Historical Evolution and Future Trends of Riverbed Dynamics Under Anthropogenic Impact and Climatic Change: A Case Study of the Ialomița River (Romania)
Abstract
1. Introduction
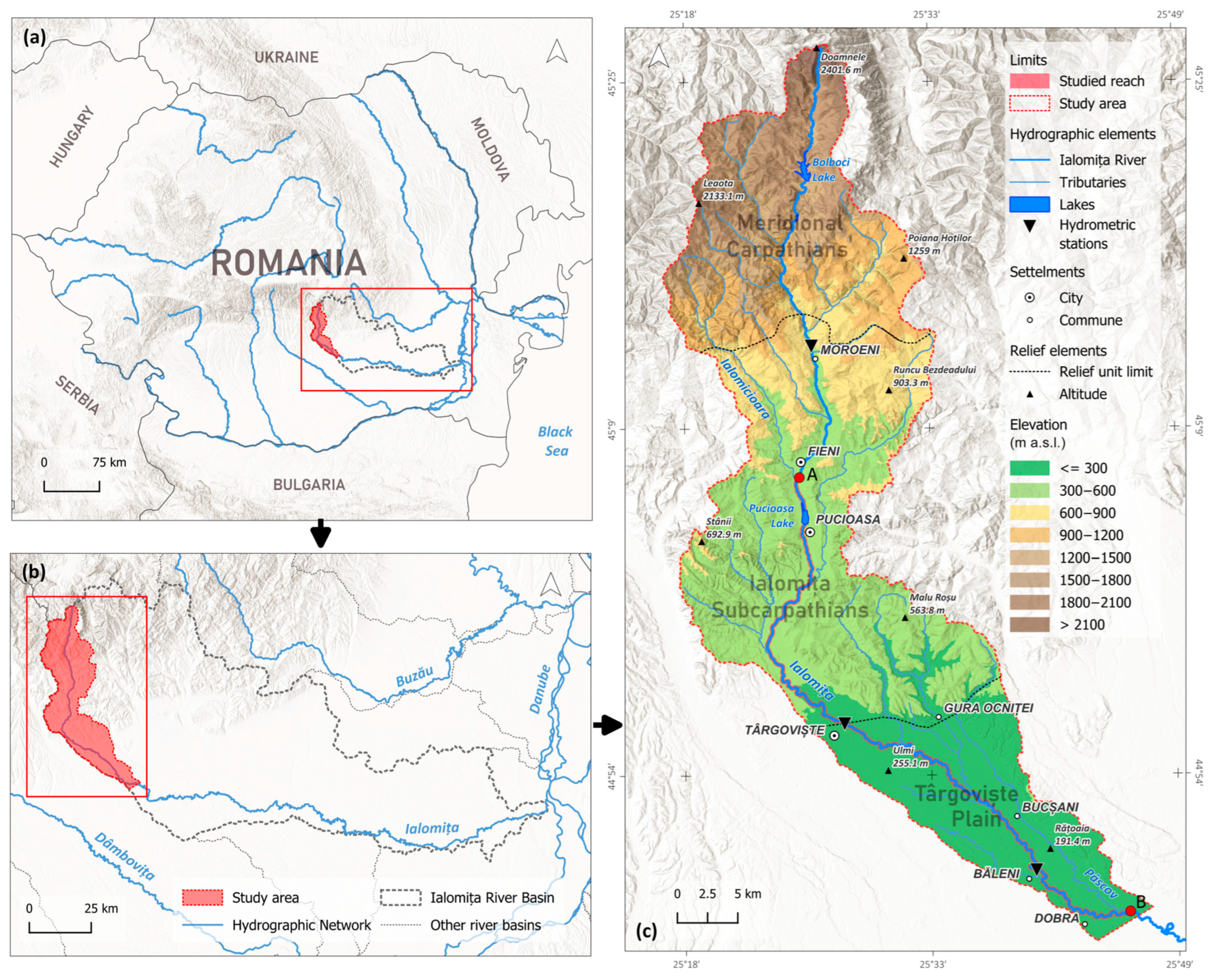
2. Study Area
2.1. General Setting
2.2. River Management and Anthropogenic Intervention
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Collection
3.1.1. Cartographic Data Description
3.1.2. Climatic and Hydrological Data
3.1.3. Anthropogenic Elements and Field Survey
3.2. GIS Processing and Integration
3.2.1. Georeferencing
3.2.2. Riverbed Planform Mapping
- The thalweg of the river (line) or central axis of the main channel [6], digitised as the approximative centreline of the main channel. In the case of orthophotos, this can vary. The imagery clearly distinguishes between shallow and deep water, indicating that the thalweg corresponds to the deeper portion of the channel.
- The active channel (polygon) [7,21], riverbed [22], fluvial area [6], or active belt/band [104] representing the area including the riverbed channel and the sedimentation zones near the channel, including bare and less vegetated bars. It may correspond with the bankfull stage of the channel, sometimes named the low floodplain.
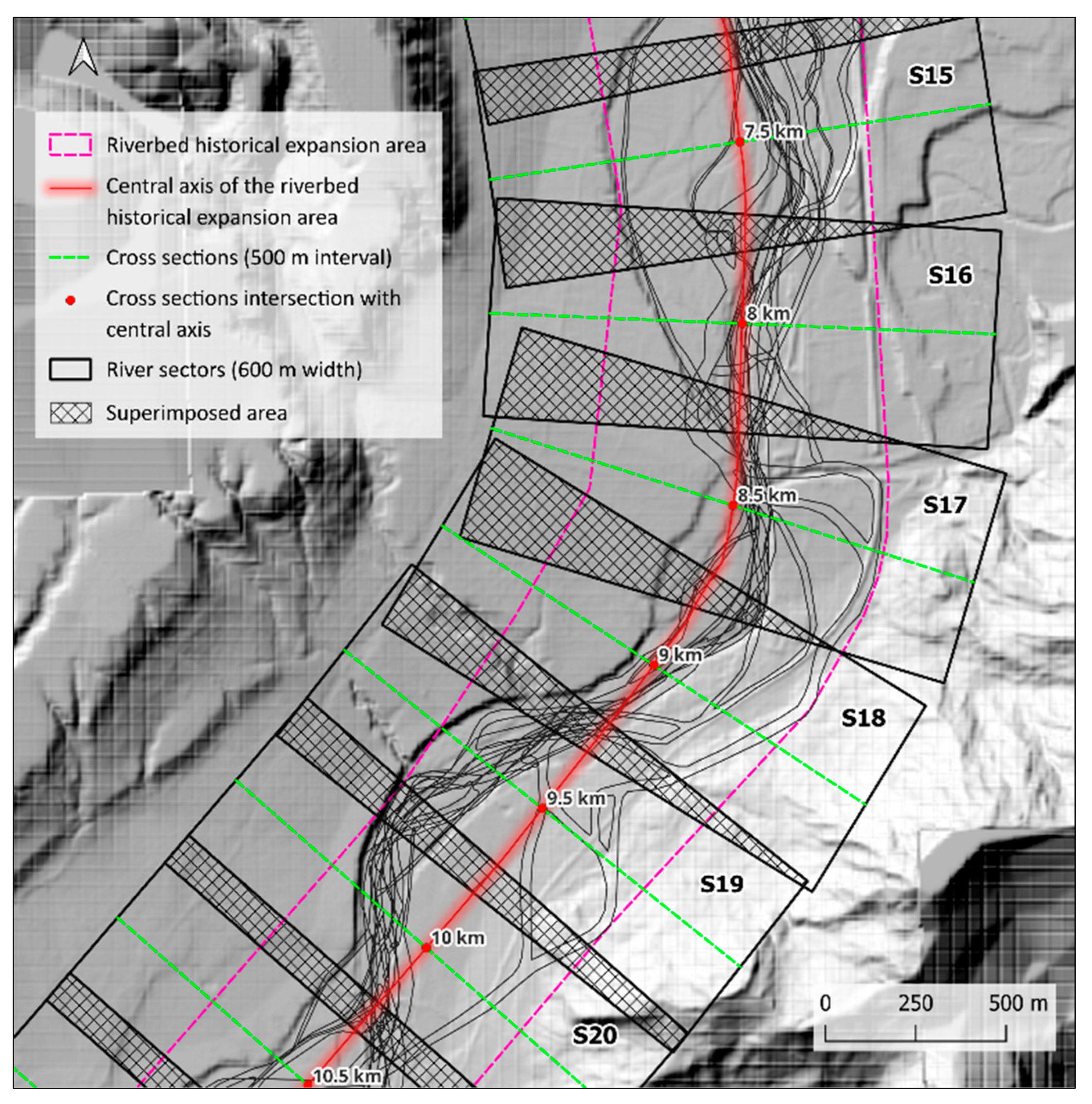
3.2.3. Riverbed Segmentation
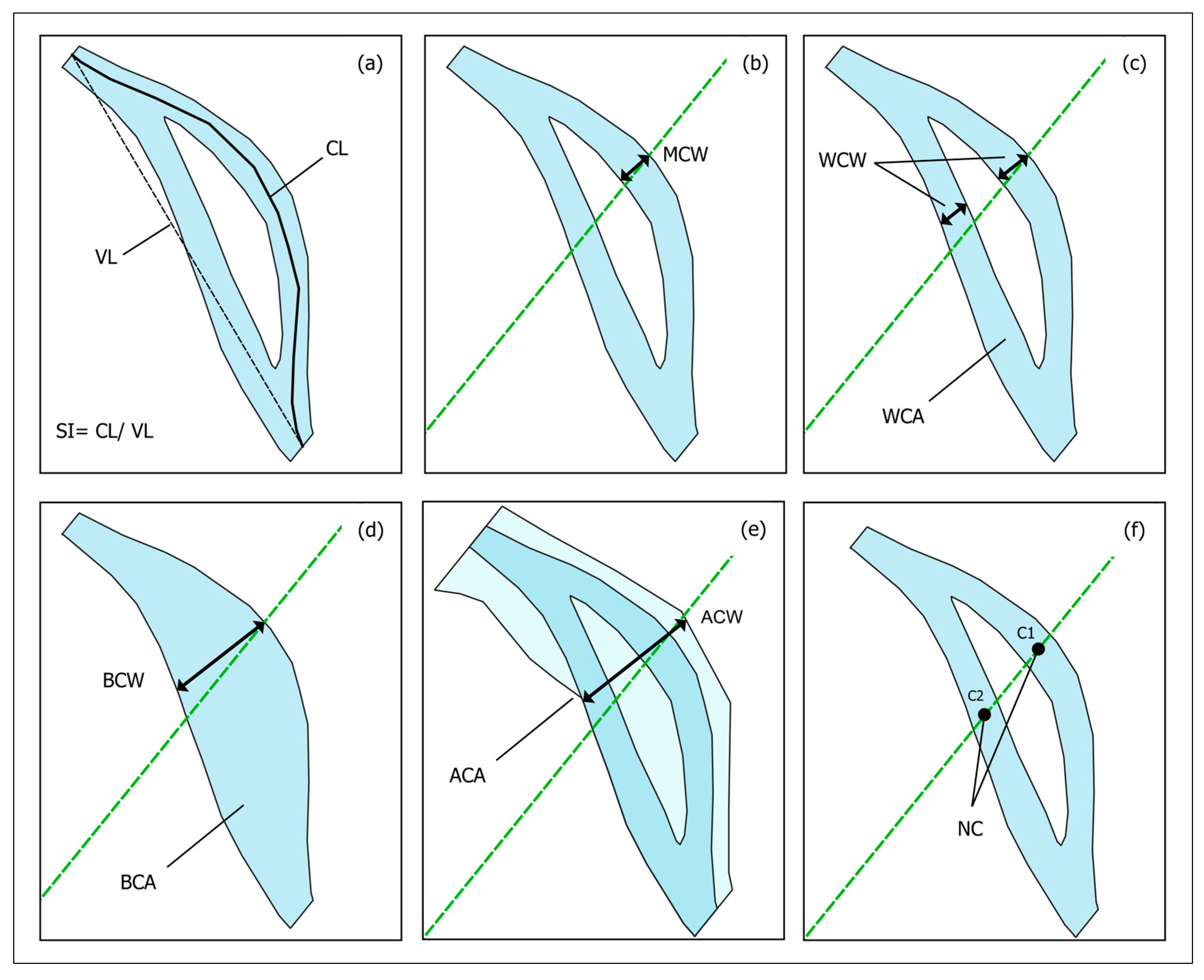
3.3. Geomorphometric Measurements
3.3.1. Parameters and Indices Measurements
3.3.2. Processing Automation
3.4. Data Analysis and Postprocessing
4. Results
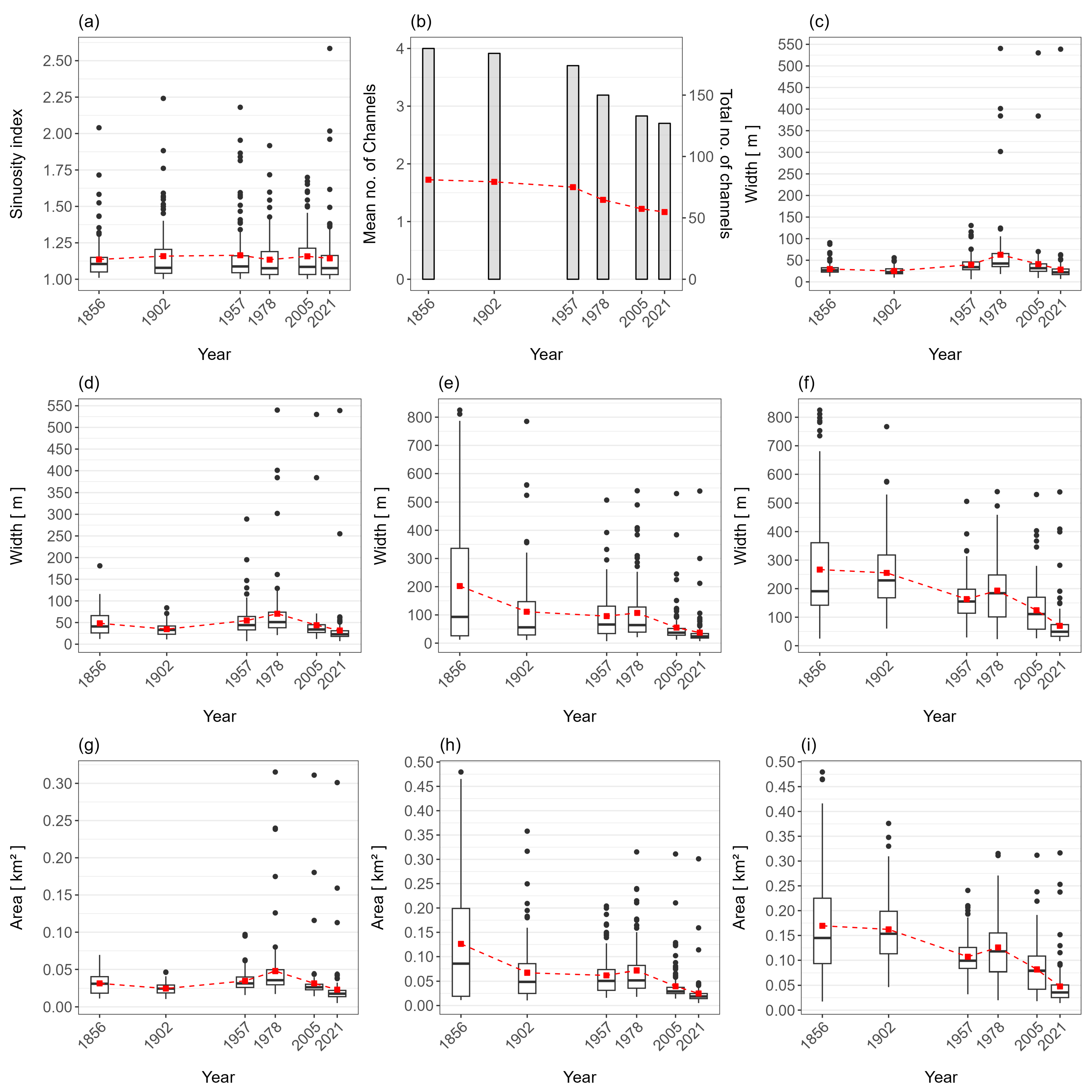
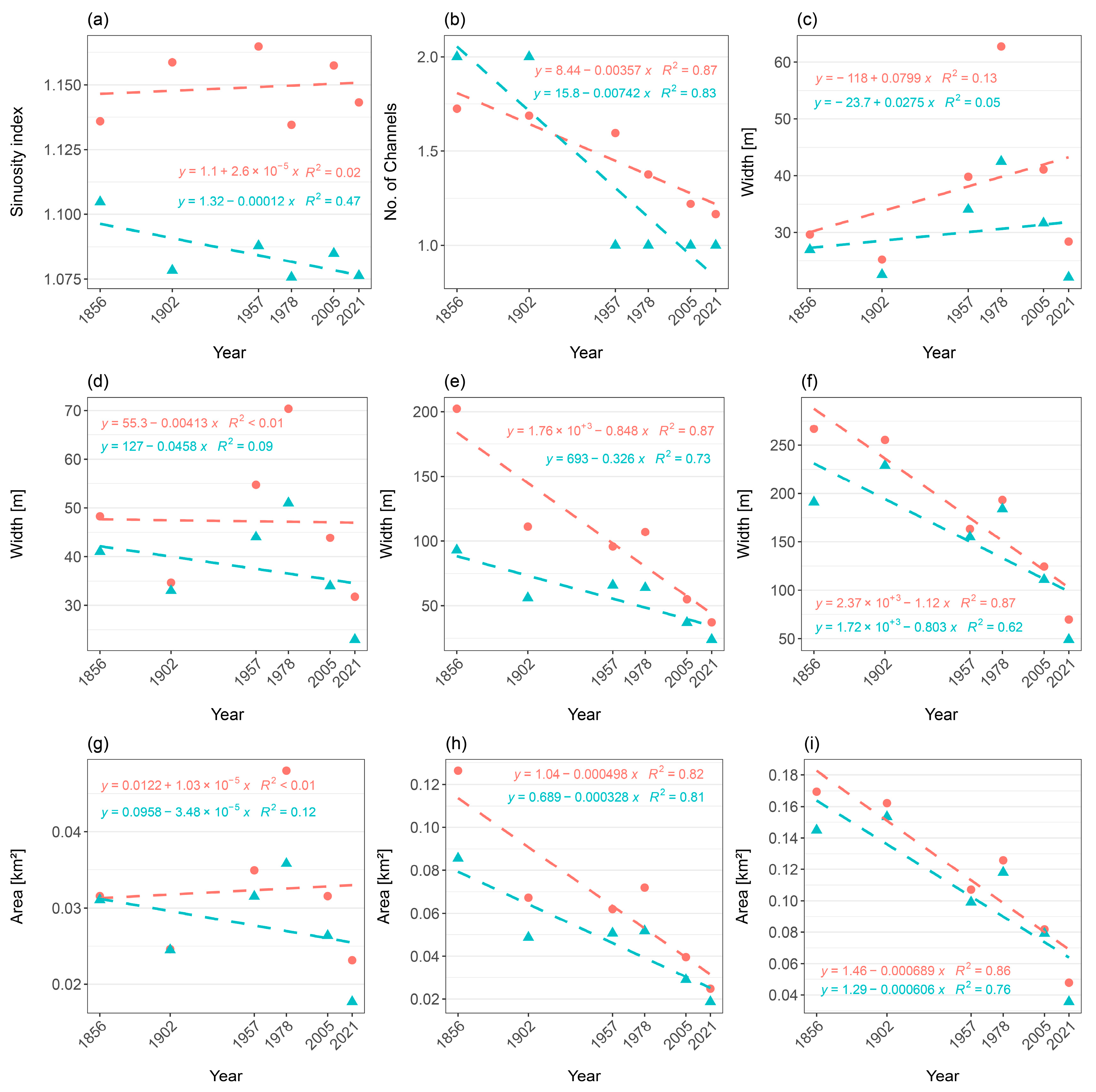
4.1. Morphometric Analysis of River Reach Between 1856–2021
4.1.1. Entire River Reach
4.1.2. Sector Scale Analysis
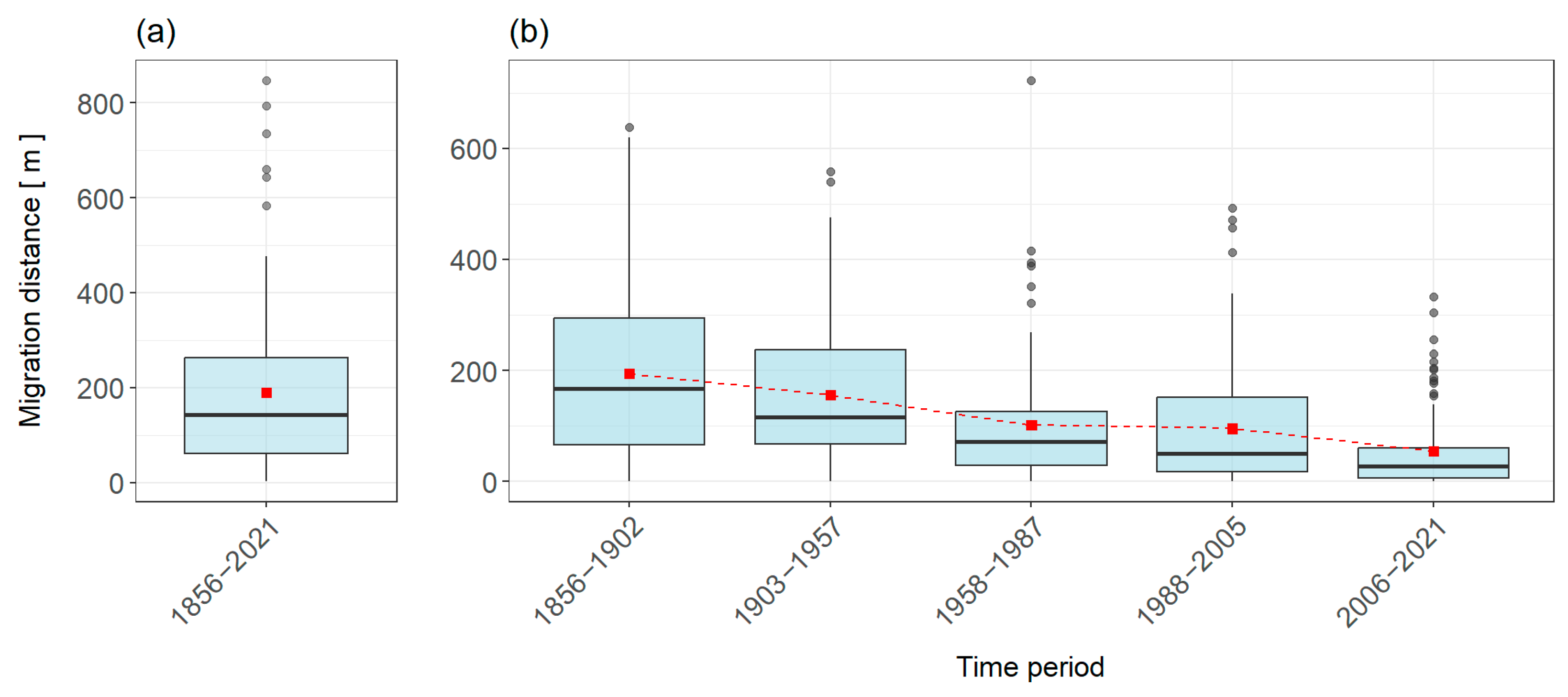
4.1.3. Riverbed Migration
4.2. HCA
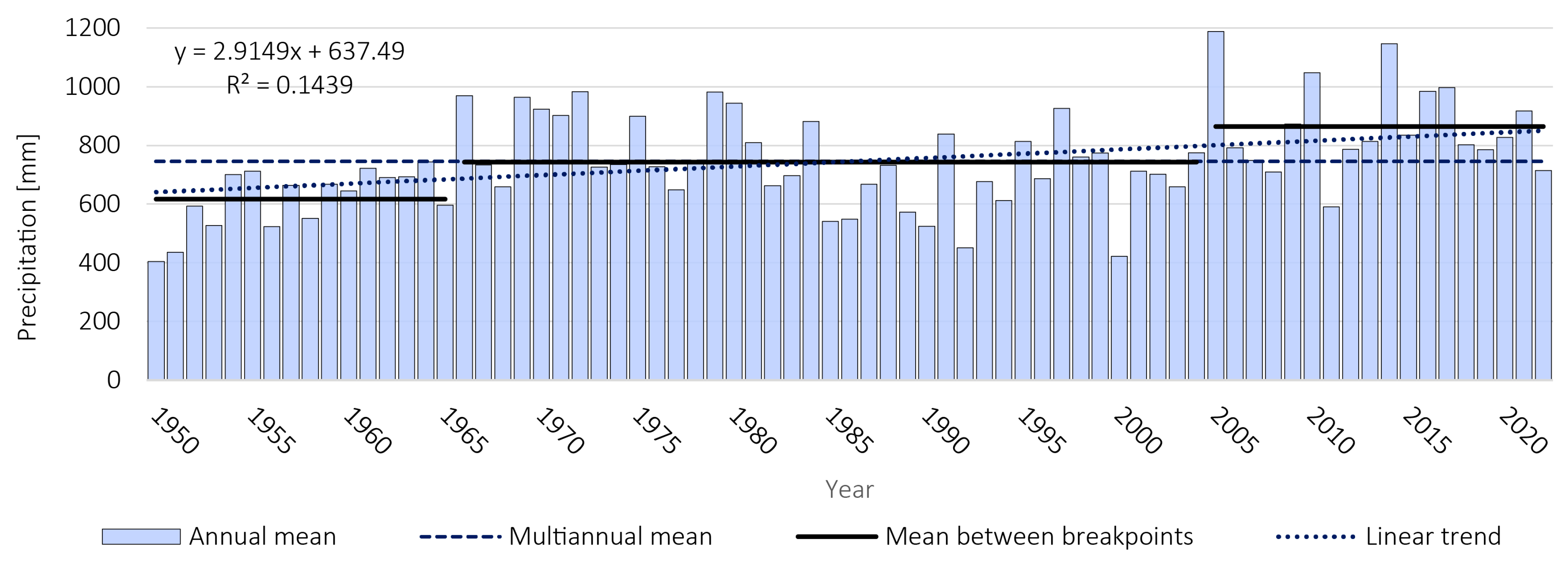
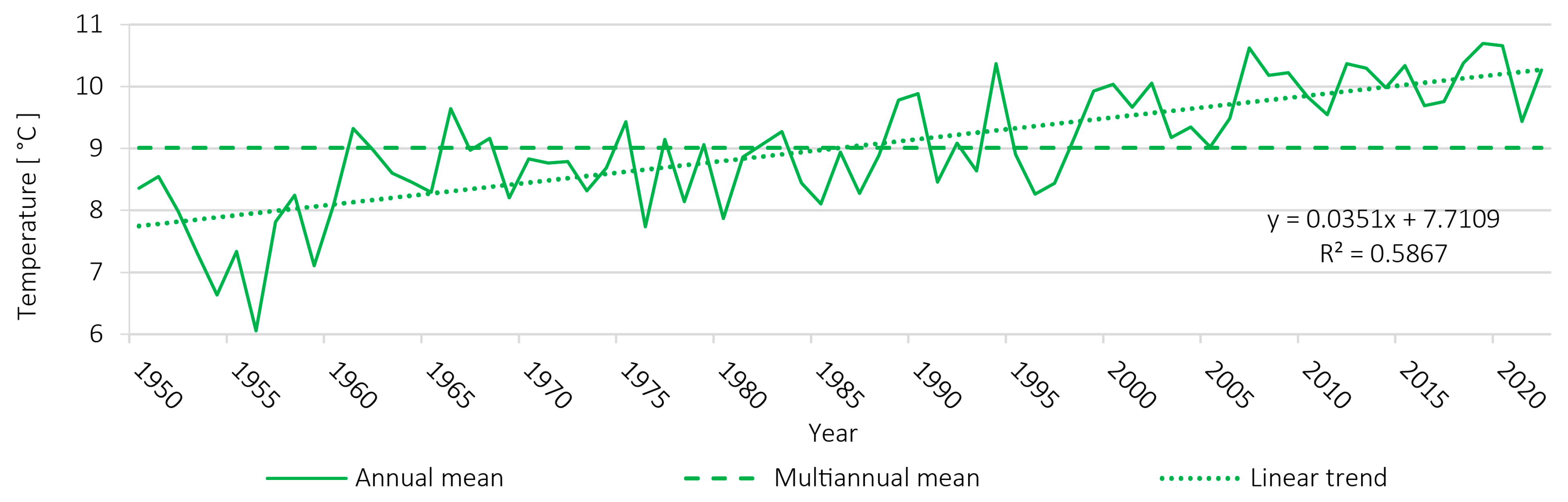
4.3. Climatic Regime and Trend
- From 1950 to 1965—with a range between 404 mm (1950) and 743 (1964) and with a mean of 617 mm.
- From 1966 to 2004—with a minimum of 422 mm in 2000 and a maximum of 973 mm in 1972. The mean value is 743 mm, which is more than 100 mm higher than the other period.
- From 2005 to 2022—with a mean value of 864 mm, annual values ranging between 590 mm in 2011 and 1188 mm in 2005. We observe the same increase in the mean value (over 100 mm) as in the previous period.
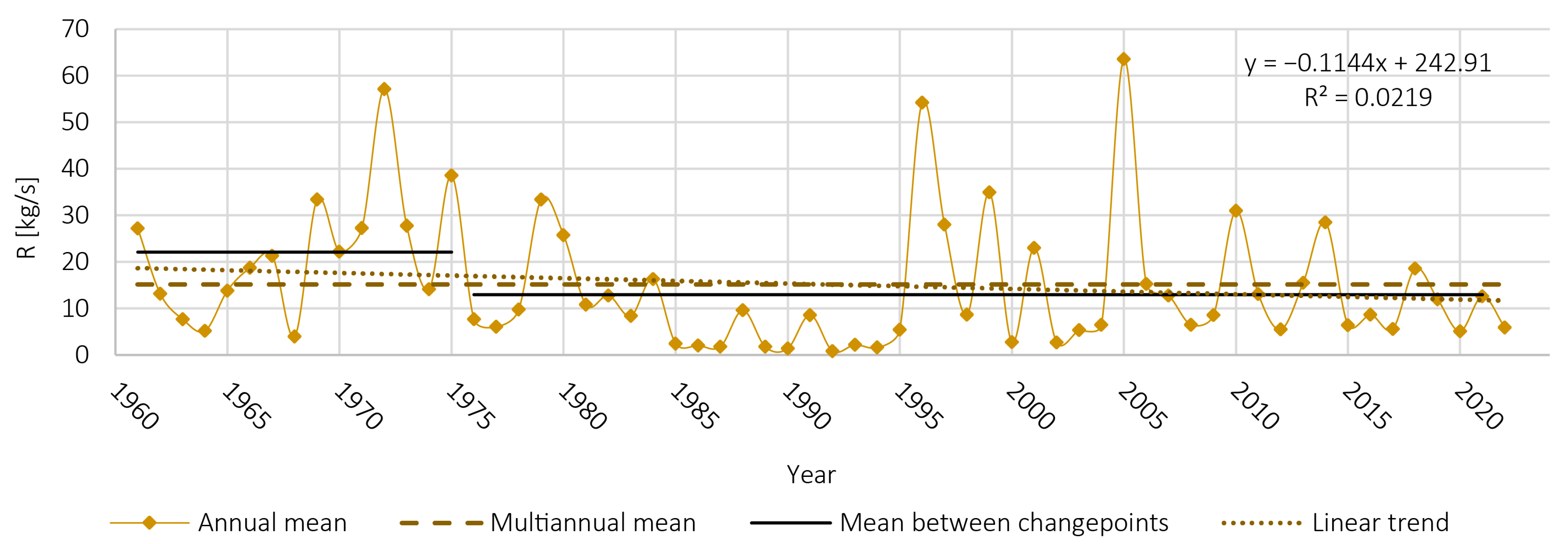
4.4. Hydrological Regime and Trend
- The first period (1961–1984) has the highest discharge, with a mean of 10.5 m3/s.
- Starting with 1985, the second period begins and lasts until 2003, characterised by a drastic change in the flow. The mean discharge drops by half, reaching 5.03 m3/s.
- The third period (2004–2022) shows an equally sudden return of the discharges near the values in the first period. The mean discharge is 8.97 m3/s.
- Period 1961–1975, with a mean of 22.09 kg/s;
- Period 1976–2022, where the mean value of R is 12.97 kg/s, significantly lower than before the change point, especially between 1985 and 1995, the values being under 10 kg/s.
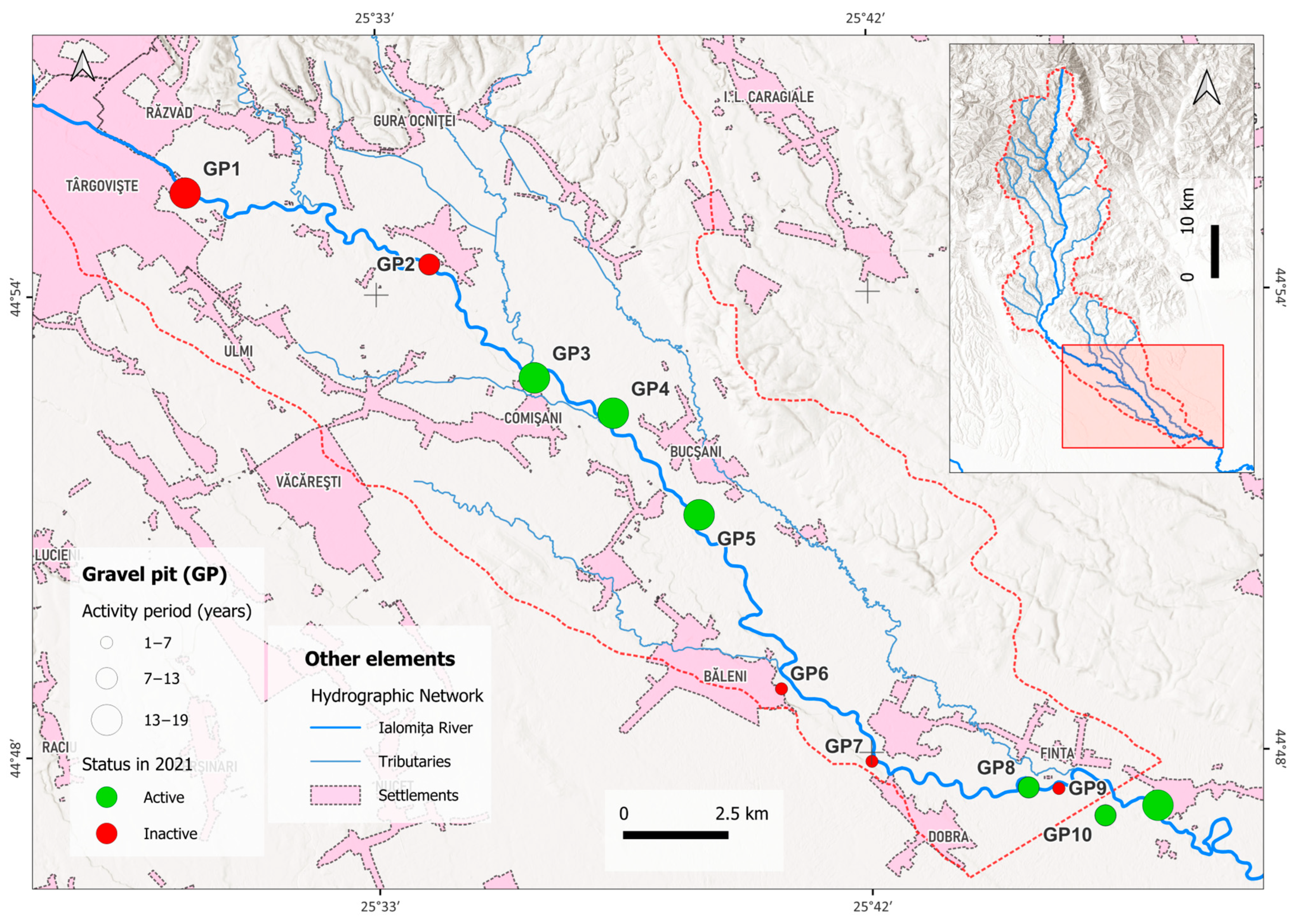
4.5. Anthropogenic Activity Assessment
4.6. Present Riverbed Dynamics
5. Discussion
- The northern sector corresponds to the Subcarpathian and contact with Târgoviște Plain areas, where clusters 1, 3, and 4 are predominant. Here, the riverbed evolution is directly influenced by anthropogenic activity which occurred in the second half of the 20th century: the construction of the Pucioasa Dam and downstream riverbed regularisation structures; the development of the urban centres of Fieni, Pucioasa, and Târgoviște; and the emergence and development of industrial activities such as the Doicești thermal power plant. Also, anthropogenic activities have caused an incision in the bedrock, thus lithologically conditioning the evolution of the riverbed in some areas.
- The southern sector overlapping the plain area generally consists of clusters 2 and 5. This area is characterised by a predominantly natural evolution of the river, the anthropogenic influence being exerted rather indirectly until the 2000s. Unlike the other zone, only rural settlements exist in the vicinity of the river. The riverbed generally has a greater space of freedom, being grafted into friable sedimentary rocks such as gravel and sand. After 2000, the appearance of the gravel pits increased the degree of anthropogenic impact with effects on the riverbed dynamics. Natural events, such as floods in 2001 and 2005, also affected the evolution of the riverbed.
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Langat, P.K.; Kumar, L.; Koech, R. Monitoring River Channel Dynamics Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques. Geomorphology 2019, 325, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Musso, N.M.; Capolongo, D.; Caldara, M.; Surian, N.; Pennetta, L. Channel Changes and Controlling Factors over the Past 150 Years in the Basento River (Southern Italy). Water 2020, 12, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvin, K.; Dasgupta, D.; Krinner, G.; Mukherji, A.; Thorne, P.W.; Trisos, C.; Romero, J.; Aldunce, P.; Barrett, K.; Blanco, G.; et al. IPCC, 2023: Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Lee, H., Romero, J., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, V.; Gillett, N.P.; Achuta Rao, K.M.; Barimalala, R.; Barreiro Parrillo, M.; Bellouin, N.; Cassou, C.; Durack, P.J.; Kosaka, Y.; McGregor, S.; et al. Human Influence on the Climate System. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 423–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caretta, M.A.; Mukherji, A.; Arfanuzzaman, M.; Betts, R.A.; Gelfan, A.; Hirabayashi, Y.; Lissner, T.K.; Liu, J.; Gunn, E.L.; Morgan, R.; et al. Water. In Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Pörtner, H.-O., Roberts, D.C., Tignor, M., Poloczanska, E.S., Mintenbeck, K., Alegría, A., Craig, M., Langsdorf, S., Löschke, S., Möller, V., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 551–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M.; Labenne, A.; Carozza, J.-M.; Valette, P. Evolutionary Trajectory of Channel Planforms in the Middle Garonne River (Toulouse, SW France) over a 130-Year Period: Contribution of Mixed Multiple Factor Analysis (MFAmix). Geomorphology 2016, 258, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandarino, A.; Pepe, G.; Cevasco, A.; Brandolini, P. Quantitative Assessment of Riverbed Planform Adjustments, Channelization, and Associated Land Use/Land Cover Changes: The Ingauna Alluvial-Coastal Plain Case (Liguria, Italy). Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, A.K.; Ohri, A.; Mishra, S. Channel Planform Dynamics of Lower Ramganga River, Ganga Basin, GIS and Remote Sensing Analyses. Geocarto Int. 2020, 35, 934–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmar, O.P.; Clifford, N.J. Planform Dynamics of the Lower Mississippi River. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2006, 31, 825–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnayaka, V.; Samarasinghe, J.T.; Gunathilake, M.B.; Muttil, N.; Rathnayake, U. Planform Changes in the Lower Mahaweli River, Sri Lanka Using Landsat Satellite Data. Land 2022, 11, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalla, R.J.; Iroumé, A.; Hernández, M.; Llena, M.; Mazzorana, B.; Vericat, D. Recent Geomorphological Evolution of a Natural River Channel in a Mediterranean Chilean Basin. Geomorphology 2018, 303, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, H.M.; Warburton, J.; Hardy, R.J. A Catchment Scale Assessment of Patterns and Controls of Historic 2D River Planform Adjustment. Geomorphology 2020, 354, 107046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langat, P.K.; Kumar, L.; Koech, R.; Ghosh, M.K. Characterisation of channel morphological pattern changes and flood corridor dynamics of the tropical Tana River fluvial systems, Kenya. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2020, 163, 103748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, N.J.; Al-Khafaji, M.S.; Alwan, I.A. Investigation of Rivers Planform Change in a Semi-Arid Region of High Vulnerability to Climate Change: A Case Study of Tigris River and Its Tributaries in Iraq. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 68, 103233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenk, J.; Khandelwal, A.; Fratkin, M.; Kumar, V.; Foufoula-Georgiou, E. High Spatiotemporal Resolution of River Planform Dynamics from Landsat: The RivMAP Toolbox and Results from the Ucayali River. Earth Space Sci. 2017, 4, 46–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercruysse, K.; Grabowski, R.C. Human Impact on River Planform within the Context of Multi-Timescale River Channel Dynamics in a Himalayan River System. Geomorphology 2021, 381, 107659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Xia, J.; Lu, J.; Deng, S.; Lin, F. Morphological Adjustments in a Meandering Reach of the Middle Yangtze River Caused by Severe Human Activities. Geomorphology 2017, 285, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliulo, P.; Bozzi, F.; Pignone, M. Assessing the Planform Changes of the Tammaro River (Southern Italy) from 1870 to 1955 Using a GIS-Aided Historical Map Analysis. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, M.; Wyżga, B.; Surian, N. Sediment Mining in Alluvial Channels: Physical Effects and Management Perspectives. River Res. Appl. 2005, 21, 805–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziliani, L.; Surian, N. Evolutionary Trajectory of Channel Morphology and Controlling Factors in a Large Gravel-Bed River. Geomorphology 2012, 173–174, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surian, N.; Rinaldi, M.; Pellegrini, L.; Audisio, C.; Maraga, F.; Teruggi, L.; Turitto, O.; Ziliani, L. Channel adjustments in northern and central Italy over the last 200 years. In Management and Restoration of Fluvial Systems with Broad Historical Changes and Human Impacts; Geological Society of America Special, Papers; James, L.A., Rathburn, S.L., Whittecar, G.R., Eds.; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 2009; Volume 451, pp. 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cencetti, C.; De Rosa, P.; Fredduzzi, A. Geoinformatics in Morphological Study of River Paglia, Tiber River Basin, Central Italy. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorpio, V.; Aucelli, P.P.C.; Giano, S.I.; Pisano, L.; Robustelli, G.; Rosskopf, C.M.; Schiattarella, M. River Channel Adjustments in Southern Italy over the Past 150years and Implications for Channel Recovery. Geomorphology 2015, 251, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorpio, V.; Andreoli, A.; Dinkelaker, N.; Marchese, E.; Coviello, V.; Gems, B.; Vignoli, G.; Comiti, F. Multi-decadal Quantification of Interactions between Coarse Sediment Fluxes and Channel Management in South Tyrol, Eastern European Alps. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2024, 49, 1869–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, M. Bed-Level Adjustments in the Po River Catchment (Northern Italy). Ital. J. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 2, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandarino, A. Morphological Adjustments of the Lower Orba River (NW Italy) since the Mid-Nineteenth Century. Geomorphology 2022, 410, 108280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenna, A.; Surian, N.; Mao, L. Alteration of Gravel-Bed River Morphodynamics in Response to Multiple Anthropogenic Disturbances: Insights from the Sediment-Starved Parma River (Northern Italy). Geomorphology 2021, 389, 107845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nones, M.; Guerrero, M.; Schippa, L.; Cavalieri, I. Remote Sensing Assessment of Anthropogenic and Climate Variation Effects on River Channel Morphology and Vegetation: Impact of Dry Periods on a European Piedmont River. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2024, 49, 1632–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenna, A.; Bizzi, S.; Surian, N. How Multiple Anthropic Pressures May Lead to Unplanned Channel Patterns: Insights from the Evolutionary Trajectory of the Po River (Italy). CATENA 2024, 234, 107598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burshtynska, K.; Hrytskiv, N.; Zayats, I.; Babiy, L.; Fijałkowska, A.; Bakuła, K. Monitoring of Channel Deformations of the Lower Dniester Using Topographic Maps and Satellite Imagery with the Implementation of GIS Technologies. Water 2024, 16, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llena, M.; Vericat, D.; Martínez-Casasnovas, J.A.; Smith, M.W. Geomorphic Adjustments to Multi-Scale Disturbances in a Mountain River: A Century of Observations. CATENA 2020, 192, 104584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baena-Escudero, R.; Rinaldi, M.; García-Martínez, B.; Guerrero-Amador, I.C.; Nardi, L. Channel Adjustments in the Lower Guadalquivir River (Southern Spain) over the Last 250 years. Geomorphology 2019, 337, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calle, M.; Alho, P.; Benito, G. Channel Dynamics and Geomorphic Resilience in an Ephemeral Mediterranean River Affected by Gravel Mining. Geomorphology 2017, 285, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.R.; Aguiar, F.C.; Martins, M.J.; Rivaes, R.; Ferreira, M.T. Long-Term Human-Generated Alterations of Tagus River: Effects of Hydrological Regulation and Land-Use Changes in Distinct River Zones. CATENA 2020, 188, 104466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyżga, B.; Zawiejska, J.; Hajdukiewicz, H. Multi-thread rivers in the Polish Carpathians: Occurrence, decline and possibilities of restoration. Quat. Int. 2016, 415, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawiejska, J.; Wyżga, B. Twentieth-Century Channel Change on the Dunajec River, Southern Poland: Patterns, Causes and Controls. Geomorphology 2010, 117, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdukiewicz, H.; Wyżga, B. Analysis of Historical Changes in Planform Geometry of a Mountain River to Inform Design of Erodible River Corridor. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 186, 106821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nádudvari, Á.; Czajka, A.; Wyżga, B.; Zygmunt, M.; Wdowikowski, M. Patterns of Recent Changes in Channel Morphology and Flows in the Upper and Middle Odra River. Water 2023, 15, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterbottom, S.J. Medium and Short-Term Channel Planform Changes on the Rivers Tay and Tummel, Scotland. Geomorphology 2000, 34, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, S.D.; van Huissteden, J.; Vandenberghe, J.; Van Dam, O.; de Gier, J.; Pleizier, I.D. Evolution of the Morphology of the River Dragonja (SW Slovenia) Due to Land-Use Changes. Geomorphology 2005, 69, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidová, A.; Lehotský, M.; Rusnák, M. Geomorphic Diversity in the Braided-Wandering Belá River, Slovak Carpathians, as a Response to Flood Variability and Environmental Changes. Geomorphology 2016, 272, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belletti, B.; Dufour, S.; Piégay, H. What Is the Relative Effect of Space and Time to Explain the Braided River Width and Island Patterns at a Regional Scale? River Res. Appl. 2015, 31, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulteau, T.; Batalla, R.J.; Chapron, E.; Valette, P.; Piégay, H. Geomorphic Effects of a Run-of-the-River Dam in a Multi-Driver Context: The Case of the Upper Garonne (Central Pyrenees). Geomorphology 2022, 408, 108243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jautzy, T.; Schmitt, L.; Rixhon, G. Historical Geomorphological Adjustments of an Upper Rhine Sub-Tributary over the Two Last Centuries (Bruche River, France). Géomorphologie Relief Process. Environ. 2022, 28, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckmann, T.; Haas, F.; Abel, J.; Rimböck, A.; Becht, M. Feeding the Hungry River: Fluvial Morphodynamics and the Entrainment of Artificially Inserted Sediment at the Dammed River Isar, Eastern Alps, Germany. Geomorphology 2017, 291, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschbach, D.; Schmitt, L.; Imfeld, G.; May, J.-H.; Payraudeau, S.; Preusser, F.; Trauerstein, M.; Skupinski, G. Long-Term Temporal Trajectories to Enhance Restoration Efficiency and Sustainability on Large Rivers: An Interdisciplinary Study. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 2717–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexeevsky, N.I.; Chalov, R.S.; Berkovich, K.M.; Chalov, S.R. Channel Changes in Largest Russian Rivers: Natural and Anthropogenic Effects. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2013, 11, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spada, D.; Molinari, P.; Bertoldi, W.; Vitti, A.; Zolezzi, G. Multi-Temporal Image Analysis for Fluvial Morphological Characterization with Application to Albanian Rivers. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlek, K.; Faivre, S. Geomorphological Changes of the Cetina River Channels since the End of the Nineteenth Century, Natural vs Anthropogenic Impacts (the Dinarides, Croatia). Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Balogh, M.; Fiala, K.; Sipos, G. Morphology of Fluvial Levee Series along a River under Human Influence, Maros River, Hungary. Geomorphology 2018, 303, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Fiala, K.; Sipos, G. Alterations of Channel Parameters in Response to River Regulation Works since 1840 on the Lower Tisza River (Hungary). Geomorphology 2008, 98, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Blanka, V. River Channel Response to Climate- and Human-Induced Hydrological Changes: Case Study on the Meandering Hernád River, Hungary. Geomorphology 2012, 175–176, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Andrási, G. Evolution of the Drava Floodplain in Hungary in the Last 100 Years. In The Drava River; Lóczy, D., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amissah, G.J.; Kiss, T.; Fiala, K. Morphological Evolution of the Lower Tisza River (Hungary) in the 20th Century in Response to Human Interventions. Water 2018, 10, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škarpich, V.; Hradecký, J.; Dušek, R. Complex transformation of the geomorphic regime of channels in the forefield of the Moravskoslezské Beskydy Mts.: Case study of the Morávka River (Czech Republic). CATENA 2013, 111, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohensinner, S.; Habersack, H.; Jungwirth, M.; Zauner, G. Reconstruction of the Characteristics of a Natural Alluvial River–Floodplain System and Hydromorphological Changes Following Human Modifications: The Danube River (1812–1991). River Res. Appl. 2004, 20, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rădoane, M.; Perșoiu, I.; Chiriloaei, F.; Cristea, I.; Robu, D. Styles of Channel Adjustments in the Last 150 Years. In Landform Dynamics and Evolution in Romania. Springer Geography; Rădoane, M., Vespremeanu-Stroe, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 489–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bălteanu, D.; Jurchescu, M.; Surdeanu, V.; Ionita, I.; Goran, C.; Urdea, P.; Rădoane, M.; Rădoane, N.; Sima, M. Recent Landform Evolution in the Romanian Carpathians and Pericarpathian Regions. In Recent Landform Evolution: The Carpatho-Balkan-Dinaric Region; Lóczy, D., Stankoviansky, M., Kotarba, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 249–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rădoane, M.; Rădoane, N.; Dumitriu, D. Geomorphological Evolution of Longitudinal River Profiles in the Carpathians. Geomorphology 2003, 50, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitriu, D. Flood Events as Geomorphic Thresholds for Channel Bed Level Change. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 16, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioana-Toroimac, G.; Zaharia, L.; Neculau, G.; Minea, G. Impact of Channel Incision on Floods: A Case Study in The South-Eastern Subcarpathians (Romania). Geogr. Environ. Sustain. 2020, 13, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rădoane, M.; Obreja, F.; Cristea, I.; Mihailă, D. Changes in the Channel-Bed Level of the Eastern Carpathian Rivers: Climatic vs. Human Control over the Last 50 Years. Geomorphology 2013, 193, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rădoane, M.; Rădoane, N.; Cristea, A.; Dinu, O. Contemporary Changes of the Prut River Channel, Romanian Border. Rev. Geomorfol. 2008, 10, 57–71. [Google Scholar]
- Rădoane, M.; Pandi, G.; Rădoane, N. Contemporary Bed Elevation Changes from the Eastern Carpathians. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2010, 5, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Grecu, F.; Ioana-Toroimac, G.; Molin, P.; Dramis, F. River channel dynamics in the contact area between the Romanian Plain and the Curvature Subcarpathians. Rev. Geomorfol. 2014, 16, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ioana-Toroimac, G.; Robert, D.; Grecu, F.; Zaharia, L. Evolution 2D de La Bande Active de La Haute Prahova (Roumanie) Durant Les 150 Dernières Années. Géomorphologie Relief Process. Environ. 2010, 16, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grecu, F.; Grigore, Ș.; Ioana-Toroimac, G.; Ghiţă, C. The Dynamics of the Danube Channel over the Last 150 Years (Giurgiu—Călărași Sector. Preliminary Data). In Proceedings of the Romanian Geomorphology Symposium, 33rd edition, Iași, Romania, 11–14 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Grecu, F.; Zaharia, L.; Ioana-Toroimac, G.; Armaș, I. Floods and Flash-Floods Related to River Channel Dynamics. In Landform Dynamics and Evolution in Romania. Springer Geography; Radoane, M., Vespremeanu-Stroe, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 821–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioana-Toroimac, G. La Dynamique Hydrogéomorphologique de La Rivière Prahova (Roumanie): Fonctionnement Actuel, Évolution Récente et Conséquences Géographiques. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bucharest, Bucharest, Romania, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Perşoiu, I.; Rădoane, M. Spatial and Temporal Controls on Historical Channel Responses—Study of an Atypical Case: Someşu Mic River, Romania. Earth Surf. Process Landf. 2011, 36, 1391–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feier, I.; Rădoane, M. Dinamica în plan orizontal a albiei minore a râului Somesu Mic, înainte de lucrarile hidrotehnice majore (1870–1968). Analele Univ. Stefan Cel Mare Suceava Sect. Geogr. 2007, 16, 5–22. [Google Scholar]
- Chiriloaei, F.; Rădoane, M. The Metamorphosis of a Braided River Channel during the Last 100 Years: Moldova River as a Case Study. Rev. Geomorfol. 2015, 17, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Chiriloaei, F.A. Analiza Cantitativa a Modificarilor Albiei Raului Moldova in Sectorul Extracarpatic. Ph.D. Thesis, “ Al. I. Cuza” University, Iași, Romania, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Perșoiu, I.; Hosu, M. Historical geomorphic analysis of Someșul Mic River (NW Romania) channel spatial and temporal behavior, as a background for the assessment of present day morphological state of the river. Rev. Geomorfol. 2019, 21, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brașovanu, L. Studiu Morfodinamic al Albiei Râului Prahova în Sectoarele Montan și Subcarpatic. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bucharest, Bucharest, Romania, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Armaș, I.; Gogoașe Nistoran, D.; Osaci-Costache, G.; Brașoveanu, L. Morpho-Dynamic Evolution Patterns of Subcarpathian Prahova River (Romania). CATENA 2013, 100, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grecu, F.; Ioana-Toroimac, G.; Osaci-Costache, G.; Zaharia, L.; Cocoș, O.; Hachemi, K.; Sălăjan, L. Dynamics of Islands and Danube River Channel Along Vedea-Călărași Sector (1856–2019): Hydrogeomorphological Approach. In The Lower Danube River. Earth and Environmental Sciences Library; Negm, A., Zaharia, L., Ioana-Toroimac, G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 43–67. [Google Scholar]
- Salit, F.; Arnaud-Fassetta, G.; Zaharia, L.; Madelin, M.; Beltrando, G. The influence of river training on channel changes during the 20th century in the Lower Siret River (Romania). Géomorphologie Relief Process. Environ. 2015, 21, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristea, I. Studiul Geomorfologic al Văii Putna Vrânceană. Ph.D. Thesis, Ștefan cel Mare University, Suceava, Romania, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Buzău-Ialomița Water Basin Administration Flood Risk Management Plan—Updated. Available online: https://inundatii.ro/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/PMRI_actualizat_ciclul-II_ABA-Buzau-Ialomita_versiune-preliminara-1.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2024).
- Geological Map of Romania, Sc. 1:200 000; Romanian Geological Institute: Bucharest, Romania, 1968.
- Geological Map of Romania, Sc. 1:200 000, Explanatory Note of Târgoviște Map Sheet L-35-XXVI; Romanian Geological Institute: Bucharest, Romania, 1968.
- Clima României. Available online: https://www.meteoromania.ro/clima/clima-romaniei/ (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- Dumitrescu, A.; Bojariu, R.; Birsan, M.-V.; Marin, L.; Manea, A. Recent Climatic Changes in Romania from Observational Data (1961–2013). Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 122, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murărescu, O.; Bretcan, P. Management of Water Resources in Upper Ialomiţa River Basin (Carpathians, Sub-Carpathians, Romania). In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Water Management and Hydraulic Engineering, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Department of Hydraulics, Hydrology and River Engineering, University of Ss. Cyril and Methodius, Skopje, North Macedonia, 1–5 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Murătoreanu, G.; Murărescu, O.; Pehoiu, G.; Sencovici, M. GIS multitemporal analysis of remote sensing images to assess the silting of anthropogenic dam lakes in the Outer Subcarpathian area. Case study: Pucioasa Accumulation Lake, Romania. J. Sci. Arts 2021, 21, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loghin, V. Modificări antropice în profilul longitudinal al Ialomiței și efecte asupra proceselor de albie (Sectorul Moroeni—Târgoviște). Analele Univ. Valahia Din Târgovişte Ser. Geogr. 1997, 1, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Activitățile Cartografice și Geodezice Habsburgice în Vechea Românie. Available online: https://geo-spatial.org/vechi/articole/activitatile-cartografice-si-geodezice-habsburgice-in-vechea-romanie (accessed on 13 August 2024).
- Timár, G. Habsburg Geodetic and Cartographic Activities in the Old Romania. Stud. şi Cercet. Ser. Geol.-Geogr. 2008, 13, 93–102. [Google Scholar]
- Osaci-Costache, G. Cartografie, 2nd ed.; Editura Universitară: Bucharest, Romania, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Planurile Directoare de Tragere. Available online: https://geo-spatial.org/vechi/download/planurile-directoare-de-tragere (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Military Topographic Maps Sc. 1:25.000. Available online: https://www.geomil.ro/Produse/HartiTopografice25GK_35# (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- Năstase, A.; Osaci-Costache, G. Topografie-Cartografie, 2nd ed.; Editura Fundaţiei România de Mâine: Bucharest, Romania, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wallachia—Second Military Survey of the Habsburg Empire|Arcanum Maps. Available online: https://maps.arcanum.com/en/map/secondsurvey-wallachia (accessed on 16 August 2023).
- Planurile Directoare de Tragere Download Service. Available online: https://www.geo-spatial.org/vechi/maps/download-planuri-tragere.php (accessed on 7 February 2023).
- Color Orthophoto Map Scale 1:5000—Visualization Service. Available online: https://inspire-geoportal.ec.europa.eu/srv/eng/catalog.search#/metadata/1623228948931r5372581473647313 (accessed on 28 October 2024).
- Cornes, R.C.; van der Schrier, G.; van den Besselaar, E.J.M.; Jones, P.D. An Ensemble Version of the E-OBS Temperature and Precipitation Data Sets. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 9391–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitrescu, A.; Birsan, M.-V. ROCADA: A Gridded Daily Climatic Dataset over Romania (1961–2013) for Nine Meteorological Variables. Nat. Hazards 2015, 78, 1045–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiemig, V.; Gomes, G.N.; Skøien, J.O.; Ziese, M.; Rauthe-Schöch, A.; Rustemeier, E.; Rehfeldt, K.; Walawender, J.P.; Kolbe, C.; Pichon, D.; et al. EMO-5: A High-Resolution Multi-Variable Gridded Meteorological Dataset for Europe. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 3249–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackeloeer, A.; Klasing, K.; Krisp, J.M.; Meng, L. Georeferencing: A Review of Methods and Applications. Ann. GIS 2014, 20, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QGIS User Guide—17.3 Georeferencerer. Available online: https://docs.qgis.org/3.34/en/docs/user_manual/working_with_raster/georeferencer.html (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Overview of Georeferencing. Available online: https://pro.arcgis.com/en/pro-app/latest/help/data/imagery/overview-of-georeferencing.htm (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Boothroyd, R.J.; Nones, M.; Guerrero, M. Deriving Planform Morphology and Vegetation Coverage From Remote Sensing to Support River Management Applications. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rădoane, M.; Perșoiu, I.; Cristea, A.; Chiriloaei, F. River Channel Planform Changes Based on Successive Cartographic Data. A Methodological Approach. Rev. Geomorfol. 2013, 15, 68–88. [Google Scholar]
- Nawfee, S.M.; Dewan, A.; Rashid, T. Integrating Subsurface Stratigraphic Records with Satellite Images to Investigate Channel Change and Bar Evolution: A Case Study of the Padma River, Bangladesh. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, L.B.; Wolman, M.G. River Channel Patterns: Braided, Meandering, and Straight; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washongton, DC, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J. R Package, version 1.6-53; Terra: Spatial Data Analysis; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=terra (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests Against Trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods, 4th ed.; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- McLeod, A.I. R Package, version 2.2.1; Kendall: Kendall Rank Correlation and Mann-Kendall Trend Test; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2005; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=Kendall (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Killick, R.; Haynes, K.; Eckley, I.A. R Package, version 2.3; Changepoint: An R Package for Changepoint Analysis; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2006; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=changepoint (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rousseeuw, P.J. Silhouettes: A Graphical Aid to the Interpretation and Validation of Cluster Analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1987, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffin-Bélanger, T.; Biron, P.M.; Larocque, M.; Demers, S.; Olsen, T.; Choné, G.; Ouellet, M.-A.; Cloutier, C.-A.; Desjarlais, C.; Eyquem, J. Freedom Space for Rivers: An Economically Viable River Management Concept in a Changing Climate. Geomorphology 2015, 251, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manea, A.; Birsan, M.-V.; Tudorache, G.; Cărbunaru, F. Changes in the Type of Precipitation and Associated Cloud Types in Eastern Romania (1961–2008). Atmos. Res. 2016, 169, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busuioc, A.; Birsan, M.; Carbunaru, D.; Baciu, M.; Orzan, A. Changes in the Large-scale Thermodynamic Instability and Connection with Rain Shower Frequency over Romania: Verification of the Clausius–Clapeyron Scaling. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 2015–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Dam/Lake Name | Construction Period | Put into Service | Dam Height (m) | Total Volume of Water (mil. m3) | Reservoir Use 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bolboci | 1976–1985 | 1988 | 55 | 19.4 | W, H, F, O |
| Scropoasa | 1928–1930 | 1930 | 26 | 0.55 | H |
| Dobrești | 1928–1930 | 1930 | 10 | 0.04 | H |
| Pucioasa | - | 1975 | 30.5 | 10.6 | W, H, F, O |
| Map Name | No. of Map Sheets | Map Sheets Nomenclature | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wallachia—Second military survey of the Habsburg Empire | 3 | Section 25.26, East Column V.VI; Section 27.28, East Column V.VI; Section 27.28, East Column VII.VIII | Austrian State Archives through the Arcanum platform: https://maps.arcanum.com/en/map/secondsurvey-wallachia (accessed on 16 August 2023). [94] |
| “Plan Director de Tragere” | 9 | 3850-Voinești, 3849-Dragomirești, 3951-Fieni, 3950-Glodeni, 3949-Târgoviște, 3948-Văcărești, 4049-Ghirdoveni, 4048-Bucșani, and 4047-Cornățelul | Geospatial community, available online at https://www.geo-spatial.org/vechi/maps/download-planuri-tragere.php (accessed on 15 August 2024). [95] |
| Romanian Military Topographic Maps—1st ed. | L-35-099-D-b, L-35-099-D-d, L-35-11-B-b, L-35-111-B-d, L-35-112-A-a, L-35-112-A-c, L-35-112-A-d, L-35-112-C-b, L-35-112-D-a | The Defence Geospatial Intelligence Agency “Division General Constantin Barozzi” | |
| Romanian Military Topographic Maps—2nd ed. | University of Bucharest, Faculty of Geography |
| Climatic Data Source | Spatial Resolution | Dataset Time Interval | Selected Time Interval | Stations in Romania | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prec. | Temp. | ||||
| ECAD | 0.1° | 1950–2024 | 1950–1960 | 29 | 26 |
| ROCADA | 0.1° | 1961–2013 | 1961–2013 | 188 | 150 |
| EMO-1 | 0.01667° | 1990–2022 | 2014–2022 | Include data from ECAD and other European databases | |
| Map Name | Georeferencing Algorithm | Total GCPs | RMSE (Mean) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wallachia—Second military survey of the Habsburg Empire | Thin Plate Spline (TPS) | 98 | 0.0020 |
| “Plan Director de Tragere” | 115 | 0.00041 | |
| Romanian Military Topographic Maps—1st ed. | Projective | 51 | 0.49 |
| Romanian Military Topographic Maps—2nd ed. | Already georeferenced | ||
| Parameter/Index | Abbreviation | Method 1, 2 | Measure Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Channel length | CL | S | m |
| Sinuosity Index | SI | S | dimensionless |
| Thalweg migration | TM | T | m |
| Wetted channel width | WCW | T | m |
| Bankfull channel width | BCW | T | m |
| Main channel width | MCW | T | m |
| Active channel width | ACW | T | m |
| Number of channels | NC | T | dimensionless |
| Wetted channel area | WCA | S | km2 |
| Bankfull channel area | BCA | S | km2 |
| Active channel area | ACA | S | km2 |
| Index/Parameters | 1856–1902 | 1903–1957 | 1958–1978 | 1988–2005 | 2006–2021 | 1856–2021 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SI | +0.08 | −0.07 | −0.03 | +0.02 | −0.08 | −0.02 |
| WCA | −0.49 | +0.74 | +1.26 | −1.91 | −1.66 | −0.23 |
| BCA | −0.90 | −0.15 | +0.52 | −2.49 | −2.31 | −2.23 |
| ACA | −0.09 | −0.63 | +0.57 | −1.92 | −2.62 | −1.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radu, A.; Comănescu, L. Historical Evolution and Future Trends of Riverbed Dynamics Under Anthropogenic Impact and Climatic Change: A Case Study of the Ialomița River (Romania). Water 2025, 17, 2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142151
Radu A, Comănescu L. Historical Evolution and Future Trends of Riverbed Dynamics Under Anthropogenic Impact and Climatic Change: A Case Study of the Ialomița River (Romania). Water. 2025; 17(14):2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142151
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadu, Andrei, and Laura Comănescu. 2025. "Historical Evolution and Future Trends of Riverbed Dynamics Under Anthropogenic Impact and Climatic Change: A Case Study of the Ialomița River (Romania)" Water 17, no. 14: 2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142151
APA StyleRadu, A., & Comănescu, L. (2025). Historical Evolution and Future Trends of Riverbed Dynamics Under Anthropogenic Impact and Climatic Change: A Case Study of the Ialomița River (Romania). Water, 17(14), 2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142151









