Ice Avalanche-Triggered Glacier Lake Outburst Flood: Hazard Assessment at Jiongpuco, Southeastern Tibet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area, Data, and Methods
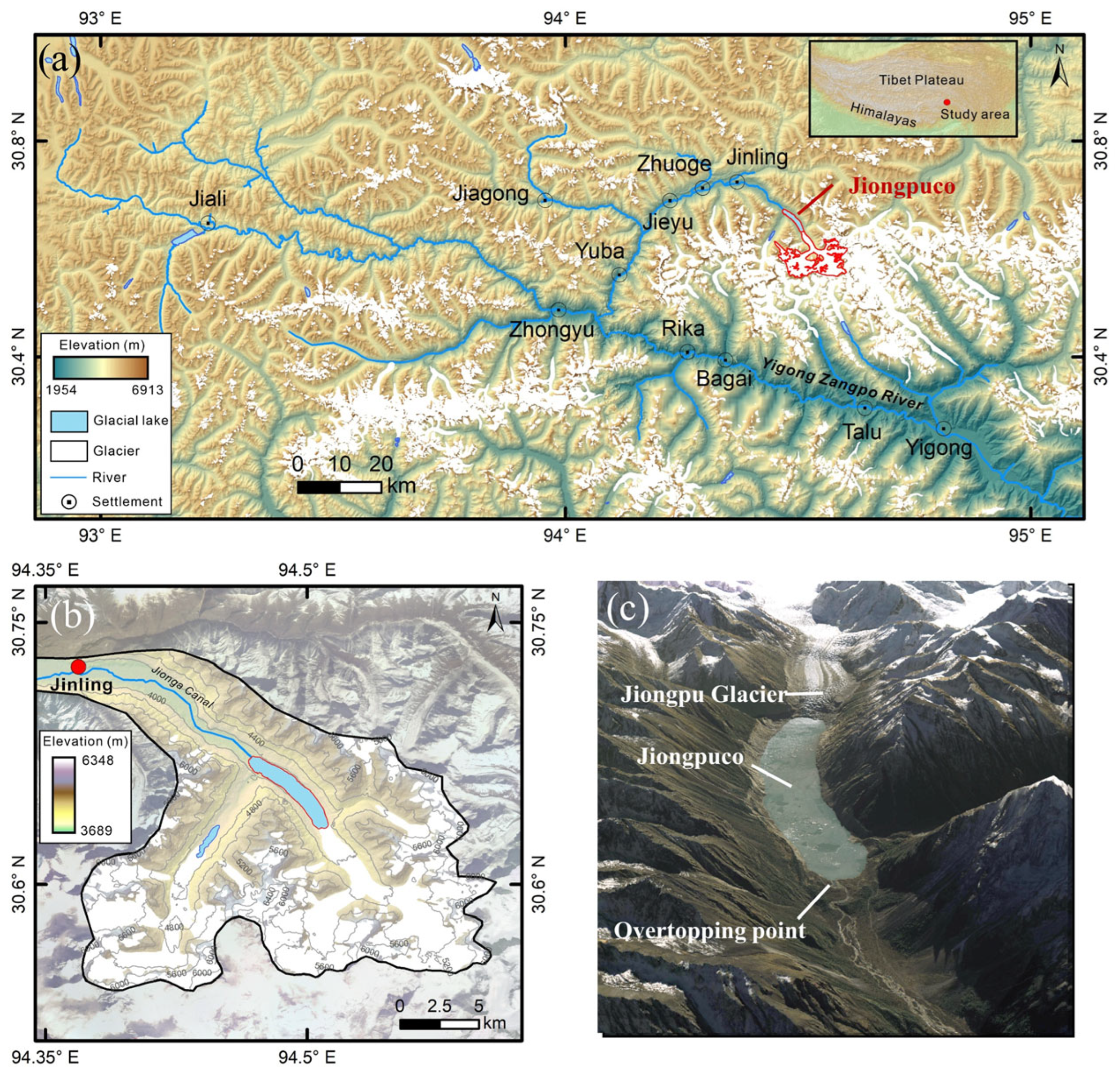
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Glacial Lake Mapping
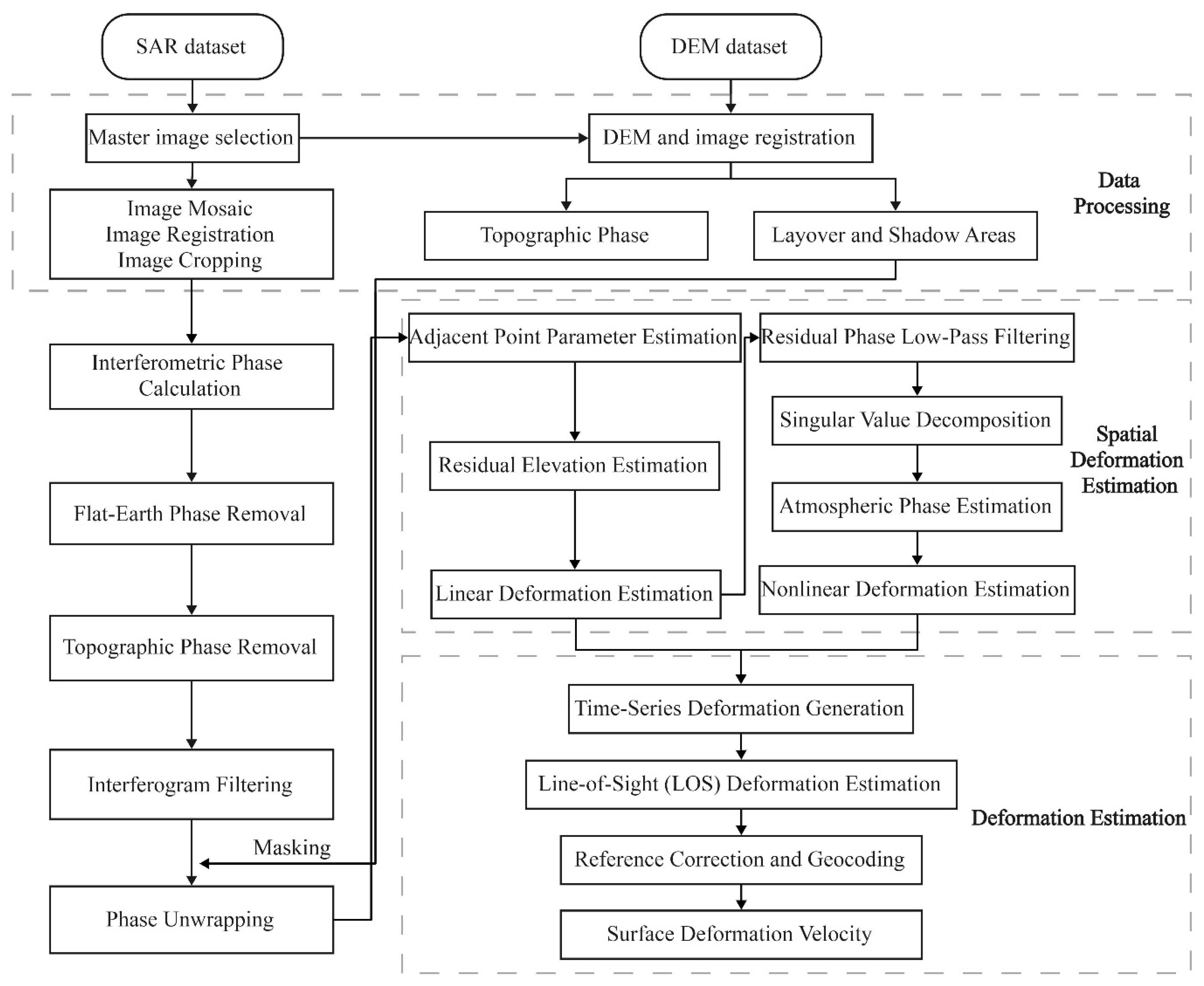
2.3. Insar Data and Methods
2.4. GLOF Simulation with R.avaflow and HEC-RAS
3. Results
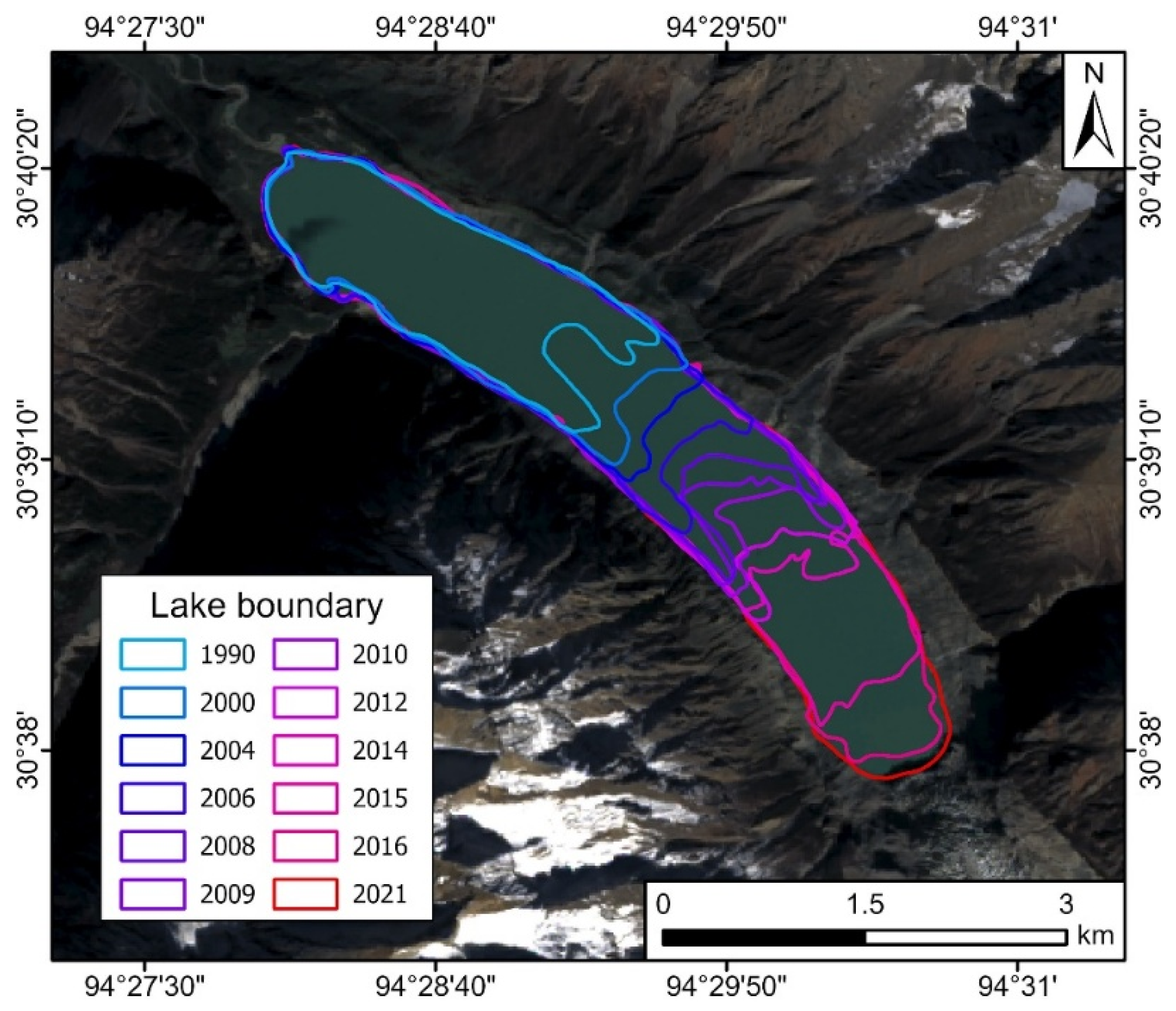
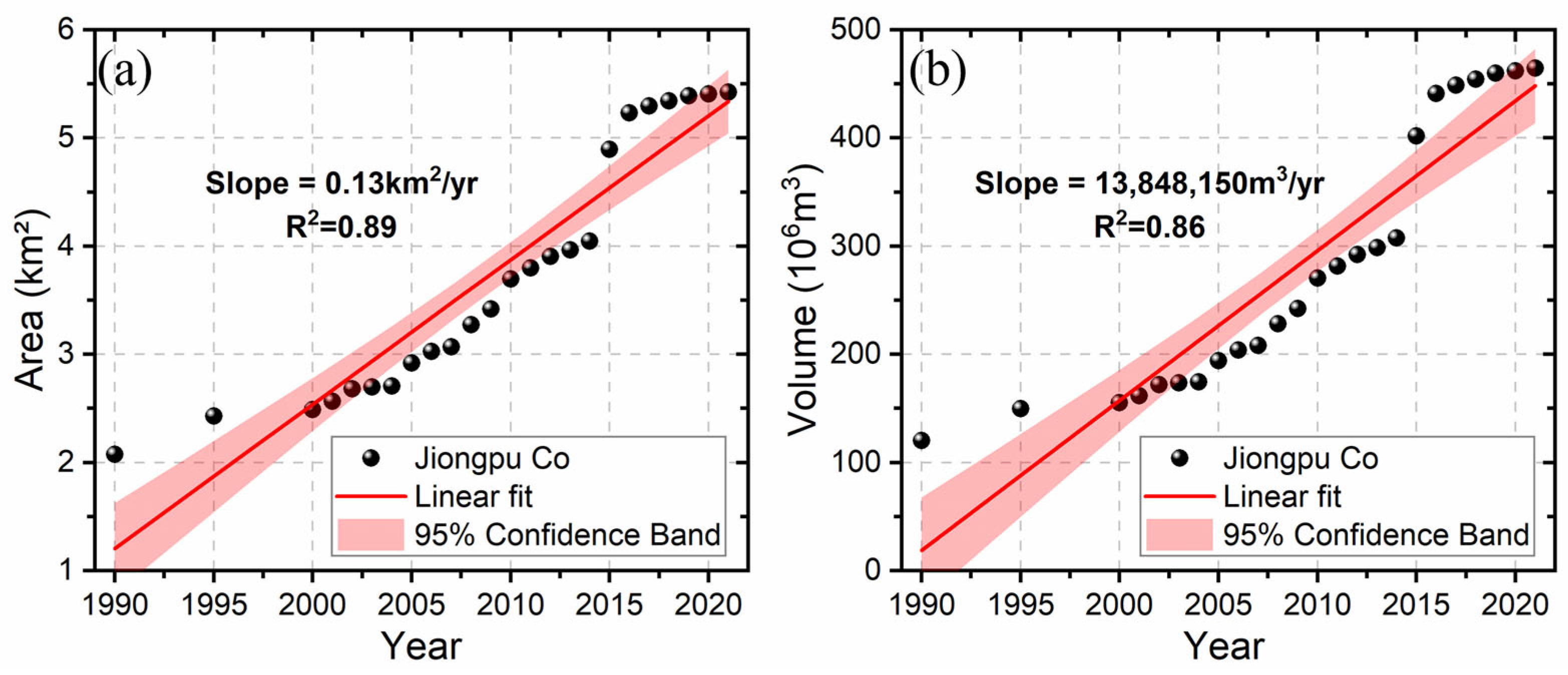
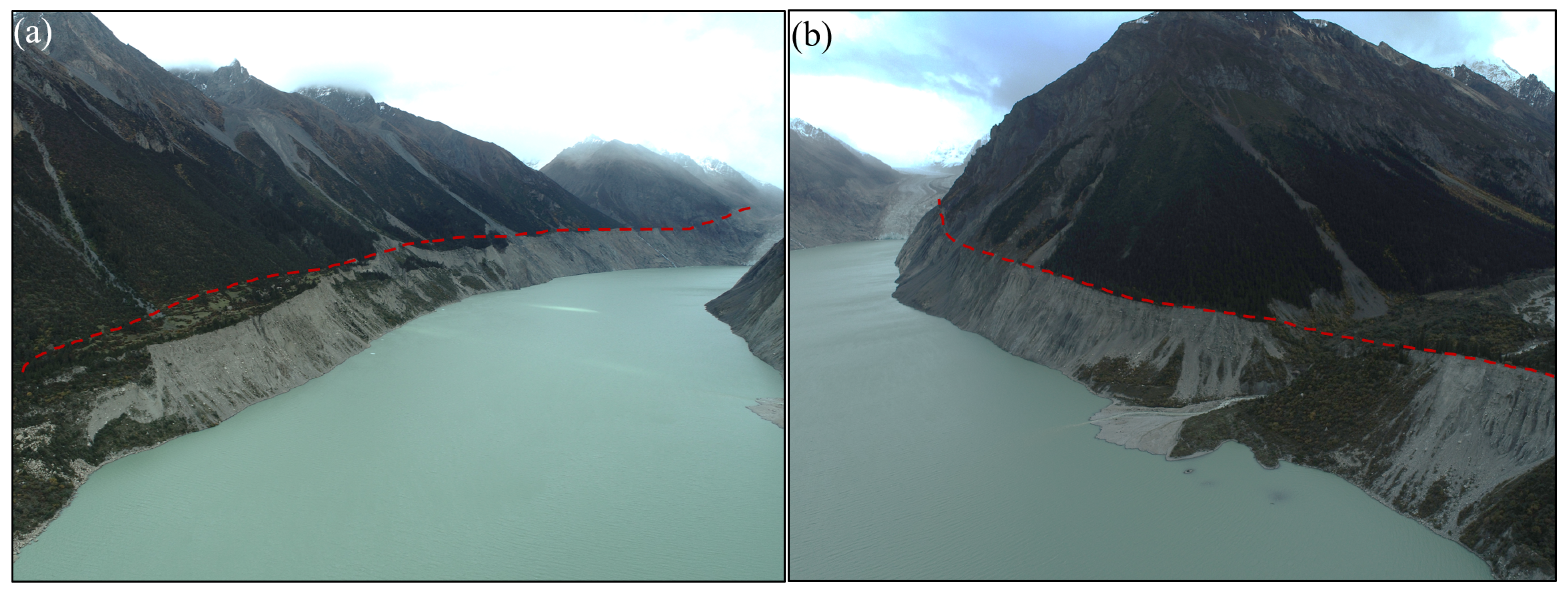
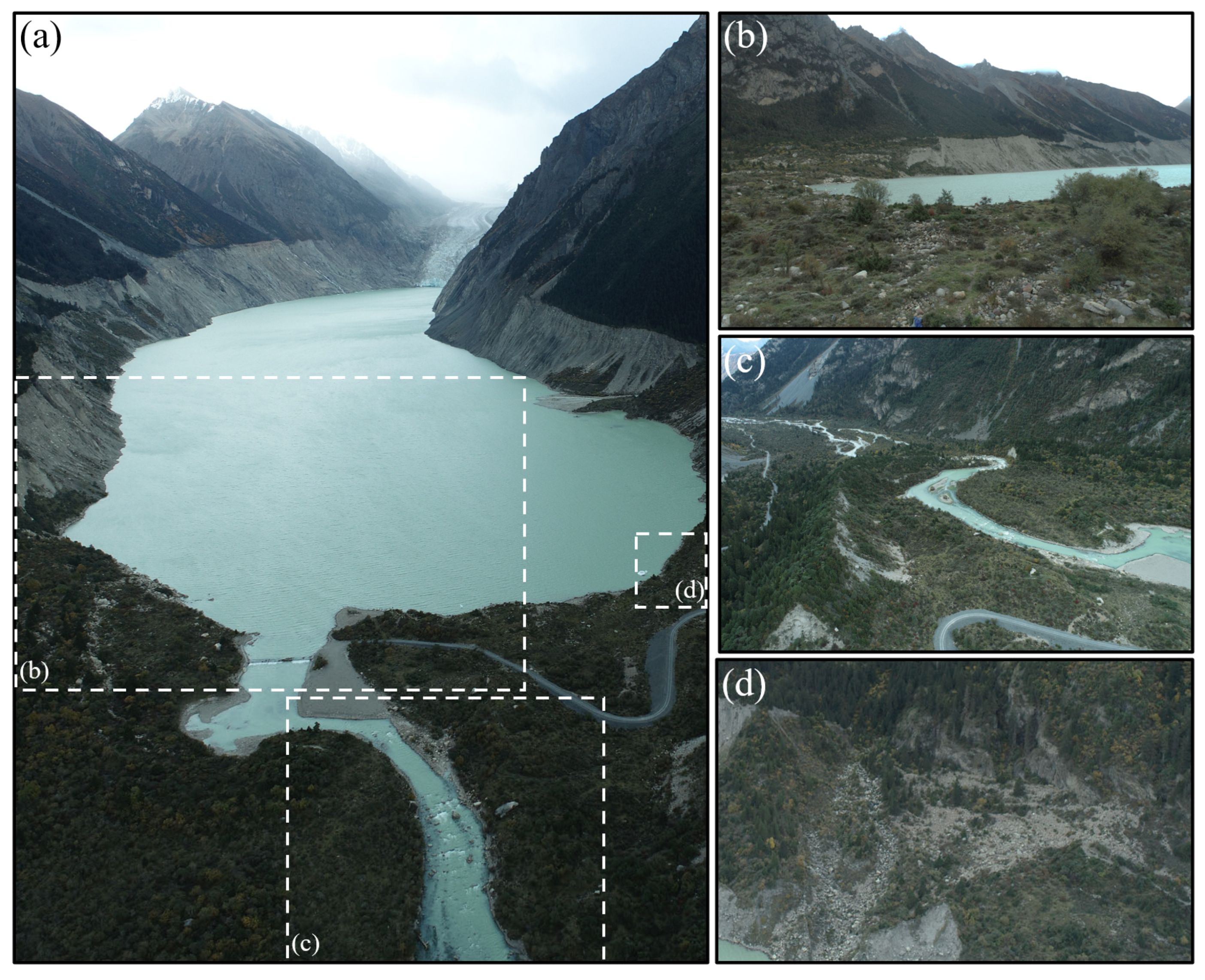
3.1. Jiongpuco Expansion
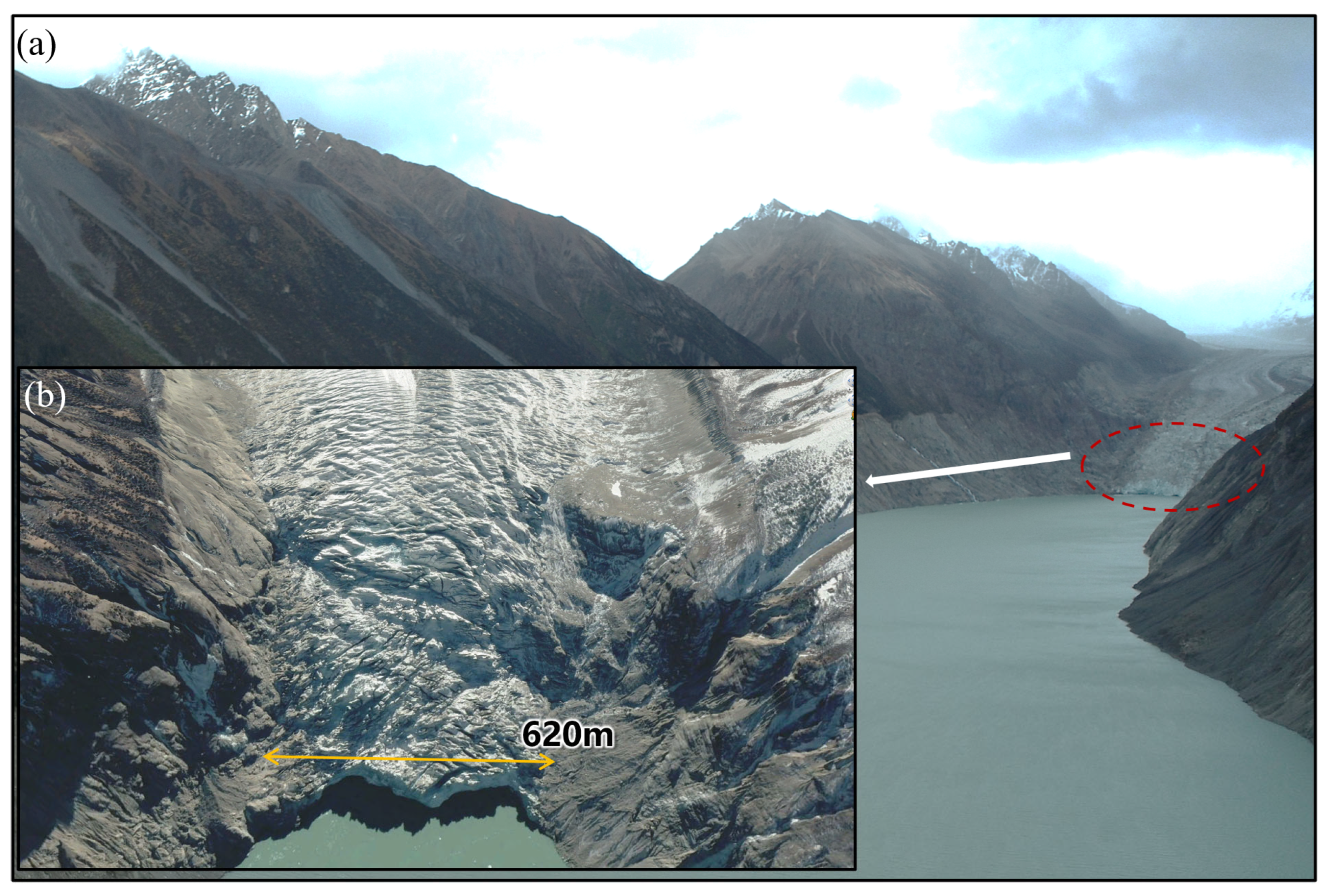
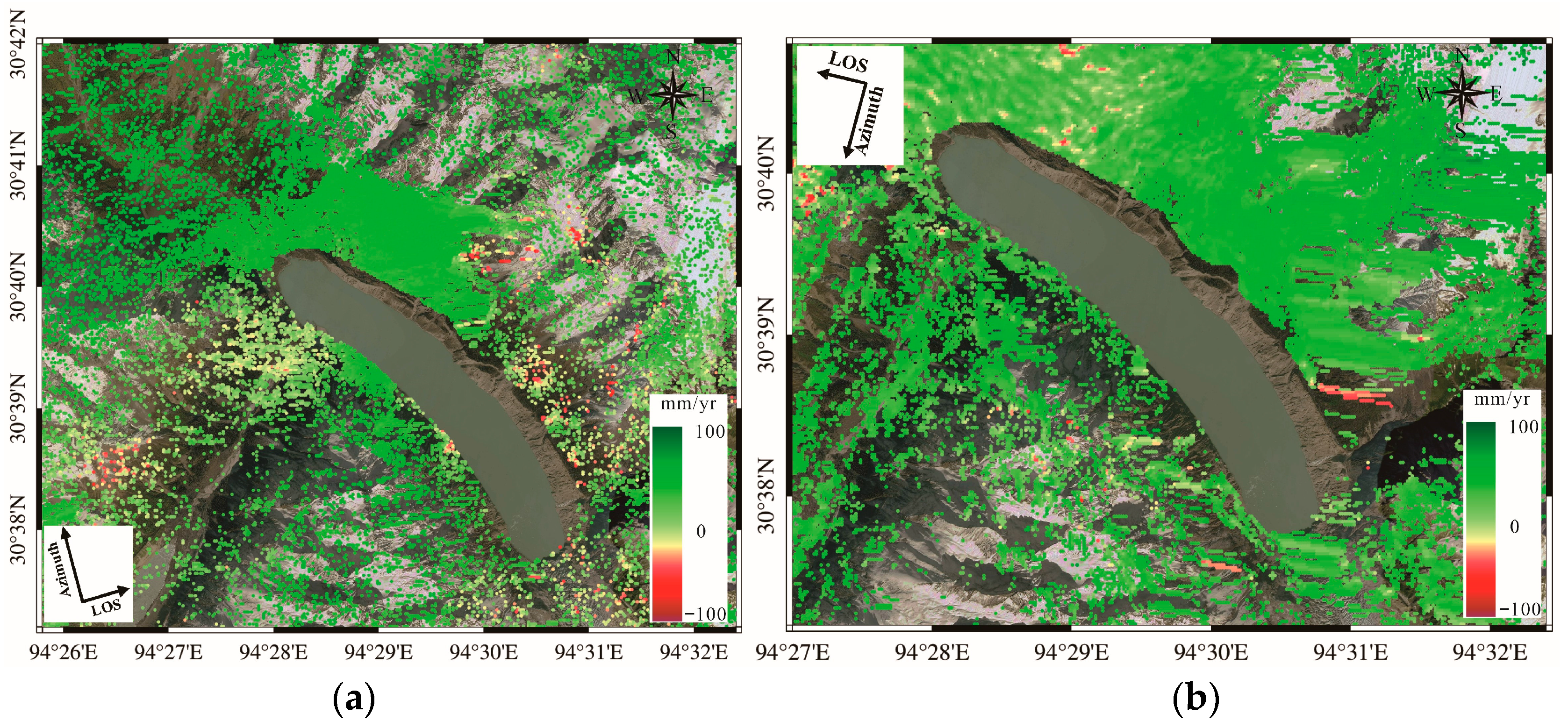
3.2. Potential Triggers of GLOF
3.3. Evaluation of Moraine Dam Erodibility
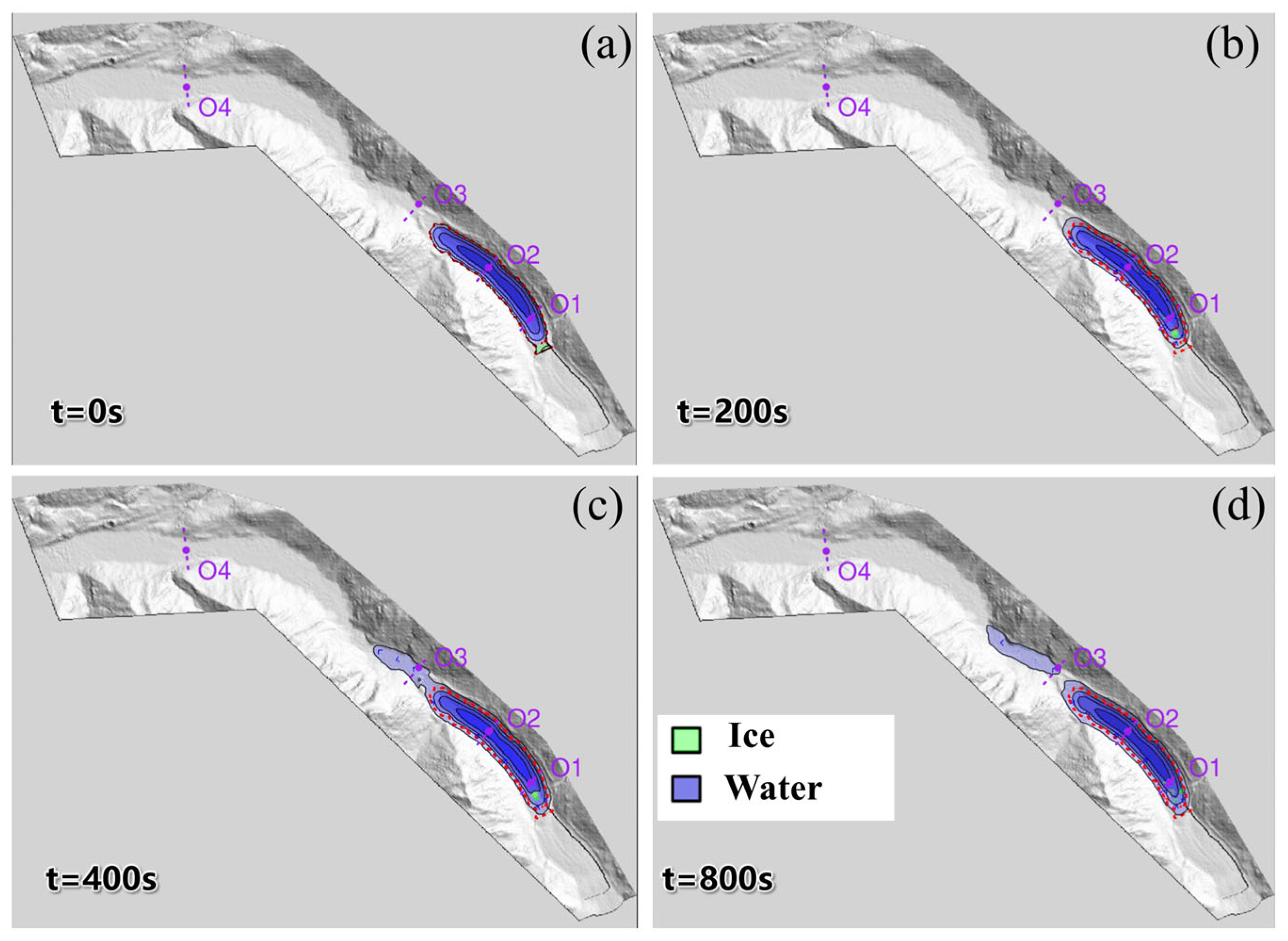
3.4. Outburst Flood
4. Discussion
4.1. Potential for Transformation from Flood to Debris Flow
4.2. Rationality of Simulated Ice Avalanche Volume and Discharge Values
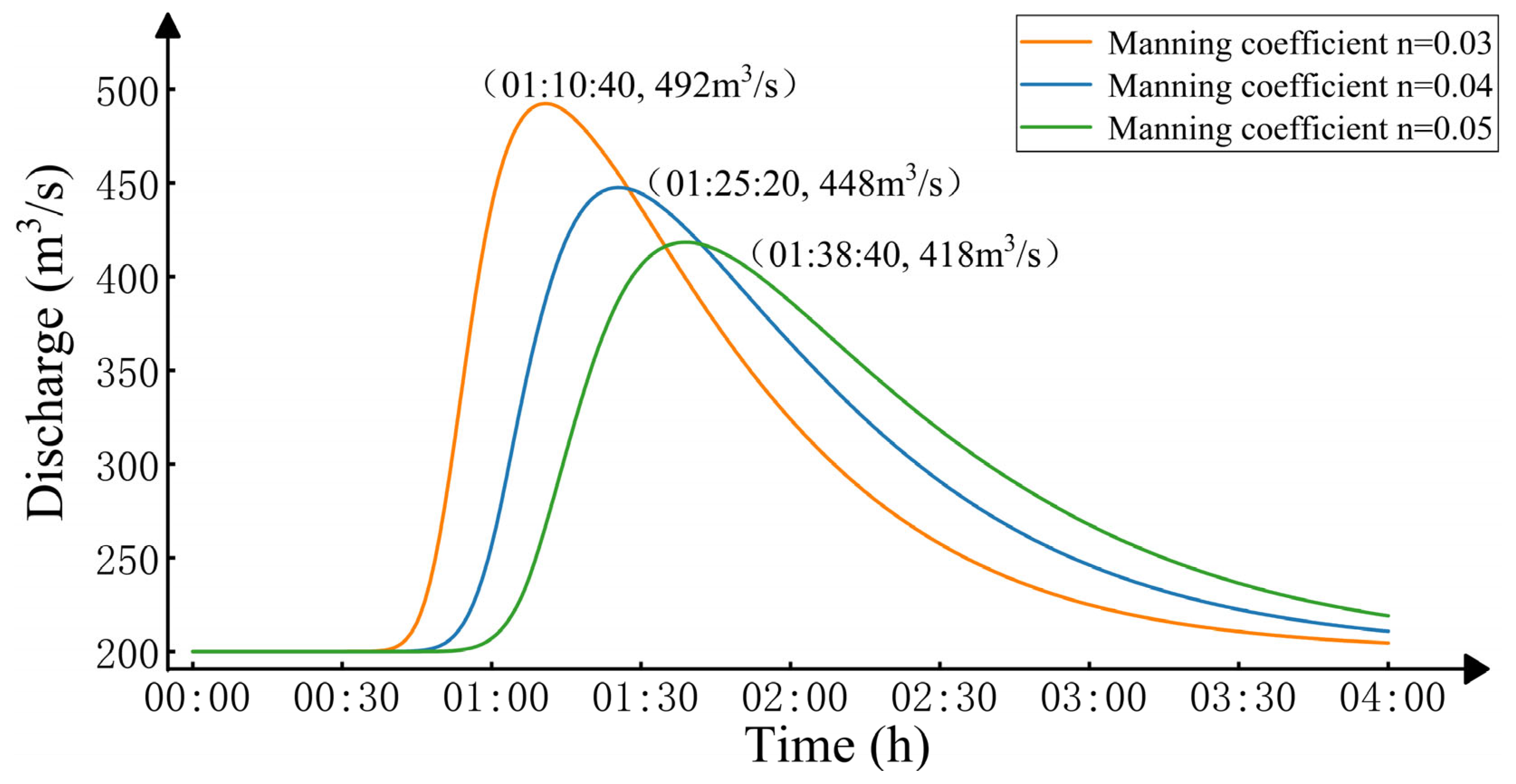
4.3. Model Reliability and Uncertainty
4.4. Implications for GLOF Risk Assessment
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Jiongpuco Lake is situated in the Yigong Zangbo River basin, along the southeastern edge of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. The lake extends over 6 km in length, with an average width of approximately 300 m, covering an area of 5.43 km2. The lake area increased from 2.08 km2 in 1990 to 5.43 km2 in 2021, reflecting a total expansion of 3.35 km2. Notably, the years 2015 and 2016 witnessed the most rapid expansion, with area increases of 0.58 km2 and 0.56 km2, respectively.
- (2)
- Interferometric SAR (InSAR) data show minimal surface deformation along the lake margins, while crevasses in the glacier tongue indicate a high risk of ice avalanches that could generate impulse waves and trigger GLOFs. Field surveys suggest the moraine dam has a flat crest and gentle downstream slope (~1.5°), implying good structural stability. Consequently, overtopping is more likely than incision-based failure.
- (3)
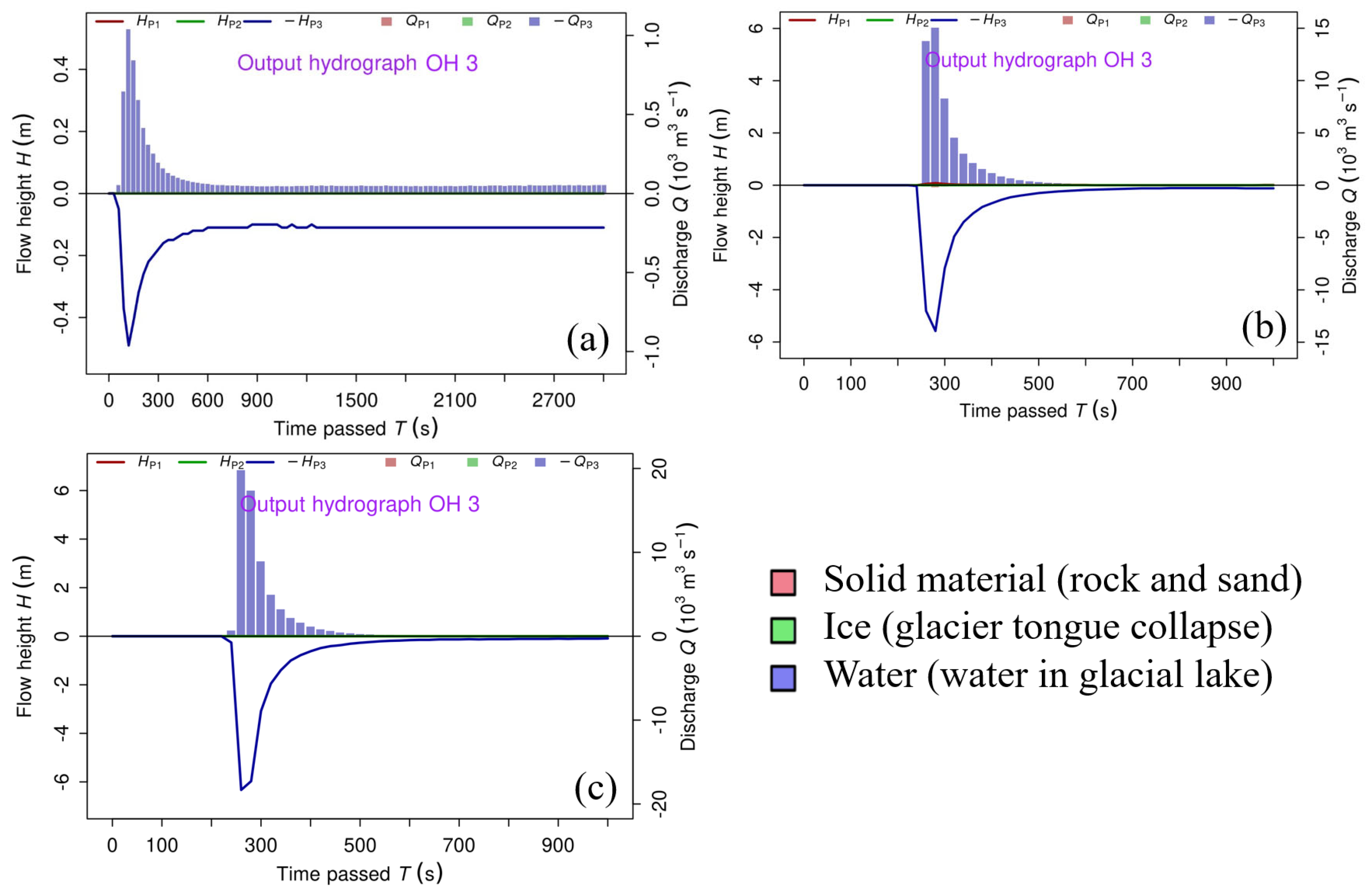
- Simulated ice avalanche scenarios involving volumes of 0.5 Mm3, 2.5 Mm3, and 5 Mm3 yield peak discharge rates of approximately 1000 m3/s, 15,000 m3/s, and 19,000 m3/s at the dam site, respectively. These estimates are consistent with empirical formulas and comparable documented GLOF cases, supporting the reliability of the simulation results.
- (4)
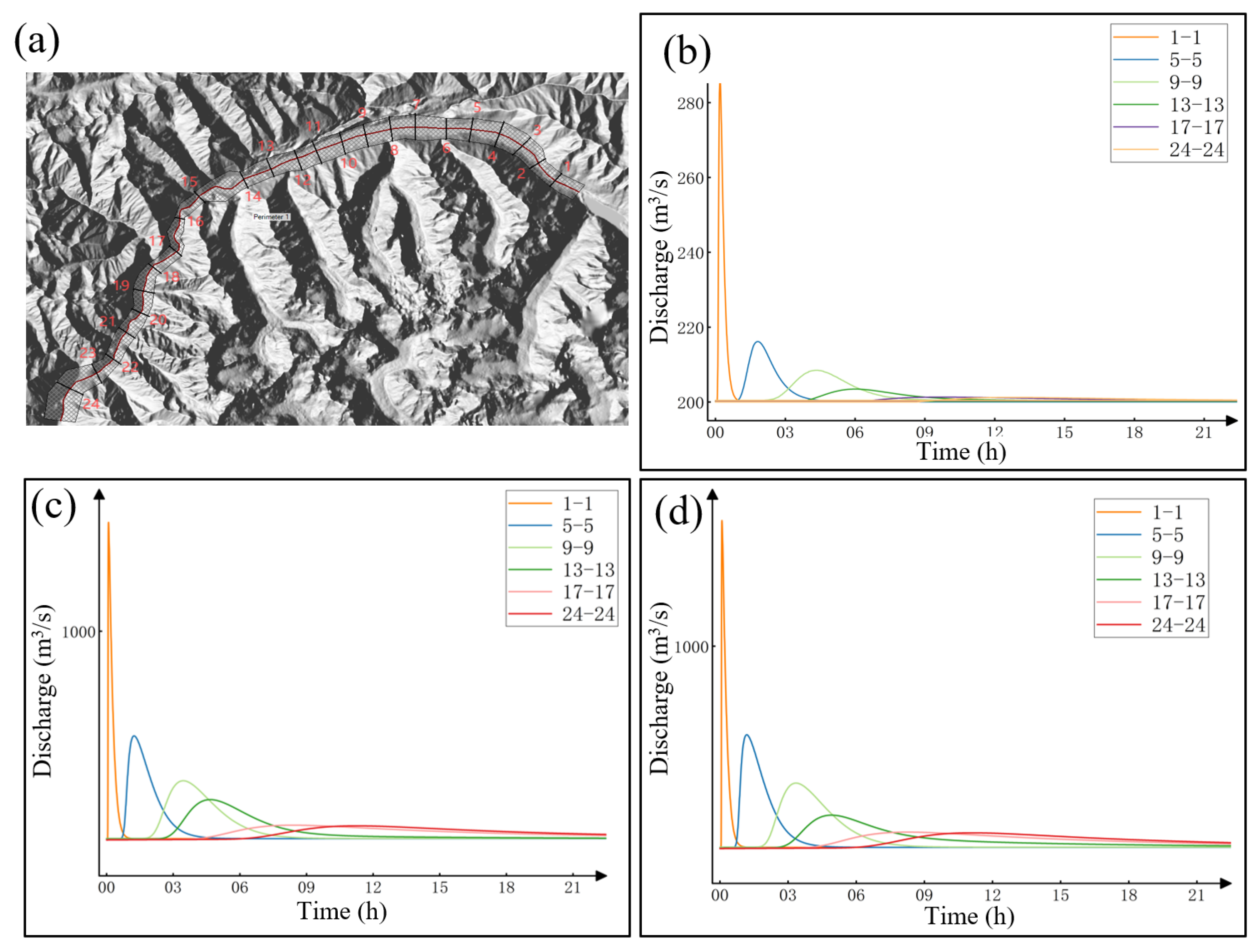
- Analysis of the outburst flood routing indicates a rapid attenuation of peak discharge within the downstream river channel. At a distance of 20 km downstream, the flood peak attenuates to near-normal flow levels. This attenuation is attributed to the relatively wide and low-gradient valley downstream of Jiongpuco Lake, which facilitates dispersion and energy dissipation of floodwaters.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, T.; Bolch, T.; Chen, D.; Gao, J.; Immerzeel, W.; Piao, S.; Su, F.; Thompson, L.; Wada, Y.; Wang, L. The imbalance of the Asian water tower. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Thompson, L.G.; Mosbrugger, V.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Y.; Luo, T.; Xu, B.; Yang, X.; Joswiak, D.R.; Wang, W. Third pole environment (TPE). Environ. Dev. 2012, 3, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, K.D.; Tang, Q. Waters From the Third Pole. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews. Water 2025, 12, e70007. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Wieland, M.; Liu, L.; Kaushik, S. Automatic extraction of glacial lakes from Landsat imagery using deep learning across the Third Pole region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 315, 114413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Fan, X.; Deng, Y.; Zou, C.; Feng, Z.; Djukem, D.L.W.; Wei, T.; Dou, X.; Xu, Q. Combining geophysics, remote sensing and numerical simulation to assess GLOFs: Case study of the Namulacuo Lake in the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Jia, L.; Miles, E.S.; Menenti, M.; Kneib, M.; Shaw, T.E.; Buri, P.; McCarthy, M.J.; Yang, W.; Pellicciotti, F. Observed and projected declines in glacier albedo across the Third Pole in the 21st century. One Earth 2024, 7, 1587–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Pritchard, H.D.; Liu, Q.; Hennig, T.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Nepal, S.; Samyn, D.; Hewitt, K. Glacial change and hydrological implications in the Himalaya and Karakoram. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, R.; Ding, X. Glacier mass balance in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau and its surroundings from the mid-1970s to 2000 based on Hexagon KH-9 and SRTM DEMs. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, F.; Berthier, E.; Wagnon, P.; Kääb, A.; Treichler, D. A spatially resolved estimate of High Mountain Asia glacier mass balances from 2000 to 2016. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowdeswell, J.A.; Hagen, J.O.; Björnsson, H.; Glazovsky, A.F.; Harrison, W.D.; Holmlund, P.; Jania, J.; Koerner, R.M.; Lefauconnier, B.; Ommanney, C.S.L. The mass balance of circum-Arctic glaciers and recent climate change. Quat. Res. 1997, 48, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xiang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Lu, A.; Yao, T. Rapid expansion of glacial lakes caused by climate and glacier retreat in the Central Himalayas. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 859–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Sheng, Y.; Ke, L.; Nie, Y.; Wang, J. Glacial lake evolution in the southeastern Tibetan Plateau and the cause of rapid expansion of proglacial lakes linked to glacial-hydrogeomorphic processes. J. Hydrol. 2016, 540, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Huang, B.; Richards, K.; Ke, L.; Hien Phan, V. Accelerated lake expansion on the Tibetan Plateau in the 2000s: Induced by glacial melting or other processes? Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 3170–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Fan, X.; Wang, X.; Yunus, A.P.; Xiong, J.; Tang, R.; Lovati, M.; van Westen, C.; Xu, Q. Spatio-temporal evolution of glacial lakes in the Tibetan Plateau over the past 30 years. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, T.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Shang, H.; Zhu, L.; Shedayi, A.A.; Yu, H.; Cheng, G.; Liu, G. Linkages of the dynamics of glaciers and lakes with the climate elements over the Tibetan Plateau. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 185, 308–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shijin, W.; Yanjun, C.; Yanqiang, W. Spatiotemporal dynamic characteristics of typical temperate glaciers in China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, M.; Guo, H.; Allen, S.; Kargel, J.S.; Haritashya, U.K.; Watson, C.S. Annual 30 m dataset for glacial lakes in High Mountain Asia from 2008 to 2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 741–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, X.; Yang, C.; Liu, Q.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Tang, Z. Glacial lake inventory of high-mountain Asia in 1990 and 2018 derived from Landsat images. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 2169–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, F.; Guo, H.; Yi, L.; Zeng, J.; Li, B. Glacial Lake area changes in high mountain asia during 1990–2020 using satellite remote sensing. Research 2022, 2022, 9821275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Fan, X.; Wang, X.; Fang, C.; Lovati, M.; Zou, C. The response of glaciers and glacial lakes to climate change in the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau over the past three decades. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 5675–5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Siegert, F.; Zhou, A.-g.; Franke, J. Glacier and glacial lake changes and their relationship in the context of climate change, Central Tibetan Plateau 1972–2010. Glob. Planet. Change 2013, 111, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Song, C. A regional-scale assessment of Himalayan glacial lake changes using satellite observations from 1990 to 2015. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 189, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingwei, Y.; Yonggang, G.; Jian, Z.; Feng, L.; Libin, S.; Deshun, Q. Spaciotemporal distribution characteristics of glacial lakes and the factors influencing the Southeast Tibetan Plateau from 1993 to 2023. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Allen, S.K.; Bao, A.; Ballesteros-Cánovas, J.A.; Huss, M.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yu, T. Increasing risk of glacial lake outburst floods from future Third Pole deglaciation. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Che, Y.; Xinggang, M. Integrated risk assessment of glacier lake outburst flood (GLOF) disaster over the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau (QTP). Landslides 2020, 17, 2849–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.; Robinson, T.R.; Dunning, S.; Rachel Carr, J.; Westoby, M. Glacial lake outburst floods threaten millions globally. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrivick, J.L.; Tweed, F.S. A global assessment of the societal impacts of glacier outburst floods. Glob. Planet. Change 2016, 144, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veh, G.; Korup, O.; Walz, A. Hazard from Himalayan glacier lake outburst floods. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veh, G.; Lützow, N.; Kharlamova, V.; Petrakov, D.; Hugonnet, R.; Korup, O. Trends, breaks, and biases in the frequency of reported glacier lake outburst floods. Earth’s Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, F.; Steiner, J.F.; Shrestha, R.; Dhungel, Y.; Joshi, S.P.; Inglis, S.; Ashraf, A.; Wali, S.; Walizada, K.M.; Zhang, T. A comprehensive and version-controlled database of glacial lake outburst floods in High Mountain Asia. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 3941–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, S.; Rai, S.; Thakur, P.; Emmer, A. Inventory and recently increasing GLOF susceptibility of glacial lakes in Sikkim, Eastern Himalaya. Geomorphology 2017, 295, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, N.; Chen, X.; Nie, Y.; Thakuri, S.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, G. Evaluation of Glacial Lake Outburst Flood susceptibility using multi-criteria assessment framework in Mahalangur Himalaya. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 8, 601288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, G.; Li, W.; Han, L.; Zhang, S.; Yao, X.; Duan, H. A robust glacial lake outburst susceptibility assessment approach validated by GLOF event in 2020 in the Nidu Zangbo Basin, Tibetan Plateau. Catena 2023, 220, 106734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, K.; Sieg, T.; Veh, G.; Fiedler, B.; Moran, T.; Peter, M.; Rottler, E.; Bronstert, A. Natural hazards in a changing world: Methods for analyzing trends and non-linear changes. Earth’s Future 2024, 12, e2023EF003553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Maharjan, S.B. Assessing national exposure and impact to glacial lake outburst floods considering uncertainty under data sparsity. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2024, 2024, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, J.; Liang, Q.; Maharjan, S.B.; Joshi, S.P. Assessing the potential impact of glacial lake outburst floods on individual objects using a high-performance hydrodynamic model and open-source data. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, N.; Chen, X.; Liu, W.; Gouli, M.R.; Zhang, C.; Shrestha, B.; Sharma, S. Glacial lake outburst floods threaten China-Nepal connectivity: Synergistic study of remote sensing, GIS and hydrodynamic modeling with regional implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, N.; Chen, X.; Shrestha, M.; Liu, W. Risk perception and vulnerability of communities in Nepal to transboundary glacial lake outburst floods from Tibet, China. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2024, 107, 104476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-q.; Cui, P.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Qi, Y.-q. Changes in glacial lakes and glaciers of post-1986 in the Poiqu River basin, Nyalam, Xizang (Tibet). Geomorphology 2007, 88, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gao, Y.; Anacona, P.I.; Lei, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, S.; Lu, A. Integrated hazard assessment of Cirenmaco glacial lake in Zhangzangbo valley, Central Himalayas. Geomorphology 2018, 306, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, N.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, M. Glacial lake inventory and lake outburst flood/debris flow hazard assessment after the Gorkha earthquake in the Bhote Koshi Basin. Water 2020, 12, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, A.; Haritashya, U.K.; Kargel, J.S.; Karki, A. Transition of a small Himalayan glacier lake outburst flood to a giant transborder flood and debris flow. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhou, W.; Chen, N.; Liu, R.; Mao, J.; Wang, T. Expanding glacial lakes and assessing outburst susceptibility of moraine-dammed lakes using logistic regression in the Yigong Tsangpo Basin, Tibet, China. Nat. Hazards 2025, 121, 6753–6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, Z.; An, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, C.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Wu, G. Early warning system for ice collapses and river blockages in the Sedongpu Valley, southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 23, 3015–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, X.; Yi, G.; Bie, X.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Lai, P. A glacial lake mapping framework in high mountain areas: A case study of the southeastern Tibetan plateau. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Hu, G.; Liu, T.; Li, C.; Qin, J.; Ge, Y. Glacier dam evolution and knickpoint migration in the Yarlung Tsangpo Gorge, eastern Himalayas, since the last glacial period. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2024, 331, 108631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Jiang, L.; Xu, Z.; Li, C.; Huang, R.; Zhou, Z.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Fan, X. Seismic and hydrological triggers for a complex cascading geohazard of the Tianmo Gully in the southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Eng. Geol. 2023, 324, 107269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, T.; He, J. Barrier lake bursting and flood routing in the Yarlung Tsangpo Grand Canyon in October 2018. J. Hydrol. 2020, 583, 124603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Chen, N.; Pudasaini, S.P.; Mergili, M.; Wang, T.; Liu, M.; Shangguan, D. Risk assessment of a glacial lake with abruptly slowing expansion, Jiongpu, Southeastern Tibet. Geomorphology 2025, 468, 109471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Bolch, T.; Yao, T.; Rounce, D.R.; Chen, W.; Veh, G.; King, O.; Allen, S.K.; Wang, M.; Wang, W. Underestimated mass loss from lake-terminating glaciers in the greater Himalaya. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 16, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.; Quincey, D. Estimating the volume of Alpine glacial lakes. Earth Surf. Dyn. 2015, 3, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Lu, Z.; Ouyang, C.; Zhao, C.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Q. Glacial lake outburst flood monitoring and modeling through integrating multiple remote sensing methods and hec-ras. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergili, M.; Fischer, J.-T.; Krenn, J.; Pudasaini, S.P. r. avaflow v1, an advanced open-source computational framework for the propagation and interaction of two-phase mass flows. Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, A.; Cook, K.L.; Rai, S.K.; Berthier, E.; Allen, S.; Rinzin, S.; de Vries, M.V.W.; Haeberli, W.; Kushwaha, P.; Shugar, D.H. The Sikkim flood of October 2023: Drivers, causes, and impacts of a multihazard cascade. Science 2025, 387, eads2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, K.L.; Andermann, C.; Gimbert, F.; Adhikari, B.R.; Hovius, N. Glacial lake outburst floods as drivers of fluvial erosion in the Himalaya. Science 2018, 362, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Mergili, M.; Emmer, A.; Allen, S.; Bao, A.; Guo, H.; Stoffel, M. The 2020 glacial lake outburst flood at Jinwuco, Tibet: Causes, impacts, and implications for hazard and risk assessment. Cryosphere Discuss. 2021, 2021, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Veh, G.; Sattar, A.; Chen, W.; Allen, S. Cascading hazards from two recent glacial lake outburst floods in the Nyainqêntanglha range, Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D.; Huggel, C.; Haeberli, W.; Kaitna, R. Unraveling driving factors for large rock–ice avalanche mobility. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2011, 36, 1948–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaub, Y.S.; Huggel, C.; Cochachin, A. Ice-avalanche scenario elaboration and uncertainty propagation in numerical simulation of rock-/ice-avalanche-induced impact waves at Mount Hualcán and Lake 513, Peru. Landslides 2016, 13, 1445–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kääb, A.; Leinss, S.; Gilbert, A.; Bühler, Y.; Gascoin, S.; Evans, S.G.; Bartelt, P.; Berthier, E.; Brun, F.; Chao, W.-A. Massive collapse of two glaciers in western Tibet in 2016 after surge-like instability. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinzin, S.; Dunning, S.; Carr, R.J.; Sattar, A.; Mergili, M. Exploring implications of input parameter uncertainties in glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF) modelling results using the modelling code r. avaflow. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2025, 25, 1841–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westoby, M.J.; Brasington, J.; Glasser, N.; Hambrey, M.; Reynolds, J.M.; Hassan, M.A.; Lowe, A. Numerical modelling of glacial lake outburst floods using physically based dam-breach models. Earth Surf. Dyn. 2015, 3, 171–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Duan, H.; Liu, N.; Du, Z.; Wang, P.; Yi, B.; Xu, J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, X. Change of moraine-dammed glacial lakes and simulation of glacial lake outburst flood in the Yi’ong Zangbo River basin. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 881285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, K.; Shrestha, H.L.; Murthy, M.; Bajracharya, B.; Shrestha, B.; Gilani, H.; Pradhan, S.; Dangol, B. Development of 2010 national land cover database for the Nepal. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 148, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter Type | Basic Parameters |
|---|---|
| Incidence Angle (°) | 33.85/43.93 |
| Orbit Direction | Ascending/Descending |
| Polarization Mode | VV + VH |
| Imaging Mode | IW |
| Spatial Resolution (m) | 5 × 20 |
| Orbit Number (Ascending/Descending) | 70/4 |
| Flight Azimuth (Ascending/Descending, °) | −10.63/−170.19 |
| Number of Images (Ascending/Descending) | 83/103 |
| Cross Section Number | Distance to Dam (km) | Scenario 0.5 Mm3 | Scenario 2.5 Mm3 | Scenario 5.0 Mm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-1 | 2.00 | 287 | 2325 | 2730 |
| 5-5 | 10.50 | 216 | 444 | 492 |
| 9-9 | 18.50 | 208 | 314 | 334 |
| 13-13 | 27.00 | 203 | 271 | 259 |
| 17-17 | 39.00 | 201 | 222 | 226 |
| 24-24 | 55.00 | 201 | 221 | 225 |
| Number | Formula [56] | Scenario 0.5 Mm3 | Scenario 2.5 Mm3 | Scenario 5.0 Mm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 551 | 1179 | 1384 | |
| 2 | 464 | 1096 | 1312 | |
| 3 | 270 | 1151 | 1562 | |
| 4 | 142 | 413 | 517 | |
| 5 | 190 | 984 | 1391 | |
| 6 | 1179 | 2968 | 3604 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, W. Ice Avalanche-Triggered Glacier Lake Outburst Flood: Hazard Assessment at Jiongpuco, Southeastern Tibet. Water 2025, 17, 2102. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142102
Li S, Li C, Li Z, Li L, Wang W. Ice Avalanche-Triggered Glacier Lake Outburst Flood: Hazard Assessment at Jiongpuco, Southeastern Tibet. Water. 2025; 17(14):2102. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142102
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shuwu, Changhu Li, Zhengzheng Li, Lei Li, and Wei Wang. 2025. "Ice Avalanche-Triggered Glacier Lake Outburst Flood: Hazard Assessment at Jiongpuco, Southeastern Tibet" Water 17, no. 14: 2102. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142102
APA StyleLi, S., Li, C., Li, Z., Li, L., & Wang, W. (2025). Ice Avalanche-Triggered Glacier Lake Outburst Flood: Hazard Assessment at Jiongpuco, Southeastern Tibet. Water, 17(14), 2102. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142102





