criteria for rotating flow cells in rectangular aquaculture tanks. Aquac. Eng. 2007, 36, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorle, J.M.R.; Terjesen, B.F.; Summerfelt, S.T. Influence of inlet and outlet placement on the hydrodynamics of culture tanks for Atlantic salmon. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 188, 105944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, S.; Reig, L.; Masaló, I.; Blanco, M.; Oca, J. Influence of tank geometry and flow pattern in fish distribution. Aquac. Eng. 2011, 44, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, L.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, X.; Gui, F.; Qu, X.; Feng, D. Investigation of the inlet layout effect on the solid waste removal in an octagonal aquaculture tank. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1035794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B.W.; Rawles, S.D.; Beck, B.H. Response of channel×blue hybrid catfish to chronic diurnal hypoxia. Aquaculture 2012, 350–353, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; He, K.; Hu, H. Design and Application of New Aeration Device Based on Recirculating Aquaculture System. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, N.; Liu, X.; Gao, X.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Z. Hydrodynamic characteristics of industrialized recirculating aquaculture systems: A comprehensive review. J. Shanghai Ocean. Univ. 2023, 32, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Ong, M.C.; Lee, J.; Kim, T. Numerical simulation of oxygen transport in land-based aquaculture tank. Aquaculture 2021, 543, 736973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorle, J.M.R.; Terjesen, B.F.; Summerfelt, S.T. Hydrodynamics of Atlantic salmon culture tank: Effect of inlet nozzle angle on the velocity field. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 158, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Hu, J.; Kong, J.; Gui, F.; Pan, X.; Feng, D. Flow field of circular recirculating aquaculture tank based on PIV. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 296–300. [Google Scholar]
- Gorle, J.M.R.; Terjesen, B.F.; Mota, V.C.; Summerfelt, S. Water velocity in commercial RAS culture tanks for Atlantic salmon smolt production. Aquac. Eng. 2018, 81, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfelt, S.T.; Mathisen, F.; Holan, A.B.; Terjesen, B.F. Survey of large circular and octagonal tanks operated at Norwegian commercial smolt and post-smolt sites. Aquac. Eng. 2016, 74, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oca, J.; Masalo, I. Flow pattern in aquaculture circular tanks: Influence of flow rate, water depth, and water inlet & outlet features. Aquac. Eng. 2013, 52, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Feng, D.; Qu, J.; Jia, C.; Gui, F.; Zhang, Q. Characteristics of flow field in a large-scale circular aquaculture tank under action of submersible thrusters. J. Dalian Fish. Univ. 2024, 39, 289–297. [Google Scholar]
- Tvinnereim, K.; Skybakmoen, S. Water Exchange and Self-Cleaning in Fish Rearing Tanks. In Aquaculture: A Biotechnology in Progress; De Pauw, N., Jaspers, E., Ackefors, H., Wilkens, N., Eds.; European Aquaculture Society: Bredene, Belgium, 1989; pp. 1041–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Almansa, C.; Masaló, I.; Reig, L.; Piedrahita, R.; Oca, J. Influence of tank hydrodynamics on vertical oxygen stratification in flatfish tanks. Aquac. Eng. 2014, 63, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhu, D.; Wang, X.; Yu, D.; Xie, J. Effects of Nonaerated Circulation Water Velocity on Nutrient Release from Aquaculture Pond Sediments. Water 2017, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, M.-G.; An, C.-H.; Cha, S.-J.; Kim, M.-J.; Kim, H.-N. A method for minimizing the zone of low water flow velocity in a bottom center drain circular aquaculture tank. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2021, 52, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venegas, P.A.; Narváez, A.L.; Arriagada, A.E.; Llancaleo, K.A. Hydrodynamic effects of use of eductors (Jet-Mixing Eductor) for water inlet on circular tank fish culture. Aquac. Eng. 2014, 59, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Zhao, Y.; Bi, C.; Chen, Y.; Ren, X.; Liu, Y. Investigation of flow field and pollutant particle distribution in the aquaculture tank for fish farming based on computational fluid dynamics. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 200, 107243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
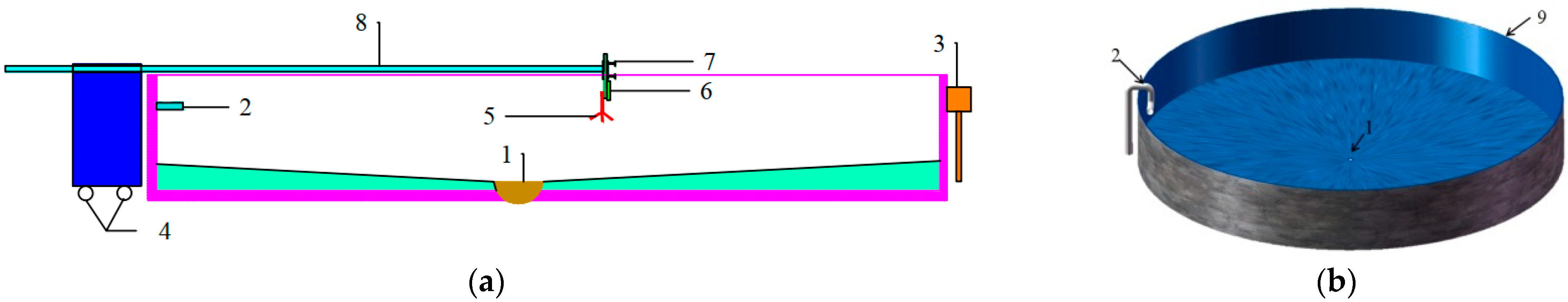
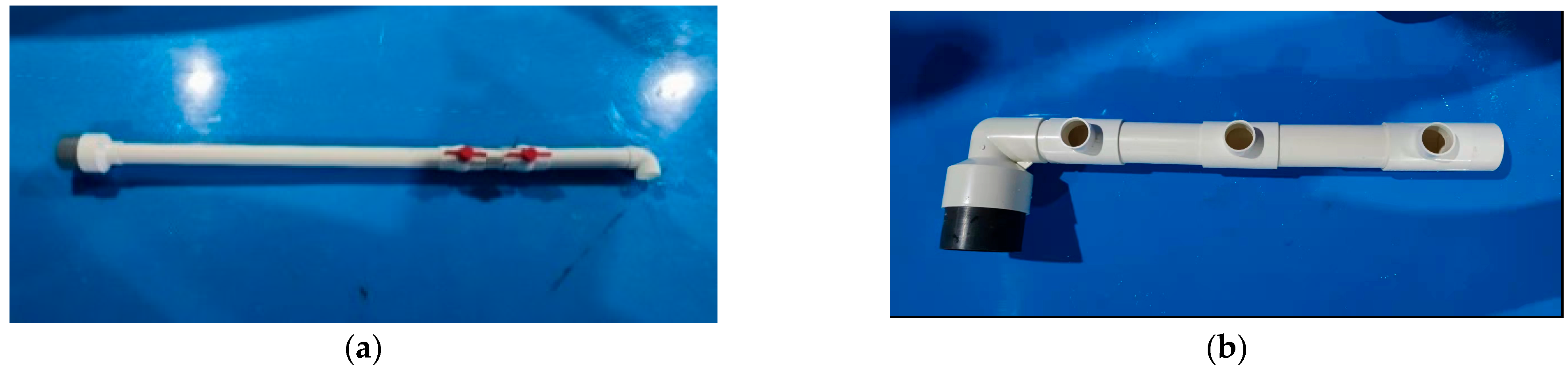
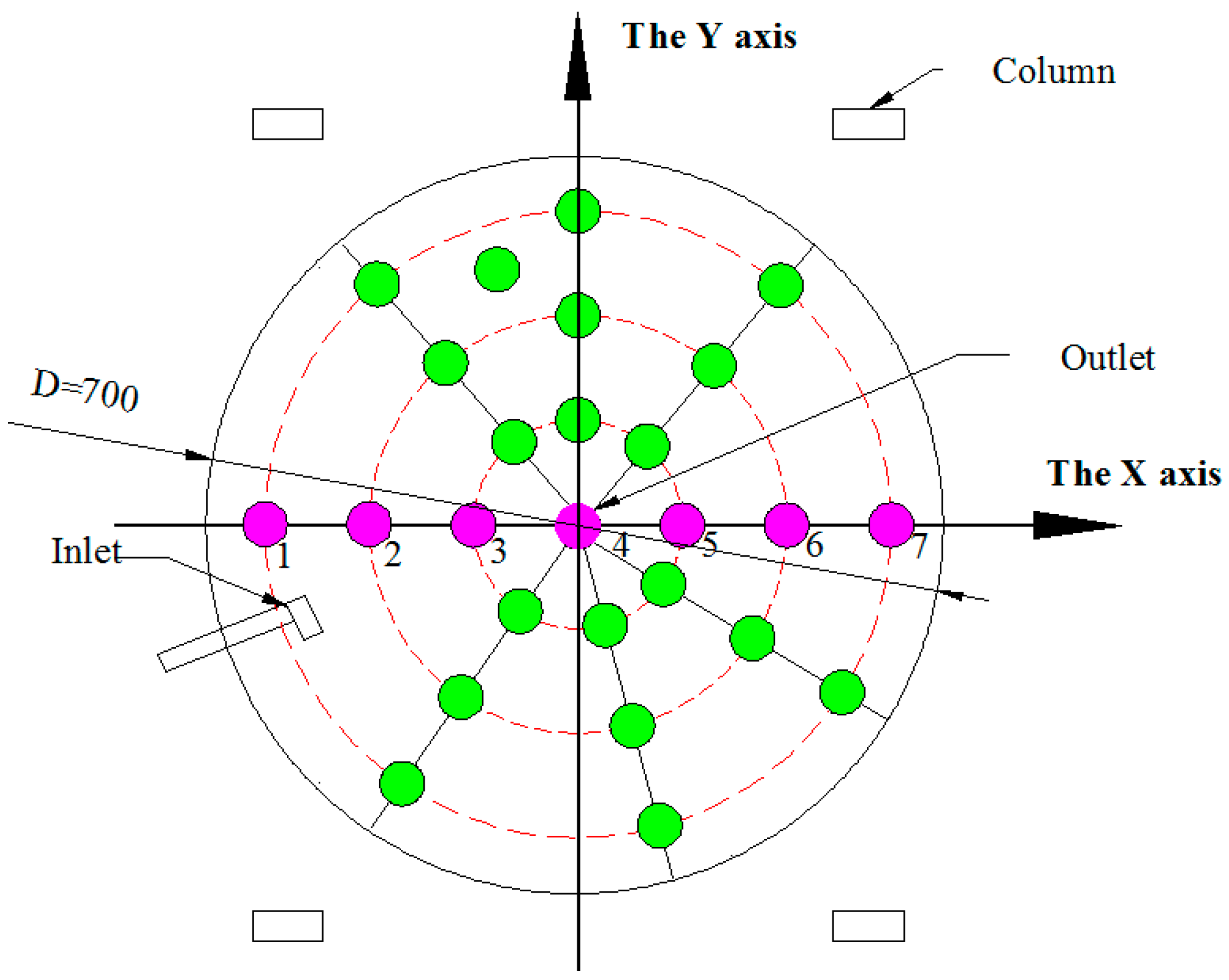

| Inlet Structure | Deployment Distance Ratio (d/r) | Flow Rate Q (L/s) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal single-pipe single-hole inlet | 2/35 | 5 | 9 |
| 1/4 | 5 | 9 | |
| 1/2 | 5 | 9 | |
| Vertical single-pipe porous inlet (0°) | 2/35 | 5 | 9 |
| 1/4 | 5 | 9 | |
| 1/2 | 5 | 9 | |
| Vertical single-pipe porous inlet (45°) | 2/35 | 5 | 9 |
| 1/4 | 5 | 9 | |
| 1/2 | 5 | 9 | |
| Point | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X-axis | −3 | −2 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Y-axis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Inlet Structure | Deployment Distance Ratio (d/r) | Average Velocity (m/s) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q = 5 L/s | Q = 9 L/s | ||
| Horizontal single-pipe single-hole inlet | 2/35 | 0.0311 | 0.0925 |
| 1/4 | 0.0251 | 0.1040 | |
| 1/2 | 0.0474 | 0.0712 | |
| Vertical single-pipe porous inlet (0°) | 2/35 | 0.0477 | 0.0717 |
| 1/4 | 0.0402 | 0.0715 | |
| 1/2 | 0.0413 | 0.0585 | |
| Vertical single-pipe porous inlet (45°) | 2/35 | 0.0606 | 0.0816 |
| 1/4 | 0.0434 | 0.0669 | |
| 1/2 | 0.0340 | 0.0444 | |
| Inlet Structure | Deployment Distance Ratio (d/r) | Uniformity Coefficient | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q = 5 L/s | Q = 9 L/s | ||
| Horizontal single-pipe single-hole inlet | 2/35 | 27.7390 | 25.5979 |
| 1/4 | 37.4454 | 28.5124 | |
| 1/2 | 48.5379 | 36.9456 | |
| Vertical single-pipe porous inlet (0°) | 2/35 | 42.5413 | 35.4940 |
| 1/4 | 42.1494 | 39.9972 | |
| 1/2 | 47.8337 | 43.5822 | |
| Vertical single-pipe porous inlet (45°) | 2/35 | 41.2978 | 37.7932 |
| 1/4 | 46.1084 | 40.4282 | |
| 1/2 | 27.7412 | 33.8592 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Gui, F.; Qi, H.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Feng, D.; Zhang, Q. Experimental Measurements on the Influence of Inlet Pipe Configuration on Hydrodynamics and Dissolved Oxygen Distribution in Circular Aquaculture Tank. Water 2025, 17, 2172. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152172
Wu Y, Chen J, Gui F, Qi H, Wang Y, Luo Y, Wu Y, Feng D, Zhang Q. Experimental Measurements on the Influence of Inlet Pipe Configuration on Hydrodynamics and Dissolved Oxygen Distribution in Circular Aquaculture Tank. Water. 2025; 17(15):2172. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152172
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yanfei, Jianeng Chen, Fukun Gui, Hongfang Qi, Yang Wang, Ying Luo, Yanhong Wu, Dejun Feng, and Qingjing Zhang. 2025. "Experimental Measurements on the Influence of Inlet Pipe Configuration on Hydrodynamics and Dissolved Oxygen Distribution in Circular Aquaculture Tank" Water 17, no. 15: 2172. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152172
APA StyleWu, Y., Chen, J., Gui, F., Qi, H., Wang, Y., Luo, Y., Wu, Y., Feng, D., & Zhang, Q. (2025). Experimental Measurements on the Influence of Inlet Pipe Configuration on Hydrodynamics and Dissolved Oxygen Distribution in Circular Aquaculture Tank. Water, 17(15), 2172. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17152172








