Surface Water Runoff Estimation of a Continuously Flooded Rice Field Using a Daily Water Balance Approach—An Irrigation Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
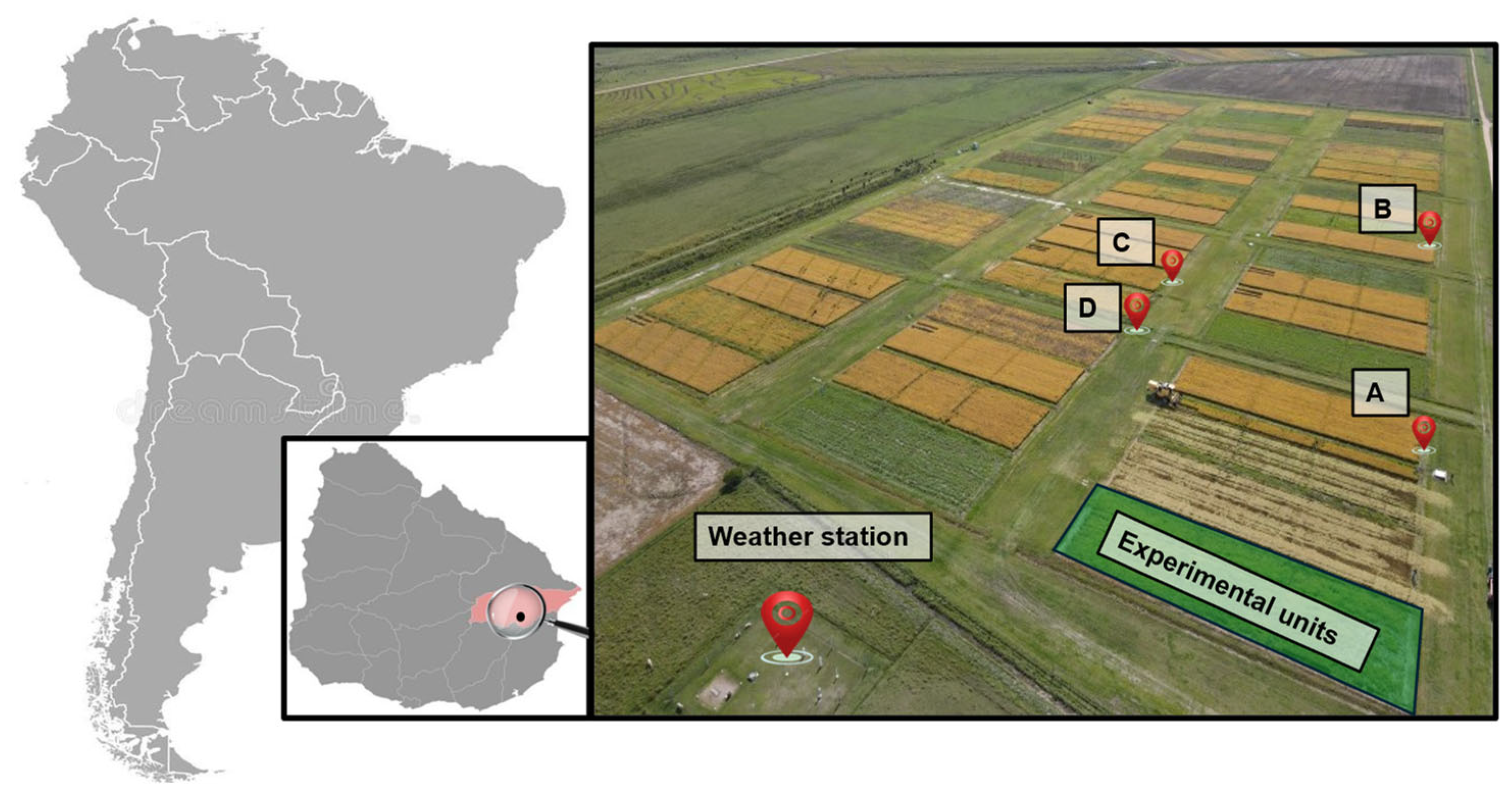
2.1. Experimental Site
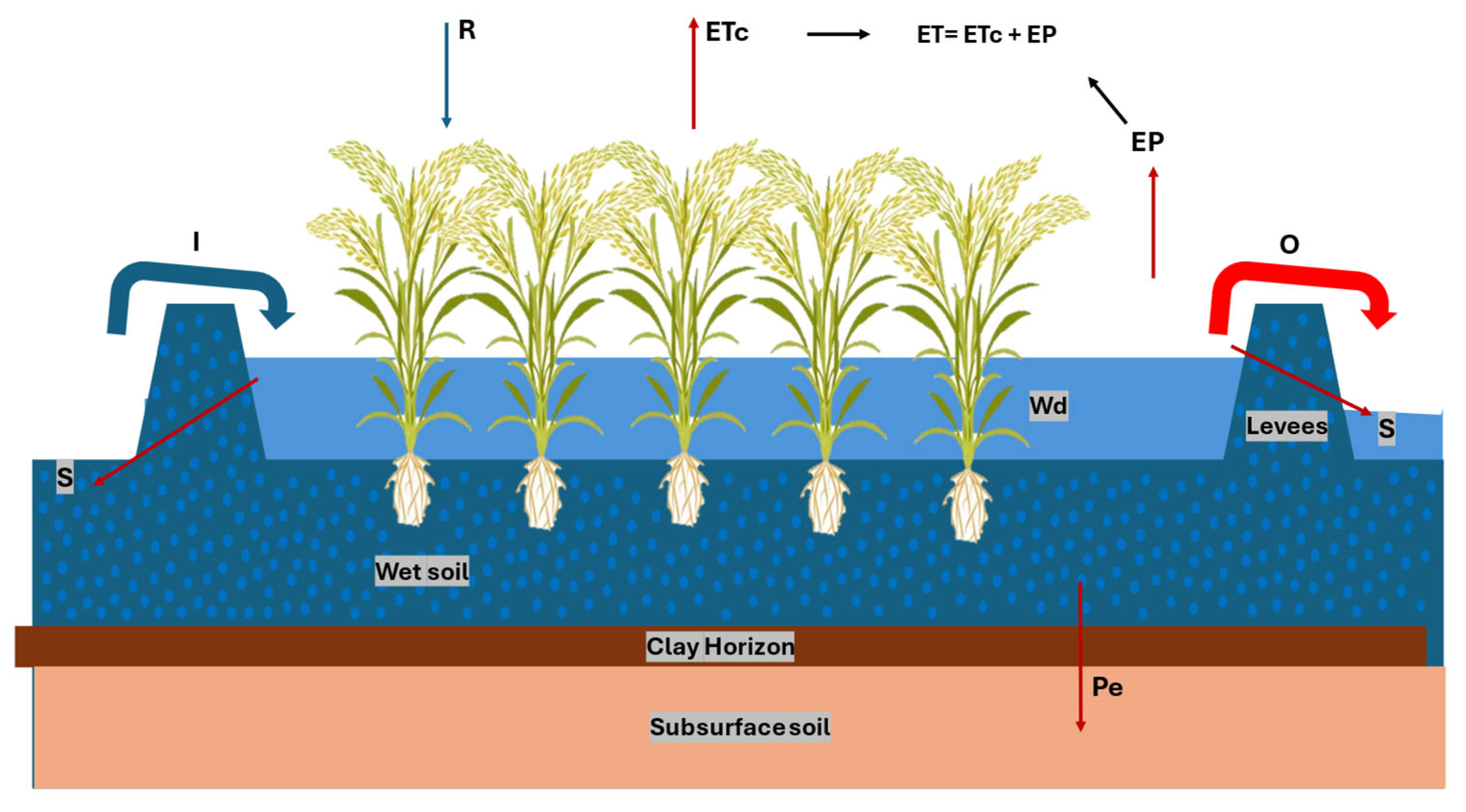
2.2. Water Balance
2.2.1. Water Input
2.2.2. Water Output
2.3. Measurement of Surface Water Outflow
2.4. Calibration and Validation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
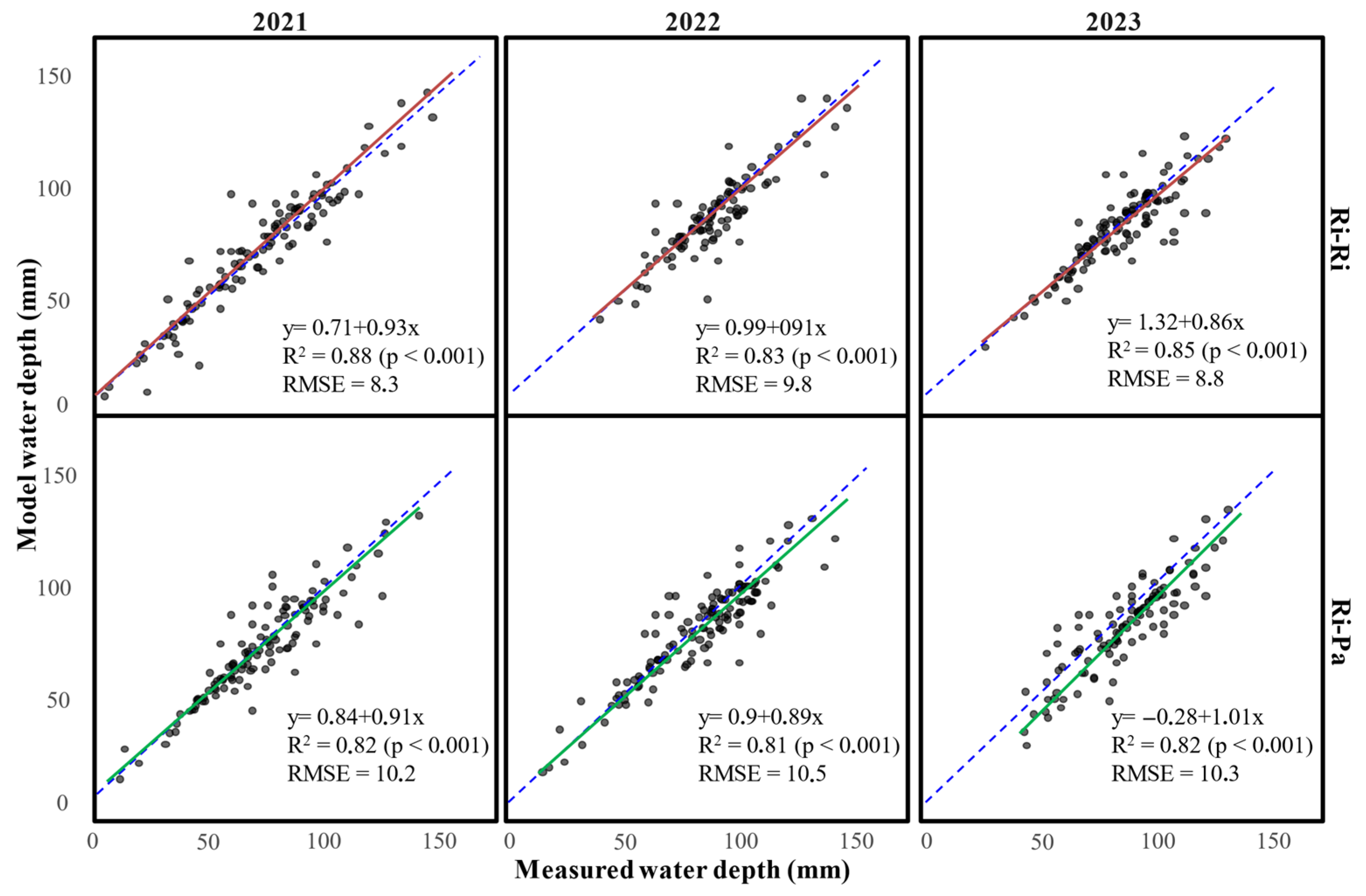
3.1. Observed vs. Estimated Water Layer Depth
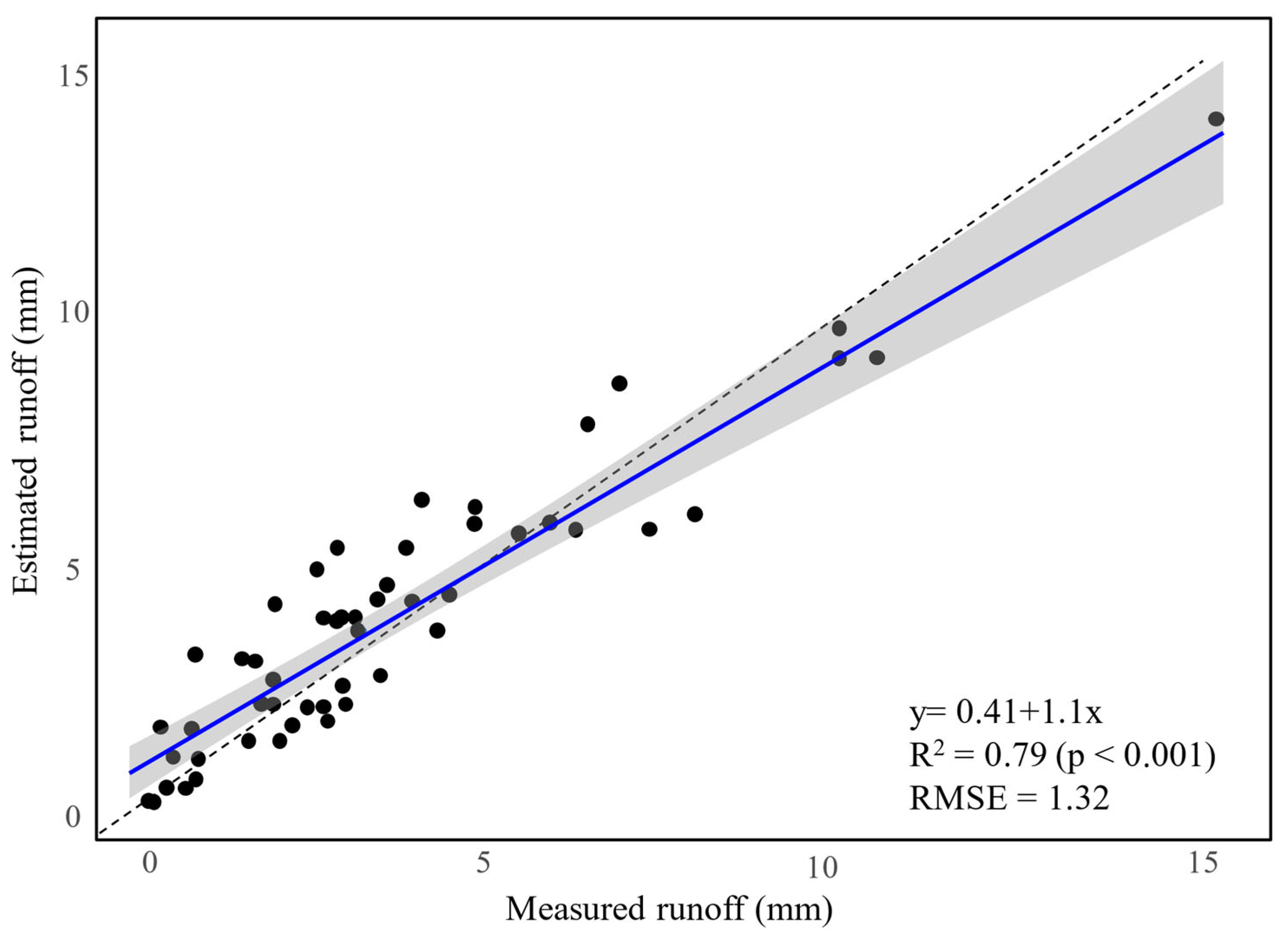
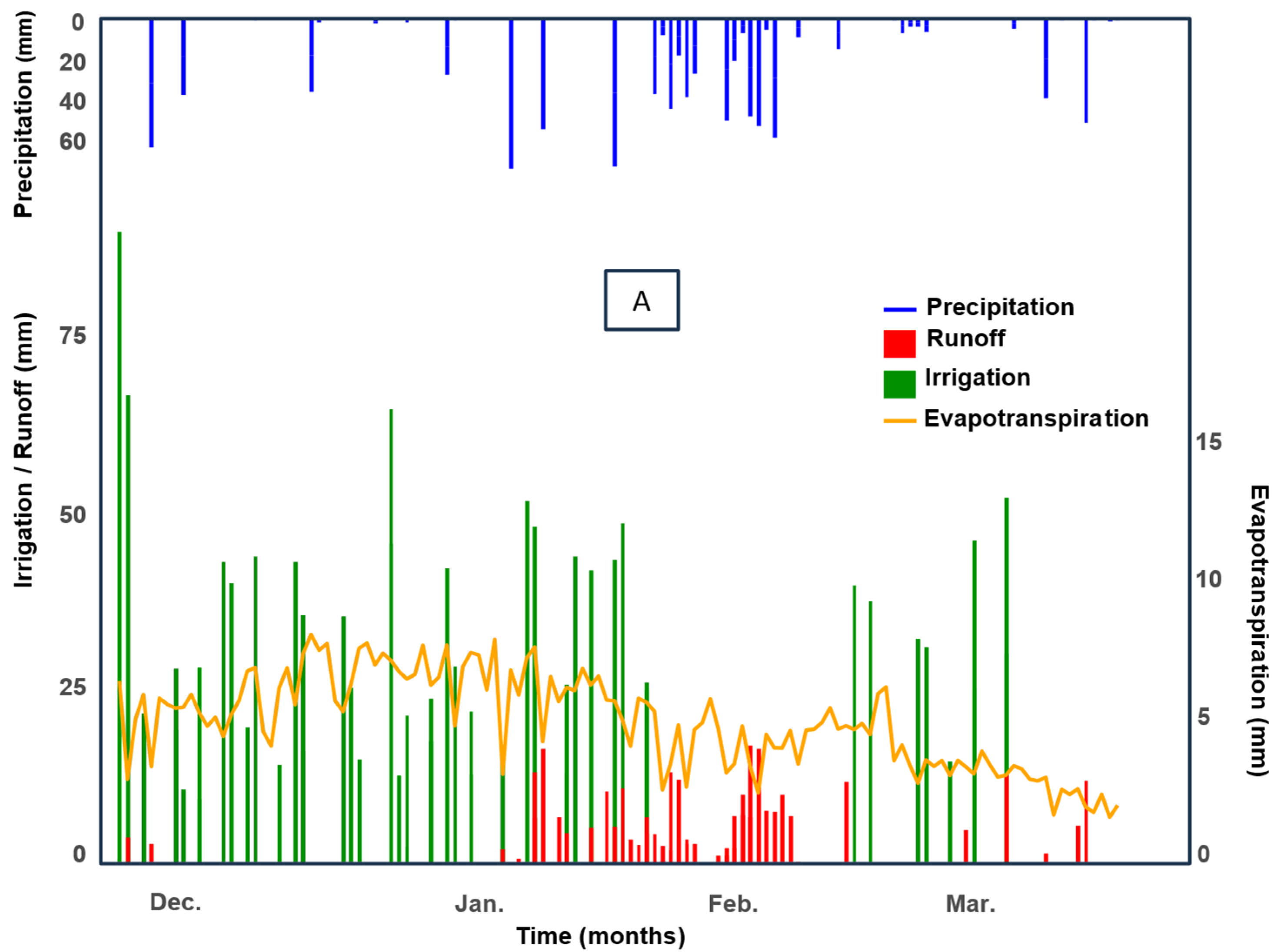
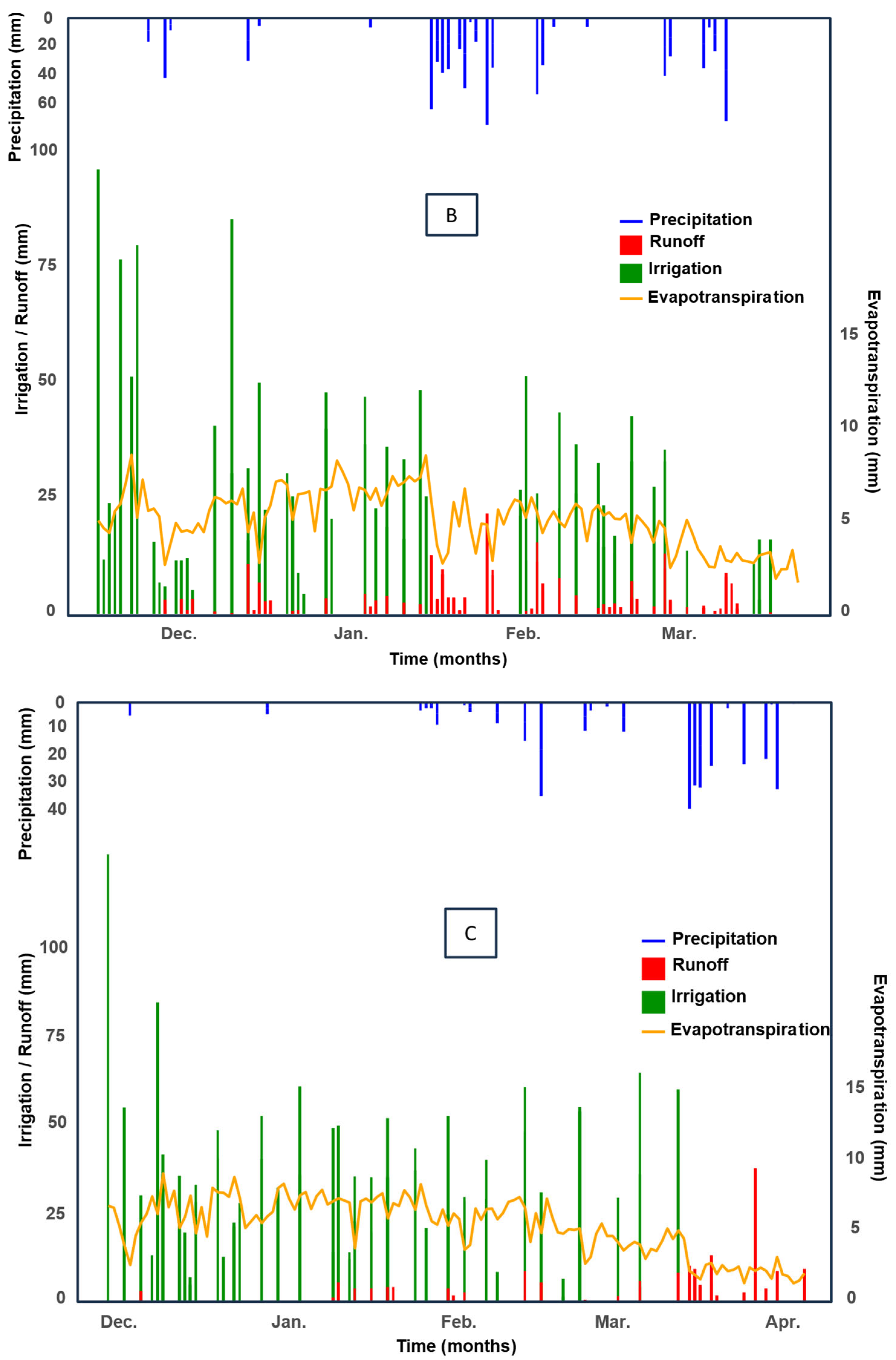
3.2. Estimation of Runoff Using the Water Balance Model
3.3. Analysis of Water Balance Components
3.4. Water Output by Runoff in the Different Rotations
4. Discussion
4.1. Estimation of Runoff Using the Water Balance Model
4.2. Rainfall Runoff
4.3. Surface Runoff Analysis
4.4. Water Output by Runoff in the Different Rotations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aktar, W.; Sengupta, D.; Chowdhury, A. Impact of Pesticides Use in Agriculture: Their Benefits and Hazards. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2009, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beketov, M.A.; Kefford, B.J.; Schäfer, R.B.; Liess, M. Pesticides Reduce Regional Biodiversity of Stream Invertebrates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11039–11043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuong, T.P.; Bouman, B.A.M. Rice Production in Water-Scarce Environments. In Water Productivity in Agriculture: Limits and Opportunities for Improvement; Kijne, J.W., Barker, R., Molden, D., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2003; pp. 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Four Billion People Facing Severe Water Scarcity. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1500323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, R.; Shivay, Y.S.; Kumar, D. Current Status, Challenges, and Opportunities in Rice Production. In Rice Production Worldwide; Chauhan, B.S., Jabran, K., Mahajan, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouman, B.A.M.; Lampayan, R.M.; Tuong, T.P. Water Management in Irrigated Rice: Coping with Water Scarcity; International Rice Research Institute: Los Baños, Philippines, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. The Green, Blue and Grey Water Footprint of Crops and Derived Crop Products. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1577–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouman, B.A.M.; Feng, L.; Tuong, T.P.; Lu, G.; Wang, H.; Feng, Y. Exploring Options to Grow Rice Using Less Water in Northern China Using a Modelling Approach: II. Quantifying Yield, Water Balance Components, and Water Productivity. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 88, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesi, C.; Chauhan, B.S. The Efficacy of Chemical Options to Control Echinochloa Crus-Galli in Dry-Seeded Rice under Alternative Irrigation Management and Field Layout. Crop Prot. 2019, 118, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, B.W.; Gaydon, D.S. Rice Growth, Yield and Water Productivity Responses to Irrigation Scheduling Prior to the Delayed Application of Continuous Flooding in South-East Australia. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 1799–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamishe, Y.; Cartwright, R.; Lee, F. Management of Rice Diseases. In Arkansas Rice Production Handbook; University of Arkansas: Little Rock, AR, USA, 2013; pp. 126–133. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, R.L.; Angus, J.F. Deep Floodwater Protects High-Nitrogen Rice Crops from Low-Temperature Damage. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 1994, 34, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiuchi, S.; Yamauchi, T.; Takahashi, H.; Kotula, L.; Nakazono, M. Mechanisms for Coping with Submergence and Waterlogging in Rice. Rice 2012, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Stanley, E.H.; Zanden, M.J.V. State of the World’s Freshwater Ecosystems: Physical, Chemical, and Biological Changes. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2011, 36, 75–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A. Managing Agricultural Phosphorus to Minimize Water Quality Impacts. Sci. Agric. 2016, 73, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R.; Huang, C.; Haney, R.L. Phosphorus Fertilization, Soil Stratification, and Potential Water Quality Impacts. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 72, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.R.; Caraco, N.F.; Correll, D.L.; Howarth, R.W.; Sharpley, A.N.; Smith, V.H. Nonpoint Pollution of Surface Waters with Phosphorus and Nitrogen. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oesterheld, M. Impacto de La Agricultura Sobre Los Ecosistemas: Fundamentos Ecológicos y Problemas Más Relevantes. Ecol. Austral. 2008, 18, 337–346. [Google Scholar]
- Khoramdel, S.; Shabahang, J.; Amin Ghafouri, A. Evaluation of Environmental Impacts for Rice Agroecosystems Using Life Cycle Assessment (LCA). Iran. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, J.J.; Reiler, E.M.; Carazo, E.; Matarrita, J.; Muñoz, A.; Cedergreen, N. Influence of Rice Field Agrochemicals on the Ecological Status of a Tropical Stream. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battello, C.; Uraga, R.; Gonnet, D.; Hill, M.; Roel, A. Guía de Buenas Prácticas En El Cultivo de Arroz En Uruguay. Guía de Buenas Prácticas en el Cultivo de Arroz en Uruguay; Asociación Cultivadores de Arroz (ACA), Gremial de Molinos Arroceros (GMA), Universidad de la República–Facultad de Agronomía (UDELAR), Instituto Nacional de Investi-gación Agropecuaria (INIA), Laboratorio Tecnológico del Uruguay (LATU): Montevideo, Uruguay, 2009; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Böcking, B.; Bandeira, S.; Carnelli, J.P.; García, C.; Marella, M.; Marco, M.; Moor, J.C.; Henderson, P.; Gusonni, A.; Lavecchia, A. Riego Intermitente una Alternativa que Debemos ir Incorporando en Nuestros Sistemas de Riego. Resumen de Tres Años de Trabajos Sobre el Tema. Resultados Experimentales Arroz Zafra 2007–2008; (INIA Serie Actividades de Difusión; 543); INIA: Tacuarembó, Uruguay, 2008; pp. 73–96. [Google Scholar]
- Roel, A.; Cantou, G.; Martinez, S.; Casales, L.; Campos, F.; Falero, I. Manejo Del Riego: Productividad Del Agua. INIA. Treinta y Tres. Arroz: Resultados Experimentales 2010–2011; (INIA Serie Actividades de Difusión; 651); INIA: Treinta y Tres, Uruguay, 2011; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Lavecchia, A.; Marchesi, C.; CAsanova, S. Manejo Del Cultivo: Riego. Resultados Experimentales de Arooz Zafra 2010–2011; (INIA Serie Actividades de Difusión; 652); INIA: Artigas/Tacuarembó, Uruguay, 2011; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Riccetto, S.; Capurro, M.C.; Roel, Á. Estrategias para minimizar el consumo de agua del cultivo de arroz en Uruguay manteniendo su productividad. Agrociencia Urug. 2017, 21, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlomagno, M.; Mathó, C.; Cantou, G.; Sanborn, J.R.; Last, J.A.; Hammock, B.D.; Roel, A.; González, D.; González-Sapienza, G. A Clomazone Immunoassay To Study the Environmental Fate of the Herbicide in Rice (Oryza sativa) Agriculture. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4367–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gonzales, B.; Santos, I.; Pareja, L.; Roel, A.; Cantou, G.; Perez-Parada, A. Surface Runoff and Decay of Glyphosate in Experimental Rice Fields. In Proceedings of the Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (SETAC) Latin America 15th Biennial Meeting, Montevideo, Uruguay, 17–20 September 2023; p. 384. [Google Scholar]
- Counce, P.A.; Keisling, T.C.; Mitchell, A.J. A Uniform, Objective, and Adaptive System for Expressing Rice Development. Crop Sci. 2000, 40, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carracelas, G.; Hornbuckle, J.; Rosas, J.; Roel, A. Irrigation Management Strategies to Increase Water Productivity in Oryza sativa (Rice) in Uruguay. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 222, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; De Maio, M.; Vidotto, F.; Sacco, D. Influence of Wet-Dry Cycles on the Temporal Infiltration Dynamic in Temperate Rice Paddies. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 154, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belder, P.; Bouman, B.A.M.; Cabangon, R.; Guoan, L.; Quilang, E.J.P.; Yuanhua, L.; Spiertz, J.H.J.; Tuong, T.P. Effect of Water-Saving Irrigation on Rice Yield and Water Use in Typical Lowland Conditions in Asia. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 65, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouman, B.A.M.; Peng, S.; Castañeda, A.R.; Visperas, R.M. Yield and Water Use of Irrigated Tropical Aerobic Rice Systems. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 74, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhir-Yadav; Humphreys, E.; Kukal, S.S.; Gill, G.; Rangarajan, R. Effect of Water Management on Dry Seeded and Puddled Transplanted Rice: Part 2: Water Balance and Water Productivity. Field Crops Res. 2011, 120, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linquist, B.; Snyder, R.; Anderson, F.; Espino, L.; Inglese, G.; Marras, S.; Moratiel, R.; Mutters, R.; Nicolosi, P.; Rejmanek, H.; et al. Water Balances and Evapotranspiration in Water- and Dry-Seeded Rice Systems. Irrig. Sci. 2015, 33, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Su, B.; Wang, H.; He, J.; Yang, Y. Analysis of the Water Balance and the Nitrogen and Phosphorus Runoff Pollution of a Paddy Field in Situ in the Taihu Lake Basin. Paddy Water Environ. 2020, 18, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D.M.; Dinerstein, E.; Wikramanayake, E.D.; Burgess, N.D.; Powell, G.V.N.; Underwood, E.C.; D’amico, J.A.; Itoua, I.; Strand, H.E.; Morrison, J.C.; et al. Terrestrial Ecoregions of the World: A New Map of Life on Earth: A New Global Map of Terrestrial Ecoregions Provides an Innovative Tool for Conserving Biodiversity. BioScience 2001, 51, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, A.; Califra, A.; Molfino, J.; Lynn, W. Keys to Soil Taxonomy for Uruguay; USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Macedo, I.; Roel, A.; Velazco, J.I.; Bordagorri, A.; Terra, J.A.; Pittelkow, C.M. Intensification of Rice-Pasture Rotations with Annual Crops Reduces the Stability of Sustainability across Productivity, Economic, and Environmental Indicators. Agric. Syst. 2022, 202, 103488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, F. The Throughfall, Stemflow, and Canopy Interception Loss in Corn and Soybean Fields in Northeast China. Water 2024, 16, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, J.H.; Smith, M.C.; Vieira, D.A.N.; Adviento-Borbe, M.A.; Reba, M.L.; Vories, E.D. Expected Irrigation Reductions Using Multiple-Inlet Rice Irrigation under Rainfall Conditions of the Lower Mississippi River Valley. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2018, 144, 04018016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, F.; Chebataroff, N.; Deambrosi, E.; Blanco, P.; Ávila, S.; Lavecchia, A.; Yang, C.; Wang, W. Riego. In Arroz-Soja: Resultados de La Experimentación Regional En Cultivos. 1983–1984; CIAAB, EEE: Treinta y Tres, Uruguay, 1984; pp. 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Koolhaas, M. Embalses agrícolas. Diseño y Construcción; Editorial Hemisferio Sur: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hamby, D.M. A Review of Techniques for Parameter Sensitivity Analysis of Environmental Models. Environ. Monit. Assess. 1994, 32, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, R.; Pereira, L.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements—FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; p. 333. [Google Scholar]
- Indata. Home—INDATA URUGUAY. Available online: https://indata.uy/ (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- Khepar, S.D.; Yadav, A.K.; Sondhi, S.K.; Siag, M. Water Balance Model for Paddy Fields under Intermittent Irrigation Practices. Irrig. Sci. 2000, 19, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; Grolemund, G. R for Data Science: Import, Tidy, Transform, Visualize, and Model Data, 1st ed.; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Sebastopol, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- GRAS INIA. GRAS- Banco de Datos Agroclimáticos|INIA. Available online: http://www.inia.uy/gras/Clima/Banco-datos-agroclimatico (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Odhiambo, L.O.; Murty, V.V.N. Modeling Water Balance Components in Relation to Field Layout in Lowland Paddy Fields. I. Model Development. Agric. Water Manag. 1996, 30, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.-H.; Yoon, G.; Ham, H.; Jung, W. Model Development for Nutrient Loading Estimates from Paddy Rice Fields in Korea. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2004, 39, 845–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinaga, I.; Miura, A.; Hitomi, T.; Hamada, K.; Shiratani, E. Runoff Nitrogen from a Large Sized Paddy Field during a Crop Period. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 87, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xie, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Yan, X.; Xing, G.; Zhu, Z. Nitrogen Fate and Environmental Consequence in Paddy Soil under Rice-Wheat Rotation in the Taihu Lake Region, China. Plant Soil 2009, 319, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, B.; Elsenbeer, H.; De Moraes, J.M. The Influence of Land-Use Changes on Soil Hydraulic Properties: Implications for Runoff Generation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 222, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Sand 1 (%) | 18 |
| Silt 1 (%) | 49 |
| Clay 1 (%) | 33 |
| Textural class | Silty clay |
| Bulk density 2 (g cm−3) | 1.5 |
| pH | 6.2 |
| Organic carbon (%) | 1.6 |
| N (%) | 0.14 |
| P Bray 1 (µg P/g) 3 | 7.8 |
| K (meq/100 gr) | 0.17 |
| 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar Radiation (KJ m−2 d−1) | 20,630 ± 5188 | 20,355 ± 5320 | 20,501 ± 5062 |
| Minimum temperature (degrees Celsius) | 15.5 ± 3.9 | 15.7 ± 4.1 | 16.2 ± 4.2 |
| Maximum temperature (degrees Celsius) | 27.8 ± 3.3 | 28.1 ± 4.0 | 30.2 ± 4.1 |
| Medium temperature (degrees Celsius) | 21.1 ± 2.6 | 21.5 ± 3.0 | 22.5 ± 3.1 |
| Total Precipitation (mm) | 667 | 556 | 282 |
| Class A Evaporation Pan “Tank A” (mm d−1) | 6.4 ± 2.7 | 6.5 ± 2.9 | 7.5 ± 3.1 |
| Eto Penman–Monteith (mm d−1) | 4.2 ± 1.2 | 4.1 ± 1.1 | 4.6 ± 1.2 |
| Wind speed (m s−1) | 2.3 ± 1.1 | 2.1 ± 0.9 | 2.4 ± 1.1 |
| 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Irrigation | 752 ± 96 | 967 ± 125 | 1076 ± 48 |
| Effective precipitation | 556 | 440 | 190 |
| Evapotranspiration | 646 ± 1.7 | 653 ± 1.5 | 654 ± 1.9 |
| Runoff | 135 ± 9.3 | 153 ± 6.2 | 67 ± 2.7 |
| Final drainage | 99 ± 16 | 61 ± 14 | 29 ± 16 |
| Percolation | 127 | 128 | 119 |
| Soil moisture variation * | −60 | −62 | −65 |
| Seepage | 38 | 38 | 36 |
| 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | Average | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total runoff (mm) | 234 | 214 | 96 | 181 |
| Runoff from irrigation (%) | 22 | 37 | 33 | 31 |
| Runoff from precipitation (%) | 35 | 34 | 37 | 35 |
| Final drainage (%) | 43 | 29 | 30 | 34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rivero, D.; Cantou, G.; Hayashi, R.; Alonso, J.; Oxley, M.; Menta, A.; González-Barrios, P.; Roel, Á. Surface Water Runoff Estimation of a Continuously Flooded Rice Field Using a Daily Water Balance Approach—An Irrigation Assessment. Water 2025, 17, 2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142069
Rivero D, Cantou G, Hayashi R, Alonso J, Oxley M, Menta A, González-Barrios P, Roel Á. Surface Water Runoff Estimation of a Continuously Flooded Rice Field Using a Daily Water Balance Approach—An Irrigation Assessment. Water. 2025; 17(14):2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142069
Chicago/Turabian StyleRivero, Diego, Guillermina Cantou, Raquel Hayashi, Jimena Alonso, Matías Oxley, Agustín Menta, Pablo González-Barrios, and Álvaro Roel. 2025. "Surface Water Runoff Estimation of a Continuously Flooded Rice Field Using a Daily Water Balance Approach—An Irrigation Assessment" Water 17, no. 14: 2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142069
APA StyleRivero, D., Cantou, G., Hayashi, R., Alonso, J., Oxley, M., Menta, A., González-Barrios, P., & Roel, Á. (2025). Surface Water Runoff Estimation of a Continuously Flooded Rice Field Using a Daily Water Balance Approach—An Irrigation Assessment. Water, 17(14), 2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142069







