Effect of Fe2O3 Nanoparticles on the Efficiency of Anammox Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biomass of Annamox
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Analysis
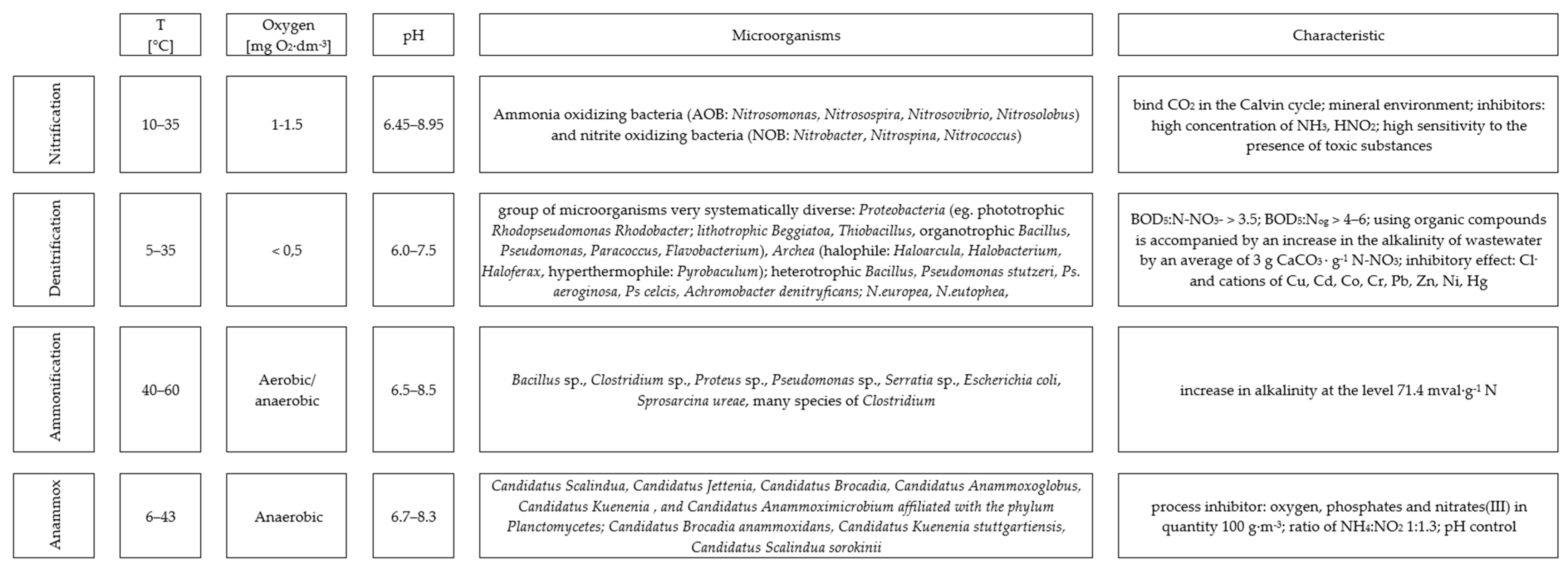
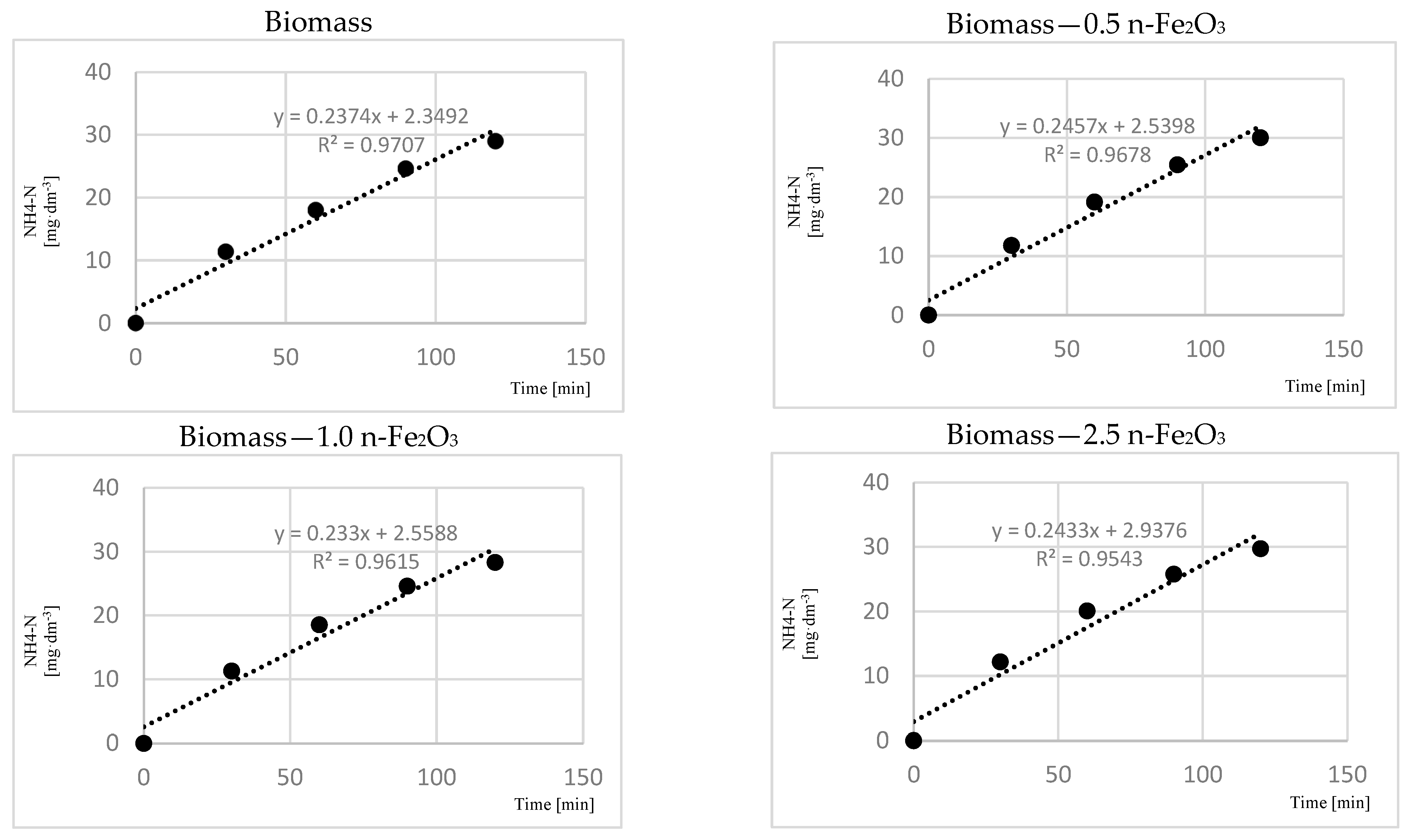
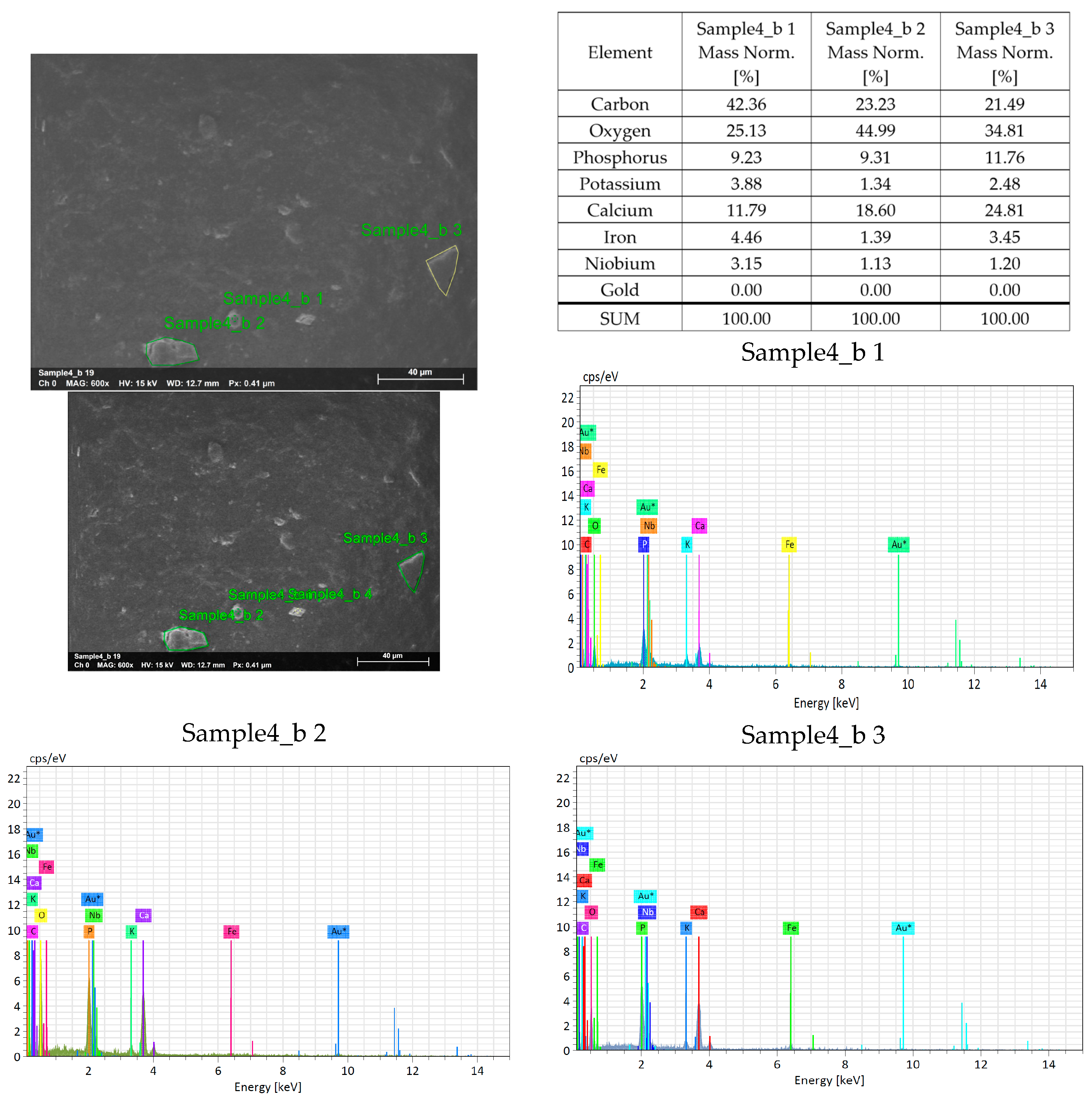
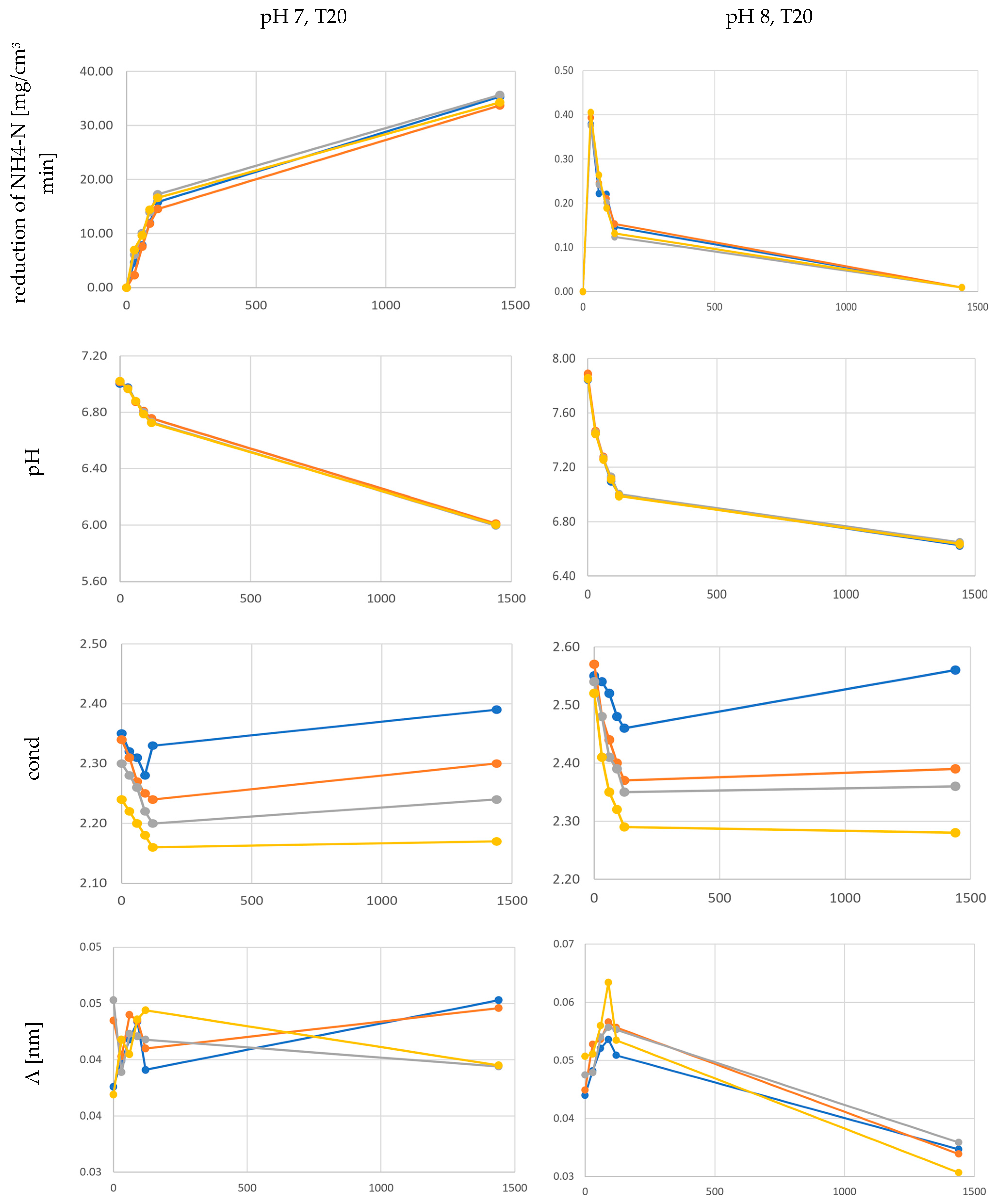
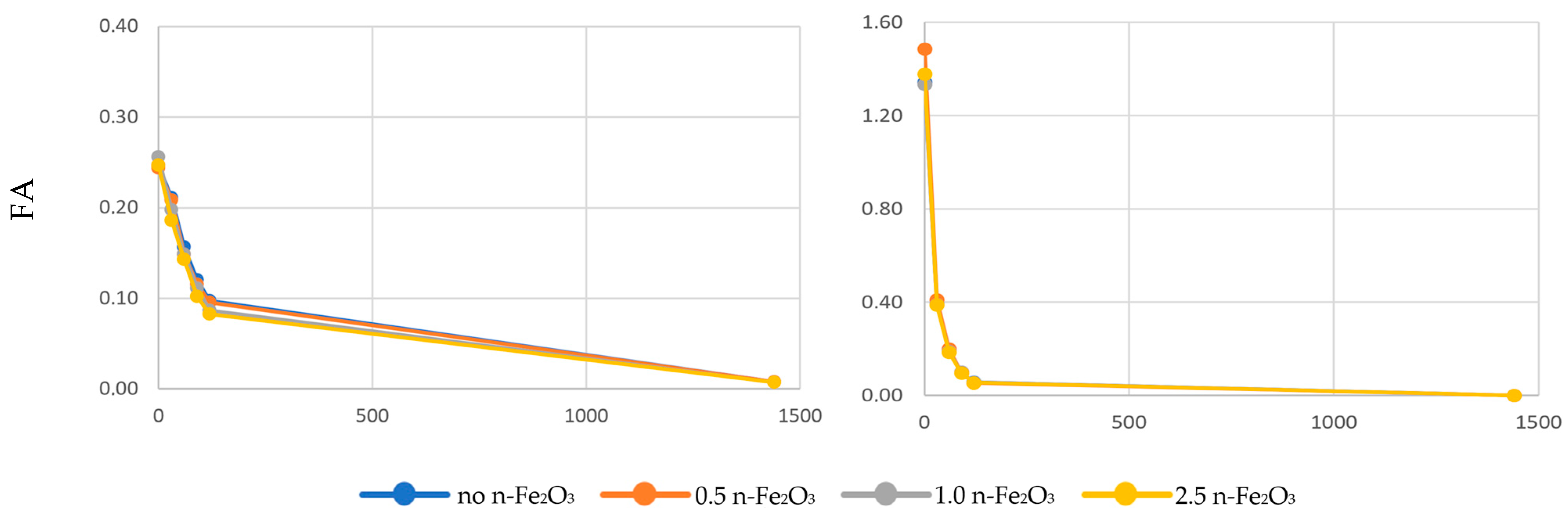
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Agglomeration
4.2. Physicochemical Parameters and the Efficiency of the Anammox Process
4.3. MONPs and the Anammox Process
4.4. Anammox Process and n-Fe2O3
5. Conclusions
- encourages better process efficiency, but only in the first 30–60 min of biomass—n-Fe2O3 contact and faster reaction of the system to the occurrence of partially anaerobic conditions,
- facilitates sedimentation and flocculation processes under pH 7 and a temperature of 20 °C, thanks to participation in the agglomeration process and creation of appropriate structures,
- reduces the agglomeration process of the biomass itself through biomass-n-Fe2O3 sorption,
- depending on the temperature, determines the efficiency of NH4-N removal and at a temperature of 30 °C the efficiency of NH4-N removal is higher for solutions with pH 8 (approx. 98% after 24 h) than for solutions with pH 7 (approx. 70% after 24 h).
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Cai, X.; Wang, Z.; Xia, S. Enhancement and mechanisms of iron-assisted anammox process. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.-R.; Li, H.; Su, J.-Q.; Zhou, G.-W. Anammox Bacteria Are Potentially Involved in Anaerobic Ammonium Oxidation Coupled to Iron(III) Reduction in the Wastewater Treatment System. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 717249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Dsane, V.F.; Jeon, H.; Jeong, S.; Oh, T.; Choi, Y. The role of magnetite (Fe3O4) particles for enhancing the performance and granulation of anammox. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 157218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassoued, A.; Dkhil, B.; Gadri, A.; Ammar, S. Control of the shape and size of iron oxide (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles synthesized through the chemical precipitation method. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 3007–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Fu, H.M.; Mao, Z.; Yan, P.; Xu, X.W.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Y.P. Fate of iron nanoparticles in anammox system: Dissolution, migration and transformation. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Xue, X. Preparation of different shaped α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles with large particles of iron oxide red. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2019, 21, 1097–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, I.; Rabajczyk, A. Metal Nanoparticles in Surface Waters—A Risk to Aquatic Organisms. Saf. Fire Technol. 2019, 54, 70–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Fan, K.; Yan, X. Iron Oxide Nanozyme: A Multifunctional Enzyme Mimetic for Biomedical Applications. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3207–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, T.; Akgul, D.; Mertoglu, D. Accumulation of TiO2 nanoparticles in the anammox bioreactor: Their effects on treatment performance and microbial dynamics. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 187, 108595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Xu, J.J.; Shi, Z.J.; Cheng, Y.F.; Ji, Z.Q.; Deng, R.; Jin, R.C. Short-term impacts of Cu, CuO, ZnO and Ag nanoparticles (NPs) on anammox sludge: CuNPs make a difference. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 235, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, S.; Sari, T.; Akgul, D. Recovery profile of anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) bacteria inhibited by ZnO nanoparticles. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 85, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdim, E.; Özkan, Z.Y.; Kurt, H.; Kocamemi, B.A. Overcoming challenges in mainstream Anammox applications: Utilization of nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 3023–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, D.; Zhang, H.; He, Y.; Zhang, S.; Dai, J.; Wen, X. Comprehensive analysis of the impacts of iron-based nanoparticles and ions on Anammox process. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 180, 108371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.-W.; Fu, H.-M.; Yan, P.; Liu, P.; Weng, X.; Fang, F.; Guo, J.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Y.-P. Deep Insights into the Roles of Iron in the Structure and Function of the Anammox Granular Sludge System. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 7896–7906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.-W.; Qi, J.; Yan, P.; Guan, Y.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Sun, Z.-H.; Zhang, L.-J.; Weng, X.; Shen, Y.; Fang, F.; et al. Insight into the structure and metabolic function of iron-rich nanoparticles in anammox bacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Hu, Y.; Liu, R.; Sheng, X.; Chen, L.; Wu, G.; Hu, H.; Zhan, X. Start up of partial nitritation-anammox process using intermittently aerated sequencing batch reactor: Performance and microbial community dynamics. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabajczyk, A.; Dusinska, M.; Yamani, N.E. Effect of time on the stability of nanoparticles of iron oxide in the environmental acids. Water Environ. Res. 2016, 89, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishorekumar, R.; Bulle, M.; Wany, A.; Gupta, K.J. An Overview of Important Enzymes Involved in Nitrogen Assimilation of Plants. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2057, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, J.; Lin, H.; Fu, Y.; Zhou, Y. Transcriptomic analysis of nitrogen metabolism pathways in Klebsiella aerogenes under nitrogen-rich conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1323160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Huang, Y.; Li, R.; Li, K.; Ren, Z.; Wu, J. Regulation of nitrogen transformation and microbial community by inoculation during livestock manure composting. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2024, 16, e13256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ribbe, M.W. Biosynthesis of the metalloclusters of molybdenum nitrogenase. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 664–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danyal, K.; Shaw, S.; Page, T.R.; Duval, S.; Horitani, M.; Marts, A.R.; Lukoyanov, D.; Dean, D.R.; Raugei, S.; Hoffman, B.M.; et al. Negative cooperativity in the nitrogenase Fe protein electron delivery cycle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E5783–E5791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altammar, K.A. A review on nanoparticles: Characteristics, synthesis, applications, and challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1155622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, Applications and Toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilén, B.M.; Keiding, K.; Nielsen, P.H. Flocculation of activated sludge flocs by stimulation of the aerobic biological activity. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3909–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharia, C.; Musteret, C.-P.; Afrasinei, M.-A. The Use of Coagulation–Flocculation for Industrial Colored Wastewater Treatment—(I) The Application of Hybrid Materials. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutegoa, E. Efficient techniques and practices for wastewater treatment: An update. Discov. Water 2024, 4, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.X.; Chai, L.Y.; Tang, C.J.; Xiao, R.; Li, B.R.; Wu, D.; Min, X.B. Influence of ZnO nanoparticles on anammox granules: The inhibition kinetics and mechanism analysis by batch assays. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 133, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chi, Z.; Yan, B. Insight into the impact of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on anammox process of subsurface-flow constructed wetlands under long-term exposure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 29584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Gao, M.; Li, S.; Guo, L.; She, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, D.; Jin, C.; et al. Magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles induced effects on performance and microbial community of activated sludge from a sequencing batch reactor under long-term exposure. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 225, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Z.; Xu, J.-J.; Shi, Z.-J.; Cheng, Y.-F.; Ji, Z.-Q.; Deng, R.; Jin, R.-C. Combined impacts of nanoparticles on anammox granules and the roles of EDTA and S2− in attenuation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 334, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Cheng, Y.F.; Xu, L.Z.; Wu, J.; Bai, Y.H.; Xu, J.J.; Shi, Z.J.; Jin, R.C. Discrepant effects of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles on anammox sludge properties: A comparison between Cu and CuO nanoparticles. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Cheng, Y.F.; Xu, L.Z.I.; Bai, Y.H.; Jin, R.C. Anammox granules show strong resistance to engineered silver nanoparticles during long-term exposure. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 259, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Cheng, Y.F.; Xu, L.Z.J.; Bai, Y.H.; Xu, J.J.; Shi, Z.J.; Shen, Y.Y.; Jin, R.C. Evaluating the effects of metal oxide nanoparticles (TiO2, Al2O3, SiO2 and CeO2) on anammox process: Performance, microflora and sludge properties. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Xie, X.; Pang, Q. Short-Term Effects of CuO, ZnO, and TiO2 Nanoparticles on Anammox. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wei, D.; Zhang, X.; Fu, H.; Chen, T.; Jia, J. An innovative strategy for inducing Anammox from partial nitrification process in a membrane bioreactor. J. Hazard. Mat. 2019, 379, 120809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakha, M.; Pal, S.; Damantarrai, D.; Panigrahi, T.K.; Mallick, B.C.; Pramanik, K.; Mallick, B.; Jha, S. Antimicrobial activity of iron oxide nanoparticle upon modulation of nanoparticle-bacteria interface. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, L.; Fang, S. Comparisons of Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Communities in Anammox Systems upon Addition of Copper-Based Nanoparticles and Copper Ion. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 7808–7816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Estrella, J.; Li, G.; Neely, S.E.; Puyol, D.; Sierra Alvarez, M.R.; Field, J.A. Elemental copper nanoparticle toxicity to anaerobic ammonium oxidation and the influence of ethylene diamine-tetra acetic acid (EDTA) on copper toxicity. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, T.; Li, J.; Liu, T.; Case, D.A.; Noodleman, L. FeMo Cofactor of Nitrogenase: A Density Functional Study of States MN, MOX, MR, and MI. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 12392–12410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groysman, S.; Holm, R.H. Biomimetic Chemistry of Iron, Nickel, Molybdenum, and Tungsten in Sulfur-Ligated Protein Sites. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 2310–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stappen, C.V.; Decamps, L.; Cutsail, G.E.; Bjornsson, R.; Henthorn, J.T.; Birrell, J.A.; DeBeer, S. The Spectroscopy of Nitrogenases. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 5005–5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baysal, C.; Burén, S.; He, W.; Jiang, X.; Capell, T.; Rubio, L.M.; Christou, P. Functional expression of the nitrogenase Fe protein in transgenic rice. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzyb, A.; Wolna-Maruwka, A.; Niewiadomska, A. The Significance of Microbial Transformation of Nitrogen Compounds in the Light of Integrated Crop Management. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntaikou, I. Microbial production of hydrogen. In Sustainable Fuel Technologies Handbook; Dutta, S., Hussain, C.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 315–337. ISBN 9780128229897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Tobias, C.R. Chapter Three—Molecular and Stable Isotope Methods to Detect and Measure Anaerobic Ammonium Oxidation (Anammox) in Aquatic Ecosystems. In Methods in Enzymology; Klotz, M.G., Stein, L.Y., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 496, pp. 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, M.; Dietl, A.; Müller, M.; Barends, T.R.M. Purification of the key enzyme complexes of the anammox pathway from DEMON sludge. Biopolymers 2021, 112, e2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moir, J.W.B.; Wehrfritz, J.M.; Spiro, S.; Richardson, D.J. The biochemical characterization of a novel non-haem-iron hydroxylamine oxidase from Paracoccus denitrificans GB17. Biochem. J. 1996, 319, 823–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, M.; Fukumori, Y.; Yamanaka, T. A Hydroxylamine-Cytochrome c Reductase Occurs in the Heterotrophic Nitrifier Arthrobacter globiformis. Plant Cell Physiol. 1985, 26, 1439–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrfritz, J.M.; Reilly, A.; Spiro, S.; Richardson, D.J. Purification of hydroxylamine oxidase from Thiosphaera pantotropha. Identification of electron acceptors that couple heterotrophic nitrification to aerobic denitrification. FEBS Lett. 1993, 335, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otte, S.; Schalk, J.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jetten, M.S. Hydroxylamine oxidation and subsequent nitrous oxide production by the heterotrophic ammonia oxidizer Alcaligenes faecalis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 51, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lin, E.; Huang, S. Heterotrophic nitrogen removal in Bacillus sp. K5: Involvement of a novel hydroxylamine oxidase. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 3461–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrfritz, J.; Carter, J.P.; Spiro, S.; Richardson, D.J. Hydroxylamine oxidation in heterotrophic nitrate-reducing soil bacteria and purification of a hydroxylamine-cytochrome c oxidoreductase from a Pseudomonas species. Arch. Microbiol. 1996, 166, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabello, P.; Roldán, M.D.; Castillo, F.; Moreno-Vivián, C. Nitrogen Cycle. In Encyclopedia of Microbiology, 3rd ed.; Schaechter, E., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 299–321. ISBN 9780123739445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, B.D.; Zehr, J.P. Chapter 30—Molecular Approaches to the Nitrogen Cycle. In Nitrogen in the Marine Environment, 2nd ed.; Capone, D.G., Bronk, D.A., Mulholland, M.R., Carpenter, E.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 1303–1344. ISBN 9780123725226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Wen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, J. Long-Term Performance of Nitrogen Removal and Microbial Analysis in an Anammox MBBR Reactor with Internal Circulation to Provide Low Concentration DO. Toxics 2022, 10, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, S. Study on the Start-Up of Anammox Process in Lab-Scale Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR). FMH606. Master’s Thesis, The University of South-Eastern Norway, Notodden, Norway, 2021; p. 61. [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi, S.; Biswas, R.; Nandy, T. Autotrophic Ammonia Removal Processes: Ecology to Technology. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 1353–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloantoa, K.M.; Khetsha, Z.P.; van Heerden, E.; Castillo, J.C.; Cason, E.D. Nitrate Water Contamination from Industrial Activities and Complete Denitrification as a Remediation Option. Water 2022, 14, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, J.P.; Burd, E.M. Other Gram-Negative and Gram-Variable Bacilli. In Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, 8th ed.; Bennett, J.E., Dolin, R., Blaser, M.J., Eds.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015; Volume 2, pp. 2667–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Cui, D.; Wang, L.; Ma, F.; Chang, C.-C.; Yang, J. Application of bioaugmentation in the rapid start-up and stable operation of biological processes for municipal wastewater treatment at low temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6622–6629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Du, Z.; Li, Y. Impacts of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes on Nutrient Removal from Wastewater and Bacterial Community Structure in Activated Sludge. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Z.; Qiao, S.; Zhou, J.; Tang, X.; Zhang, J. Fast start-up of Anammox process with appropriate ferrous iron concentration. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 170, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-F.; Huang, B.-C.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Cheng, Y.-F.; Fan, N.-S.; Jin, R.-C. Recent advances regarding the impacts of engineered nanomaterials on the anaerobic ammonium oxidation process: Performances and mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 3501–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Chen, Y.; Lv, L.; Ahmad, H.A.; Ni, S.-Q.; Ren, L.; Cui, Z.; Fang, X.; Qiao, Z.; Ding, S. Transformation of the zero valent iron dosage effect on anammox after long-term culture: From inhibition to promotion. Process Biochem. 2019, 78, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyman, M.R.; Russell, S.A.; Ely, R.L.; Willoamson, K.J.; Arp, D.J. Inhibition, Inactivation, and Recovery of Ammonia-Oxidizing Activity in Cometabolism of Trichloroethylene by Nitrosomonas europaea. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1480–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, O.; Schweighofer, P.; Svardal, K. Nitrification inhibition—A method for the estimation of actual maximum autotrophic growth rates in activated sludge systems. Water Sci. Tech. 1994, 30, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektienė, R.; Rimeika, M.; Zalieckienė, E.; Šaulys, V.; Zagorskis, A. Determination of Organic Matter by UV Absorption in the Ground Water. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2012, 20, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshin, G.; Chow, C.W.K.; Fabris, R.; Drikas, M. Absorbance spectroscopy based examination of effects of coagulation on the reactivity of fractions of natural organic matter with varying apparent molecular weights. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Peng, L.; Wang, D.; Ni, B. The roles of free ammonia (FA) in biological wastewater treatment processes: A review. Environ. Intern. 2019, 123, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, I.; Dosta, J.; Fajardo, C.; Campos, J.L.; Mosquera-Corral, A.; Méndez, R. Short- and long-term effects of ammonium and nitrite on the Anammox process. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 95, S170–S174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rabajczyk, A.; Qiu, S.; Zhan, X. Effect of Fe2O3 Nanoparticles on the Efficiency of Anammox Process. Water 2025, 17, 2100. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142100
Rabajczyk A, Qiu S, Zhan X. Effect of Fe2O3 Nanoparticles on the Efficiency of Anammox Process. Water. 2025; 17(14):2100. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142100
Chicago/Turabian StyleRabajczyk, Anna, Songkai Qiu, and Xinmin Zhan. 2025. "Effect of Fe2O3 Nanoparticles on the Efficiency of Anammox Process" Water 17, no. 14: 2100. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142100
APA StyleRabajczyk, A., Qiu, S., & Zhan, X. (2025). Effect of Fe2O3 Nanoparticles on the Efficiency of Anammox Process. Water, 17(14), 2100. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142100







