Exploring the Effects of Fillers and Cultivation Conditions on Microbial-Algal Biofilm Formation and Cattle Wastewater Treatment Efficiency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Characterization Analysis of Biofilms Attached to Fillers
3.1.1. Biomass Dry Weight and Biofilm Formation Rate
3.1.2. Formation of Microbial-Algal Biofilms Under Microscope
3.1.3. Changes in Chlorophyll Content
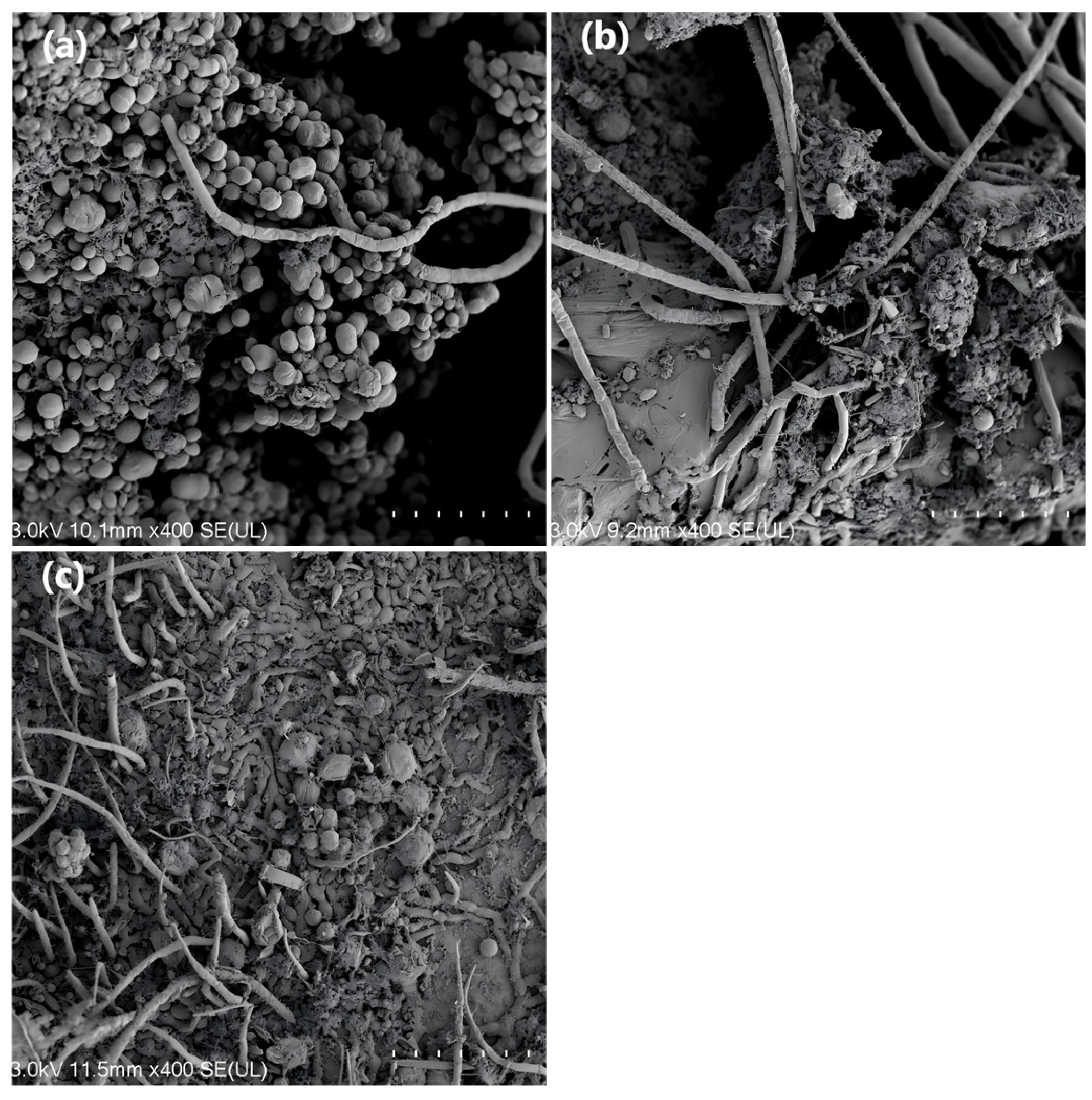
3.1.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis of Microbial-Algal Biofilms
3.1.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
3.1.6. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Analysis
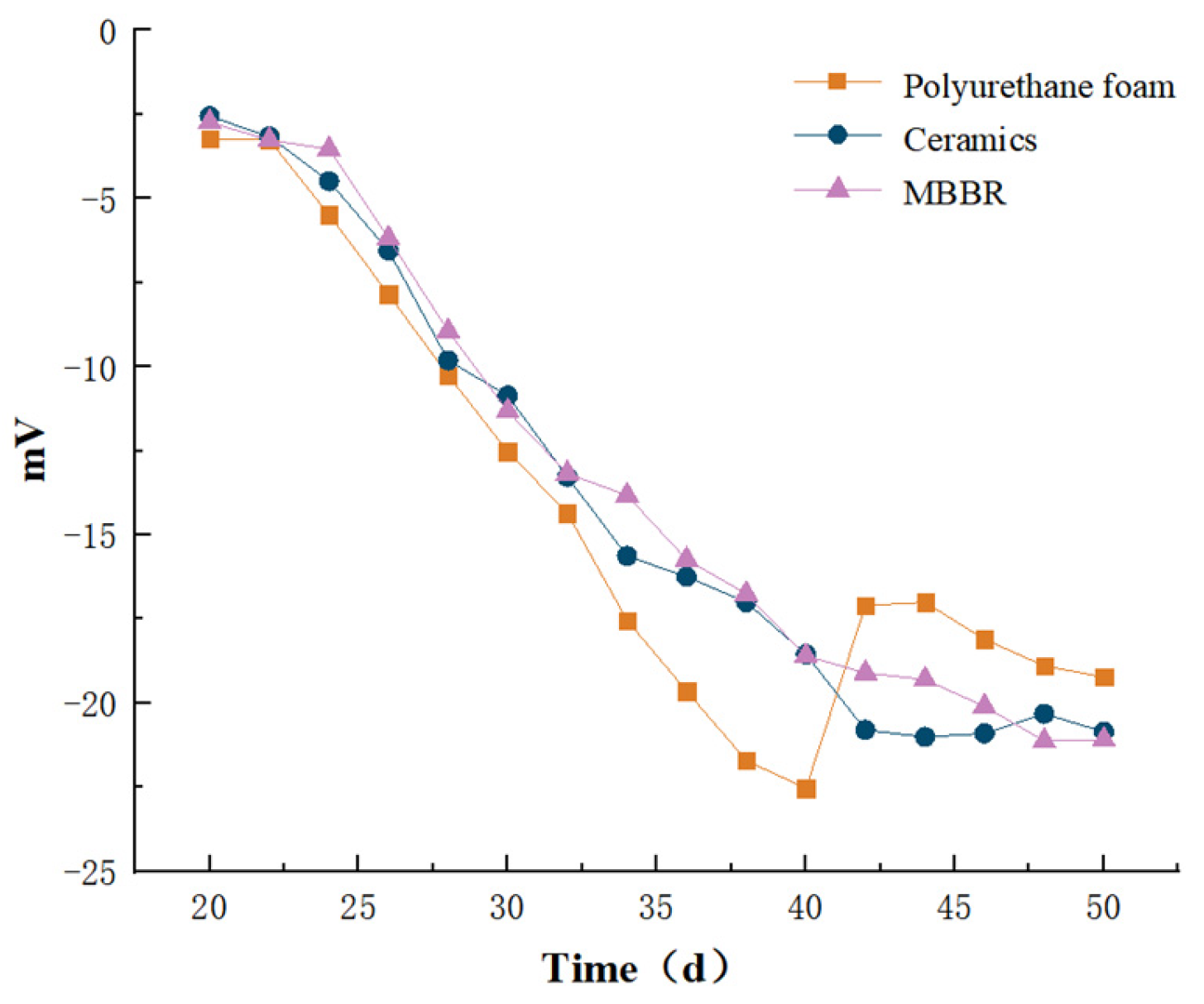
3.1.7. Zeta Potential Analysis
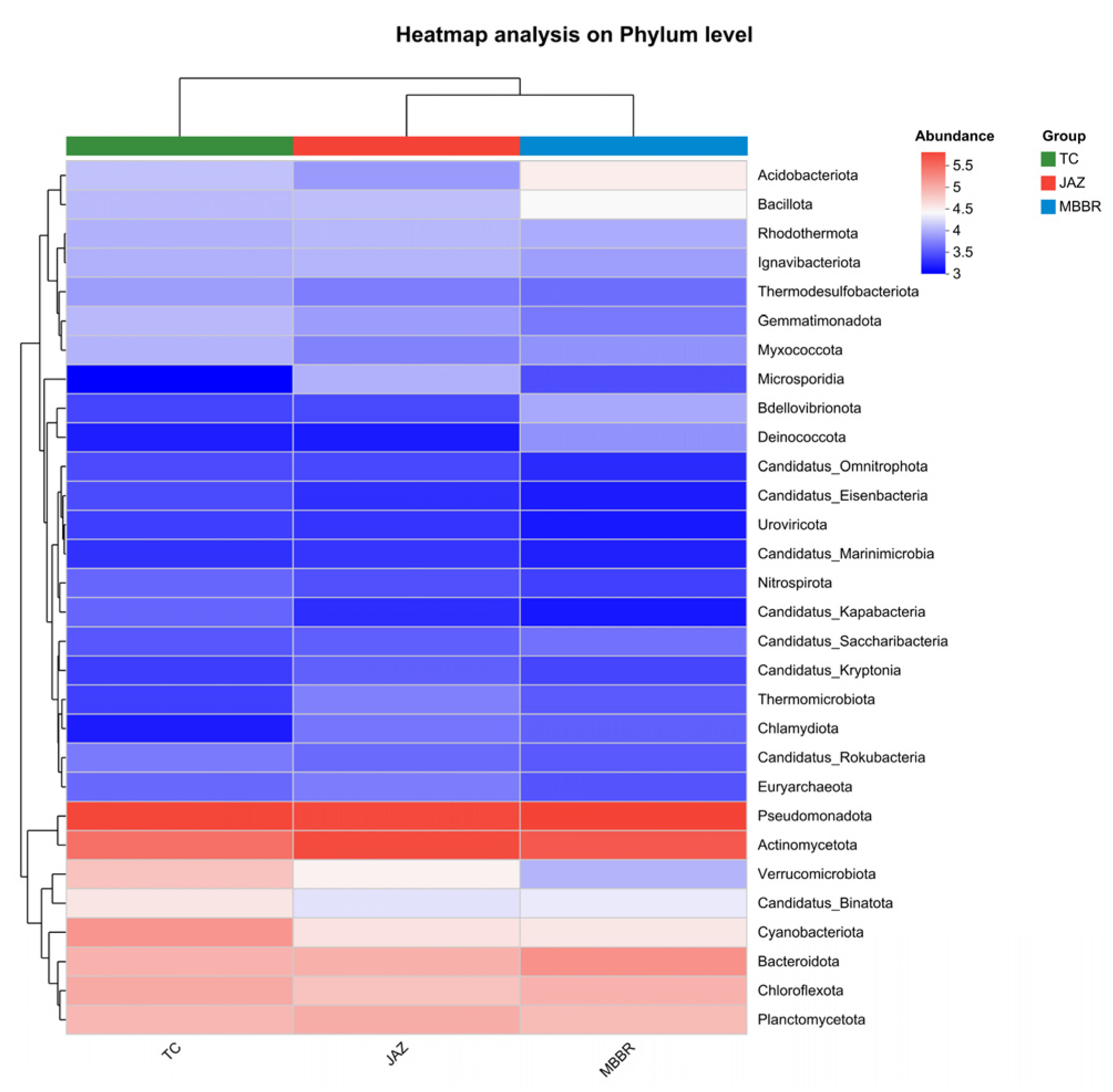
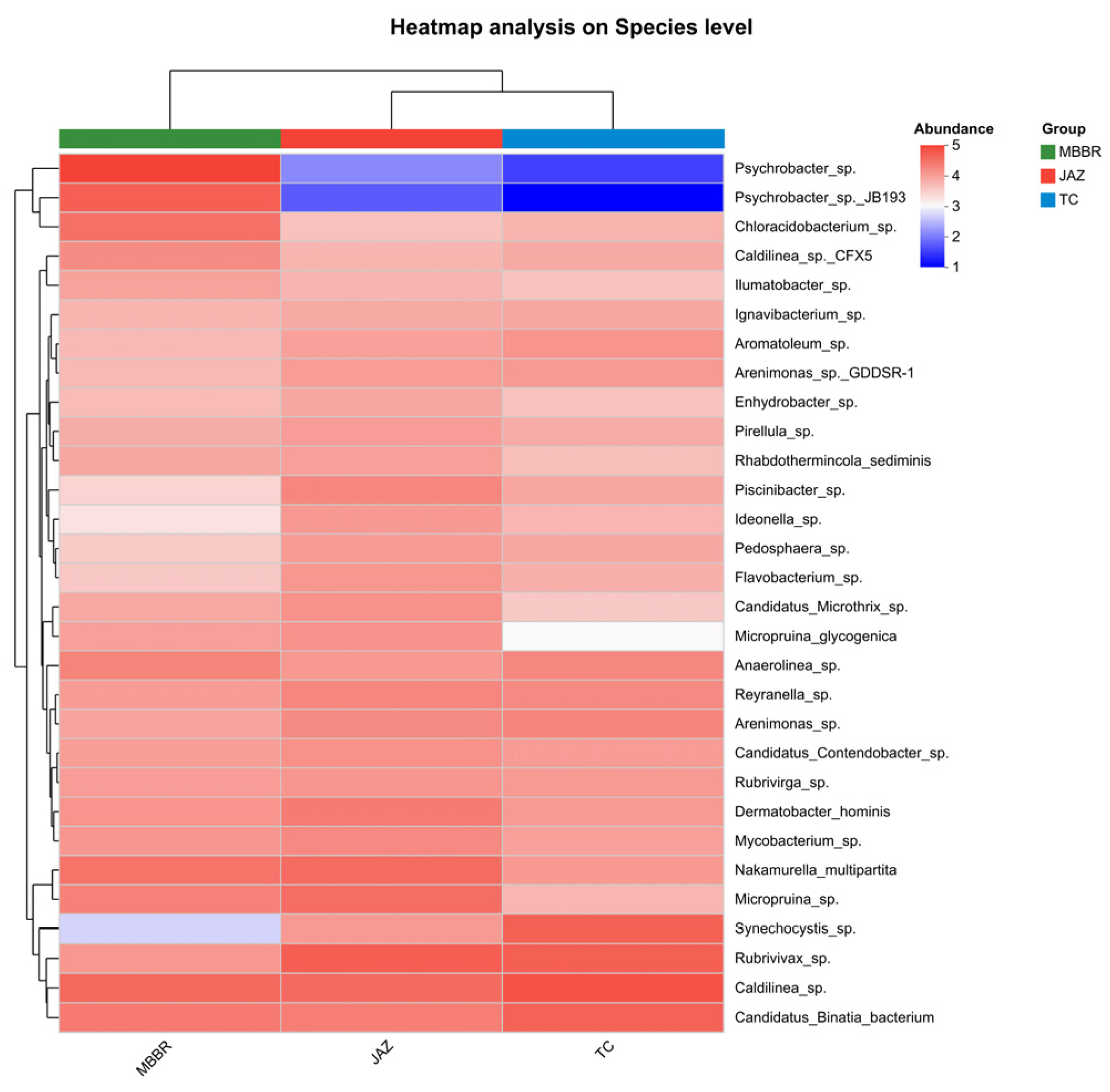
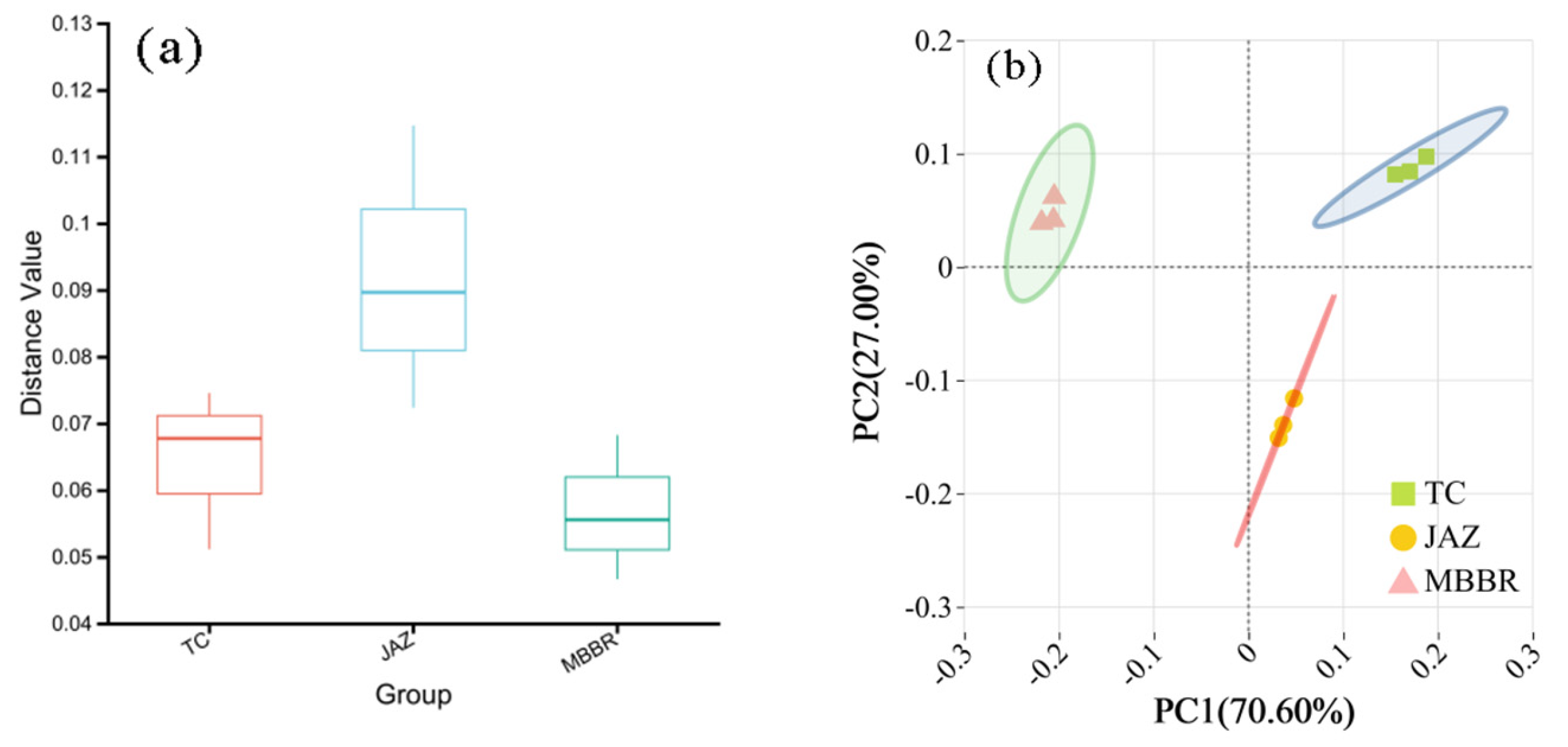
3.2. Analysis of Microbial Community Characteristics
3.2.1. Analysis of Community Structural Diversity
3.2.2. Beta Diversity Analysis
3.3. Factors Influencing Microbial-Algal Biofilm Photoreactors
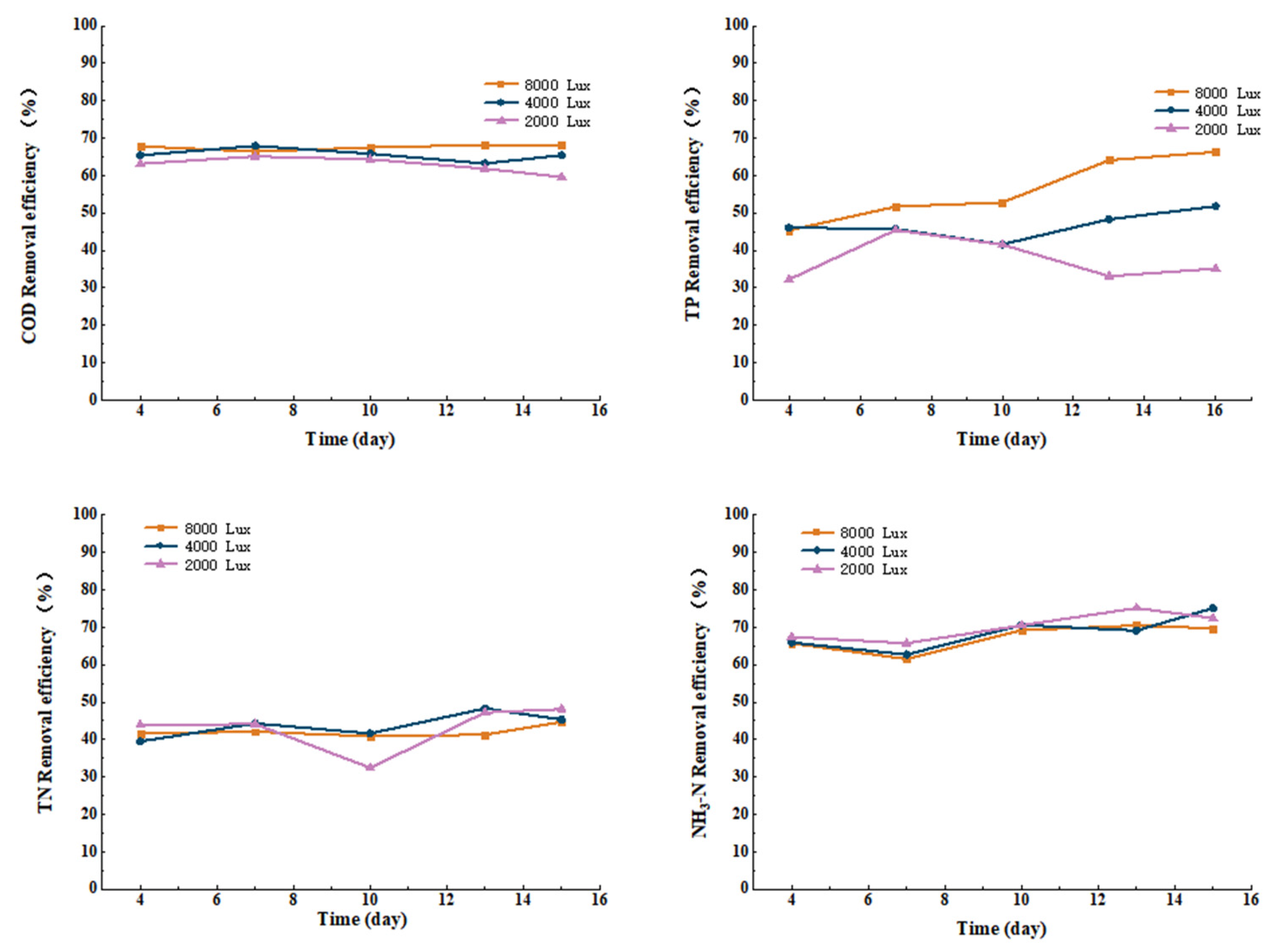
3.3.1. Effect of Light Intensity on COD, TN, TP, and Ammonia Nitrogen Removal from Cattle Wastewater by Microbial-Algal Biofilms
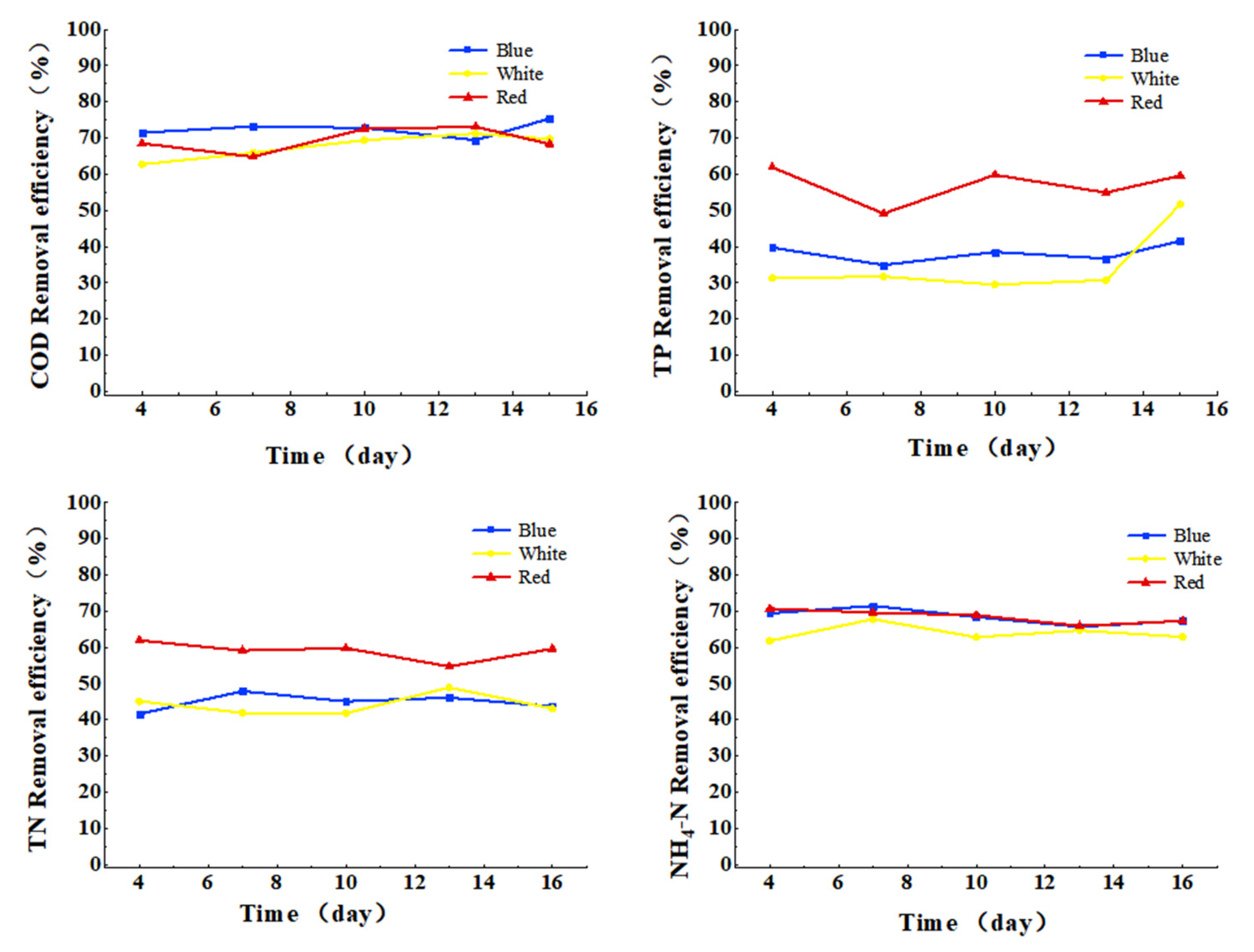
3.3.2. Effect of Light Color on COD, TN, TP, and Ammonia Nitrogen Removal from Cattle Wastewater by Microbial-Algal Biofilms
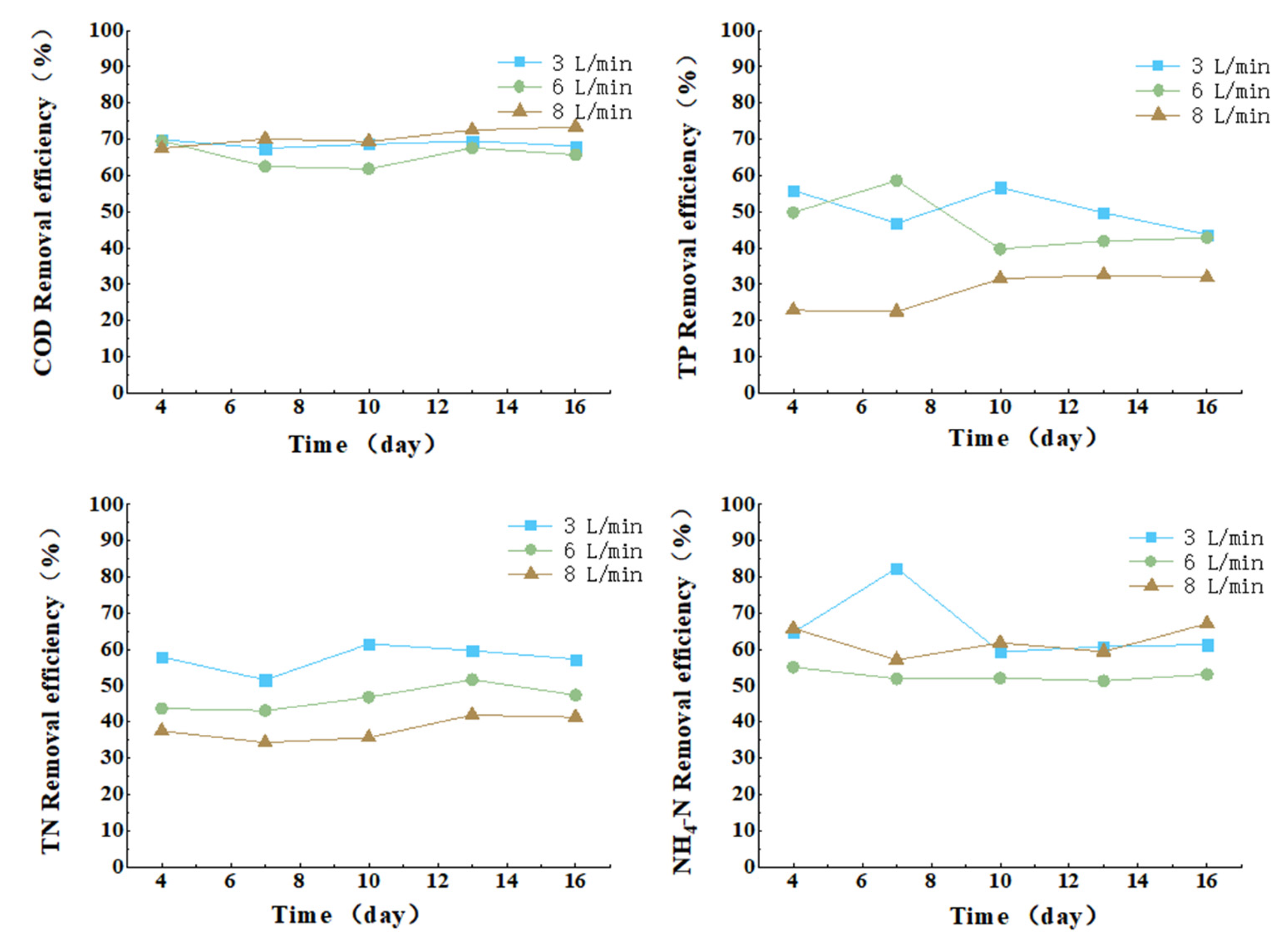
3.3.3. Effect of Aeration Intensity on COD, TN, TP, and Ammonia Nitrogen Removal from Cattle Wastewater by Microbial-Algal Biofilms
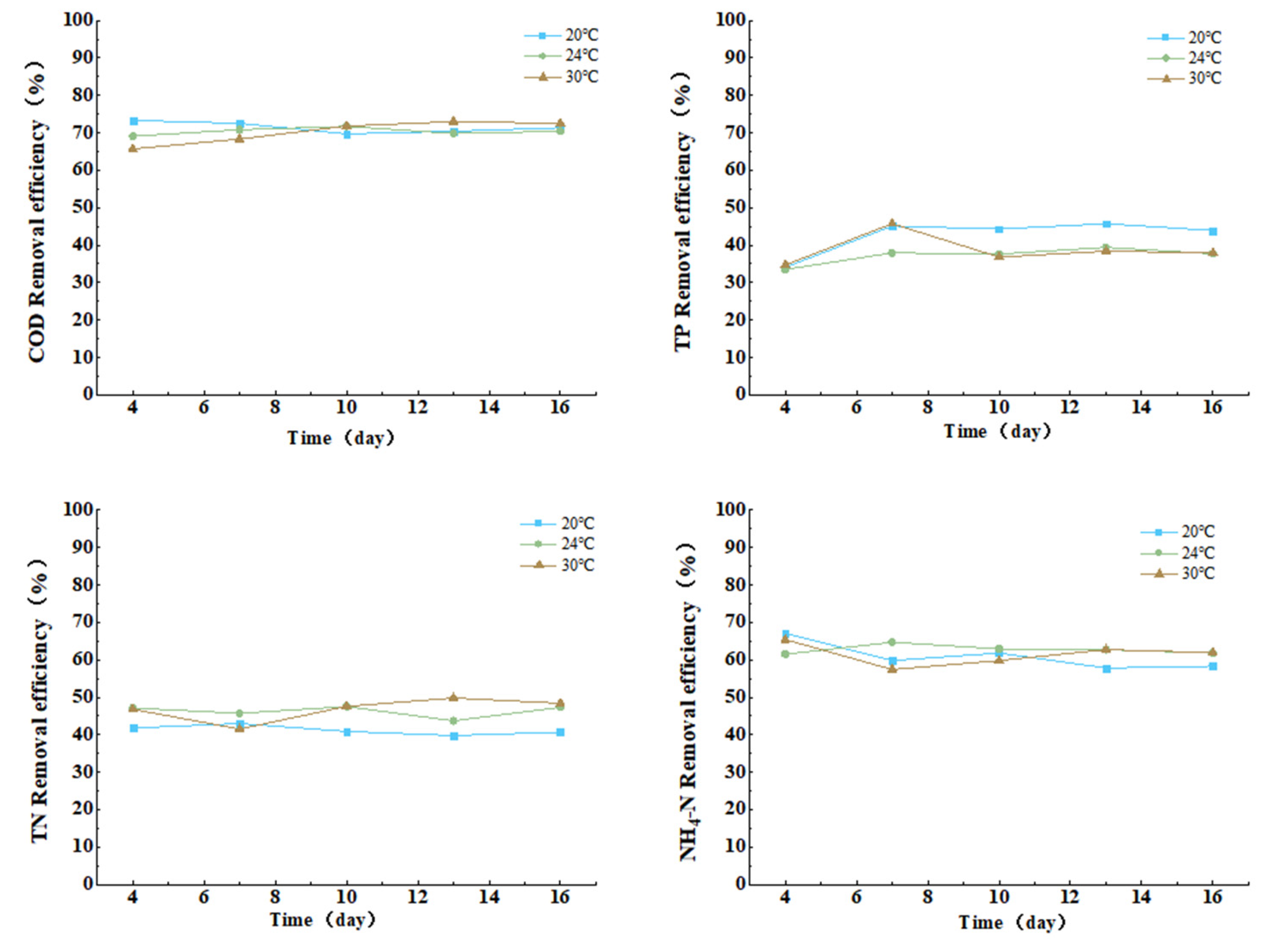
3.3.4. Effect of Temperature on COD, TN, TP, and Ammonia Nitrogen Removal from Cattle Wastewater by Microbial-Algal Biofilms
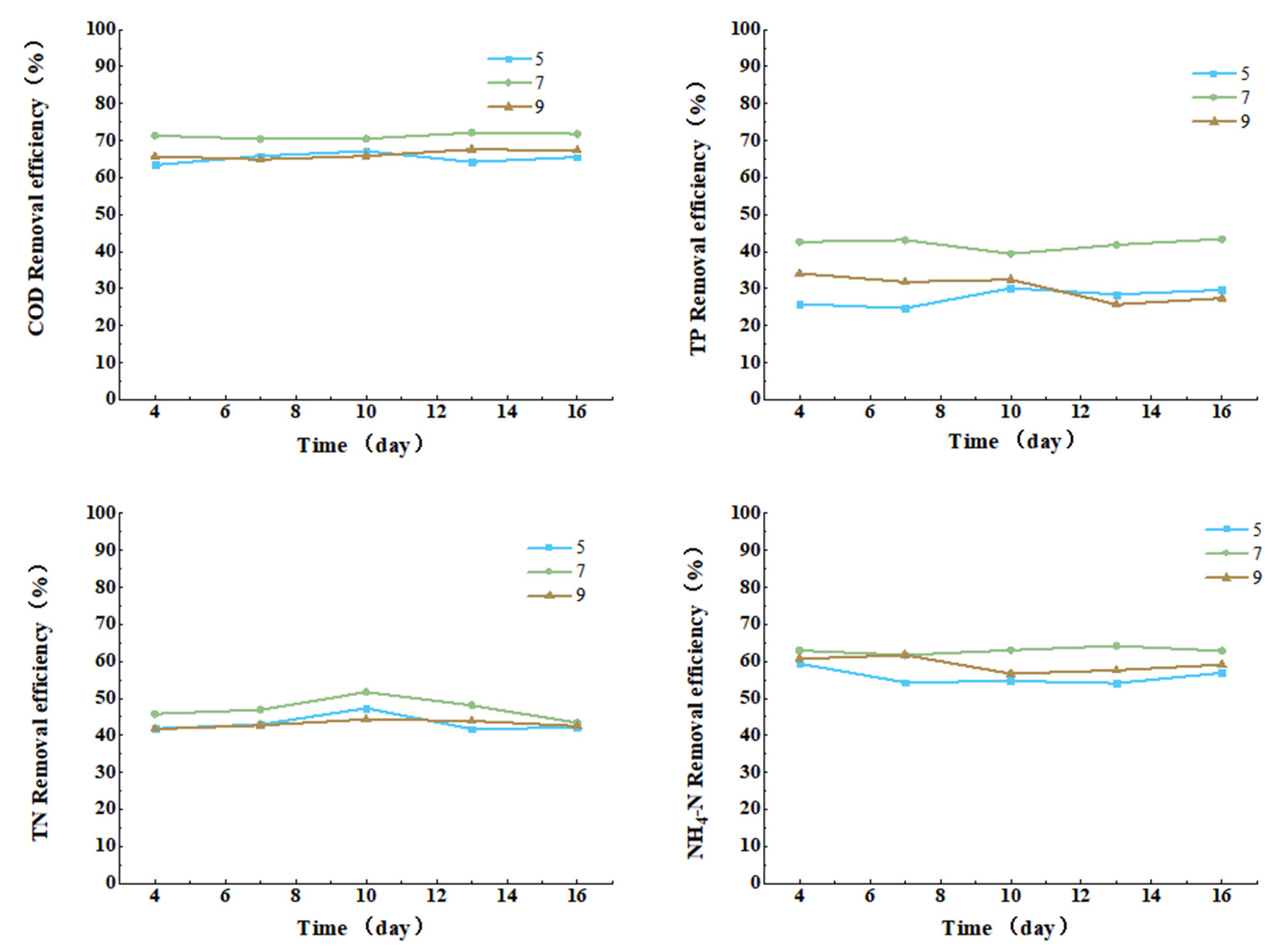
3.3.5. Effect of pH on COD, TN, TP, and Ammonia Nitrogen Removal from Cattle Wastewater by Microbial-Algal Biofilms
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.; Feng, C.; Duan, Y.; Wang, P.; Peng, C.; Li, Z.; Yu, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, F. Ecological risk under the dual threat of heavy metals and antibiotic resistant Escherichia coli in swine-farming wastewater in Shandong Province, China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 319, 120998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Lu, Z.; Xie, T.; Wang, L.; Mo, C. Nitrogen and phosphorus removal by coupling Anaerobic ammonia oxidation reaction with algal-bacterial symbiotic system. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qv, M.; Dai, D.; Liu, D.; Wu, Q.; Tang, C.; Li, S.; Zhu, L. Towards advanced nutrient removal by microalgae-bacteria symbiosis system for wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 370, 128574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qixin, L.; Xuan, F.; Zhiya, S.; Wenxin, S.; Shuo, W.; Ji, L. Enhanced wastewater treatment performance by understanding the interaction between algae and bacteria based on quorum sensing. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 354, 127161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wu, L.; Guo, Y.; Lens, P.N.; Shi, W. Rapid establishment of algal bacterial granular sludge system by applying mycelial pellets in a lab-scale photo-reactor under low aeration conditions: Performance and mechanism analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 322, 121183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, F. Treatment of antibiotic containing wastewater with self-suspended algae-bacteria symbiotic particles: Removal performance and reciprocal mechanism. Chemosphere 2023, 323, 138240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.J.; Chen, X.; Yao, L.P.; Zhang, R.Q. Application and prospect of microalgae biotechnology in carbon neutralization. China Biotechnol. 2022, 42 (Suppl. 1), 160–173. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.H.; He, W.H.; Xiang, T.Y.; Shan, Z.D. Algal-bacterial symbiotic SBBR for biogas slurry treatment from pig farm. Technol. Water Treat. 2018, 44, 118–122. [Google Scholar]
- Bilad, M.R.; Arafat, H.A.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Membrane technology in microalgae cultivation and harvesting: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1283–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.C.; Cheng, X.; Zeng, X. Mechanisms and applications of bacterial-algal symbiotic systems for pollutant removal from wastewater. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2018, 38, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Li, W.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, W.; Cui, F.; Lens, P.N.; Tay, J.H. Microalgal-bacterial consortia: From interspecies interactions to biotechnological applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 118, 109563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.W.; Ma, Z.K. Biofilmsewage treatment technology and biofilm carrier. Jiangsu Chem. Ind. 2004, 32, 36–38. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, M.; Zhao, X.; Mascarenhas, V.; Wen, Z. Effects of the surface physico-chemical properties and the surface textures on the initial colonization and the attached growth in algal biofilm. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, R.; Venugopalan, V.P.; Satpathy, K.K.; Nair, K.V.K.; Rao, V.N.R. Laboratory studies on adhesion of microalgae to hard substrates. Hydrobiologia 2004, 512, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oruganti, R.K.; Katam, K.; Show, P.L.; Gadhamshetty, V.; Upadhyayula, V.K.K.; Bhattacharyya, D. A comprehensive review on the use of algal-bacterial systems for wastewater treatment with emphasis on nutrient and micropollutant removal. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 10412–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Lin, G.H.; Cai, Z.H. Roles of microbes in matter cycles in phycosphere niche. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 27, 2708–2716. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, R.; Zheng, Y. Overview of microalgal extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and their application. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1225–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Zhu, L.; Chen, L.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J. Detection Techniques for Extracellular Polymeric Substances in Biofilms: A Review. BioResources 2016, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y. Behaviour of bacterial extracellular polymeric substances from activated sludge: A review. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 32, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, H.; Neu, T.R.; Wulkow, M. Modelling the structure and function of extracellular polymeric substances in biofilms with new numerical techniques. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Li, J.; Qiao, H.; Lin, A.; Wang, G. Immobilization of Chlorella sorokiniana GXNN 01 in alginate for removal of N and P from synthetic wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 114, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. HJ 828—2017 Water Quality—Determination of the Chemical Oxygen Demand—Dichromate Method; Issued on 2017-03-30, implemented on 2017-05-01; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. HJ 636—2012 Water Quality—Determination of Total Nitrogen—Alkaline Potassium Persulfate Digestion UV Spectrophotometric Method; Issued on 2012-02-29, implemented on 2012-06-01; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012.
- GB/T 11893-1989; Water Quality—Determination of Total Phosphorus—Ammonium Molybdate Spectrophotometric Method. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1989.
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. HJ 535—2009 Water Quality—Determination of Ammonia Nitrogen—Nessler’s Reagent Spectrophotometry; Issued on 2009-12-31, implemented on 2010-04-01; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, W.; Zheng, X.Y.; Xiang, W.; Qu, J.X.; Zhao, Z.L.; Yang, C.F. The FTIR study on the response of extracellular polymer substances to sludge retention time. Ind. Water Treat. 2020, 40, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.H.; Song, R.H.; Teng, S.X.; Gao, M.M.; Ni, J.Y.; Liu, F.F.; Wang, S.G.; Gao, B.Y. Characteristics and mechanisms of Cu(II) biosorption by disintegrated aerobic granules. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Quan, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, T.; Quan, W. Accelerated startup of moving bed biofilm process with novel electrophilic suspended biofilm carriers. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 315, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, W.-S.; Huang, L.-N. Microbial diversity in extreme environments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesaano, M.; Sims, R.C. Algal biofilm based technology for wastewater treatment. Algal Res. 2014, 5, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, R.; Nair, K.V.K.; Rao, V.N.R.; Venugopalan, V.P. Nutrient dynamics and successional changes in a lentic freshwater biofilm. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 1893–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeselers, G.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Muyzer, G. Heterotrophic pioneers facilitate phototrophic biofilm development. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 54, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huesemann, M.; Crowe, B.; Waller, P.; Chavis, A.; Hobbs, S.; Edmundson, S.; Wigmosta, M. A validated model to predict microalgae growth in outdoor pond cultures subjected to fluctuating light intensities and water temperatures. Algal Res. 2016, 13, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltsev, Y.; Maltseva, K.; Kulikovskiy, M.; Maltseva, S. Influence of light conditions on microalgae growth and content of lipids, carotenoids, and fatty acid composition. Biology 2021, 10, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foladori, P.; Petrini, S.; Andreottola, G. How suspended solids concentration affects nitrification rate in microalgal-bacterial photobioreactors without external aeration. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.C.; Zuo, W.; Tian, Y.; Sun, N.; Wang, Z.W.; Zhang, J. Effect of aeration rate on performance and stability of algal-bacterial symbiosis system to treat domestic wastewater in sequencing batch reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 222, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werker, A.G.; Dougherty, J.M.; McHenry, J.L.; Van Loon, W.A. Treatment variability for wetland wastewater treatment design in cold climates. Ecol. Eng. 2002, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmo, O.R.; Van der Steen, N.P.; Gijzen, H.J. Nitrogen mass balance across pilot-scale algae and duckweed-based wastewater stabilisation ponds. Water Res. 2004, 38, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.C.; Carpenter, E.J. A kinetic approach to the effect of temperature on algal growth 1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1974, 19, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raven, J.A.; Geider, R.J. Temperature and algal growth. New Phytol. 1988, 110, 441–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Jiang, F.; Wang, L.; Yang, C. Design of photobioreactors for mass cultivation of photosynthetic organisms. Engineering 2017, 3, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.H.; Zheng, H.D.; Qiu, D.G.; Lin, Y.Q.; Xu, Y.B.; Chen, C.Z. Analysis of bacterial community structure in biofilters with different fillers using high-throughput sequencing. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2023, 42, 550–557. [Google Scholar]
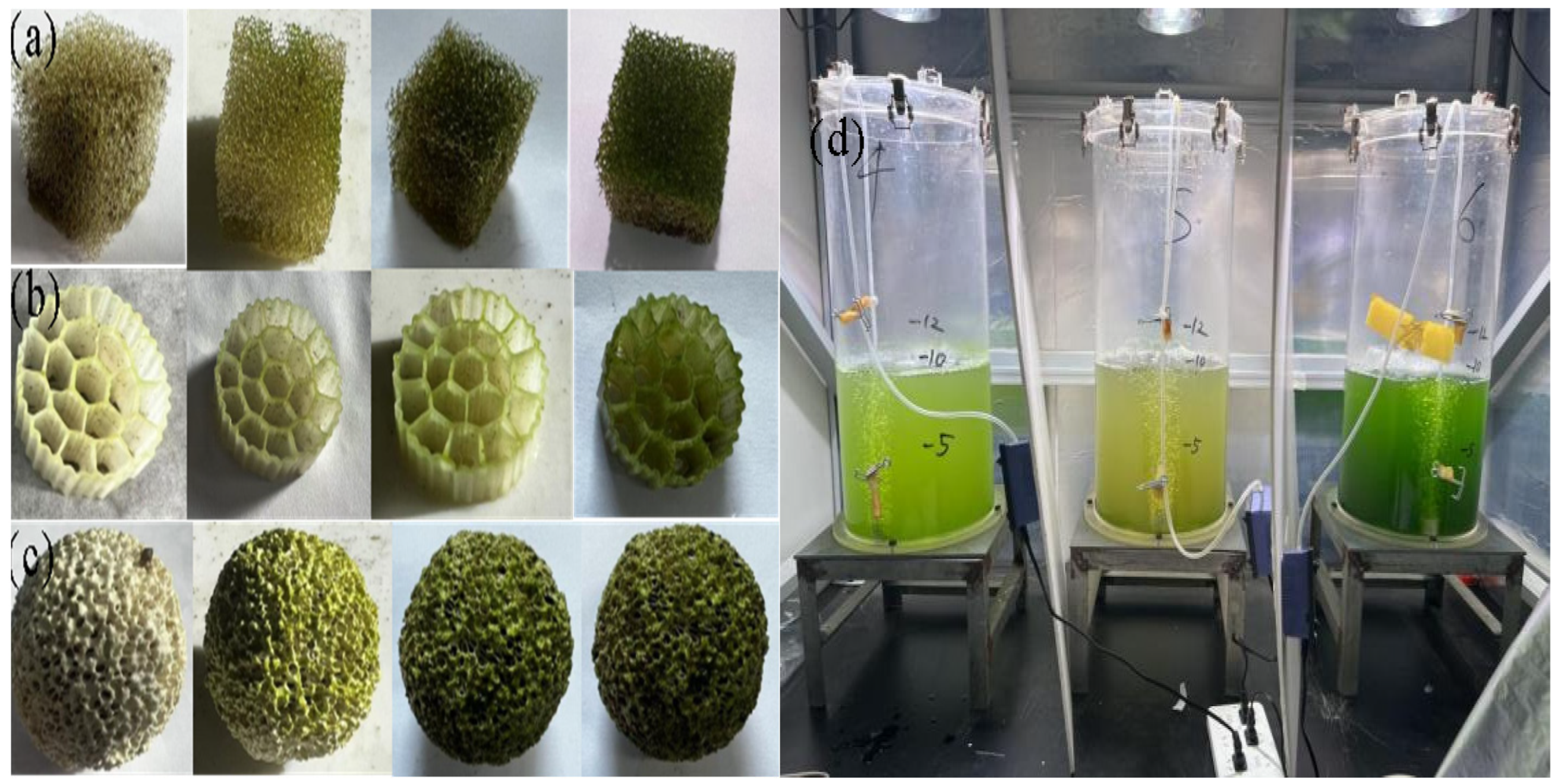
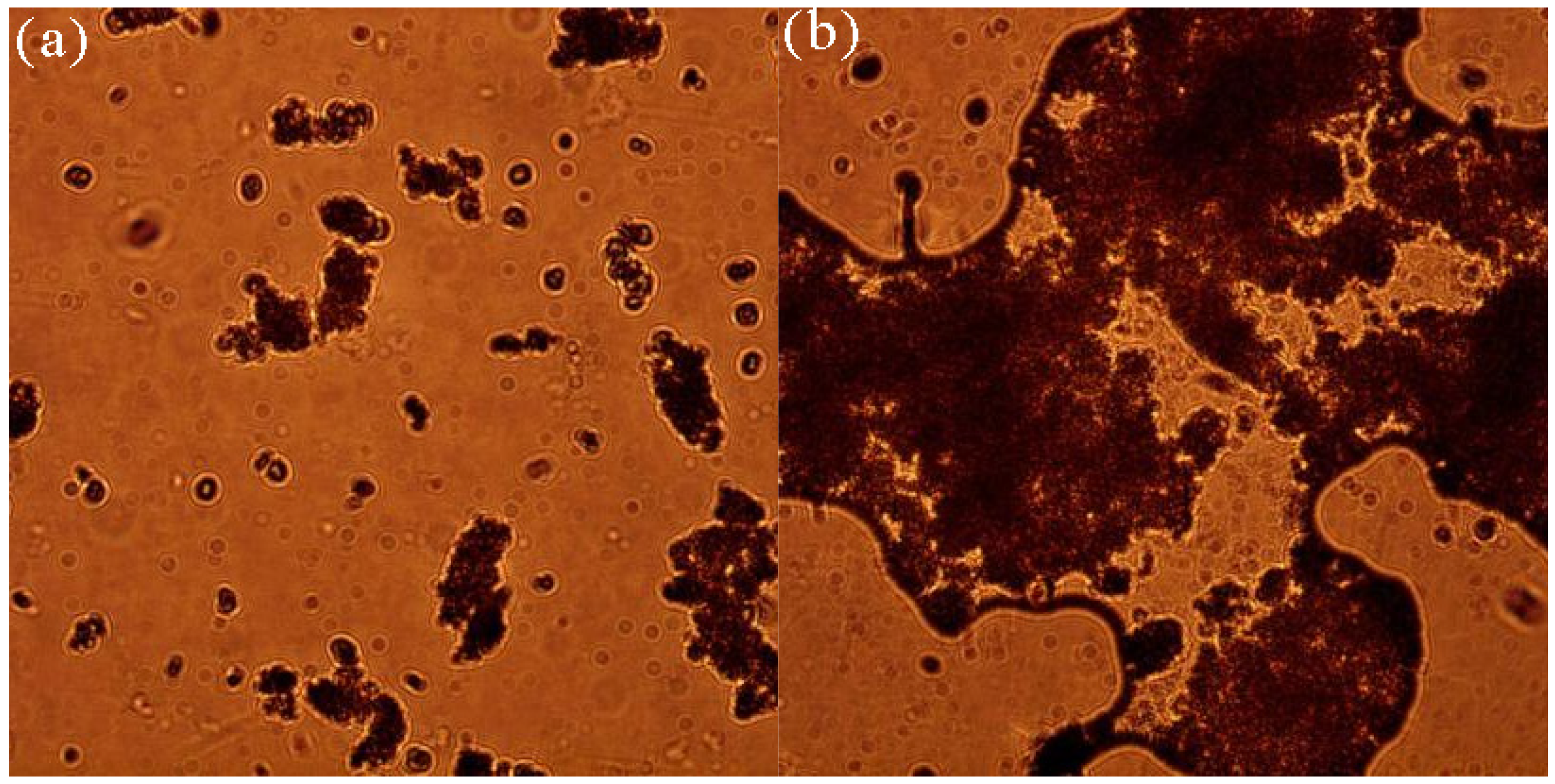
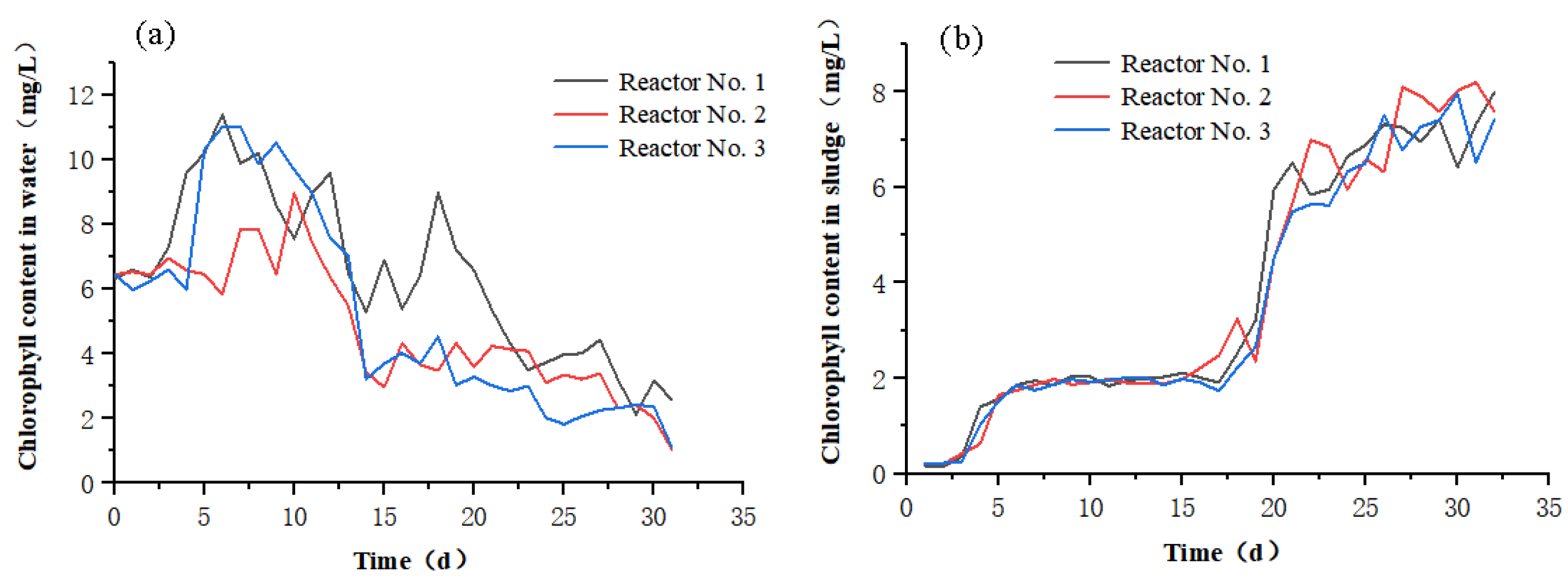


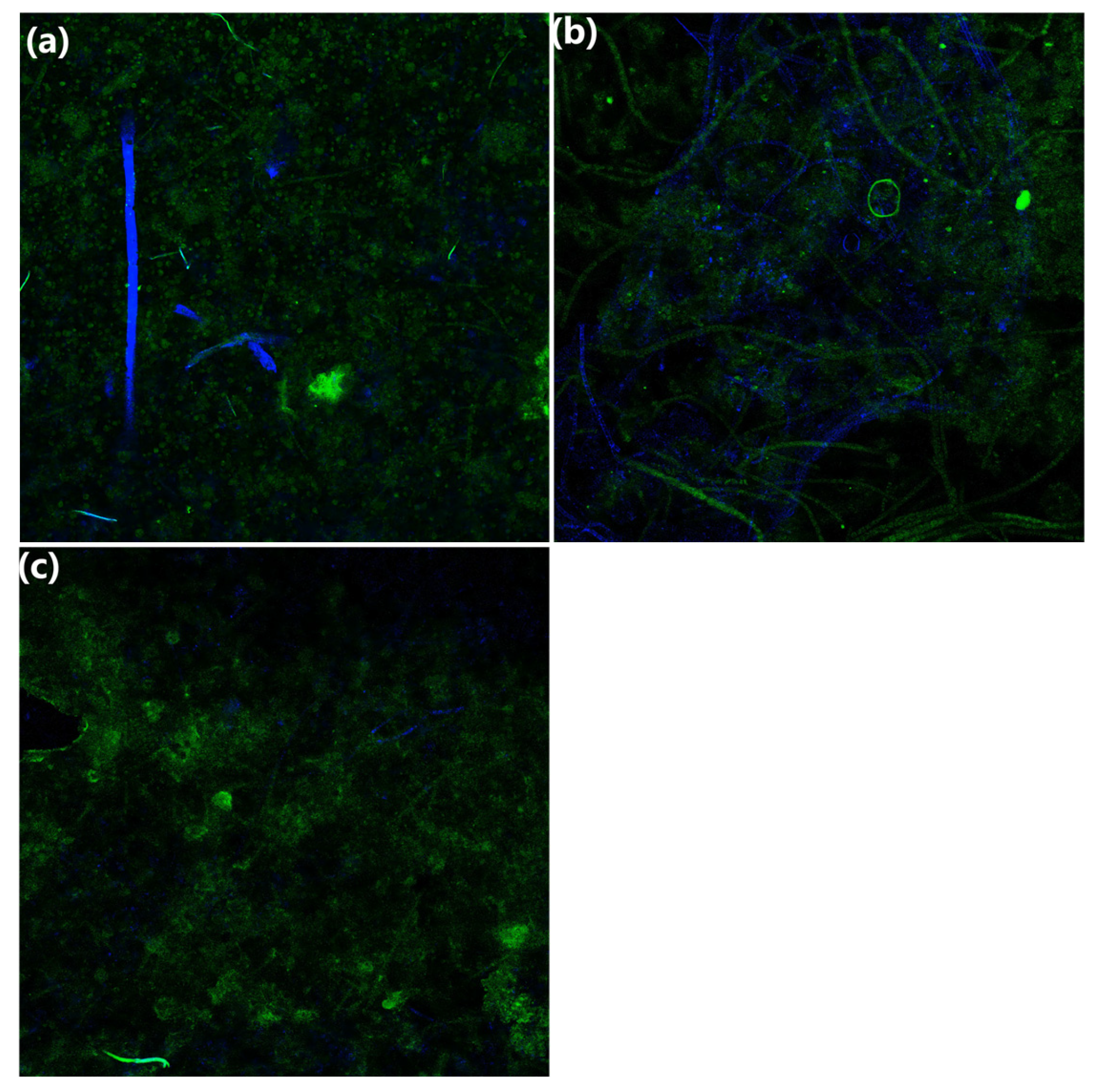
| Filler | Biofilm Dry Weight (mg) | Biofilm Formation Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane sponge | 92.41 | 68.71 |
| Ceramic filler | 103.4 | 10.03 |
| MBBR filler | 1572.1 | 9.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Wu, L.; Li, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, C.; Sun, S. Exploring the Effects of Fillers and Cultivation Conditions on Microbial-Algal Biofilm Formation and Cattle Wastewater Treatment Efficiency. Water 2025, 17, 1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121835
Zhang W, Wu L, Li M, Chen Y, Li C, Wang C, Sun S. Exploring the Effects of Fillers and Cultivation Conditions on Microbial-Algal Biofilm Formation and Cattle Wastewater Treatment Efficiency. Water. 2025; 17(12):1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121835
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Weice, Lei Wu, Ming Li, Yuting Chen, Chenyang Li, Cong Wang, and Shiyao Sun. 2025. "Exploring the Effects of Fillers and Cultivation Conditions on Microbial-Algal Biofilm Formation and Cattle Wastewater Treatment Efficiency" Water 17, no. 12: 1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121835
APA StyleZhang, W., Wu, L., Li, M., Chen, Y., Li, C., Wang, C., & Sun, S. (2025). Exploring the Effects of Fillers and Cultivation Conditions on Microbial-Algal Biofilm Formation and Cattle Wastewater Treatment Efficiency. Water, 17(12), 1835. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121835





