Hydrochemical Characteristics and Formation Mechanisms of Groundwater in the Nanmiao Emergency Groundwater Source Area, Yichun, Western Jiangxi, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
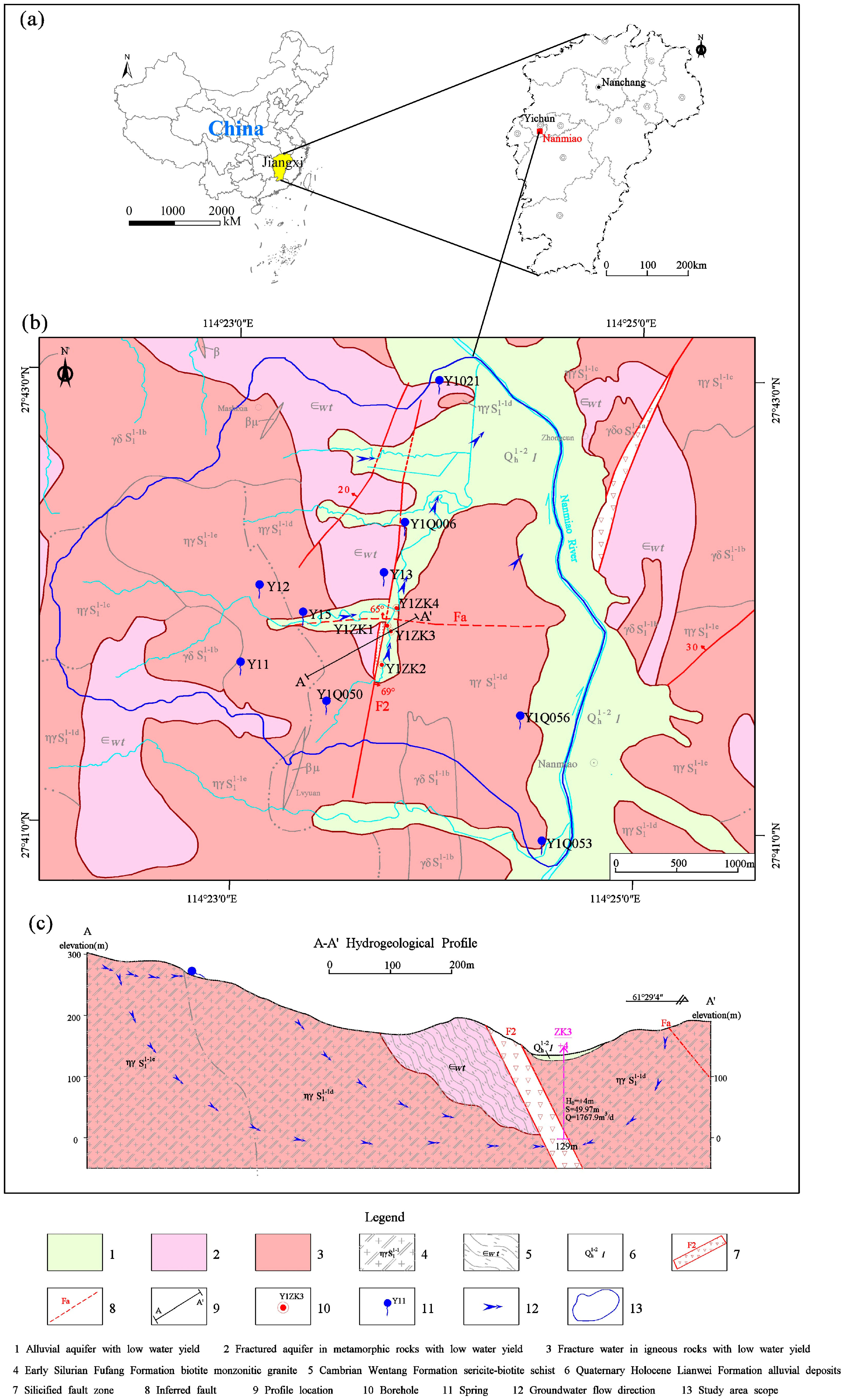
2. Study Area
2.1. Location, Climate and Hydrologic Features
2.2. Geological Setting and Hydrogeology
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Field Sampling and Analytical Techniques
3.2. Data Quality Reliability Test
3.3. Research Methods
4. Results
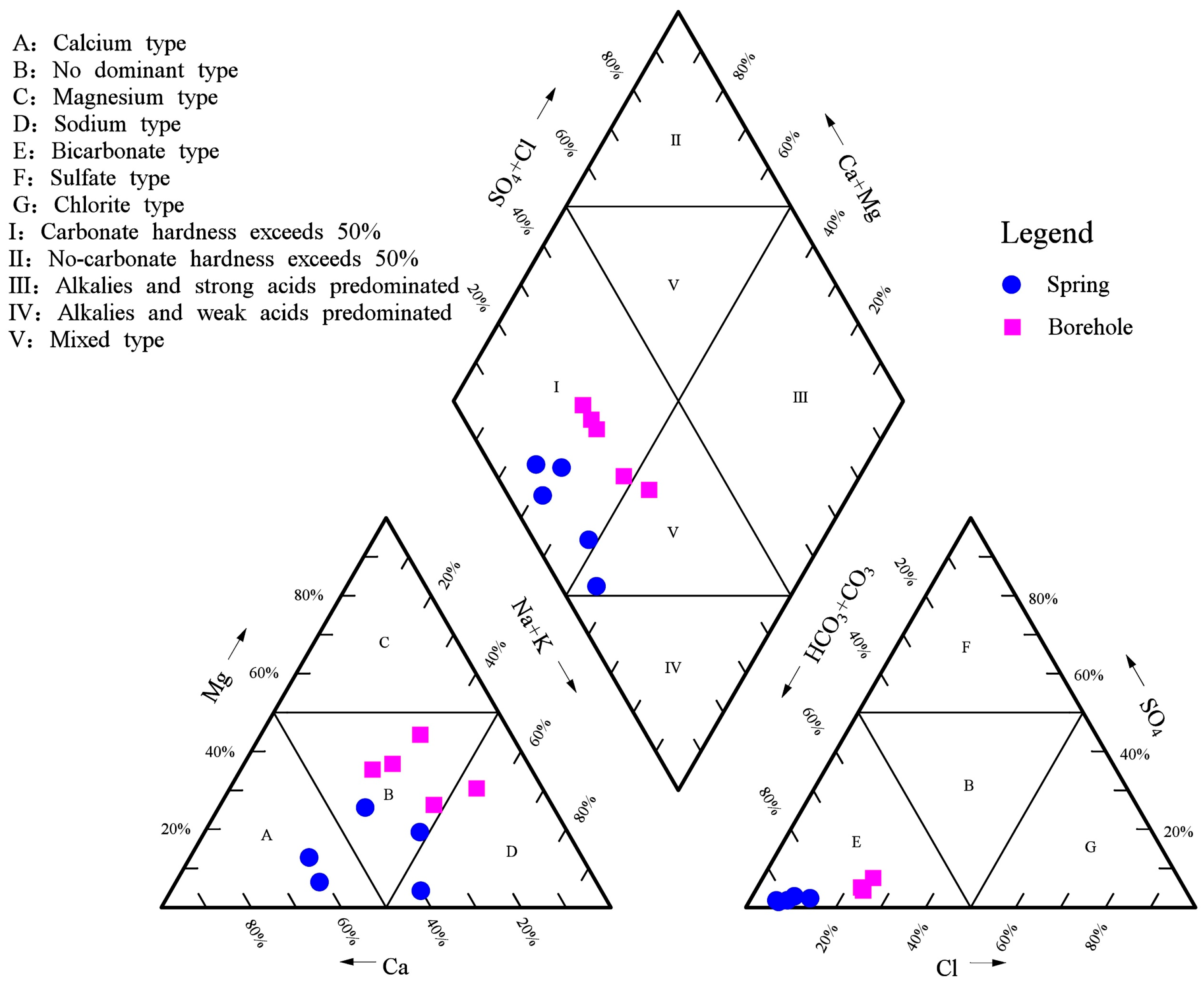
4.1. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Types
4.1.1. Characteristics of Hydrochemical Components
4.1.2. Characteristics of Hydrochemical Types
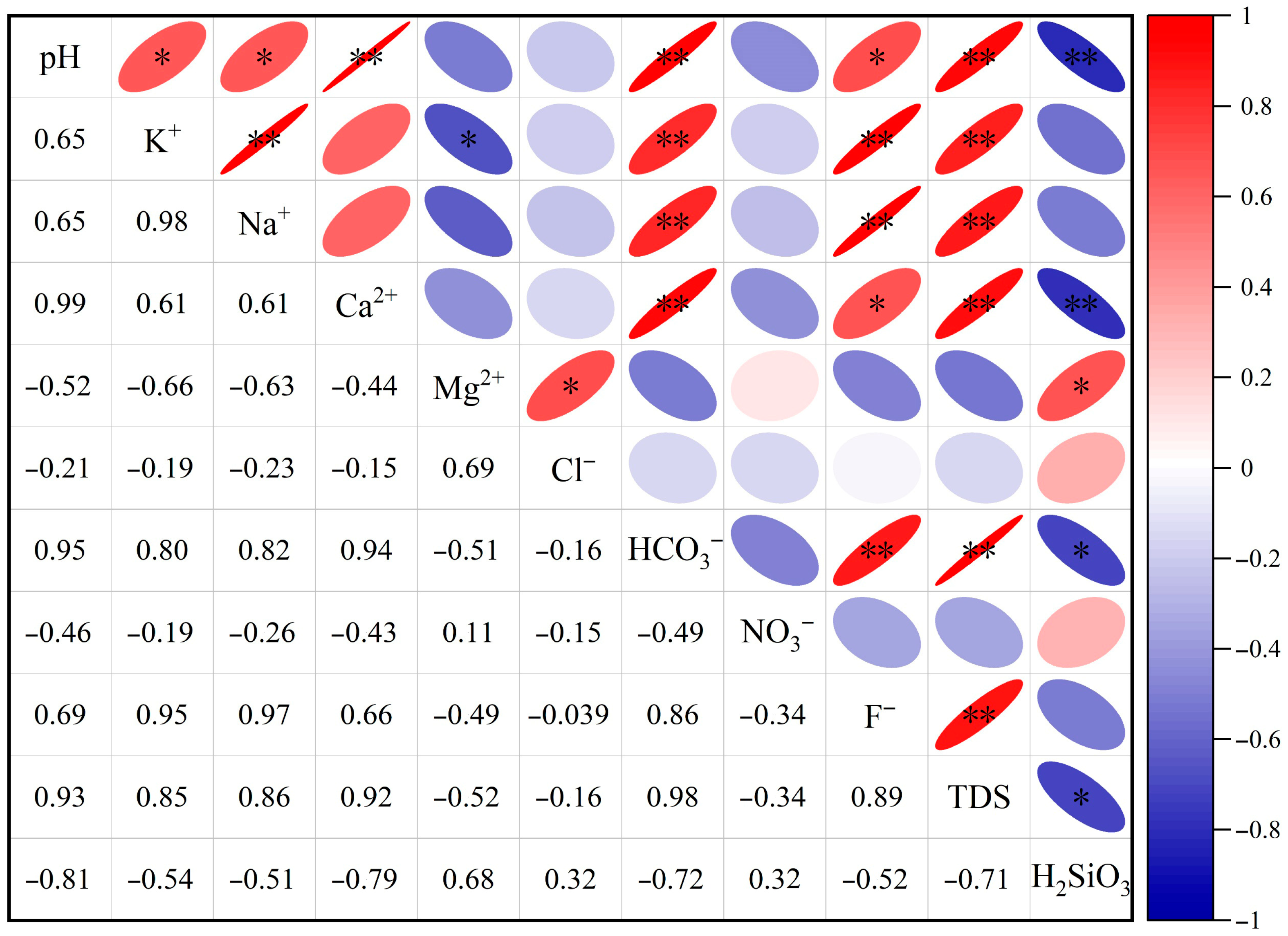
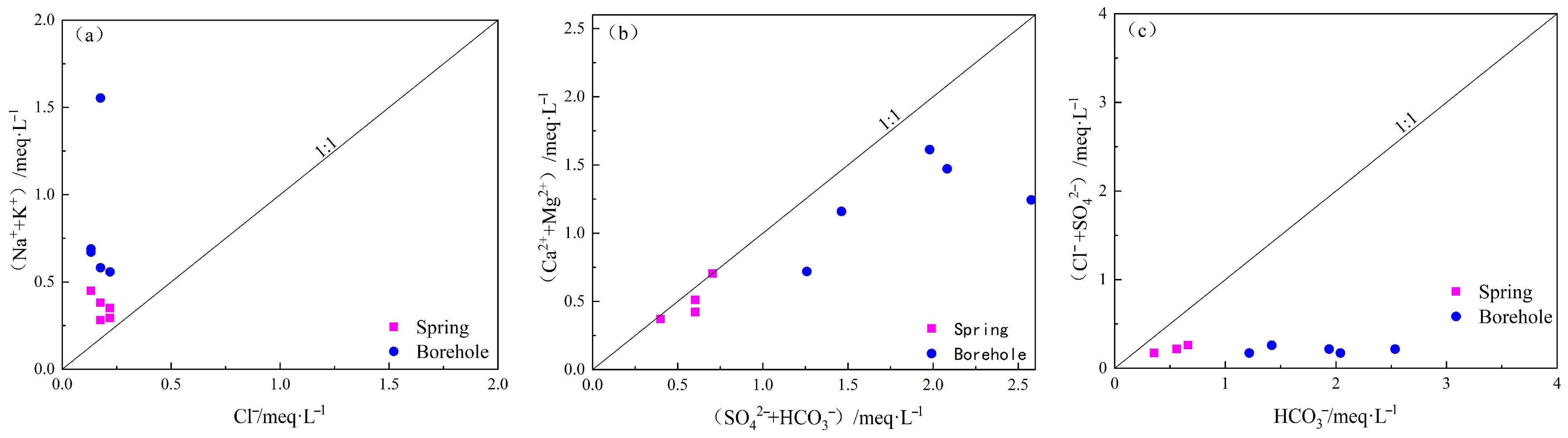
4.1.3. Ion Correlation Analysis
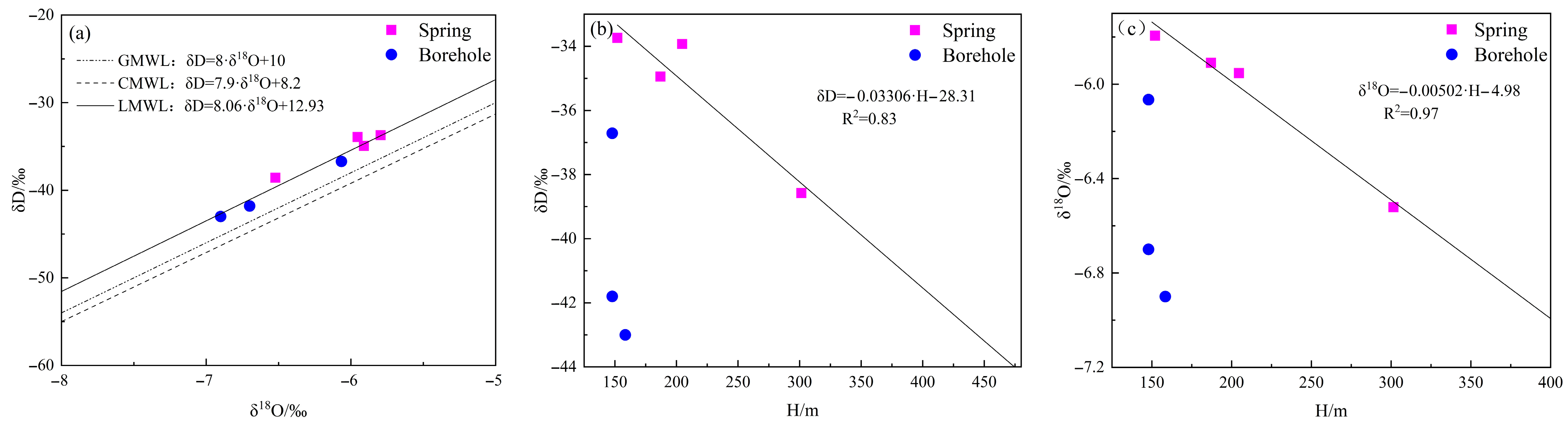
4.1.4. Characteristics of Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes
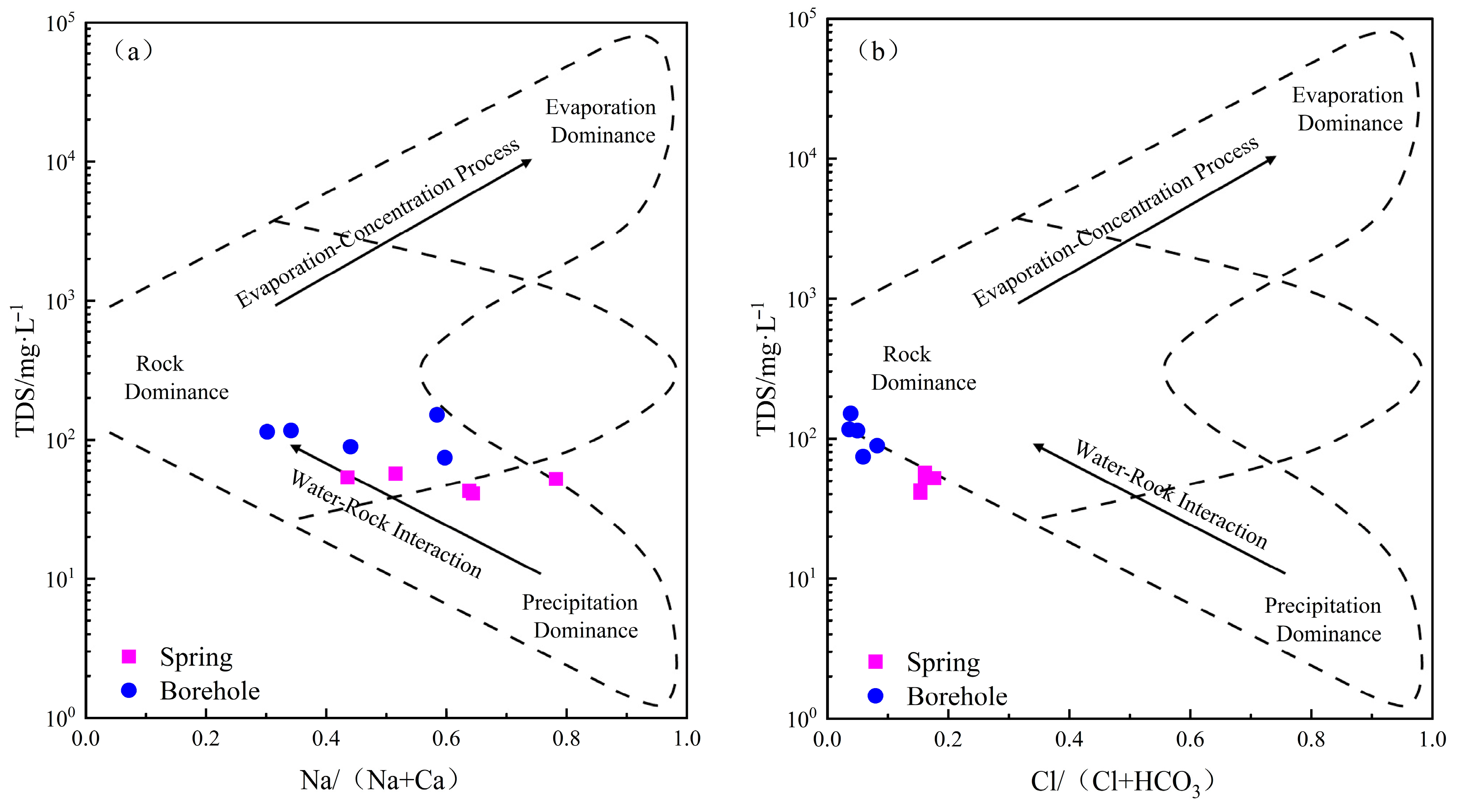
4.2. Analysis of the Causes of Hydrochemical Characteristics
5. Discussion
5.1. Hydrochemical Genesis Mechanisms of Groundwater
5.1.1. Leaching Effect
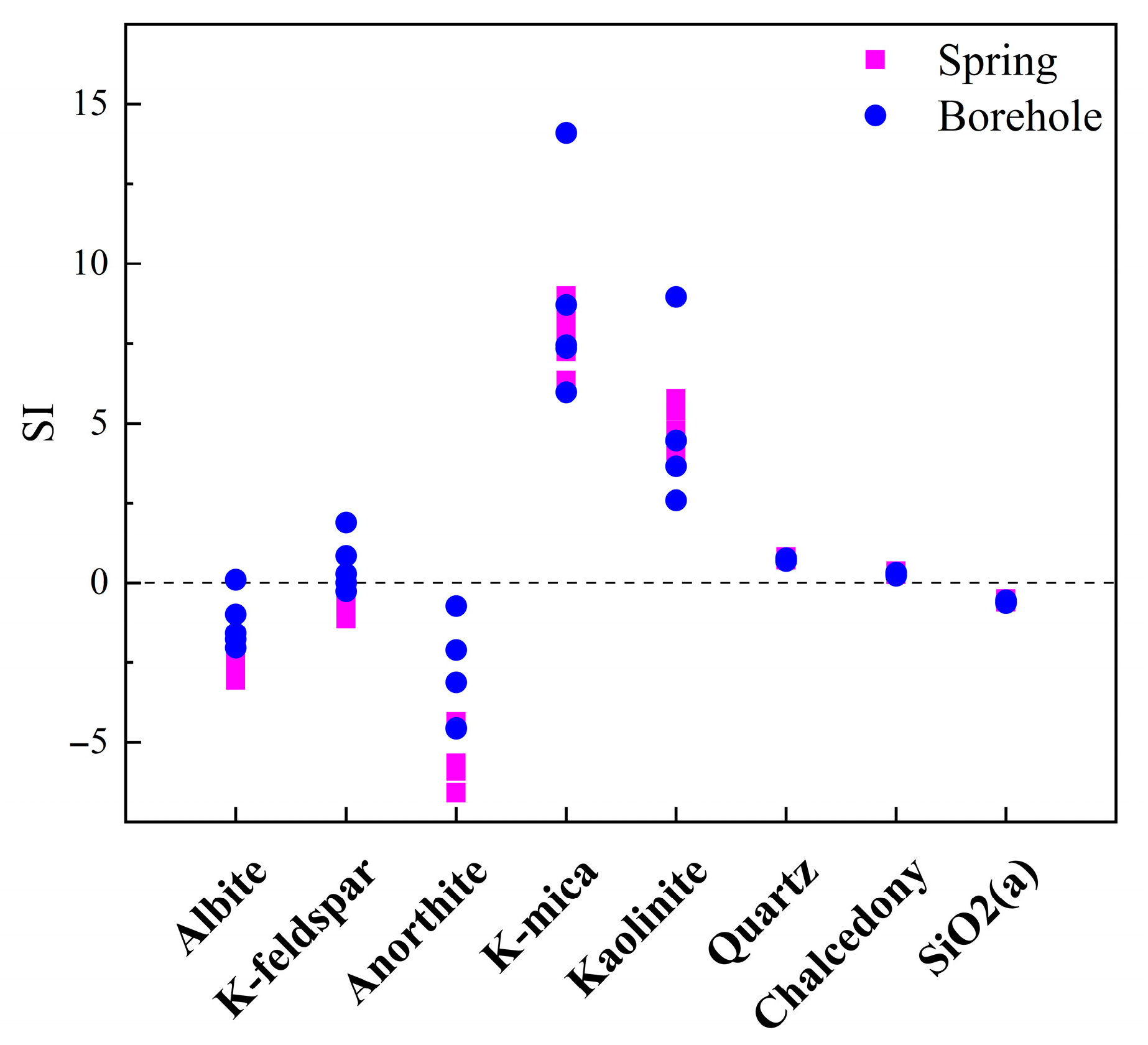
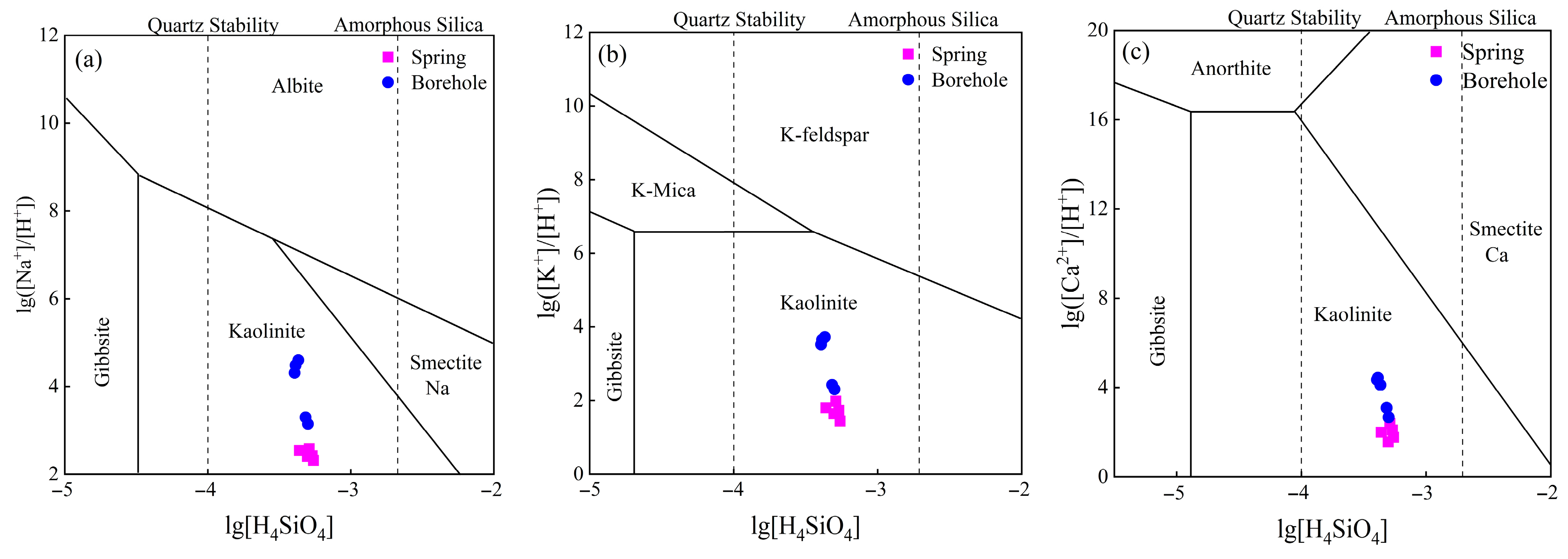
5.1.2. Mineral Dissolution Equilibrium
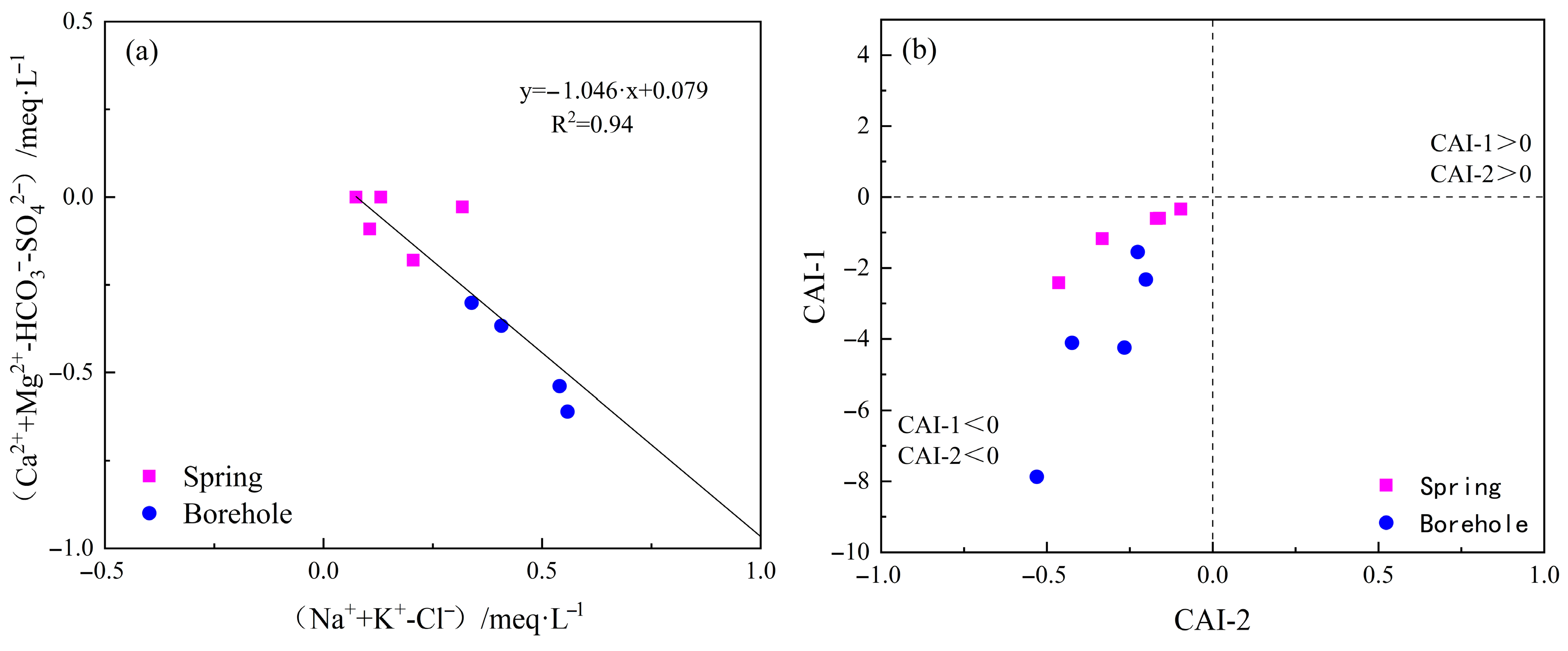
5.1.3. Cation Exchange Effect
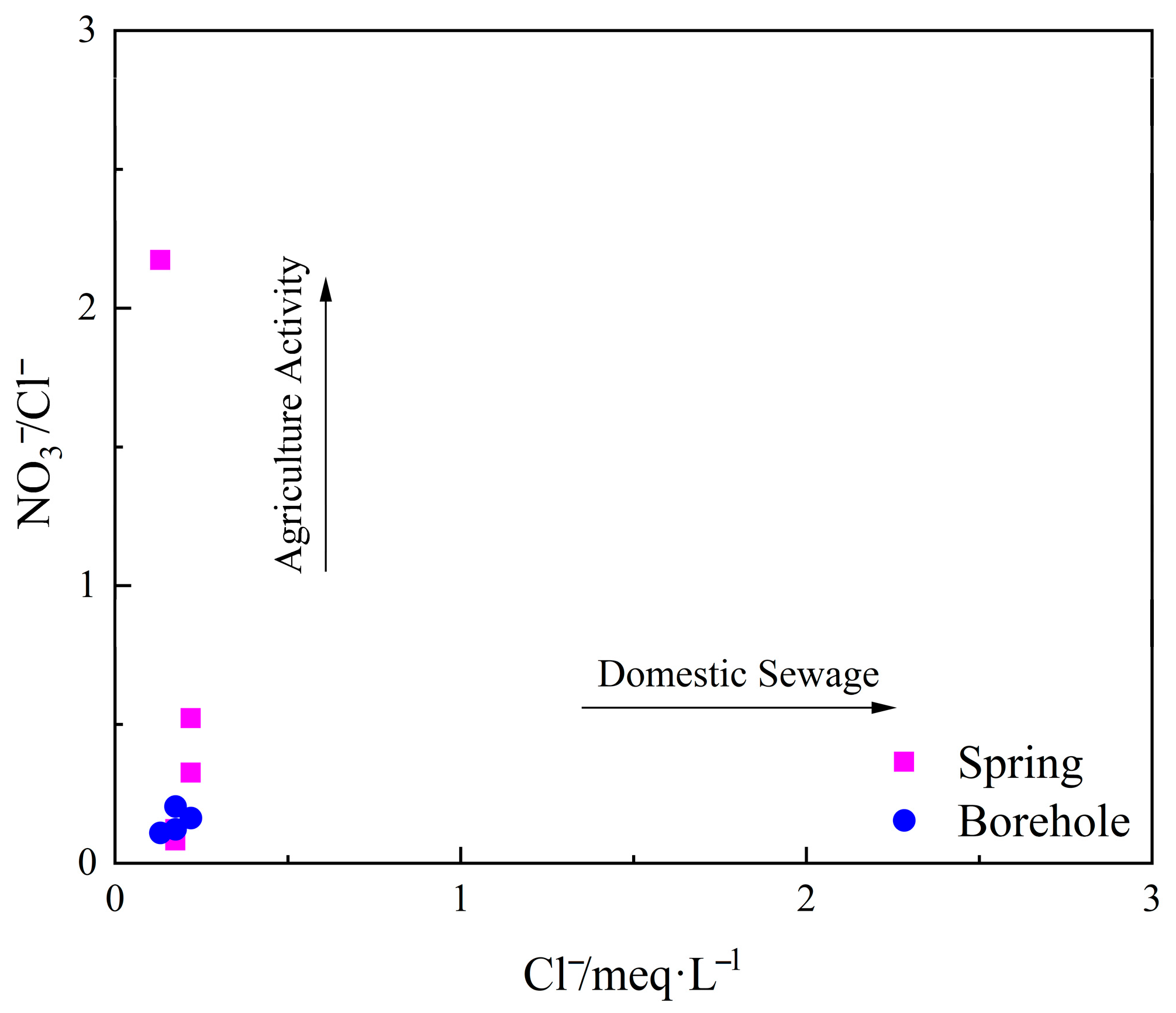
5.1.4. Impact of Human Activities
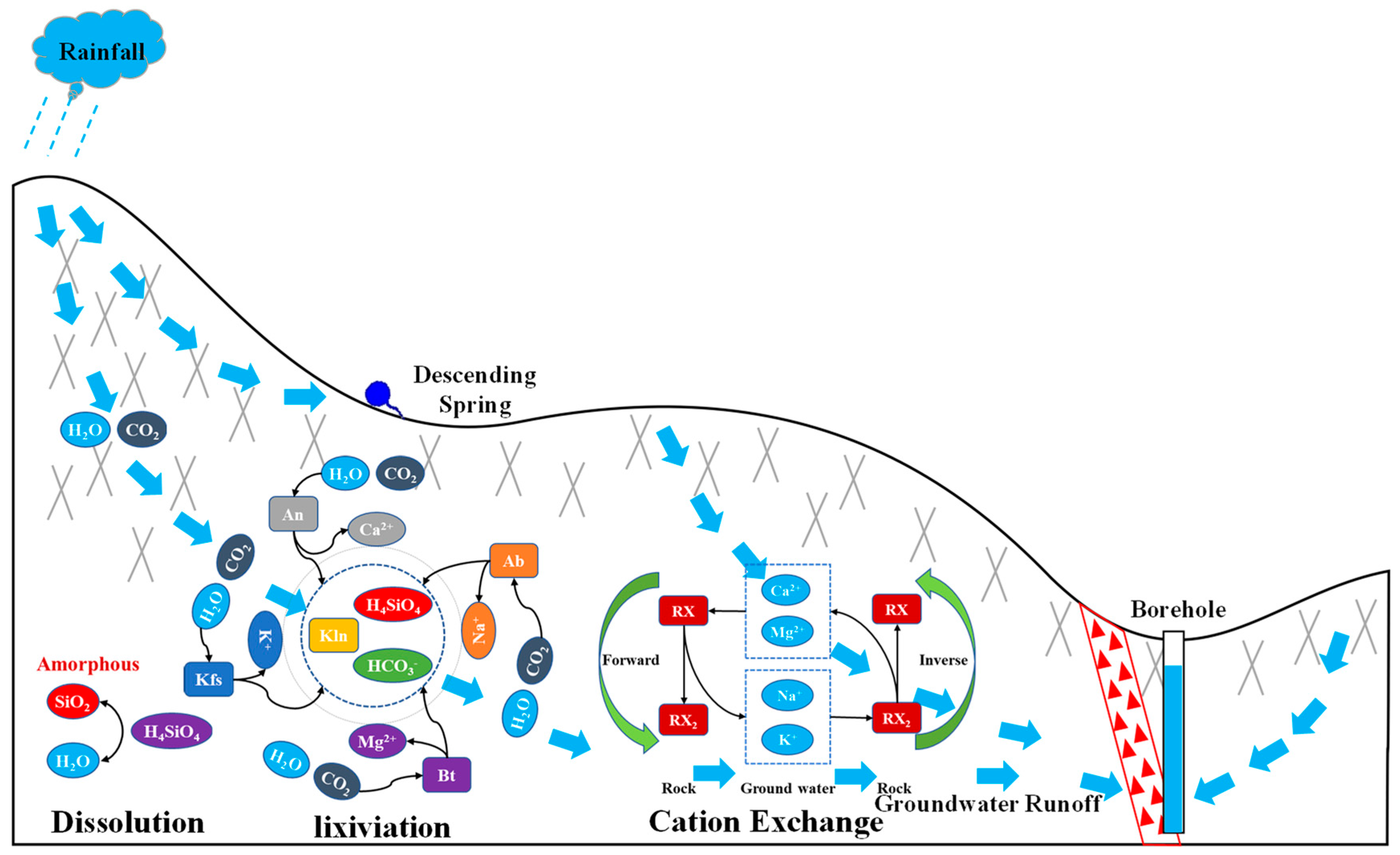
5.2. Conceptual Model for the Formation of Regional Groundwater Hydrochemical Characteristics
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, J.; Liu, X.; Jasechko, S.; Berghuijs, W.R.; Wang, K.; Liu, C.; Reichstein, M.; Jung, M.; Koirala, S. Majority of global river flow sustained by groundwater. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, T.; Befus, K.M.; Jasechko, S.; Luijendijk, E.; Cardenas, M.B. The global volume and distribution of modern groundwater. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 9, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wu, Z.; Wang, P.; Wu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Guan, X.; Xu, H.; et al. Plant-groundwater interactions in drylands: A review of current research and future perspectives. Agr. For. Meteorol. 2023, 341, 109636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Roderick, M.L.; Yang, D.; Wang, Z.; Ruan, F.; McVicar, T.R.; Zhang, S.; Beck, H.E. Streamflow stationarity in a changing world. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 064096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarini, G.; Wasko, C. Humans, climate and streamflow. Upsala J. Med. Sci. 2021, 11, 725–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, M.M. Floods and droughts are intensifying globally. Nat. Water 2023, 1, 226–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Wang, Y.; Ji, P.; Wu, P.; Sheffield, J.; Otkin, J.A. A global transition to flash droughts under climate change. Science 2023, 380, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Shao, J.; Qiu, H. Characteristics and countermeasures of summer and autumn drought in the Yangtze River Basin in 2022. China Flood Drought Manag. 2023, 33, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Y.; Lyu, J.; Su, Z.; Gao, H.; Dong, R. Analysis and thinking on Summer-Autumn drought in the Yangtze River Basin in 2022. China Flood Drought Manag. 2023, 33, 30–33, 66. [Google Scholar]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Fakhreddine, S.; Rateb, A.; de Graaf, I.; Famiglietti, J.; Gleeson, T.; Grafton, R.Q.; Jobbagy, E.; Kebede, S.; Kolusu, S.R.; et al. Global water resources and the role of groundwater in a resilient water future. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrba, J.; Renaud, F.G. Overview of groundwater for emergency use and human security. Hydrogeol. J. 2016, 24, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Xia, C.; Zhang, W.; Meng, X.; Meng, J. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanisms of groundwater in west Zoucheng City, Shandong Province, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, J.; Wang, P.; Wang, T.; Li, Y. Groundwater-fed oasis in arid Northwest China: Insights into hydrological and hydrochemical processes. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 126154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C. Groundwater recharge and hydrogeochemical evolution in the Ejina Basin, northwest China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Xiao, C.; Liang, X.; Wu, S. Influences of pH and CO2 on the formation of Metasilicate mineral water in Changbai Mountain, Northeast China. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1657–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, X. Source and influencing factors of metasilicic acid in mixed geothermal waters. Geothermics 2024, 123, 103098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Jia, C.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z. Characteristics and genesis of high-quality metasilicate mineral water in Liaocheng City, Shandong Province. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Sun, X.; Wei, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, W.; Huang, X.; Li, X.; Yin, Z.; Liu, W. Formation mechanism of metasilicate mineral water in Chengde, Hebei Province: Evidence from rock weathering and water-rock interaction. Geol. China 2022, 49, 1088–1113. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B. Characteristics and genetic analysis of Meiying metasilicic acid mineral water in Zhao’an County, Fujian Province. Miner. Resour. Geol. 2025, 39, 322–334. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Jin, M.; Wang, J. Insights into groundwater salinization from hydrogeochemical and isotopic evidence in an arid inland basin. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 3108–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, S.; Fu, Y. Demonstration on Emergency Groundwater Field in Hongtang Bay, Sanya City of Hainan Province. S. China Geol. 2021, 37, 330–338. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. Hydrogeological Characteristics and Optimal Selection of Groundwater Emergency Water Source in PMain Urban Area of Ningde City, Fujian Province. Geol. Fujian 2020, 39, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Nan, Y.; Guo, G.; Dai, Y.; Xing Chao, Z.; Yao, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, L. Characteristics of Multi-Timescale Evolution in Water Level Dynamics and Regulation for Safe Water Supply at the Zhangfang Emergency Backup Water Source in Beijing. Geol. Bull. China 2025, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M. Analysis of groundwater exploitation risk and emergency water supply capacity in acertain area of Maoming city. Yunnan Geol. 2024, 43, 567–571. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Luo, Y.; Zeng, C.; Zhong, Q.; Xiao, Z.; Mao, X.; Cao, F. Selenium accumulation in plant foods and selenium intake of residents in a moderately selenium-enriched area of Mingyueshan, Yichun, China. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 116, 105089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Liu, K.; Yan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, J.; Yu, K.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Yu, C. The difference in hydrochemical characteristics of geothermal water between the eastern and western parts of the Wugongshan area and its genetic mechanism. J. Geochem. Explor. 2024, 266, 107575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Yu, S.; Bai, X. Report on the Investigation and Evaluation of Emergency Groundwater Source Sites in Major Cities of Jiangxi Province; Hydrogeological Brigade, Jiangxi Provincial Geological Bureau: Nanchang, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Liu, K.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, J.; Jia, W.; Zhang, S.; Sun, J. Geochemical and Isotopic Techniques Constraints on the Origin, Evolution, and Residence Time of Low-Enthalpy Geothermal Water in Western Wugongshan, China. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2024, 98, 801–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Du, C.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Zheng, Z. Research on Characteristics of Spatial and Temporal Variations of Acid Rain in Jiangxi Province Over the Past Twelve Years and the Impact of Acid Gas Emissions. J. Gannan Norm. Univ. 2024, 45, 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P. The Acid Rain in Jiangxi Province of Hydrogen, Oxygen, Sulfur Isotopecharacteristics and Origin. Master’s Thesis, East China University of Technology, Nanchang, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L. Hydrogeochemistry of Hot Springs in Yichun Area of Jiangxi Province. Master’s Thesis, East China University of Technology, Nanchang, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey, B.D.; Jurgens, B.C.; Belitz, K. Tritium as an Indicator of Modern, Mixed, and Premodern Groundwater Age; U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2019; pp. 2019–5090.
- Telloli, C.; Rizzo, A.; Salvi, S.; Pozzobon, A.; Marrocchino, E.; Vaccaro, C. Characterization of groundwater recharge through tritium measurements. Adv. Geosci. 2022, 57, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Sun, Z.; Jia, L.; Tian, H.; Guo, X.; Du, J.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Jia, L. Formation mechanism of strontium and metasilicic acid groundwater in the Lianhuashan area, Changchun, Jilin Province. Geol. China 2023, 50, 181–191. [Google Scholar]

| Types | Sample Code | pH | K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | CO32− | HCO3− | NO3− | F− | TDS | H2SiO3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unconfined water (descending springs) | Y1021 | 5.98 | 2.30 | 6.70 | 6.30 | 4.67 | 7.78 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 40.45 | 7.09 | 0.04 | 57.23 | 41.93 |
| Y1Q006 | 6.23 | 2.30 | 5.40 | 7.00 | 4.25 | 7.78 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 40.45 | 4.43 | 0.04 | 53.75 | 39.98 | |
| Y1Q050 | 6.05 | 2.30 | 7.40 | 4.20 | 2.55 | 6.22 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 34.23 | 0.89 | 0.04 | 42.82 | 34.07 | |
| Y1Q053 | 5.94 | 1.30 | 5.70 | 3.15 | 4.25 | 6.22 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 34.23 | 1.33 | 0.03 | 41.16 | 42.75 | |
| Y1Q056 | 5.84 | 2.60 | 8.80 | 2.45 | 2.97 | 4.67 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 21.78 | 17.72 | 0.03 | 52.31 | 38.80 | |
| maximum | 6.23 | 2.60 | 8.80 | 7.00 | 4.67 | 7.78 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 40.45 | 17.72 | 0.04 | 57.23 | 42.75 | |
| minimum | 5.84 | 1.30 | 5.40 | 2.45 | 2.55 | 4.67 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 21.78 | 0.89 | 0.03 | 41.16 | 34.07 | |
| mean | 6.01 | 2.16 | 6.80 | 4.62 | 3.74 | 6.53 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 34.23 | 6.29 | 0.04 | 49.45 | 39.51 | |
| variation | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.20 | 0.43 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 1.09 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.09 | |
| Confined water (boreholes) | Y1ZK1 | 7.73 | 3.50 | 13.80 | 26.60 | 1.70 | 4.67 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 124.46 | 0.89 | 0.15 | 116.75 | 32.31 |
| Y1ZK2 | 6.40 | 3.30 | 13.50 | 9.10 | 3.18 | 4.67 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 74.22 | 0.89 | 0.12 | 74.21 | 39.13 | |
| Y1ZK3 a | 7.64 | 3.20 | 11.50 | 26.60 | 3.40 | 6.22 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 118.23 | 2.22 | 0.16 | 114.50 | 31.73 | |
| Y1ZK3 b | 7.49 | 7.20 | 31.50 | 22.40 | 1.49 | 6.22 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 154.62 | 1.33 | 0.50 | 151.07 | 33.69 | |
| Y1ZK4 | 6.63 | 2.60 | 11.30 | 14.35 | 5.31 | 7.78 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 86.59 | 2.22 | 0.18 | 89.24 | 37.72 | |
| maximum | 7.73 | 7.20 | 31.50 | 26.60 | 5.31 | 7.78 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 154.62 | 2.22 | 0.50 | 151.07 | 39.13 | |
| minimum | 6.40 | 2.60 | 11.30 | 9.10 | 1.49 | 4.67 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 74.22 | 0.89 | 0.12 | 74.21 | 31.73 | |
| mean | 7.18 | 3.96 | 16.32 | 19.81 | 3.02 | 5.91 | 2.00 | 0.00 | 111.62 | 1.51 | 0.22 | 109.15 | 34.92 | |
| variation | 0.09 | 0.47 | 0.52 | 0.39 | 0.51 | 0.22 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.29 | 0.45 | 0.71 | 0.27 | 0.10 |
| Types | Sample Code | Sampling Elevation (m) | δ18O (‰) | δD (‰) | 3H (TU) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unconfined water (descending springs) | Y11 | 301.529 | −6.52 | −38.58 | / |
| Y12 | 204.635 | −5.95 | −33.93 | / | |
| Y13 | 152.005 | −5.79 | −33.74 | / | |
| Y15 | 187.067 | −5.91 | −34.94 | / | |
| Confined water (boreholes) | Y14 (Y1ZK4) | 147.840 | −6.07 | −36.71 | 2.5 |
| Y1ZK2 | 158.390 | −6.90 | −43.00 | 2.29 | |
| Y14 (Y1ZK4)-1 | 147.840 | −6.70 | −41.80 | 1.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, S.; Wang, T.; Bai, X.; Chen, G.; Wan, P.; Chen, S.; Chen, Q.; Wan, H.; Deng, F. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Formation Mechanisms of Groundwater in the Nanmiao Emergency Groundwater Source Area, Yichun, Western Jiangxi, China. Water 2025, 17, 2063. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142063
Yu S, Wang T, Bai X, Chen G, Wan P, Chen S, Chen Q, Wan H, Deng F. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Formation Mechanisms of Groundwater in the Nanmiao Emergency Groundwater Source Area, Yichun, Western Jiangxi, China. Water. 2025; 17(14):2063. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142063
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Shengpin, Tianye Wang, Ximin Bai, Gongxin Chen, Pingqiang Wan, Shifeng Chen, Qianqian Chen, Haohui Wan, and Fei Deng. 2025. "Hydrochemical Characteristics and Formation Mechanisms of Groundwater in the Nanmiao Emergency Groundwater Source Area, Yichun, Western Jiangxi, China" Water 17, no. 14: 2063. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142063
APA StyleYu, S., Wang, T., Bai, X., Chen, G., Wan, P., Chen, S., Chen, Q., Wan, H., & Deng, F. (2025). Hydrochemical Characteristics and Formation Mechanisms of Groundwater in the Nanmiao Emergency Groundwater Source Area, Yichun, Western Jiangxi, China. Water, 17(14), 2063. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142063







