Potential Function of Microbial Mats in Regard to Water Chemistry and Carbonate Precipitation in the Alkaline Waterbody Lake Van (Turkey)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geochemical Background
3. Methods
3.1. Sampling Sites
3.2. Analytical Methods
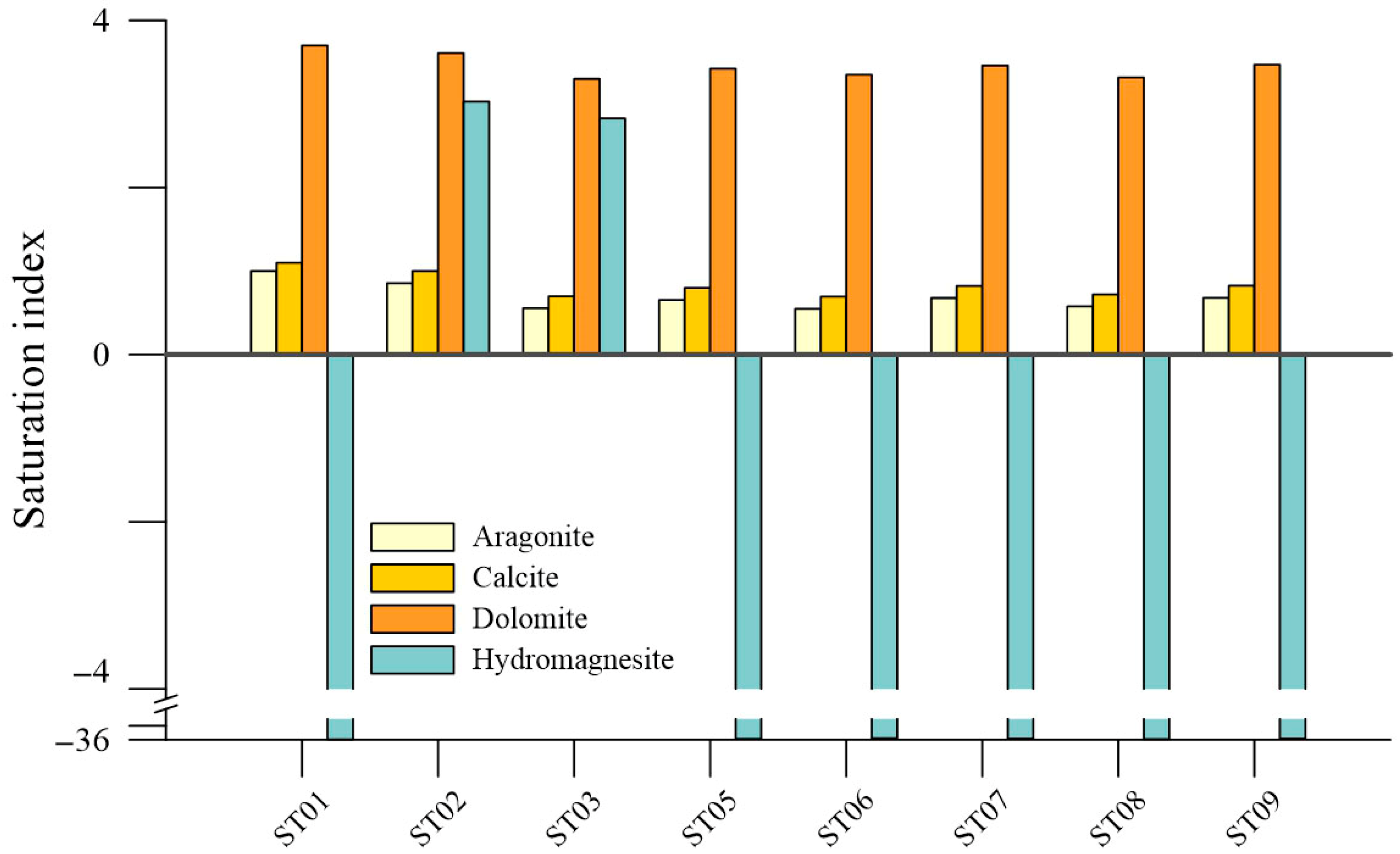
4. Results and Discussion
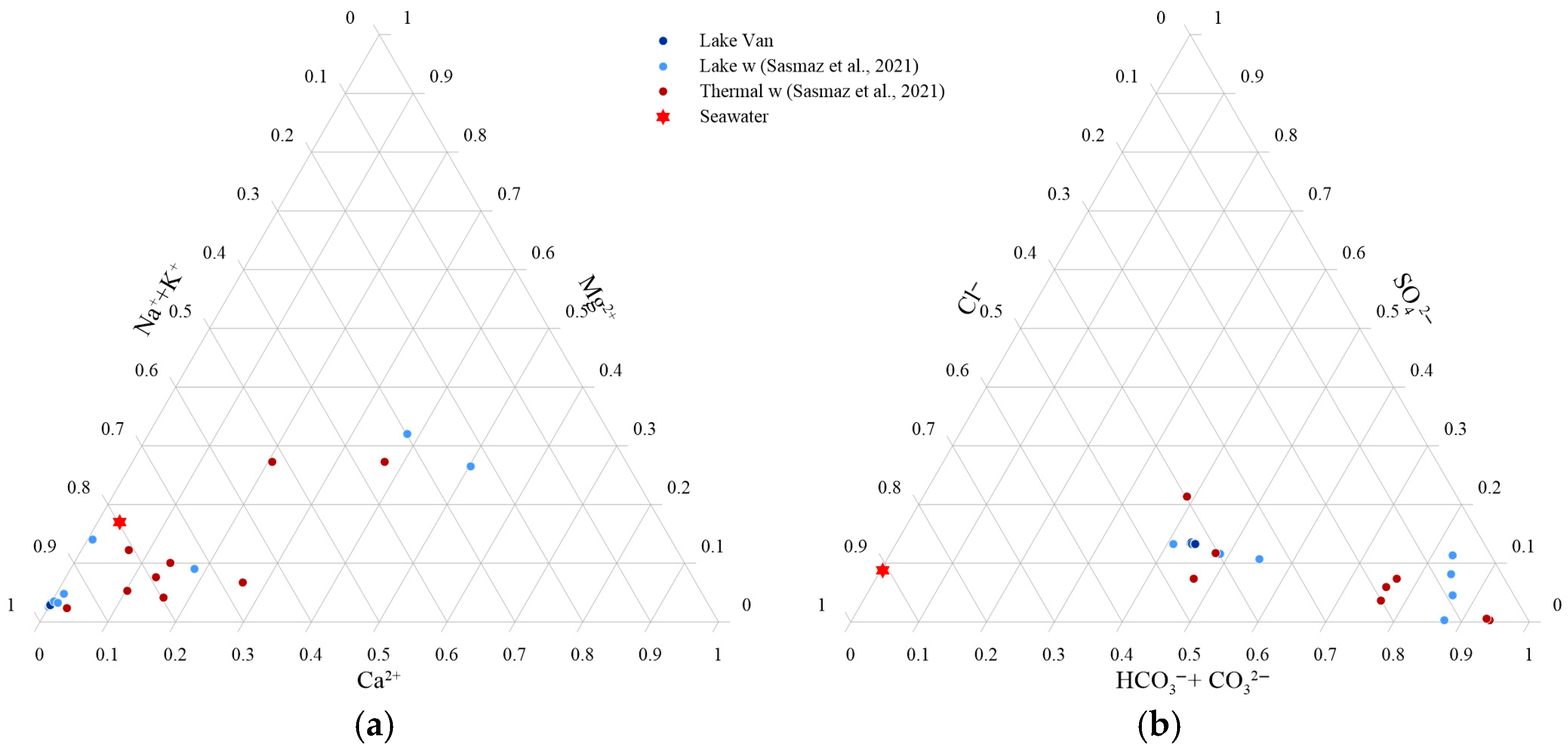
4.1. General Aspects of Water Chemistry
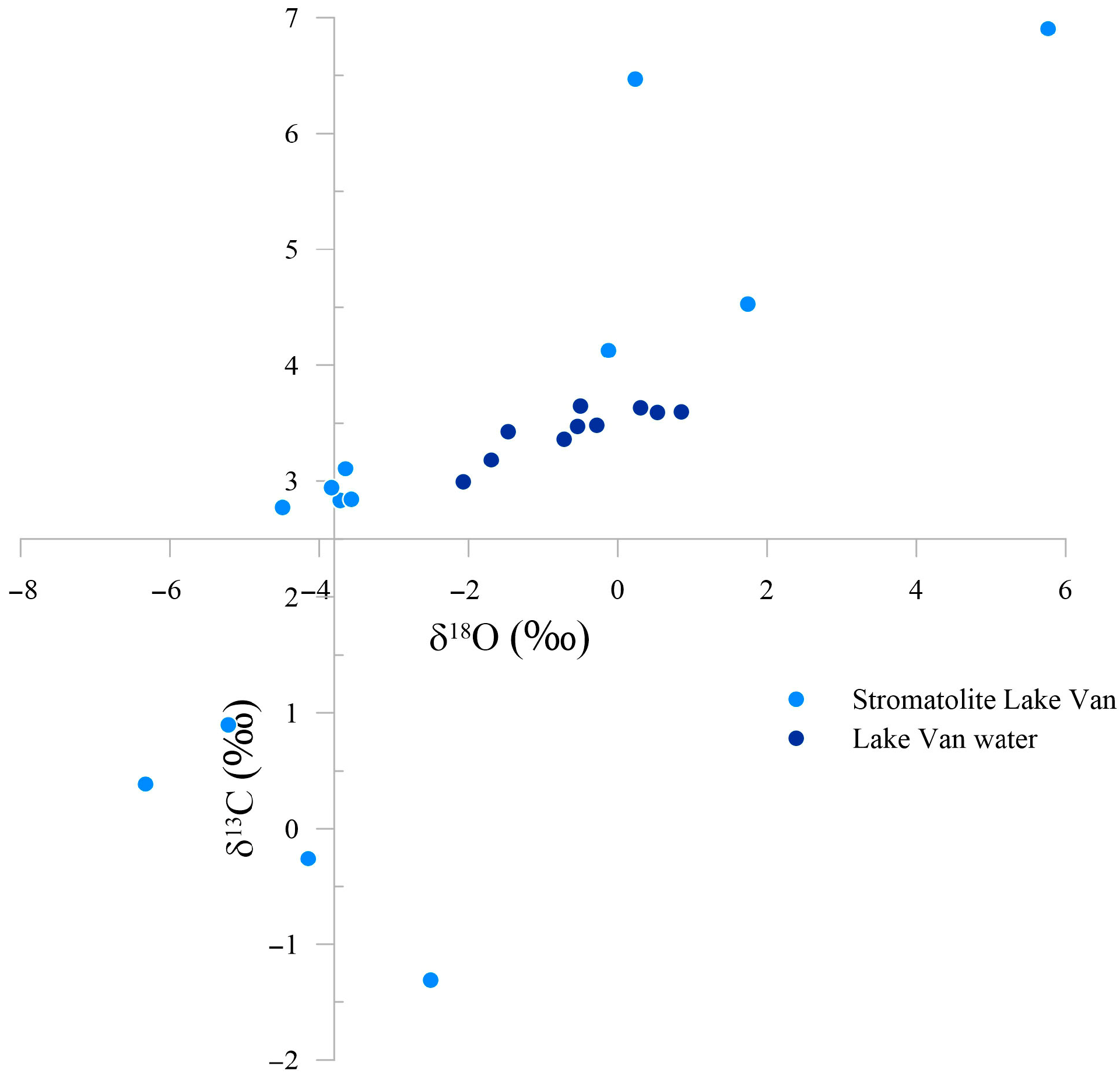
4.2. Isotopic Compositions of Water and Carbonates
4.3. SEM Observations Made Regarding the Carbonates
4.4. REE Behavior in Lake Water
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kempe, S. Hydrographie, Warven-Chronologie und organische Geochemie des Van Sees, Ost Türkei. Mitt. Geol.-Paleaont. Inst. Univ. Hambg. 1977, 47, 123–208. [Google Scholar]
- Kempe, S.; Kaźmierczak, J. Modern soda lakes: Model environments for an early alkaline ocean. In Modelling in Natural Sciences—Design, Validation and Case Studies; Müller, T., Müller, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003; pp. 309–322. [Google Scholar]
- Eugster, H.P.; Hardie, L.A. Saline lakes. In Lakes: Chemistry, Geology, Physics; Lerman, A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 237–289. [Google Scholar]
- Lerman, A.; Stumm, W. CO2 storage and alkalinity trends in lakes. Water Res. 1989, 23, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempe, S.; Kazmierczak, J.; Degens, E.T. The soda ocean concept and its bearing on biotic evolution. In Origin, Evolution, and Modern Aspects of Biomineralization in Plants and Animals; Crick, R.E., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1989; pp. 29–43. [Google Scholar]
- Dupraz, C.; Reid, R.P.; Braissant, O.; Decho, A.W.; Norman, R.S.; Visscher, P.T. Processes of carbonate precipitation in modern microbial mats. Earth Sci. Rev. 2009, 96, 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visscher, P.T.; Stolz, J.F. Microbial mats as bioreactors: Populations, processes, and products. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2005, 219, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arp, G.; Hofmann, J.; Reitner, J. Microbial fabric formation in spring mounds (‘Microbialites’) of alkaline salt lakes in the Badain Jaran Sand sea, PR China. Palaios 1998, 13, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arp, G.; Reimer, A.; Reitner, J. Biofilm exopolymers control microbialite formation at thermal springs discharging into the alkaline Pyramid Lake, Nevada, USA. Sediment. Geol. 1999, 126, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasmaz, A.; Zuddas, P.; Cangemi, M.; Piazzese, D.; Ozek, G.; Venturi, M.; Censi, P. Elements in neutral-alkaline waters: Case study of Lake Van hydrothermal system, Turkey. J. Geochem. Explor. 2021, 226, 106784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempe, S.; Kazmierczak, J.; Landmann, G.; Konuk, T.; Reimer, A.; Lipp, A. Largest known microbialites discovered in Lake Van, Turkey. Nature 1991, 349, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Garcia, P.; Kazmierczak, J.; Benzerara, K.; Kempe, S.; Guyot, F.; Moreira, D. Bacterial diversity and carbonate precipitation in the giant microbialites from the highly alkaline Lake Van, Turkey. Extremophiles 2005, 9, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantrell, K.J.; Byrne, R.H. Rare earth element complexation by carbonate and oxalate ions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1987, 51, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, R.H.; Kim, K.H. Rare earth element scavenging in seawater. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 2645–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Byrne, R.H. Complexation of trivalent rare-earth elements (Ce, Eu, Gd, Tb, Yb) by carbonate ions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 295–302. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, R.H.; Sholkovitz, E.R. Marine chemistry and geochemistry of the lanthanides. In Handbook of the Physics and Chemistry of the Rare Earths; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; Voloume 23, Chapter 158; pp. 497–593. [Google Scholar]
- Bertram, C.J.; Elderfield, H. The geochemical balance of the rare earth elements and neodymium isotopes in the oceans. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 1957–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baar, H.J.W.; Bacon, M.P.; Brewer, P.G. Rare earth element distributions with a positive Ce anomaly in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Nature 1983, 301, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Censi, P.; Inguaggiato, C.; Chiavetta, S.; Schembri, C.; Sposito, F.; Censi, V.; Zuddas, P. The behaviour of zirconium, hafnium and rare earth elements during the crystallisation of halite and other salt minerals. Chem. Geol. 2017, 453, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Censi, P.; Raso, M.; Saiano, F.; Zuddas, P.; Oliveri, E. Zr/Hf ratio and REE behaviour: A coupled indication of lithogenic input in marginal basins and deep-sea brines. Deep-Sea Res. II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2019, 164, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, B.A.; Klinkhammer, G.P.; McManus, J. Rare earth elements in pore waters of marine sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 1265–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibo, D.S.; Nozaki, Y. Rare earth elements in seawater: Particle association, shale-normalization, and Ce oxidation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M. Controls on the fractionation of isovalent trace elements in magmatic and aqueous systems: Evidence from Y/Ho, Zr/Hf, and lanthanide tetrad effect. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1996, 123, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Censi, P.; Sirota, I.; Zuddas, P.; Lensky, N.G.; Crouvi, O.; Cangemi, M.; Piazzese, D. Rare earths release from dissolving atmospheric dust and their accumulation into crystallising halite: The Dead Sea example. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 875, 162682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raso, M.; Censi, P.; Saiano, F. Simultaneous determinations of zirconium, hafnium, yttrium and lanthanides in seawater according to a co-precipitation technique onto iron-hydroxide. Talanta 2013, 116, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capasso, G.; Favara, R.; Grassa, F.; Inguaggiato, S.; Longo, M. On-line technique for preparing and measuring stable carbon isotope of total dissolved inorganic carbon in water samples (d13CTDIC). Ann. Geophys.-Italy 2005, 48, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, H.; Gulc, N.; Hilton, D.R.; Aydin, H.; Halldorsson, S.A. Spatial variations in gas and stable isotope compositions of thermal fluids around Lake Van: Implications for crust–mantle dynamics in eastern Turkey. Chem. Geol. 2012, 300–301, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasvanoglu, S. Hydrogeochemistry of thermal and mineralized waters in the Diyadin (Agri) area, Eastern Turkey. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 38, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horita, J.; Rozanski, K.; Cohen, S. Isotope effects in the evaporation of water: A status report of the Craig–Gordon model. Isotopes Environ. Health Stud. 2008, 44, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, J.R.; Adami, L.H. The oxygen isotope partition function ratio of water and the structure of liquid water. J. Phys. Chem. 1969, 73, 1553–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinson, M.; Clayton, R.N. Carbon-13 fractionation between aragonite and water. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1969, 33, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanek, C.S.; Grossman, E.L.; Morse, J.W. Carbon isotope fractionation in synthetic aragonite and calcite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1992, 56, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Lopez, C.; Romanek, C.S.; Caballero, E. Carbon isotope fractionation in synthetic magnesian calcite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, J.; Nehrke, G.; Joens, N.; Immenhauser, A.; Kwiencien, O. Re ning the interpretation of lacustrine carbonate isotope records: Implications of a mineralogy-specific Lake Van case study. Chem Geol. 2019, 513, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millero, F.J. Stability constants for the formation of rare earth-inorganic complexes as a function of ionic strength. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1992, 56, 3123–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.R.; Byrne, R.H. Carbonate complexation of yttrium and the rare earth elements in natural waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migdisov, A.A.; Williams-Jones, A.E.; Wagner, T. An experimental study of the solubility and speciation of the rare earth elements (III) in fluoride- and chloride-bearing aqueous solutions at temperatures up to 300 °C. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 7087–7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, T. Rare earth element (REE)-silicic acid complexes in seawater to explain the incorporation of REEs in opal and the “leftover” REEs in surface water: New interpretation of dissolved REE distribution profiles. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2013, 113, 174–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monji, A.B.; Ahmadi, S.J.; Zolfonoun, E. Selective biosorption of zirconium and hafnium from acidic aqueous solutions by rice bran, wheat bran and Platanus Orientalis tree leaves. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Censi, P.; Cangemi, M.; Brusca, L.; Madonia, P.; Saiano, F.; Zuddas, P. The behaviour of rare-earth elements, Zr and Hf during biologically-mediated deposition of silica-stromatolites and carbonate-rich microbial mats. Gondwana Res. 2015, 27, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Byrne, R.H. Comprehensive investigation of yttrium and rare earth element complexation by carbonate ions using ICP-mass spectrometry. J. Sol. Chem. 1998, 27, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Lyons, W.B. The rare earth element geochemistry of Mono Lake water and the importance of carbonate complexing. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1994, 39, 1141–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Lyons, W.B.; Bird, D.A. Rare earth element concentrations and speciation in alkaline lakes from the western USA. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 773–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrich, R.; Renaut, R.W.; Bonli, T. Trace-element composition of cherts from alkaline lakes in the east African rift: A probe for ancient counterparts. Spec. Publ. 2002, 73, 277–298. [Google Scholar]
- Moller, P.; Bau, M. Rare-earth patterns with positive cerium anomaly in alkaline waters from Lake Van, Turkey. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1993, 117, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Tanaka, K. EXAFS study on the cause of enrichment of heavy REEs on bacterial cell surfaces. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 5443–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
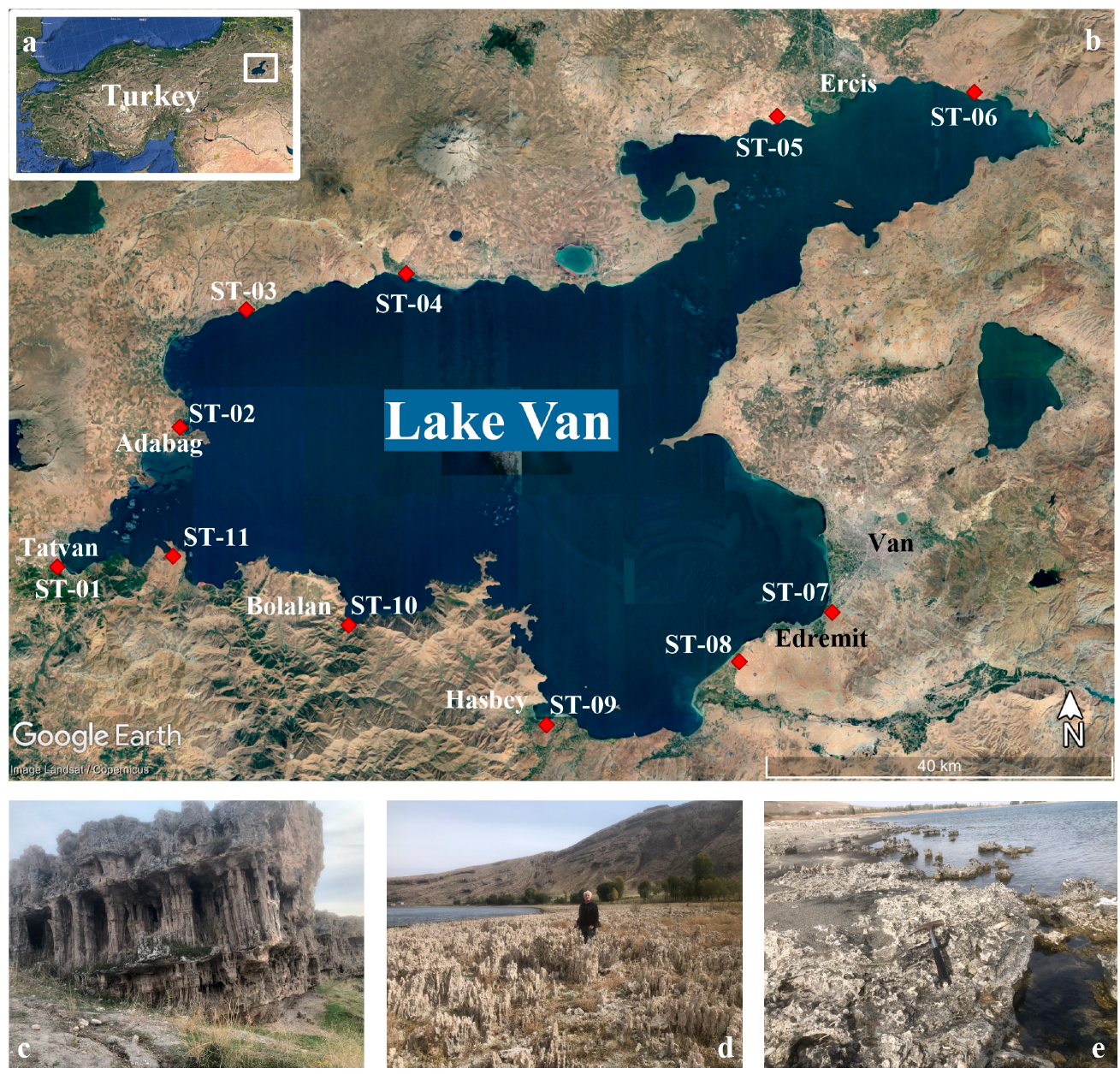




| Sample | Location | Longitude (E) | Latitude (N) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ST-01 | Tatvan | 42.305124° | 38.482524° |
| ST-02 | Adabağ | 42.452715° | 38.637806° |
| ST-03 | Ahlat | 42.532471° | 38.759970° |
| ST-04 | Adilcevaz | 42.795610° | 38.786339° |
| ST-05 | Ercis W | 43.279248° | 38.959671° |
| ST-06 | Ercis E | 43.530767° | 38.984128° |
| ST-07 | Edremit E | 43.311378° | 38.431562° |
| ST-08 | Edremit SW | 43.180271° | 38.382668° |
| ST-09 | Hasbey | 42.941726° | 38.329994° |
| ST-10 | Bolalan | 42.687062° | 38.429276° |
| ST-11 | Tatvan E | 42.436072° | 38.505397° |
| A | B | B-A | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ST-01 | 3.47 | 2.83 | −0.64 |
| ST-02 | 3.48 | 4.53 | 1.04 |
| ST-03 | 3.18 | 2.94 | −0.24 |
| ST-05 | 3.36 | 6.47 | 3.11 |
| ST-06 | 3.60 | 4.13 | 0.53 |
| ST-07 | 3.59 | −1.31 | −4.90 |
| ST-08 | 2.99 | 0.39 | −2.60 |
| ST-09 | 3.65 | 2.77 | −0.88 |
| ST-10 | 3.43 | −0.26 | −3.69 |
| ST-11 | 3.64 | 6.90 | 3.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cangemi, M.; Oliveri, Y.; Sasmaz, B.; Censi, P.; Sasmaz, A. Potential Function of Microbial Mats in Regard to Water Chemistry and Carbonate Precipitation in the Alkaline Waterbody Lake Van (Turkey). Water 2025, 17, 2060. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142060
Cangemi M, Oliveri Y, Sasmaz B, Censi P, Sasmaz A. Potential Function of Microbial Mats in Regard to Water Chemistry and Carbonate Precipitation in the Alkaline Waterbody Lake Van (Turkey). Water. 2025; 17(14):2060. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142060
Chicago/Turabian StyleCangemi, Marianna, Ygor Oliveri, Bilge Sasmaz, Paolo Censi, and Ahmet Sasmaz. 2025. "Potential Function of Microbial Mats in Regard to Water Chemistry and Carbonate Precipitation in the Alkaline Waterbody Lake Van (Turkey)" Water 17, no. 14: 2060. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142060
APA StyleCangemi, M., Oliveri, Y., Sasmaz, B., Censi, P., & Sasmaz, A. (2025). Potential Function of Microbial Mats in Regard to Water Chemistry and Carbonate Precipitation in the Alkaline Waterbody Lake Van (Turkey). Water, 17(14), 2060. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142060








