Spatiotemporal Variations in Observed Rain-on-Snow Events and Their Intensities in China from 1978 to 2020
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Daily ROS Event Definition
2.2.2. Discrimination of Precipitation Type
2.2.3. Daily Snowmelt
2.2.4. Calculation of Influencing Factors
2.2.5. Trend Analysis
2.2.6. Correlation Analysis
3. Results
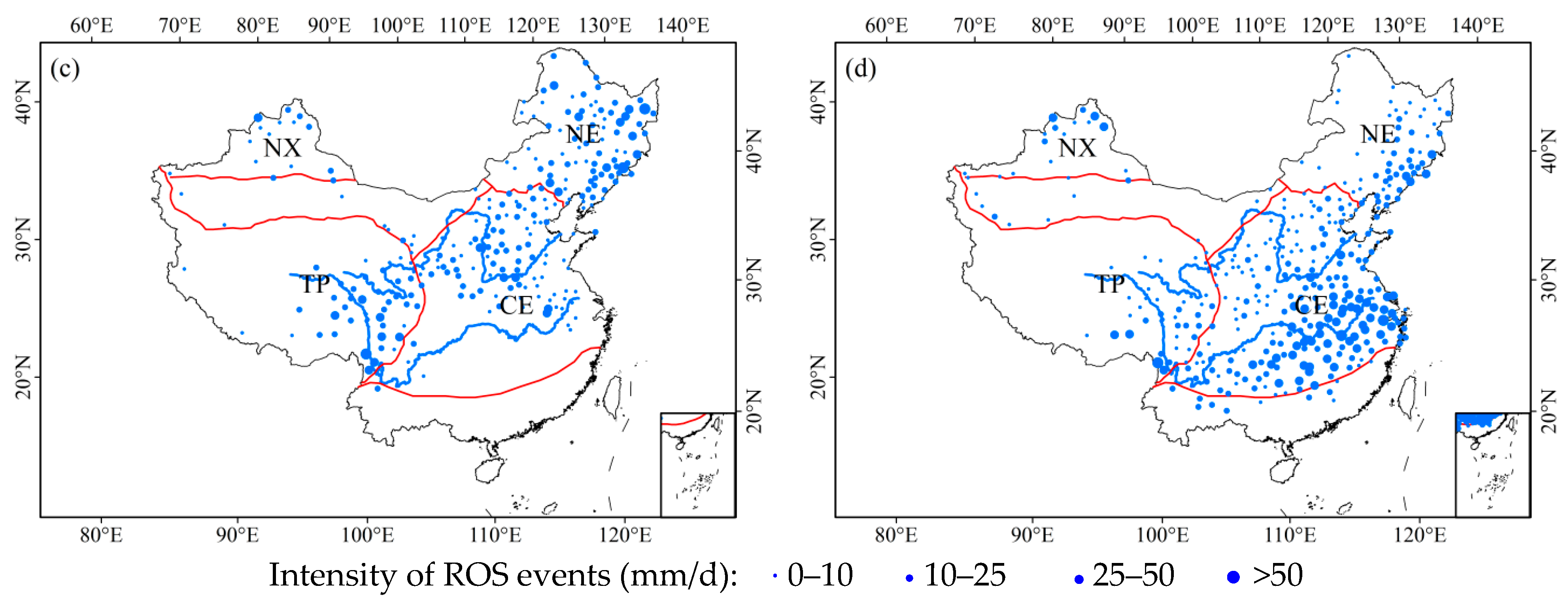
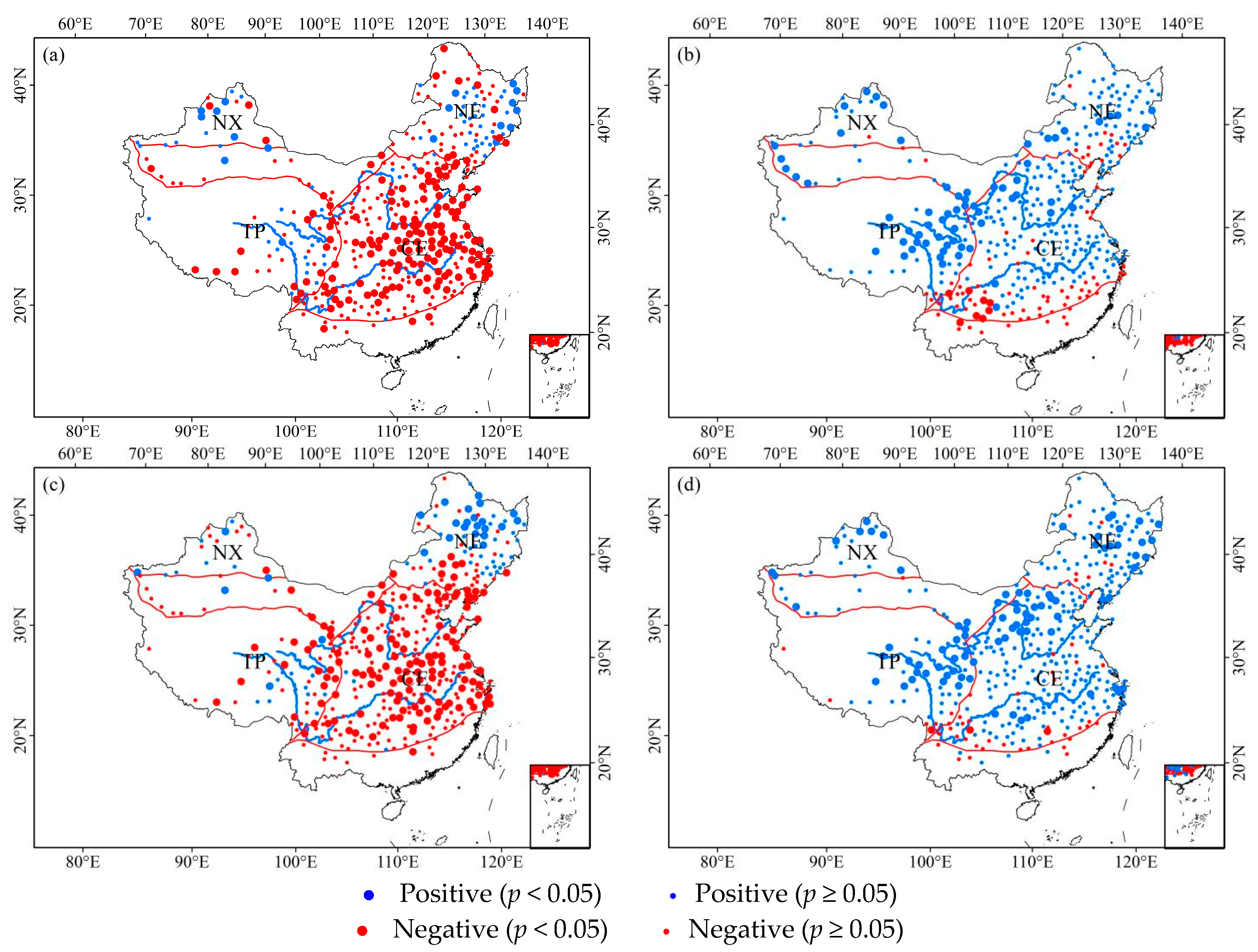
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Patterns for ROS Events in China
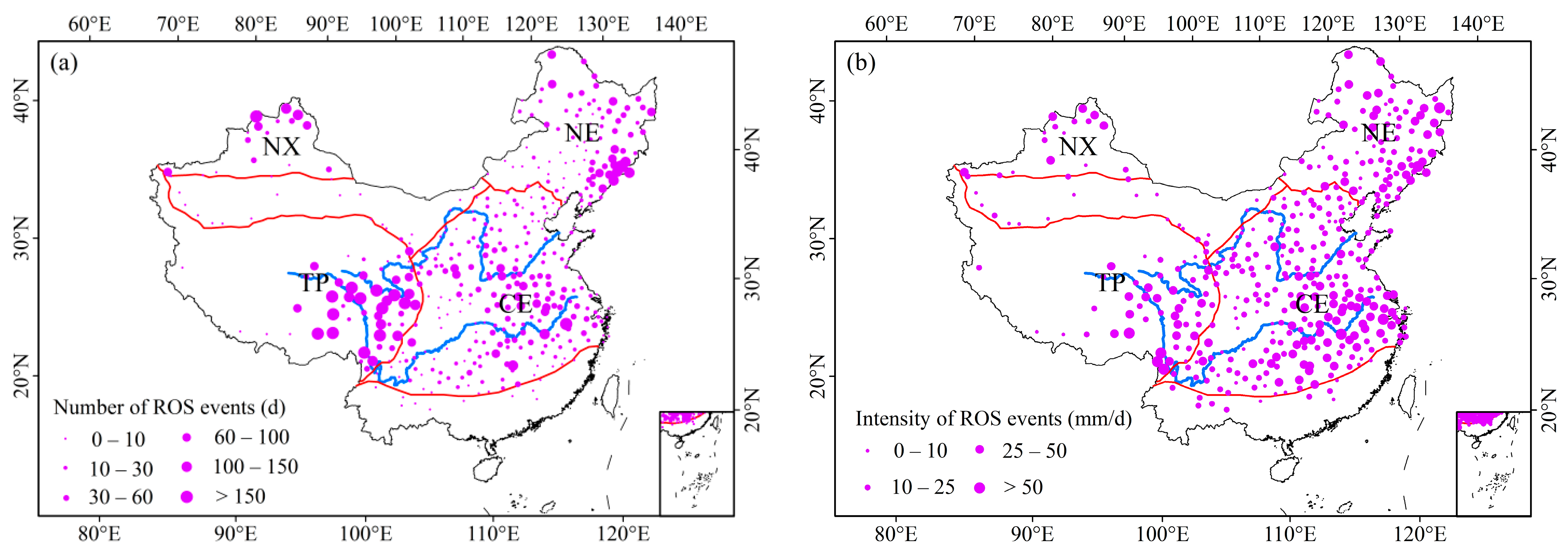
3.1.1. Spatial Distribution
3.1.2. Seasonality Distribution
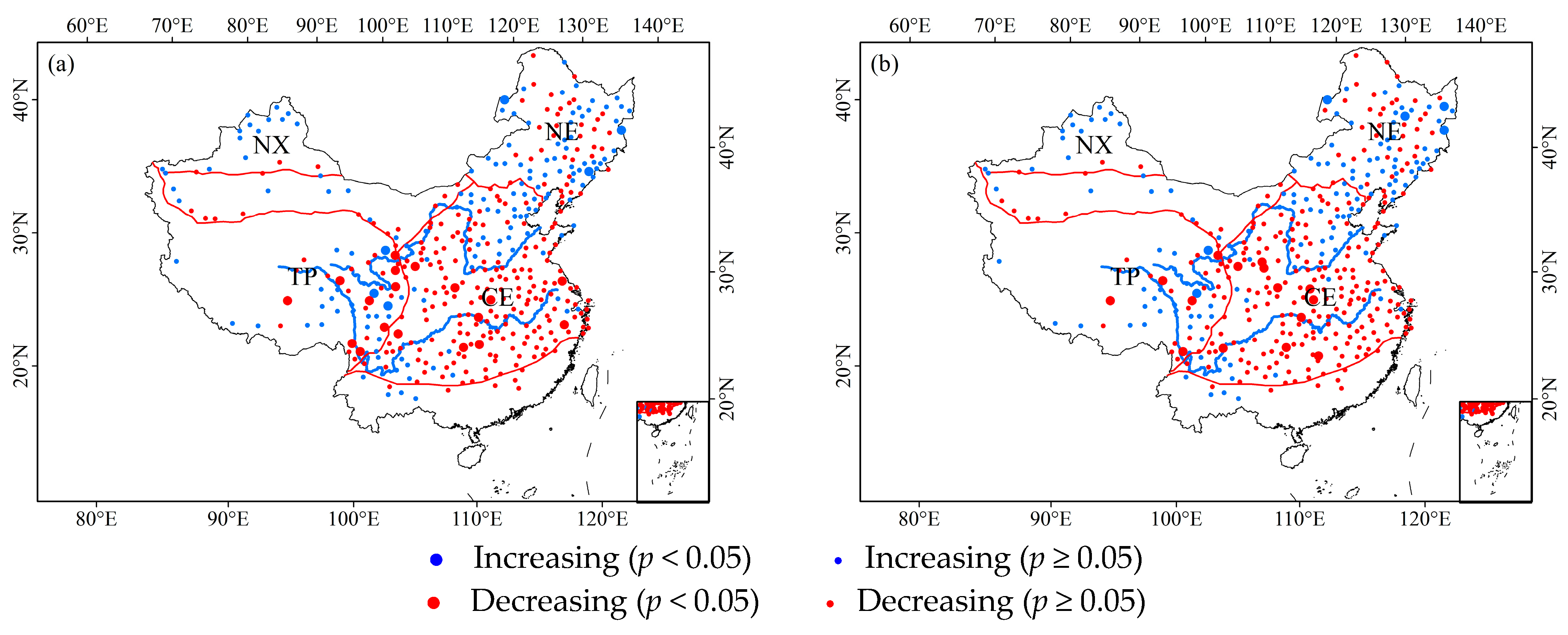
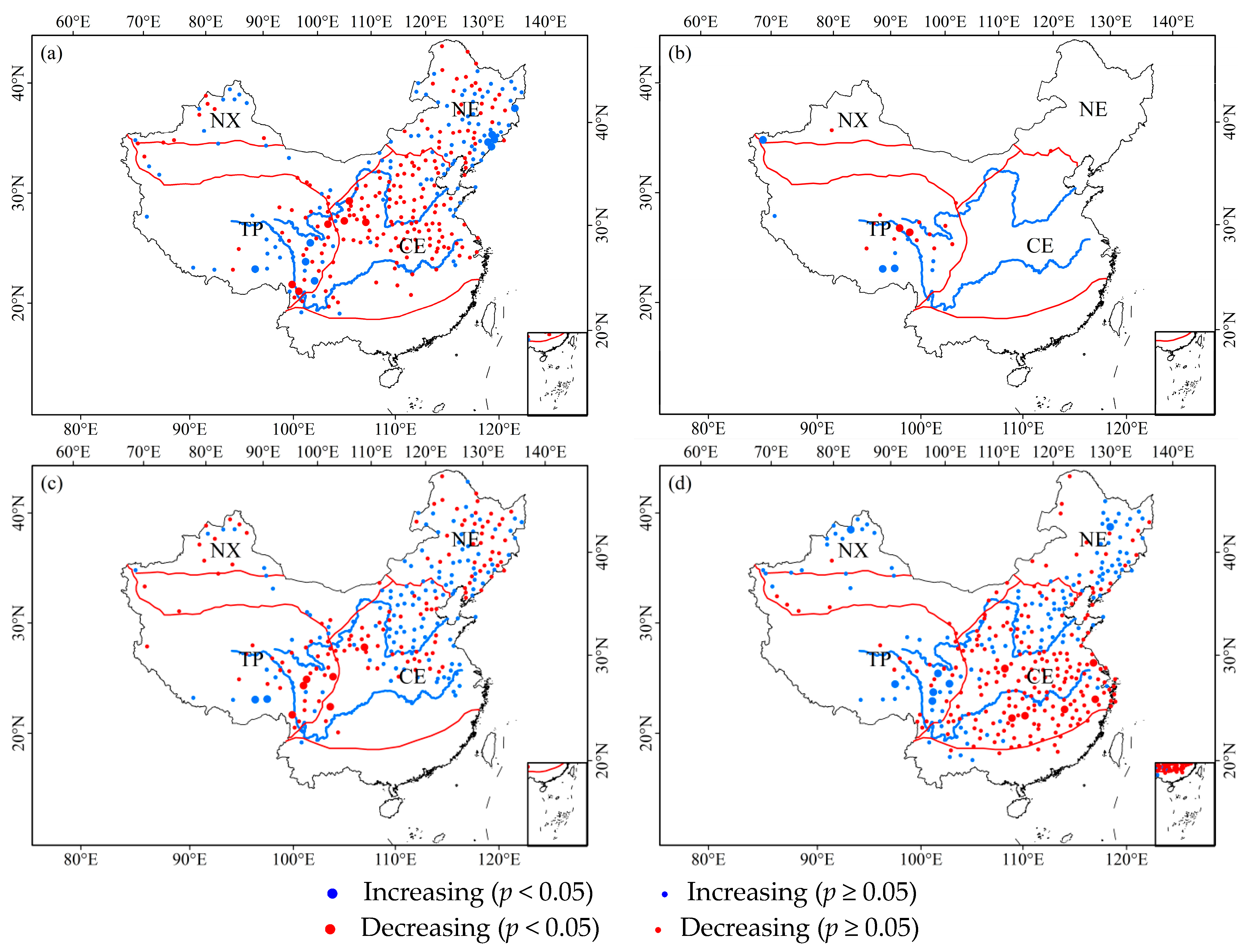
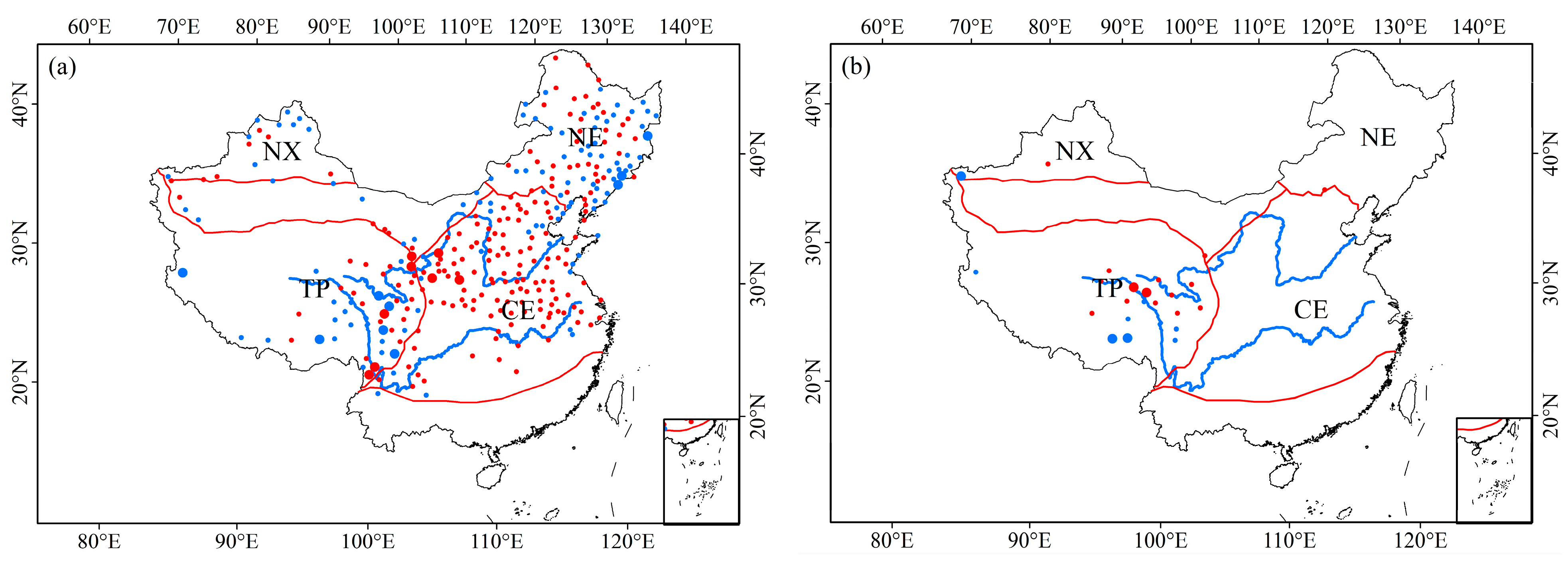
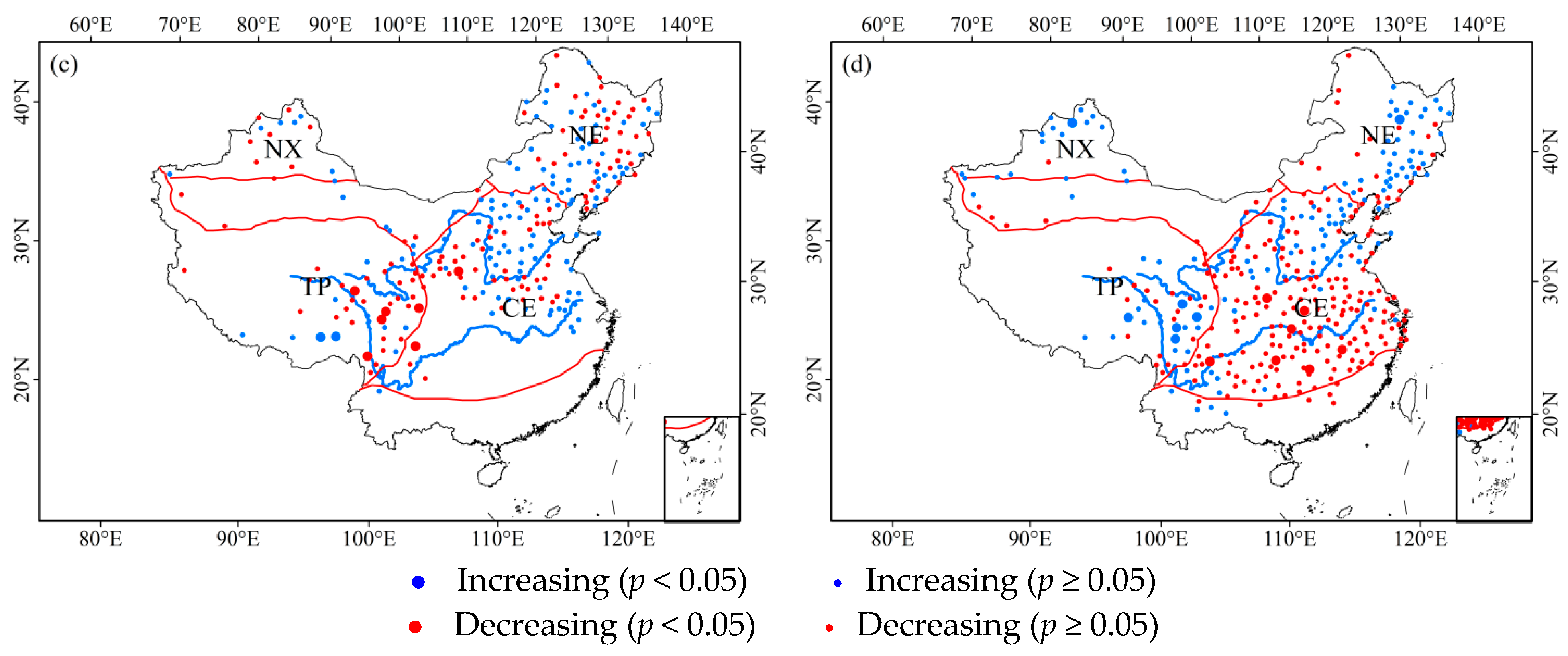
3.2. Trends in ROS Events in China
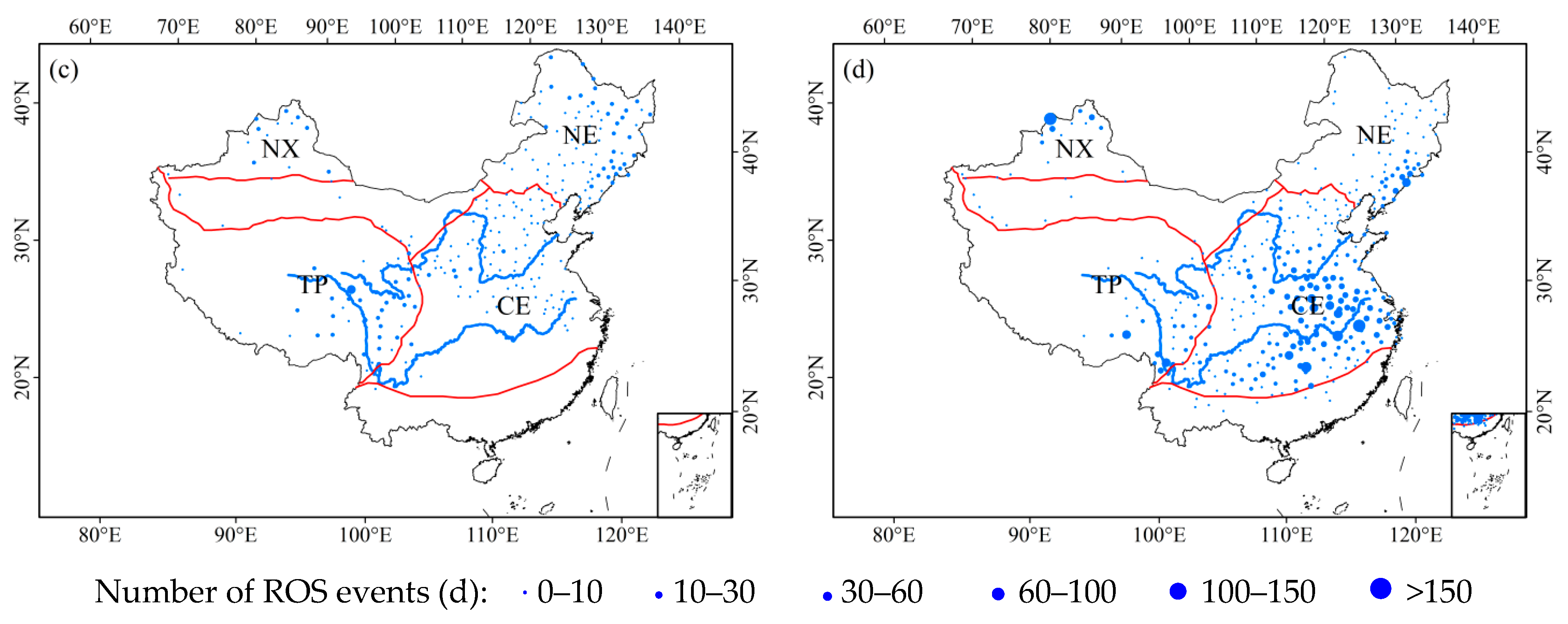
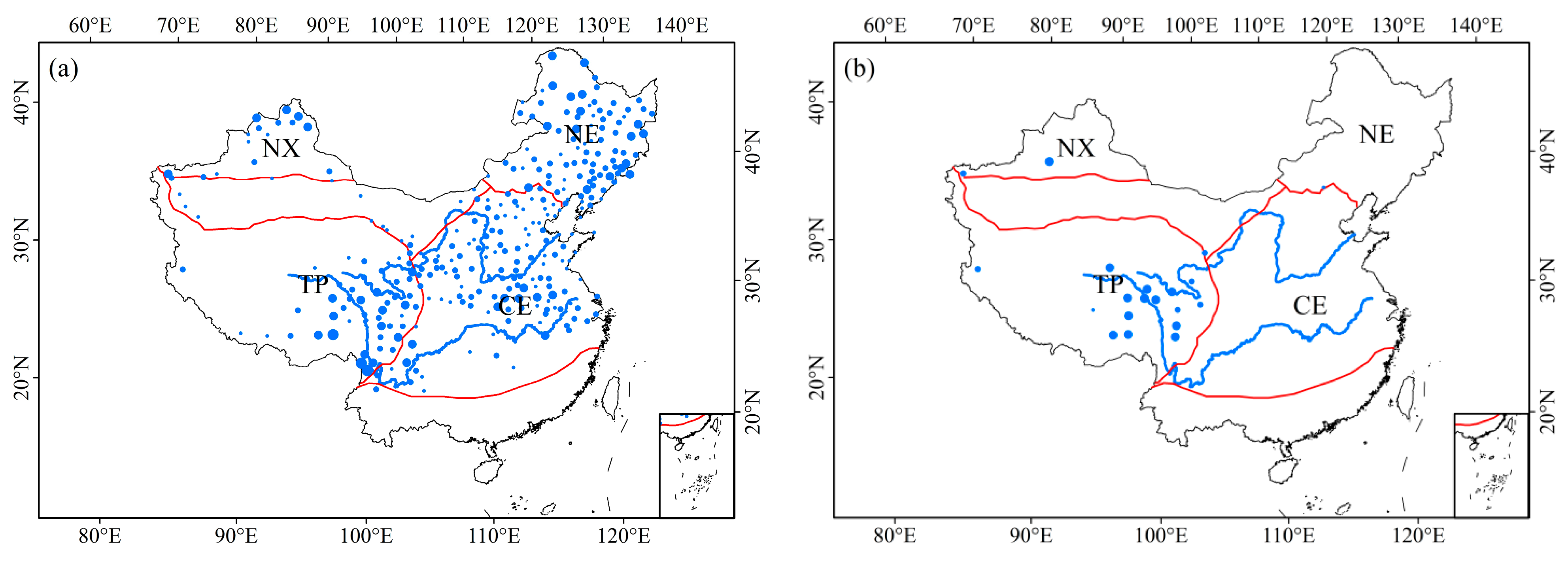
3.2.1. Inter-Annual Trends
3.2.2. Seasonality Trends
3.3. Factors Influencing Changes in ROS Events
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of ROS Events in China
4.2. Spatiotemporal Changes in ROS Events and Their Driving Factors in China
4.3. Limitations and Further Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, C.G.; Kirchner, P.B.; Kimball, J.S.; Kim, Y.; Du, J. Rain-on-snow events in Alaska, their frequency and distribution from satellite observations. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 075004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Spitzbart, G.; Hübl, H.; Weinmeister, H.W. Hydrological response of snowpack under rain-on-snow events: A field study. J. Hydrol. 1997, 202, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, H.; Raymond, C.F. Snow stability during rain. J. Glaciol. 1993, 39, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huntington, T.G.; Hodgkins, G.A.; Keim, B.D.; Dudley, R.W. Changes in the proportion of precipitation occurring as snow in New England (1949–2000). J. Clim. 2004, 17, 2626–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, D.; Link, T.; Winstral, A.; Garen, D. Simulating snowmelt processes during rain-on-snow over a semi-arid mountain basin. Ann. Glaciol. 2001, 32, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.W.; Chen, R.S.; Liu, Y.W.; Zhao, Y.N.; Liu, Z.W.; Liu, J.F. The impact of rain-on-snow events on the snowmelt process: A field study. Hydrol. Process. 2023, 37, e15019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennert, K.J.; Roe, G.; Putkonen, J.; Bitz, C.M. Soil thermal and ecological impacts of rain on snow events in the circumpolar Arctic. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 2302–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.A. Development and testing of snow pack energy balance equations. Water Resour. Res. 1968, 4, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, D.T.; Ficklin, D.L.; Robeson, S.M. Incorporating rain-on-snow into the SWAT model results in more accurate simulations of hydrologic extremes. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putkonen, J.; Roe, G.J. Rain-on-snow events impact soil temperatures and affect ungulate survival. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Ye, H.; Jones, J. Trends and variability in rain-on-snow events. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 7115–7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeroy, J.W.; Fang, X.; Marks, D.G. The cold rain-on-snow event of June 2013 in the Canadian Rockies-characteristics and diagnosis. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 2899–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahedifard, F.; AghaKouchak, A.; Ragno, E.; Shahrokhabadi, S.; Mallakpour, I. Lessons from the Oroville dam. Science 2017, 355, 1139–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezen, C.; Šraj, M.; Medved, A.; Bezak, N. Investigation of rain-on-snow floods under climate change. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stimberis, J.; Rubin, C.M. Glide avalanche response to an extreme rain-on-snow event, Snoqualmie Pass, Washington, USA. J. Glaciol. 2011, 57, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, G.J.; Clark, M.P.; Hay, L.E. Rain-on-snow events in the western United States. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musselman, K.N.; Lehner, F.; Ikeda, K.; Clark, M.P.; Prein, A.F.; Liu, C.; Barlage, M.; Rasmussen, R. Projected increases and shifts in rain-on-snow flood risk over western North America. Nat. Clim. Change 2018, 8, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudiger, D.; Kohn, I.; Stahl, K.; Weiler, M. Large-scale analysis of changing frequencies of rain-on-snow events with flood-generation potential. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 2695–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, T.P.; Adam, J.C.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Potential impacts of a warming climate on water availability in snow-dominated regions. Nature 2005, 438, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.J.; Mi, D.S. Distribution of snow cover in China. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 1983, 5, 9–18. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.X.; Li, D.L. Spatial-temporal variations of snow cover days and the maximum depth of snow cover in China during recent 50 years. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2012, 34, 247–256. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ke, C.Q.; Li, X.C.; Xie, H.; Ma, D.H.; Liu, X.; Kou, C. Variability in snow cover phenology in China from 1952 to 2010. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 755–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.J.; Wu, Z.N.; Mu, X.M.; Gao, P.; Zhao, G.J.; Sun, W.Y.; Gu, C.J. Spatiotemporal changes in snow cover over China during 1960–2013. Atmos. Res. 2019, 218, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhang, D.H.; Wan, J.H.; Cui, M.Y.; Zhang, S.Q. Mapping reveals contrasting change patterns of rain-on-snow events in China during 2001 to 2018. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 129089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.W.; Chen, R.S.; Liu, Z.W.; Zhao, Y.N.; Liu, Y.W.; Wu, W.T. Spatiotemporal variability of rain-on-snow events in the arid region of Northwest China. J. Arid Land 2024, 16, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Luo, C.J.; Lu, H. The spatial and temporal distribution of rain-on-snow events and their driving factors in China. Hydrol. Process. 2025, 39, e70098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groisman, P.Y.; Sun, B.; Vose, R.S.; Lawrimore, J.H.; Whitfield, P.H.; Førland, E.; Hanssen-Bauer, I.; Serreze, M.C.; Razuvaev, V.N.; Alekseev, G.V. Contemporary climate changes in high latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere: Daily time resolution. In Proceedings of the 14th Symposium on Global Change and Climate Variations, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–13 February 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Morán-Tejeda, E.; López-Moreno, J.I.; Stoffel, M.; Beniston, M. Rain-on-snow events in Switzerland: Recent observations and projections for the 21st century. Clim. Res. 2016, 71, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Würzer, S.; Jonas, T.; Wever, N.; Lehning, M. Influence of initial snowpack properties on runoff formation during rain-on-snow events. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 1801–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.H.; Yang, K.; Qin, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.Y.; He, X.B. The dependence of precipitation types on surface elevation and meteorological conditions and its parameterization. J. Hydrol. 2014, 513, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, K.S.; Winchell, T.S.; Livneh, B.; Molotch, N.P. Spatial variation of the rain–snow temperature threshold across the Northern Hemisphere. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Duan, W.; Zhang, Q.; Chuan, W. Incorporating relative humidity improves the accuracy of precipitation phase discrimination in High Mountain Asia. Atmos. Res. 2022, 271, 106094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.C.; Cohen, J.; Rawlins, M. Discrimination of solid from liquid precipitation over northern Eurasia using surface atmospheric conditions. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, F.W. On the computation of saturation vapor pressure. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1967, 6, 203–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Pilon, P.; Cavadias, G. Power of the Mann–Kendall and Spearman’s rho tests for detecting monotonic trends in hydrological series. J. Hydrol. 2002, 259, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhanang, S.M.; Frei, A.; Zion, M.; Schneiderman, E.M.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Pierson, D. Rain-on-snow runoff events in New York. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 3035–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.H.; Liu, Y.B.; Zhang, C.; Su, F.G.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y.H.; Li, W.H.; Chen, D.L. Research progress on moisture source change of prscipitation over the Tibetan Plateau and its surrounding areas. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 43, 1002–1009. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Su, F.G.; Tang, Q.H.; Gao, H.K.; Yan, H.D.; Peng, H.; Xiao, S.B. Contributions of moisture sources to precipitation in the major drainage basins in the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2022, 65, 1088–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
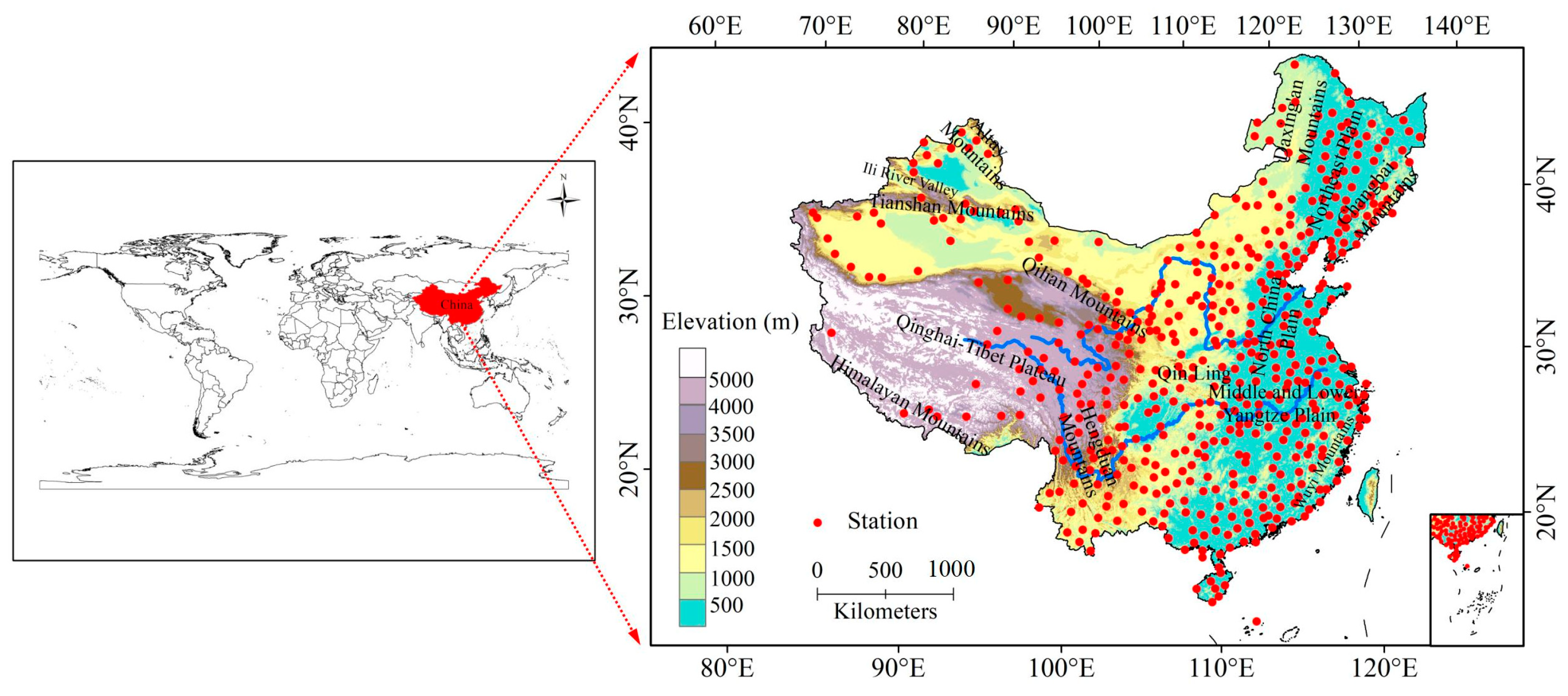



| Region | Elevation (m) | Number of Stations |
|---|---|---|
| China | 0–500 | 284 |
| 500–1000 | 61 | |
| 1000–1500 | 75 | |
| 1500–2000 | 28 | |
| 2000–2500 | 14 | |
| 2500–3000 | 16 | |
| >3000 | 35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.; Chen, R.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, G. Spatiotemporal Variations in Observed Rain-on-Snow Events and Their Intensities in China from 1978 to 2020. Water 2025, 17, 2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142114
Yang Z, Chen R, Wang X, Liu Z, Li X, Liu G. Spatiotemporal Variations in Observed Rain-on-Snow Events and Their Intensities in China from 1978 to 2020. Water. 2025; 17(14):2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142114
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zhiwei, Rensheng Chen, Xiongshi Wang, Zhangwen Liu, Xiangqian Li, and Guohua Liu. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Variations in Observed Rain-on-Snow Events and Their Intensities in China from 1978 to 2020" Water 17, no. 14: 2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142114
APA StyleYang, Z., Chen, R., Wang, X., Liu, Z., Li, X., & Liu, G. (2025). Spatiotemporal Variations in Observed Rain-on-Snow Events and Their Intensities in China from 1978 to 2020. Water, 17(14), 2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142114







