Abstract
Rapid rises in water levels due to heavy rainfall can lead to the accumulation of floating debris, posing significant challenges for both water quality and resource management. However, real-time monitoring of floating debris remains difficult due to the discrepancy between meteorological conditions and the timing of debris accumulation. To address this limitation, this study proposes an amplitude change detection (ACD) model based on time-series synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imagery, which is less affected by weather conditions. The model statistically distinguishes floating debris from open water based on their differing scattering characteristics. The ACD approach was applied to 18 pairs of Sentinel-1 SAR images acquired over Daecheong Reservoir from June to September 2024. A stringent type I error threshold (α < 1 × 10−8) was employed to ensure reliable detection. The results revealed a distinct cumulative effect, whereby the detected debris area increased immediately following rainfall events. A positive correlation was observed between 10-day cumulative precipitation and the debris-covered area. For instance, on 12 July, a floating debris area of 0.3828 km2 was detected, which subsequently expanded to 0.4504 km2 by 24 July. In contrast, on 22 August, when rainfall was negligible, no debris was detected (0 km2), indicating that precipitation was a key factor influencing the detection sensitivity. Comparative analysis with optical imagery further confirmed that floating debris tended to accumulate near artificial barriers and narrow channel regions. Overall, this study demonstrates that this spatial pattern suggests the potential to use detection results to estimate debris transport pathways and inform retrieval strategies.
1. Introduction
During the summer season each year, floating debris emerges as a significant issue in various rivers and lakes across South Korea. In particular, abrupt rises in water levels due to heavy rainfall events concentrate floating waste around dam areas, posing substantial challenges to water resource and quality management [1]. Floating debris in key water bodies such as rivers, lakes, and watersheds undergoes degradation and releases organic matter, microplastics, and hazardous chemicals (e.g., heavy metals), which can promote algal blooms, deplete dissolved oxygen, and lead to the suffocation of aquatic organisms and the destruction of habitats. Specifically, floating debris deteriorates benthic ecosystems and fish spawning grounds by covering lakebeds and riverbeds; and contributes to bio-contamination as birds, fish, and mammals become entangled in waste or ingest microplastics, leading to increased biological toxicity [2]. Furthermore, as many lakes and dams serve as sources of drinking and agricultural water, the presence of floating waste not only escalates water purification costs but can also hinder purification altogether. Hence, early detection and the establishment of an efficient management system for floating debris are essential for the stable operation of water infrastructure and the preservation of healthy aquatic ecosystems.
In the summer of 2024, floating debris was predominantly generated during the monsoon season spanning from 19 June to 27 July. The debris was primarily composed of vegetative materials such as wood and grass, along with a portion of domestic waste including plastics [3]. By late August 2024, approximately 23,526 tons of floating debris had accumulated in 17 major dams managed by the Ministry of Environment and Korea Water Resources Corporation, including those on the Han, Nakdong, Geum, Yeongsan, and Seomjin Rivers [3]. On average, around 68,000 tons of floating debris are collected annually, requiring significant manpower. Thus, understanding the generation mechanisms of floating debris, such as precipitation patterns, and building a comprehensive record of occurrence data are critical for timely and effective responses [4]. Equally important is the provision of near real-time information regarding the location and quantity of floating debris.
Because floating waste generated by heavy rainfall often spreads across inaccessible and expansive areas, satellite and airborne imagery is commonly used for monitoring purposes [5]. In this context, satellite remote sensing has been demonstrated as an effective tool for observation [6]. In particular, passive optical remote sensing sensors have been utilized to monitor and track large floating debris in both retrospective and near real-time applications. These include medium-resolution sensors such as MODIS, GOCI, OLCI, and VIIRS as well as mid to high resolution sensors like Landsat OLI or Sentinel-2 MSI [7,8,9].
However, optical imagery is inherently constrained by weather conditions. All optical sensors are affected by clouds, as light signals cannot penetrate them, and it is estimated that approximately 70% of the ocean is covered by clouds at any given time [10]. Therefore, the observation of large floating algae using optical remote sensing becomes difficult on cloudy days [11]. In contrast, synthetic aperture radar (SAR) is an active sensing technique that can overcome such limitations by providing high-resolution ocean observations regardless of weather or time of day [12]. Theoretically, SAR observations can complement optical remote sensing in the detection of large floating materials. Weather-independent SAR imagery is particularly useful for environmental monitoring through time-series analysis of changes in lakes before and after debris events [13]. The capacity of SAR for detecting seasonal cycles of lakes, for example, on the Tibetan Plateau, has been validated in multiple studies [14], as well as in applications for delineating water boundaries and mapping inundated areas in lakes [15,16,17].
Nevertheless, relatively few studies have focused on identifying the spatial distribution of floating debris in lakes and rivers during heavy rainfall, or on monitoring debris accumulation driven by typhoons or sudden changes in precipitation [7,18,19]. Such topics have largely appeared in the context of ocean area rather than inland area [20]. To date, it remains unclear under what specific conditions SAR imagery can detect floating debris across diverse and spatially extensive lake environments. A further limitation of current SAR-based studies is the substantial time required for image processing and interpretation [21].
However, with the emergence of satellite-based remote sensing data platforms, it has become possible to detect flood-related impacts in near real time and to perform long-term time-series analyses [22]. Building on this technological advancement, the present study aims to develop a time-series-based floating debris detection model by applying the amplitude change detection (ACD) technique to Sentinel-1 SAR imagery provided by the European Space Agency (ESA). The proposed model is designed to effectively analyze floating debris widely distributed across large inland water bodies and to establish a responsive observation system under extreme weather conditions such as heavy rainfall. Ultimately, this research aims to improve monitoring accessibility for floating debris in lakes and reservoirs, which play a critical role in the supply of drinking water and management of water quality during flood events.
The specific objectives of this study are as follows. First, under the assumption that SAR backscatter intensity follows a specific probability distribution function, we model the scattering differences between open water and floating debris using a statistical estimation approach. Second, based on this statistical assumption, we propose a spatial monitoring framework that applies to pre- and post-flood time-series SAR imagery to detect the accumulation of floating debris over time.
2. Study Area and Materials
2.1. Study Area
The study area was Daecheong Reservoir, located in the central inland region of South Korea, as shown in Figure 1. Daecheong Reservoir is situated approximately 16 km northeast of downtown Daejeon in the upper reaches of the Geum River. It is a man-made reservoir with a surface area of 72.8 km2 and a storage capacity of 1.49 km3 [23]. Annually, approximately 1.3 km3 of water from Daecheong Reservoir is supplied for domestic and industrial use, serving as a drinking water source for residents of the Chungcheong provinces, Daejeon Metropolitan City, and Jeollabuk-do.
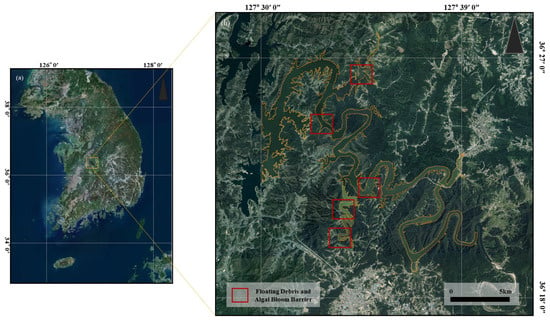
Figure 1.
Location of the study area: (a) South Korea; (b) Daecheong Lake.
Accordingly, water quality management in the reservoir is of paramount importance. The boundary of the study area, Daecheong Lake, was delineated using lake polygon data from the National Base Map provided by the National Geographic Information Institute (NGII) of Korea [24]. Additional specific zones within the lake, where floating debris and algal bloom barriers had been deployed, were selected as regions of interest (ROIs) for detailed analysis [25], as highlighted with red outlines in Figure 1.
To understand the current conditions of the study area and the occurrence of floating waste, relevant data on waste collected from 2015 to 2024 were compiled from the Ministry of Environment and summarized in Table 1 [26]. Between 2013 and 2020, a total of 53,542 tons of floating debris were recorded in Daecheong Reservoir [26] and approximately 4433 tons were introduced into the reservoir in 2024.

Table 1.
Annual Floating Debris Accumulation at Dams in the Geum River (2015–2024).
In this study, we conducted experiments using the developed detection algorithm for the year 2024, which was identified as a representative case of floating debris occurrence, based on the Sentinel-1 image archive. On average, although approximately 5300 tons of floating debris enter Daecheong Reservoir during the flood season each year, the actual amount varies greatly depending on rainfall levels. The inflowing debris primarily consists of vegetative materials from riverbanks with some portion presumed to be domestic waste originating from adjacent areas such as floodplains (Figure 2) [3].

Figure 2.
Field photographs of Daecheong Reservoir (a) before and (b) after removal of floating debris in 2024.
2.2. Dataset
As part of the effort to detect floating debris in inland waters, this study primarily utilized Sentinel-1A SAR data and supplemented the analysis with optical imagery of Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8-9 for visual validation. Both satellite missions offer globally available, up-to-date observations capable of capturing large-scale floating debris phenomena in the same geographic areas, thereby aligning well with the objectives of this research.
Each Sentinel-1 satellite follows a sun-synchronous orbit with a 12-day revisit cycle and 175 relative orbit tracks [27]. In this study, data from ascending relative orbit 54 and 127 were utilized (Table 2). Sentinel-1 SAR operates in the C-band (5.3 GHz/5.7 cm wavelength) and provides data with a spatial resolution of 10 × 10 m and a swath width of approximately 250 km [28]. The SAR images were acquired in Interferometric Wide (IW) swath mode, which covers a 250 km-wide area at a 10 m spatial resolution, with incidence angles ranging from 29° to 46°. All Sentinel-1 imagery used in this study were ground range detected, high-resolution (GRDH) products that had been preprocessed using the Sentinel application platform (SNAP 11.0.0, European Space Agency, Frascati, Italy). Subsequent processing was conducted on a local server.

Table 2.
Specifications of Sentinel-1 GRD data utilized in this study.
The dataset consists of imagery acquired over Daecheong Reservoir in South Korea during the 2024 flood season, spanning from June to September. Since the occurrence of floating debris varied by month, only SAR scenes corresponding to periods of floods with confirmed debris presence were selected for analysis. For visual interpretation, Sentinel-2 optical imagery was used to manually identify floating debris, and images within ±2 days of the SAR acquisition date were also included for visual interpretation and cross-validation. In total, 18 SAR scenes and 11 optical scenes were collected for the June–September 2024 period, as shown in Table 1.
3. Methodology
To classify floating debris within the lake, this study employed the ACD technique, leveraging differences in radar backscatter characteristics between floating debris and water surfaces [13]. The technique was applied to Sentinel-1 GRDH imagery to detect floating debris introduced into inland water bodies during heavy rainfall events. The analysis was based on a two-date comparison of single-polarization backscatter intensity, assuming that surface scattering changes due to debris would cause statistically significant differences in radar amplitude. The key assumption is that floating debris introduced after heavy rainfall significantly increases local backscatter due to volume scattering, compared with the relatively smooth, specular nature of open water [29].
The overall workflow for applying the ACD method is presented in Figure 3. As described in Section 2.2, the preprocessing of Sentinel-1 imagery using the SNAP 11.0.0 included orbit correction, radiometric calibration, multilooking, range doppler terrain correction, and a conversion process into DB with default parameters applied throughout.
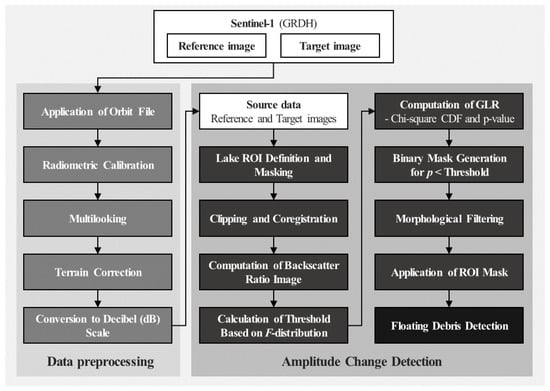
Figure 3.
Dataflow of this study.
To operationalize this method, reference and target images were preprocessed to extract local subsets over the ROIs, defined by a user-supplied ROI mask in GeoTIFF format indicating the lake boundary. The pixel-wise ratio of the backscatter amplitude values between the reference and target images was computed, and a statistical hypothesis testing between image pairs was applied using an F-distribution model. The null hypothesis (H0) assumed that there would be no change in backscatter intensity between the two SAR images, while the alternative hypothesis (H1) posited that a statistically significant change would occur; these hypothesis test was formulated as follows:
where and denote the backscatter intensity values at pixel (x, y) from the reference and target SAR images, respectively.
Changes between SAR images were analyzed using ACD, and the intensity ratio between two images was calculated according to the following equation [30]:
This ratio represents the relative difference in pixel values between two time points, and it was evaluated to determine whether the observed change deviated from the expected distribution under a normal or F-distribution probability model. A test statistic function was based on the generalized likelihood ratio (GLR):
where m is the number of looks (multi-look equivalent) used for statistical smoothing; m is empirically set to control sensitivity. Based on this, a p-value map was computed as follows:
where is the is the chi-squared cumulative distribution function with degrees of freedom . Then, a threshold for statistical testing was calculated, and each observation was evaluated to determine whether it exceeded the threshold.
A change was considered to have occurred when , where dt is a threshold determined based on the F-distribution. A pixel was classified as changed if the p-value fell below a stringent threshold derived from a high-confidence significance level (e.g., α = 1 × 10−8). The degrees of freedom and were calculated as follows.
where μ denotes the mean of the ratio values, and m is the number of looks (multi-look factor), which was set to 12 in this study. The value of m was chosen based on empirical practice, where it was found to provide stable detection performance while minimizing speckle noise effects. The parameter m acts as a scaling factor that adjusts the overall sensitivity of the detection process, balancing the trade-off between true positive and false positive rates. The parameter influences the sensitivity of change detection by amplifying the response to potential signal variations. In contrast, the parameter serves to suppress variability in the reference state, thereby reducing the likelihood of false detections.
The initial binary mask generated from the detection results was refined by applying a morphological filter to suppress noise and remove small isolated regions. Furthermore, to isolate floating debris specifically accumulated near known debris barriers, an additional spatial mask was introduced. Only changes within the union of the main ROI and debris trap zones were retained in the final detection map. The entire processing chain was implemented in Python 3.12.3 (Python Software Foundation, Wilmington, DE, USA) and utilized open-source libraries including Rasterio and GDAL for image handling, and SARPY 1.3.0 (Naval Research Laboratory, Washington, DC, USA) for Sentinel-1 metadata parsing and statistical modeling.
The proposed methodology was applied to a total of 18 Sentinel-1 images acquired between June and September 2024. For the floating debris events that occurred in 2024, the type I error tolerance—i.e., the probability of falsely detecting a change where none exists—was set to α < 1 × 10−8. Subsequently, the detection results were validated through comparative analysis with co-temporal optical imagery.
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Results of Floating Debris Detection
The theoretical detectability of floating debris in SAR imagery depends on whether spatial contrast is present within the image. Floating debris typically consists of small leaves, stems, branches, and various types of general waste [31]. These materials often protrude above the water surface, acting as small scatterers that increase surface roughness and enhance radar backscatter, thereby creating positive contrast in SAR imagery. Based on this mechanism, the ACD method based on variations in radar backscatter intensity between Sentinel-1 SAR images was applied to detect floating debris. The analysis was conducted by pairwise comparisons between a reference image (acquired on 5 July 2024) and 18 subsequent images over the same ROI. For each of the 18 image pairs, p-value thresholds were calculated, and binary detection masks were generated.
The ACD algorithm relies on the statistical distribution of the backscatter ratio between two time points, with the critical threshold determined using an F-distribution derived from the degrees of freedom (dfn, dfd). Regions where the p-value falls below the threshold are considered to exhibit statistically significant change and are thus likely to indicate the presence of floating debris. To focus the analysis on probable debris accumulation zones, detection was restricted to areas corresponding to known water bodies and locations with debris containment structures. These were determined using a consistent setting (m = 12, dfn = mean_ratio × m × 40, dfd = mean_ratio × m × 4), where higher values indicate stricter detection criteria. The number of pixels identified in each binary mask was used to estimate debris-covered area, which was then analyzed both visually and statistically.
Based on the ACD analysis framework, statistical thresholds were calculated to determine significant changes between image pairs. The corresponding p-value thresholds for all 18 image pairs are summarized in Table 3. Most p-value thresholds ranged between 0.71 and 0.74, with statistical significance typically assessed around a mean threshold of ~0.727. Lower p-values following intense rainfall (e.g., 12 July: p = 0.7365) coincided with high debris detection areas. Conversely, higher p-values (e.g., 22 August: p = 0.7206) corresponded with zero debris detection, confirming the sensitivity of the detection algorithm to hydrometeorological changes. Self-comparison of the reference image from 5 July yielded negligible or no detection (p = 0.7185; 0 detected pixels), suggesting proper baseline stability.

Table 3.
Quantitative detection results of floating debris area with precipitation observed during the research period.
As shown in Figure 4, the SAR imagery successfully detected floating debris in areas where large accumulations were present, exhibiting higher backscatter intensity compared with adjacent open water. This effect is attributed to the fact that dense floating debris reflects radar signals more strongly than the surrounding water surface [32]. All detection results were compared against rainfall data collected from the Daecheong Dam gauge station on the Geum River.
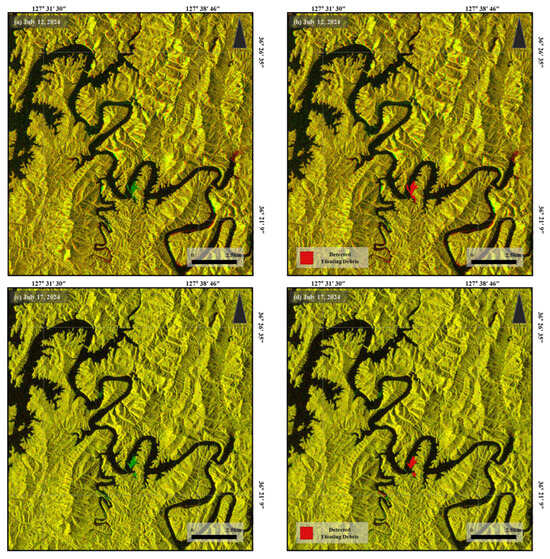
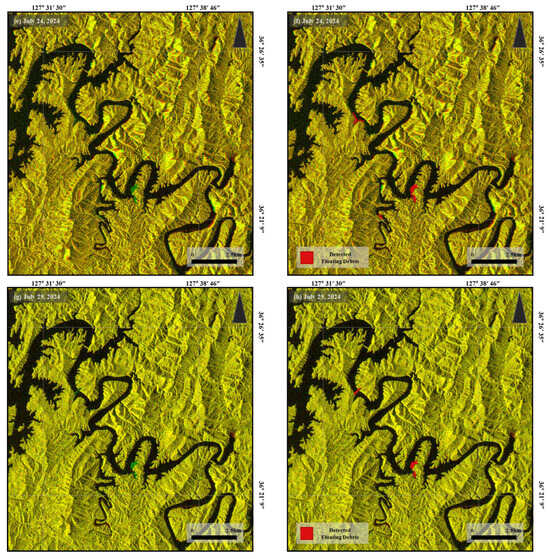
Figure 4.
Example pairs of Sentinel-1 SAR images and corresponding floating debris detection results: (a,c,e,g) input image pairs (Band 1: reference; Band 2: target); (b,d,f,h) detected floating debris shown as binary masks.
Cumulative rainfall was calculated using hydrological datasets from South Korea’s multipurpose dams and weirs. For each satellite acquisition between 1 June and 30 September 2024, cumulative rainfall totals were calculated over 3-, 5-, and 10-day periods preceding and including the image acquisition date (Table 3). Analysis of the precipitation data revealed several distinct patterns in rainfall intensity and temporal distribution. Notably, extreme rainfall events occurred on 12 July and 22 September, with 5-day cumulative precipitation reaching 269.88 mm and 209.58 mm, and 10-day totals reaching 331.87 mm and 209.71 mm, respectively. These events reflect short-term but intense rainfall conditions, suggesting sustained hydrological impact even beyond the rainfall period. The delayed effect of precipitation must be considered, as accumulated rainfall may have continued to influence surface runoff and debris transport despite the absence of new rainfall [33].
The results showed a clear increase in detected debris areas during and following high-rainfall periods. For instance, on 30 June, with a 5-day cumulative rainfall of 68.53 mm, approximately 0.0659 km2 of floating debris was detected. On 12 July, a day of intense rainfall (269.88 mm daily, 331.87 mm over 10 days), the detected debris area increased to 0.3828 km2. Additional large-scale detections followed on 17 July (0.338 km2) and 24 July (0.4504 km2), with elevated levels maintained through 29 July (0.2741 km2). This trend from mid to late July suggests an accumulation effect induced by the 12 July rainfall event as shown in Figure 4. Similar patterns persisted on 5 August (11.9 mm daily rainfall) with 0.2476 km2 of debris, and 0.2508 km2 was detected on 22 September with 5-day rainfall at 209.58 mm. In contrast, the area of detection decreased during the second half of August, consistent with the timing of national debris collection efforts [3].
Conversely, minimal rainfall and dry periods, such as 17 August and 3 September, resulted in negligible precipitation totals (daily, 5-day, and 10-day rainfall close to 0 mm), indicating probable drought conditions with minimal debris inflow. On 10 August (0 mm daily rainfall) and 22 August (2.64 mm), the corresponding debris areas detected were 0.0703 km2 and 0 km2, respectively. These results underscore the strong influence of rainfall on debris detection, while also highlighting that detection is affected by other factors such as image acquisition timing, debris movement and retention, and the presence of artificial barriers.
To further investigate the influence of cumulative rainfall and temporal lag on the detected floating debris, a correlation analysis was conducted using daily precipitation data and the corresponding debris detection results. Cumulative rainfall windows ranging from 1 to 15 days were tested, with time shifts from 0 to 10 days prior to each SAR acquisition. For example, when the accumulation window was set to 5 days and the time shift to 3 days, rainfall was summed from 8 to 4 days before the detection date.
For each combination of accumulated days and time shifts, the Pearson correlation coefficient (r) and corresponding p-value were calculated between the cumulative rainfall and detected debris area on the acquisition date. The resulting correlation coefficients were visualized using a heatmap as Figure 5, with the x-axis representing the number of days shifted and the y-axis indicating the accumulation window size. A separate heatmap was also generated for p-values, where values smaller than 0.0001 were labeled as “<0.0001” for clarity.
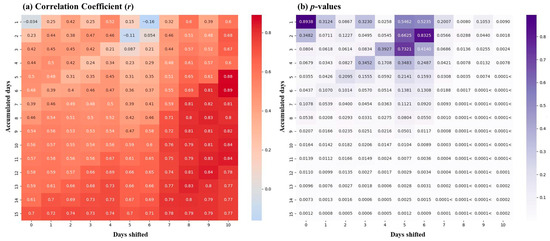
Figure 5.
Heatmap of (a) Pearson correlation coefficients r and (b) p-values between accumulated rainfall and detected area of floating debris across varying accumulation windows and shift periods.
The heatmaps revealed that floating debris occurrence is not significantly influenced by single-day rainfall or short accumulation periods (e.g., 1–2 days). Instead, statistically significant correlations were observed for accumulation periods exceeding five days. Notably, detection of debris was more closely associated with delayed rainfall accumulated over a longer time span (e.g., more than a week), rather than immediate precipitation events. These findings suggest that in future predictive models of floating debris occurrence, both the appropriate time shift and accumulation period should be carefully considered when using rainfall data as an input variable.
These findings confirm that the ACD-based detection method provides a valid statistical framework for analyzing the relationship between rainfall and floating debris dynamics. Specifically, the analysis revealed increased areas of debris detected immediately after rainfall, proportional relationships with cumulative rainfall, and lagged accumulation effects across the time series. While some exceptions were observed due to site-specific physical or environmental conditions, the overall pattern demonstrates that 10-day cumulative rainfall serves as a valuable indicator of hydrological stress, influencing debris transport and accumulation.
4.2. Visual Interpretation and Evaluation
To assess whether the detected floating debris accurately corresponded to actual presence of debris, a comparative analysis was conducted using co-located image pairs of Sentinel-1 SAR and optical imagery acquired within two days of each other (Figure 6). Due to the limited availability of optical images during heavy rainfall periods when floating debris is most likely to occur, only a subset of usable image pairs listed in Table 2 was matched and analyzed. The comparison focused primarily on July and September, when substantial debris was detected in the SAR imagery. In this analysis, visual evidence of floating debris observed in the optical images served as a reference indicator of true debris presence, against which the SAR-based detections were evaluated.
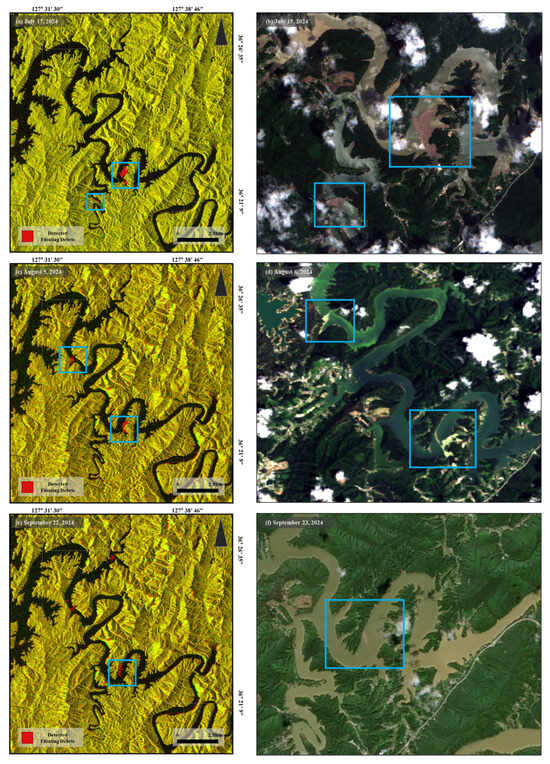
Figure 6.
Visual comparison results with regions of interest marked with boxes: (a,c,e) SAR-based floating debris detection results, and (b,d,f) corresponding optical images acquired within two days.
The average temporal difference between the SAR and optical image acquisitions was approximately two days. While the overall spatial patterns of debris patches appeared similar between the two image types, slight positional discrepancies were observed likely due to surface currents or water movement. Notably, the blue boxes in the figures highlight regions of visual correspondence between the SAR and optical images, emphasizing their spatial agreement.
In addition to the use of visual interpretation based on optical imagery, an accuracy assessment was conducted by generating reference data through manual inspection of minimally cloud-affected optical images within the ROIs (Table 4). Evaluation metrics include precision, recall, F1 score, intersection over the union (IoU), and the corresponding detected and reference areas. Overall, high agreement was observed in mid-July (e.g., 12 and 17 July) and early August (e.g., 5 August), when F1 scores exceeded 0.65, indicating reliable detection of high-density floating debris following major rainfall events. In contrast, detection performance deteriorated significantly in late August and September.

Table 4.
Accuracy metrics for floating debris detection based on optical reference image comparison.
These discrepancies can be attributed to several factors. First, spatial resolution differences between Sentinel-1 SAR (10 m) and the reference imagery (Sentinel-2 at 10 m or Landsat 8/9 at 30 m) may have led to under- or over-estimation of reference areas. Second, temporal mismatches of up to ±2 days between SAR and optical acquisitions can result in changes in debris distribution due to water flow, wind, or post-rainfall runoff. For example, on 22 September, although some debris was visually confirmed in the reference image, the SAR-based detection is likely to have underestimated the area due to debris displacement or dissipation.
5. Conclusions
This study presents an approach for the efficient monitoring and systematic management of floating debris that rapidly accumulates in large inland water bodies following extreme rainfall events. Specifically, we developed and implemented a near real-time detection method that integrates ACD using all-weather SAR imagery with a statistically robust significance index-based detection function. The effectiveness of the proposed method was demonstrated through its application to a series of floating debris events that occurred in Daecheong Reservoir—a major source of drinking water in South Korea—during the monsoon and typhoon season from June to September 2024. The results clearly indicate the model’s capacity for quantitative detection and its practical applicability in operational contexts.
Compared with prior work, this study offers a quantitative, time-series-based detection of floating debris in inland waters. Qi et al. [18] assessed the capability of Sentinel-1 SAR to detect marine floating matter, demonstrating feasibility for algal detection but limiting their analysis to single-date, qualitative assessments. In contrast, this study applied a statistically robust detection algorithm to a time series of SAR imagery to quantitatively monitor debris dynamics and examine correlations with rainfall events. Seo et al. [19] used ocean color imagery and particle-tracking models to analyze the movement of flood-driven debris, yet their approach did not involve direct spatial detection or quantitative area estimation of debris. In the current study, debris-covered areas were quantified based on actual SAR detection. Park and Kang [22] analyzed temporal waterbody changes using SAR and optical imagery; however, their focus remained on the waterbody area rather than on the floating debris. The present study was conducted focused on detecting a specific physical target—floating debris—through a time-series SAR framework.
The findings show that the proposed methodology overcomes the spatial and temporal limitations of conventional field-based and visual inspection methods, enabling timely and objective detection of debris distribution across large aquatic environments. Notably, the SAR-based analysis revealed spatial concentrations of floating debris around physical structures such as containment booms, and it clearly visualized debris in designated collection zones such as near Seokho-ri. These insights provide a valuable scientific basis for the development of predictive debris transport models and region-specific collection strategies.
The key conclusions of this study are as follows. First, quantitative SAR-based detection can enable the precise identification of high-density debris accumulation zones. It allows strategic allocation of limited collection resources and prioritization of targeted cleanup operations enhancing management efficiency. Second, the proposed methodology offers a cost-effective and scalable solution for continuous monitoring across large reservoir systems. By providing early warning of potential pollution, it contributes meaningfully to the protection of water quality in essential drinking water supplies. Third, the all-weather, day-and-night observation capability of Sentinel-1 SAR significantly improves the speed, objectivity, and spatial extent of debris monitoring, combined with the proposed algorithm’s high sensitivity to subtle signal changes.
Nonetheless, it is important to recognize that SAR imagery is inherently subject to noise effects from wind-induced surface roughness or wave activity, which may result in false negatives, i.e., failure to detect debris that is actually present. Careful interpretation of results is therefore essential. To address these limitations, future work should consider multi-source data fusion by integrating drone-based imagery and high-resolution optical satellite data with different spectral characteristics to improve detection reliability.
Also, the parameters of the ACD-based debris detection algorithm were uniformly fixed and applied across all image pairs to ensure consistency and practical applicability in this study. While this approach offers the advantage of standardized detection across diverse time-series images, it also presents a limitation in that it does not fully account for variations in local and temporal conditions such as rainfall intensity, hydrological dynamics, or image quality. In particular, in cases where debris variations are minimal or image quality is compromised, fixed parameter settings may lead to reduced true positive rates or inflated false positive rates due to insufficient sensitivity adjustment. Future research should consider incorporating adaptive parameter tuning mechanisms that respond dynamically to environmental conditions, in order to improve the accuracy and reliability of debris detection.
In conclusion, this study empirically demonstrates that advanced SAR-based quantitative detection techniques can serve as a critical tool for monitoring floating debris in large inland water bodies. Furthermore, the applicability of the proposed method can be extended beyond reservoirs to include rivers, estuaries, and coastal environments, where system-specific investigations are required. Expanding and refining this approach across various water resource management scenarios holds potential for contributing to sustainable water governance and the preservation of healthy aquatic ecosystems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.Y. and M.-J.L.; Data curation, S.L. and B.J.; Formal analysis, J.L. (Jinhee Lee); Funding acquisition, J.L. (Jeongho Lee); Investigation, B.J., J.L. and J.H.; Methodology, S.L., B.J. and J.L.; Resources, D.Y., J.L. (Jeongho Lee) and J.H.; Software, D.Y.; Supervision, M.-J.L.; Validation, S.L.; Visualization, S.L.; Writing—original draft, S.L.; Writing—review and editing, M.-J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This paper was written following the research work of GP2025-05 funded by the Korea Environment Institute (KEI) and also the research 2025-016 funded by K-water Research Institute.
Data Availability Statement
The original Sentinel-1 GRD data analyzed in this study were freely obtained from the Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem (https://browser.dataspace.copernicus.eu/, accessed on 29 April 2025), an official open-access platform for Copernicus Earth Observation data.
Acknowledgments
During the preparation of this manuscript, the authors used ChatGPT (OpenAI, GPT-4) to assist with English language editing and to improve clarity. The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kim, S.-W.; Cho, Y.-H.; Chae, M.-H.; KiL, G.-B.; Seok, K.-S. Characteristics of organic matters in small streams into the daecheong reservoir. J. Environ. Anal. Health Toxicol. 2020, 23, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, B.C.; Forsberg, B.R.; Kasper, D.; Amaral, J.H.; de Vasconcelos, M.R.; de Sousa, O.P.; Cunha, F.A.; Bastos, W.R. The influence of inundation and lake morphometry on the dynamics of mercury in the water and plankton in an amazon floodplain lake. Hydrobiologia 2017, 790, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environment. Completion of Floating Debris Removal Following Heavy Rainfall [Press Release]. 12 September 2024. Available online: https://www.korea.kr/briefing/pressReleaseView.do?newsId=156650459 (accessed on 29 April 2025).
- Park, Y.; Kim, S.; Chon, K.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, J.-K. Impacts of heavy rain and floodwater on floating debris entering an artificial lake (daecheong reservoir, korea) during the summer. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 219, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.; Howd, P.; Sallenger, A.; Lillycrop, J.; Farris, G.; Smith, G.; Crane, M.; Demas, C.; Robbins, L.; Lavoie, D. Estimation of post-katrina debris volume: An example from coastal mississippi. In Science and the storms: The USGS response to the hurricanes of 2005 (No. 1306); US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2007; pp. 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Murch, B.; Barnes, B.B.; Wang, M.; Maréchal, J.-P.; Franks, J.; Johnson, D.; Lapointe, B.; Goodwin, D.; Schell, J. Sargassum watch warns of incoming seaweed. Eos 2016, 97, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topouzelis, K.; Papakonstantinou, A.; Garaba, S.P. Detection of floating plastics from satellite and unmanned aerial systems (plastic litter project 2018). Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 79, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, B.; Sannigrahi, S.; Sarkar Basu, A.; Pilla, F. Development of novel classification algorithms for detection of floating plastic debris in coastal waterbodies using multispectral sentinel-2 remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C. Remote detection of marine debris using satellite observations in the visible and near infrared spectral range: Challenges and potentials. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 259, 112414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.D.; Platnick, S.; Menzel, W.P.; Ackerman, S.A.; Hubanks, P.A. Spatial and temporal distribution of clouds observed by modis onboard the terra and aqua satellites. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 3826–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.; Ma, R.; Cao, Z.; Shen, M.; Hu, M.; Xiong, J. Monitoring fractional floating algae cover over eutrophic lakes using multisensor satellite images: Modis, viirs, goci, and olci. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Yan, C.; Lv, S.; Sun, H.; Xue, S.; Li, Q.; Zhou, L.; Edwing, D.; Edwing, K.; Geng, X. Synthetic aperture radar for geosciences. Rev. Geophys. 2024, 62, e2023RG000821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, D.; Yu, H.-e.; Lee, M.-J. Detection of floating debris in the lake using statistical properties of synthetic aperture radar pulses. Geo Data 2023, 5, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, T. Seasonal cycles of lakes on the tibetan plateau detected by sentinel-1 sar data. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Wu, L.; Huang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, J.; Li, N. Water-body segmentation for sar images: Past, current, and future. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horritt, M.; Mason, D.; Luckman, A. Flood boundary delineation from synthetic aperture radar imagery using a statistical active contour model. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 2489–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Liu, D. A local thresholding approach to flood water delineation using sentinel-1 sar imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 159, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Wang, M.; Hu, C.; Holt, B. On the capacity of sentinel-1 synthetic aperture radar in detecting floating macroalgae and other floating matters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 280, 113188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.; Park, Y.-G.; Kim, K. Tracking flood debris using satellite-derived ocean color and particle-tracking modeling. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 161, 111828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.M.; Azevedo, L. Automatic detection and identification of floating marine debris using multispectral satellite imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veci, L.; Prats-Iraola, P.; Scheiber, R.; Collard, F.; Fomferra, N.; Engdahl, M. In The Sentinel-1 Toolbox. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Kang, K.-m. Research of water-related disaster monitoring using satellite bigdata based on google earth engine cloud computing platform. Korean J. Remote Sens. 2022, 38, 1761–1775. [Google Scholar]
- K-water. Water Safety Services. Available online: https://www.kwater.or.kr/eng/busi/resoPage.do?s_mid=1179 (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- V-World. Available online: https://www.vworld.kr/dtmk/dtmk_ntads_s002.do?searchKeyword=%ED%98%B8%EC%86%8C&searchSvcCde=&searchOrganization=&searchBrmCode=&searchTagList=&searchFrm=&pageIndex=1&gidmCd=&gidsCd=&sortType=00&svcCde=MK&dsId=20250121DS00020&listPageIndex=1 (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Ministry of Environment. Installation of an Algal Bloom Containment Boom in the Chudong Area of Daecheong Reservoir [Press Release]. Available online: https://www.me.go.kr/gg/web/board/read.do?menuId=2290&boardMasterId=237&boardCategoryId=&boardId=355751 (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- K-water. Floating Debris Collection Records of Daecheong Reservoir, 2015–2024; K-water: Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 2024; Unpublished internal document obtained via information disclosure request. [Google Scholar]
- European Union/ESA/Copernicus. Sentinel-1 Sar Grd: C-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar Ground Range Detected, Log Scaling. Available online: https://developers.google.com/earth-engine/datasets/catalog/COPERNICUS_S1_GRD (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Sentinel Hub. Available online: https://docs.sentinel-hub.com/api/latest/data/sentinel-1-grd/ (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Gulácsi, A.; Kovács, F. Sentinel-1-imagery-based high-resolution water cover detection on wetlands, aided by google earth engine. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conradsen, K.; Nielsen, A.A.; Skriver, H. Determining the points of change in time series of polarimetric sar data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 3007–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocamora, C.; Puerto, H.; Abadía, R.; Brugarolas, M.; Martínez-Carrasco, L.; Cordero, J. Floating debris in the low segura river basin (spain): Avoiding litter through the irrigation network. Water 2021, 13, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Fockert, A.; Eleveld, M.; Bakker, W.; Felício, J.M.; Costa, T.; Vala, M.; Marques, P.; Leonor, N.; Moreira, A.; Costa, J. Assessing the detection of floating plastic litter with advanced remote sensing technologies in a hydrodynamic test facility. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, Q.; Su, D.; Li, P.; He, Z. Experimental study of the impact of rainfall characteristics on runoff generation and soil erosion. J. Hydrol. 2012, 424, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).