Analysis of Hotspots in the Field of Sulfonamides Treatment: A Bibliometric Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Sources and Analysis Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Analysis Methods
3. Research Status Analysis
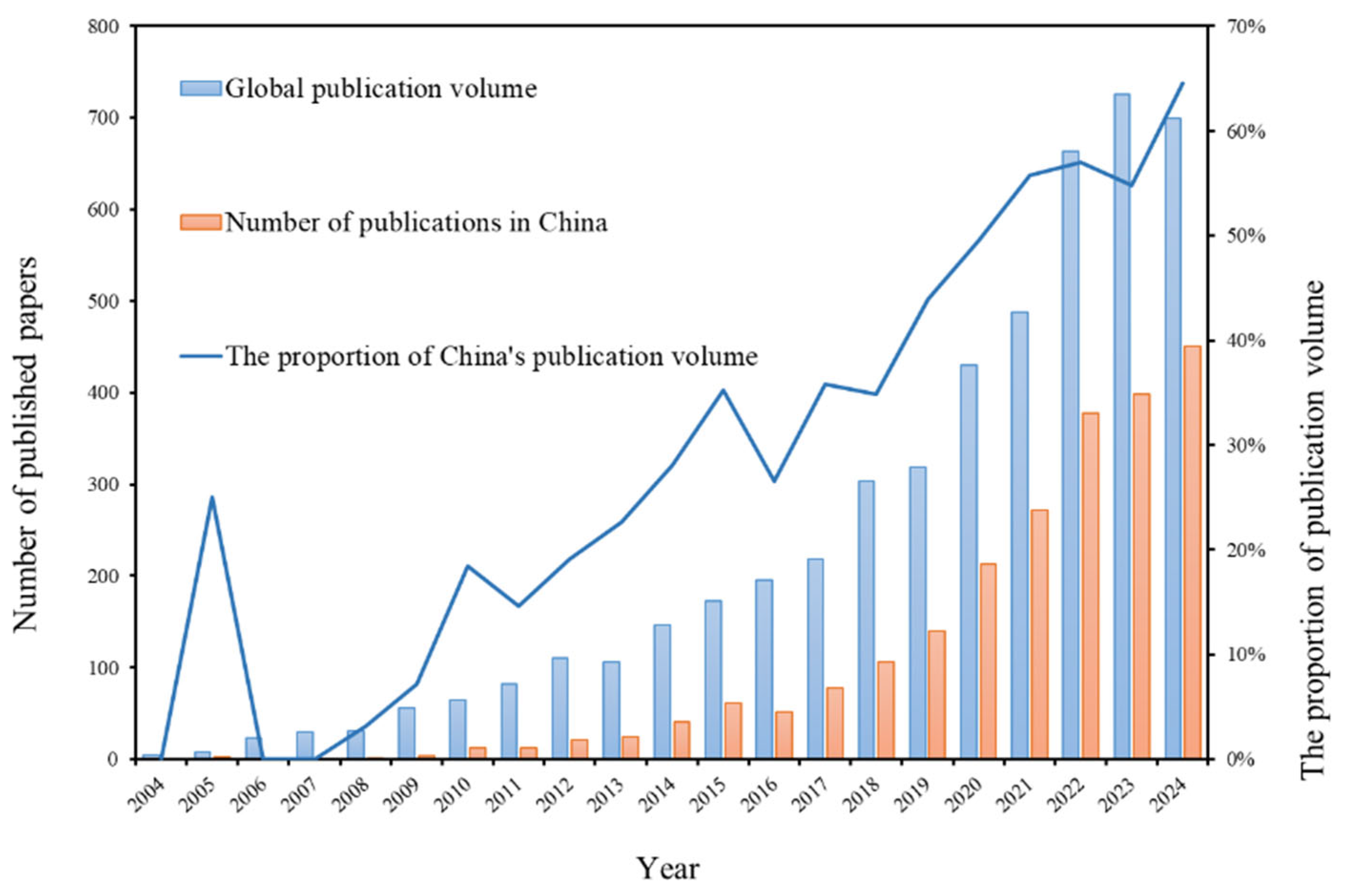
3.1. The Number of Published Papers and Its Changing Trend
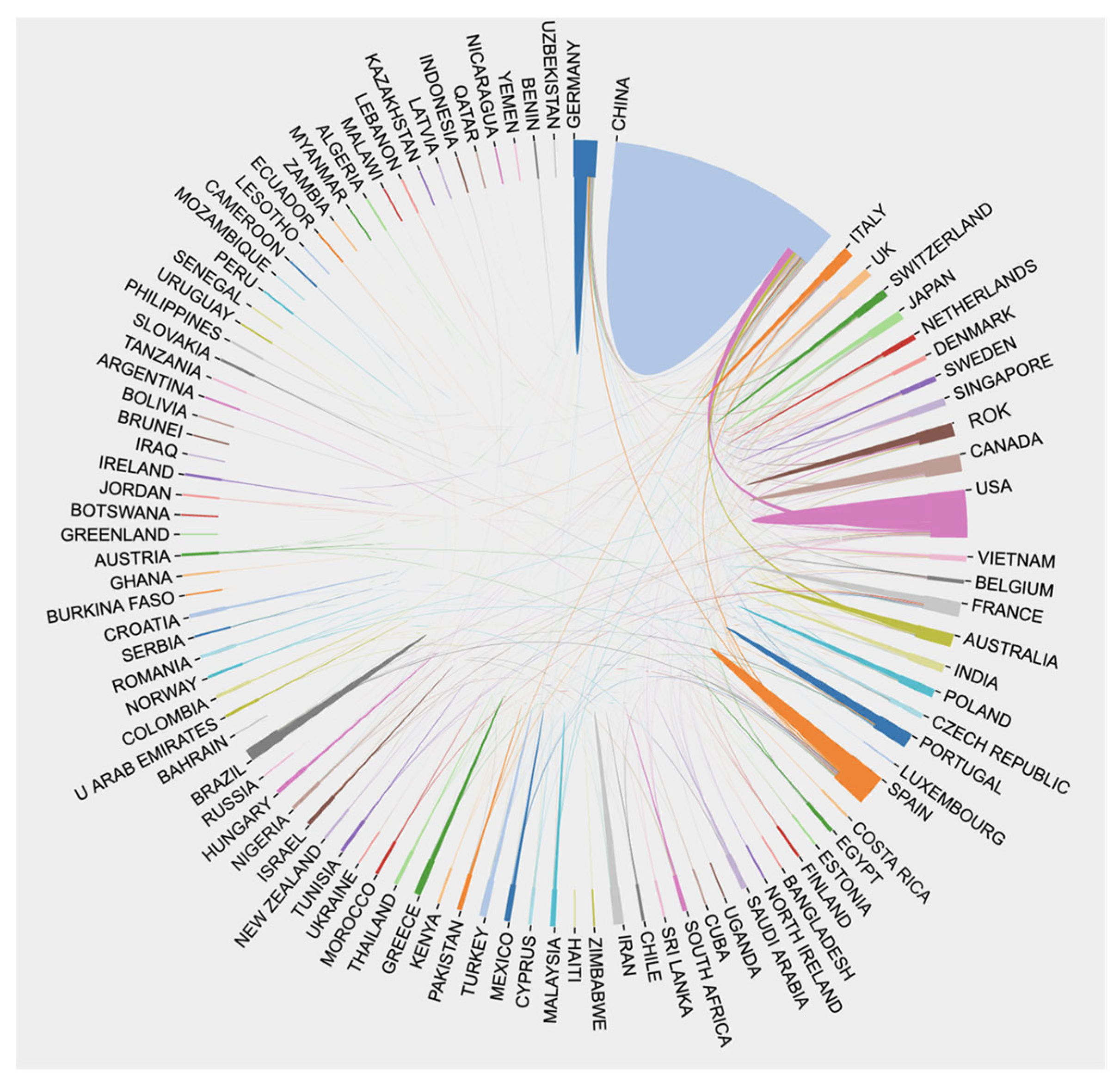
3.2. Analysis of Issuing Country and Cooperation
3.3. Analysis of Issuing Institution
3.4. Keyword-Based Bibliometrics Analysis
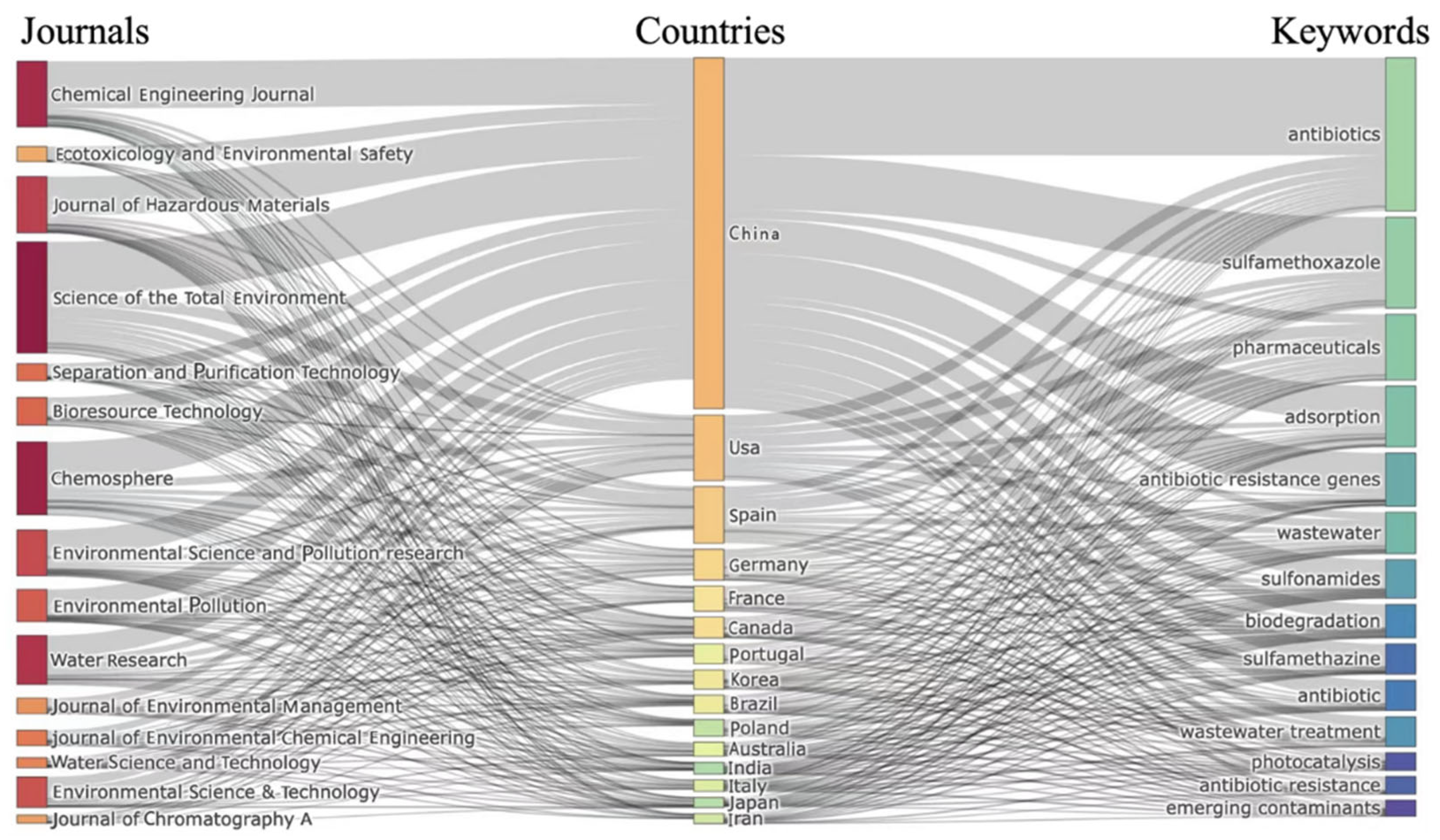
3.4.1. Topic Analysis: Analysis of Hot Journals, Published Countries and High-Frequency Keywords
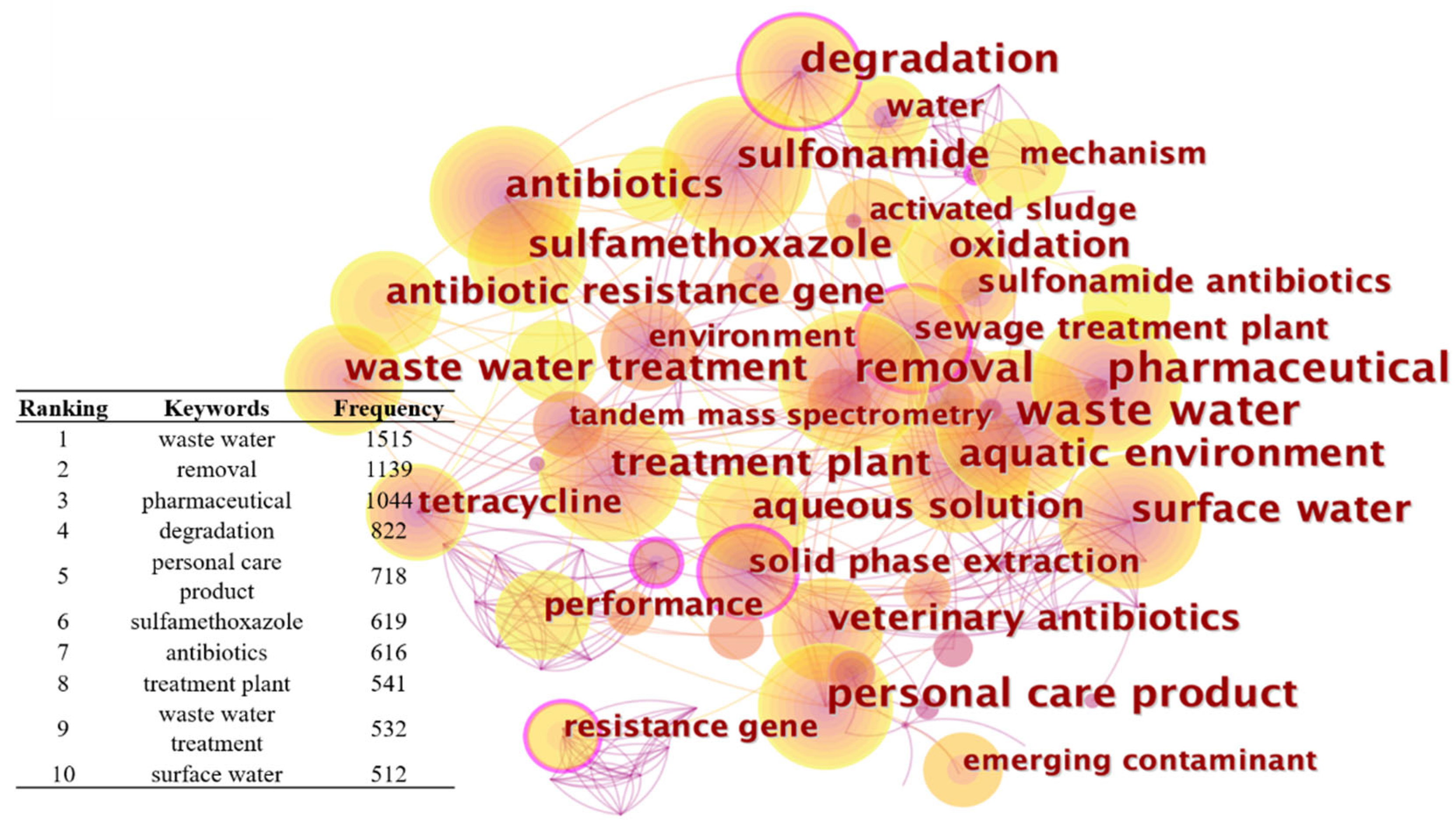
3.4.2. Co-Occurrence Analysis: Co-Occurrence Network Diagram Analysis of SAs in Wastewater
3.4.3. Cluster Analysis: Classification Analysis of SAs Research Topics in Wastewater
3.4.4. Hot Spot Analysis: The Keywords of SAs Hot Spot Analysis over Time in Wastewater
4. Discussion
4.1. Types and Toxicity of SAs
4.2. Source of SAs in Water Environment
| Survey Region | Constituent | Influent Concentration (ng/L) | Effluent Concentration (ng/L) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spain | SMX | 260 | 160 | [25] |
| SDZ | 49.1~1240 | 8.75~286 | [21] | |
| STZ | 7.31~142 | 0.7~73 | ||
| SMR | 2.13~7.37 | 0.205~1.93 | ||
| Republic of Korea | SMX | 49~410 | 47~397 | [26] |
| Beijing, China | SMX | 290~1000 | 130~460 | [27] |
| SPD | 110~470 | 36~330 | ||
| SMZ | 8.8~11 | 7.8~10 | ||
| Guangdong, China | SDZ | 15.4 | 4.12 | [20] |
| SMZ | 19.3 | 9.3 | ||
| SMX | 405 | 106 | ||
| SMM | 5.6 | nd * | ||
| SPD | 39.6 | 16.3 | ||
| SMX | 290~1000 | 130~460 | ||
| SPD | 110~470 | 36~330 | ||
| SMZ | 8.8~11 | 7.8~10 | ||
| USA | SMX | 650~4255 | 86~4145 | [2] |
| UK | SMX | 20~274 | 4~44 | [28] |
| Dalian, China | SDZ | nd~212.7 | nd~150.4 | [29] |
| SMX | 4.3~850 | 3.2~780.9 | ||
| STZ | nd~4.1 | nd~2.4 | ||
| SMR | nd~3.8 | nd~0.4 | ||
| SMM | nd~13.4 | nd~3.3 |
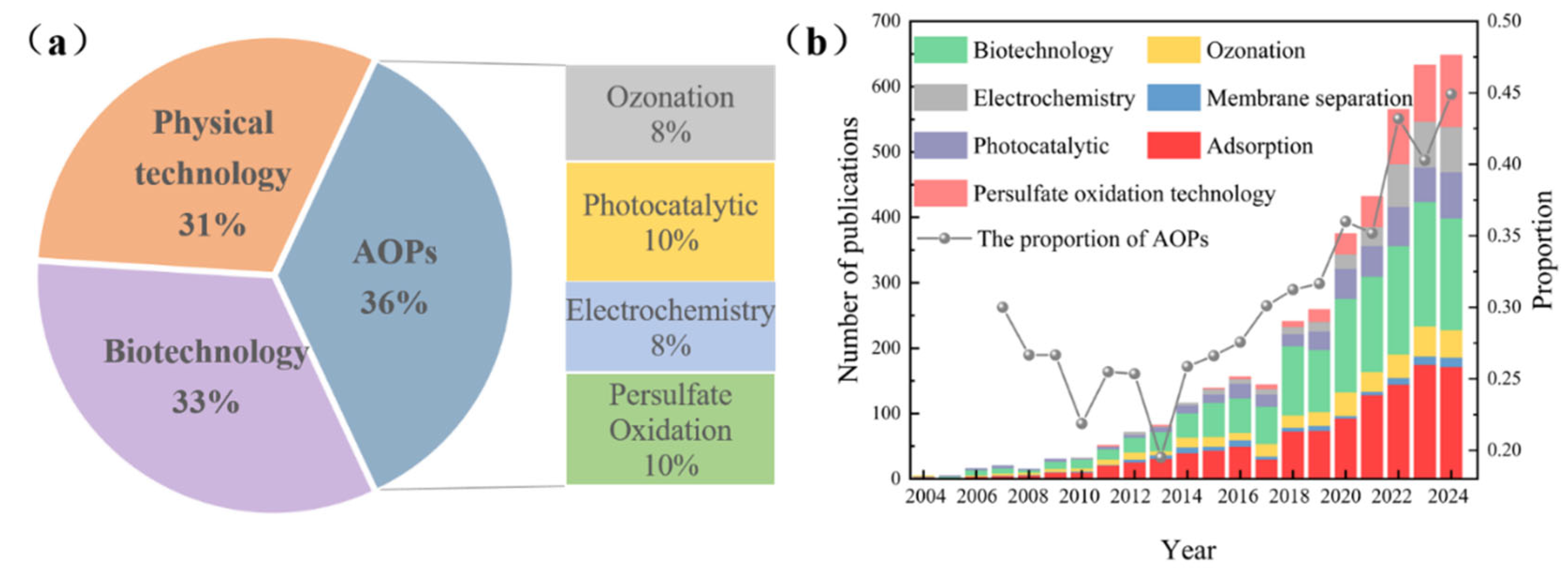
4.3. Advances in Water Treatment Technology Based on Sulfonamides
5. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zainab, S.M.; Junaid, M.; Xu, N.; Malik, R.N. Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistant Genes (ARGs) in Groundwater: A Global Review on Dissemination, Sources, Interactions, Environmental and Human Health Risks. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, P.; Zhu, Q.; Liao, C.; Jiang, G. Occurrence, Fate, and Risk Assessment of Typical Tetracycline Antibiotics in the Aquatic Environment: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 141975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, W.; Cui, H.; Jia, X.; Huang, X. Occurrence and Ecotoxicity of Sulfonamides in the Aquatic Environment: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Du, J.; Zhou, X.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, H.; Chang, J.; Ren, N. Selective Degradation of Sulfonamide Antibiotics by Peroxymonosulfate Alone: Direct Oxidation and Nonradical Mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 2539–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yang, X.; Ji, Y.; Wei, J. Sulfate Radical-Based Oxidation of the Antibiotics Sulfamethoxazole, Sulfisoxazole, Sulfathiazole, and Sulfamethizole: The Role of Five-Membered Heterocyclic Rings. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Zhou, L.; Lin, Z.; Kuang, B.; Zhu, G.; Jia, J.; Wang, T. Iron-Modified Biochar Boosts Anaerobic Digestion of Sulfamethoxazole Pharmaceutical Wastewater: Performance and Microbial Mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y. Effects of Emerging Pollutants on the Occurrence and Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance Genes: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chu, L.; Wojnárovits, L.; Takács, E. Occurrence and Fate of Antibiotics, Antibiotic Resistant Genes (ARGs) and Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria (ARB) in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant: An Overview. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. CiteSpace II: Detecting and Visualizing Emerging Trends and Transient Patterns in Scientific Literature. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2006, 57, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software Survey: VOSviewer, a Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Yuan, R. A Visualization Analysis of Biblioshiny Based Measurement of Digital Reading Studies. Libr. Inf. Stud. 2021, 14, 100–108. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, T. Water Ten solid lines—Interpretation of the Action Plan for Water Pollution Control. Environ. Prot. Sci. 2015, 41, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Xu, L. Research on the evolution of bibliometrics and the Knowledge graph of the research Frontier. J. Libr. Sci. China 2010, 36, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cheng, X.; Meng, H.; Selvaraj, K.K.; Li, H.; He, H.; Du, W.; Yang, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, L. Past, Present, and Future Perspectives on the Assessment of Bioavailability/Bioaccessibility of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: A 20-Year Systemic Review Based on Scientific Econometrics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Su, Z.; Lai, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Insights into the Fate and Removal of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance Genes Using Biological Wastewater Treatment Technology. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, X.; Liu, F.; Fu, W.; Lin, L.; Li, B. Comparison of Chemical and Biological Degradation of Sulfonamides: Solving the Mystery of Sulfonamide Transformation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.; Huang, J.; Cheng, X.; Pan, G.; Fan, M.; Cai, X. Theoretical study on bond dissociation energy of polyethylene terephthalate dimer modulates. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 37, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, H. Toxicity and ecological risk assessment of complex residues of antibiotics in surface water to aquatic organisms. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2018, 13, 149–160. [Google Scholar]
- Mohapatra, S.; Huang, C.-H.; Mukherji, S.; Padhye, L. Corrigendum to “Occurrence and Fate of Pharmaceuticals in WWTPs in India and Comparison with a Similar Study in the United States” [Chemosphere 159 526–535]. Chemosphere 2023, 322, 138161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.-J.; Ying, G.-G.; Liu, S.; Zhao, J.-L.; Chen, F.; Zhang, R.-Q.; Peng, F.-Q.; Zhang, Q.-Q. Simultaneous Determination of Human and Veterinary Antibiotics in Various Environmental Matrices by Rapid Resolution Liquid Chromatography–Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1244, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Galán, M.J.; González Blanco, S.; López Roldán, R.; Díaz-Cruz, S.; Barceló, D. Ecotoxicity Evaluation and Removal of Sulfonamides and Their Acetylated Metabolites during Conventional Wastewater Treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 437, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biošić, M.; Mitrevski, M.; Babić, S. Environmental Behavior of Sulfadiazine, Sulfamethazine, and Their Metabolites. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 9802–9812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Ji, M.; Zhai, H.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y. Occurrence of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in WWTP Effluent-Receiving Water Bodies and Reclaimed Wastewater Treatment Plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 148919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Zhang, S.; Chen, M.; Song, N.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Q. Pollution levels and risk assessment of 12 sulfonamides in surface water of Nanjing Section of Yangtze River. Environ. Chem. 2018, 37, 505–512. [Google Scholar]
- Hijosa-Valsero, M.; Fink, G.; Schlüsener, M.P.; Sidrach-Cardona, R.; Martín-Villacorta, J.; Ternes, T.; Bécares, E. Removal of Antibiotics from Urban Wastewater by Constructed Wetland Optimization. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, W.-J.; Lee, J.-W.; Lee, E.-S.; Shin, S.-K.; Hwang, S.-R.; Oh, J.-E. Occurrence and Distribution of Pharmaceuticals in Wastewater from Households, Livestock Farms, Hospitals and Pharmaceutical Manufactures. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Shi, Y.; Li, W.; Niu, H.; Liu, J.; Cai, Y. Occurrence of antibiotics in eight sewage treatment plants in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Dinsdale, R.M.; Guwy, A.J. The Removal of Pharmaceuticals, Personal Care Products, Endocrine Disruptors and Illicit Drugs during Wastewater Treatment and Its Impact on the Quality of Receiving Waters. Water Res. 2009, 43, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, H.; Du, J.; Qu, Y.; Shen, C.; Tan, F.; Chen, J.; Quan, X. Occurrence, Removal, and Risk Assessment of Antibiotics in 12 Wastewater Treatment Plants from Dalian, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 16478–16487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, C.; Yau, M.; Bolton, J.R.; Qiang, Z. Sulfamethazine Degradation in Water by the VUV/UV Process: Kinetics, Mechanism and Antibacterial Activity Determination Based on a Mini-Fluidic VUV/UV Photoreaction System. Water Res. 2017, 108, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Li, Y.; Han, S.; Ma, J. Adsorptive Removal of Antibiotics from Aqueous Solution Using Carbon Materials. Chemosphere 2016, 153, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Sun, X.; Meng, Y.; Yu, N.; Liu, J. Photodegradation of Sulfamethoxypyridazine in UV/Co(II)/Peroxymonosulfate System: Kinetics, Influencing Factors, Degradation Pathways, and Toxicity Assessment. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2021, 232, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chávez, A.M.; Beltrán, F.J.; López, J.; Javier Rivas, F.; Álvarez, P.M. On the Importance of Reactions in the Proximity of the Gas–Water Interface: Application to Direct Ozone Reactions of Antibiotics in Water. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 458, 141408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiao, K.; Zhao, H. The Debatable Role of Singlet Oxygen in Persulfate-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes. Water Res. 2023, 235, 119925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ji, G.; Li, A. Degradation of Antibiotic Pollutants by Persulfate Activated with Various Carbon Materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Chen, J.; Show, P.L.; Yang, Q.; Ke, J.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, R.; Liu, Y. Evaluating the Application of Antibiotic Treatment Using Algae-Algae/Activated Sludge System. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 130966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Guo, W.; Du, J.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, H.; Wu, Q.; Chang, J.; Ren, N. Heteroatoms Doped Graphene for Catalytic Ozonation of Sulfamethoxazole by Metal-Free Catalysis: Performances and Mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Ding, W.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, L.; Huang, Y. Reinventing MoS2 Co-Catalytic Fenton Reaction: Oxygen-Incorporation Mediating Surface Superoxide Radical Generation. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 1973–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.; Wu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Li, M.; Qiang, Z. Accelerated Degradation of Sulfamethazine in Water by VUV/UV Photo-Fenton Process: Impact of Sulfamethazine Concentration on Reaction Mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekhar, B.; Venkateshwaran, U.; Durairaj, N.; Divyapriya, G.; Nambi, I.M.; Joseph, A. Comprehensive Treatment of Urban Wastewaters Using Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation Process. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 266, 110469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Ma, Y.; Chen, F.; Yao, F.; Sun, J.; Wang, S.; Yi, K.; Hou, L.; Li, X.; Wang, D. Recent Advances in Photo-Activated Sulfate Radical-Advanced Oxidation Process (SR-AOP) for Refractory Organic Pollutants Removal in Water. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Activation of Persulfate (PS) and Peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and Application for the Degradation of Emerging Contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Yi, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H. Cu2+ Activated Persulfate for Sulfamethazine Degradation. Chemosphere 2020, 257, 127294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Lin, S.; Zhang, W.; Farooq, U.; Shen, G.; Hu, S. Kinetic and Mechanistic Investigations of the Degradation of Sulfachloropyridazine in Heat-Activated Persulfate Oxidation Process. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 346, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Luo, Z.; Wei, Z.; Luo, S.; Spinney, R.; Yang, W.; Dionysiou, D.D. Activation of Peroxymonosulfate/Persulfate by Nanomaterials for Sulfate Radical-Based Advanced Oxidation Technologies. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2018, 19, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Xing, K.; Lv, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, H.; Yao, Y. Nitrogen-Doped Porous Carbon Encapsulating Iron Nanoparticles for Enhanced Sulfathiazole Removal via Peroxymonosulfate Activation. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Ferronato, C.; Salvador, A.; Yang, X.; Chovelon, J.-M. Degradation of Ciprofloxacin and Sulfamethoxazole by Ferrous-Activated Persulfate: Implications for Remediation of Groundwater Contaminated by Antibiotics. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, E.; Muhammad, S.; Sun, H.; Wang, S. Activated Carbons as Green and Effective Catalysts for Generation of Reactive Radicals in Degradation of Aqueous Phenol. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 21905–21910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, P.; Yue, Q.; Li, Y.; Gao, B.; Xu, X. Removal of Sulfamethoxazole from Water via Activation of Persulfate by Fe3C@NCNTs Including Mechanism of Radical and Nonradical Process. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 122004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari Moghaddam, M.; Nabizadeh, R.; Dehghani, M.H.; Akbarpour, B.; Azari, A.; Yousefi, M. Performance Investigation of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework—8 (ZIF-8) in the Removal of Trichloroethylene from Aqueous Solutions. Microchem. J. 2019, 150, 104185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Gong, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y. In Situ Growth of ZIF-67 on a Nickel Foam as a Three-Dimensional Heterogeneous Catalyst for Peroxymonosulfate Activation. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 26377–26382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.-Y.A.; Chang, H.-A. Zeolitic Imidazole Framework-67 (ZIF-67) as a Heterogeneous Catalyst to Activate Peroxymonosulfate for Degradation of Rhodamine B in Water. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 53, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, M.; Niu, J.; Brusseau, M.L.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, C.; Deng, S.; Wan, J. Ferrous Metal-Organic Frameworks with Strong Electron-Donating Properties for Persulfate Activation to Effectively Degrade Aqueous Sulfamethoxazole. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 394, 125044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Fu, H.; Wang, F.-X.; Zhang, X.-W.; Wang, P.; Zhao, C.; Wang, C.-C. Enhanced Catalytic Sulfamethoxazole Degradation via Peroxymonosulfate Activation over Amorphous CoSx@SiO2 Nanocages Derived from ZIF-67. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 126998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Peng, X.; Zeng, P.; Shen, L.; Li, M.; Guo, Y. Removal of Sulfonamides by Persulfate-Based Advanced Oxidation: A Mini Review. Chemosphere 2025, 370, 143874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, J.; Orge, C.A.; Faria, J.L.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Soares, O.S.G.P. Sulfamethoxazole Degradation by Combination of Advanced Oxidation Processes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4054–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
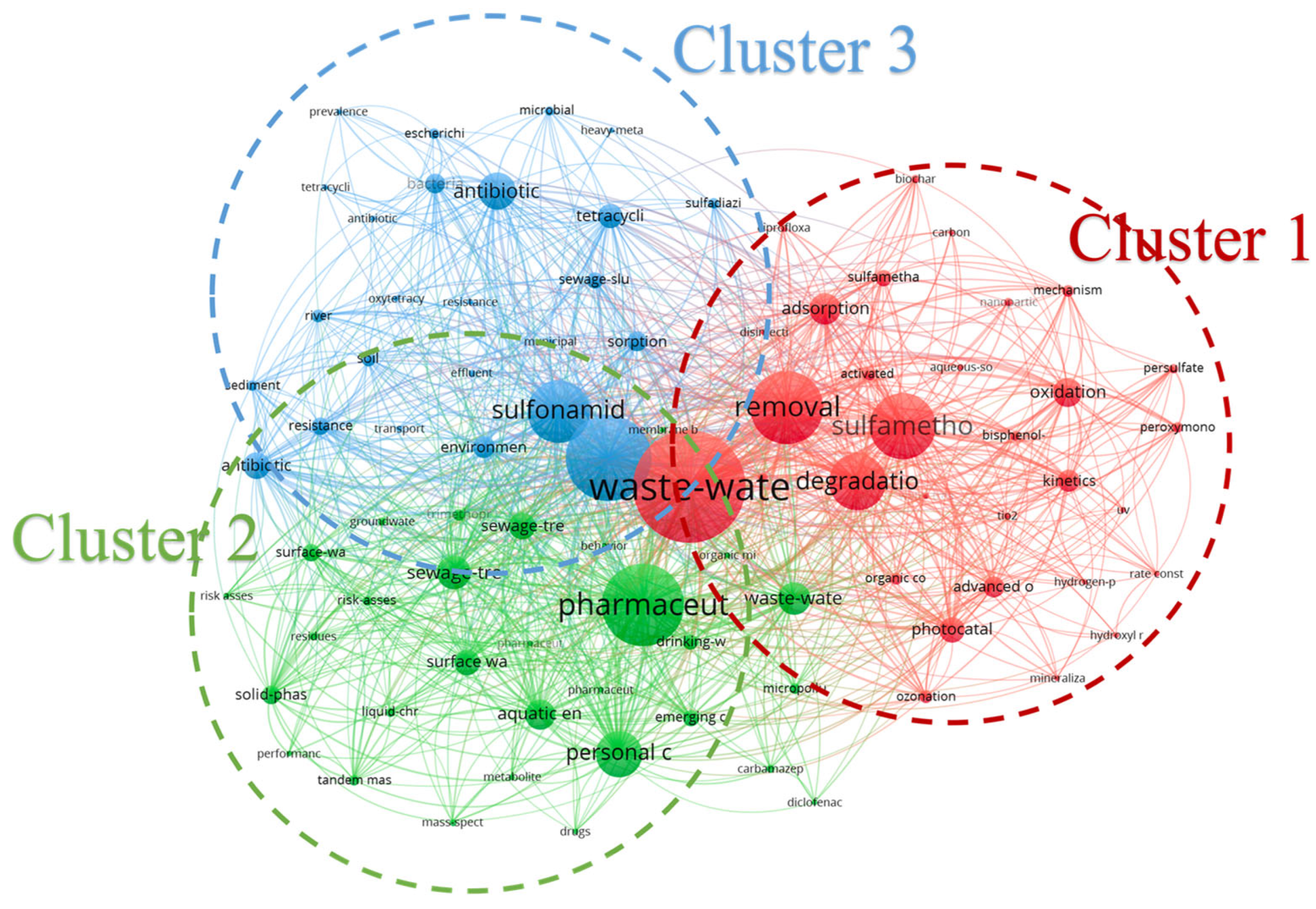
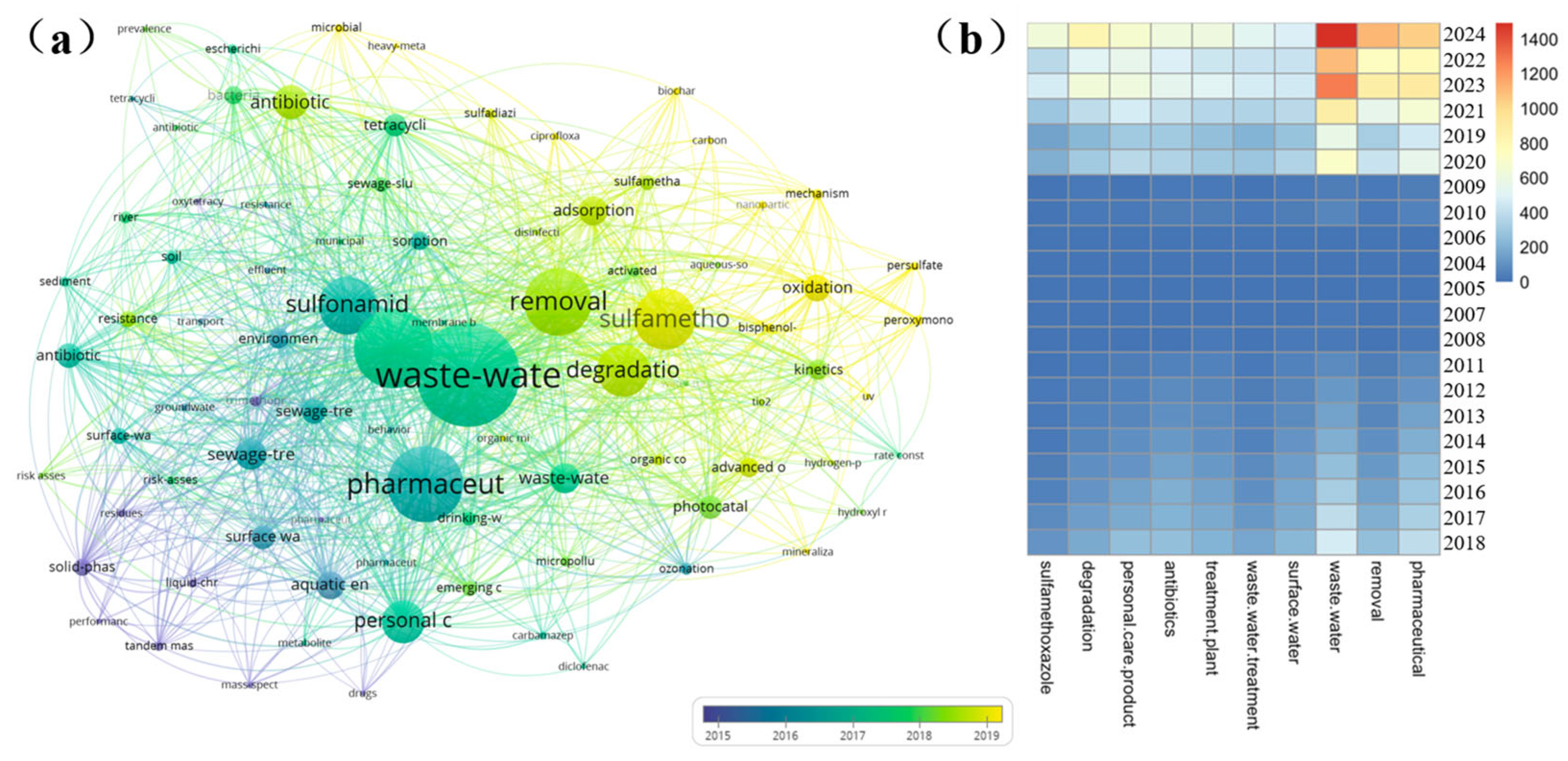
| Ranking | Country/Region | Number | Total Citation Frequency | Citations per Article | H-Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | 2266 | 77,363 | 39.03 | 133 |
| 2 | USA | 592 | 41,944 | 72.94 | 107 |
| 3 | Spain | 411 | 22,798 | 57.71 | 83 |
| 4 | Germany | 284 | 15,382 | 55.82 | 62 |
| 5 | Canada | 180 | 8884 | 50.6 | 52 |
| 6 | France | 158 | 6400 | 41.54 | 44 |
| 7 | Australia | 150 | 7643 | 51.73 | 45 |
| 8 | Republic of Korea | 145 | 8150 | 57.2 | 47 |
| 9 | Brazil | 137 | 2826 | 21.55 | 31 |
| 10 | Portugal | 110 | 4267 | 39.71 | 34 |
| Ranking | Institution | Number | Total Citation Frequency | Citations per Article | H-Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chinese Academy of Sciences | 348 | 18,614 | 55.63 | 77 |
| 2 | Tsinghua University | 178 | 6605 | 39.16 | 45 |
| 3 | Harbin Institute of Technology | 129 | 4746 | 37.76 | 39 |
| 4 | University of Chinese Academy of Sciences | 120 | 4606 | 39.13 | 39 |
| 5 | Spanish Higher Scientific Council | 109 | 8457 | 79.39 | 50 |
| 6 | French National Centre for Scientific Research | 95 | 3986 | 42.83 | 35 |
| 7 | Tongji University | 92 | 2946 | 32.75 | 33 |
| 8 | Research Center for ECO Environmental Science | 90 | 5035 | 56.87 | 41 |
| Compound | Molecular Formula | Chemical Construction | Molecular Mass (g/mol) | Acidity Coefficient pKa | LD50 mg/kg | Bio Enrichment | CAS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfamethoxazole | C10H11N3O3S | 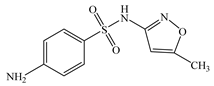 | 253.28 | pKa1 = 2.10 pKa2 = 5.30 | 1.47 | 1.23 | 723-46-6 |
| Sulfamethazine | C12H14N4O2S | 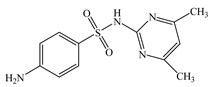 | 278.33 | pKa1 = 2.65 pKa2 = 7.40 | 1.59 | 0.41 | 57-68-1 |
| Sulfadiazine | C10H10N4O2S | 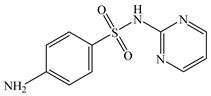 | 250.28 | pKa1 = 2.72 pKa2 = 8.56 | 1.47 | 0.24 | 68-35-9 |
| Sulfamerazine | C11H12N4O2S | 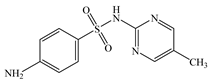 | 264.30 | pKa1 = 2.10 pKa2 = 6.28 | 1.54 | 0.30 | 127-79-7 |
| Sulfathiazole | C9H9N3O2S2 | 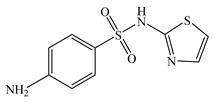 | 255.32 | pKa1 = 2.08 pKa2 = 7.07 | 1.99 | 0.35 | 72-14-0 |
| Sulfamethizole | C9H10N4O2S2 | 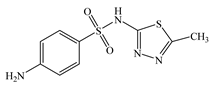 | 270.33 | pKa1 = 5.45 pKa2 = 7.40 | 2.10 | 0.32 | 144-82-1 |
| Sulfachloropyridazine | C10H9CIN4O2S | 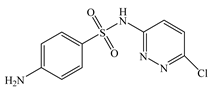 | 284.72 | - | 1.81 | 0.69 | 80-32-0 |
| Sulfisoxazole | C11H13N3O3S | 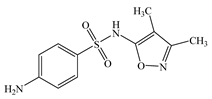 | 267.3 | - | 1.58 | 0.70 | 127-69-5 |
| Sulfamethoxypyridazine | C11H12N4O3S | 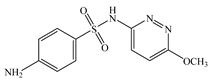 | 280.30 | pKa1 = 2.18 pKa2 = 7.19 | 1.78 | 0.42 | 80-35-3 |
| Sulfamonomethoxine | C11H12N4O3S | 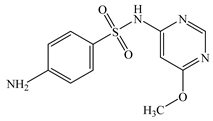 | 280.30 | pKa1 = 2.00 pKa2 = 6.01 | 1.48 | 0.30 | 1220-83-3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Qian, F.; Su, J. Analysis of Hotspots in the Field of Sulfonamides Treatment: A Bibliometric Review. Water 2025, 17, 1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121792
Wang J, Liu X, Qian F, Su J. Analysis of Hotspots in the Field of Sulfonamides Treatment: A Bibliometric Review. Water. 2025; 17(12):1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121792
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jian, Xinyao Liu, Feng Qian, and Jie Su. 2025. "Analysis of Hotspots in the Field of Sulfonamides Treatment: A Bibliometric Review" Water 17, no. 12: 1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121792
APA StyleWang, J., Liu, X., Qian, F., & Su, J. (2025). Analysis of Hotspots in the Field of Sulfonamides Treatment: A Bibliometric Review. Water, 17(12), 1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121792





