Polyethyleneimine-Modified Magnetic Multivalent Iron Derived from Iron-Based Waterwork Sludge for Cr(VI) Adsorption and Reduction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
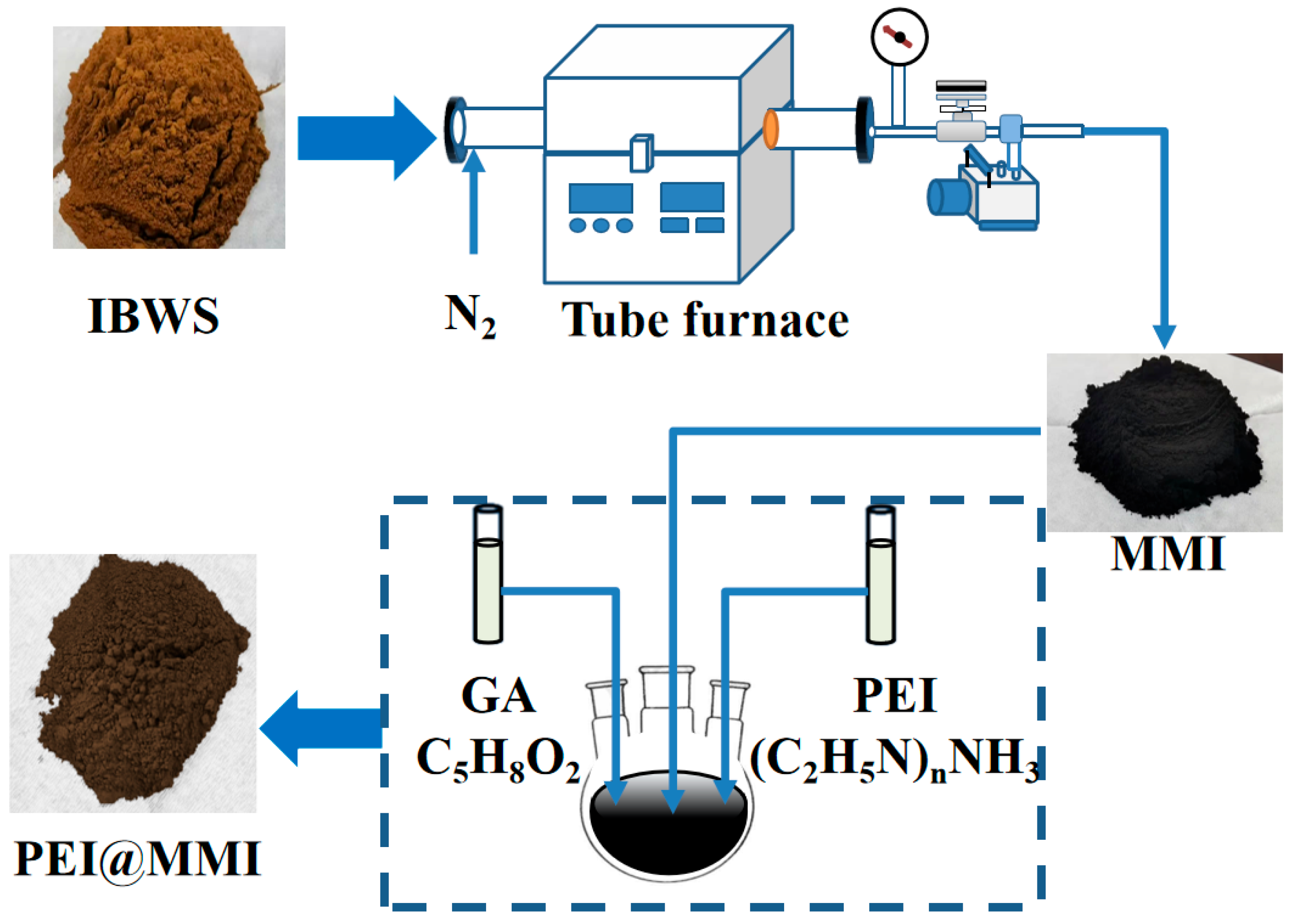
2.1. Adsorbent Preparation
2.2. Preparation of Cr(VI)-Containing Solution
2.3. Cr(VI) Adsorption Experiments
2.4. Adsorbent Characterization
2.5. Regeneration and Reuse of the Adsorbent
3. Results and Discussion
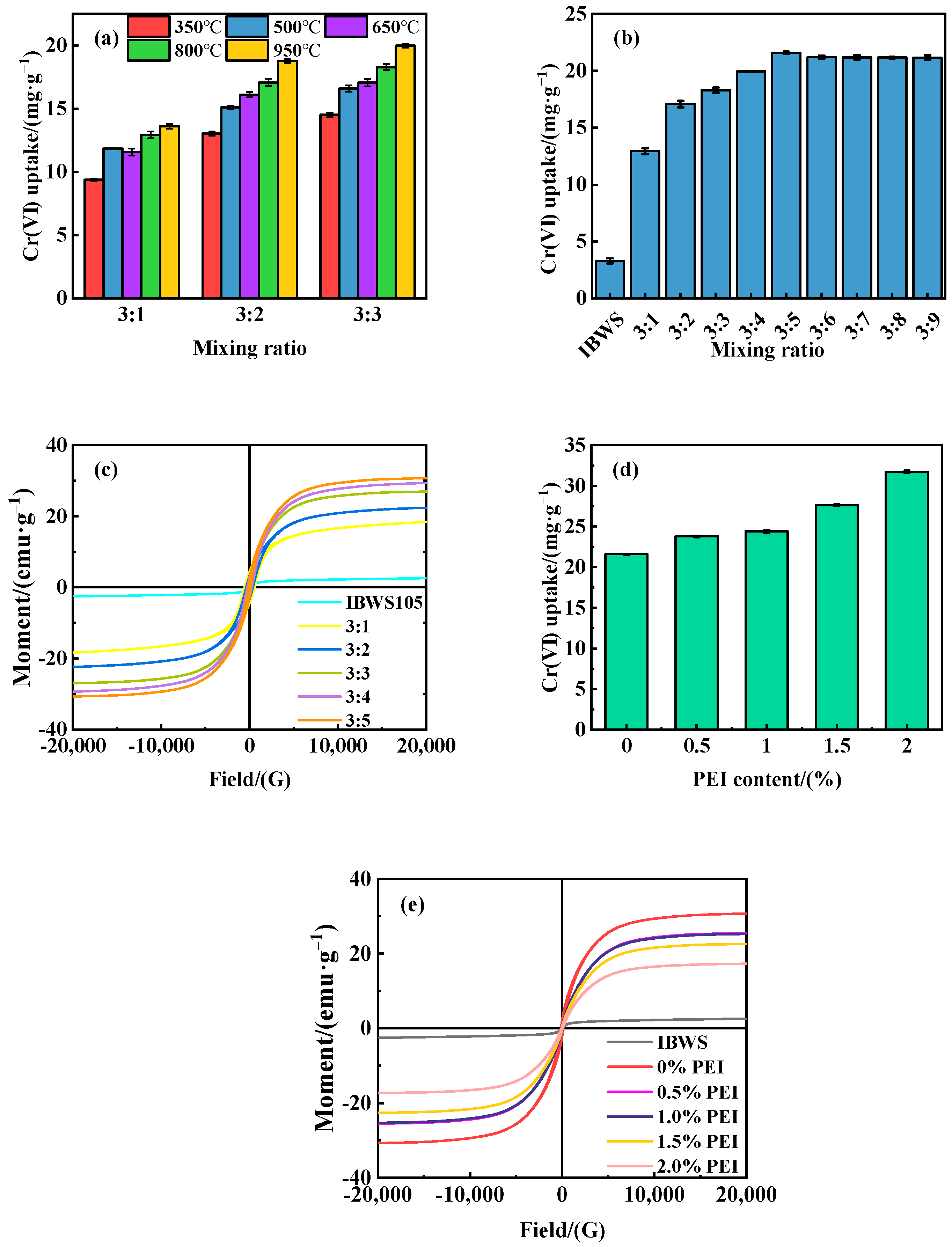
3.1. Adsorbent Preparation
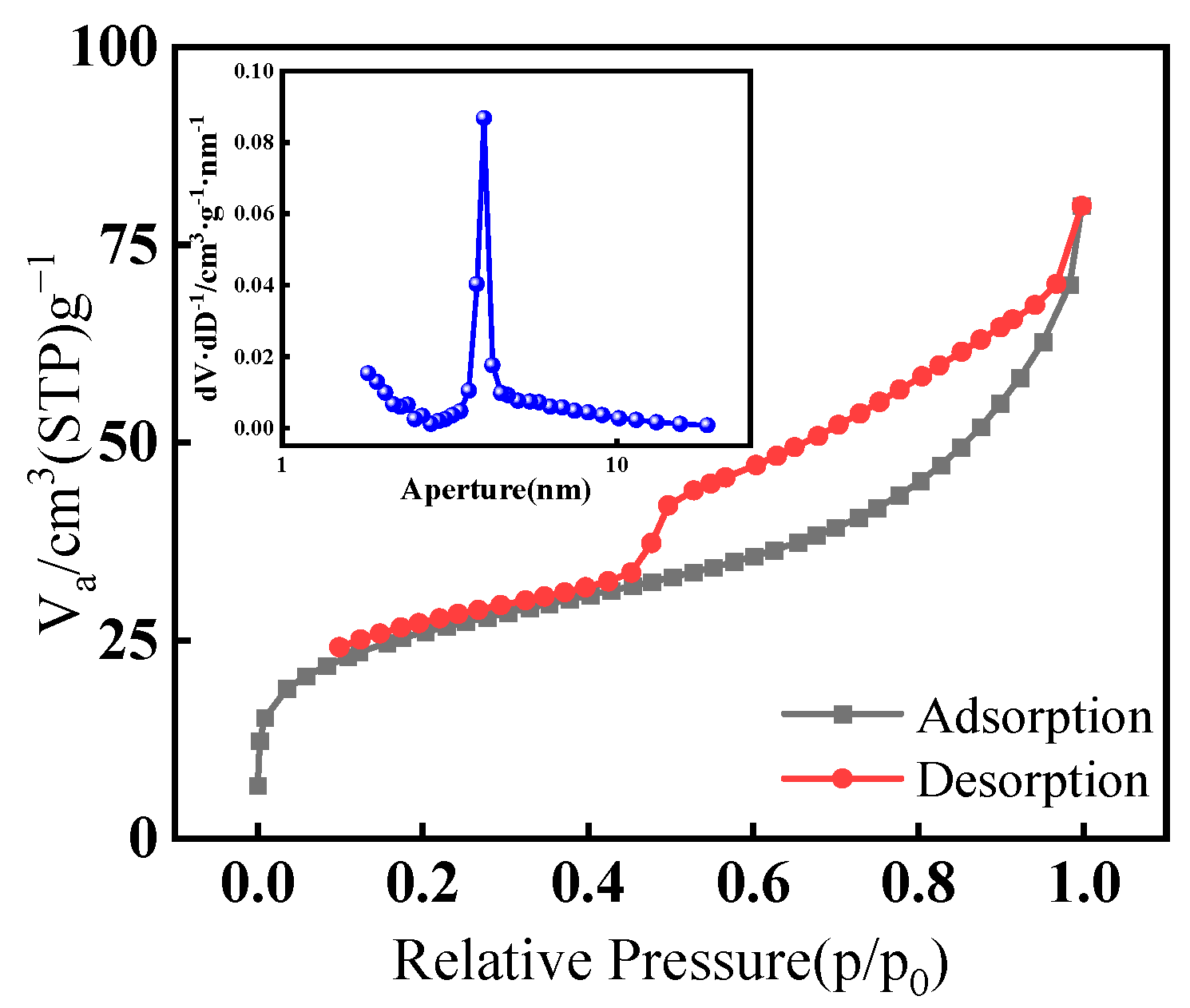
3.2. Adsorbent Characterization
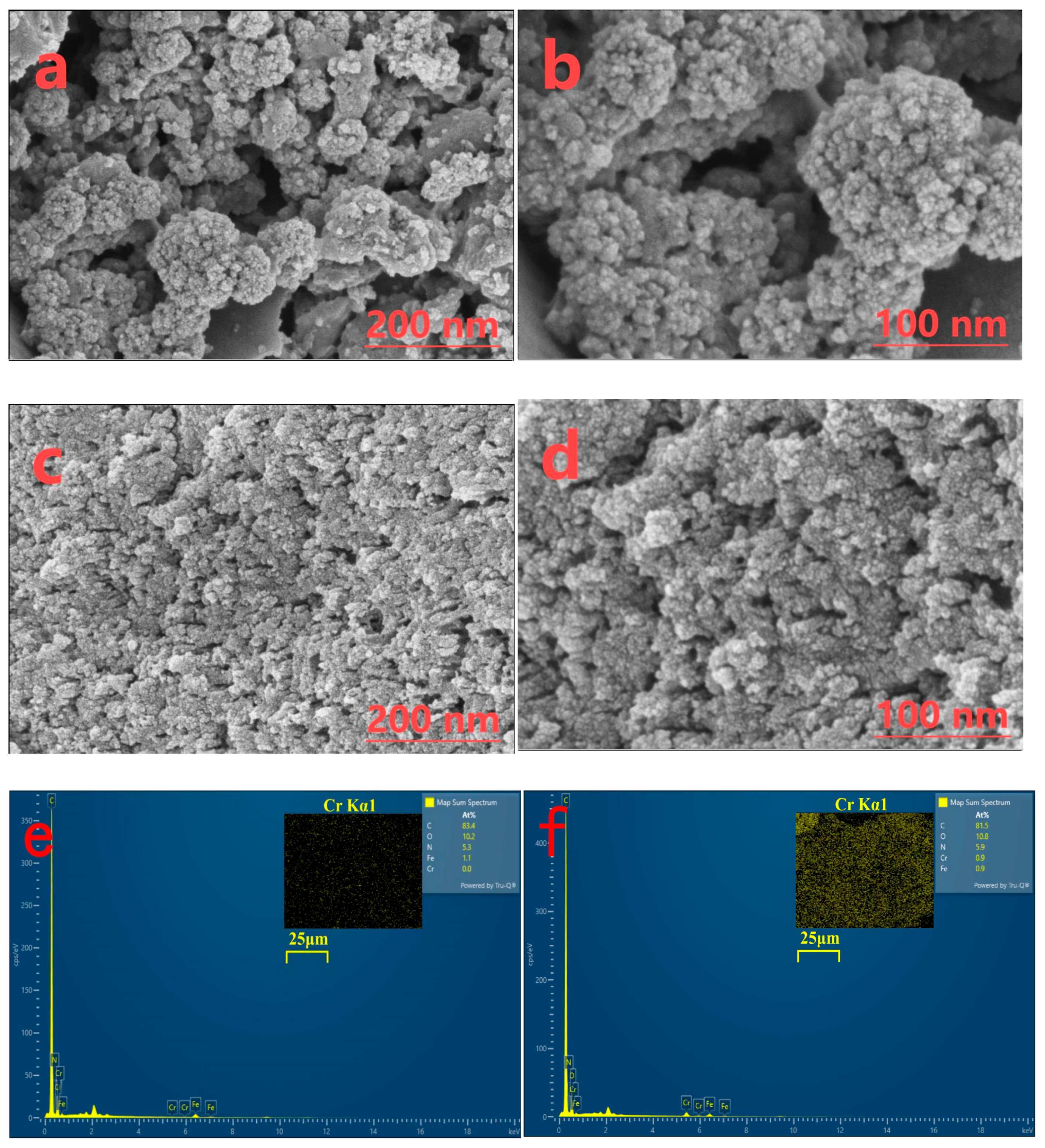
3.2.1. SEM
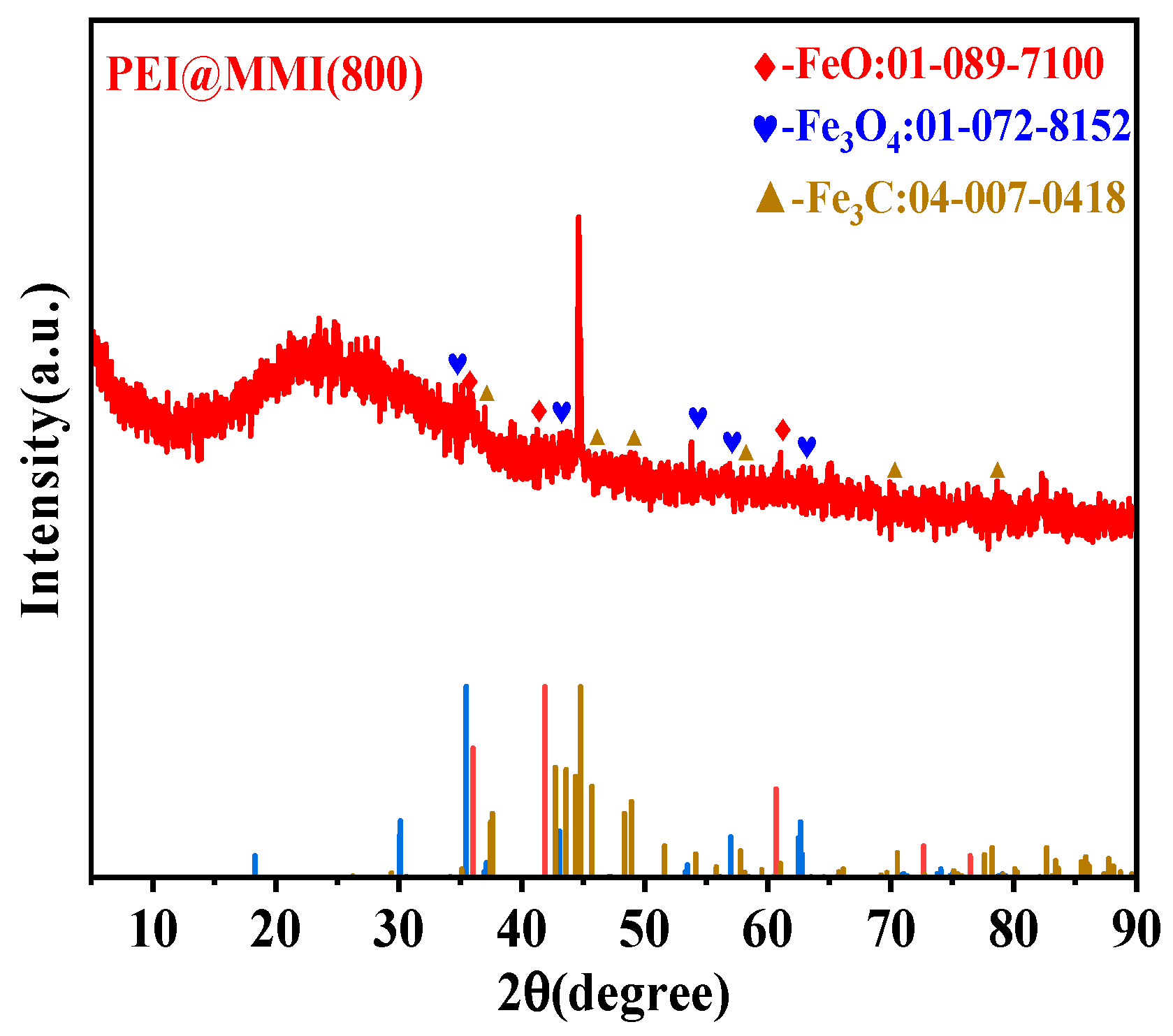
3.2.2. XRD
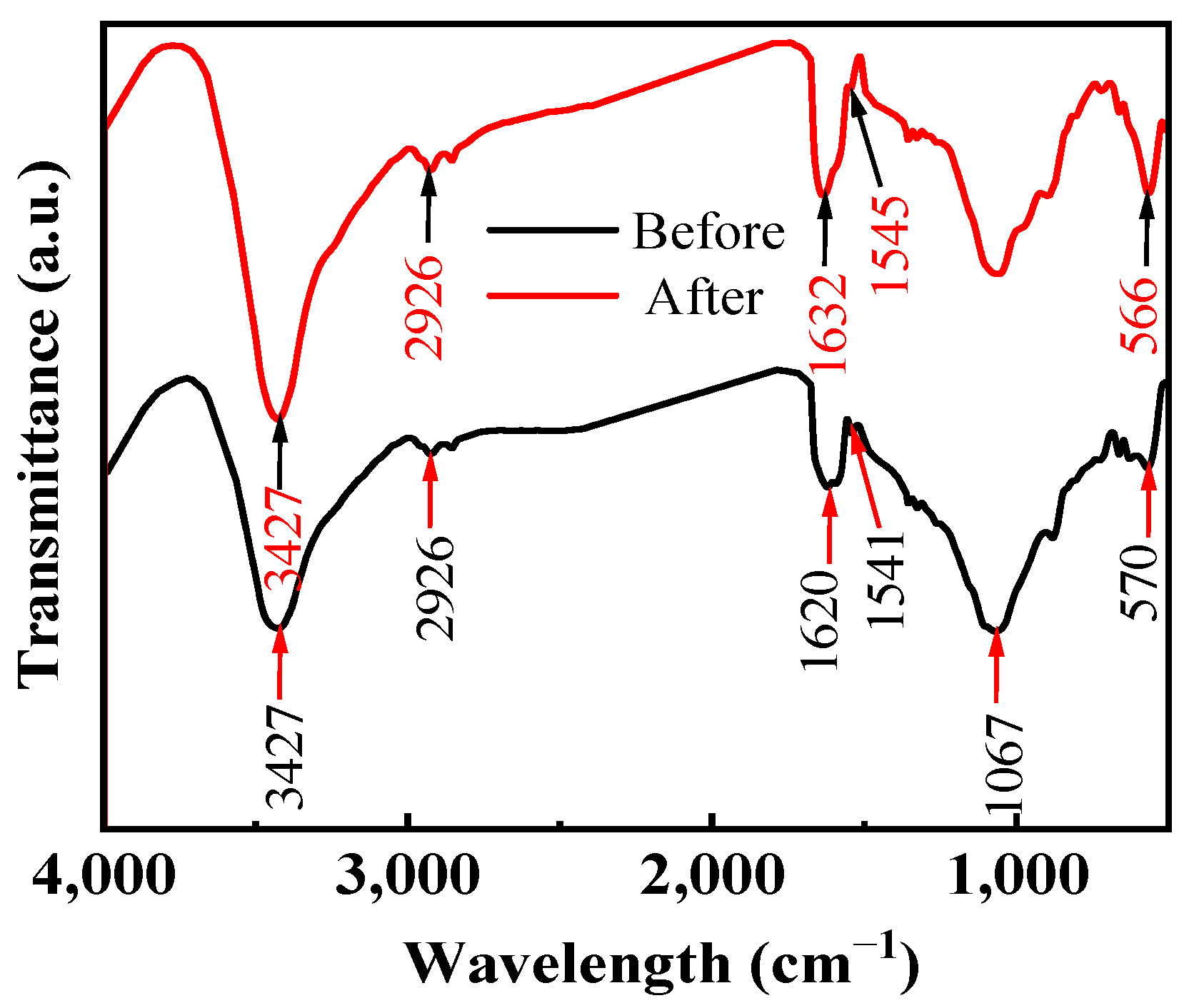
3.2.3. FTIR
3.3. Static Cr(VI) Adsorption
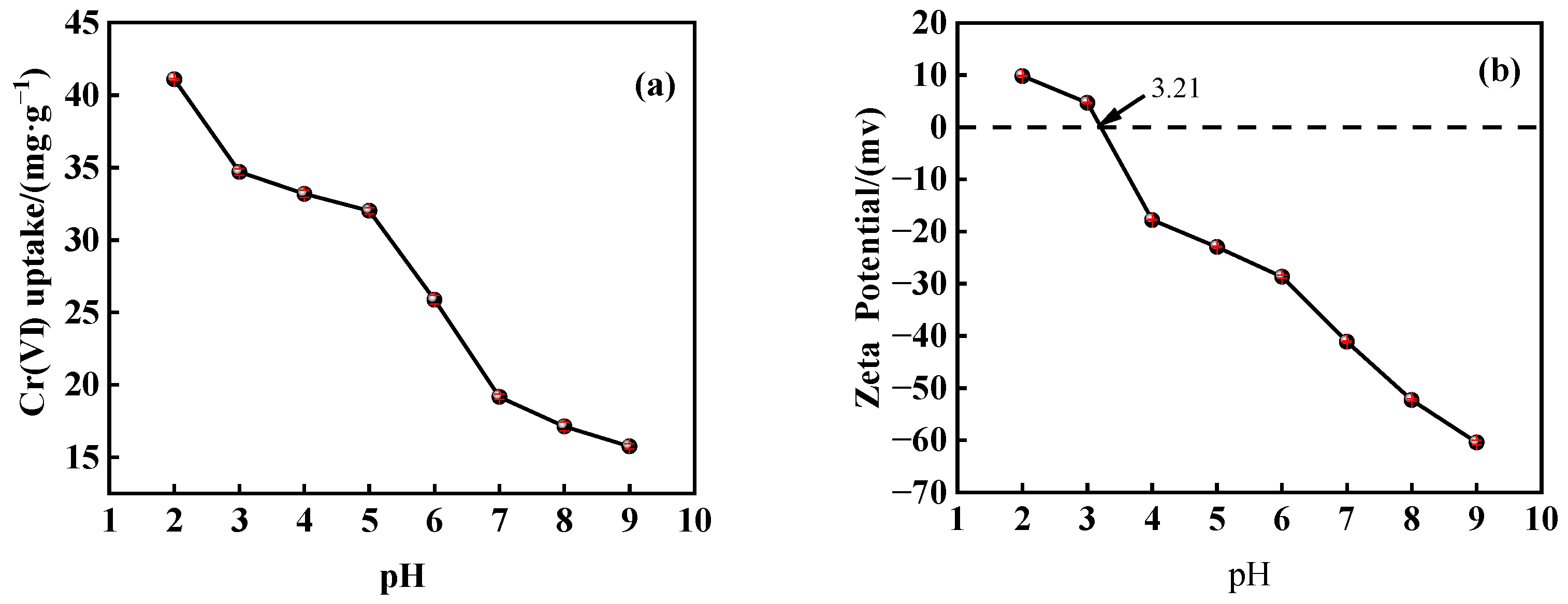
3.3.1. Effect of Solution pH
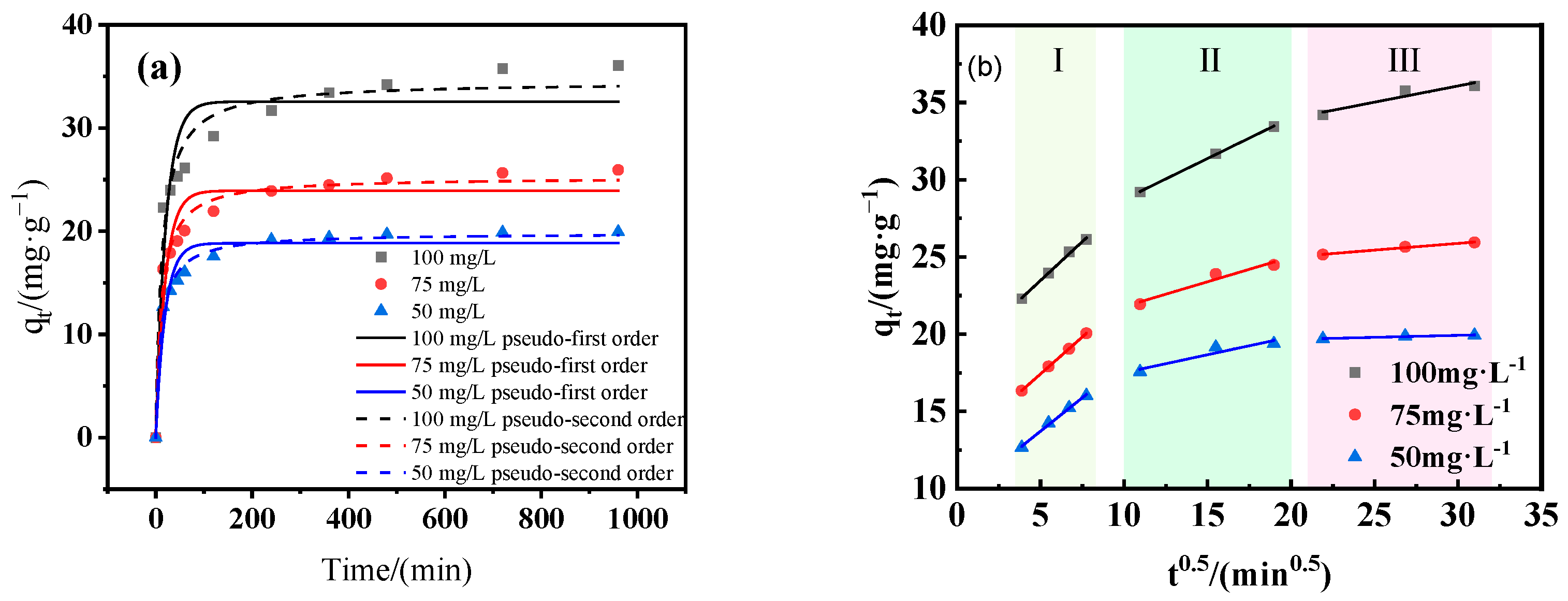
3.3.2. Adsorption Kinetics
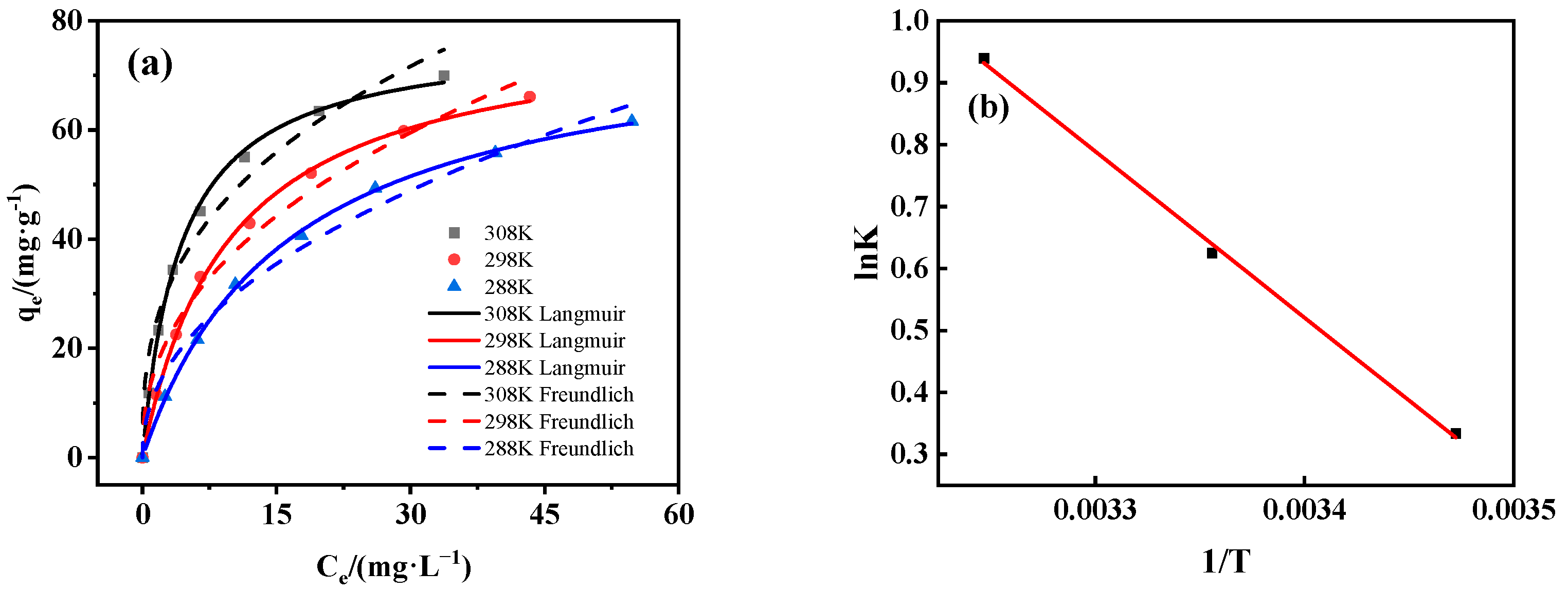
3.3.3. Adsorption Isotherm and Thermodynamics
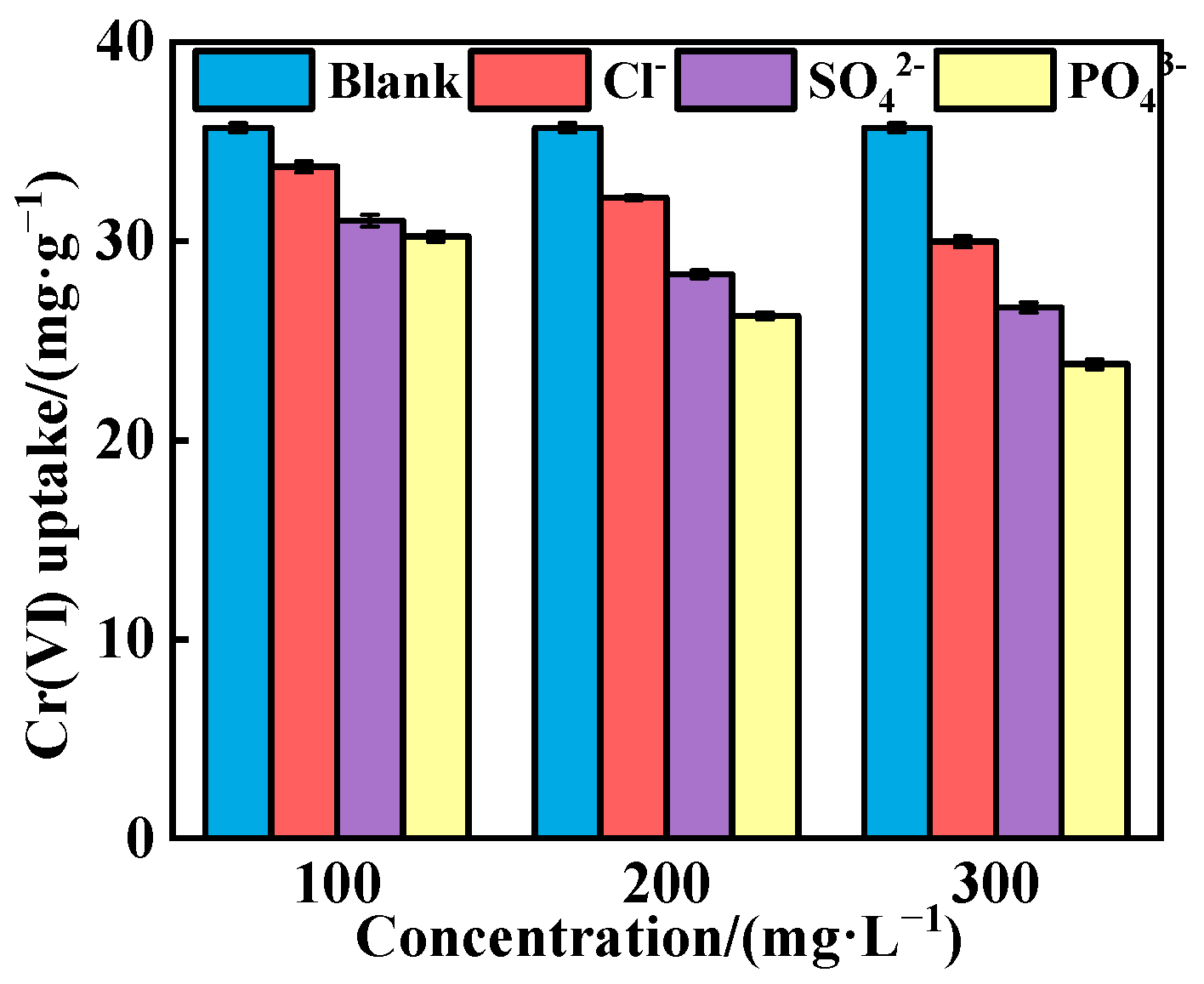
3.3.4. Influence of Co-Existing Anions
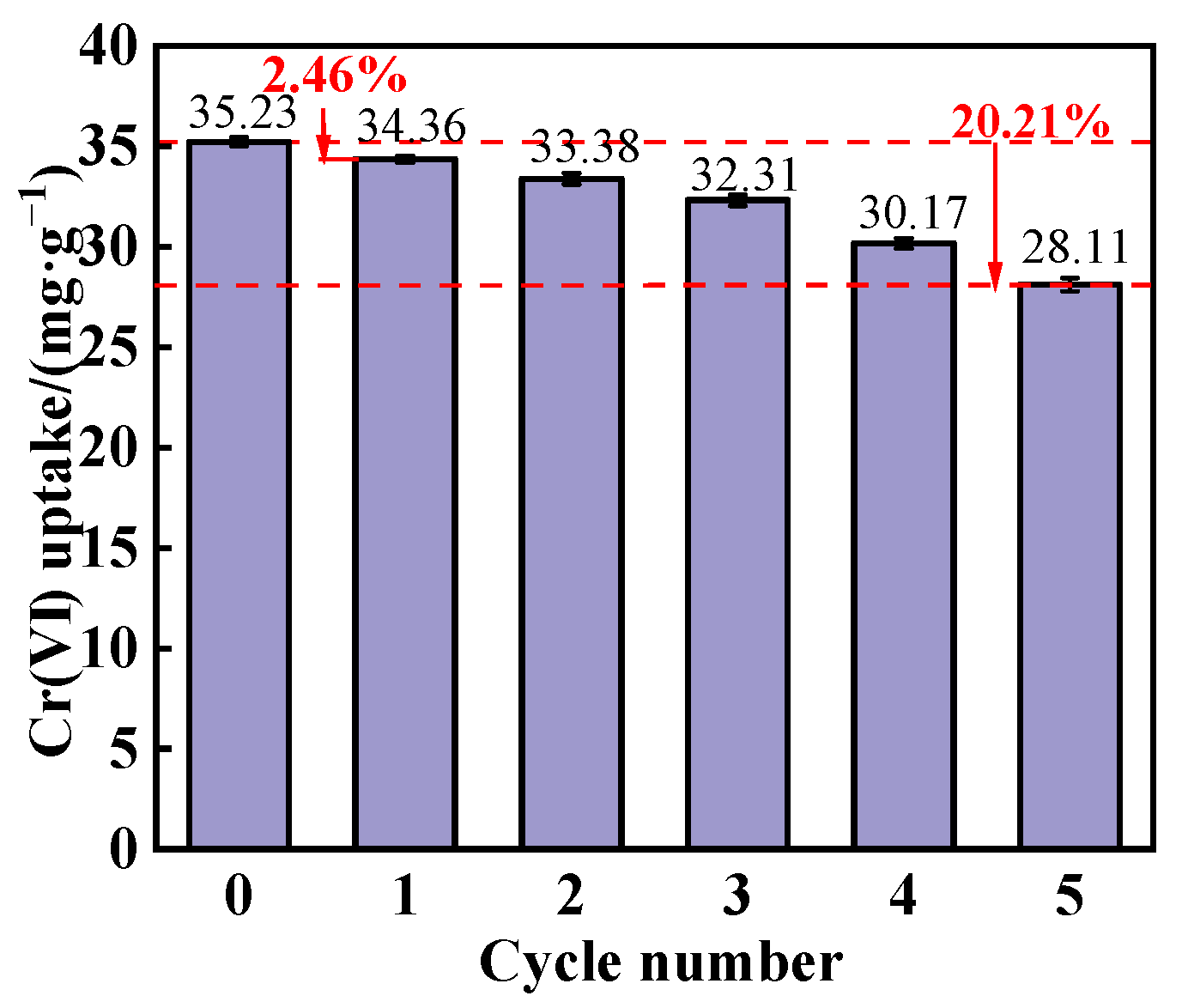
3.3.5. Reusability of the Adsorbent
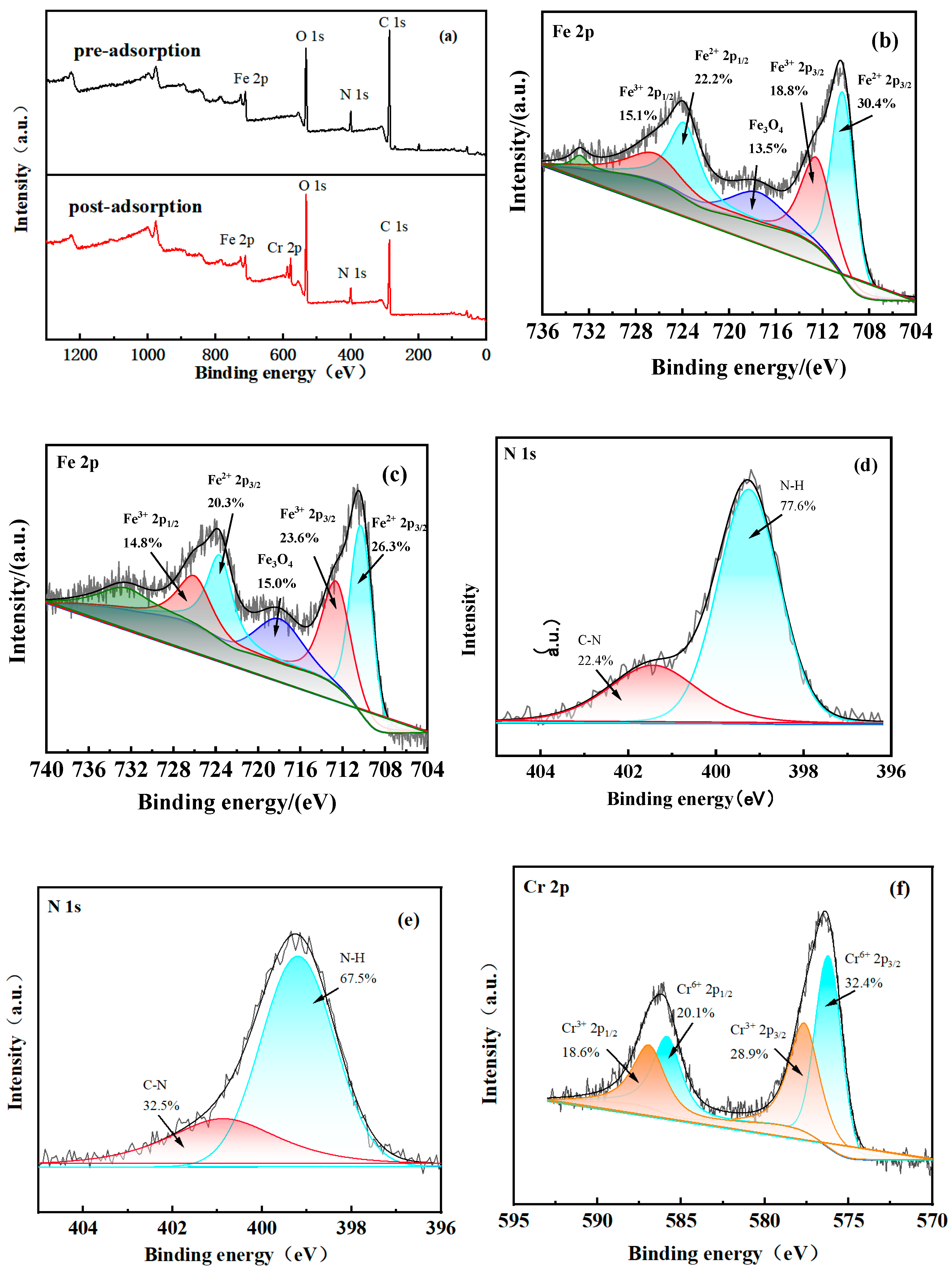
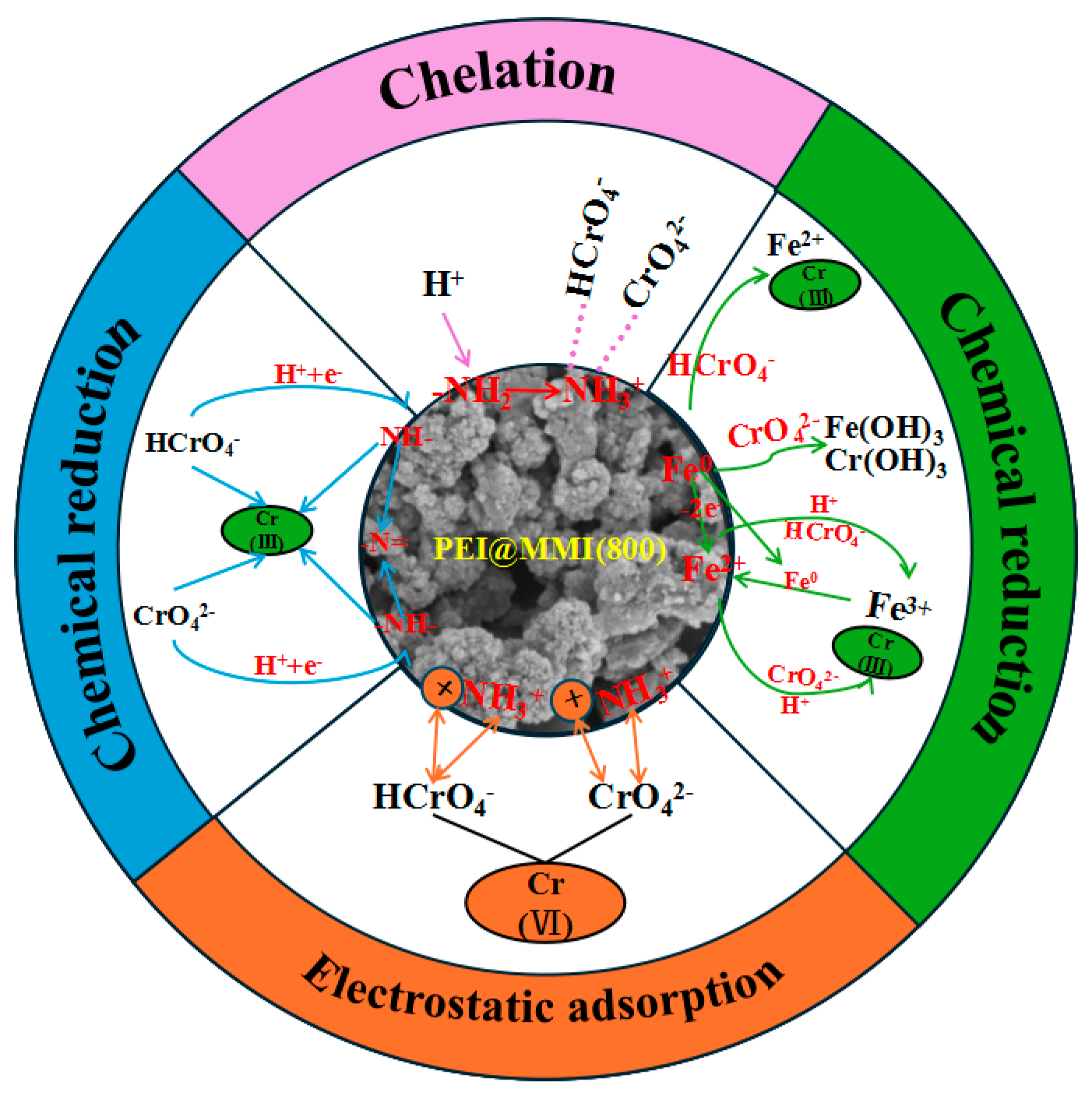
3.3.6. Cr(VI) Adsorption Mechanism Exploration
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The adsorption of Cr(VI) by PEI@MMI(800) was significantly influenced by pH. The Cr(VI) adsorption capacity decreased from 41.09 mg/g to 15.75 mg/g as the pH increased from 2 to 9, indicating a strong pH-dependent behavior.
- (2)
- The adsorption process was well described by the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and the Langmuir isotherm model. Thermodynamic analysis revealed that the adsorption process was spontaneous and endothermic in nature.
- (3)
- Cl−, SO42− and PO43− weakened Cr(VI) adsorption, with their inhibitory effects following the order Cl− < SO42− < PO43−. Additionally, higher concentrations of these anions led to lower Cr(VI) adsorption capacities.
- (4)
- After five cycles of reuse, PEI@MMI(800) lost 20.21% of its initial Cr(VI) adsorption capacity, suggesting that while the composite exhibited good reusability, there was a gradual decline in performance over multiple cycles.
- (5)
- The primary mechanisms for Cr(VI) removal by PEI@MMI(800) were identified as electrostatic adsorption, as well as chelation of Cr(VI) by PEI. Additionally, the reduction of Cr(VI) to Cr(III) significantly contributed to the overall removal efficiency.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duan, J.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, P.; Wang, F. Enhanced adsorption of Cr (VI) from aqueous solutions by CTAB-modified schwertmannite: Adsorption performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2024, 208, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göde, F.; Yılmaz, A.; Aktaş, A.H.; Pehlivan, E. Artificial neural network approach to model Cr (III) and Cr (VI) adsorption by NACS and BCS. Appl. Water Sci. 2024, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahakifar, F.; Dashtinejad, M.; Sepehrian, H.; Samadfam, M.; Fasihi, J.; Yadollahi, A. Intensification of Cr (VI) adsorption using activated carbon adsorbent modified with ammonium persulfate. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Jiang, Y.; Dai, M.; Hou, X.; Peng, C. Active biochar-supported iron oxides for Cr (VI) removal from groundwater: Kinetics, stability and the key role of FeO in electron-transfer mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Ayati, A.; Ghanbari, S.; Orooji, Y.; Tanhaei, B.; Karimi, F.; Alizadeh, M.; Rouhi, J.; Fu, L.; Sillanpää, M. Recent advances in removal techniques of Cr (VI) toxic ion from aqueous solution: A comprehensive review. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 329, 115062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.; Xu, W.; Chang, S.; Chen, S. Polyamidoamine dendrimers modified MXene and its high-performance adsorption behavior for Cr (VI). J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 399, 124406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, M.; Rahman, S.T.; Li, X.; Wang, G. Enhancing Cr (VI) Adsorption of Chestnut Shell Biochar through H3PO4 Activation and Nickel Doping. Molecules 2024, 29, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Shi, T.; Akram, M.; Wang, L.; Wan, J.; Gao, B.; Pan, J. Fe doping enhanced Cr (VI) adsorption efficiency of cerium-based adsorbents: Adsorption behaviors and inner removal mechanisms. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2024, 673, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Liang, F.; Wang, F.; Zhou, H.; Liang, P. Selective adsorption of Cr (VI) by nitrogen-doped hydrothermal carbon in binary system. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Yan, X.; Peacock, C.L.; Zhang, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Feng, X.; Liu, F.; Yin, H. Adsorption of Cr (VI) on Al-substituted hematites and its reduction and retention in the presence of Fe2+ under conditions similar to subsurface soil environments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Chai, J.; Wang, Y.; Du, Q.; Shi, J.; Xu, Z. Enhanced photocatalytic reduction of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution using Fe0/TiO2-based polymeric nanocomposites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 110312–110323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, J.; Joe-Wong, C.; Maher, K. Cr (VI) reduction by Fe (II) sorbed to silica surfaces. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Yang, Z.; Xian, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, T.; Pu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Adsorption and reduction of Cr (VI) by a novel nanoscale FeS/chitosan/biochar composite from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ye, X.; Chen, D.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, S.; Li, J.; Li, H. Chromium(VI) removal from synthetic solution using novel zero-valent iron biochar composites derived from iron-rich sludge via one-pot synthesis. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Duan, X.; Tie, J. One-pot synthesis of a magnetic Zn/iron-based sludge/biochar composite for aqueous Cr (VI) adsorption. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.-H.; Lee, S.-C.; Ko, M.; Yoon, S.; Lee, J.; Park, J.-A.; Kim, S.-B. Adsorption of Hg(II) on polyethyleneimine-functionalized carboxymethylcellulose beads: Characterization, toxicity tests, and adsorption experiments. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 241, 124516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Z.; Jiang, B. Efficient adsorption of fluoride ions by polyethyleneimine modified diatomite under different conditions in a fixed bed column. Desalin. Water Treat. 2023, 307, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zheng, S.; Sun, T.; Gao, G.; Sun, Y.; Jia, H.; Zhu, X. Simultaneous adsorption and reduction of Cr (VI) on Potamogeton·crispus biochar supported nanoscale zero-valent iron: Electro- and sepctro-chemical mechanism. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2024, 155, 105259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Liu, S.; Tan, X.; Chen, Q.; Ye, J.; Sun, A.; Liu, N. Peroxydisulfate activation by magnetic nanoflakes zero-valent iron/graphitized carbon composites for norfloxacin removal: Synergistic effect of 1O2 with surface Fe(IV). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 342, 126841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Beyazay, T.; Tüysüz, H. Effect of Alkali-and Alkaline-Earth-Metal Promoters on Silica-Supported Co-Fe Alloy for Autocatalytic CO2Fixation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2024, 63, e202316110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Yu, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Tang, X.; Wu, S.; He, B.; Lan, H.; Li, S.; Yue, Q.; et al. Regulating the thickness of the carbon coating layer in iron/carbon heterostructures to enhance the catalytic performance for oxygen evolution reaction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 642, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alterary, S.S.; AlKhamees, A. Synthesis, surface modification, and characterization of Fe3O4@ SiO2 core@ shell nanostructure. Green Process. Synth. 2021, 10, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoobi, M.; Khalilvand-Sedagheh, M.; Ramazani, A.; Asadgol, Z.; Forootanfar, H.; Faramarzi, M.A. Synthesis of polyethyleneimine (PEI) and β-cyclodextrin grafted PEI nanocomposites with magnetic cores for lipase immobilization and esterification. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-H.; Hsien, Y. Adsorption Behaviors of Nucleic Acid by Cationic Magnetic Nanoparticles. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 284–287, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathumba, P.; Kuvarega, A.T.; Dlamini, L.N.; Malinga, S.P. Synthesis and characterisation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles prepared within hyperbranched polyethylenimine polymer template using a modified sol–gel method. Mater. Lett. 2017, 195, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, M.E.-S. Polyethylenimine-functionalized magnetic amorphous carbon fabricated from oil palm leaves as a novel adsorbent for Hg(II) from aqueous solutions. Egypt. J. Pet. 2018, 27, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebbar, V.; Bhajantri, R. Conductivity study of thermally stabilized RuO2/polythiophene nanocomposites. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1942, 040007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ye, S.; Zhang, W.; He, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, M.; Nie, Z. Magnetic Ion-Imprinted Materials for Selective Adsorption of Cr (VI): Adsorption Behavior and Mechanism Study. Molecules 2024, 29, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhao, B.; Guo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Pak, T.; Li, G. Preparation of mesoporous batatas biochar via soft-template method for high efficiency removal of tetracycline. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Qi, M.; Song, J.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Gao, Z. Adsorption of polyphenolic compounds by sodium alginate-modified starch nanoparticles in a multiphase system: Kinetic, thermodynamic and release characteristics studies. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 162, 110900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wei, Y.; Wu, H.; Yuan, P.; Bu, H.; Tan, X. Efficient and sustainable phosphate removal and recovery from wastewater with zinc-substituted magnetite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 360, 130642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Liu, C.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Qiu, Z. Effective adsorption of Congo red by an innovative biochar/LDH-derived MIL-100(Al): Investigation of coexisting pollutants and mechanism revelation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 359, 130670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, K.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, R.; Zhao, L. ZhengRemoval of aqueous Cr (Ⅵ) by green synthesized sulfide iron nanoparticles loaded corn straw biochar: Performance, mechanism, and DFT calculations. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 670, 160729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Gotoh, T.; Nakai, S. Hexavalent Chromium Removal by an Ascorbic Acid Functionalized Polymer Hydrogel Adsorbent: The Effect of Physicochemical Factors. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 2105–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Zhang, X.; Bi, F.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Tao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Polyethylenimine-grafted nitrogen-doping magnetic biochar for efficient Cr (VI) decontamination: Insights into synthesis and adsorption mechanisms. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 313, 120103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Wang, D.; Meng, H.; Du, M.; Lin, Y.; Dong, Z.; Wang, A.; Wang, Y. Flexible noble-metal-free Fe-based metallic glasses as highly efficient oxygen evolution electrodes. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2024, 646, 123208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, H. Valence State and Catalytic Activity of Ni-Fe Oxide Embedded in Carbon Nanotube Catalysts. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Li, M.; Meng, J.; Hei, P.; Wang, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, X.-X. Electrochemical Storage of Ammonium Versus Metal Ions in Bimetallic Hydroxide for Sustainable Aqueous Batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 34, 2310437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalse, N.M.; De, M. Adsorptive desulfurization of thiophenic sulfur compounds using nitrogen modified graphene. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 331, 125693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shi, X.; Wei, B.; Liao, S. Preparation of MIL-53 (Cr) and MIL-101 (Cr)/reduced graphene oxide/polyaniline composites for Cr (VI) adsorption. J. Porous Mater. 2025, 32, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, B.; Lv, J.; He, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Wågberg, T.; Hu, G. Facile synthesis of sodium lignosulfonate/polyethyleneimine/sodium alginate beads with ultra-high adsorption capacity for Cr (VI) removal from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, J.; Chen, L.; Guan, Y. Novel co-polymerization of polypyrrole/polyaniline on ferrate modified biochar composites for the efficient adsorption of hexavalent chromium in water. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Wang, R.; Li, L.; Zhao, J.; Liu, B. Ultra-high capacity and anti-interference for Cr (VI) removal by tannin-polyvinylimine modified graphite carbon nitride. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Kinetic Models | Parameters | C0 (mg/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 75 | 100 | ||
| Pseudo-first order | qe (mg/g) | 18.84 | 23.92 | 32.55 |
| k1 (min−1) | 0.0006 | 0.004 | 0.004 | |
| R2 | 0.945 | 0.928 | 0.902 | |
| Pseudo-second order | k2 [g/(mg·min)] | 0.00464 | 0.00350 | 0.00233 |
| qe(mg/g) | 19.820 | 25.236 | 34.476 | |
| R2 | 0.990 | 0.980 | 0.967 | |
| Intraparticle diffusion | ki1 [mg/(g·min0.5)] | 1.005 | 0.957 | 0.866 |
| C1 | 18.445 | 12.641 | 9.392 | |
| R12 | 0.996 | 0.999 | 0.996 | |
| ki2 [mg/(g·min0.5)] | 0.529 | 0.322 | 0.232 | |
| C2 | 22.318 | 18.561 | 15.187 | |
| R22 | 0.999 | 0.948 | 0.892 | |
| ki3 [mg/(g·min0.5)] | 0.210 | 0.088 | 0.026 | |
| C3 | 29.765 | 23.253 | 19.139 | |
| R32 | 0.900 | 0.989 | 0.934 | |
| T (K) | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg/g) | b | R2 | kf (Ln·mg1–n/g) | n | R2 | |
| 288 | 79.233 | 0.062 | 0.999 | 10.117 | −0.463 | 0.981 |
| 298 | 79.927 | 0.103 | 0.998 | 13.897 | −0.428 | 0.979 |
| 308 | 77.447 | 0.233 | 0.997 | 21.267 | −0.357 | 0.969 |
| ΔS0 (kJ/mol·K) | ∆H0 (kJ/mol) | ∆G0 (kJ/mol) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 288 | 298 | 308 | ||
| 0.080 | 22.309 | −0.731 | −1.531 | −2.331 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tie, J.; Wang, H.; Zheng, J.; Yan, M.; Shao, S.; Duan, X.; Ye, Z. Polyethyleneimine-Modified Magnetic Multivalent Iron Derived from Iron-Based Waterwork Sludge for Cr(VI) Adsorption and Reduction. Water 2025, 17, 1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131945
Tie J, Wang H, Zheng J, Yan M, Shao S, Duan X, Ye Z. Polyethyleneimine-Modified Magnetic Multivalent Iron Derived from Iron-Based Waterwork Sludge for Cr(VI) Adsorption and Reduction. Water. 2025; 17(13):1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131945
Chicago/Turabian StyleTie, Jingxi, Huawen Wang, Junkai Zheng, Mengjia Yan, Sihao Shao, Xiaohan Duan, and Zhaoyong Ye. 2025. "Polyethyleneimine-Modified Magnetic Multivalent Iron Derived from Iron-Based Waterwork Sludge for Cr(VI) Adsorption and Reduction" Water 17, no. 13: 1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131945
APA StyleTie, J., Wang, H., Zheng, J., Yan, M., Shao, S., Duan, X., & Ye, Z. (2025). Polyethyleneimine-Modified Magnetic Multivalent Iron Derived from Iron-Based Waterwork Sludge for Cr(VI) Adsorption and Reduction. Water, 17(13), 1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17131945






