Multi-Algorithm Comparison for Water Quality Retrieval: Integrating Landsat-8 OLI and Machine Learning in Karst Plateau Reservoirs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Field Measurement Data
2.3. Remote Sensing Data Acquisition and Processing
Remote Sensing Image Preprocessing
2.4. Machine Learning Algorithms
2.4.1. Support Vector Regression
2.4.2. Backpropagation Neural Network
2.4.3. Genetic Algorithm–Backpropagation Neural Network
2.4.4. Particle Swarm Optimization–Backpropagation Neural Network
2.4.5. Random Forest
2.4.6. Convolutional Neural Networks
2.4.7. Extreme Learning Machine
2.4.8. XGBoost Extreme Gradient Boosting Algorithm
2.5. Evaluation of the Accuracy of the BP Neural Network Model
3. Results
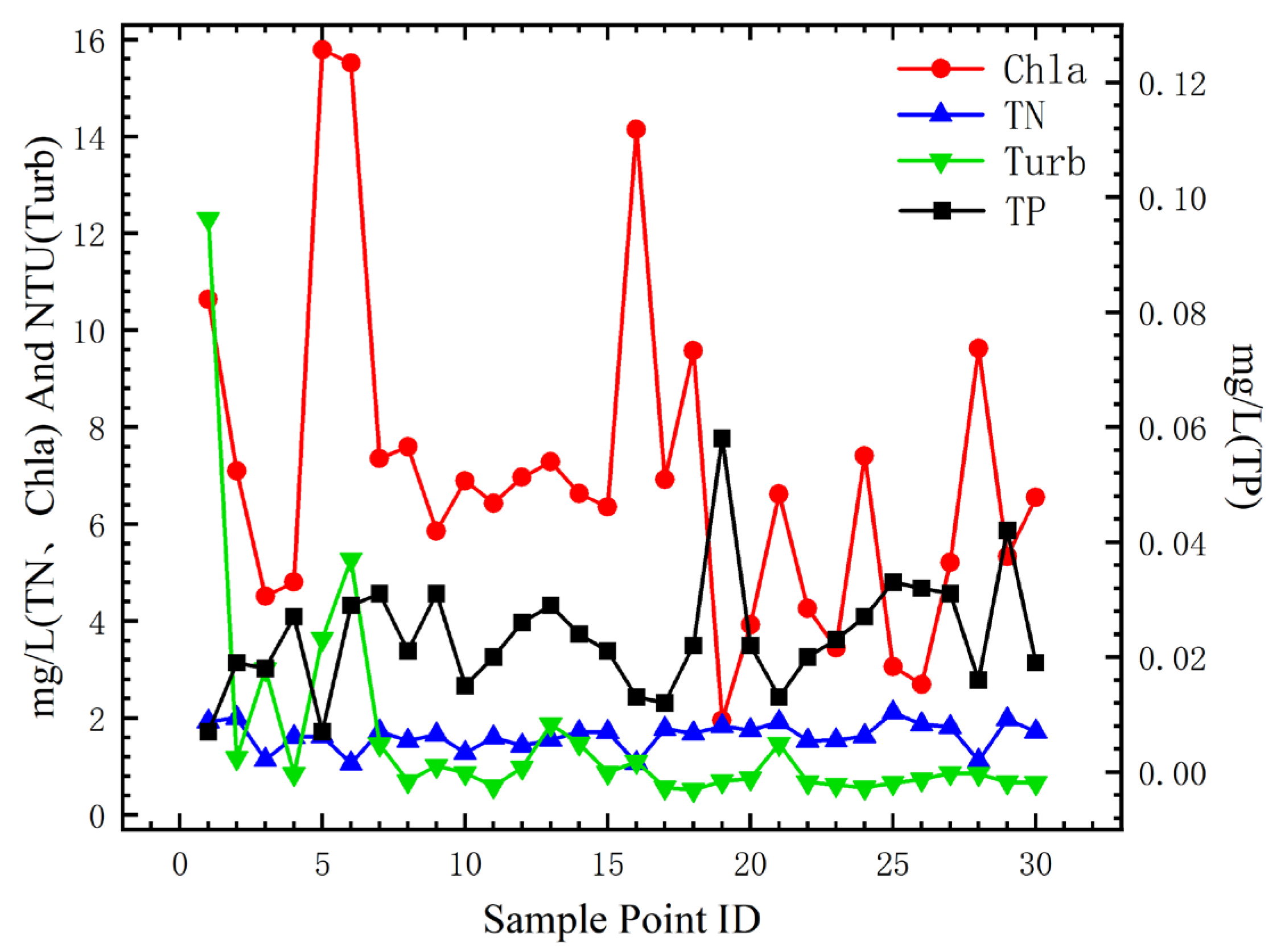
3.1. Pingzhai Reservoir Water Quality Information
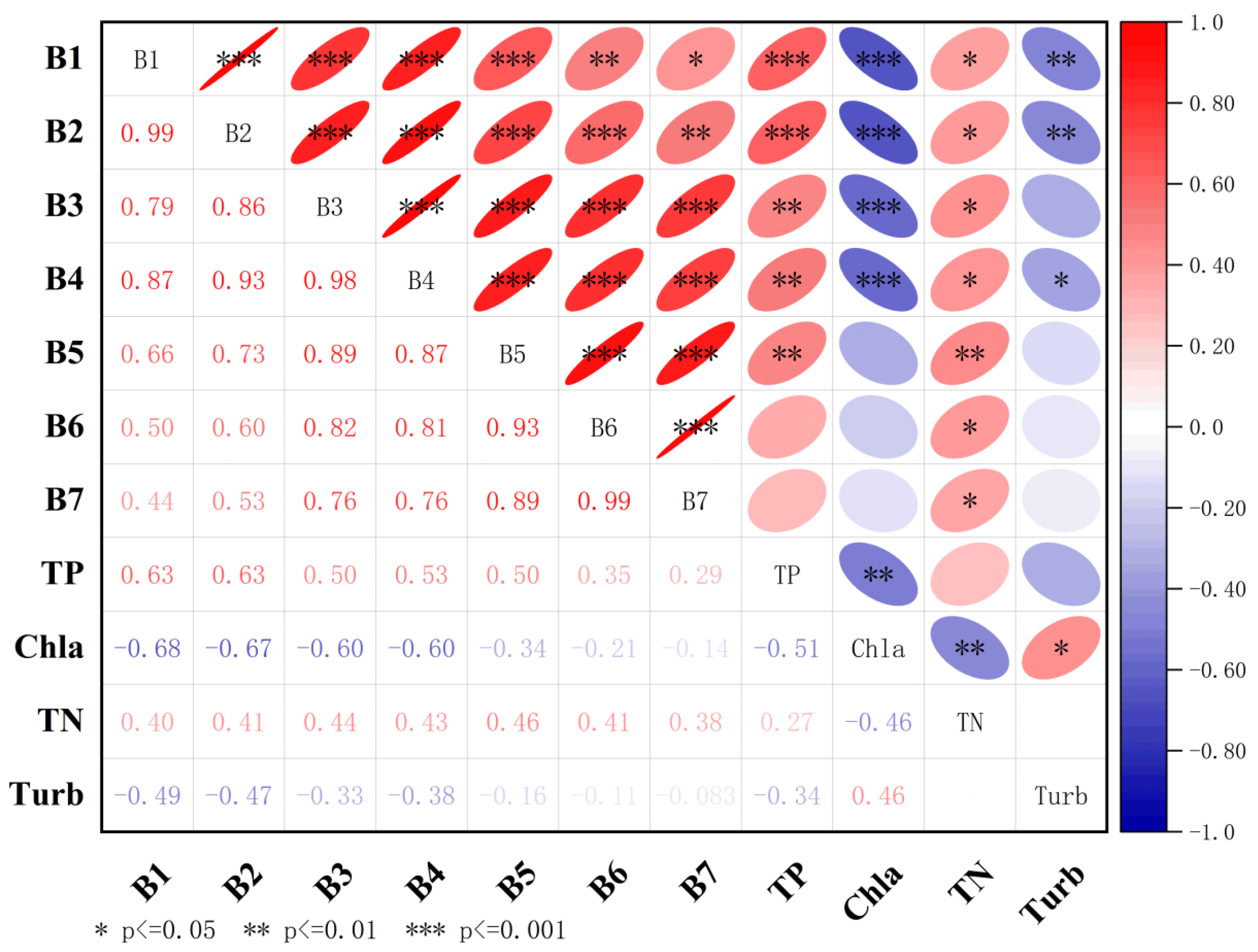
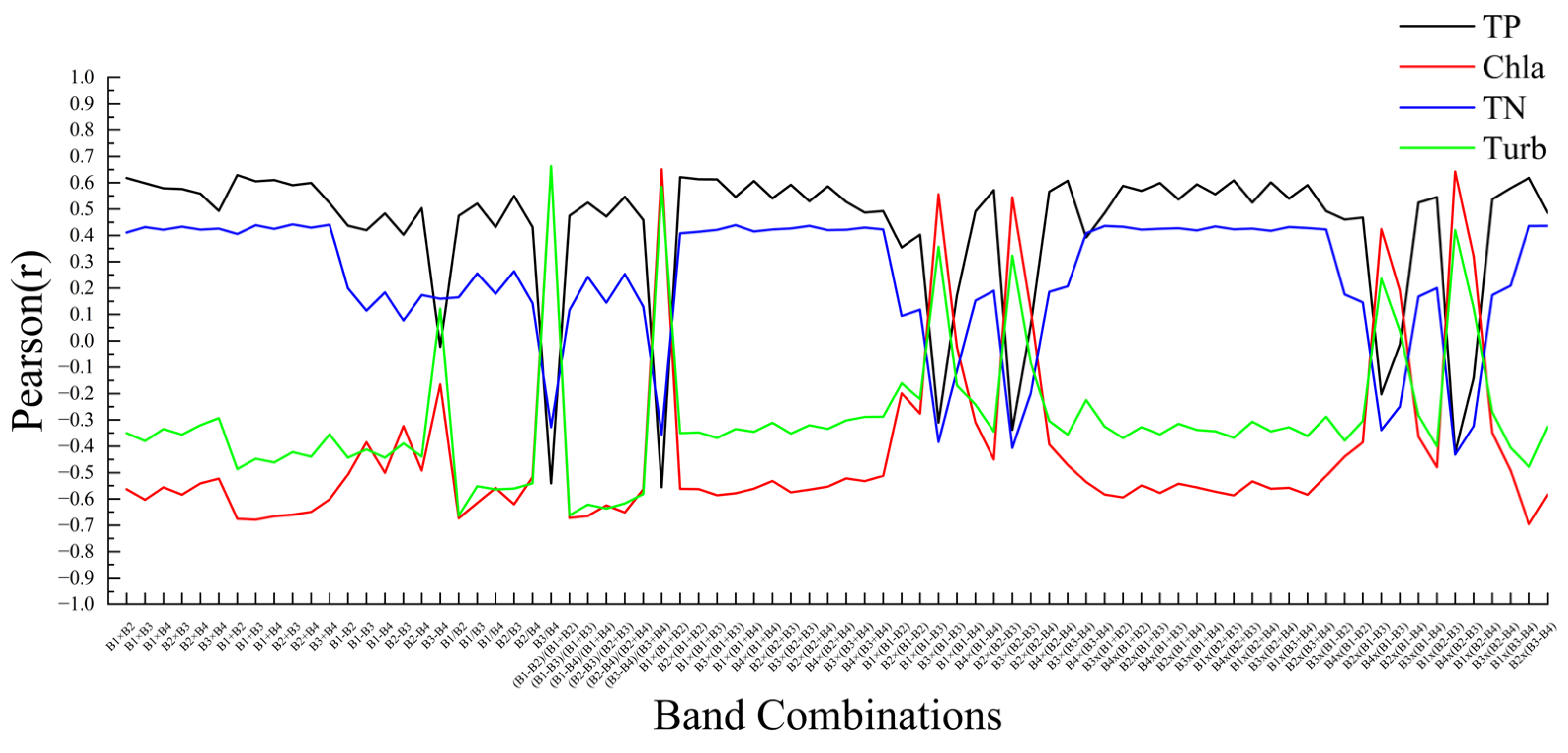
3.2. Correlation Analysis
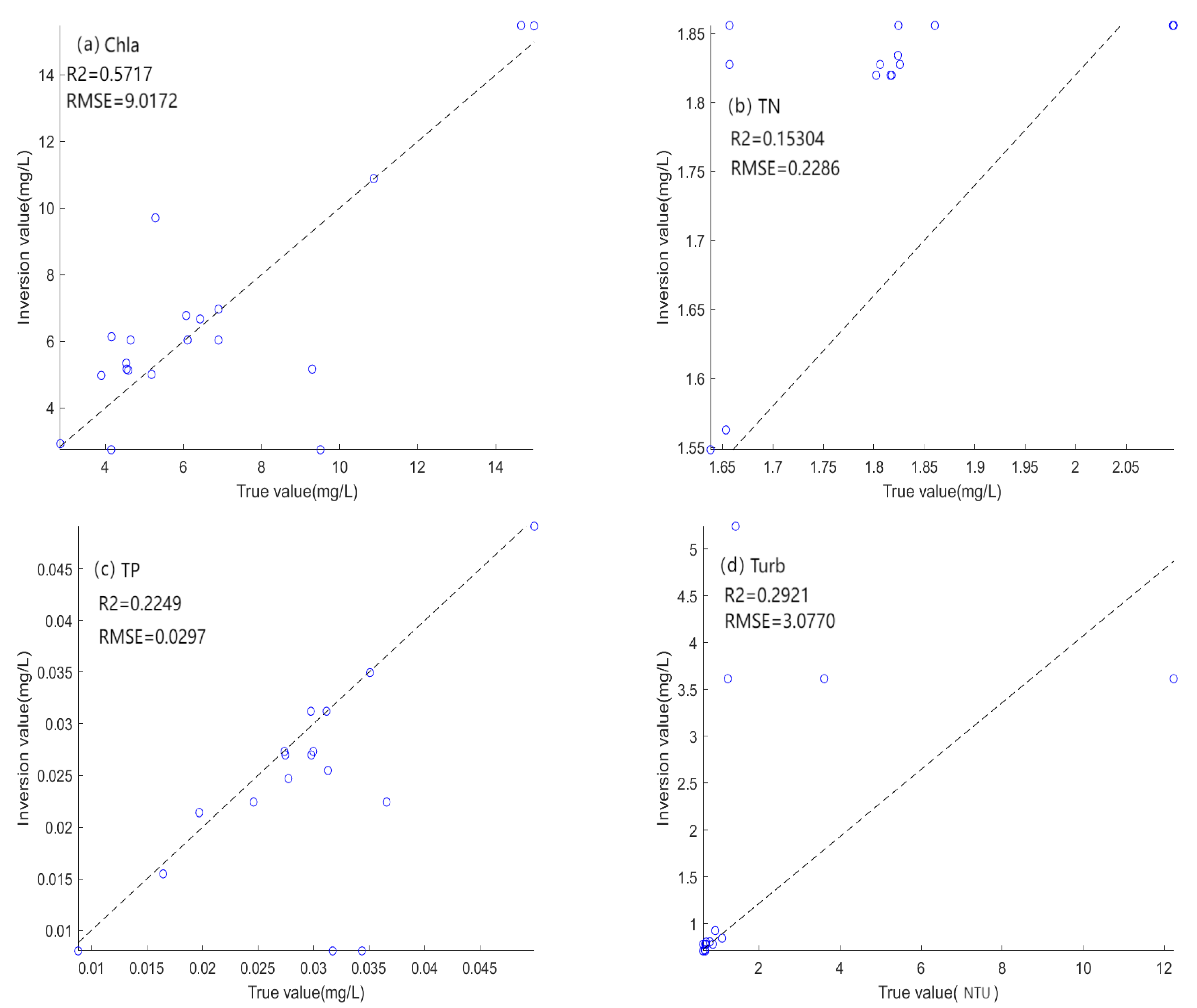
3.3. Multiple Regression Inversion Modeling
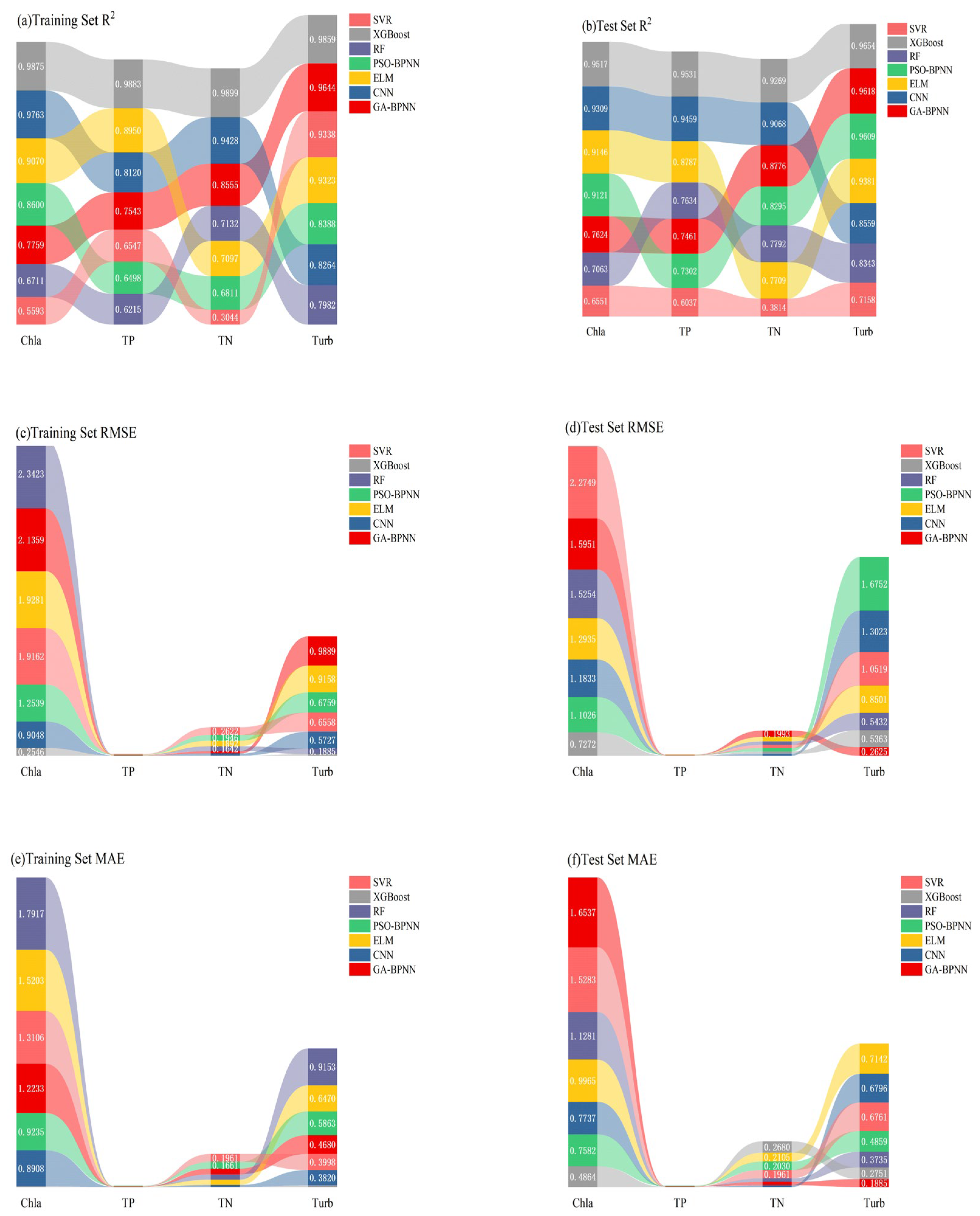
3.4. Machine Learning Inversion Model Construction
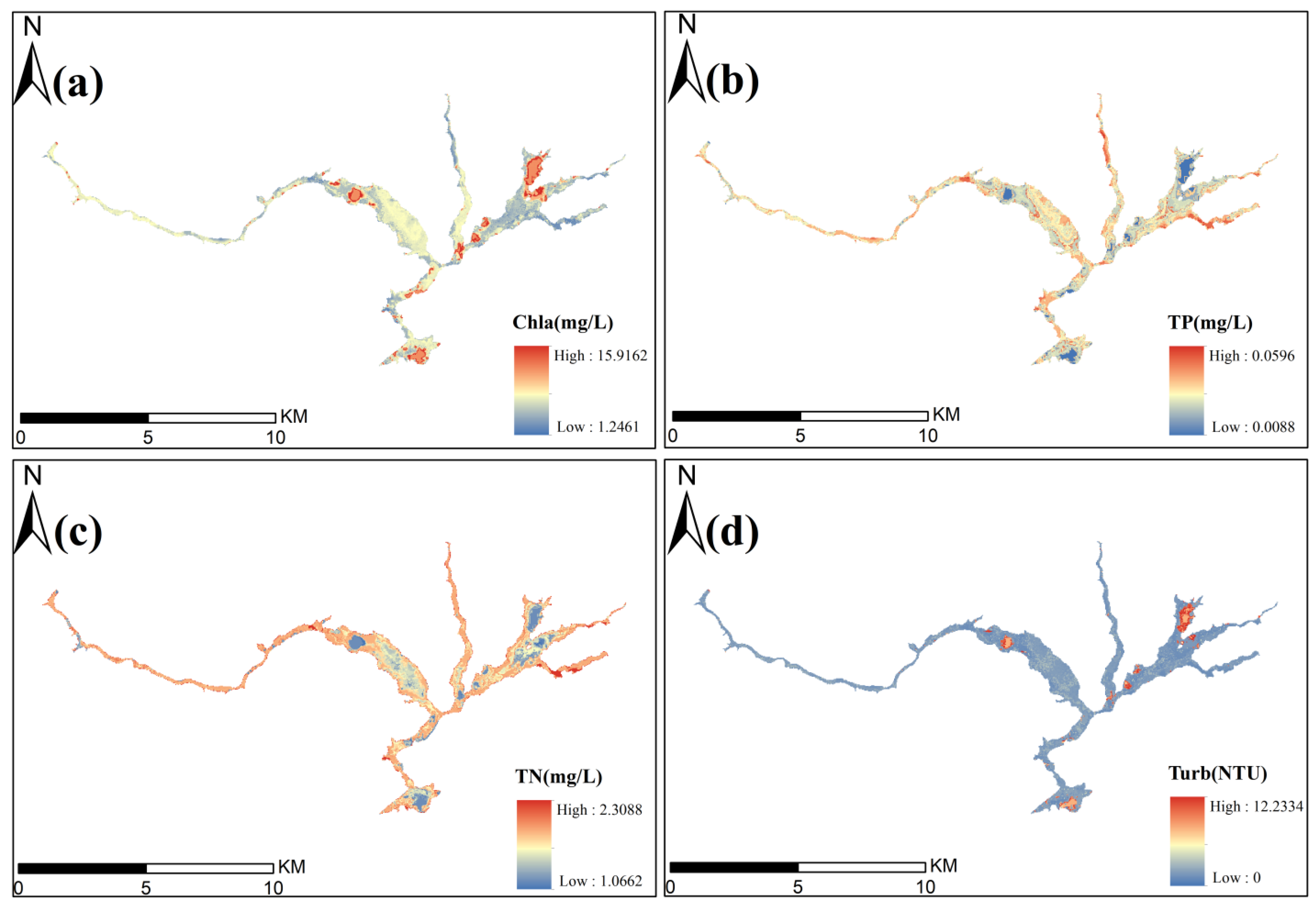
3.5. Spatial Distribution of WQIs in Pingzhai Reservoir
3.6. Analysis of the Applicability of the Model over Time
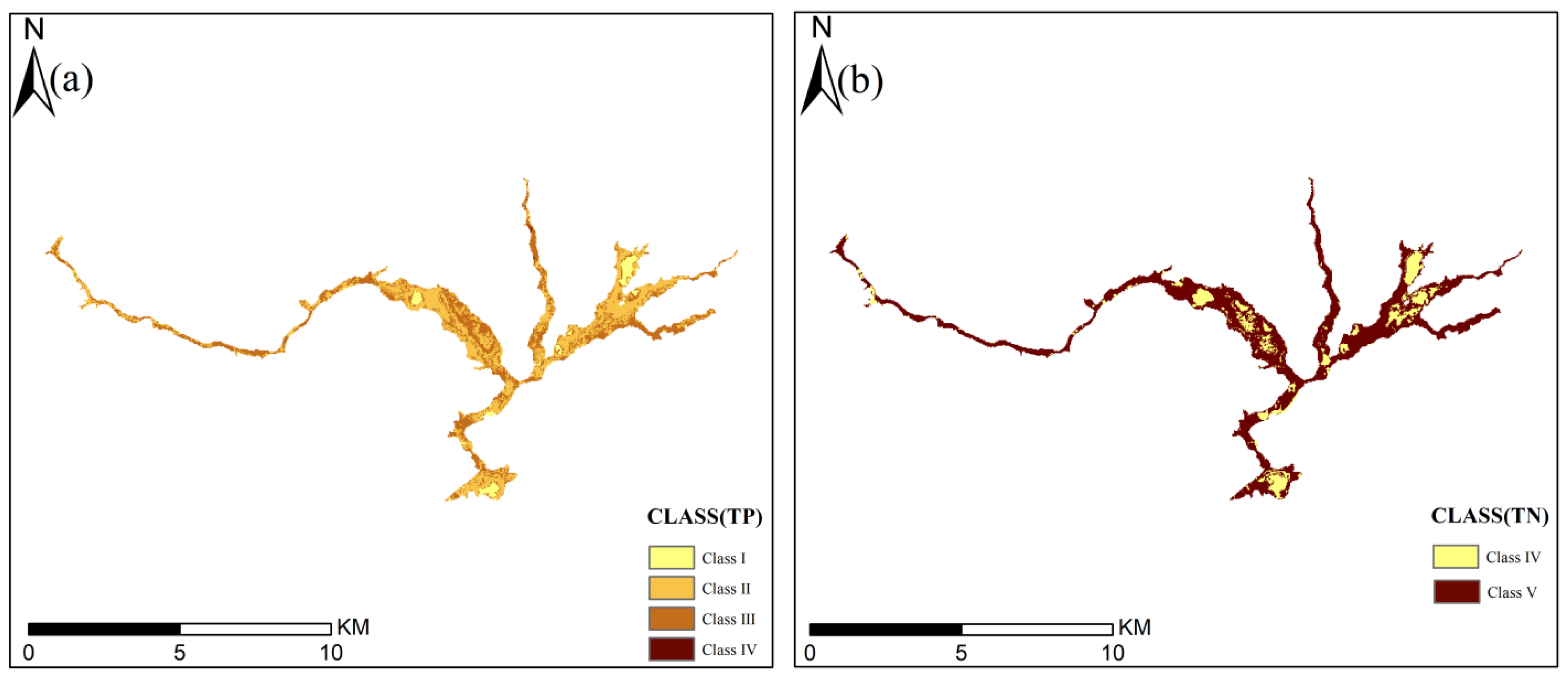
3.7. Water Quality Classification of Pingzhai Reservoir
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence Between Chla, TN, TP, and Turb in Pingzhai Reservoir
4.2. Model Performance Analysis
4.3. Limitations and Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, T.; Qiu, S.; Mao, S.X.; Bao, R.; Deng, H.B. Evaluating Water Resource Accessibility in Southwest China. Water 2019, 11, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.R.; Bodirsky, B.L.; Rijneveld, R.; Beier, F.; Bak, M.P.; Batool, M.; Droppers, B.; Popp, A.; van Vliet, M.T.H.; Strokal, M. A triple increase in global river basins with water scarcity due to future pollution. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, E.A.; Allen, G.H.; Riggs, R.M.; Gao, H.L.; Li, Y.; Carey, C.C. Bridging the divide between inland water quantity and quality with satellite remote sensing: An interdisciplinary review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2024, 11, e1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Gong, C.L.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, Y.; He, D.G.; Hu, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, Z. Seasonal Monitoring Method for TN and TP Based on Airborne Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Shen, M.; Liu, W.H.; Ma, Y.X.; Shi, H.; Zhang, J.T.; Liu, D. Developing remote sensing methods for monitoring water quality of alpine rivers on the Tibetan Plateau. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 1384–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, A.; Elshemy, M.; Zeidan, B. Water quality monitoring of Lake Burullus (Egypt) using Landsat satellite imageries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 15687–15700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Wang, B.; Wu, Y.L.; Wang, Q.J.; Huang, Z.J.; Wang, C.L. Urban river water quality monitoring based on self-optimizing machine learning method using multi-source remote sensing data. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Guo, H.W.; Xu, W.; Zhu, X.T.; Wang, B.; Zeng, Q.H.; Mai, Y.Q.; Huang, J.H.J. Remote sensing retrieval of inland water quality parameters using Sentinel-2 and multiple machine learning algorithms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 18617–18630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.F.; Wang, Z.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Xia, H.Q.; Cao, L.Q. Transparency Estimation of Narrow Rivers by UAV-Borne Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 168137–168153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Retana, A.; Becerril-Piña, R.; Fonseca, C.R.; Gomez-Albores, M.A.; Gaytan-Aguilar, S.; Hernández-Téllez, M.; Mastachi-Loza, C.A. Assessment of Regression Models for Surface Water Quality Modeling via Remote Sensing of a Water Body in the Mexican Highlands. Water 2023, 15, 3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.C.; Xie, Z.J.; Jin, X. Using Ensemble Learning for Remote Sensing Inversion of Water Quality Parameters in Poyang Lake. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yépez, S.; Velásquez, G.; Torres, D.; Saavedra-Passache, R.; Pincheira, M.; Cid, H.; Rodríguez-López, L.; Contreras, A.; Frappart, F.; Cristóbal, J.; et al. Spatiotemporal Variations in Biophysical Water Quality Parameters: An Integrated In Situ and Remote Sensing Analysis of an Urban Lake in Chile. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, T.H. A Machine-Learning-Based Framework for Retrieving Water Quality Parameters in Urban Rivers Using UAV Hyperspectral Images. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.L.; Lao, Z.A.; Liang, Y.Y.; Sun, J.; He, X.; Deng, T.F.; He, W.; Fan, D.L.; Gao, E.R.; Hou, Q.L. Evaluating optically and non-optically active water quality and its response relationship to hydro-meteorology using multi-source data in Poyang Lake, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Shi, K.Y.; Ming, X.; Cong, M.Q.; Liu, X.Y.; Guo, W.J. A Comparative Study of the COD Hyperspectral Inversion Models in Water Based on the Maching Learning. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2022, 42, 2353–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Jiang, J.; Wang, F.Y.; Luo, Y.R.; Lei, X.D.; Lai, C.G.; Wu, X.S.; Xu, M.H. Retrieving Eutrophic Water in Highly Urbanized Area Coupling UAV Multispectral Data and Machine Learning Algorithms. Water 2023, 15, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagan, V.; Peterson, K.T.; Maimaitijiang, M.; Sidike, P.; Sloan, J.; Greeling, B.A.; Maalouf, S.; Adams, C. Monitoring inland water quality using remote sensing: Potential and limitations of spectral indices, bio-optical simulations, machine learning, and cloud computing. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 205, 103187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.W.; Huang, J.J.; Zhu, X.T.; Tian, S.; Wang, B.L. Spatiotemporal variation reconstruction of total phosphorus in the Great Lakes since 2002 using remote sensing and deep neural network. Water Res. 2024, 255, 121493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.D.; Li, W.; Cao, X.Y.; He, B.Y.; Feng, Q.; Yang, F.; Liu, H.; Kutser, T.; Xu, M.; Xiao, F.; et al. Spatial-temporal distribution of labeled set bias remote sensing estimation: An implication for supervised machine learning in water quality monitoring. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 131, 103959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.D.; Huang, M.T. Inversion of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Donghu Lake Based on Machine Learning Algorithm. Water 2021, 13, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.H.; Gong, Z.J.; Zheng, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.B. Inland Reservoir Water Quality Inversion and Eutrophication Evaluation Using BP Neural Network and Remote Sensing Imagery: A Case Study of Dashahe Reservoir. Water 2021, 13, 2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.H.; Cui, J.Y.; Dong, W.; Xiao, Y.F.; Xu, M.M.; Liu, S.W.; Wan, J.H.; Li, Z.W.; Zhang, J. Remote Sensing Inversion of Typical Offshore Water Quality Parameter Concentration Based on Improved SVR Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.Z.; Wu, H.H.; Jin, H.Y.; Yang, G.; Wu, X.X. Remote Sensing Inversion of Suspended Matter Concentration Using a Neural Network Model Optimized by the Partial Least Squares and Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithms. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhou, C.; Wang, X.X.; Meng, Q.H.; Chen, Y.L. Remote Sensing Quantitative Retrieval of Chlorophyll a and Trophic Level Index in Main Seagoing Rivers of Lianyungang. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2023, 43, 3314–3320. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, B.; Wen, Z.; Jiang, Y.C.; Gao, S.; Lv, G.N. Sea surface temperature inversion model for infrared remote sensing images based on deep neural network. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 99, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.J.; Liu, T.Y.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Tian, S.F.; Ye, C.Y.; Nie, Z. Remote sensing inversion of the Zabuye Salt Lake in Tibet, China using LightGBM algorithm. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 10, 1022280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Zhou, Z.F.; Kong, J.; Wen, C.C.; Li, S.H.; Zhang, Y.R.; Xie, J.T.; Wang, C. Monitoring Chlorophyll-a concentration in karst plateau lakes using Sentinel 2 imagery from a case study of pingzhai reservoir in Guizhou, China. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 55, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H. Reservoir Capacity Calculation of Karst Underground Reservoir Associated with Pingzhai Reservoir in Deep Canyon Area of Upper Reaches of Wujiang River. Resour. Environ. Eng. 2021, 35, 478–483. [Google Scholar]
- Renau-Pruñonosa, A.; Morell, I.; Pulido-Velazquez, D. A Methodology to Analyse and Assess Pumping Management Strategies in Coastal Aquifers to Avoid Degradation Due to Seawater Intrusion Problems. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 4823–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Zhou, Z.F.; Zhang, H.T.; Dan, Y.S. Quantifying the impact of human activities on water quality based on spatialization of social data: A case study of the Pingzhai Reservoir Basin. Water Supply 2020, 20, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Rastogi, R. Parametric non-parallel support vector machines for pattern classification. Mach. Learn. 2024, 113, 1567–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Bao, J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Yang, M.M. Research on parameter selection method for support vector machines. Appl. Intell. 2018, 48, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.M.; Zhuansun, Y.X.; Liu, C.S.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.Y. Design of Intrusion Detection System for Internet of Things Based on Improved BP Neural Network. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 106043–106052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.D.; Kong, Y.X.; He, N.Y.; Qiu, Z.G.; Lu, Z.G. Prediction and Analysis of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in the Western Waters of Hong Kong Based on BP Neural Network. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Fu, X.L.; Li, H.H.; Wang, F.; Duan, W.J.; Zhang, L.Q.; Liu, M. Prediction of lake chlorophyll concentration using the BP neural network and Sentinel-2 images based on time features. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 87, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Song, B.Y.; Wen, X.F.; Zhao, D.Z.; Cheng, X.J.; Hu, C.F.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z.H. VIP-BP model for retrieving chlorophyll a concentration in the river by using remote sensing data. Water Qual. Res. J. Can. 2017, 52, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.J.; Ma, H.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, C.Q.; Li, Z.L. Soil Salinity Inversion Model Based on BPNN Optimization Algorithm for UAV Multispectral Remote Sensing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 6038–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Dong, X.; Ruan, S.M.; Shi, L. A parallel integrated learning technique of improved particle swarm optimization and BP neural network and its application. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantas, C.J.; Castellano, J.G.; Moral-García, S.; Abellán, J. A comparison of random forest based algorithms: Random credal random forest versus oblique random forest. Soft Comput. 2019, 23, 10739–10754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Yinglan, A.; Wang, Y.T.; Fang, Q.Q.; Tang, R. Study on remote sensing inversion and temporal-spatial variation of Hulun lake water quality based on machine learning. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2024, 260, 104282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y.; Fu, L.; Lu, T.C.; Huang, H.; Kong, L.R.; Xu, Y.Q.; Zhang, C. Medium-Sized Lake Water Quality Parameters Retrieval Using Multispectral UAV Image and Machine Learning Algorithms: A Case Study of the Yuandang Lake, China. Drones 2023, 7, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Chen, C.; Cao, N.X.; Jiang, Z.H.; Liu, C.J.; Oke, S.A.; Jim, C.; Zheng, K.X.; Zhang, F. High spatial resolution inversion of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) concentrations in Ebinur Lake of arid Xinjiang, China: Implications for surface water quality monitoring. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 132, 104022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zou, B.; Wen, Y.M.; Long, Y.H.; Zhou, S.L. Research on Inversion Mechanism of Chlorophyll-A Concentration in Water Bodies Using a Convolutional Neural Network Model. Water 2021, 13, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Z.F. Regularization incremental extreme learning machine with random reduced kernel for regression. Neurocomputing 2018, 321, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Shi, K.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.L.; Li, N.; Wang, W.J.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Zhi, W.; Liu, M.L.; Li, Y.; et al. Improving remote sensing estimation of Secchi disk depth for global lakes and reservoirs using machine learning methods. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 1367–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.H.; Guo, L.; Tao, Z.; Li, Y.A.; Zhan, Y.; Li, S.L.; Zhao, Y. Water Quality Inversion Framework for Taihu Lake Based on Multilayer Denoising Autoencoder and Ensemble Learning. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.T.; Mu, X.; Chen, P.; Wang, B.A.; Choi, J.; Park, H.; Xu, S.; Wu, Y.L.; Yang, H. Machine learning-based inversion of water quality parameters in typical reach of the urban river by UAV multispectral data. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.W.; Dai, S.N.; Wen, X.L.; Qian, C.; Luo, F.; Xu, J.Q.; Wang, X.D.; Li, Y.; Xi, Y.L. Chlorophyll-nutrient relationship changes with lake type, season and small-bodied zooplankton in a set of subtropical shallow lakes. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Li, C.Y.; Shi, X.H.; Sun, B. Spatial and Temporal Distribution Characteristics of Chlorophyll A Contentand lts Influencing Factor Analysis in Hulun Lake of Cold and Dry Areas. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2019, 28, 1434–1442. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X. Changes of Hydrochemistry and Dissolved lnorganic Carbon DurincThermal Stratification in Pingzhai Reservoir. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2021, 30, 936–945. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.S.A.; Hasan, K.; Alam, K. The Use of an Aeration System to Prevent Thermal Stratification of Water Bodies: Pond, Lake and Water Supply Reservoir. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Wang, C.Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Wu, J.; Liu, L.L. Aerosol pollution alters the diurnal dynamics of sun and shade leaf photosynthesis through different mechanisms. Plant Cell Environ. 2022, 45, 2943–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.L.; Fu, B.L.; Li, S.Z.; Lao, Z.N.; Deng, T.F.; He, W.; He, H.C.; Chen, Z.K. Monitoring multi-water quality of internationally important karst wetland through deep learning, multi-sensor and multi-platform remote sensing images: A case study of Guilin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D. Challenges and main research advances of low-altitude remote sensing forcrops in southwest plateau mountains. J. Guizhou Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2021, 39, 51–59. [Google Scholar]

| Sensor | Band Name | Bandwidth (μm) | Resolution (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operational Land Imager (OLI) | Band 1 Coastal | 0.43–0.45 | 30 |
| Band 2 Blue | 0.45–0.51 | 30 | |
| Band 3 Green | 0.53–0.59 | 30 | |
| Band 4 Red | 0.64–0.67 | 30 | |
| Band 5 NIR | 0.85–0.88 | 30 | |
| Band 6 SWIR 1 | 1.57–1.65 | 30 | |
| Band 7 SWIR 2 | 2.11–2.29 | 30 | |
| Band 8 Pan | 0.50–0.68 | 15 | |
| Band 9 Cirrus | 1.36–1.38 | 30 | |
| Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) | Band 10 TIRS 1 | 10.6–11.19 | 100 |
| Band 11 TIRS 2 | 11.5–12.51 | 100 |
| WQIs | Model | R2 | RMSE | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chla | Chla = 900.418 × B1 − 12.812 × B1/B2 − 516.495 × (B1 + B3) + 29.404 | 0.653 | 2.1209 | 1.5385 |
| TP | TP = 0.131 × B2 + 0.266 × (B1 + B2) + 0.009 | 0.396 | 0.0083 | 0.0057 |
| TN | TN = 8.964 × B5 + 5.083 × (B2 + B3) − 5.908 × B3 + 1.381 | 0.277 | 0.2251 | 0.1840 |
| Turb | Turb = 2.671 × (B3/B4) − 3.731 × (B1/B2) − 2.073 [(B1 − B2)/(B1 + B2)] + 0.049 | 0.552 | 1.5064 | 1.0757 |
| Class | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | Ⅴ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN <= (mg/L) | 0.2 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 |
| TP <= (mg/L) | 0.01 | 0.025 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| 7/21 | 7/22 | 7/23 | 7/24 | 7/25 | 7/26 | 7/27 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WS1 | 35,175.44 | 61,735.55 | 61,886.89 | 63,728.33 | 69,642.79 | 71,569.75 | 42,283.63 |
| WS2 | 47,498.55 | 67,062.06 | 58,931.36 | 64,571.72 | 69,273.40 | 69,832.78 | 47,005.43 |
| WS3 | 41,796.61 | 64,079.02 | 69,123.27 | 68,803.67 | 68,653.37 | 77,863.41 | 49,377.34 |
| AVR | 41,490.0 | 64,292.21 | 63,313.84 | 65,701.24 | 69,189.85 | 73,088.65 | 46,222.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, R.; Zhou, Z.; Kong, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Ding, C.; Li, R.; Zhang, X. Multi-Algorithm Comparison for Water Quality Retrieval: Integrating Landsat-8 OLI and Machine Learning in Karst Plateau Reservoirs. Water 2025, 17, 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121781
Xie R, Zhou Z, Kong J, Wang C, Wang Y, Li L, Ding C, Li R, Zhang X. Multi-Algorithm Comparison for Water Quality Retrieval: Integrating Landsat-8 OLI and Machine Learning in Karst Plateau Reservoirs. Water. 2025; 17(12):1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121781
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Rukai, Zhongfa Zhou, Jie Kong, Cui Wang, Yanbi Wang, Li Li, Caixia Ding, Rui Li, and Xinyue Zhang. 2025. "Multi-Algorithm Comparison for Water Quality Retrieval: Integrating Landsat-8 OLI and Machine Learning in Karst Plateau Reservoirs" Water 17, no. 12: 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121781
APA StyleXie, R., Zhou, Z., Kong, J., Wang, C., Wang, Y., Li, L., Ding, C., Li, R., & Zhang, X. (2025). Multi-Algorithm Comparison for Water Quality Retrieval: Integrating Landsat-8 OLI and Machine Learning in Karst Plateau Reservoirs. Water, 17(12), 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17121781





