Tracing Sulfate Sources of Surface Water and Groundwater in Liuyang River Basin Based on Hydrochemistry and Environmental Isotopes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
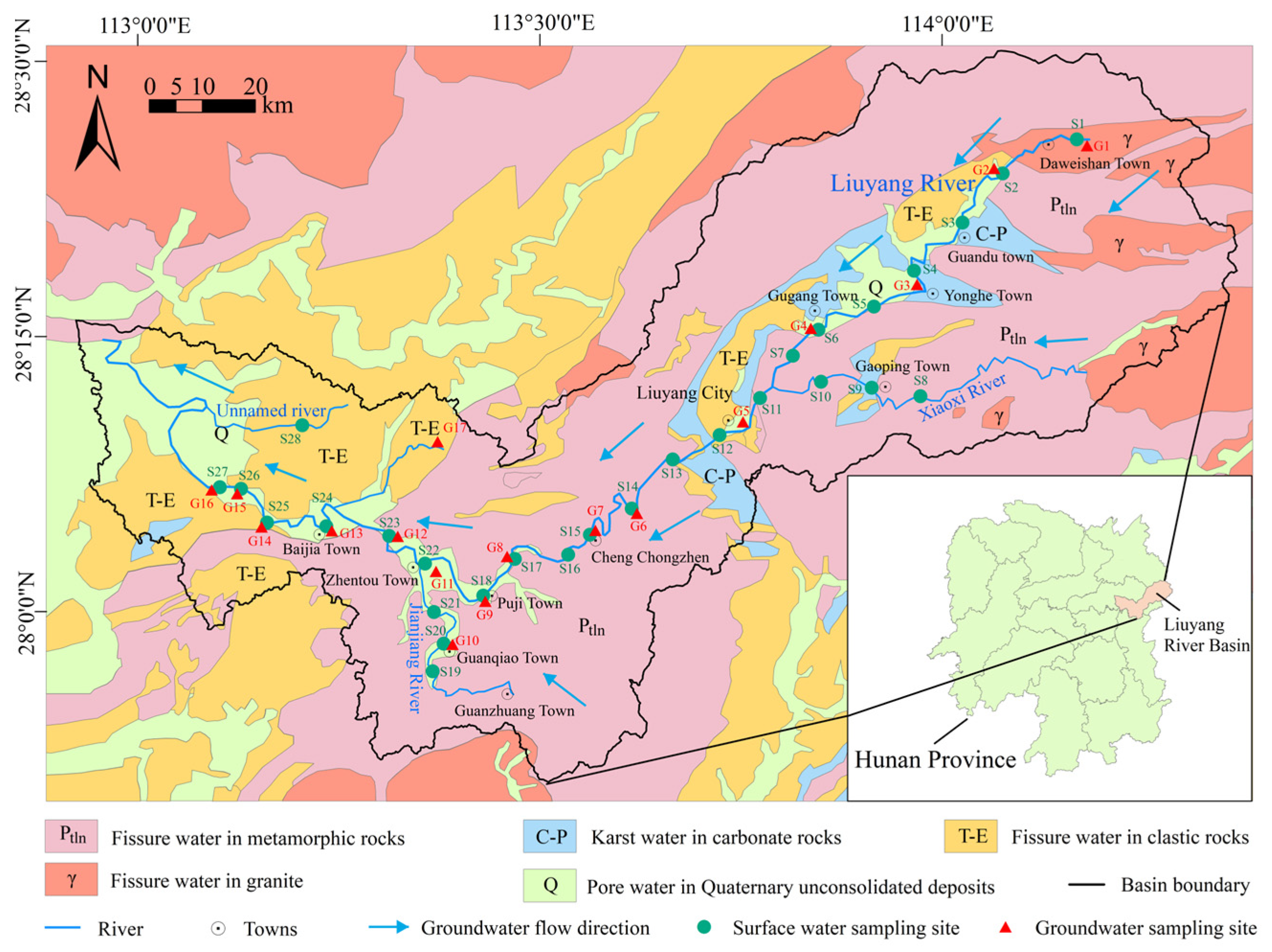
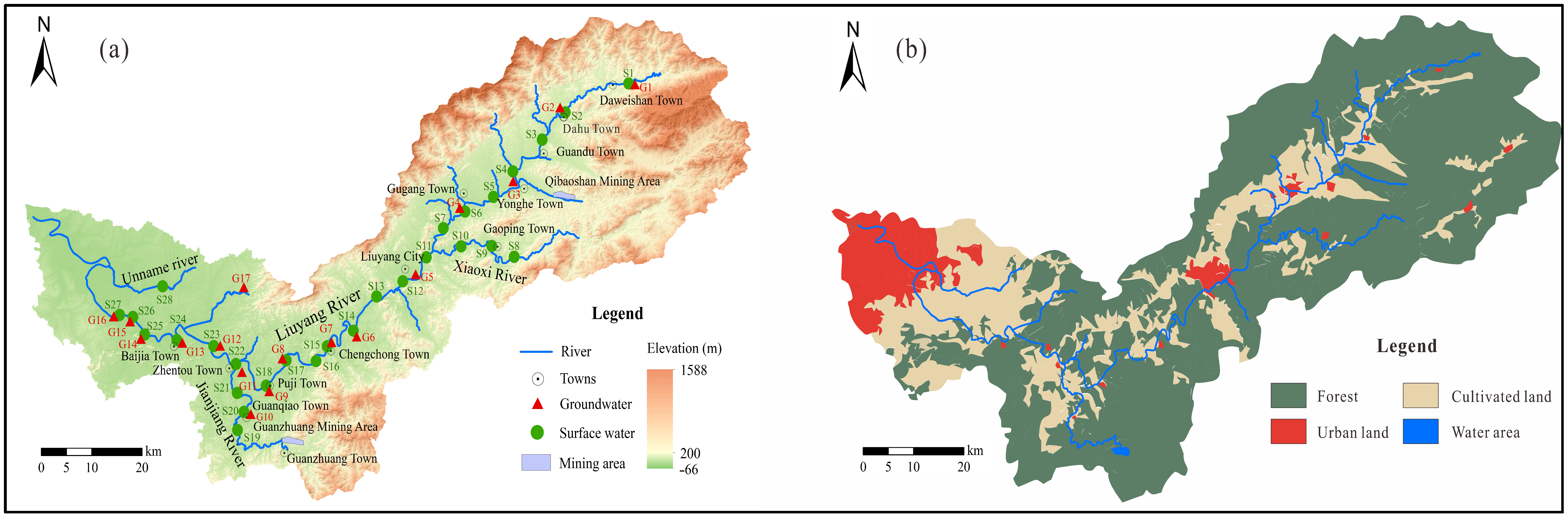
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. The Stable Isotope Mixing Models in R (Simmr)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydrochemical Characteristics
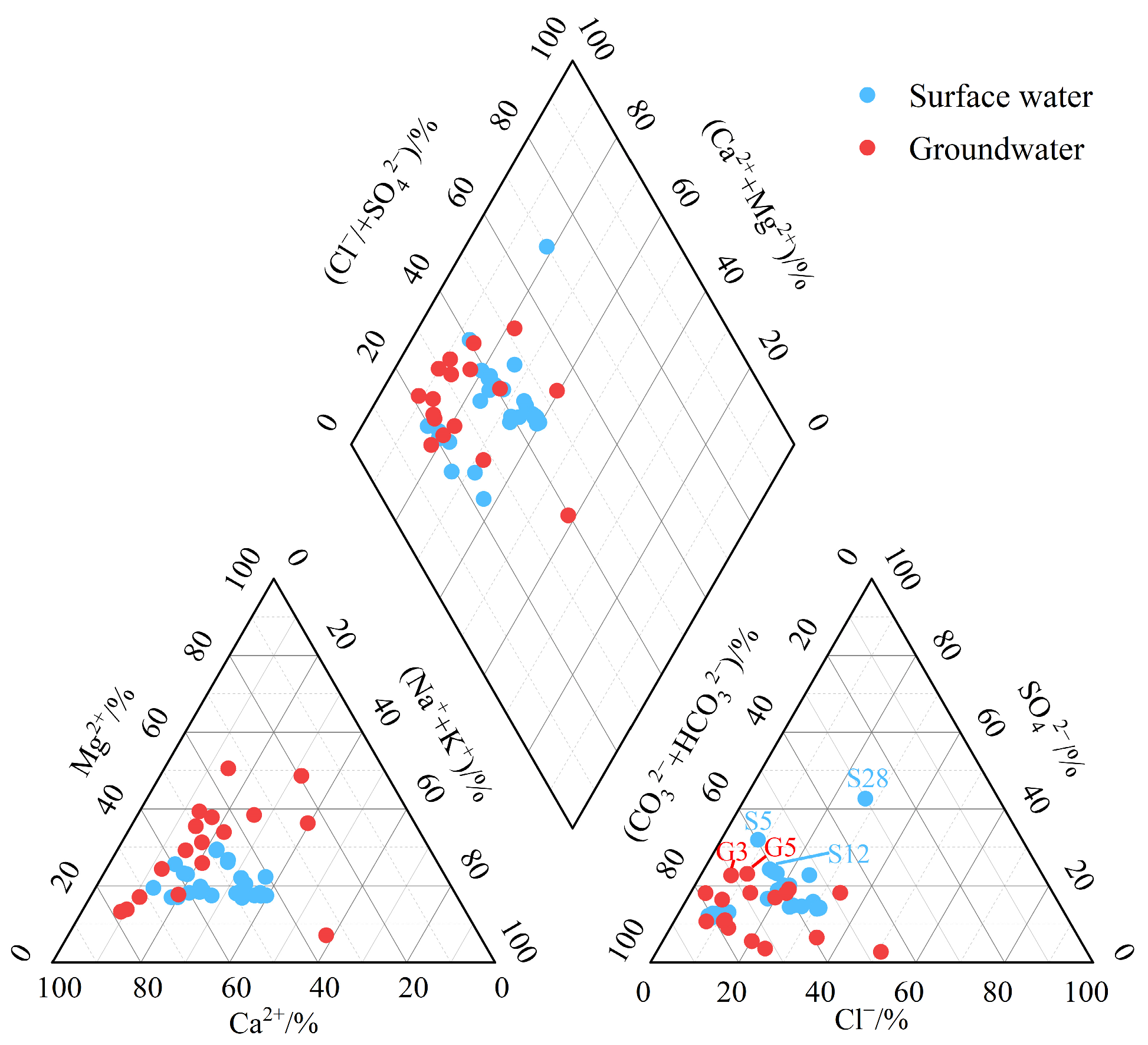
3.1.1. Hydrochemical Compositions and Types
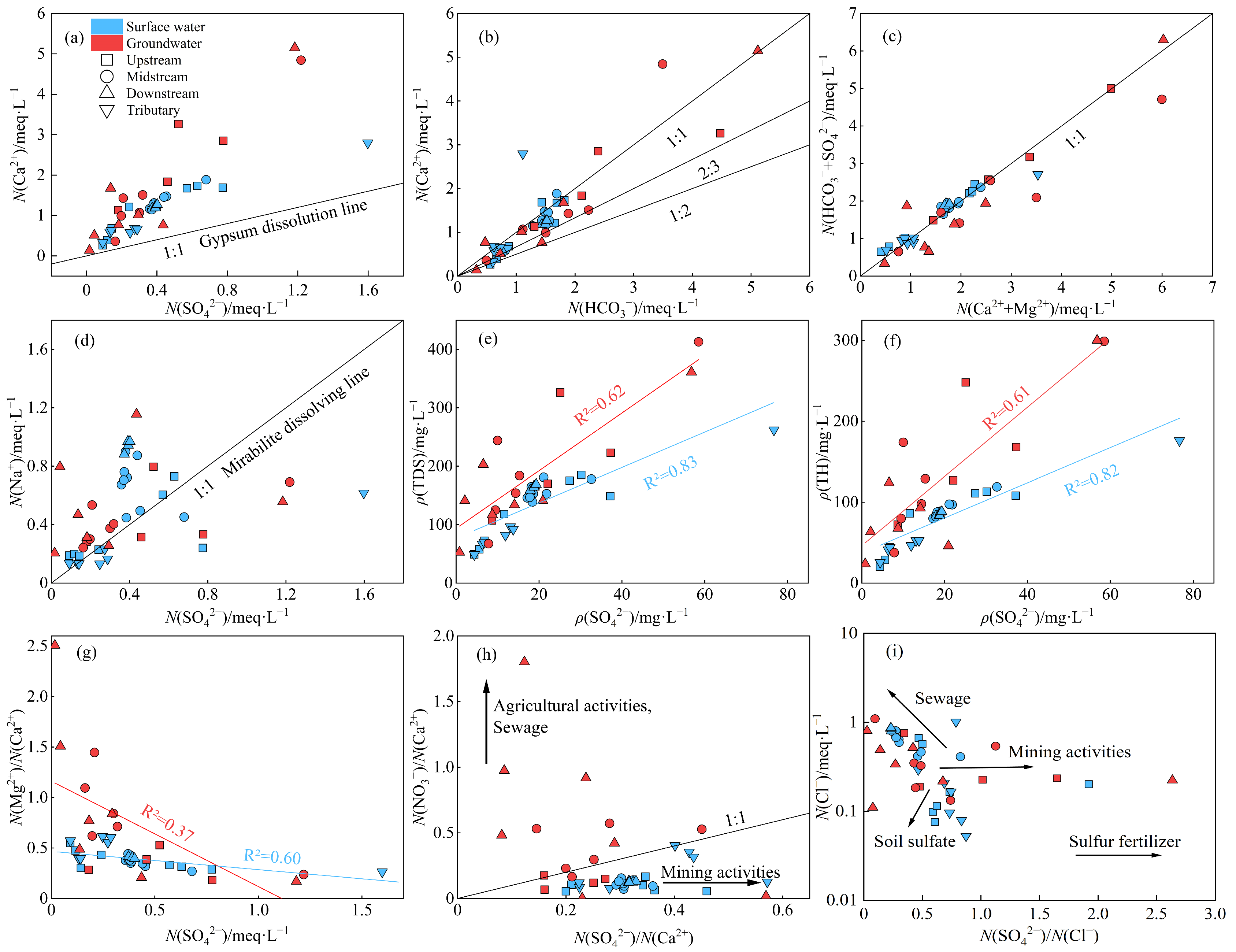
3.1.2. Sulfate Characteristics
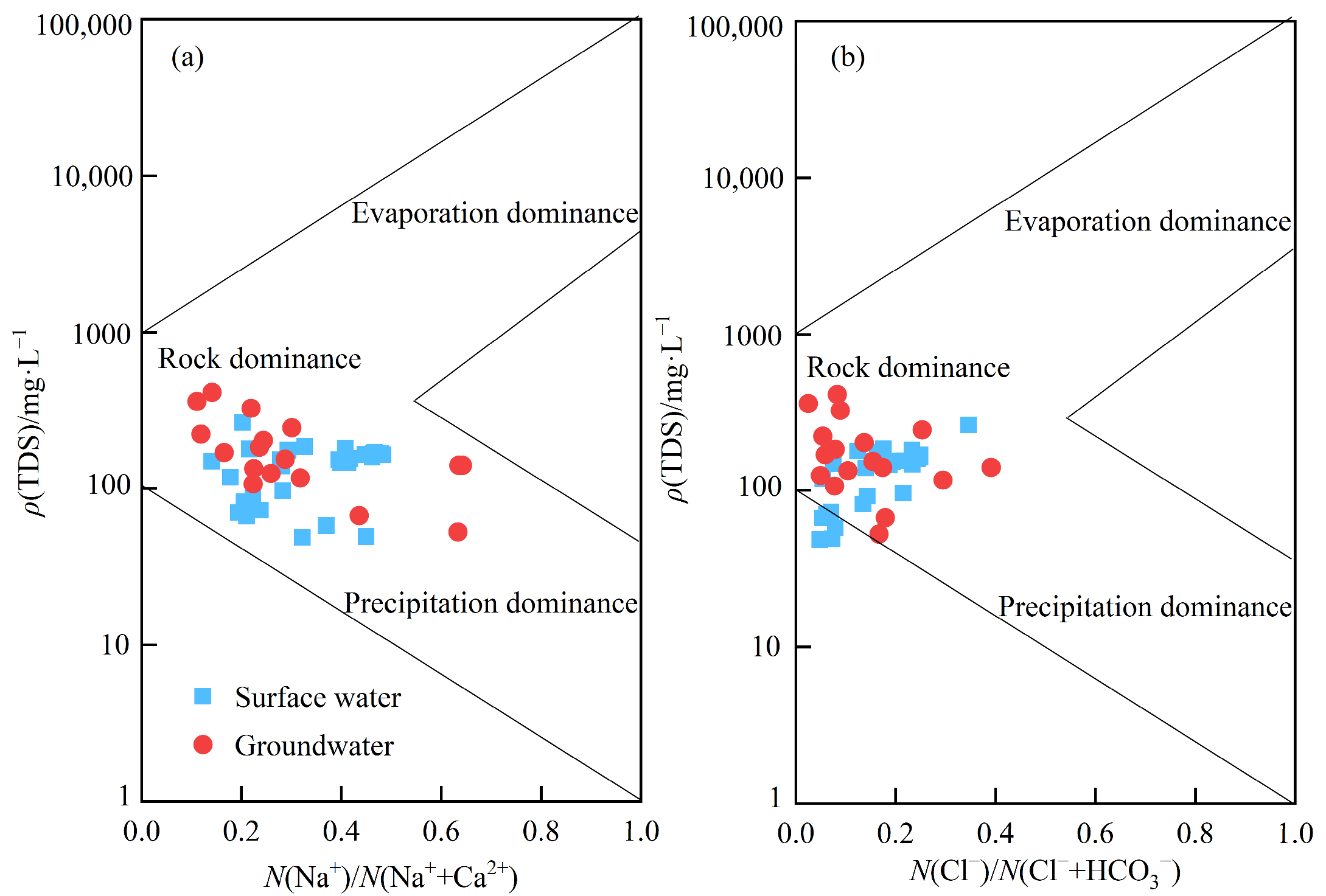
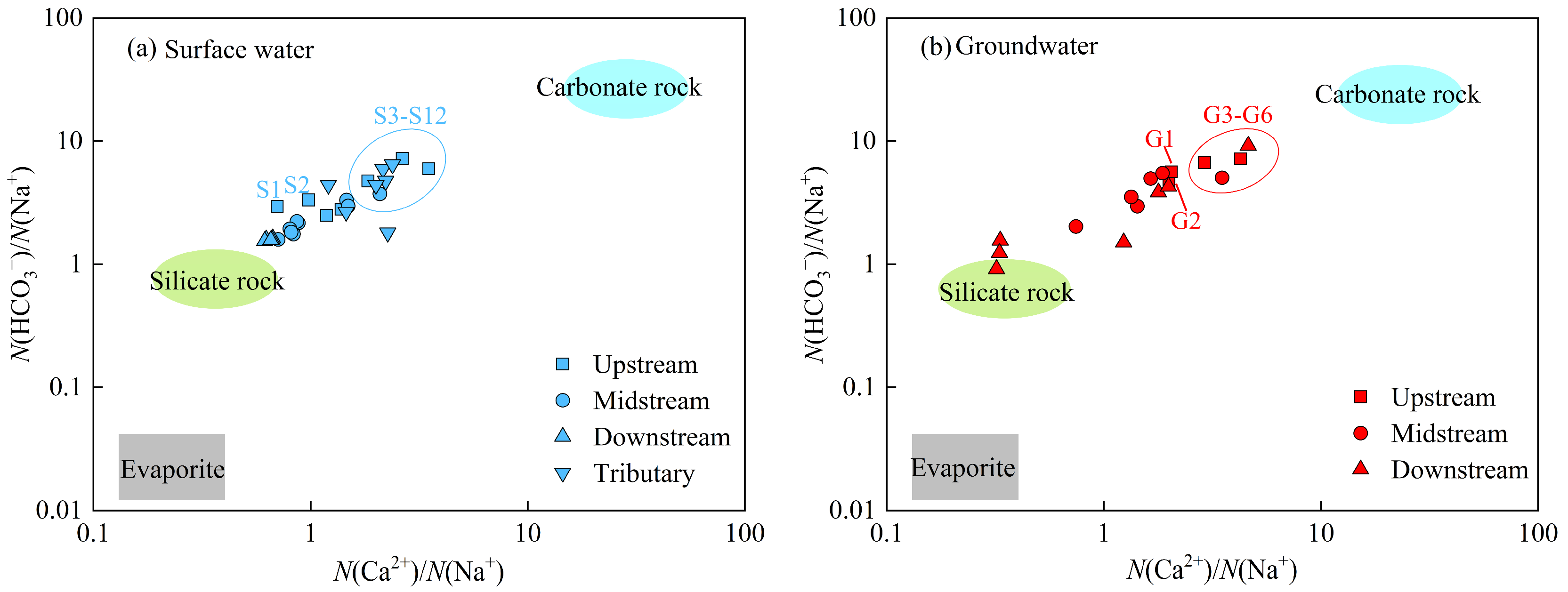
3.2. Hydrochemical Analysis of Sulfate Sources
3.3. Isotopic Analysis of Sulfate Sources
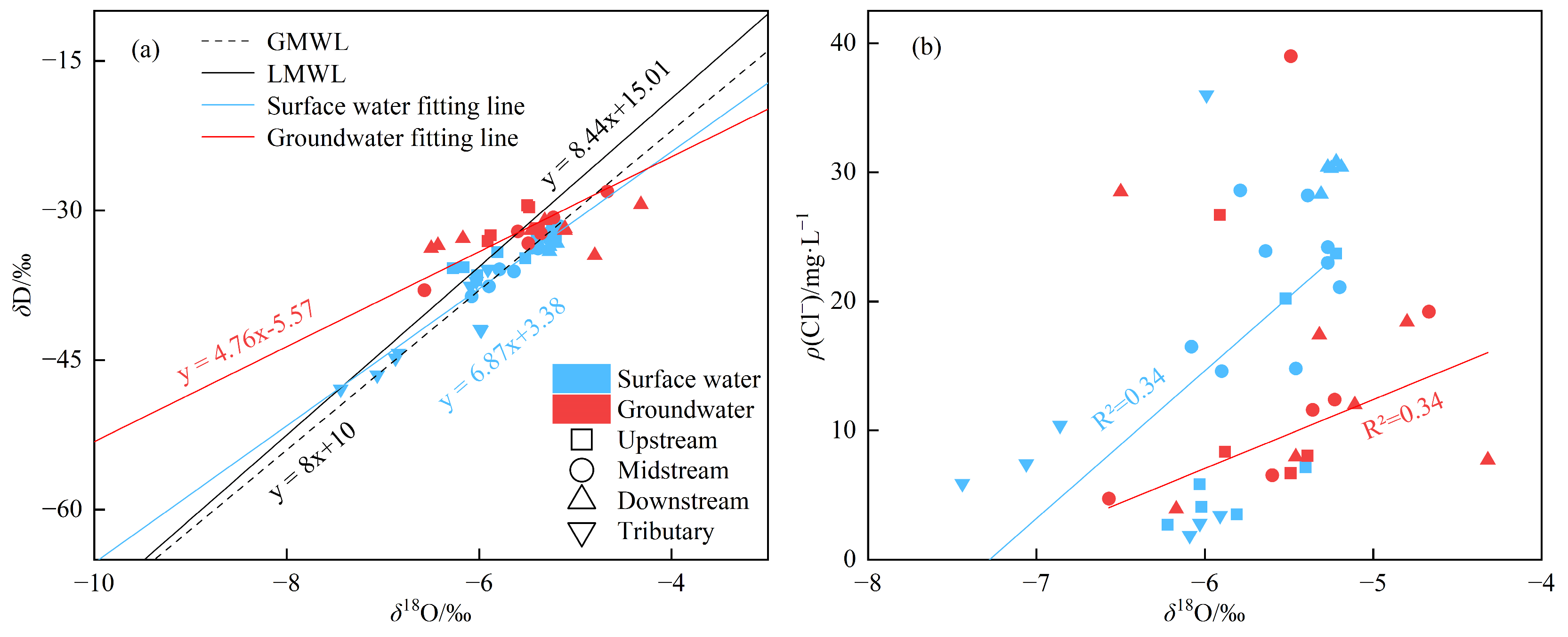
3.3.1. Analysis of Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes
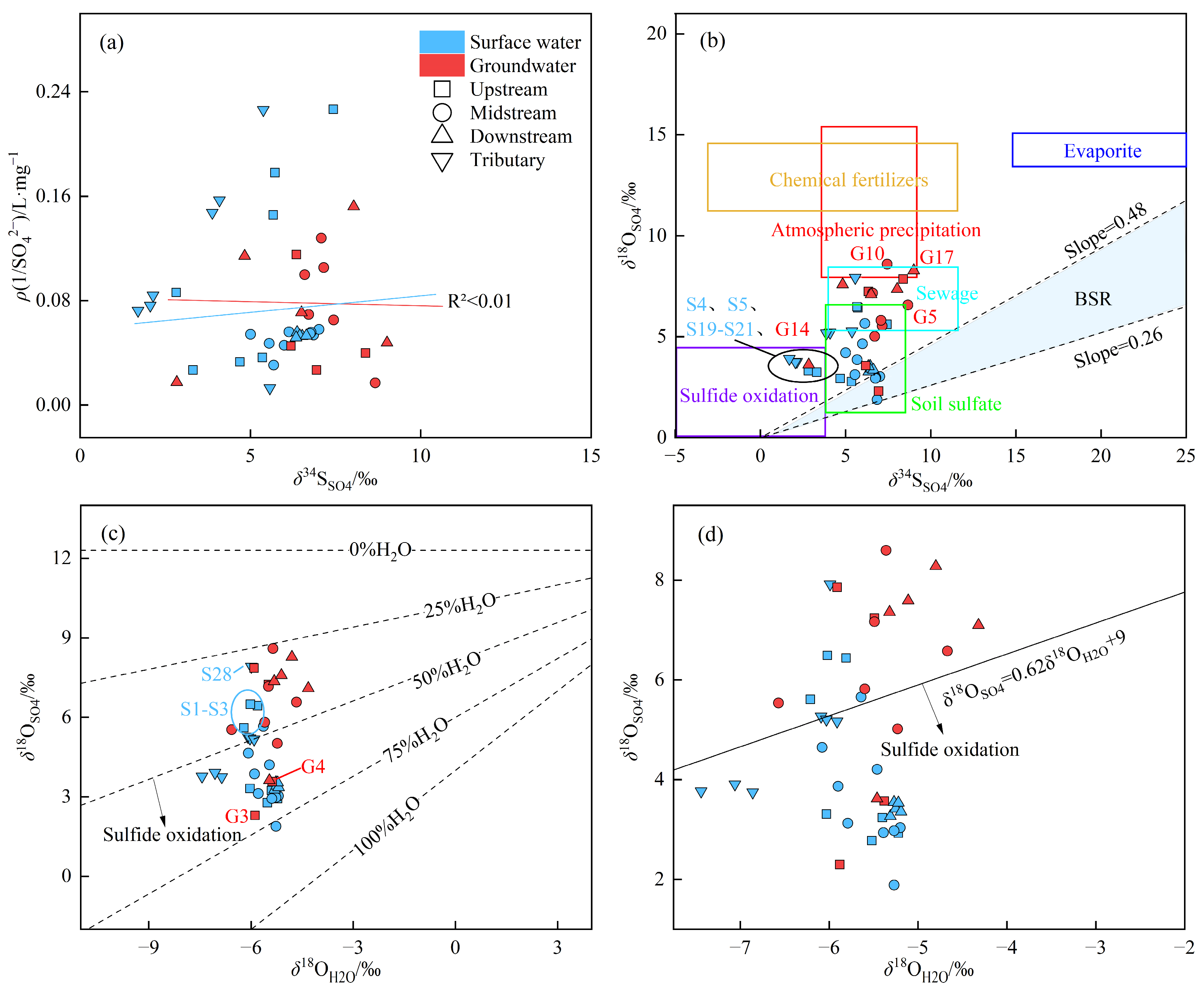
3.3.2. Sulfur and Oxygen Isotopic Composition of Sulfate
3.3.3. Analysis of Sulfur and Oxygen Isotopes
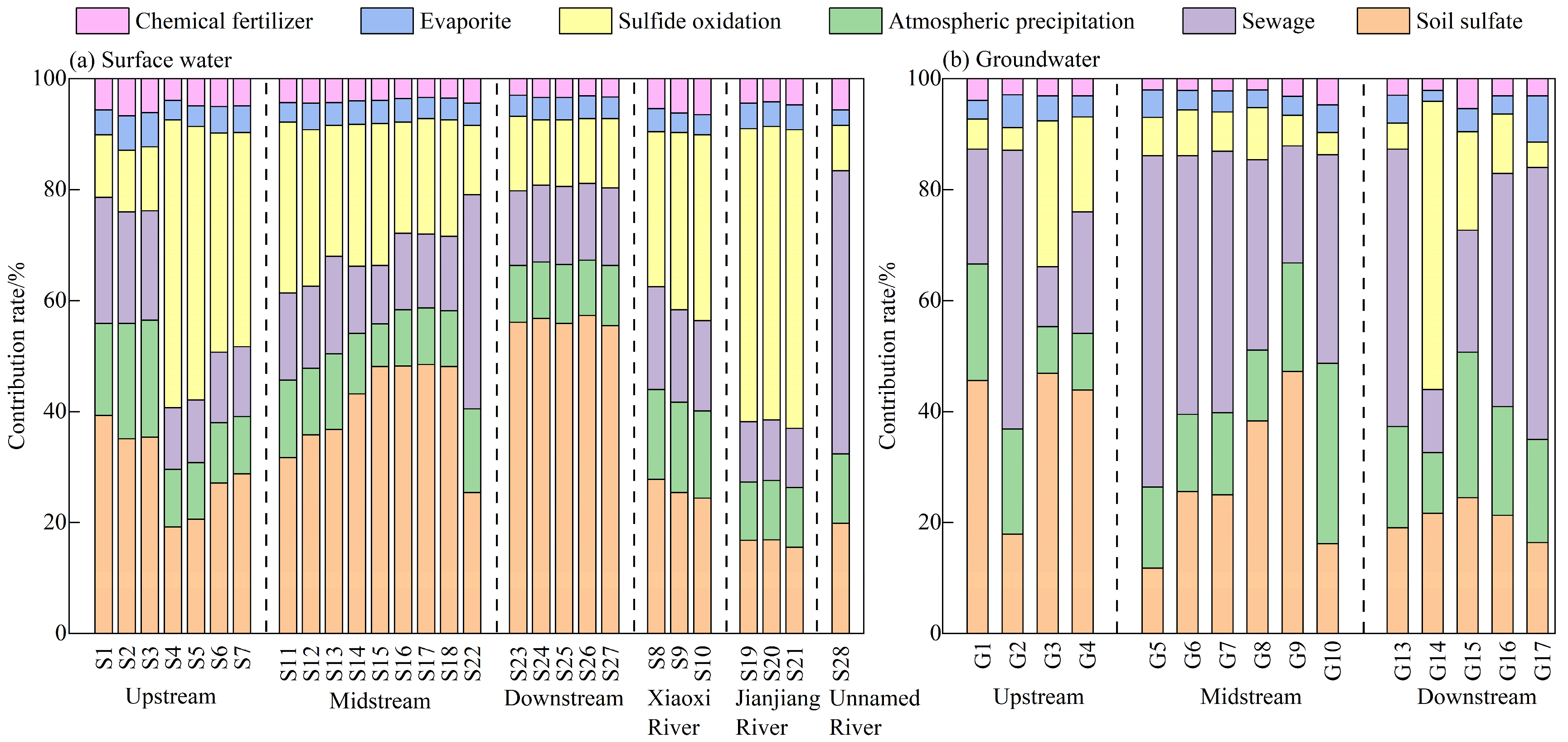
3.3.4. Sulfate Contributions from Different Sources
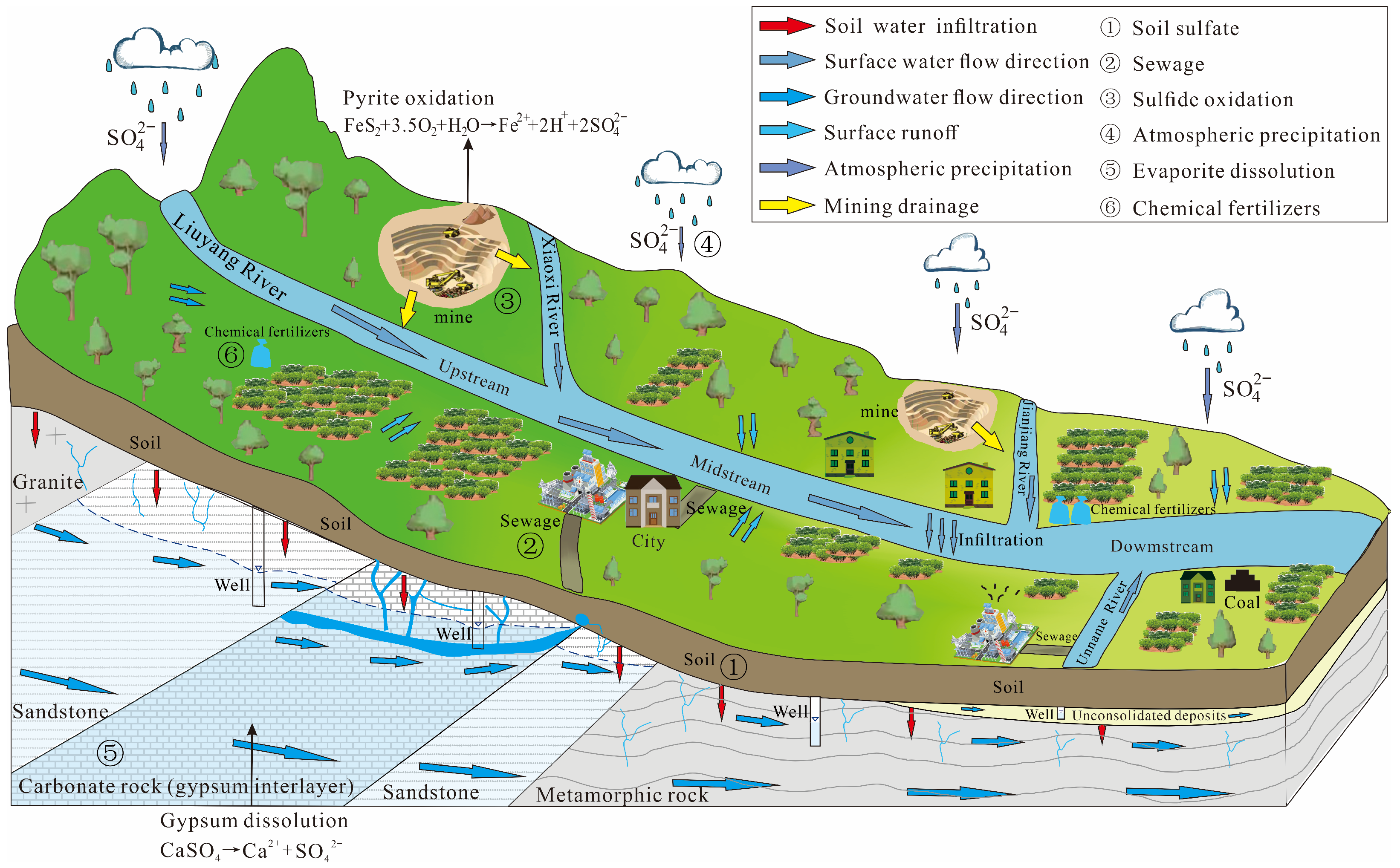
3.4. Sulfate Migration and Transformation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldscheider, N.; Chen, Z.; Auler, A.S.; Bakalowicz, M.; Broda, S.; Drew, D.; Hartmann, J.; Jiang, J.; Moosdorf, N.; Stevanovic, Z.; et al. Global distribution of carbonate rocks and karst water resources. Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 28, 1661–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pu, X.; Wang, W.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Meng, M. Surface water environmental carrying capacity and surface water quality based on economy-society-environment nexus-Evidence from China. Water-Energy Nexus 2023, 6, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, S.; Ma, S.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Gao, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y. Quantile regression illuminates the heterogeneous effect of water quality on phytoplankton in Lake Taihu, China. Water 2024, 16, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, K.; Ma, M.; Xu, J. Research on the mechanism of sulfate pollution of groundwater in Jiaozuo area. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 3517, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gani, A.; Hussain, A.; Pathak, S.; Ahmed, S.; Omar, P.J. Impact of pollutants on groundwater quality and health risk assessment of Quaternary aquifers in Northern India. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2025, 29, 4024039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipović, M.; Terzić, J.; Reberski, J.L.; Vlahović, I. Utilizing a multi-tracer method to investigate sulphate contamination: Novel insights on hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater in intricate karst systems. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 27, 101350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zheng, L.; Dong, X.; Jiang, C.; Wei, X. Sources and mixing of sulfate contamination in the water environment of a typical coal mining city, China: Evidence from stable isotope characteristics. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 2865–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnunen, P.; Kyllönen, H.; Kaartinen, T.; Mäkinen, J.; Heikkinen, J.; Miettinen, V. Sulphate removal from mine water with chemical, biological and membrane technologies. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 2017, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Wang, C.; Qu, S.; Liao, F.; Wang, G.; Shi, Z. Source and evolution of sulfate in the multi-layer groundwater system in an abandoned mine—Insight from stable isotopes and Bayesian isotope mixing model. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klipsch, S.; Herwartz, D.; Voigt, C.; Münker, C.; Chong, G.; Böttcher, M.E.; Staubwasser, M. Sulfate sources, biologic cycling, and mobility in Atacama Desert soils revealed by isotope signatures. Glob. Planet. Change 2023, 230, 104290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Xiao, H.; Xiao, H.; Xu, Y. The oxygen and sulfur isotopic compositions of soluble sulfate in the needles of Pinus massoniana Lamb.: Source discrimination and contribution estimation. J. Geochem. Explor. 2020, 208, 106402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Lu, C. Tracing sulfate origin and transformation in an area with multiple sources of pollution in northern China by using environmental isotopes and Bayesian isotope mixing model. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tostevin, R.; Turchyn, A.V.; Farquhar, J.; Johnston, D.T.; Eldridge, D.L.; Bishop, J.K.B.; McIlvin, M. Multiple sulfur isotope constraints on the modern sulfur cycle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 396, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Pang, Z.; Gong, Q.; Li, N.; Liao, D.; Luo, Z. Oxygen and sulfur isotope systematics of dissolved sulfate in a nonvolcanic geothermal system: Sulfate source, evolution and impact on geothermometers. Water 2025, 17, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, Y.; Rafter, T.A. Isotopic behaviour of sulphate oxygen in the bacterial reduction of sulphate. Geochem. J. 1973, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Cheng, L.; Li, C.; Zheng, L. A hydrochemical and multi-isotopic study of groundwater sulfate origin and contribution in the coal mining area. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 248, 114286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Chen, X.; Dong, X.; Wei, X.; Jiang, C.; Tang, Q. Using δ34S-SO4 and δ18O-SO4 to trace the sources of sulfate in different types of surface water from the Linhuan coal-mining subsidence area of Huaibei, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 181, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L. Combining hydrochemistry and isotopes to unravel sulfate sources in karst groundwater: A case study from southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147312. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Song, X.; Currell, J.M. Identification of anthropogenic and natural inputs of sulfate into a karstic coastal groundwater system in northeast China: Evidence from major ions, δ13CDIC and δ34SSO4. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 1983–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Q. Research advances in identifying sulfate contamination sources of water environment by using stable isotopes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, J.; Huang, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z. Sources of dissolved heavy metals in river water of the Yiluo River Basin based on sulfur isotope of sulfate. China Environ. Sci. 2019, 39, 2549–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xue, T.; Xiao, J.; Chai, N.; Gong, S. Significant influence of water diversion and anthropogenic input on riverine sulfate based on sulfur and oxygen isotopes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Takahashi, Y.; Strosnider, W.H.J.; Kogure, T.; Wu, P.; Cao, X. Tracing and quantifying contributions of end members to karst water at a coalfield in southwest China. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogramaci, S.; McLean, L.; Skrzypek, G. Hydrochemical and stable isotope indicators of pyrite oxidation in carbonate-rich environment; the Hamersley Basin, Western Australia. J. Hydrol. 2017, 545, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, D.; Hupfer, M.; Cabezas, A.; Jurasinski, G.; Audet, J.; Kleeberg, A.; McInnes, R.; Kristiansen, S.M.; Petersen, R.J.; Liu, H.; et al. Sulphate in freshwater ecosystems: A review of sources, biogeochemical cycles, ecotoxicological effects and bioremediation. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 212, 103446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Jiang, C.; Li, C.; Zheng, L. Tracing sulfate source and transformation in the groundwater of the linhuan coal mining area, huaibei coalfield, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Pang, Z.; Huang, T.; Li, Y.; Tian, J.; Luo, J.; Qian, T. Chemical and isotopic evidences on evaporite dissolution as the origin of high sulfate water in a karst geothermal reservoir. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 145, 105419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, N.; Canals, À.; Soler, A. Using dual-isotope data to trace the origin and processes of dissolved sulphate: A case study in Calders stream (Llobregat basin, Spain). Aquat. Geochem. 2007, 13, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, A.C.; Inger, R.; Bearhop, S.; Jackson, A.L. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: Coping with too much variation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Zou, L.; Tang, Y.; Chen, H.; Tang, Y.; Yu, L.; Li, H.; Liu, F. Assessment and temporospatial characteristics of water quality in Liuyang River based on homogeneity. Hunan Agric. Sci. 2021, 10, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, B. Analyzing the source of sulfate in karst groundwater based on a Bayesian stable isotope mixing model: A case study of Xujiagou Spring Area, Northern China. Water 2025, 17, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, D.; Wu, C.; Zhang, K.; Liu, J.; Liu, A.; Liu, C. Age and sources of the ore-forming material for the Qibaoshan Cu-polymetallic deposit in Hu’nan Province: Evidence from quartz vein Rb-Sr isotopic dating and S-Pb isotopes. Geol. Bull. China 2017, 36, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, C. A preliminary study on sulfate reduction bacteria behaviors in groundwater by sulfur and carbon isotopes: A case study in Jiaozuo City, China. Ecotoxicology 2014, 23, 2014–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillardet, J.; Dupre, B.; Louvat, P.; Allègre, C.J. Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers. Chem. Geol. 1999, 159, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olea-Olea, S.; Silva-Aguilera, R.A.; Alcocer, J.; Escolero, O.; Morales-Casique, E.; Florez-Peñaloza, J.R.; Almora-Fonseca, K.A.; Oseguera, L.A. Water–rock interaction processes in groundwater and flows in a maar lake in Central Mexico. Water 2024, 16, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Meng, Z.; Jiao, W. Hydrological and pollution processes in mining area of Fenhe river basin in China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, J.; Telmer, K. The role of sulfur in chemical weathering and atmospheric CO2 fluxes: Evidence from major ions, δ13C-DIC, and δ34S-SO4 in rivers of the Canadian Cordillera. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 5441–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Zeng, J.; Liang, J.; Yuan, D.; Jiao, Y.; Peng, C.; Pan, X. Impacts of acid mine drainage on karst aquifers: Evidence from hydrogeochemistry, stable sulfur and oxygen isotopes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, W.; Wang, J.; Kang, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, W.; Li, X. Hydrochemical analysis and groundwater suitability for drinking and irrigation in an arid agricultural area of the northwest China. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2023, 259, 104256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Li, R.; Ferrer, A.S.N.; Xiong, S.; Zou, P.; Peng, H. Hydrochemical characteristics and quality assessment of shallow groundwater in Yangtze River Delta of eastern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 57215–57231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lang, Y.; Satake, H.; Wu, J.; Li, S. Identification of anthropogenic and natural inputs of sulfate and chloride into the karstic groundwater of Guiyang, SW China: Combined δ37Cl and δ34S approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5421–5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Xu, L.; Qu, Z. Interaction between groundwater and surface water in the Qujiang River Basin in China: Evidence from chemical isotope measurements. Water 2023, 15, 3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Hou, X.; Ma, J.; Gao, M.; Bai, Z.; Fu, C.; Gui, C.; Zuo, X. Combining stable isotope (2H, 18O, and 87Sr/86Sr) and hydrochemistry to understand hydrogeochemical processes in karst groundwater system, Xin’an, northern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yao, T.; Huang, H. Monitoring and analysis of stable isotopes of the near surface water vapor in Changsha. Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.K.; Kumar, P.; Prajapati, P.; Bhanot, K.; Wadhwa, U.; Tomar, G.; Goyal, R.; Prasad, B.; Sharma, B. Study of hydrochemical and geochemical characteristics and solute fluxes in Upper Ganga Basin, India. J. Asian Earth Sci. X 2022, 8, 100108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Martínez, J.A.; Mora, A.; Mahlknecht, J.; Kaown, D.; Barceló, D. Determining nitrate and sulfate pollution sources and transformations in a coastal aquifer impacted by seawater intrusion—A multi-isotopic approach combined with self-organizing maps and a Bayesian mixing model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, C. Using dual isotopic data to track the sources and behaviors of dissolved sulfate in the western North China plain. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 52, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, A.; Gan, Y.; Yu, T.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y. Controls on the δ34S and δ18O of dissolved sulfate in the Quaternary aquifers of the North China Plain. J. Hydrol. 2011, 400, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosono, T.; Tokunaga, T.; Tsushima, A.; Shimada, J. Combined use of δ13C, δ15N, and δ34S tracers to study anaerobic bacterial processes in groundwater flow systems. Water Res. 2014, 54, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, D.; Antwi, E.O.; Skrzypek, G.; Adu-Gyamfi, J.; Heng, L.; Attiogbe, F. Tracing sulfate sources in a tropical agricultural catchment with a stable isotope Bayesian mixing model. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Shi, Z.; Ding, X.; Ge, L.; Xiong, M.; Zhang, Q.; Lai, W.; Ge, L. Identification of anthropogenic and natural inputs of sulfate into river system of carbonate Zn-Pb mining area in southwest China: Evidence from hydrochemical composition, δ34SSO4 and δ18OSO4. Water 2024, 16, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wu, P.; Zhou, S.; Sun, J.; Han, Z. Tracing the origin and geochemical processes of dissolved sulphate in a karst-dominated wetland catchment using stable isotope indicators. J. Hydrol. 2018, 562, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balci, N.; Shanks, W.C.; Mayer, B.; Mandernack, K.W. Oxygen and sulfur isotope systematics of sulfate produced by bacterial and abiotic oxidation of pyrite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 3796–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Kobayashi, T.; Strosnider, W.H.J.; Wu, P. Stable sulfur and oxygen isotopes as geochemical tracers of sulfate in karst waters. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xie, R.; Cao, W. Tracing the source and behaviour of sulphate in karst reservoirs, using stable isotopes and Bayesian isotopic-mixing models. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 958, 177994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Identification of Nitrate and Sulfate Sources and Their Increasing Mechanism in Karst Water System of Jinan Spring Catchment Based on Hydrochemistry and Multi-Isotopes. Doctor’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Martínez, J.A.; Mora, A.; Knappett, P.S.K.; Ornelas-Soto, N.; Mahlknecht, J. Tracking nitrate and sulfate sources in groundwater of an urbanized valley using a multi-tracer approach combined with a Bayesian isotope mixing model. Water Res. 2020, 182, 115962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Present Situation of Environmental Quality and Control Measures in Liuyang River Section. Master’s Thesis, Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]



| Statistic | TDS | EC | K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | HCO3− | SO42− | Cl− | NO3− | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg·L−1 | μS·cm−1 | mg·L−1 | |||||||||
| Surface water | Max | 262 | 518.20 | 7.01 | 22.30 | 55.90 | 8.83 | 111 | 76.70 | 36 | 21.80 |
| Min | 48.70 | 75 | 1.85 | 3.01 | 5.30 | 1.75 | 34 | 4.42 | 1.87 | 1.58 | |
| Mean | 134.45 | 281.47 | 4.34 | 11.99 | 22.99 | 5.13 | 76.23 | 19.06 | 17.15 | 8.70 | |
| Groundwater | Max | 413 | 759.90 | 7.34 | 22.60 | 103 | 24.80 | 312 | 58.50 | 28.50 | 89.20 |
| Min | 52.90 | 86.80 | 0.74 | 4.73 | 2.74 | 1.90 | 19.60 | 0.81 | 3.92 | 0.66 | |
| Mean | 186.07 | 351.79 | 2.40 | 10.86 | 34.47 | 9.79 | 114.70 | 18.75 | 14.07 | 26.45 | |
| Statistic | Surface Water | Groundwater | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upstream | Midstream | Downstream | Tributaries | Upstream | Midstream | Downstream | ||
| δD (%) | Max | −32.05 | −31.60 | −33.28 | −35.85 | −29.55 | −28.09 | −29.39 |
| Min | −37.02 | −38.55 | −34.07 | −47.86 | −33.13 | −38.02 | −34.52 | |
| Mean | −34.63 | −34.88 | −33.59 | −41.99 | −31.39 | −32.41 | −32.31 | |
| δ18O (%) | Max | −5.20 | −5.16 | −5.19 | −5.91 | −5.38 | −4.67 | −4.32 |
| Min | −6.27 | −6.08 | −5.35 | −7.44 | −5.91 | −6.57 | −6.50 | |
| Mean | −5.74 | −5.51 | −5.26 | −6.47 | −5.59 | −5.49 | −5.47 | |
| Sources | δ34SSO4 (‰) | δ18OSO4 (‰) | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Standard Deviation | Average | Standard Deviation | ||
| Atmospheric precipitation | 5.90 | 1.80 | 9.40 | 1.64 | [48] |
| Soil sulfate | 5.48 | 1.99 | 3.66 | 2.78 | [48] |
| Sulfide oxidation | −0.10 | 4.90 | −0.50 | 3.03 | [32] |
| Sewage | 8.70 | 2.40 | 6.86 | 1.60 | [47] |
| Evaporite | 22.50 | 7.50 | 14.00 | 1.00 | [49] |
| Chemical fertilizers | 2.30 | 7.70 | 16.10 | 4.00 | [50] |
| Towns | Quantity | Towns | Quantity | Towns | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daweishan | 17 | Gaoping | 28 | Zhentou | 35 |
| Dahu | 23 | Gugang | 33 | Puji | 18 |
| Yonghe | 20 | Liuyang | 199 | Guanqiao | 13 |
| Guandu | 14 | Chengchong | 44 | Baijia | 7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H. Tracing Sulfate Sources of Surface Water and Groundwater in Liuyang River Basin Based on Hydrochemistry and Environmental Isotopes. Water 2025, 17, 2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142105
Wang L, Li Y, Zhang Y, Liu W, Zhang H. Tracing Sulfate Sources of Surface Water and Groundwater in Liuyang River Basin Based on Hydrochemistry and Environmental Isotopes. Water. 2025; 17(14):2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142105
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lei, Yi Li, Yanpeng Zhang, Wei Liu, and Hongxin Zhang. 2025. "Tracing Sulfate Sources of Surface Water and Groundwater in Liuyang River Basin Based on Hydrochemistry and Environmental Isotopes" Water 17, no. 14: 2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142105
APA StyleWang, L., Li, Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, W., & Zhang, H. (2025). Tracing Sulfate Sources of Surface Water and Groundwater in Liuyang River Basin Based on Hydrochemistry and Environmental Isotopes. Water, 17(14), 2105. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142105







